BERKELEY PAR LAB. UPC-THRILLE Demo. Chang-Seo Park
|
|
|
- Rosamund Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BERKELEY PAR LAB UPC-THRILLE Demo Chang-Seo Park 1
2 Correctness Group Highlights Active Testing for Java, C, and UPC Practical, easy-to-use tools for finding bugs, with sophisticated program analysis internally Lightweight Specs for Parallelism By focusing just on parallelism, can we develop simple specifications that greatly improve or ability to find real parallelism bugs? Concurrit DSL for testing parallel code 2
3 Lightweight Parallel Specs Goal: Lightweight specifications for parallelism correctness. Easy for programmers to write Greatly increase effectiveness in testing, debugging, and verifying parallel programs Semantic determinism [FSE 09 (best paper), CACM 10, ICSE 10 (IFIP TC2 Manfred Paul)]. Semantic atomicity [ASPLOS 11]. Nondeterministic sequential specs for parallel correctness [HotPar 10, PLDI 11, PPoPP 12]. 3
4 Key: Decompose effort in addressing parallelism and functional correctness Parallel Satisfies? program Parallelism Correctness. Functional specification ϕ Functional Correctness. Parallel program Nondeterministic sequential program Functional specification ϕ 4
5 NDSeq for SEJITS Debugging Goal: Localize bug in a SEJITS execution. Pure Python Code Nondeterministic Python Code Nondeterministic C++ Code Parallel C++ Code Pure Python Trace? Nondeterministic Python Trace? Nondeterministic Error. C++ Trace? Parallel C++ Trace 5
6 Correctness Group Highlights Active Testing for Java, C, and UPC Practical, easy-to-use tools for finding bugs, with sophisticated program analysis internally Lightweight Specs for Parallelism Easy to write and, with testing, effective in finding real parallelism bugs Determinism, atomicity, and NDSeq Concurrit DSL for Testing Parallel Code Can we combine programmer intuition with testing techniques to find, reproduce bugs? 6
7 Concurrit: Domain Specific Language for Writing Concurrent Tests Insights/ideas about thread schedules Software Under Test P1 P2 C1 C2 q w e r t y u + Test in Concurrit DSL Systematically explore all-and-only thread schedules specified by DSL Specify a set of schedules in formal, concise, and convenient way
8 BERKELEY PAR LAB Concurrit Demo Tayfun Elmas 8
9 Simple Test for an Apache bug BERKELEY PAR LAB 9
10 Concurrit To appear in PLDI Implementation: DSL embedded in C++ Available at Can write tests for Unit testing: Both manual and automated (Pin) instrumentation System testing: Manual instrumentation (lightweight and portable) Test servers, e.g. Memcached, MySQL, Apache Httpd.
11 Example: Producer/consumer P1 P2 Produce Produce Bounded buffer tail q w e r t y u Consume C1 head C2 Consume Error: Consumer reads from uninitialized cell. 11
12 How to reproduce a concurrency error? (Consumer reads from uninitialized cell.) Software Under Test P1 P2 C1 C2 Run 1000 times: No guarantee Insert sleeps: Useful but ad hoc, informal Concurrit approach q w e r t y u Write test to search for buggy schedules 12
13 Concurrit: Domain Specific Language for Writing Concurrent Tests Insights/ideas about thread schedules Software Under Test P1 P2 C1 C2 q w e r t y u + Test in Concurrit DSL Systematically explore all-and-only thread schedules specified by DSL Specify a set of schedules in formal, concise, and convenient way
14 SearchAll: Search all schedules Capture threads from SUT TESTCASE() { TVAR(P1); TVAR(P2); TVAR(C1); TVAR(C2); Instrumented to control Software Under Test (SUT) Produce Consume P1 C1 P2 C2 Produce Consume } WAIT_FOR_DISTINCT_THREADS( (P1, P2), ENTERS(producer_routine)); WAIT_FOR_DISTINCT_THREADS( (C1, C2), ENTERS(consumer_routine)); WHILE (!ALL_ENDED(P1, P2, C1, C2)) { TVAR(t); } CHOOSE_THREAD_BACKTRACK( t, (P1, P2, C1, C2)); RUN_THREAD_THROUGH( t, READS() WRITES() CALLS() ENTERS() RETURNS());
15 SearchAll: Search all schedules Run captured threads TESTCASE() { TVAR(P1); TVAR(P2); TVAR(C1); TVAR(C2); Instrumented to control Software Under Test (SUT) Produce Consume P1 C1 P2 C2 Produce Consume } WAIT_FOR_DISTINCT_THREADS( (P1, P2), ENTERS(producer_routine)); WAIT_FOR_DISTINCT_THREADS( (C1, C2), ENTERS(consumer_routine)); WHILE (!ALL_ENDED(P1, P2, C1, C2)) { TVAR(t); } CHOOSE_THREAD_BACKTRACK( t, (P1, P2, C1, C2)); RUN_THREAD_THROUGH( t, READS() WRITES() CALLS() ENTERS() RETURNS());
16 SearchInFunc: Localize search to particular functions and operations TESTCASE() { TVAR(P1); TVAR(P2); TVAR(C1); TVAR(C2); Instrumented to control Software Under Test (SUT) Produce Consume P1 C1 P2 C2 Produce Consume } WAIT_FOR_DISTINCT_THREADS( (P1, P2), ENTERS(bounded_buf_put)); WAIT_FOR_DISTINCT_THREADS( (C1, C2), ENTERS(bounded_buf_get)); WHILE (!ALL_ENDED(P1, P2, C1, C2)) { TVAR(t); } CHOOSE_THREAD_BACKTRACK( t, (P1, P2, C1, C2)); RUN_THREAD_THROUGH( t, ENTERS() RETURNS() HITS_MANUAL_PC());
17 P1 BuggySchedule TESTCASE() { Insert item to buffer C1 Check item and prepare to read C2 Read item and update head Read from new head (uninitialized slot) } TVAR(P1); TVAR(C1); TVAR(C2); WAIT_FOR_THREAD( P1, ENTERS(bounded_buf_put)); WAIT_FOR_DISTINCT_THREADS( (C1, C2), ENTERS(bounded_buf_get)); RUN_THREAD_THROUGH( P1, RETURNS(bounded_buf_put)); RUN_THREAD_THROUGH( C1, HITS_MANUAL_PC(42)); RUN_THREAD_THROUGH( C2, RETURNS(bounded_buf_get)); RUN_THREAD_THROUGH(C1, ENDS()); // ERROR! 17
18 Where We Ended Up Active Testing for Java, C, and UPC Practical, easy-to-use tools for finding bugs, with sophisticated program analysis internally Lightweight Specs for Parallelism Easy to write and, with testing, effective in finding real parallelism bugs Determinism, atomicity, and NDSeq Concurrit DSL for Testing Parallel Code Combine programmer intuition with automated testing techniques to find, reproduce bugs. 18
Berkeley Parlab P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y
 EECS Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Berkeley Parlab P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y CONCURRIT: Tes&ng Concurrent Programs with Programmable State- Space Explora&on (A
EECS Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Berkeley Parlab P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y CONCURRIT: Tes&ng Concurrent Programs with Programmable State- Space Explora&on (A
NDSeq: Runtime Checking for Nondeterministic Sequential Specs of Parallel Correctness
 EECS Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y NDSeq: Runtime Checking for Nondeterministic Sequential Specs of Parallel Correctness Jacob Burnim,
EECS Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y NDSeq: Runtime Checking for Nondeterministic Sequential Specs of Parallel Correctness Jacob Burnim,
Active Testing for Concurrent Programs
 Active Testing for Concurrent Programs Pallavi Joshi Mayur Naik Chang-Seo Park Koushik Sen 1/8/2009 ParLab Retreat ParLab, UC Berkeley Intel Research Overview Checking correctness of concurrent programs
Active Testing for Concurrent Programs Pallavi Joshi Mayur Naik Chang-Seo Park Koushik Sen 1/8/2009 ParLab Retreat ParLab, UC Berkeley Intel Research Overview Checking correctness of concurrent programs
Active Testing for Concurrent Programs
 Active Testing for Concurrent Programs Pallavi Joshi, Mayur Naik, Chang-Seo Park, Koushik Sen 12/30/2008 ROPAS Seminar ParLab, UC Berkeley Intel Research Overview ParLab The Parallel Computing Laboratory
Active Testing for Concurrent Programs Pallavi Joshi, Mayur Naik, Chang-Seo Park, Koushik Sen 12/30/2008 ROPAS Seminar ParLab, UC Berkeley Intel Research Overview ParLab The Parallel Computing Laboratory
Semantic Atomicity for Multithreaded Programs!
