Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign
|
|
|
- Felicia Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Unit 10.3d Process Mapping Gane-Sarson Notation Slide 1 Welcome to the Gane-Sarson Notation for Data Flow Diagrams Subunit. This is the third Subunit of the Process Mapping Unit. 1
2 Upon successful completion of this sub-unit the student is able to: Describe Gane-Sarson notation (symbols and conventions) for process diagramming. Read a data flow diagram in Gane-Sarson notation and describe the information generated and used, and the path of that information through the system. Slide 2 This subunit provides details about Gane-Sarson notation for data flow diagrams. We describe the standard diagramming symbols and conventions so that you will be able to read a Gane-Sarson data flow diagram and understand the data content and flow being communicated. This sub-unit does not cover other parts of Gane-Sarson notation, and is not meant to teach you how to draw the diagrams, only to understand and interpret them in case you encounter them in practice. 2
3 Methods for Diagramming Processes Process Aspects Context Process steps Data flow steps Information content Data transformation Flow control and state Roles involved ISO 5807 Yourdon text x Gane- Sarson text x text UML E-R diagram Slide 3 Each of the methods for diagramming a process has its own set of capabilities. Gane-Sarson represents the process context (that is, the process or system boundaries, interactions with the outside world, and the major functions). It also represents information content, the order or sequence of the data flow steps involved in the process, transformations that occur or should occur, and the roles of the persons completing the steps in the process. While Gane and Sarson recognized the importance of representing information content and flow control, they did so through text data dictionaries (lists of the data elements) and structured English If-Then type statements. Since these are not graphic representations, we will not cover them here. Gane and Sarson represented context, data flow and data transformation through one diagram type, the Data Flow Diagram (DFD). Their approach used a high-level DFD to show context, and a more detailed (or series of more detailed) diagrams to show data flow steps. Data transformation is represented on the DFD by a process symbol that indicates that data transformation occurs. Then the actual transformation is specified using text. 3
4 Background Gane-Sarson notation was introduced in Chris Gane and Trish Sarson s 1977 book Structured Systems Analysis: Tools and Techniques Gane-Sarson notation is used for data flow diagrams. Although we have not seen Gane-Sarson notation used in healthcare, this notation is used in systems analysis and health IT analysts might encounter Gane-Sarson style diagrams. Slide 4 Gane-Sarson notation was introduced in Chris Gane and Trish Sarson s 1977 book Structured Systems Analysis: Tools and Techniques. The book was later published in 1979 by Prentice-Hall. Gane-Sarson notation is used for data flow diagrams. Although we have not seen Gane-Sarson notation used in healthcare, process analysts might encounter Gane-Sarson style diagrams, thus, we provide introductory-level information to the notation. 4
5 Use Gane-Sarson notation is specific to data flow diagrams to show the movement, transformation and storage of data. Slide 5 Gane-Sarson notation is specific to data flow diagrams which show the movement, transformation and storage of data. 5
6 Simplified On-line Appointment Scheduling Example Patient Web inquiry Accept / decline request 1 Check appointment availability Inquiry / reply Office schedule 2 Check current patient Inquiry / reply Admin. database Slide 6 This is an example of a simplified on-line appointment scheduling Gane-Sarson diagram. Note that the patient enters a web inquiry which generates 2 checks against different databases, and the information is returned to the patient for acceptance. 6
7 Gane-Sarson Symbols Entity Entity Double square 1 Process Rounded rectangle Data flow Arrow Data store Open-ended rectangle Slide 7 Gane-Sarson uses these four symbols. Entities show the people, roles, organizations or other things with which the system communicates, i.e. sources or consumers of data. Processes are shown by square rectangles with rounded corners. They represent the various individual functions that the system carries out to transform data inputs into outputs. Process boxes can be numbered to show the sequence in which they are carried out. Flows are shown by straight arrows. They are the connections between the entities, processes, and data stores. They represent the information that the processes require as input and the information they generate as output. Data stores are shown by an open-ended long rectangle. They represent collections of data that the system must access (read from or write to) or remember for some period of time. Data stores typically exist as files or databases. 7
8 Entities Entity Patient Entity Nurse Entity Nurse Entities represent people, organizations, or other things that interact with the system. send or consume information If the same entity is shown more than once in a diagram, a diagonal line is added to the lower right-hand corner to visually distinguish it Medical assistant Entity Medical assistant Entity Slide 8 Entities represent people, organizations, or other things that interact with the system, i.e. entities are outside of the system, that is they are part of a process, but external to the information system. Entities send or consume information, and in Gane-Sarson notation are also called sources or sinks of information. If the same entity is shown more than once in a diagram, a diagonal line is added to the lower right-hand corner to visually distinguish it. For example, if the Nurse entity was drawn twice, to keep from having a lot of criss-crossing lines, a single diagonal line would be added to the lower right-hand corner. Further, if a medical assistant entity was similarly drawn twice on the same diagram, two diagonal lines would be added to visually distinguish it from the Nurse and patient entities. 8
9 Process 1 Assess patient Processes transform data Process should be named or described with a single word (a verb), phrase, or simple sentence that describes what the process does. Similar to other notations, a good name will generally consist of a verb-object phrase such as check availability. In some cases, the process are named for a role, an organization, or a machine that performs the process. Slide 9 Processes transform data The Process should be named or described with a single word (a verb), phrase, or simple sentence that describes what the process does. Similar to other notations, a good name will generally consist of a verb-object phrase such as check availability. In some cases, the processes are named for a role, an organization, or a machine that performs the process. Processes are given a number in the upper right-hand corner; this is an identifier and does NOT imply sequence. Optionally, processes can also have a lower section, similar in appearance to the process identifier part at the top, in which the role or machine that accomplishes the process, or the physical location of the process is undertaken. 9
10 Flow prescription A data flow is a pipe through which data travel Straight lines indicate flow or movement of information Flow names indicate the meaning of the data that moves along the flow. A flow can: represent only one type of data, e.g., request or reply, OR consolidate several elementary data flows into one flow, e.g., request and reply the same content may have a different meaning in different parts of the system Every line needs an arrow head to indicate direction of the data flow Slide 10 Similar to ISO 5807, Gane-Sarson notation uses straight arrows Arrows should be named to indicate the meaning of the data that moves along the flow, i.e., a noun. Data flows with a verb name signify a process that has been omitted. Data flow in and out of a process must be altered in some way, i.e., not labeled the same thing. A flow can: represent only one type of data, e.g., request or reply, OR consolidate several elementary dataflows into one flow, e.g., request and reply. This is dependent on the intended detail-level of the diagram. The same content may have a different meaning in different parts of the system, e.g., address (as input by the receptionist) versus address after validation with the directory. Arrows indicate direction of the data flow, i.e., from the practice EMR to the pharmacy. 10
