Enterprise Java Unit 1- Chapter 6 Prof. Sujata Rizal
|
|
|
- Lewis Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction JDBC is a Java standard that provides the interface for connecting from Java to relational databases. The JDBC standard is defined by Sun Microsystems and implemented through the standard java.sql interfaces. This allows individual providers to implement and extend the standard with their own JDBC drivers. JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity, which is a standard Java API for database -independent connectivity between the Java programming language and a wide range of databases. The JDBC library includes APIs for each of the tasks commonly associated with database usage: Making a connection to a database Creating SQL or MySQL statements Executing that SQL or MySQL queries in the database Viewing & Modifying the resulting records JDBC API is a Java API that can access any kind of tabular data, especially data stored in a Relational Database. JDBC works with Java on a variety of platforms, such as Windows, Mac OS, and the various versions of UNIX. Design of JDBC Just as Java was designed to provide platform independence from hardware/software platforms, so too JDBC has been designed to provide some degree of database independence for developers. JDBC is designed to provide a database-neutral API for accessing relational databases from different vendors. Just as a Java application does not need to be aware of the operating system platform on which it is running, so too JDBC has been designed so that the database application can use the same methods to access data regardless of the underlying database product. JDBC was developed to work with the most common type of database: the relational database. This is not to say that JDBC cannot be used with another type of database. In fact, there are JDBC drivers that allow the API to be used to connect to both high-end, mainframe databases, which are not relational, and to access flat files and spreadsheets as databases (which are definitely not relational). But the reality is that JDBC is most commonly used with relational databases. The technical definition of a relational database is a database that stores data as a collection of related entities. These entities are composed of attributes that describe the entity, and each entity has a collection of rows. Another way to think about a relational database is that it stores information on real-world objects (the entities). The information about the objects is contained in the attributes for the object. 1
2 Since real world objects have some type of relation to each other, we must have a facility for expressing relations between the objects in the database. The relationships between the database objects is described using a query language, the most popular of which is the Structured Query Language (SQL). JavaSoft's JDBC consists of two layers: the JDBC API and the JDBC Driver Manager API. The JDBC API is the top layer and is the programming interface in Java to structured query language (SQL) which is the standard for accessing relational databases. The JDBC API communicates with the JDBC Driver Manager API, sending it various SQL statements. The manager communicates (transparent to the programmer) with the various third party drivers (provided by Database vendors like Oracle) that actually connect to the database and return the information from the query. JDBC Architecture: The JDBC API supports both two-tier and three-tier processing models for database access but in general JDBC Architecture consists of two layers: JDBC API: This provides the application-to-jdbc Manager connection. JDBC Driver API: This supports the JDBC Manager-to-Driver Connection. The JDBC API uses a driver manager and database-specific drivers to provide transparent connectivity to heterogeneous databases. The JDBC driver manager ensures that the correct driver is used to access each data source. The driver manager is capable of supporting multiple concurrent drivers connected to multiple heterogeneous databases. Following is the architectural diagram, which shows the location of the driver manager with respect to the JDBC drivers and the Java application: Fig. Architectural diagram 2
3 Common JDBC Components: The JDBC API provides the following interfaces and classes: DriverManager: This class manages a list of database drivers. Matches connection requests from the java application with the proper database driver using communication subprotocol. The first driver that recognizes a certain subprotocol under JDBC will be used to establish a database Connection. Driver: This interface handles the communications with the database server. You will interact directly with Driver objects very rarely. Instead, you use DriverManager objects, which manages objects of this type. It also abstracts the details associated with working with Driver objects Connection : This interface with all methods for contacting a database. The connection object represents communication context, i.e., all communication with database is through connection object only. Statement : You use objects created from this interface to submit the SQL statements to the database. Some derived interfaces accept parameters in addition to executing stored procedures. ResultSet: These objects hold data retrieved from a database after you execute an SQL query using Statement objects. It acts as an iterator to allow you to move through its data. SQLException: This class handles any errors that occur in a database application. JDBC configuration What is JDBC Driver? JDBC drivers implement the defined interfaces in the JDBC API for interacting with your database server. For example, using JDBC drivers enable you to open database connections and to interact with it by sending SQL or database commands then receiving results with Java. The Java.sql package that ships with JDK contains various classes with their behaviours defined and their actual implementaions are done in third-party drivers. Third party vendors implement the java.sql.driver interface in their database driver. JDBC Drivers Types: JDBC driver implementations vary because of the wide variety of operating systems and hardware platforms in which Java operates. Sun has divided the implementation types into four categories, Types 1, 2, 3, and 4, which is explained below: 3
4 Type 1: JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver: In a Type 1 driver, a JDBC bridge is used to access ODBC drivers installed on each client machine. Using ODBC requires configuring on your system a Data Source Name (DSN) that represents the target database. When Java first came out, this was a useful driver because most databases only supported ODBC access but now this type of driver is recommended only for experimental use or when no other alternative is available. The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver uses ODBC driver to connect to the database. The JDBC- ODBC bridge driver converts JDBC method calls into the ODBC function calls. This is now discouraged because of thin driver. The JDBC-ODBC bridge that comes with JDK 1.2 is a good example of this kind of driver. Advantages: easy to use. can be easily connected to any database. Disadvantages: Fig. Type 1: JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver Performance degraded because JDBC method call is converted into the ODBC function calls. The ODBC driver needs to be installed on the client machine. Type 2: JDBC-Native API: The Native API driver uses the client-side libraries of the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into native calls of the database API. It is not written entirely in java. In a Type 2 driver, JDBC API calls are converted into native C/C++ API calls which are unique to the database. These drivers typically provided by the database vendors and used in the same manner as the JDBC-ODBC Bridge, the vendor-specific driver must be 4
5 installed on each client machine. If we change the Database we have to change the native API as it is specific to a database and they are mostly obsolete now but you may realize some speed increase with a Type 2 driver, because it eliminates ODBC's overhead. The Oracle Call Interface (OCI) driver is an example of a Type 2 driver. Advantage: Fig. Type 2: JDBC-Native API performance upgraded than JDBC-ODBC bridge driver. Disadvantage: The Native driver needs to be installed on the each client machine. The Vendor client library needs to be installed on client machine. Type 3: JDBC-Net pure Java: In a Type 3 driver, a three-tier approach is used to accessing databases. The JDBC clients use standard network sockets to communicate with an middleware application server. The socket information is then translated by the middleware application server into the call format required by the DBMS, and forwarded to the database server. This kind of driver is extremely flexible, since it requires no code installed on the client and a single driver can actually provide access to multiple databases. You can think of the application server as a JDBC "proxy," meaning that it makes calls for the client application. As a result, you need some knowledge of the application server's configuration in order to effectively use this driver type. Your application server might use a Type 1, 2, or 4 driver to communicate with the database, understanding the nuances will prove helpful. 5
6 Advantage: Fig. Type 3: JDBC-Net pure Java No client side library is required because of application server that can perform many tasks like auditing, load balancing, logging etc. Disadvantages: Network support is required on client machine. Requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier. Maintenance of Network Protocol driver becomes costly because it requires databasespecific coding to be done in the middle tier. Type 4: 100% pure Java Thin driver: In a Type 4 driver, a pure Java-based driver that communicates directly with vendor's database through socket connection. This is the highest performance driver available for the database and is usually provided by the vendor itself. This kind of driver is extremely flexible, you don't need to install special software on the client or server. Further, these drivers can be downloaded dynamically. MySQL's Connector/J driver is a Type 4 driver. Because of the proprietary nature of their network protocols, database vendors usually supply type 4 drivers. 6