 P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y Semantic Atomicity for Multithreaded Programs! Jacob Burnim, George Necula, Koushik Sen! Parallel Computing Laboratory! University of California, Berkeley!
P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y Semantic Atomicity for Multithreaded Programs! Jacob Burnim, George Necula, Koushik Sen! Parallel Computing Laboratory! University of California, Berkeley!
Lightweight Fault Detection in Parallelized Programs
 Lightweight Fault Detection in Parallelized Programs Li Tan UC Riverside Min Feng NEC Labs Rajiv Gupta UC Riverside CGO 13, Shenzhen, China Feb. 25, 2013 Program Parallelization Parallelism can be achieved
Lightweight Fault Detection in Parallelized Programs Li Tan UC Riverside Min Feng NEC Labs Rajiv Gupta UC Riverside CGO 13, Shenzhen, China Feb. 25, 2013 Program Parallelization Parallelism can be achieved
Multi-level Debugging for Multi-stage, Parallelizing Compilers
 Multi-level Debugging for Multi-stage, Parallelizing Compilers Richard Xia Tayfun Elmas Shoaib Ashraf Kamil Armando Fox Koushik Sen Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California
Multi-level Debugging for Multi-stage, Parallelizing Compilers Richard Xia Tayfun Elmas Shoaib Ashraf Kamil Armando Fox Koushik Sen Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California
A Causality-Based Runtime Check for (Rollback) Atomicity
 A Causality-Based Runtime Check for (Rollback) Atomicity Serdar Tasiran Koc University Istanbul, Turkey Tayfun Elmas Koc University Istanbul, Turkey RV 2007 March 13, 2007 Outline This paper: Define rollback
A Causality-Based Runtime Check for (Rollback) Atomicity Serdar Tasiran Koc University Istanbul, Turkey Tayfun Elmas Koc University Istanbul, Turkey RV 2007 March 13, 2007 Outline This paper: Define rollback
Hybrid Static-Dynamic Analysis for Statically Bounded Region Serializability
 Hybrid Static-Dynamic Analysis for Statically Bounded Region Serializability Aritra Sengupta, Swarnendu Biswas, Minjia Zhang, Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni ASPLOS 2015, ISTANBUL, TURKEY Programming
Hybrid Static-Dynamic Analysis for Statically Bounded Region Serializability Aritra Sengupta, Swarnendu Biswas, Minjia Zhang, Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni ASPLOS 2015, ISTANBUL, TURKEY Programming
Nondeterminism is Unavoidable, but Data Races are Pure Evil
 Nondeterminism is Unavoidable, but Data Races are Pure Evil Hans-J. Boehm HP Labs 5 November 2012 1 Low-level nondeterminism is pervasive E.g. Atomically incrementing a global counter is nondeterministic.
Nondeterminism is Unavoidable, but Data Races are Pure Evil Hans-J. Boehm HP Labs 5 November 2012 1 Low-level nondeterminism is pervasive E.g. Atomically incrementing a global counter is nondeterministic.