11 Data Store EMR A collection of data at rest Can be in computerized or noncomputerized format Stores are passive; processes put data in or read data D1 Claims database Slide 11 The store is used to model a collection of data at rest. Data stores can be in computerized or non-computerized form, such as paper charts, microfiche, index cards, etc. Stores are passive; processes put data in or read data. Like processes, data stores can be given an identifying number, e.g., D1, D2, etc., where the D denotes a data store and the number serves as a unique identifier. Like entities, data stores can be drawn more than once on a diagram to avoid crisscrossed lines, in this case, a vertical line is added to the closed end of the data store shape. 11
12 Event List? Unlike Yourdon notation, Gane-Sarson does not use an event list to indicate things that stimulate action from the system. Things that stimulate action from a system are indicated by entities. Slide 12 Unlike Yourdon notation, Gans-Sarson does not use an event list to indicate things that stimulate action from the system. Things that stimulate action from a system are indicated by entities. 12
13 Diagram levels are Diagram Levels a roll-up and drill-down functional decomposition is used to represent each process in more detailed steps / processes Context diagram is highest level There are as many lower-levels as needed Slide 13 Gane-Sarson, like Yourdon notation uses leveled diagrams, that is, a roll-up and drill-down approach where increasing levels of detail are shown on successive diagrams. A process called functional decomposition is used to represent each process in more detailed steps / processes. Each process in a DFD can be exploded to become a DFD. When this is done, decimal numbers can be used to identify the process while maintaining the links to the parent or higher level process on the parent diagram. Context diagram is highest level There are as many lower-levels as needed 13
14 Conventions Meaningful names Number processes and data stores Make sure the DFD is internally consistent and consistent with any associated DFDs. Exceptions are shown on lower-level diagrams Slide 14 Choose meaningful names for processes, flows, stores, and terminators. Number the processes and data stores. Make sure the DFD is internally consistent and consistent with any associated DFDs. Exceptions and error handling are shown on lower-level diagrams. 14
15 Aesthetics The size of the shapes should be consistent throughout the diagram. This limits the length of the name Color shading for shapes and arrows may be used to visually show different types of entities, processes, data stores or flows. Arrows in Gane-Sarson are straight and horizontal or vertical. Slide 15 The size of the shapes should be consistent throughout the diagram. This limits the length of the name. We found no guidance on the use of color shading for shapes or arrows, and expect that since the notation was developed in the 1970 s that color was not commonly used on the diagrams. However, today, color may be used to visually show different types of entities, processes, data stores or flows. Arrows in Gane-Sarson are straight, and horizontal or vertical i.e., no diagonal or curved arrow lines. Double headed arrows can be used instead of two separate arrows in opposite directions, such as to represent request and reply. 15
16 Rules for Correctness Entities may not send data directly to other entities send data directly to data stores get data directly from data stores No spontaneous data creation No black holes Source: Ken Hopkins, Newman College, 2001 Slide 16 Entities may not send data directly to other entities Entities may not send data directly to data stores (data must be processed in some way first) Entities may not get data directly from data stores (data must be processed in some way first) Information is neither created nor destroyed, it must come from and go to somewhere. Information comes from and goes to entities and data stores via processes. Watch for spontaneous data creation and black holes. Note: in-only data stores may be ok, as when being read by another system. Also out-only data stores may be ok, as when getting data from another system. Data flows with a verb name signify a process that has been omitted 16
17 Maintenance Gane-Sarson is a set of symbols and conventions named for the people who developed it. There is no formal maintenance organization. Individuals use and adapt it to suit their needs. Slide 17 Like Yourdon notation, Gane-Sarson is a set of symbols and conventions named for the people who developed it. Gane-Sarson notation has not been adopted as a standard. As such, there is no formal maintenance organization. Individuals use and adapt it to suit their needs. 17
18 References 1. Chris Gane and Trish Sarson, Structured Systems Analysis: Tools and Techniques, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ Slide 18 This reference is provided for your use. 18
Slide 1 Welcome to Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign: Process Mapping: Gane-Sarson Notation. This is Lecture d.
 WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture D Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating Process Diagrams Process Mapping Gane-Sarson Notation
WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture D Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating Process Diagrams Process Mapping Gane-Sarson Notation
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign
 Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign This material Comp0_Unit3d was developed by Duke University, funded by the Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the National
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign This material Comp0_Unit3d was developed by Duke University, funded by the Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the National
Lecture c, Process Mapping: Yourdon Notation for Data Flow Diagrams, covers Yourdon notation for data flow diagrams.
 WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture C Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating Process Diagrams Process Mapping Yourdon Notation
WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture C Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating Process Diagrams Process Mapping Yourdon Notation
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign
 Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Process Mapping: Yourdon Notation for Data Flow Diagrams This material Comp10_Unit3c was developed by Duke University, funded by the Department
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Process Mapping: Yourdon Notation for Data Flow Diagrams This material Comp10_Unit3c was developed by Duke University, funded by the Department
System Analysis & design
 Assiut University Faculty of Computers and Information System Analysis & design Year 2 Academic Year 2014/ 2015 Term (2) 5 A PICTURE IS WORTH A 1,000 WORDS A process model is a graphical way of representing
Assiut University Faculty of Computers and Information System Analysis & design Year 2 Academic Year 2014/ 2015 Term (2) 5 A PICTURE IS WORTH A 1,000 WORDS A process model is a graphical way of representing
Slide 1 Welcome to Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign: Process Mapping: Entity-Relationship Diagrams. This is Lecture e.
 WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture E Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating Process Diagrams Process Mapping UML notation for
WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture E Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating Process Diagrams Process Mapping UML notation for
Audio Transcripts. Workflow Analysis. Optional Lectures
 Audio Transcripts Workflow Analysis Optional Lectures WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture A Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating
Audio Transcripts Workflow Analysis Optional Lectures WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture A Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating
Working with Health IT Systems is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- ShareAlike 3.0 Unported license.