7 Advantage: Better performance than all other drivers. No software is required at client side or server side. Disadvantage: Drivers depends on the Database. Which Driver should be used? If you are accessing one type of database, such as Oracle, Sybase, or IBM, the preferred driver type is 4. If your Java application is accessing multiple types of databases at the same time, type 3 is the preferred driver. Type 2 drivers are useful in situations where a type 3 or type 4 driver is not available yet for your database. The type 1 driver is not considered a deployment-level driver and is typically used for development and testing purposes only. After you've installed the appropriate driver, it's time to establish a database connection using JDBC. The programming involved to establish a JDBC connection is fairly simple. Here are these simple five steps: Register the Driver Create a Connection Create SQL Statement Execute SQL Statement Closing the connection 7
8 In this example we are using MySql as the database. So we need to know following information for the mysql database: Driver class: The driver class for the mysql database is com.mysql.jdbc.driver. Connection URL: The connection URL for the mysql database is jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sujata where jdbc is the API, mysql is the database, localhost is the server name on which mysql is running, we may also use IP address, 3306 is the port number and sujata is the database name. We may use any database, in such case, you need to replace the sujata with your database name. Username: The default username for the mysql database is root. Password: Password is given by the user at the time of installing the mysql database. In this example, we are going to use root as the password. Import JDBC Packages: The Import statements tell the Java compiler where to find the classes you reference in your code and are placed at the very beginning of your source code. To use the standard JDBC package, which allows you to select, insert, update, and delete data in SQL tables, add the following imports to your source code: import java.sql.*; import oracle.jdbc.driver.*; import oracle.sql.*; Load and Register JDBC Driver: You must register the your driver in your program before you use it. Registering the driver is the process by which the Oracle driver's class file is loaded into memory so it can be utilized as an implementation of the JDBC interfaces. You need to do this registration only once in your program. Class.forName(): The most common approach to register a driver is to use Java's Class.forName() method to dynamically load the driver's class file into memory, which automatically registers it. This method is preferable because it allows you to make the driver registration configurable and portable. Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver"); Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); Connecting to Database: The getconnection() method is an overloaded method that takes three parameters, one each for the URL, username, and password. Only one parameter for the database URL. In this case, the URL contains the username 8
9 and password. Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, username, passwd); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL); Here each form requires a database URL. A database URL is an address that points to your database. Formulating a database URL is where most of the problems associated with establishing a connection occur. Following table lists down popular JDBC driver names and database URL. RDBMS JDBC driver name URL format MySQL com.mysql.jdbc.driver jdbc:mysql://hostname/ databasename ORACLE DB2 Sybase oracle.jdbc.driver.oracledriver jdbc:oracle:thin:@hostname:port Number:databaseName COM.ibm.db2.jdbc.net.DB2Driver jdbc:db2:hostname:port Number/databaseName com.sybase.jdbc.sybdriver jdbc:sybase:tds:hostname: Number/databaseName port All the highlighted part in URL format is static and you need to change only remaining part as per your database setup. Create Connection Object: Using a database URL with a username and password: The most commonly used form of getconnection() requires you URL, a username, and a password: to pass a database Assuming you are using Oracle's thin driver, you'll specify a host:port:databasename value for the database portion of the URL. If you have a host at TCP/IP address with a host name of amrood, and your Oracle listener is configured to listen on port 1521, and your database name is EMP, then complete database URL would then be: jdbc:oracle:thin:@amrood:1521:emp Now you have to call getconnection() method with appropriate username and password to get a Connection object as follows: String URL = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@amrood:1521:emp"; String USER = "username"; String PASS = "password" 9
10 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASS); Querying the Database Statement sql_stmt = conn.createstatement(); Executing the Query and Returning a ResultSet ResultSet rset = sql_stmt.executequery ("SELECT empno, ename, sal, deptno FROM emp ORDER BY ename"); Alternatively, the SQL statement can be placed in a string and then this string passed to the executequery() function. This is shown below. String sql = "SELECT empno, ename, sal, deptno FROM emp ORDER BY ename"; ResultSet rset = sql_stmt.executequery(sql); Closing JDBC connections: At the end of your JDBC program, it is required explicitly close all the connections to the database to end each database session. However, if you forget, Java's garbage collector will close the connection when it cleans up stale objects. Relying on garbage collection, especially in database programming, is very poor programming practice. You should make a habit of always closing the connection with the close() method associated with connection object. To ensure that a connection is closed, you could provide a finally block in your code. A finally block always executes, regardless if an exception occurs or not. rset.close(); (ResultSet object) sql_stmt.close(); (Statement Object) conn.close(); (Connection object) Interfaces Statement JDBC Statements Once a connection is obtained we can interact with the database. The JDBC Statement, CallableStatement, and PreparedStatement interfaces define the methods and properties that enable you to send SQL or PL/SQL commands and receive data from your database. PreparedStatement Recommended Use Use for general-purpose access to your database. Useful when you are using static SQL statements at runtime. The Statement interface cannot accept parameters. Use when you plan to use the SQL statements many times. The PreparedStatement interface accepts input parameters at runtime. 10
11 CallableStatement Use when you want to access database stored procedures. The CallableStatement interface can also accept runtime input parameters. The Statement Objects: Creating Statement Object: Before you can use a Statement object to execute a SQL statement, you need to create using the Connection object's createstatement( ) method, as in the following example: Statement stmt = null; try { stmt = conn.createstatement( ); catch (SQLException e) { finally { one Closing Statement Obeject: Just as you close a Connection object to save database resources, for the same reason you should also close the Statement object. A simple call to the close() method will do the job. If you close the Connection object first it will close the Statement object as well. However, you should always explicitly close the Statement object to ensure proper cleanup. Statement stmt = null; try { stmt = conn.createstatement( ); catch (SQLException e) { finally { stmt.close(); The PreparedStatement Objects: The PreparedStatement interface extends the Statement interface which gives you 11
12 added functionality with a couple of advantages over a generic Statement object. This statement gives you the flexibility of supplying arguments dynamically. Creating PreparedStatement Object: PreparedStatement pstmt = null; try { String SQL = "Update Employees SET age =? WHERE id =?"; pstmt = conn.preparestatement(sql); catch (SQLException e) { finally { Closing PreparedStatement Obeject: Just as you close a Statement object, for the same reason you should also close the PreparedStatement object. A simple call to the close() method will do the job. If you close the Connection object first it will close the PreparedStatement object as well. However, you should always explicitly close the PreparedStatement object to ensure proper cleanup. PreparedStatement pstmt = null; try { String SQL = "Update Employees SET age =? WHERE id =?"; pstmt = conn.preparestatement(sql); catch (SQLException e) { finally { pstmt.close(); 12
13 The CallableStatement Objects: Just as a Connection object creates the Statement and PreparedStatement objects, it also creates the CallableStatement object which would be used to execute a call to a database stored procedure. Creating CallableStatement Object: Suppose, you need to execute the following Oracle stored procedure: CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE getempname (EMP_ID IN NUMBER, EMP_FIRST OUT VARCHAR) AS BEGIN SELECT first INTO EMP_FIRST FROM Employees WHERE ID = EMP_ID; END; NOTE: Above stored procedure has been written for Oracle. Stored procedure - For MySQL as follows to create it in EMP database: DELIMITER $$ DELIMITER ; DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `EMP`.`getEmpName` $$ CREATE PROCEDURE `EMP`.`getEmpName` (IN EMP_ID INT, OUT EMP_FIRST VARCHAR(255)) BEGIN SELECT first INTO EMP_FIRST FROM Employees WHERE ID = EMP_ID; END $$ Closing CallableStatement Obeject: Just as you close other Statement object, for the same reason you should also close the CallableStatement object. A simple call to the close() method will do the job. If you close the Connection object first it will close the CallableStatement object as well. However, you should always explicitly close the CallableStatement object to ensure proper cleanup. CallableStatement cstmt = null; try { String SQL = "{call getempname (?,?)"; cstmt = conn.preparecall (SQL); catch (SQLException e) { finally { cstmt.close(); 13
JDBC Drivers Type. JDBC drivers implement the defined interfaces in the JDBC API for interacting with your database server.