Diagnosing Production-Run Concurrency-Bug Failures. Shan Lu University of Wisconsin, Madison
 Diagnosing Production-Run Concurrency-Bug Failures Shan Lu University of Wisconsin, Madison 1 Outline Myself and my group Production-run failure diagnosis What is this problem What are our solutions CCI
Diagnosing Production-Run Concurrency-Bug Failures Shan Lu University of Wisconsin, Madison 1 Outline Myself and my group Production-run failure diagnosis What is this problem What are our solutions CCI
Slides by Y. Nir-Buchbinder, adapted by O. Agmon Ben-Yehuda 1/30
 Application of Synchronization Coverage Arkady Bron, Eitan Farchi, Yonit Magid, Yarden Nir-Buchbinder, Shmuel Ur PPoPP 2005 Presented in the spring 2011 Seminar on Advanced Topics in Concurrent Programming
Application of Synchronization Coverage Arkady Bron, Eitan Farchi, Yonit Magid, Yarden Nir-Buchbinder, Shmuel Ur PPoPP 2005 Presented in the spring 2011 Seminar on Advanced Topics in Concurrent Programming
Lecture 13 Condition Variables
 Lecture 13 Condition Variables Contents In this lecture, you will learn Condition Variables And how to use CVs to solve The Producer/Consumer (Bounded Buffer) Problem Review Thus far we have developed
Lecture 13 Condition Variables Contents In this lecture, you will learn Condition Variables And how to use CVs to solve The Producer/Consumer (Bounded Buffer) Problem Review Thus far we have developed
C++ Memory Model. Don t believe everything you read (from shared memory)
 C++ Memory Model Don t believe everything you read (from shared memory) The Plan Why multithreading is hard Warm-up example Sequential Consistency Races and fences The happens-before relation The DRF guarantee
C++ Memory Model Don t believe everything you read (from shared memory) The Plan Why multithreading is hard Warm-up example Sequential Consistency Races and fences The happens-before relation The DRF guarantee
Leveraging the Short-Term Memory of Hardware to Diagnose Production-Run Software Failures. Joy Arulraj, Guoliang Jin and Shan Lu
 Leveraging the Short-Term Memory of Hardware to Diagnose Production-Run Software Failures Joy Arulraj, Guoliang Jin and Shan Lu Production-Run Failure Diagnosis Goal Figure out root cause of failure on
Leveraging the Short-Term Memory of Hardware to Diagnose Production-Run Software Failures Joy Arulraj, Guoliang Jin and Shan Lu Production-Run Failure Diagnosis Goal Figure out root cause of failure on
Lightweight Data Race Detection for Production Runs
 Lightweight Data Race Detection for Production Runs Swarnendu Biswas, UT Austin Man Cao, Ohio State University Minjia Zhang, Microsoft Research Michael D. Bond, Ohio State University Benjamin P. Wood,
Lightweight Data Race Detection for Production Runs Swarnendu Biswas, UT Austin Man Cao, Ohio State University Minjia Zhang, Microsoft Research Michael D. Bond, Ohio State University Benjamin P. Wood,
Toward Efficient Strong Memory Model Support for the Java Platform via Hybrid Synchronization
 Toward Efficient Strong Memory Model Support for the Java Platform via Hybrid Synchronization Aritra Sengupta, Man Cao, Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni 1 PPPJ 2015, Melbourne, Florida, USA Programming
Toward Efficient Strong Memory Model Support for the Java Platform via Hybrid Synchronization Aritra Sengupta, Man Cao, Michael D. Bond and Milind Kulkarni 1 PPPJ 2015, Melbourne, Florida, USA Programming
A Classification of Concurrency Bugs in Java Benchmarks by Developer Intent
 A Classification of Concurrency Bugs in Java Benchmarks by Developer Intent M. Erkan Keremoglu, Serdar Tasiran, Tayfun Elmas Center for Advanced Design Technologies @ Koc University http://designtech.ku.edu.tr
A Classification of Concurrency Bugs in Java Benchmarks by Developer Intent M. Erkan Keremoglu, Serdar Tasiran, Tayfun Elmas Center for Advanced Design Technologies @ Koc University http://designtech.ku.edu.tr
NDSeq: Runtime Checking for Nondeterministic Sequential Specifications of Parallel Correctness
 NDSeq: Runtime Checking for Nondeterministic Sequential Specifications of Parallel Correctness Jacob Burnim Tayfun Elmas George Necula Koushik Sen Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences,
NDSeq: Runtime Checking for Nondeterministic Sequential Specifications of Parallel Correctness Jacob Burnim Tayfun Elmas George Necula Koushik Sen Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences,
PROCESSES AND THREADS
 PROCESSES AND THREADS A process is a heavyweight flow that can execute concurrently with other processes. A thread is a lightweight flow that can execute concurrently with other threads within the same
PROCESSES AND THREADS A process is a heavyweight flow that can execute concurrently with other processes. A thread is a lightweight flow that can execute concurrently with other threads within the same
DMP Deterministic Shared Memory Multiprocessing
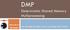 DMP Deterministic Shared Memory Multiprocessing University of Washington Joe Devietti, Brandon Lucia, Luis Ceze, Mark Oskin A multithreaded voting machine 2 thread 0 thread 1 while (more_votes) { load
DMP Deterministic Shared Memory Multiprocessing University of Washington Joe Devietti, Brandon Lucia, Luis Ceze, Mark Oskin A multithreaded voting machine 2 thread 0 thread 1 while (more_votes) { load
Efficient Data Race Detection for Unified Parallel C
 P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y Efficient Data Race Detection for Unified Parallel C ParLab Winter Retreat 1/14/2011" Costin Iancu, LBL" Nick Jalbert, UC Berkeley" Chang-Seo Park,
P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y Efficient Data Race Detection for Unified Parallel C ParLab Winter Retreat 1/14/2011" Costin Iancu, LBL" Nick Jalbert, UC Berkeley" Chang-Seo Park,
Concurrency & Multithreading
 Concurrency & Multithreading Multithreaded Programming Pieter Hijma Multithreaded Programming Multithreaded Programming is really difficult. Problems race conditions non-determinism deadlock termination
Concurrency & Multithreading Multithreaded Programming Pieter Hijma Multithreaded Programming Multithreaded Programming is really difficult. Problems race conditions non-determinism deadlock termination
Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis
 Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis http://d3s.mff.cuni.cz Pavel Parízek CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics Symbolic execution Pavel Parízek Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis
Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis http://d3s.mff.cuni.cz Pavel Parízek CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics Symbolic execution Pavel Parízek Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis
Introducing Shared-Memory Concurrency
 Race Conditions and Atomic Blocks November 19, 2007 Why use concurrency? Communicating between threads Concurrency in Java/C Concurrency Computation where multiple things happen at the same time is inherently
Race Conditions and Atomic Blocks November 19, 2007 Why use concurrency? Communicating between threads Concurrency in Java/C Concurrency Computation where multiple things happen at the same time is inherently
DoubleChecker: Efficient Sound and Precise Atomicity Checking
 DoubleChecker: Efficient Sound and Precise Atomicity Checking Swarnendu Biswas, Jipeng Huang, Aritra Sengupta, and Michael D. Bond The Ohio State University PLDI 2014 Impact of Concurrency Bugs Impact
DoubleChecker: Efficient Sound and Precise Atomicity Checking Swarnendu Biswas, Jipeng Huang, Aritra Sengupta, and Michael D. Bond The Ohio State University PLDI 2014 Impact of Concurrency Bugs Impact
System Software. Computer Science and Engineering College of Engineering The Ohio State University. Lecture 13
 System Software Computer Science and Engineering College of Engineering The Ohio State University Lecture 13 Road Map Lectures Administration Abstract machine characteristics Version control Software engineering
System Software Computer Science and Engineering College of Engineering The Ohio State University Lecture 13 Road Map Lectures Administration Abstract machine characteristics Version control Software engineering
Cooperari A tool for cooperative testing of multithreaded Java programs
 Cooperari A tool for cooperative testing of multithreaded Java programs Eduardo R. B. Marques, Francisco Martins, Miguel Simões! LASIGE/Departamento de Informática Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade
Cooperari A tool for cooperative testing of multithreaded Java programs Eduardo R. B. Marques, Francisco Martins, Miguel Simões! LASIGE/Departamento de Informática Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade
Model Checking Software with
 Model Checking Software with Patrice Godefroid Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies PASTE 2004 Page 1 June 2004 Model Checking A B C deadlock Each component is modeled by a FSM. Model Checking = systematic
Model Checking Software with Patrice Godefroid Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies PASTE 2004 Page 1 June 2004 Model Checking A B C deadlock Each component is modeled by a FSM. Model Checking = systematic
Reasoning About The Implementations Of Concurrency Abstractions On x86-tso. By Scott Owens, University of Cambridge.