 Working with Health IT Systems is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- ShareAlike 3.0 Unported license. Johns Hopkins University. Welcome to the Fundamentals of Health Workflow
Working with Health IT Systems is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- ShareAlike 3.0 Unported license. Johns Hopkins University. Welcome to the Fundamentals of Health Workflow
Data Flow Diagrams System Analysis ( (
 7 Data Flow Diagrams System Analysis (1932475( Kendall & Kendall 7-1 Data Flow Diagrams A top down approach to diagramming data movement, it moves from general to specific. Graphically characterize data
7 Data Flow Diagrams System Analysis (1932475( Kendall & Kendall 7-1 Data Flow Diagrams A top down approach to diagramming data movement, it moves from general to specific. Graphically characterize data
Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1
 Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1 Learning Objectives Explain process modeling Discuss data-flow diagramming mechanics, definitions, and rules Discuss balancing data-flow
Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1 Learning Objectives Explain process modeling Discuss data-flow diagramming mechanics, definitions, and rules Discuss balancing data-flow
Session 2b: structured specifications Purpose and criteria Structured specification components Introduction to dataflow diagrams
 Session 2b: structured specifications Purpose and criteria Structured specification components Introduction to dataflow diagrams COMP 320 / 420, Spring, 2018 Conrad Weisert Criteria for the ESD (from session
Session 2b: structured specifications Purpose and criteria Structured specification components Introduction to dataflow diagrams COMP 320 / 420, Spring, 2018 Conrad Weisert Criteria for the ESD (from session
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign
 Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Unit 10.3f Process Mapping Entity-Relationship Diagrams Slide 1 Welcome to the Entity-Relationship Diagrams Subunit. This is the fifth and
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Unit 10.3f Process Mapping Entity-Relationship Diagrams Slide 1 Welcome to the Entity-Relationship Diagrams Subunit. This is the fifth and
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign
 Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign This material Comp10_Unit3b was developed by Duke University, funded by the Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the National
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign This material Comp10_Unit3b was developed by Duke University, funded by the Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the National
CHAPTER 19: Building a Preliminary Behavioral Model
 1 z 7 CHAPTER 19: Building a Preliminary Behavioral Model Things are always at their best in their beginning. Blaise Pascal Lettres Provinciales, 1656-1657, no. 4 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: Why a
1 z 7 CHAPTER 19: Building a Preliminary Behavioral Model Things are always at their best in their beginning. Blaise Pascal Lettres Provinciales, 1656-1657, no. 4 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: Why a
1. The narratives, diagrams, charts, and other written materials that explain how a system works are collectively called
 CH 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The narratives, diagrams, charts, and other written materials that explain how a system works are collectively called a) documentation. b) data flows. c) flowcharts. d) schema.
CH 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The narratives, diagrams, charts, and other written materials that explain how a system works are collectively called a) documentation. b) data flows. c) flowcharts. d) schema.
We move from a general information system to a Computer Based Information System
 Introduction to Information Systems: In this section of the course we start to think of the computer as just being a component in a system which may contain one or many computers linked together. An Information
Introduction to Information Systems: In this section of the course we start to think of the computer as just being a component in a system which may contain one or many computers linked together. An Information
Data and Process Modeling
 Chapter 5 Data and Process Modeling 5 CHAPTER Data and Process Modeling Chapter 5 is the second of four chapters in the systems analysis phase of the SDLC. This chapter discusses data and process modeling
Chapter 5 Data and Process Modeling 5 CHAPTER Data and Process Modeling Chapter 5 is the second of four chapters in the systems analysis phase of the SDLC. This chapter discusses data and process modeling
Data Process Modeling: Context Diagrams & Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
 Introduction Data Process Modeling: Context Diagrams & Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) MIS 374 When designing/building an information system for an organization, you should consider the following questions regarding
Introduction Data Process Modeling: Context Diagrams & Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) MIS 374 When designing/building an information system for an organization, you should consider the following questions regarding
(Murlidhar Group of Institutions,Bhavnagar Road, Rajkot) by:-assit. Prof. Vijay Vora (SOOADM) MCA-III
 Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
Unit 6 - Software Design and Development LESSON 10 DESIGN TOOLS, INPUTS, OUTPUTS, STORYBOARDS
 Unit 6 - Software Design and Development LESSON 10 DESIGN TOOLS, INPUTS, OUTPUTS, STORYBOARDS Previously Key features of programming languages Software Development Lifecycle Using tools to demonstrate
Unit 6 - Software Design and Development LESSON 10 DESIGN TOOLS, INPUTS, OUTPUTS, STORYBOARDS Previously Key features of programming languages Software Development Lifecycle Using tools to demonstrate
Functional Modeling with Data Flow Diagrams
 Functional Modeling with Data Flow Diagrams Amasi Elbakush 5771668 Teaching Assistant : Daniel Alami Utrecht University 1 Introduction Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) are a visual representation of the flow
Functional Modeling with Data Flow Diagrams Amasi Elbakush 5771668 Teaching Assistant : Daniel Alami Utrecht University 1 Introduction Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) are a visual representation of the flow
An Introduction to Business Process Modeling using Data Flow Diagrams
 An Introduction to Business Process Modeling using Data Flow Diagrams BSAD 141 Dave Novak BDIS: 2.2 (61-77) Lecture Overview Systems and Business processes Business process models Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
An Introduction to Business Process Modeling using Data Flow Diagrams BSAD 141 Dave Novak BDIS: 2.2 (61-77) Lecture Overview Systems and Business processes Business process models Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A process has a: 1) A) pronoun label B) noun phrase label C) verb phrase label D) adjective
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A process has a: 1) A) pronoun label B) noun phrase label C) verb phrase label D) adjective
Process Modeling. Chapter 7. Class 05: Process Modeling 1