 JDBC Drivers Type 1 What is JDBC Driver? JDBC drivers implement the defined interfaces in the JDBC API for interacting with your database server. For example, using JDBC drivers enable you to open database
JDBC Drivers Type 1 What is JDBC Driver? JDBC drivers implement the defined interfaces in the JDBC API for interacting with your database server. For example, using JDBC drivers enable you to open database
SNS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, Coimbatore
 SNS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, Coimbatore 641 107 Accredited by NAAC UGC with A Grade Approved by AICTE and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai IT6503 WEB PROGRAMMING UNIT 03 JDBC JDBC Overview JDBC implementation
SNS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, Coimbatore 641 107 Accredited by NAAC UGC with A Grade Approved by AICTE and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai IT6503 WEB PROGRAMMING UNIT 03 JDBC JDBC Overview JDBC implementation
About the Tutorial. Audience. Prerequisites. Copyright & Disclaimer
 About the Tutorial JDBC API is a Java API that can access any kind of tabular data, especially data stored in a Relational Database. JDBC works with Java on a variety of platforms, such as Windows, Mac
About the Tutorial JDBC API is a Java API that can access any kind of tabular data, especially data stored in a Relational Database. JDBC works with Java on a variety of platforms, such as Windows, Mac
Unit 3 - Java Data Base Connectivity
 Two-Tier Database Design The two-tier is based on Client-Server architecture. The direct communication takes place between client and server. There is no mediator between client and server. Because of
Two-Tier Database Design The two-tier is based on Client-Server architecture. The direct communication takes place between client and server. There is no mediator between client and server. Because of
UNIT-3 Java Database Client/Server
 UNIT-3 Java Database Client/Server TOPICS TO BE COVERED 3.1 Client-Server Design: Two-Tier Database Design, Three-Tier Database Design 3.2 The JDBC API: The API Components, Database Creation, table creation
UNIT-3 Java Database Client/Server TOPICS TO BE COVERED 3.1 Client-Server Design: Two-Tier Database Design, Three-Tier Database Design 3.2 The JDBC API: The API Components, Database Creation, table creation
e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Web Technology Module: JDBC INTRODUCTION Module No: CS/WT/26 Quadrant 2 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Web Technology Module: JDBC INTRODUCTION Module No: CS/WT/26 Quadrant 2 e-text Learning Objectives This module gives an introduction about Java Database
e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Web Technology Module: JDBC INTRODUCTION Module No: CS/WT/26 Quadrant 2 e-text Learning Objectives This module gives an introduction about Java Database
JDBC. Sun Microsystems has included JDBC API as a part of J2SDK to develop Java applications that can communicate with databases.
 JDBC The JDBC TM API is the application programming interface that provides universal data access for the Java TM platform. In other words, the JDBC API is used to work with a relational database or other
JDBC The JDBC TM API is the application programming interface that provides universal data access for the Java TM platform. In other words, the JDBC API is used to work with a relational database or other
Questions and Answers. A. A DataSource is the basic service for managing a set of JDBC drivers.
 Q.1) What is, in terms of JDBC, a DataSource? A. A DataSource is the basic service for managing a set of JDBC drivers B. A DataSource is the Java representation of a physical data source C. A DataSource
Q.1) What is, in terms of JDBC, a DataSource? A. A DataSource is the basic service for managing a set of JDBC drivers B. A DataSource is the Java representation of a physical data source C. A DataSource
JDBC. Oracle ODBC SP API SP API. SQL server C function calls. SQL server ODBC SP API. Oracle DSN Oracle ODBC Oracle
 How to Interact with DataBase? THETOPPERSWAY.COM Generally every DB vendor provides a User Interface through which we can easily execute SQL query s and get the result (For example Oracle Query Manager
How to Interact with DataBase? THETOPPERSWAY.COM Generally every DB vendor provides a User Interface through which we can easily execute SQL query s and get the result (For example Oracle Query Manager
UNIT III - JDBC Two Marks
 UNIT III - JDBC Two Marks 1.What is JDBC? JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity, which is a standard Java API for databaseindependent connectivity between the Java programming language and a wide
UNIT III - JDBC Two Marks 1.What is JDBC? JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity, which is a standard Java API for databaseindependent connectivity between the Java programming language and a wide
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) 25.1 What is JDBC?
 PART 25 Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) 25.1 What is JDBC? JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity, which is a standard Java API for database-independent connectivity between the Java programming
PART 25 Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) 25.1 What is JDBC? JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity, which is a standard Java API for database-independent connectivity between the Java programming
CSC System Development with Java. Database Connection. Department of Statistics and Computer Science. Budditha Hettige
 CSC 308 2.0 System Development with Java Database Connection Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science Budditha Hettige 1 From database to Java There are many brands of database: Microsoft
CSC 308 2.0 System Development with Java Database Connection Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science Budditha Hettige 1 From database to Java There are many brands of database: Microsoft
Part I: Stored Procedures. Introduction to SQL Programming Techniques. CSC 375, Fall 2017
 Introduction to SQL Programming Techniques CSC 375, Fall 2017 The Six Phases of a Project: Enthusiasm Disillusionment Panic Search for the Guilty Punishment of the Innocent Praise for non-participants
Introduction to SQL Programming Techniques CSC 375, Fall 2017 The Six Phases of a Project: Enthusiasm Disillusionment Panic Search for the Guilty Punishment of the Innocent Praise for non-participants
Kyle Brown Knowledge Systems Corporation by Kyle Brown and Knowledge Systems Corporation
 Kyle Brown Knowledge Systems Corporation 1 What is the JDBC? What other persistence mechanisms are available? What facilities does it offer? How is it used? 2 JDBC is the Java DataBase Connectivity specification
Kyle Brown Knowledge Systems Corporation 1 What is the JDBC? What other persistence mechanisms are available? What facilities does it offer? How is it used? 2 JDBC is the Java DataBase Connectivity specification
Introduction JDBC 4.1. Bok, Jong Soon
 Introduction JDBC 4.1 Bok, Jong Soon javaexpert@nate.com www.javaexpert.co.kr What is the JDBC TM Stands for Java TM Database Connectivity. Is an API (included in both J2SE and J2EE releases) Provides
Introduction JDBC 4.1 Bok, Jong Soon javaexpert@nate.com www.javaexpert.co.kr What is the JDBC TM Stands for Java TM Database Connectivity. Is an API (included in both J2SE and J2EE releases) Provides
JDBC Architecture. JDBC API: This provides the application-to- JDBC Manager connection.