 Reasoning About The Implementations Of Concurrency Abstractions On x86-tso By Scott Owens, University of Cambridge. Plan Intro Data Races And Triangular Races Examples 2 sequential consistency The result
Reasoning About The Implementations Of Concurrency Abstractions On x86-tso By Scott Owens, University of Cambridge. Plan Intro Data Races And Triangular Races Examples 2 sequential consistency The result
Secure Virtual Architecture: Using LLVM to Provide Memory Safety to the Entire Software Stack
 Secure Virtual Architecture: Using LLVM to Provide Memory Safety to the Entire Software Stack John Criswell, University of Illinois Andrew Lenharth, University of Illinois Dinakar Dhurjati, DoCoMo Communications
Secure Virtual Architecture: Using LLVM to Provide Memory Safety to the Entire Software Stack John Criswell, University of Illinois Andrew Lenharth, University of Illinois Dinakar Dhurjati, DoCoMo Communications
Beyond Reduction... Busy Acquire. Busy Acquire. alloc. alloc. Non-Serial Execution: Serial Execution: Atomic but not reducible
 Busy Acquire Beyond Reduction... if (CAS(m,0,1)) break; if (m == 0) { m = 1; return true; else { return false; 1 2 Busy Acquire if (CAS(m,0,1)) break; Non-Serial Execution: (fails) (fails) (succeeds) Serial
Busy Acquire Beyond Reduction... if (CAS(m,0,1)) break; if (m == 0) { m = 1; return true; else { return false; 1 2 Busy Acquire if (CAS(m,0,1)) break; Non-Serial Execution: (fails) (fails) (succeeds) Serial
Parallel Computer Architecture Spring Memory Consistency. Nikos Bellas
 Parallel Computer Architecture Spring 2018 Memory Consistency Nikos Bellas Computer and Communications Engineering Department University of Thessaly Parallel Computer Architecture 1 Coherence vs Consistency
Parallel Computer Architecture Spring 2018 Memory Consistency Nikos Bellas Computer and Communications Engineering Department University of Thessaly Parallel Computer Architecture 1 Coherence vs Consistency
Optimistic Shared Memory Dependence Tracing
 Optimistic Shared Memory Dependence Tracing Yanyan Jiang1, Du Li2, Chang Xu1, Xiaoxing Ma1 and Jian Lu1 Nanjing University 2 Carnegie Mellon University 1 powered by Understanding Non-determinism Concurrent
Optimistic Shared Memory Dependence Tracing Yanyan Jiang1, Du Li2, Chang Xu1, Xiaoxing Ma1 and Jian Lu1 Nanjing University 2 Carnegie Mellon University 1 powered by Understanding Non-determinism Concurrent
Maximal Causality Reduction for TSO and PSO. Shiyou Huang Jeff Huang Parasol Lab, Texas A&M University
 Maximal Causality Reduction for TSO and PSO Shiyou Huang Jeff Huang huangsy@tamu.edu Parasol Lab, Texas A&M University 1 A Real PSO Bug $12 million loss of equipment curpos = new Point(1,2); class Point
Maximal Causality Reduction for TSO and PSO Shiyou Huang Jeff Huang huangsy@tamu.edu Parasol Lab, Texas A&M University 1 A Real PSO Bug $12 million loss of equipment curpos = new Point(1,2); class Point
Isolating Failure-Inducing Thread Schedules
 Isolating Failure-Inducing Thread Schedules by Jong-Deok Choi - IBM T.J. Watson Research Center and Andreas Zeller - Saarland University Marlene Hochrieser FMV - Institute for Formal Models and Verification
Isolating Failure-Inducing Thread Schedules by Jong-Deok Choi - IBM T.J. Watson Research Center and Andreas Zeller - Saarland University Marlene Hochrieser FMV - Institute for Formal Models and Verification
Introduction to MATLAB application deployment
 Introduction to application deployment Antti Löytynoja, Application Engineer 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Technical Computing with Products Access Explore & Create Share Options: Files Data Software Data
Introduction to application deployment Antti Löytynoja, Application Engineer 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Technical Computing with Products Access Explore & Create Share Options: Files Data Software Data
Rely-Guarantee References for Refinement Types over Aliased Mutable Data
 Rely-Guarantee References for Refinement Types over Aliased Mutable Data Colin S. Gordon, Michael D. Ernst, and Dan Grossman University of Washington PLDI 2013 Static Verification Meets Aliasing 23 x:ref
Rely-Guarantee References for Refinement Types over Aliased Mutable Data Colin S. Gordon, Michael D. Ernst, and Dan Grossman University of Washington PLDI 2013 Static Verification Meets Aliasing 23 x:ref
Efficient, Deterministic, and Deadlock-free Concurrency
 Efficient, Deterministic Concurrency p. 1/31 Efficient, Deterministic, and Deadlock-free Concurrency Nalini Vasudevan Columbia University Efficient, Deterministic Concurrency p. 2/31 Data Races int x;
Efficient, Deterministic Concurrency p. 1/31 Efficient, Deterministic, and Deadlock-free Concurrency Nalini Vasudevan Columbia University Efficient, Deterministic Concurrency p. 2/31 Data Races int x;
RobinHood: Tail Latency-Aware Caching Dynamically Reallocating from Cache-Rich to Cache-Poor
 RobinHood: Tail Latency-Aware Caching Dynamically Reallocating from -Rich to -Poor Daniel S. Berger (CMU) Joint work with: Benjamin Berg (CMU), Timothy Zhu (PennState), Siddhartha Sen (Microsoft Research),
RobinHood: Tail Latency-Aware Caching Dynamically Reallocating from -Rich to -Poor Daniel S. Berger (CMU) Joint work with: Benjamin Berg (CMU), Timothy Zhu (PennState), Siddhartha Sen (Microsoft Research),
Developing and Testing Java Microservices on Docker. Todd Fasullo Dir. Engineering
 Developing and Testing Java Microservices on Docker Todd Fasullo Dir. Engineering Agenda Who is Smartsheet + why we started using Docker Docker fundamentals Demo - creating a service Demo - building service
Developing and Testing Java Microservices on Docker Todd Fasullo Dir. Engineering Agenda Who is Smartsheet + why we started using Docker Docker fundamentals Demo - creating a service Demo - building service
Productive Design of Extensible Cache Coherence Protocols!