 Process Modeling Chapter 7 Class 05: Process Modeling 1 Process Design Seldom the responsibility of the database designer or DBA However, understanding the basics aids communication with the process designers
Process Modeling Chapter 7 Class 05: Process Modeling 1 Process Design Seldom the responsibility of the database designer or DBA However, understanding the basics aids communication with the process designers
Process Modeling. Business Process Example. Process Design
 Process Modeling Chapter 7 Class 05: Process Modeling 1 Process Design Seldom the responsibility of the database designer or DBA However, understanding the basics aids communication with the process designers
Process Modeling Chapter 7 Class 05: Process Modeling 1 Process Design Seldom the responsibility of the database designer or DBA However, understanding the basics aids communication with the process designers
17/03/2018. Meltem Özturan
 Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Traditional Analysis Model Data flow diagrams Process description Data flow definiton Data store definition (Entity-Relationship
Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Traditional Analysis Model Data flow diagrams Process description Data flow definiton Data store definition (Entity-Relationship
Class diagrams. Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2. Class Diagrams: details. Class diagram for a simple watch
 Class diagrams Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2 CS 4354 Summer II 2014 Jill Seaman Used to describe the internal structure of the system. Also used to describe the application domain. They describe
Class diagrams Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2 CS 4354 Summer II 2014 Jill Seaman Used to describe the internal structure of the system. Also used to describe the application domain. They describe
Analysis and Design for Systems h. 9 th Edition
 Analysis and Design for Systems h 9 th Edition Chapter 5 Data and Process Analysis Chapter Objectives Describe data and process modeling dli concepts and tools, including data flow diagrams, a data dictionary,
Analysis and Design for Systems h 9 th Edition Chapter 5 Data and Process Analysis Chapter Objectives Describe data and process modeling dli concepts and tools, including data flow diagrams, a data dictionary,
CHAPTER 4 Data and Process Modeling (Phase 2: Systems Analysis)
 CHAPTER 4 Data and Process Modeling (Phase 2: Systems Analysis) Jakrapop Maisen DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS A data flow diagram (DFD) shows how data moves through an information system but does not show program
CHAPTER 4 Data and Process Modeling (Phase 2: Systems Analysis) Jakrapop Maisen DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS A data flow diagram (DFD) shows how data moves through an information system but does not show program
5Using Drawings, Pictures. and Graphs. Drawing in ReportSmith. Chapter
 5Chapter 5Using Drawings, Pictures Chapter and Graphs Besides system and custom report styles, ReportSmith offers you several means of achieving variety and impact in your reports, by: Drawing objects
5Chapter 5Using Drawings, Pictures Chapter and Graphs Besides system and custom report styles, ReportSmith offers you several means of achieving variety and impact in your reports, by: Drawing objects
System Analysis and Design. Data Flow Diagram. System Analysis and Design
 Data Flow Diagram 1 Data Flow diagram The dataflow diagram is a modeling tool that allows us to picture a system as a network of functional processes, connected to one another by pipelines and holding
Data Flow Diagram 1 Data Flow diagram The dataflow diagram is a modeling tool that allows us to picture a system as a network of functional processes, connected to one another by pipelines and holding
Process Modeling. Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU
 Process Modeling Based on Chapter 9 of Whitten, Bentley, and Dittman: Systems Analysis and Design for the Global Enterprise (7th Ed). McGraw Hill. 2007 Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU 2 Models: Logical and
Process Modeling Based on Chapter 9 of Whitten, Bentley, and Dittman: Systems Analysis and Design for the Global Enterprise (7th Ed). McGraw Hill. 2007 Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU 2 Models: Logical and
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign
 Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Process Mapping Diagramming Tools Process Mapping Diagramming Tools Learning Objectives 1. Articulate the value of process mapping. 2. Describe
Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign Process Mapping Diagramming Tools Process Mapping Diagramming Tools Learning Objectives 1. Articulate the value of process mapping. 2. Describe
An Automatic Tool for Checking Consistency between Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
 An Automatic Tool for Checking Consistency between Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) Rosziati Ibrahim, Siow Yen Yen Abstract System development life cycle (SDLC) is a process uses during the development of any
An Automatic Tool for Checking Consistency between Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) Rosziati Ibrahim, Siow Yen Yen Abstract System development life cycle (SDLC) is a process uses during the development of any
Structured Modeling Methods. Lecture 15: Advantages and Disadvantages. University of Toronto Department of Computer Science.
 Lecture 15: Structured Modeling Methods Basics of Structured Analysis Notations used Modeling Process Variants SADT SASS SSADM SRD Advantages and Disadvantages 2001, Steve Easterbrook CSC444 Lec15 1 Definition
Lecture 15: Structured Modeling Methods Basics of Structured Analysis Notations used Modeling Process Variants SADT SASS SSADM SRD Advantages and Disadvantages 2001, Steve Easterbrook CSC444 Lec15 1 Definition
Modelling as a Communication Tool: Introduction to Process Modelling. Modelling. Simplification in modelling. Representation in modelling
 CSE104 - Information Systems 1 Modelling as a Communication Tool: Introduction to Process Modelling The requirements specification document Must be communicated to key stakeholders Should contain: Functions
CSE104 - Information Systems 1 Modelling as a Communication Tool: Introduction to Process Modelling The requirements specification document Must be communicated to key stakeholders Should contain: Functions
Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay. Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II)
 Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II) We will continue our discussion on process modeling. In the previous lecture
Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II) We will continue our discussion on process modeling. In the previous lecture
Overview. What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies
 Overview What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies Information Systems What is a system? Why do systems fail? What is systems analysis and design? How do we do systems analysis?
Overview What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies Information Systems What is a system? Why do systems fail? What is systems analysis and design? How do we do systems analysis?