 JDBC PROGRAMMING JDBC JDBC Java DataBase Connectivity Useful for database driven applications Standard API for accessing relational databases Compatible with wide range of databases Current Version JDBC
JDBC PROGRAMMING JDBC JDBC Java DataBase Connectivity Useful for database driven applications Standard API for accessing relational databases Compatible with wide range of databases Current Version JDBC
The Design of JDBC The Structured Query Language Basic JDBC Programming Concepts Query Execution Scrollable and Updatable Result Sets
 Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 13 Topics to be covered The Design of JDBC The Structured Query Language Basic JDBC Programming Concepts Query Execution Scrollable and Updatable Result Sets Introducing
Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 13 Topics to be covered The Design of JDBC The Structured Query Language Basic JDBC Programming Concepts Query Execution Scrollable and Updatable Result Sets Introducing
Programming in Java
 320341 Programming in Java Fall Semester 2014 Lecture 16: Introduction to Database Programming Instructor: Slides: Jürgen Schönwälder Bendick Mahleko Objectives This lecture introduces the following -
320341 Programming in Java Fall Semester 2014 Lecture 16: Introduction to Database Programming Instructor: Slides: Jürgen Schönwälder Bendick Mahleko Objectives This lecture introduces the following -
Working with Databases and Java
 Working with Databases and Java Pedro Contreras Department of Computer Science Royal Holloway, University of London January 30, 2008 Outline Introduction to relational databases Introduction to Structured
Working with Databases and Java Pedro Contreras Department of Computer Science Royal Holloway, University of London January 30, 2008 Outline Introduction to relational databases Introduction to Structured
Topic 12: Database Programming using JDBC. Database & DBMS SQL JDBC
 Topic 12: Database Programming using JDBC Database & DBMS SQL JDBC Database A database is an integrated collection of logically related records or files consolidated into a common pool that provides data
Topic 12: Database Programming using JDBC Database & DBMS SQL JDBC Database A database is an integrated collection of logically related records or files consolidated into a common pool that provides data
JDBC - INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
 JDBC - INTERVIEW QUESTIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/jdbc/jdbc_interview_questions.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Dear readers, these JDBC Interview Questions have been designed specially to get
JDBC - INTERVIEW QUESTIONS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/jdbc/jdbc_interview_questions.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Dear readers, these JDBC Interview Questions have been designed specially to get
PESIT Bangalore South Campus
 INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST II Date : 20-09-2016 Max Marks: 50 Subject & Code: JAVA & J2EE (10IS752) Section : A & B Name of faculty: Sreenath M V Time : 8.30-10.00 AM Note: Answer all five questions 1) a)
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST II Date : 20-09-2016 Max Marks: 50 Subject & Code: JAVA & J2EE (10IS752) Section : A & B Name of faculty: Sreenath M V Time : 8.30-10.00 AM Note: Answer all five questions 1) a)
Database connectivity (I) ()
 Agenda Lecture (06) Database connectivity (I) () Dr. Ahmed ElShafee Introduction Relational Database SQL Database Programming JDBC Overview Connecting DB 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Spring 2011, Distributed
Agenda Lecture (06) Database connectivity (I) () Dr. Ahmed ElShafee Introduction Relational Database SQL Database Programming JDBC Overview Connecting DB 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU Spring 2011, Distributed
JDBC SHORT NOTES. Abstract This document contains short notes on JDBC, their types with diagrams. Rohit Deshbhratar [ address]
![JDBC SHORT NOTES. Abstract This document contains short notes on JDBC, their types with diagrams. Rohit Deshbhratar [ address] JDBC SHORT NOTES. Abstract This document contains short notes on JDBC, their types with diagrams. Rohit Deshbhratar [ address]](/thumbs/79/78971151.jpg) JDBC SHORT NOTES Abstract This document contains short notes on JDBC, their types with diagrams. Rohit Deshbhratar [Email address] JDBC Introduction: Java DataBase Connectivity, commonly known as JDBC,
JDBC SHORT NOTES Abstract This document contains short notes on JDBC, their types with diagrams. Rohit Deshbhratar [Email address] JDBC Introduction: Java DataBase Connectivity, commonly known as JDBC,
Database Programming. Week 9. *Some of the slides in this lecture are created by Prof. Ian Horrocks from University of Oxford
 Database Programming Week 9 *Some of the slides in this lecture are created by Prof. Ian Horrocks from University of Oxford SQL in Real Programs We have seen only how SQL is used at the generic query interface
Database Programming Week 9 *Some of the slides in this lecture are created by Prof. Ian Horrocks from University of Oxford SQL in Real Programs We have seen only how SQL is used at the generic query interface
MANTHLY TEST SEPTEMBER 2017 QUESTION BANK CLASS: XII SUBJECT: INFORMATICS PRACTICES (065)
 MANTHLY TEST SEPTEMBER 2017 QUESTION BANK CLASS: XII SUBJECT: INFORMATICS PRACTICES (065) DATABASE CONNECTIVITY TO MYSQL Level- I Questions 1. What is the importance of java.sql.*; in java jdbc connection?
MANTHLY TEST SEPTEMBER 2017 QUESTION BANK CLASS: XII SUBJECT: INFORMATICS PRACTICES (065) DATABASE CONNECTIVITY TO MYSQL Level- I Questions 1. What is the importance of java.sql.*; in java jdbc connection?
Cyrus Shahabi Computer Science Department University of Southern California C. Shahabi
 Application Programming for Relational Databases Cyrus Shahabi Computer Science Department University of Southern California shahabi@usc.edu 1 Overview JDBC Package Connecting to databases with JDBC Executing
Application Programming for Relational Databases Cyrus Shahabi Computer Science Department University of Southern California shahabi@usc.edu 1 Overview JDBC Package Connecting to databases with JDBC Executing
Application Programming for Relational Databases
 Application Programming for Relational Databases Cyrus Shahabi Computer Science Department University of Southern California shahabi@usc.edu 1 Overview JDBC Package Connecting to databases with JDBC Executing
Application Programming for Relational Databases Cyrus Shahabi Computer Science Department University of Southern California shahabi@usc.edu 1 Overview JDBC Package Connecting to databases with JDBC Executing
This lecture. Databases - JDBC I. Application Programs. Database Access End Users
 This lecture Databases - I The lecture starts discussion of how a Java-based application program connects to a database using. (GF Royle 2006-8, N Spadaccini 2008) Databases - I 1 / 24 (GF Royle 2006-8,
This lecture Databases - I The lecture starts discussion of how a Java-based application program connects to a database using. (GF Royle 2006-8, N Spadaccini 2008) Databases - I 1 / 24 (GF Royle 2006-8,
Discuss setting up JDBC connectivity. Demonstrate a JDBC program Discuss and demonstrate methods associated with JDBC connectivity
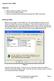 Objectives Discuss setting up JDBC connectivity. Demonstrate a JDBC program Discuss and demonstrate methods associated with JDBC connectivity Setting Up JDBC Before you can begin to utilize JDBC, you must