 P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y Productive Design of Extensible Cache Coherence Protocols!! Henry Cook, Jonathan Bachrach,! Krste Asanovic! Par Lab Summer Retreat, Santa Cruz June
P A R A L L E L C O M P U T I N G L A B O R A T O R Y Productive Design of Extensible Cache Coherence Protocols!! Henry Cook, Jonathan Bachrach,! Krste Asanovic! Par Lab Summer Retreat, Santa Cruz June
TERN: Stable Deterministic Multithreading through Schedule Memoization
 TERN: Stable Deterministic Multithreading through Schedule Memoization Heming Cui, Jingyue Wu, Chia-che Tsai, Junfeng Yang Columbia University Appeared in OSDI 10 Nondeterministic Execution One input many
TERN: Stable Deterministic Multithreading through Schedule Memoization Heming Cui, Jingyue Wu, Chia-che Tsai, Junfeng Yang Columbia University Appeared in OSDI 10 Nondeterministic Execution One input many
Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures
 Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures Presented by Brian Walker Senior Software Engineer, Video Product Line, Tektronix, Inc. Pacific Northwest Software Quality Conference,
Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures Presented by Brian Walker Senior Software Engineer, Video Product Line, Tektronix, Inc. Pacific Northwest Software Quality Conference,
Automatic Generation of Program Specifications
 Automatic Generation of Program Specifications Jeremy Nimmer MIT Lab for Computer Science http://pag.lcs.mit.edu/ Joint work with Michael Ernst Jeremy Nimmer, page 1 Synopsis Specifications are useful
Automatic Generation of Program Specifications Jeremy Nimmer MIT Lab for Computer Science http://pag.lcs.mit.edu/ Joint work with Michael Ernst Jeremy Nimmer, page 1 Synopsis Specifications are useful
Motivation. Overview. Scalable Dynamic Analysis for Automated Fault Location and Avoidance. Rajiv Gupta. Program Execution
 Motivation Scalable Dynamic Analysis for Automated Fault Location and Avoidance Rajiv Gupta Funded by NSF grants from CPA, CSR, & CRI programs and grants from Microsoft Research Software bugs cost the
Motivation Scalable Dynamic Analysis for Automated Fault Location and Avoidance Rajiv Gupta Funded by NSF grants from CPA, CSR, & CRI programs and grants from Microsoft Research Software bugs cost the
Modeling pilot project at Ericsson Expert Analytics
 Modeling pilot project at Ericsson Expert Analytics Gábor Ferenc Kovács, Gergely Dévai ELTE-Soft, ELTE University, Ericsson Ericsson Modeling Days, Stockholm, 13-14 September 2016 Overview Background of
Modeling pilot project at Ericsson Expert Analytics Gábor Ferenc Kovács, Gergely Dévai ELTE-Soft, ELTE University, Ericsson Ericsson Modeling Days, Stockholm, 13-14 September 2016 Overview Background of
Unit- and Sequence Test Generation with HOL-TestGen
 Unit- and Sequence Test Generation with HOL-TestGen Tests et Methodes Formelles Prof. Burkhart Wolff Univ - Paris-Sud / LRI 16.6.2015 B.Wolff - HOL-TestGen 1 Overview HOL-TestGen and its Business-Case
Unit- and Sequence Test Generation with HOL-TestGen Tests et Methodes Formelles Prof. Burkhart Wolff Univ - Paris-Sud / LRI 16.6.2015 B.Wolff - HOL-TestGen 1 Overview HOL-TestGen and its Business-Case
Identifying Security Critical Properties for the Dynamic Verification of a Processor
 Identifying Security Critical Properties for the Dynamic Verification of a Processor Rui Zhang, Natalie Stanley, Christopher Griggs, Andrew Chi, Cynthia Sturton 04-12-2017, ASLOS XI AN CHINA 1 Processor
Identifying Security Critical Properties for the Dynamic Verification of a Processor Rui Zhang, Natalie Stanley, Christopher Griggs, Andrew Chi, Cynthia Sturton 04-12-2017, ASLOS XI AN CHINA 1 Processor
Failure Sketching: A Technique for Automated Root Cause Diagnosis of In-Production Failures
 Failure Sketching: A Technique for Automated Root Cause Diagnosis of In-Production Failures Baris Kasikci, Benjamin Schubert, Cristiano Pereira, Gilles Pokam, George Candea Debugging In-Production Software
Failure Sketching: A Technique for Automated Root Cause Diagnosis of In-Production Failures Baris Kasikci, Benjamin Schubert, Cristiano Pereira, Gilles Pokam, George Candea Debugging In-Production Software
11/19/2013. Imperative programs
 if (flag) 1 2 From my perspective, parallelism is the biggest challenge since high level programming languages. It s the biggest thing in 50 years because industry is betting its future that parallel programming
if (flag) 1 2 From my perspective, parallelism is the biggest challenge since high level programming languages. It s the biggest thing in 50 years because industry is betting its future that parallel programming
Fully Automatic and Precise Detection of Thread Safety Violations
 Fully Automatic and Precise Detection of Thread Safety Violations Michael Pradel and Thomas R. Gross Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich 1 Motivation Thread-safe classes: Building blocks for concurrent
Fully Automatic and Precise Detection of Thread Safety Violations Michael Pradel and Thomas R. Gross Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich 1 Motivation Thread-safe classes: Building blocks for concurrent
Processes & Threads. Concepts: processes - units of sequential execution.