BPMN Working Draft. 1. Introduction
 1. Introduction The Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) has developed a standard Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN). The primary goal of BPMN is to provide a notation that is readily understandable
1. Introduction The Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) has developed a standard Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN). The primary goal of BPMN is to provide a notation that is readily understandable
Lab 16: Visio Introduction
 Lab 16: Visio Introduction () CONTENTS 1 Visio- Introduction to DFD Data Flow Diagraming... 2 1.1 In-Lab... 3 1.1.1 In-Lab Materials... 3 1.1.2 In-Lab Instructions... 3 2 Getting started: Let s decompose
Lab 16: Visio Introduction () CONTENTS 1 Visio- Introduction to DFD Data Flow Diagraming... 2 1.1 In-Lab... 3 1.1.1 In-Lab Materials... 3 1.1.2 In-Lab Instructions... 3 2 Getting started: Let s decompose
Module 5. Function-Oriented Software Design. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Function-Oriented Software Design Lesson 12 Structured Design Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson the student will be able to: Identify the aim of structured design. Explain
Module 5 Function-Oriented Software Design Lesson 12 Structured Design Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson the student will be able to: Identify the aim of structured design. Explain
Requirements Engineering
 Requirements Engineering Semi-Formal Specification: Structural Functional Requirements Structured Analysis Data Flow Diagrams SADT IDEF0 1 Back to the past GO/AO OO SA (DT) DFD SADT IDEF (Back to the future)
Requirements Engineering Semi-Formal Specification: Structural Functional Requirements Structured Analysis Data Flow Diagrams SADT IDEF0 1 Back to the past GO/AO OO SA (DT) DFD SADT IDEF (Back to the future)
COMN 1.1 Reference. Contents. COMN 1.1 Reference 1. Revision 1.1, by Theodore S. Hills, Copyright
 COMN 1.1 Reference 1 COMN 1.1 Reference Revision 1.1, 2017-03-30 by Theodore S. Hills, thills@acm.org. Copyright 2015-2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 2 1.1 Release 1.1... 3 1.2 Release 1.0... 3 1.3 Release
COMN 1.1 Reference 1 COMN 1.1 Reference Revision 1.1, 2017-03-30 by Theodore S. Hills, thills@acm.org. Copyright 2015-2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 2 1.1 Release 1.1... 3 1.2 Release 1.0... 3 1.3 Release
FLOW CHART AND PSEUDO CODE
 FLOW CHART AND PSEUDO CODE Flowchart A Flowchart is a pictorial representation of an algorithm. The First flowchart is made by John Von Newman in 1945. It is a symbolic diagram of operation sequence, dataflow,
FLOW CHART AND PSEUDO CODE Flowchart A Flowchart is a pictorial representation of an algorithm. The First flowchart is made by John Von Newman in 1945. It is a symbolic diagram of operation sequence, dataflow,
Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities: Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m18877 1 Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities: Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
OpenStax-CNX module: m18877 1 Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities: Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
Class diagrams. Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2. Class Diagrams: details. Class diagram for a simple watch
 Class diagrams Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2 CS 4354 Summer II 2015 Jill Seaman Used to describe the internal structure of the system. Also used to describe the application domain. They describe
Class diagrams Modeling with UML Chapter 2, part 2 CS 4354 Summer II 2015 Jill Seaman Used to describe the internal structure of the system. Also used to describe the application domain. They describe
22/09/2012 INFO2110. Copyright Warning. Revision of class diagram. Overview. Purpose of class diagram. Generalization Relationship
 22/09/202 INFO20 Copyright Warning System Analysis and Modelling Semester 2, 202 Lecture 8, Structural Modelling (II) COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 969 WARNING This material has been
22/09/202 INFO20 Copyright Warning System Analysis and Modelling Semester 2, 202 Lecture 8, Structural Modelling (II) COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 969 WARNING This material has been
STRUCTURED ANALYSIS AND SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
 r STRUCTURED ANALYSIS AND SYSTEM SPECIFICATION by Tom DeMarco Foreword by P.J. Plauger =3p YOURDDN PRESS =fm P T R PRENTICE HALL Englewood Cliffs, NJ 07632 PAGE PARTI: BASIC CONCEPTS 1. The Meaning of
r STRUCTURED ANALYSIS AND SYSTEM SPECIFICATION by Tom DeMarco Foreword by P.J. Plauger =3p YOURDDN PRESS =fm P T R PRENTICE HALL Englewood Cliffs, NJ 07632 PAGE PARTI: BASIC CONCEPTS 1. The Meaning of
Object-Oriented Systems Analysis and Design Using UML
 10 Object-Oriented Systems Analysis and Design Using UML Systems Analysis and Design, 8e Kendall & Kendall Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Learning Objectives Understand
10 Object-Oriented Systems Analysis and Design Using UML Systems Analysis and Design, 8e Kendall & Kendall Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Learning Objectives Understand
Chapter 3 System Models
 March 16, 2009 Introduction Graphical models aid in requirements and development Introduction Graphical models aid in requirements and development Different perspectives are possible: external: context
March 16, 2009 Introduction Graphical models aid in requirements and development Introduction Graphical models aid in requirements and development Different perspectives are possible: external: context
Alabama State Standards correlated to Merit Software Math Programs
 Alabama State Standards correlated to Merit Software Math Programs The Classroom Improvement Section is responsible for the development, implementation, and assessment of the minimum curriculum content
Alabama State Standards correlated to Merit Software Math Programs The Classroom Improvement Section is responsible for the development, implementation, and assessment of the minimum curriculum content
BPMN Getting Started Guide
 Enterprise Studio BPMN Getting Started Guide 2017-09-21 Applies to: Enterprise Studio 3.0.0, Team Server 3.0.0 Table of contents 1 About modeling with BPMN 5 1.1 What is BPMN? 5 1.2 BPMN modeling 5 1.3
Enterprise Studio BPMN Getting Started Guide 2017-09-21 Applies to: Enterprise Studio 3.0.0, Team Server 3.0.0 Table of contents 1 About modeling with BPMN 5 1.1 What is BPMN? 5 1.2 BPMN modeling 5 1.3
CSE 403: Software Engineering, Spring courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse403/15sp/ UML Class Diagrams. Emina Torlak
 CSE 403: Software Engineering, Spring 2015 courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse403/15sp/ UML Class Diagrams Emina Torlak emina@cs.washington.edu Outline Designing classes Overview of UML UML class diagrams
CSE 403: Software Engineering, Spring 2015 courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse403/15sp/ UML Class Diagrams Emina Torlak emina@cs.washington.edu Outline Designing classes Overview of UML UML class diagrams
OO Techniques & UML Class Diagrams
 OO Techniques & UML Class Diagrams SE3A04 Tutorial Jason Jaskolka Department of Computing and Software Faculty of Engineering McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada jaskolj@mcmaster.ca October 17,
OO Techniques & UML Class Diagrams SE3A04 Tutorial Jason Jaskolka Department of Computing and Software Faculty of Engineering McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada jaskolj@mcmaster.ca October 17,
UML Component Diagrams A.Y 2018/2019
 UML Component Diagrams A.Y 2018/2019 Component diagrams Component diagrams are integral to building your software system. Drawn out with UML diagramming software, they help your team understand the structure
UML Component Diagrams A.Y 2018/2019 Component diagrams Component diagrams are integral to building your software system. Drawn out with UML diagramming software, they help your team understand the structure
Chapter No 13 Batch Management Information Systems. Management Information Systems. Compiled By: Muzammil Ahmad Khan and Kashif Shaikh
 Chapter 13 Compiled By: Muzammil Ahmad Khan Muhammad Kashif Shaikh HS-107 : Course Objectives: Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: Understand the role of Information
Chapter 13 Compiled By: Muzammil Ahmad Khan Muhammad Kashif Shaikh HS-107 : Course Objectives: Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: Understand the role of Information
Chapter 9. Process Modeling. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Process Modeling McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives Define systems modeling and differentiate logical and physical models. Define
Chapter 9 Process Modeling McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives Define systems modeling and differentiate logical and physical models. Define
SYSTEMS DESIGN THROUGH THE USER INTERFACE. Jim Underwood School of Computing Sciences University of Technology, Sydney
 Jim Underwood School of Computing Sciences University of Technology, Sydney First Annual Conference on Information Systems Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, 6th February 1990 ABSTRACT This paper
Jim Underwood School of Computing Sciences University of Technology, Sydney First Annual Conference on Information Systems Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, 6th February 1990 ABSTRACT This paper
Basically, a graph is a representation of the relationship between two or more variables.