Objectives Discuss setting up JDBC connectivity. Demonstrate a JDBC program Discuss and demonstrate methods associated with JDBC connectivity Setting Up JDBC Before you can begin to utilize JDBC, you must
Lecture 2. Introduction to JDBC
 Lecture 2 Introduction to JDBC Introducing JDBC According to Sun, JDBC is not an acronym, but is commonly misinterpreted to mean Java DataBase Connectivity JDBC: is an API that provides universal data
Lecture 2 Introduction to JDBC Introducing JDBC According to Sun, JDBC is not an acronym, but is commonly misinterpreted to mean Java DataBase Connectivity JDBC: is an API that provides universal data
JDBC [Java DataBase Connectivity]
![JDBC [Java DataBase Connectivity] JDBC [Java DataBase Connectivity]](/thumbs/91/107154516.jpg) JDBC [Java DataBase Connectivity] Introduction Almost all the web applications need to work with the data stored in the databases. JDBC is Java specification that allows the Java programs to access the
JDBC [Java DataBase Connectivity] Introduction Almost all the web applications need to work with the data stored in the databases. JDBC is Java specification that allows the Java programs to access the
Database Programming Overview. COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems. Database Programming. JDBC Interfaces. JDBC Overview
 COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems Database Programming Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Database Programming Overview Most user interaction with
COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems Database Programming Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Database Programming Overview Most user interaction with
Unit 2 JDBC Programming
 Q1. What is JDBC? Explain the types of JDBC drivers? Ans. What is JDBC? JDBC is an API, which is used in java programming for interacting with database. JDBC (Java DataBase Connection) is the standard
Q1. What is JDBC? Explain the types of JDBC drivers? Ans. What is JDBC? JDBC is an API, which is used in java programming for interacting with database. JDBC (Java DataBase Connection) is the standard
SQL in a Server Environment
 SQL in a Server Environment Vaidė Narváez Computer Information Systems January 13th, 2011 The Three-Tier Architecture Application logic components Copyright c 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as
SQL in a Server Environment Vaidė Narváez Computer Information Systems January 13th, 2011 The Three-Tier Architecture Application logic components Copyright c 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as
Marcin Luckner Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Mathematics and Information Science
 Marcin Luckner Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Mathematics and Information Science mluckner@mini.pw.edu.pl http://www.mini.pw.edu.pl/~lucknerm } JDBC ("Java Database Connectivity ) is a set
Marcin Luckner Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Mathematics and Information Science mluckner@mini.pw.edu.pl http://www.mini.pw.edu.pl/~lucknerm } JDBC ("Java Database Connectivity ) is a set
CSCI/CMPE Object-Oriented Programming in Java JDBC. Dongchul Kim. Department of Computer Science University of Texas Rio Grande Valley
 CSCI/CMPE 3326 Object-Oriented Programming in Java JDBC Dongchul Kim Department of Computer Science University of Texas Rio Grande Valley Introduction to Database Management Systems Storing data in traditional
CSCI/CMPE 3326 Object-Oriented Programming in Java JDBC Dongchul Kim Department of Computer Science University of Texas Rio Grande Valley Introduction to Database Management Systems Storing data in traditional
ERwin and JDBC. Mar. 6, 2007 Myoung Ho Kim
 ERwin and JDBC Mar. 6, 2007 Myoung Ho Kim ERwin ERwin a popular commercial ER modeling tool» other tools: Dia (open source), Visio, ConceptDraw, etc. supports database schema generation 2 ERwin UI 3 Data
ERwin and JDBC Mar. 6, 2007 Myoung Ho Kim ERwin ERwin a popular commercial ER modeling tool» other tools: Dia (open source), Visio, ConceptDraw, etc. supports database schema generation 2 ERwin UI 3 Data
Top 50 JDBC Interview Questions and Answers
 Top 50 JDBC Interview Questions and Answers 1) What is the JDBC? JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC is a Java API that communicates with the database and execute SQLquery. 2) What is a JDBC
Top 50 JDBC Interview Questions and Answers 1) What is the JDBC? JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC is a Java API that communicates with the database and execute SQLquery. 2) What is a JDBC
Intoduction to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity-- Connecting to DBMS)
 Intoduction to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity-- Connecting to DBMS) Oracle JDBC Tutorial & Documentation http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/jdbc/basics/ Connector-J, MySql JDBC Driver Documentation,
Intoduction to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity-- Connecting to DBMS) Oracle JDBC Tutorial & Documentation http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/jdbc/basics/ Connector-J, MySql JDBC Driver Documentation,
CSE 308. Database Issues. Goals. Separate the application code from the database
 CSE 308 Database Issues The following databases are created with password as changeit anticyber cyber cedar dogwood elm clan Goals Separate the application code from the database Encourages you to think
CSE 308 Database Issues The following databases are created with password as changeit anticyber cyber cedar dogwood elm clan Goals Separate the application code from the database Encourages you to think
About Database Adapters
 About Database Adapters Sun Microsystems, Inc. 4150 Network Circle Santa Clara, CA 95054 U.S.A. Part No: 820 5069 07/08/08 Copyright 2007 Sun Microsystems, Inc. 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara, CA 95054
About Database Adapters Sun Microsystems, Inc. 4150 Network Circle Santa Clara, CA 95054 U.S.A. Part No: 820 5069 07/08/08 Copyright 2007 Sun Microsystems, Inc. 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara, CA 95054
Java Database Connectivity
 Java Database Connectivity INTRODUCTION Dr. Syed Imtiyaz Hassan Assistant Professor, Deptt. of CSE, Jamia Hamdard (Deemed to be University), New Delhi, India. s.imtiyaz@jamiahamdard.ac.in Agenda Introduction
Java Database Connectivity INTRODUCTION Dr. Syed Imtiyaz Hassan Assistant Professor, Deptt. of CSE, Jamia Hamdard (Deemed to be University), New Delhi, India. s.imtiyaz@jamiahamdard.ac.in Agenda Introduction
1. PhP Project. Create a new PhP Project as shown below and click next
 1. PhP Project Create a new PhP Project as shown below and click next 1 Choose Local Web Site (Apache 24 needs to be installed) Project URL is http://localhost/projectname Then, click next We do not use
1. PhP Project Create a new PhP Project as shown below and click next 1 Choose Local Web Site (Apache 24 needs to be installed) Project URL is http://localhost/projectname Then, click next We do not use
Lab # 9. Java to Database Connection
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 4113: Lab # 9 Java to Database Connection Eng. Haneen El-Masry December, 2014 2 Objective In this lab, we turn
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 4113: Lab # 9 Java to Database Connection Eng. Haneen El-Masry December, 2014 2 Objective In this lab, we turn
More Database Programming. CS157A Chris Pollett Nov. 2, 2005.