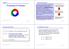 Chapter 2 Processes & Threads concurrent processes We structure complex systems as sets of simpler activities, each represented as a sequential process. Processes can overlap or be concurrent, so as to
Chapter 2 Processes & Threads concurrent processes We structure complex systems as sets of simpler activities, each represented as a sequential process. Processes can overlap or be concurrent, so as to
Chapter 2. Processes & Threads. Concurrency: processes & threads 1. Magee/Kramer
 Chapter 2 Processes & Threads Concurrency: processes & threads 1 concurrent processes We structure complex systems as sets of simpler activities, each represented as a sequential process. Processes can
Chapter 2 Processes & Threads Concurrency: processes & threads 1 concurrent processes We structure complex systems as sets of simpler activities, each represented as a sequential process. Processes can
A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems
 SHIM:A A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems p. 1/28 A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Joint work with Olivier Tardieu SHIM:A
SHIM:A A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems p. 1/28 A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Joint work with Olivier Tardieu SHIM:A
A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems
 A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Joint work with Olivier Tardieu SHIM:A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems p. 1/38 Definition
A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Joint work with Olivier Tardieu SHIM:A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems p. 1/38 Definition
Helgi Sigurbjarnarson
 Nickel A Framework for Design and Verification of Information Flow Control Systems Helgi Sigurbjarnarson, Luke Nelson, Bruno Castro-Karney, James Bornholt, Emina Torlak, and Xi Wang.org Enforcing information
Nickel A Framework for Design and Verification of Information Flow Control Systems Helgi Sigurbjarnarson, Luke Nelson, Bruno Castro-Karney, James Bornholt, Emina Torlak, and Xi Wang.org Enforcing information
Static and Dynamic Program Analysis: Synergies and Applications
 Static and Dynamic Program Analysis: Synergies and Applications Mayur Naik Intel Labs, Berkeley CS 243, Stanford University March 9, 2011 Today s Computing Platforms Trends: parallel cloud mobile Traits:
Static and Dynamic Program Analysis: Synergies and Applications Mayur Naik Intel Labs, Berkeley CS 243, Stanford University March 9, 2011 Today s Computing Platforms Trends: parallel cloud mobile Traits:
A Trace Simplification Technique for Effective Debugging of Concurrent Programs
 A Trace Simplification Technique for Effective Debugging of Concurrent Programs Nicholas Jalbert EECS Department, UC Berkeley, CA, USA jalbert@cs.berkeley.edu Koushik Sen EECS Department, UC Berkeley,
A Trace Simplification Technique for Effective Debugging of Concurrent Programs Nicholas Jalbert EECS Department, UC Berkeley, CA, USA jalbert@cs.berkeley.edu Koushik Sen EECS Department, UC Berkeley,
Concurrency in Java Prof. Stephen A. Edwards
 Concurrency in Java Prof. Stephen A. Edwards The Java Language Developed by James Gosling et al. at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s Originally called Oak, first intended application was as an OS for
Concurrency in Java Prof. Stephen A. Edwards The Java Language Developed by James Gosling et al. at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s Originally called Oak, first intended application was as an OS for
Sequential Consistency & TSO. Subtitle
 Sequential Consistency & TSO Subtitle Core C1 Core C2 data = 0, 1lag SET S1: store data = NEW S2: store 1lag = SET L1: load r1 = 1lag B1: if (r1 SET) goto L1 L2: load r2 = data; Will r2 always be set to
Sequential Consistency & TSO Subtitle Core C1 Core C2 data = 0, 1lag SET S1: store data = NEW S2: store 1lag = SET L1: load r1 = 1lag B1: if (r1 SET) goto L1 L2: load r2 = data; Will r2 always be set to
Chapter 5 Concurrency: Mutual Exclusion. and. Synchronization. Operating Systems: Internals. and. Design Principles
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 5 Concurrency: Mutual Exclusion and Synchronization Seventh Edition By William Stallings Designing correct routines for controlling concurrent
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 5 Concurrency: Mutual Exclusion and Synchronization Seventh Edition By William Stallings Designing correct routines for controlling concurrent
Visualizing the Synchronization of Java-Threads with UML
 Visualizing the Synchronization of Java-Threads with UML Katharina Mehner Annika Wagner University of Paderborn Department of Computer Science D-33095 Paderborn, Germany {mehner awa@upb.de Abstract Concurrent
Visualizing the Synchronization of Java-Threads with UML Katharina Mehner Annika Wagner University of Paderborn Department of Computer Science D-33095 Paderborn, Germany {mehner awa@upb.de Abstract Concurrent
G52CON: Concepts of Concurrency
 G52CON: Concepts of Concurrency Lecture 1: Introduction Brian Logan School of Computer Science bsl@cs.nott.ac.uk Outline of this lecture" why concurrency... applications of concurrency sequential vs concurrent
G52CON: Concepts of Concurrency Lecture 1: Introduction Brian Logan School of Computer Science bsl@cs.nott.ac.uk Outline of this lecture" why concurrency... applications of concurrency sequential vs concurrent
Embedded System Programming
 Embedded System Programming Multicore ES (Module 40) Yann-Hang Lee Arizona State University yhlee@asu.edu (480) 727-7507 Summer 2014 The Era of Multi-core Processors RTOS Single-Core processor SMP-ready
Embedded System Programming Multicore ES (Module 40) Yann-Hang Lee Arizona State University yhlee@asu.edu (480) 727-7507 Summer 2014 The Era of Multi-core Processors RTOS Single-Core processor SMP-ready
SEDA: An Architecture for Well-Conditioned, Scalable Internet Services
 SEDA: An Architecture for Well-Conditioned, Scalable Internet Services Matt Welsh, David Culler, and Eric Brewer Computer Science Division University of California, Berkeley Operating Systems Principles
SEDA: An Architecture for Well-Conditioned, Scalable Internet Services Matt Welsh, David Culler, and Eric Brewer Computer Science Division University of California, Berkeley Operating Systems Principles
A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems
 A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Joint work with Olivier Tardieu SHIM:A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems p. 1/30 Definition
A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Joint work with Olivier Tardieu SHIM:A Deterministic Concurrent Language for Embedded Systems p. 1/30 Definition
Synchronization in Concurrent Programming. Amit Gupta
 Synchronization in Concurrent Programming Amit Gupta Announcements Project 1 grades are out on blackboard. Detailed Grade sheets to be distributed after class. Project 2 grades should be out by next Thursday.
Synchronization in Concurrent Programming Amit Gupta Announcements Project 1 grades are out on blackboard. Detailed Grade sheets to be distributed after class. Project 2 grades should be out by next Thursday.
Differential program verification
 Differential program verification Shuvendu K. Lahiri Research in Software Engineering (RiSE), Microsoft Research Redmond, WA Involved in building static assertion checkers HAVOC [POPL 06, 08, 09, CAV 09,
Differential program verification Shuvendu K. Lahiri Research in Software Engineering (RiSE), Microsoft Research Redmond, WA Involved in building static assertion checkers HAVOC [POPL 06, 08, 09, CAV 09,
Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization
 Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization Stavros Tripakis, Edward A. Lee UC Berkeley EECS 144/244 Fall 2014 Copyright 2014, E. A. Lee, J. Roydhowdhury, S. A. Seshia, S. Tripakis
Fundamental Algorithms for System Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization Stavros Tripakis, Edward A. Lee UC Berkeley EECS 144/244 Fall 2014 Copyright 2014, E. A. Lee, J. Roydhowdhury, S. A. Seshia, S. Tripakis
Automatic Testing of Sequential and Concurrent Substitutability
 Automatic Testing of Sequential and Concurrent Substitutability Michael Pradel and Thomas R. Gross Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich 1 Motivation void bar(foo f) { f.m();... } bar() expects functionality
Automatic Testing of Sequential and Concurrent Substitutability Michael Pradel and Thomas R. Gross Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich 1 Motivation void bar(foo f) { f.m();... } bar() expects functionality
Transaction Memory for Existing Programs Michael M. Swift Haris Volos, Andres Tack, Shan Lu, Adam Welc * University of Wisconsin-Madison, *Intel
 Transaction Memory for Existing Programs Michael M. Swift Haris Volos, Andres Tack, Shan Lu, Adam Welc * University of Wisconsin-Madison, *Intel Where do TM programs ome from?! Parallel benchmarks replacing
Transaction Memory for Existing Programs Michael M. Swift Haris Volos, Andres Tack, Shan Lu, Adam Welc * University of Wisconsin-Madison, *Intel Where do TM programs ome from?! Parallel benchmarks replacing
Verifying a Concurrent Garbage Collector using a Rely-Guarantee Methodology
 Verifying a Concurrent Garbage Collector using a Rely-Guarantee Methodology Yannick Zakowski David Cachera Delphine Demange Gustavo Petri David Pichardie Suresh Jagannathan Jan Vitek Automatic memory management
Verifying a Concurrent Garbage Collector using a Rely-Guarantee Methodology Yannick Zakowski David Cachera Delphine Demange Gustavo Petri David Pichardie Suresh Jagannathan Jan Vitek Automatic memory management
Do you have to reproduce the bug on the first replay attempt?