 1 Drawing Graphs Introduction In recent years, the CSEC Integrated Science Examination, Paper 02, deals with graphical analysis. That is, data is presented in a tabular format and the student is asked
1 Drawing Graphs Introduction In recent years, the CSEC Integrated Science Examination, Paper 02, deals with graphical analysis. That is, data is presented in a tabular format and the student is asked
Topic. Section 4.1 (3, 4)
 Topic.. California Standards: 6.0: Students graph a linear equation and compute the x- and y-intercepts (e.g., graph x + 6y = ). They are also able to sketch the region defined by linear inequality (e.g.,
Topic.. California Standards: 6.0: Students graph a linear equation and compute the x- and y-intercepts (e.g., graph x + 6y = ). They are also able to sketch the region defined by linear inequality (e.g.,
Ch 4: Requirements Engineering. What are requirements?
 Ch 4: Engineering What are? Functional and non-functional The software document specification engineering processes elicitation and analysis validation management The descriptions of what the system should
Ch 4: Engineering What are? Functional and non-functional The software document specification engineering processes elicitation and analysis validation management The descriptions of what the system should
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING. Lecture 6. By: Latifa ALrashed. Networks and Communication Department
 1 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Networks and Communication Department Lecture 6 By: Latifa ALrashed Outline q q q q q q q q Define the concept of the software life cycle in software engineering. Identify the system
1 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Networks and Communication Department Lecture 6 By: Latifa ALrashed Outline q q q q q q q q Define the concept of the software life cycle in software engineering. Identify the system
Ali Khan < Project Name > Design Document. Version 1.0. Group Id: S1. Supervisor Name: Sir.
 < Project Name > Design Document Version 1.0 Group Id: S1. Supervisor Name: Sir. Revision History Date Version Description Author Table of Contents 1. Introduction of Design Document 2. Entity Relationship
< Project Name > Design Document Version 1.0 Group Id: S1. Supervisor Name: Sir. Revision History Date Version Description Author Table of Contents 1. Introduction of Design Document 2. Entity Relationship
DFD Symbols. Process. Data Store Data Store Data Store
 ? Context Diagram Level 1 Diagram Level 2 Diagram DFD Symbols External Entity Source/Sink User Data Flow Process Process Data Store Data Store Data Store Rule for naming a process: The Joe Test A process
? Context Diagram Level 1 Diagram Level 2 Diagram DFD Symbols External Entity Source/Sink User Data Flow Process Process Data Store Data Store Data Store Rule for naming a process: The Joe Test A process
Data Flow Diagrams Examples
 1 of 6 20-Jan-12 1:42 AM Information Systems College of Business Administration University of Missouri - St. Louis Data Flow Diagrams Examples We will study a variety of diagramming tools this semester.
1 of 6 20-Jan-12 1:42 AM Information Systems College of Business Administration University of Missouri - St. Louis Data Flow Diagrams Examples We will study a variety of diagramming tools this semester.
5th GRADE MATHEMATICS
 5th GRADE MATHEMATICS 2018-2019 Year-at-a-Glance Place Value and Decimal Fractions Multi-digit number and decimal fraction operations Addition and Subtraction of Fractions Multiplication and Division of
5th GRADE MATHEMATICS 2018-2019 Year-at-a-Glance Place Value and Decimal Fractions Multi-digit number and decimal fraction operations Addition and Subtraction of Fractions Multiplication and Division of
Represent entities and relations with diagrams
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define data modeling terms Describe E-R Model Identify entities and relations Represent entities and relations with diagrams WHAT IS DATA MODELING? A data model is a collection of concepts
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define data modeling terms Describe E-R Model Identify entities and relations Represent entities and relations with diagrams WHAT IS DATA MODELING? A data model is a collection of concepts
SYSTEM DESIGN. 1 Introduction: 1.1 Overview: 1.2 Scope:
 SYSTEM DESIGN 1 Introduction: The purpose of System Design is to create a technical solution that satisfies the functional requirements for the system. During analysis, the focus is on what needs to be
SYSTEM DESIGN 1 Introduction: The purpose of System Design is to create a technical solution that satisfies the functional requirements for the system. During analysis, the focus is on what needs to be
Maths. Formative Assessment/key piece of work prior to end of unit: Term Autumn 1
 Term Autumn 1 3 weeks Negative numbers Multiples and factors Common factors Prime numbers Ordering decimal numbers Rounding Square numbers and square roots Prime factor decomposition LCM and HCF Square
Term Autumn 1 3 weeks Negative numbers Multiples and factors Common factors Prime numbers Ordering decimal numbers Rounding Square numbers and square roots Prime factor decomposition LCM and HCF Square
Lab Manual. Object Oriented Analysis And Design. TE(Computer) VI semester
 Lab Manual Object Oriented Analysis And Design TE(Computer) VI semester Index Sr. No. Title of Programming Assignment Page No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Study of Use Case Diagram Study of Activity Diagram Study
Lab Manual Object Oriented Analysis And Design TE(Computer) VI semester Index Sr. No. Title of Programming Assignment Page No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Study of Use Case Diagram Study of Activity Diagram Study
Lecture Notes. Structured Systems Analysis
 Lecture Notes Structured Systems Analysis Lecture 3 Structured Analysis & Data Flow Diagrams Written by Dr. Fred Grossman Copyright 1999 Fred Grossman All Rights Reserved Structured Systems Analysis Structured
Lecture Notes Structured Systems Analysis Lecture 3 Structured Analysis & Data Flow Diagrams Written by Dr. Fred Grossman Copyright 1999 Fred Grossman All Rights Reserved Structured Systems Analysis Structured
7. UML Sequence Diagrams Page 1 of 1
 7. UML Sequence Diagrams Page 1 of 1 Sequence Diagram in UML In the last article, we saw Activity diagrams, the notations to be used in Activity diagrams, their significance, and how to build an Activity
7. UML Sequence Diagrams Page 1 of 1 Sequence Diagram in UML In the last article, we saw Activity diagrams, the notations to be used in Activity diagrams, their significance, and how to build an Activity
Meltem Özturan
 Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 1 2 Modeling System Requirements Object Oriented Approach to Requirements OOA considers an IS as a set of objects that work together to carry out the function.
Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 1 2 Modeling System Requirements Object Oriented Approach to Requirements OOA considers an IS as a set of objects that work together to carry out the function.
INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design
 INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design Session 13 Systems Analysis and Construction Tools Lecturer: Prof. Ellis Edwin Badu, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eebadu@ug.edu.gh College of Education
INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design Session 13 Systems Analysis and Construction Tools Lecturer: Prof. Ellis Edwin Badu, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eebadu@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Chapter : Analysis Modeling
 Chapter : Analysis Modeling Requirements Analysis Requirements analysis Specifies software s operational characteristics Indicates software's interface with other system elements Establishes constraints
Chapter : Analysis Modeling Requirements Analysis Requirements analysis Specifies software s operational characteristics Indicates software's interface with other system elements Establishes constraints
SRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINERRING AND TECHNOLOGY THIRUPACHUR,THIRUVALLUR UNIT I OOAD PART A
 SRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINERRING AND TECHNOLOGY THIRUPACHUR,THIRUVALLUR UNIT I OOAD PART A 1. What is an object? An object is a combination of data and logic; the representation of some realworld
SRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINERRING AND TECHNOLOGY THIRUPACHUR,THIRUVALLUR UNIT I OOAD PART A 1. What is an object? An object is a combination of data and logic; the representation of some realworld
13/11/2017. Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515
 Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Data Flow Diagram (DFD) A graphical system model that shows all of the main requirements for an information
Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Data Flow Diagram (DFD) A graphical system model that shows all of the main requirements for an information
Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane
 Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane Movies create the illusion of movement by showing us 24 images per second. When the human eye processes 24 images per second it is interpreted in our
Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane Movies create the illusion of movement by showing us 24 images per second. When the human eye processes 24 images per second it is interpreted in our
Measures of Dispersion
 Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
What is a Class Diagram? A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships
 Class Diagram What is a Class Diagram? A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships Why do we need Class Diagram? Focus on the conceptual and specification
Class Diagram What is a Class Diagram? A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships Why do we need Class Diagram? Focus on the conceptual and specification
What is a Class Diagram? Class Diagram. Why do we need Class Diagram? Class - Notation. Class - Semantic 04/11/51
 What is a Class Diagram? Class Diagram A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships Why do we need Class Diagram? Focus on the conceptual and specification
What is a Class Diagram? Class Diagram A diagram that shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships Why do we need Class Diagram? Focus on the conceptual and specification
Scope & Sequence Overview - Stage 1, Year 2
 Scope & Sequence Overview - Stage 1, Year 2 Whole Numbers 1 applies place value, informally, to count, order, read and represent two- and three-digit numbers - MA1-4NA count forwards, count backwards,
Scope & Sequence Overview - Stage 1, Year 2 Whole Numbers 1 applies place value, informally, to count, order, read and represent two- and three-digit numbers - MA1-4NA count forwards, count backwards,
Software Development. Designing Software
 Software Development Designing Software Modules Modular programming is a software design technique that emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent, interchangeable modules, such
Software Development Designing Software Modules Modular programming is a software design technique that emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent, interchangeable modules, such
Design and UML Class Diagrams
 Design and UML Class Diagrams 1 Suggested reading: Practical UML: A hands on introduction for developers http://dn.codegear.com/article/31863 UML DistilledCh. 3, by M. Fowler How do people draw / write
Design and UML Class Diagrams 1 Suggested reading: Practical UML: A hands on introduction for developers http://dn.codegear.com/article/31863 UML DistilledCh. 3, by M. Fowler How do people draw / write
Structured Analysis and Structured Design
 Structured Analysis and Structured Design - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis - Structured Design Ver. 1.5 Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr http://dslab.konkuk.ac.kr References Modern
Structured Analysis and Structured Design - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis - Structured Design Ver. 1.5 Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr http://dslab.konkuk.ac.kr References Modern
Year Long Mathematics Plan Fourth Grade First Quarter: Discovering Patterns and Relationships (~5 weeks)
 Year Long Mathematics Plan Fourth Grade First Quarter: Discovering Patterns and Relationships (~5 weeks) *Concepts covered: patterns, relationships, T-tables, and graphs. *Critical Content: comparing,
Year Long Mathematics Plan Fourth Grade First Quarter: Discovering Patterns and Relationships (~5 weeks) *Concepts covered: patterns, relationships, T-tables, and graphs. *Critical Content: comparing,
Learning Microsoft Word By Greg Bowden. Chapter 10. Drawing Tools. Guided Computer Tutorials
 Learning Microsoft Word 2007 By Greg Bowden Chapter 10 Drawing Tools Guided Computer Tutorials www.gct.com.au PUBLISHED BY GUIDED COMPUTER TUTORIALS PO Box 311 Belmont, Victoria, 3216, Australia www.gct.com.au