 More Database Programming CS157A Chris Pollett Nov. 2, 2005. Outline JDBC SQLJ Introduction Last day we went over some JDBC and SQLJ code examples from prior classes. Today, we will discuss JDBC and SQLJ
More Database Programming CS157A Chris Pollett Nov. 2, 2005. Outline JDBC SQLJ Introduction Last day we went over some JDBC and SQLJ code examples from prior classes. Today, we will discuss JDBC and SQLJ
Database Application Development
 Database Application Development Linda Wu (CMPT 354 2004-2) Topics SQL in application code Embedded SQL JDBC SQLJ Stored procedures Chapter 6 CMPT 354 2004-2 2 SQL in Application Code SQL commands can
Database Application Development Linda Wu (CMPT 354 2004-2) Topics SQL in application code Embedded SQL JDBC SQLJ Stored procedures Chapter 6 CMPT 354 2004-2 2 SQL in Application Code SQL commands can
Java and the Java DataBase Connectivity (JDBC) API. Todd Kaufman April 25, 2002
 Java and the Java DataBase Connectivity (JDBC) API Todd Kaufman April 25, 2002 Agenda BIO Java JDBC References Q&A Speaker 4 years Java experience 4 years JDBC experience 3 years J2EE experience BS from
Java and the Java DataBase Connectivity (JDBC) API Todd Kaufman April 25, 2002 Agenda BIO Java JDBC References Q&A Speaker 4 years Java experience 4 years JDBC experience 3 years J2EE experience BS from
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 21 of 162
 import java.sql.*; public class FirstExample { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/emp";
import java.sql.*; public class FirstExample { // JDBC driver name and database URL static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/emp";
CHAPTER 44. Java Stored Procedures
 CHAPTER 44 Java Stored Procedures 752 Oracle Database 12c: The Complete Reference You can write stored procedures, triggers, object type methods, and functions that call Java classes. In this chapter,
CHAPTER 44 Java Stored Procedures 752 Oracle Database 12c: The Complete Reference You can write stored procedures, triggers, object type methods, and functions that call Java classes. In this chapter,
You write standard JDBC API application and plug in the appropriate JDBC driver for the database the you want to use. Java applet, app or servlets
 JDBC Stands for Java Database Connectivity, is an API specification that defines the following: 1. How to interact with database/data-source from Java applets, apps, servlets 2. How to use JDBC drivers
JDBC Stands for Java Database Connectivity, is an API specification that defines the following: 1. How to interact with database/data-source from Java applets, apps, servlets 2. How to use JDBC drivers
SQL and Java. Database Systems Lecture 20 Natasha Alechina
 Database Systems Lecture 20 Natasha Alechina In this Lecture SQL in Java SQL from within other Languages SQL, Java, and JDBC For More Information Sun Java tutorial: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/jdbc
Database Systems Lecture 20 Natasha Alechina In this Lecture SQL in Java SQL from within other Languages SQL, Java, and JDBC For More Information Sun Java tutorial: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/jdbc
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 Chapter 10 Outline Database Programming: Techniques and Issues Embedded SQL, Dynamic SQL, and SQLJ Database Programming with Function Calls: SQL/CLI and JDBC Database Stored Procedures and SQL/PSM Comparing
Chapter 10 Outline Database Programming: Techniques and Issues Embedded SQL, Dynamic SQL, and SQLJ Database Programming with Function Calls: SQL/CLI and JDBC Database Stored Procedures and SQL/PSM Comparing
PERSİSTENCE OBJECT RELATİON MAPPİNG
 PERSİSTENCE Most of the applications require storing and retrieving objects in a persistent storage mechanism. This chapter introduces how to store and retrieve information in a persistent storage with
PERSİSTENCE Most of the applications require storing and retrieving objects in a persistent storage mechanism. This chapter introduces how to store and retrieve information in a persistent storage with
Databases and MySQL. COMP 342: Programming Methods. 16 September Databases and MySQL
 Databases and MySQL COMP 342: Programming Methods 16 September 2008 Databases and MySQL Database basics What is a database? A database consists of some number of tables. Each table consists of field names
Databases and MySQL COMP 342: Programming Methods 16 September 2008 Databases and MySQL Database basics What is a database? A database consists of some number of tables. Each table consists of field names
How to program applications. CS 2550 / Spring 2006 Principles of Database Systems. SQL is not enough. Roadmap
 How to program applications CS 2550 / Spring 2006 Principles of Database Systems 05 SQL Programming Using existing languages: Embed SQL into Host language ESQL, SQLJ Use a library of functions Design a
How to program applications CS 2550 / Spring 2006 Principles of Database Systems 05 SQL Programming Using existing languages: Embed SQL into Host language ESQL, SQLJ Use a library of functions Design a
DataBase Lab JAVA-DATABASE CONNECTION. Eng. Haneen El-masry
 In the name of Allah Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department ECOM 4113 DataBase Lab Lab # 9 JAVA-DATABASE CONNECTION El-masry 2013 Objective In this lab, we turn
In the name of Allah Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department ECOM 4113 DataBase Lab Lab # 9 JAVA-DATABASE CONNECTION El-masry 2013 Objective In this lab, we turn
Database Application Development
 CS 461: Database Systems Database Application Development supplementary material: Database Management Systems Sec. 6.2, 6.3 DBUtils.java, Student.java, Registrar.java, RegistrarServlet.java, PgRegistrar.sql
CS 461: Database Systems Database Application Development supplementary material: Database Management Systems Sec. 6.2, 6.3 DBUtils.java, Student.java, Registrar.java, RegistrarServlet.java, PgRegistrar.sql
Database Server. 2. Allow client request to the database server (using SQL requests) over the network.
 Database Server Introduction: Client/Server Systems is networked computing model Processes distributed between clients and servers. Client Workstation (usually a PC) that requests and uses a service Server
Database Server Introduction: Client/Server Systems is networked computing model Processes distributed between clients and servers. Client Workstation (usually a PC) that requests and uses a service Server
Introduction to SQL & Database Application Development Using Java
 Introduction to SQL & Database Application Development Using Java By Alan Andrea The purpose of this paper is to give an introduction to relational database design and sql with a follow up on how these
Introduction to SQL & Database Application Development Using Java By Alan Andrea The purpose of this paper is to give an introduction to relational database design and sql with a follow up on how these
JAVA AND DATABASES. Summer 2018
 JAVA AND DATABASES Summer 2018 JDBC JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) an API for working with databases in Java (works with any tabular data, but focuses on relational databases) Works with 3 basic actions:
JAVA AND DATABASES Summer 2018 JDBC JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) an API for working with databases in Java (works with any tabular data, but focuses on relational databases) Works with 3 basic actions:
Asst.Prof.Eng. IOAN-GHEORGHE RAŢIU, PhD Asst.Prof. NICOLETA DAVID. George Bariţiu University, Braşov
 WORKING WITH DATABASES IN JAVA Asst.Prof.Eng. IOAN-GHEORGHE RAŢIU, PhD Asst.Prof. NICOLETA DAVID George Bariţiu University, Braşov Abstract A database represents a modality of storing some information
WORKING WITH DATABASES IN JAVA Asst.Prof.Eng. IOAN-GHEORGHE RAŢIU, PhD Asst.Prof. NICOLETA DAVID George Bariţiu University, Braşov Abstract A database represents a modality of storing some information
Persistency Patterns. Repository and DAO
 Persistency Patterns Repository and DAO 1 Repository pattern Basically, the Repository pattern just means putting a façade over your persistence system so that you can shield the rest of your application
Persistency Patterns Repository and DAO 1 Repository pattern Basically, the Repository pattern just means putting a façade over your persistence system so that you can shield the rest of your application
(C) Global Journal of Engineering Science and Research Management
 ANDROID BASED SECURED PHOTO IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM USING DIGITAL WATERMARKING Prof.Abhijeet A.Chincholkar *1, Ms.Najuka B.Todekar 2, Ms.Sunita V.Ghai 3 *1 M.E. Digital Electronics, JCOET Yavatmal, India.
ANDROID BASED SECURED PHOTO IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM USING DIGITAL WATERMARKING Prof.Abhijeet A.Chincholkar *1, Ms.Najuka B.Todekar 2, Ms.Sunita V.Ghai 3 *1 M.E. Digital Electronics, JCOET Yavatmal, India.
SQL: Programming. Announcements (September 25) Motivation. CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems. Pros and cons of SQL.