 Do you have to reproduce the bug on the first replay attempt? PRES: Probabilistic Replay with Execution Sketching on Multiprocessors Soyeon Park, Yuanyuan Zhou University of California, San Diego Weiwei
Do you have to reproduce the bug on the first replay attempt? PRES: Probabilistic Replay with Execution Sketching on Multiprocessors Soyeon Park, Yuanyuan Zhou University of California, San Diego Weiwei
Tom Ball Sebastian Burckhardt Madan Musuvathi Microsoft Research
 Tom Ball (tball@microsoft.com) Sebastian Burckhardt (sburckha@microsoft.com) Madan Musuvathi (madanm@microsoft.com) Microsoft Research P&C Parallelism Concurrency Performance Speedup Responsiveness Correctness
Tom Ball (tball@microsoft.com) Sebastian Burckhardt (sburckha@microsoft.com) Madan Musuvathi (madanm@microsoft.com) Microsoft Research P&C Parallelism Concurrency Performance Speedup Responsiveness Correctness
Implementing Symmetric Multiprocessing in LispWorks
 Implementing Symmetric Multiprocessing in LispWorks Making a multithreaded application more multithreaded Martin Simmons, LispWorks Ltd Copyright 2009 LispWorks Ltd Outline Introduction Changes in LispWorks
Implementing Symmetric Multiprocessing in LispWorks Making a multithreaded application more multithreaded Martin Simmons, LispWorks Ltd Copyright 2009 LispWorks Ltd Outline Introduction Changes in LispWorks
CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 23: Programming Languages. Aaron Bauer Winter 2014
 CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 23: Programming Languages Aaron Bauer Winter 2014 Choosing a Programming Language Most of the time you won t have a choice about what programming language to
CSE373: Data Structure & Algorithms Lecture 23: Programming Languages Aaron Bauer Winter 2014 Choosing a Programming Language Most of the time you won t have a choice about what programming language to
Automatically Repairing Concurrency Bugs with ARC MUSEPAT 2013 Saint Petersburg, Russia
 Automatically Repairing Concurrency Bugs with ARC MUSEPAT 2013 Saint Petersburg, Russia David Kelk, Kevin Jalbert, Jeremy S. Bradbury Faculty of Science (Computer Science) University of Ontario Institute
Automatically Repairing Concurrency Bugs with ARC MUSEPAT 2013 Saint Petersburg, Russia David Kelk, Kevin Jalbert, Jeremy S. Bradbury Faculty of Science (Computer Science) University of Ontario Institute
Fast dynamic program analysis Race detection. Konstantin Serebryany May
 Fast dynamic program analysis Race detection Konstantin Serebryany May 20 2011 Agenda Dynamic program analysis Race detection: theory ThreadSanitizer: race detector Making ThreadSanitizer
Fast dynamic program analysis Race detection Konstantin Serebryany May 20 2011 Agenda Dynamic program analysis Race detection: theory ThreadSanitizer: race detector Making ThreadSanitizer
Problems with Concurrency. February 19, 2014
 with Concurrency February 19, 2014 s with concurrency interleavings race conditions dead GUI source of s non-determinism deterministic execution model 2 / 30 General ideas Shared variable Access interleavings
with Concurrency February 19, 2014 s with concurrency interleavings race conditions dead GUI source of s non-determinism deterministic execution model 2 / 30 General ideas Shared variable Access interleavings
First-Class Synchronization Barriers. Franklyn Turbak Wellesley College
 First-Class Synchronization Barriers Franklyn Turbak Wellesley College Overview What is a Synchronization Barrier? Dimensions of Barriers Synchrons: First-Class Barriers with a Variable Number of Participants
First-Class Synchronization Barriers Franklyn Turbak Wellesley College Overview What is a Synchronization Barrier? Dimensions of Barriers Synchrons: First-Class Barriers with a Variable Number of Participants
Yuxi Chen, Shu Wang, Shan Lu, and Karthikeyan Sankaralingam *
 Yuxi Chen, Shu Wang, Shan Lu, and Karthikeyan Sankaralingam * * 2 q Synchronization mistakes in multithreaded programs Thread 1 Thread 2 If(ptr){ tmp = *ptr; ptr = NULL; } Segfault q Common q Hard to diagnose
Yuxi Chen, Shu Wang, Shan Lu, and Karthikeyan Sankaralingam * * 2 q Synchronization mistakes in multithreaded programs Thread 1 Thread 2 If(ptr){ tmp = *ptr; ptr = NULL; } Segfault q Common q Hard to diagnose
More Synchronization; Concurrency in Java. CS 475, Spring 2018 Concurrent & Distributed Systems
 More Synchronization; Concurrency in Java CS 475, Spring 2018 Concurrent & Distributed Systems Review: Semaphores Synchronization tool that provides more sophisticated ways (than Mutex locks) for process
More Synchronization; Concurrency in Java CS 475, Spring 2018 Concurrent & Distributed Systems Review: Semaphores Synchronization tool that provides more sophisticated ways (than Mutex locks) for process
Unifying Events & Logs into the Cloud
 Unifying Events & Logs into the Cloud October 05, 2015 CloudOpen/LinuxCon, Dublin Eduardo Silva eduardo@treasuredata.com @edsiper About Me Eduardo Silva Github & Twitter Personal Blog @edsiper http://edsiper.linuxchile.cl
Unifying Events & Logs into the Cloud October 05, 2015 CloudOpen/LinuxCon, Dublin Eduardo Silva eduardo@treasuredata.com @edsiper About Me Eduardo Silva Github & Twitter Personal Blog @edsiper http://edsiper.linuxchile.cl
A taxonomy of race. D. P. Helmbold, C. E. McDowell. September 28, University of California, Santa Cruz. Santa Cruz, CA
 A taxonomy of race conditions. D. P. Helmbold, C. E. McDowell UCSC-CRL-94-34 September 28, 1994 Board of Studies in Computer and Information Sciences University of California, Santa Cruz Santa Cruz, CA
A taxonomy of race conditions. D. P. Helmbold, C. E. McDowell UCSC-CRL-94-34 September 28, 1994 Board of Studies in Computer and Information Sciences University of California, Santa Cruz Santa Cruz, CA
Practical Concurrency. Copyright 2007 SpringSource. Copying, publishing or distributing without express written permission is prohibited.