Learning Microsoft Word 2007 By Greg Bowden Chapter 10 Drawing Tools Guided Computer Tutorials www.gct.com.au PUBLISHED BY GUIDED COMPUTER TUTORIALS PO Box 311 Belmont, Victoria, 3216, Australia www.gct.com.au
How to Make a Sign. Eagle Plasma LLC. Accessing the included step by step.dxf files
 Eagle Plasma LLC How to Make a Sign Accessing the included step by step.dxf files The following tutorial is designed to teach beginners, screen by screen, to create a simple sign project. In this lesson
Eagle Plasma LLC How to Make a Sign Accessing the included step by step.dxf files The following tutorial is designed to teach beginners, screen by screen, to create a simple sign project. In this lesson
Alignment of Business and IT - ArchiMate. Dr. Barbara Re
 Alignment of Business and IT - ArchiMate Dr. Barbara Re What is ArchiMate? ArchiMate is a modelling technique ("language") for describing enterprise architectures. It presents a clear set of concepts within
Alignment of Business and IT - ArchiMate Dr. Barbara Re What is ArchiMate? ArchiMate is a modelling technique ("language") for describing enterprise architectures. It presents a clear set of concepts within
AllFusion Process Modeler
 AllFusion Process Modeler User Guide r7.2 This documentation and any related computer software help programs (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for the end user s informational purposes
AllFusion Process Modeler User Guide r7.2 This documentation and any related computer software help programs (hereinafter referred to as the Documentation ) is for the end user s informational purposes
6/20/2018 CS5386 SOFTWARE DESIGN & ARCHITECTURE LECTURE 5: ARCHITECTURAL VIEWS C&C STYLES. Outline for Today. Architecture views C&C Views
 1 CS5386 SOFTWARE DESIGN & ARCHITECTURE LECTURE 5: ARCHITECTURAL VIEWS C&C STYLES Outline for Today 2 Architecture views C&C Views 1 Components and Connectors (C&C) Styles 3 Elements Relations Properties
1 CS5386 SOFTWARE DESIGN & ARCHITECTURE LECTURE 5: ARCHITECTURAL VIEWS C&C STYLES Outline for Today 2 Architecture views C&C Views 1 Components and Connectors (C&C) Styles 3 Elements Relations Properties
EXCEL SPREADSHEET TUTORIAL
 EXCEL SPREADSHEET TUTORIAL Note to all 200 level physics students: You will be expected to properly format data tables and graphs in all lab reports, as described in this tutorial. Therefore, you are responsible
EXCEL SPREADSHEET TUTORIAL Note to all 200 level physics students: You will be expected to properly format data tables and graphs in all lab reports, as described in this tutorial. Therefore, you are responsible
OBJECT ORIENTED MODELLING & DESIGN 1
 OBJECT ORIENTED MODELLING & DESIGN 1 Contents 1. OBJECT ORIENTED CONCEPTS... 6 OBJECT... 6 CLASS... 6 CLASS vs OBJECT... 6 WHAT IS OBJECT ORIENTED?... 6 OBJECT ORIENTED METHODOLOGY... 7 ADVANTAGES OF OBJECT
OBJECT ORIENTED MODELLING & DESIGN 1 Contents 1. OBJECT ORIENTED CONCEPTS... 6 OBJECT... 6 CLASS... 6 CLASS vs OBJECT... 6 WHAT IS OBJECT ORIENTED?... 6 OBJECT ORIENTED METHODOLOGY... 7 ADVANTAGES OF OBJECT
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks
 Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
WORD XP/2002 USER GUIDE. Task- Formatting a Document in Word 2002
 University of Arizona Information Commons Training Page 1 of 21 WORD XP/2002 USER GUIDE Task- Formatting a Document in Word 2002 OBJECTIVES: At the end of this course students will have a basic understanding
University of Arizona Information Commons Training Page 1 of 21 WORD XP/2002 USER GUIDE Task- Formatting a Document in Word 2002 OBJECTIVES: At the end of this course students will have a basic understanding
Entity Relationship Modelling
 Entity Relationship Modelling Overview Database Analysis Life Cycle Components of an Entity Relationship Diagram What is a relationship? Entities, attributes, and relationships in a system The degree of
Entity Relationship Modelling Overview Database Analysis Life Cycle Components of an Entity Relationship Diagram What is a relationship? Entities, attributes, and relationships in a system The degree of
Developing Shlaer-Mellor Models Using UML
 Developing Shlaer-Mellor Models Using UML Stephen J. Mellor Neil Lang Project Technology, Inc. 10940 Bigge Street San Leandro, California 94577 (510) 567-0255 http://www.projtech.com This position paper
Developing Shlaer-Mellor Models Using UML Stephen J. Mellor Neil Lang Project Technology, Inc. 10940 Bigge Street San Leandro, California 94577 (510) 567-0255 http://www.projtech.com This position paper
How To Title: Scan and File into ICS Purpose: To scan and file information into the patient s medical record Audience: All Staff Date: June 21, 2013
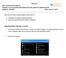 There are two ways to import medical records into ICS: A. Scan paper document(s) utilizing a scanner B. Import documents from a file, folder or Right Fax Acquiring images through a scanner: 1. Check that
There are two ways to import medical records into ICS: A. Scan paper document(s) utilizing a scanner B. Import documents from a file, folder or Right Fax Acquiring images through a scanner: 1. Check that
3.1. 3x 4y = 12 3(0) 4y = 12. 3x 4y = 12 3x 4(0) = y = x 0 = 12. 4y = 12 y = 3. 3x = 12 x = 4. The Rectangular Coordinate System
 3. The Rectangular Coordinate System Interpret a line graph. Objectives Interpret a line graph. Plot ordered pairs. 3 Find ordered pairs that satisfy a given equation. 4 Graph lines. 5 Find x- and y-intercepts.
3. The Rectangular Coordinate System Interpret a line graph. Objectives Interpret a line graph. Plot ordered pairs. 3 Find ordered pairs that satisfy a given equation. 4 Graph lines. 5 Find x- and y-intercepts.
23. Action-Oriented Design Methods
 Fakultät Informatik - Institut Software- und Multimediatechnik - Softwaretechnologie Prof. Aßmann - Softwaretechnologie II 23. Action-Oriented Design Methods Prof. Dr. Uwe Aßmann Technische Universität
Fakultät Informatik - Institut Software- und Multimediatechnik - Softwaretechnologie Prof. Aßmann - Softwaretechnologie II 23. Action-Oriented Design Methods Prof. Dr. Uwe Aßmann Technische Universität