 SQL: Programming CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements (September 25) 2 Homework #2 due this Thursday Submit to Yi not through Jun s office door Solution available this weekend No class
SQL: Programming CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements (September 25) 2 Homework #2 due this Thursday Submit to Yi not through Jun s office door Solution available this weekend No class
SQL: Programming Midterm in class next Thursday (October 5)
 Announcements (September 28) 2 Homework #1 graded Homework #2 due today Solution available this weekend SQL: Programming Midterm in class next Thursday (October 5) Open book, open notes Format similar
Announcements (September 28) 2 Homework #1 graded Homework #2 due today Solution available this weekend SQL: Programming Midterm in class next Thursday (October 5) Open book, open notes Format similar
JDBC, Transactions. Niklas Fors JDBC 1 / 38
 JDBC, Transactions SQL in Programs Embedded SQL and Dynamic SQL JDBC Drivers, Connections, Statements, Prepared Statements Updates, Queries, Result Sets Transactions Niklas Fors (niklas.fors@cs.lth.se)
JDBC, Transactions SQL in Programs Embedded SQL and Dynamic SQL JDBC Drivers, Connections, Statements, Prepared Statements Updates, Queries, Result Sets Transactions Niklas Fors (niklas.fors@cs.lth.se)
Oracle Database 10g Java Web
 Oracle Database 10g Java Web 2005 5 Oracle Database 10g Java Web... 3... 3... 4... 4... 4 JDBC... 5... 5... 5 JDBC... 6 JDBC... 8 JDBC... 9 JDBC... 10 Java... 11... 12... 12... 13 Oracle Database EJB RMI/IIOP...
Oracle Database 10g Java Web 2005 5 Oracle Database 10g Java Web... 3... 3... 4... 4... 4 JDBC... 5... 5... 5 JDBC... 6 JDBC... 8 JDBC... 9 JDBC... 10 Java... 11... 12... 12... 13 Oracle Database EJB RMI/IIOP...
JDBC 3.0. Java Database Connectivity. 1 Java
 JDBC 3.0 Database Connectivity 1 Contents 1 JDBC API 2 JDBC Architecture 3 Steps to code 4 Code 5 How to configure the DSN for ODBC Driver for MS-Access 6 Driver Types 7 JDBC-ODBC Bridge 8 Disadvantages
JDBC 3.0 Database Connectivity 1 Contents 1 JDBC API 2 JDBC Architecture 3 Steps to code 4 Code 5 How to configure the DSN for ODBC Driver for MS-Access 6 Driver Types 7 JDBC-ODBC Bridge 8 Disadvantages
CHAPTER 2 JDBC FUNDAMENTALS
 CHAPTER 2 JDBC FUNDAMENTALS OBJECTIVES After completing JDBC Fundamentals, you will be able to: Know the main classes in the JDBC API, including packages java.sql and javax.sql Know the difference between
CHAPTER 2 JDBC FUNDAMENTALS OBJECTIVES After completing JDBC Fundamentals, you will be able to: Know the main classes in the JDBC API, including packages java.sql and javax.sql Know the difference between
SQL in a Server Environment (ii)
 ICS 321 Spring 2012 SQL in a Server Environment (ii) Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa 03/19/2012 Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
ICS 321 Spring 2012 SQL in a Server Environment (ii) Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa 03/19/2012 Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa
Chapter 13 Introduction to SQL Programming Techniques
 Chapter 13 Introduction to SQL Programming Techniques Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 13 Outline Database Programming: Techniques and Issues Embedded
Chapter 13 Introduction to SQL Programming Techniques Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 13 Outline Database Programming: Techniques and Issues Embedded
SQL in a Server Environment
 ICS 321 Fall 2011 SQL in a Server Environment Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa 11/02/2011 Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa 1 Three
ICS 321 Fall 2011 SQL in a Server Environment Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa 11/02/2011 Lipyeow Lim -- University of Hawaii at Manoa 1 Three
Embedded SQL. csc343, Introduction to Databases Diane Horton with examples from Ullman and Widom Fall 2014
 Embedded SQL csc343, Introduction to Databases Diane Horton with examples from Ullman and Widom Fall 2014 Problems with using interactive SQL Standard SQL is not Turing-complete. E.g., Two profs are colleagues
Embedded SQL csc343, Introduction to Databases Diane Horton with examples from Ullman and Widom Fall 2014 Problems with using interactive SQL Standard SQL is not Turing-complete. E.g., Two profs are colleagues
JDBC BASIC 19/05/2012. Objectives. Java Database Connectivity. Definitions of JDBC. Part 1. JDBC basic Working with JDBC Adv anced JDBC programming
 Objectives Java Database Connectivity JDBC basic Working with JDBC Adv anced JDBC programming By Võ Văn Hải Faculty of Information Technologies Summer 2012 2/27 Definitions of JDBC JDBC APIs, which provides
Objectives Java Database Connectivity JDBC basic Working with JDBC Adv anced JDBC programming By Võ Văn Hải Faculty of Information Technologies Summer 2012 2/27 Definitions of JDBC JDBC APIs, which provides
Why use a database? You can query the data (run searches) You can integrate with other business systems that use the same database You can store huge
 175 Why use a database? You can query the data (run searches) You can integrate with other business systems that use the same database You can store huge numbers of records without the risk of corruption
175 Why use a database? You can query the data (run searches) You can integrate with other business systems that use the same database You can store huge numbers of records without the risk of corruption
O ne of the most important features of JavaServer
 INTRODUCTION TO DATABASES O ne of the most important features of JavaServer Pages technology is the ability to connect to a Databases store and efficiently manage large collections of information. JSP
INTRODUCTION TO DATABASES O ne of the most important features of JavaServer Pages technology is the ability to connect to a Databases store and efficiently manage large collections of information. JSP
Pieter van den Hombergh. March 25, 2018
 ergh Fontys Hogeschool voor Techniek en Logistiek March 25, 2018 ergh/fhtenl March 25, 2018 1/25 JDBC JDBC is a Java database connectivity technology (Java Standard Edition platform) from Oracle Corporation.
ergh Fontys Hogeschool voor Techniek en Logistiek March 25, 2018 ergh/fhtenl March 25, 2018 1/25 JDBC JDBC is a Java database connectivity technology (Java Standard Edition platform) from Oracle Corporation.
