Information Retrieval and Organisation
|
|
|
- Prosper Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Information Retrieval and Organisation Dell Zhang Birkbeck, University of London 2015/16
2 IR Chapter 04 Index Construction
3 Hardware In this chapter we will look at how to construct an inverted index Many design decisions for indexing (and information retrieval in general) are based on hardware constraints We begin by reviewing hardware basics in this lecture
4 Hardware Basics Access to data is much faster in memory than on disk: roughly 10x. Disk seeks No data is transferred from disk while the disk head is being positioned. Therefore, transferring one large chunk of data from disk to memory is faster than transferring many small chunks. Disk I/O is block-based Reading and writing of entire blocks (as opposed to smaller chunks). Block sizes: 8KB to 256 KB Servers used in IR systems typically have several GB of main memory, sometimes tens of GB; a few orders of magnitude larger disk space.
5 Some Numbers symbol statistic value s average seek time 5 ms = s b transfer time per byte 0.02 µs = s processor s clock rate 10 9 s 1 p lowlevel operation 0.01 µs = 10 8 s (e.g. compare & swap a word) size of main memory several GB size of disk space 1 TB or more
6 Reuters RCV1 Collection Shakespeare s Collected Works are not large enough for demonstrating many of the points in this lecture. As an example for applying scalable index construction algorithms, we will use the Reuters RCV1 collection that consists of English newswire articles sent over the wire in 1995 and 1996.
7 Reuters RCV1 Collection
8 Reuters RCV1 Collection Corpus statistics symbol statistic value N documents 800,000 L avg. # word tokens per document 200 M terms (= word types) 400,000 avg. # bytes per word token (incl. spaces/punct.) 6 avg. # bytes per word token (without spaces/punct.) 4.5 avg. # bytes per term (= word type) 7.5 T non-positional postings 100,000,000
9 Index Construction Straightforward approach: 1. Make a pass through the collection assembling all term-docid pairs 2. Sort pairs (using term as the dominant key, docid as the secondary key) 3. Organize docids for each term into a postings list (and compute statistics like term and document frequencies)
10 Example
11 Example
12 Sort-based Index Construction As we build index, we parse docs one at a time. The final postings for any term are incomplete until the end. At bytes per postings entry, it demands a lot of space for large collections. T = 100,000,000 in the case of RCV1 Actually, we can probably do 100,000,000 in memory, but typical collections are even larger than RCV1. Thus, we need to store intermediate results on disk.
13 Sort-based Index Construction To make index construction more efficient, we represent terms as termids (instead of strings) Build mapping from terms to termids on the fly (or do a two-pass approach, first compiling the vocabulary) Sorting T = 100,000,000 records on disk using standard in-memory algorithms is too slow too many disk seeks We need an external sorting algorithm that minimizes the amount of random I/O
14 External Sorting Divide up the data into blocks that can fit in main memory Sort each block in main memory Sort the data by merging two (or more) blocks in separate steps
15 Merging Blocks
16 Replacement Selection It s even possible to sort blocks that are larger than main memory: output main memory input (16) (16) (26) (16) (26) (33) (16) (26) (33) (50)
17 External Sorting and Inverted Indexes 12-byte (4+4+4) postings: (termid, docid, document frequency) To simplify things a bit, we re looking at non-positional indexes Techniques can be extended to positional ones Must now sort T = 100,000,000 such 12-byte postings by termid,docid
18 External Sorting and Inverted Indexes Define a block to consist of 10,000,000 such postings We can easily fit that many postings into memory. We will have 10 such blocks for RCV1. Basic idea of algorithm: Accumulate postings for each block, sort, write to disk. Then merge the blocks into one long sorted order.
19 Merging Postings Blocks
20 Another Problem Our assumption was: we can keep the dictionary in memory. We need the dictionary (which grows dynamically) in order to implement a term to termid mapping. Actually, we could work with term,docid postings instead of termid,docid postings but then intermediate files become very large. We would end up with a scalable, but very slow index construction method. So we need to come up with another solution
21 Single-Pass In-Memory Indexing Abbreviation: SPIMI Key ideas (1) Generate separate dictionaries for each block: no need to maintain term-termid mapping across blocks. (2) Don t sort immediately: accumulate postings in postings lists as they occur. With these two ideas we can generate a complete inverted index for each block. These separate indexes can then be merged into one big index.