 Practical Concurrency Agenda Motivation Java Memory Model Basics Common Bug Patterns JDK Concurrency Utilities Patterns of Concurrent Processing Testing Concurrent Applications Concurrency in Java 7 2
Practical Concurrency Agenda Motivation Java Memory Model Basics Common Bug Patterns JDK Concurrency Utilities Patterns of Concurrent Processing Testing Concurrent Applications Concurrency in Java 7 2
Causes of Software Failures
 Causes of Software Failures Hardware Faults Permanent faults, e.g., wear-and-tear component Transient faults, e.g., bit flips due to radiation Software Faults (Bugs) (40% failures) Nondeterministic bugs,
Causes of Software Failures Hardware Faults Permanent faults, e.g., wear-and-tear component Transient faults, e.g., bit flips due to radiation Software Faults (Bugs) (40% failures) Nondeterministic bugs,
Concurrent Models of Computation
 Concurrent Models of Computation Edward A. Lee Robert S. Pepper Distinguished Professor, UC Berkeley EECS 219D: Concurrent Models of Computation Fall 2011 Copyright 2011, Edward A. Lee, All rights reserved
Concurrent Models of Computation Edward A. Lee Robert S. Pepper Distinguished Professor, UC Berkeley EECS 219D: Concurrent Models of Computation Fall 2011 Copyright 2011, Edward A. Lee, All rights reserved
4/6/2011. Model Checking. Encoding test specifications. Model Checking. Encoding test specifications. Model Checking CS 4271
 Mel Checking LTL Property System Mel Mel Checking CS 4271 Mel Checking OR Abhik Roychoudhury http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~abhik Yes No, with Counter-example trace 2 Recap: Mel Checking for mel-based testing
Mel Checking LTL Property System Mel Mel Checking CS 4271 Mel Checking OR Abhik Roychoudhury http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~abhik Yes No, with Counter-example trace 2 Recap: Mel Checking for mel-based testing
Program logics for relaxed consistency
 Program logics for relaxed consistency UPMARC Summer School 2014 Viktor Vafeiadis Max Planck Institute for Software Systems (MPI-SWS) 1st Lecture, 28 July 2014 Outline Part I. Weak memory models 1. Intro
Program logics for relaxed consistency UPMARC Summer School 2014 Viktor Vafeiadis Max Planck Institute for Software Systems (MPI-SWS) 1st Lecture, 28 July 2014 Outline Part I. Weak memory models 1. Intro
Using Intel VTune Amplifier XE and Inspector XE in.net environment
 Using Intel VTune Amplifier XE and Inspector XE in.net environment Levent Akyil Technical Computing, Analyzers and Runtime Software and Services group 1 Refresher - Intel VTune Amplifier XE Intel Inspector
Using Intel VTune Amplifier XE and Inspector XE in.net environment Levent Akyil Technical Computing, Analyzers and Runtime Software and Services group 1 Refresher - Intel VTune Amplifier XE Intel Inspector
Deterministic Replay and Data Race Detection for Multithreaded Programs
 Deterministic Replay and Data Race Detection for Multithreaded Programs Dongyoon Lee Computer Science Department - 1 - The Shift to Multicore Systems 100+ cores Desktop/Server 8+ cores Smartphones 2+ cores
Deterministic Replay and Data Race Detection for Multithreaded Programs Dongyoon Lee Computer Science Department - 1 - The Shift to Multicore Systems 100+ cores Desktop/Server 8+ cores Smartphones 2+ cores
Introduction to programming with semaphores Fri 1 Sep 2017
 Introduction to programming with semaphores Fri 1 Sep 2017 K. V. S. Prasad Dept of Computer Science Chalmers University Lecture 2 of TDA384/DIT301, August October2017 Assignments? How s it going with the
Introduction to programming with semaphores Fri 1 Sep 2017 K. V. S. Prasad Dept of Computer Science Chalmers University Lecture 2 of TDA384/DIT301, August October2017 Assignments? How s it going with the
Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer
 Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer The Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer ensures application reliability and security by detecting application vulnerabilities, including memory leaks and memory
Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer The Oracle Developer Studio Code Analyzer ensures application reliability and security by detecting application vulnerabilities, including memory leaks and memory
Synchronization. CSCI 5103 Operating Systems. Semaphore Usage. Bounded-Buffer Problem With Semaphores. Monitors Other Approaches
 Synchronization CSCI 5103 Operating Systems Monitors Other Approaches Instructor: Abhishek Chandra 2 3 Semaphore Usage wait(s) Critical section signal(s) Each process must call wait and signal in correct
Synchronization CSCI 5103 Operating Systems Monitors Other Approaches Instructor: Abhishek Chandra 2 3 Semaphore Usage wait(s) Critical section signal(s) Each process must call wait and signal in correct
Optimal Instrumentation of Data-flow in Concurrent Data Structures
 Optimal Instrumentation of Data-flow in Concurrent Data Structures Samaneh Navabpour 1, Borzoo Bonakdarpour 2, and Sebastian Fischmeister 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University
Optimal Instrumentation of Data-flow in Concurrent Data Structures Samaneh Navabpour 1, Borzoo Bonakdarpour 2, and Sebastian Fischmeister 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University
PerfGuard: Binary-Centric Application Performance Monitoring in Production Environments
 PerfGuard: Binary-Centric Application Performance Monitoring in Production Environments Chung Hwan Kim, Junghwan Rhee *, Kyu Hyung Lee +, Xiangyu Zhang, Dongyan Xu * + Performance Problems Performance
PerfGuard: Binary-Centric Application Performance Monitoring in Production Environments Chung Hwan Kim, Junghwan Rhee *, Kyu Hyung Lee +, Xiangyu Zhang, Dongyan Xu * + Performance Problems Performance
An Introduction to Python (TEJ3M & TEJ4M)
 An Introduction to Python (TEJ3M & TEJ4M) What is a Programming Language? A high-level language is a programming language that enables a programmer to write programs that are more or less independent of
An Introduction to Python (TEJ3M & TEJ4M) What is a Programming Language? A high-level language is a programming language that enables a programmer to write programs that are more or less independent of
CS 153 Design of Operating Systems
 CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Winter 19 Lecture 2: Historical perspective Instructor: Nael Abu-Ghazaleh Last time What is an OS? What roles does it play? Today: Historic evolution of Operating Systems
CS 153 Design of Operating Systems Winter 19 Lecture 2: Historical perspective Instructor: Nael Abu-Ghazaleh Last time What is an OS? What roles does it play? Today: Historic evolution of Operating Systems