COMP102: Introduction to Databases, 23
 COMP102: Introduction to Databases, 23 Dr Muhammad Sulaiman Khan Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool U.K. 04 April, 2011 Programming with SQL Specific topics for today: Client/Server
COMP102: Introduction to Databases, 23 Dr Muhammad Sulaiman Khan Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool U.K. 04 April, 2011 Programming with SQL Specific topics for today: Client/Server
Database Application Development
 CS 500: Fundamentals of Databases Database Application Development supplementary material: Database Management Systems Sec. 6.2, 6.3 DBUtils.java, Student.java, Registrar.java, RegistrarServlet.java, PgRegistrar.sql
CS 500: Fundamentals of Databases Database Application Development supplementary material: Database Management Systems Sec. 6.2, 6.3 DBUtils.java, Student.java, Registrar.java, RegistrarServlet.java, PgRegistrar.sql
CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems. JDBC in Review. - Lab 2 -
 CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems JDBC in Review - - Department of Computing Science University of Alberta What Is JDBC? JDBC is a programming interface JDBC allows developers using java to gain access
CMPUT 391 Database Management Systems JDBC in Review - - Department of Computing Science University of Alberta What Is JDBC? JDBC is a programming interface JDBC allows developers using java to gain access
SAS ODBC Driver. Overview: SAS ODBC Driver. What Is ODBC? CHAPTER 1
 1 CHAPTER 1 SAS ODBC Driver Overview: SAS ODBC Driver 1 What Is ODBC? 1 What Is the SAS ODBC Driver? 2 Types of Data Accessed with the SAS ODBC Driver 3 Understanding SAS 4 SAS Data Sets 4 Unicode UTF-8
1 CHAPTER 1 SAS ODBC Driver Overview: SAS ODBC Driver 1 What Is ODBC? 1 What Is the SAS ODBC Driver? 2 Types of Data Accessed with the SAS ODBC Driver 3 Understanding SAS 4 SAS Data Sets 4 Unicode UTF-8
Chapter 1 An introduction to relational databases and SQL
 Chapter 1 An introduction to relational databases and SQL Murach's MySQL, C1 2015, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc. Slide 1 Objectives Knowledge Identify the three main hardware components of a client/server
Chapter 1 An introduction to relational databases and SQL Murach's MySQL, C1 2015, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc. Slide 1 Objectives Knowledge Identify the three main hardware components of a client/server
Instructor: Jinze Liu. Fall 2008
 Instructor: Jinze Liu Fall 2008 Database Project Database Architecture Database programming 2 Goal Design and implement a real application? Jinze Liu @ University of Kentucky 9/16/2008 3 Goal Design and
Instructor: Jinze Liu Fall 2008 Database Project Database Architecture Database programming 2 Goal Design and implement a real application? Jinze Liu @ University of Kentucky 9/16/2008 3 Goal Design and
Database Access with JDBC. Dr. Jens Bennedsen, Aarhus University, School of Engineering Aarhus, Denmark
 Database Access with JDBC Dr. Jens Bennedsen, Aarhus University, School of Engineering Aarhus, Denmark jbb@ase.au.dk Overview Overview of JDBC technology JDBC drivers Seven basic steps in using JDBC Retrieving
Database Access with JDBC Dr. Jens Bennedsen, Aarhus University, School of Engineering Aarhus, Denmark jbb@ase.au.dk Overview Overview of JDBC technology JDBC drivers Seven basic steps in using JDBC Retrieving
Introduction to JDBC. JDBC: Java Database Connectivity. Why Access a Database with Java? Compilation. Six Steps. Packages to Import
 Introduction to JDBC JDBC: Java Database Connectivity JDBC is used for accessing databases from Java applications Information is transferred from relations to objects and vice-versa databases optimized
Introduction to JDBC JDBC: Java Database Connectivity JDBC is used for accessing databases from Java applications Information is transferred from relations to objects and vice-versa databases optimized
Chapter 3 DB-Gateways
 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 3 DB-Gateways Outline Coupling DBMS and programming languages
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 3 DB-Gateways Outline Coupling DBMS and programming languages
ABOUT CORE JAVA COURSE SCOPE:
 ABOUT CORE JAVA COURSE SCOPE: JAVA based business programs perform well because constant JAVA requirements help designers to create multilevel programs with a component centered approach. JAVA growth allows
ABOUT CORE JAVA COURSE SCOPE: JAVA based business programs perform well because constant JAVA requirements help designers to create multilevel programs with a component centered approach. JAVA growth allows
SQL-PL Interface. Murali Mani. Perl /CGI with Oracle/mySQL Install your own web server and use servlets with JDBC and Oracle/mySQL
 SQL-PL Interface Some Possible Options Web Interface Perl /CGI with Oracle/mySQL Install your own web server and use servlets with JDBC and Oracle/mySQL Non-Web Interface JDBC with Oracle/mySQL Also other
SQL-PL Interface Some Possible Options Web Interface Perl /CGI with Oracle/mySQL Install your own web server and use servlets with JDBC and Oracle/mySQL Non-Web Interface JDBC with Oracle/mySQL Also other
JDBC Programming: Intro
 JDBC Programming: Intro Most interaction with DB is not via interactive interface Most people interact via 1. Application programs directly 2. Apps over the internet There are 3 general approaches to developing
JDBC Programming: Intro Most interaction with DB is not via interactive interface Most people interact via 1. Application programs directly 2. Apps over the internet There are 3 general approaches to developing
Java application using JDBC to connect to a database.
 JDBC(JAVA DATABASE CONNECTIVITY) The Java JDBC API enables Java applications to connect to relational databases via a standard API, so your Java applications become independent (almost) of the database
JDBC(JAVA DATABASE CONNECTIVITY) The Java JDBC API enables Java applications to connect to relational databases via a standard API, so your Java applications become independent (almost) of the database
Embedded SQL. csc343, Introduction to Databases Renée J. Miller and Fatemeh Nargesian and Sina Meraji Winter 2018
 Embedded SQL csc343, Introduction to Databases Renée J. Miller and Fatemeh Nargesian and Sina Meraji Winter 2018 Problems with using interactive SQL Standard SQL is not Turing-complete. E.g., Two profs
Embedded SQL csc343, Introduction to Databases Renée J. Miller and Fatemeh Nargesian and Sina Meraji Winter 2018 Problems with using interactive SQL Standard SQL is not Turing-complete. E.g., Two profs
Calling SQL from a host language (Java and Python) Kathleen Durant CS 3200
 Calling SQL from a host language (Java and Python) Kathleen Durant CS 3200 1 SQL code in other programming languages SQL commands can be called from within a host language (e.g., C++ or Java) program.
Calling SQL from a host language (Java and Python) Kathleen Durant CS 3200 1 SQL code in other programming languages SQL commands can be called from within a host language (e.g., C++ or Java) program.
Introduction to Databases
 JAVA JDBC Introduction to Databases Assuming you drove the same number of miles per month, gas is getting pricey - maybe it is time to get a Prius. You are eating out more month to month (or the price
JAVA JDBC Introduction to Databases Assuming you drove the same number of miles per month, gas is getting pricey - maybe it is time to get a Prius. You are eating out more month to month (or the price
Chapter 16: Databases
 Chapter 16: Databases Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 16 discusses the following main topics: Introduction to Database
Chapter 16: Databases Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 16 discusses the following main topics: Introduction to Database
Accessing databases in Java using JDBC
 Accessing databases in Java using JDBC Introduction JDBC is an API for Java that allows working with relational databases. JDBC offers the possibility to use SQL statements for DDL and DML statements.
Accessing databases in Java using JDBC Introduction JDBC is an API for Java that allows working with relational databases. JDBC offers the possibility to use SQL statements for DDL and DML statements.
Chapter 3 DB-Gateways
 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 3 DB-Gateways Outline Coupling DBMS and programming languages
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Deßloch AG Heterogene Informationssysteme Geb. 36, Raum 329 Tel. 0631/205 3275 dessloch@informatik.uni-kl.de Chapter 3 DB-Gateways Outline Coupling DBMS and programming languages
Oracle Database Jdbc Developer's Guide And Reference 10g Release 2
 Oracle Database Jdbc Developer's Guide And Reference 10g Release 2 Database Java Developer's Guide In releases prior to Oracle Database 10g release 2 (10.2), Java classes in the database cannot be audited
Oracle Database Jdbc Developer's Guide And Reference 10g Release 2 Database Java Developer's Guide In releases prior to Oracle Database 10g release 2 (10.2), Java classes in the database cannot be audited
Creating Enterprise and WorkGroup Applications with 4D ODBC
 Creating Enterprise and WorkGroup Applications with 4D ODBC Page 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 4D ODBC is an application development tool specifically designed to address the unique requirements of the client/server
Creating Enterprise and WorkGroup Applications with 4D ODBC Page 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 4D ODBC is an application development tool specifically designed to address the unique requirements of the client/server
DQpowersuite. Superior Architecture. A Complete Data Integration Package
 DQpowersuite Superior Architecture Since its first release in 1995, DQpowersuite has made it easy to access and join distributed enterprise data. DQpowersuite provides an easy-toimplement architecture
DQpowersuite Superior Architecture Since its first release in 1995, DQpowersuite has made it easy to access and join distributed enterprise data. DQpowersuite provides an easy-toimplement architecture