22 Single-Pass In-Memory Indexing Sketch of algorithm: Scan through all documents If the term occurs for the first time, add it to the dictionary and allocate a new (short) postings list If the term already exists in the dictionary, append docid at the end of its postings list. When there is no space left, double the allocated space for postings list. When we run out of memory, sort dictionary, sort postings lists, write them to disk, and then begin a new block When we are through with scanning documents, merge all blocks
23 Single-Pass In-Memory Indexing
24 Distributed Indexing For Web-scale indexing, we must use a distributed computer cluster Individual machines are fault-prone: they can unpredictably slow down or fail. How do we exploit such a pool of machines? MapReduce. Now we have a new module Cloud Computing to cover such topics.
25 Dynamic Indexing Up to now, we have assumed that collections are static. However, they rarely are (especially for Web search engines). Documents are inserted, deleted and modified. This means that the dictionary and the postings lists have to be modified. Periodically reconstructing the entire index is usually too expensive
26 Quick Fix Maintain big main index on disk New docs go into small auxiliary index in memory Search across both, merge results Periodically, merge auxiliary index into one main index Deletions: Invalidation bit-vector for deleted docs Filter docs returned by index using this invalidation bit-vector: only return valid docs to user.
27 Issue with Auxiliary Indexes Frequent merges; poor performance during merge Actually, merging of the auxiliary index into the main index could be efficient if we keep a separate file for each postings list But then we would need a lot of files (there can be millions of postings lists in an IR system). Handling this number of files usually not efficient For the moment, let s assume that we store index in one big file Reality lies somewhere in between e.g., split very large postings lists, collect postings lists of length 1 in one file
28 Costs of Merging Assume that we will process a total of T postings and have an auxiliary index of size n i.e., there will be T /n merges Each posting will be handled at least once (when merging it into the main index) i.e., costs for handling postings in the order of T 2 /n We can do better than that by doing logarithmic merging Compromises between having one big main index and millions of small ones
29 Logarithmic Merging Start with an in-memory auxiliary index Z 0 of size n When limit n is reached, an index I 0 of size 2 0 n is created on disk Next time Z 0 is full, it is merged with I 0 to create an index Z 1 of size 2 1 n If I1 doesn t exist yet, Z 1 is stored as I 1 Otherwise, Z 1 is merged with I 1 to create Z 2 of size 2 2 n (sizes double with each step) Continue with Z2 in the same way
30 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0
31 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0 I 0
32 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... I 0
33 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0 I 0
34 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0 I 0 Z 1 I 1
35 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... I 1
36 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0 I 1
37 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0 I 0 I 1
38 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... I 0 I 1
39 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0 I 0 I 1
40 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0 I 0 Z 1 I 1
41 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 1 I 1 Z 2 I 2
42 First Few Steps... n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... I 2
43 First Few Steps (Overview) n 2 0 n 2 1 n 2 2 n 2 3 n... Z 0 Z 0 I 0 I 0 Z 0 I 0 Z 0 I 0 Z 1 I 1 I 1 Z 1 I 1 Z 2 I 2 Z 0 I 1 Z 0 I 0 I 1 I 0 I 1 Z 0 I 0 I 1 Z 0 I 0 Z 1 I 1 I 2
44 Algorithm of Logarithmic Merging
45 Costs of Logarithmic Merging What do we gain from doing logarithmic merging? We have log 2 (T /n) levels in indexing scheme Each posting is processed once on each level So, total costs are T log2 (T /n) Example for n=1000
46 Disadvantages? Slow-down of query processing: we have to merge results from log 2 (T /n) indexes (as opposed to just two) We still need to merge very large indexes occasionally. However: this will happen less frequently the merged indexes will on average be smaller Having multiple indexes complicates maintenance of collection-wide statistics Sometimes, rebuilding index from scratch can be better depends on the frequency of updates
47 Summary Hardware puts constraints on index construction Main memory is scarce We want to avoid random I/O on disk Additional challenges for distributed and dynamic indexing
Index Construction 1
 Index Construction 1 October, 2009 1 Vorlage: Folien von M. Schütze 1 von 43 Index Construction Hardware basics Many design decisions in information retrieval are based on hardware constraints. We begin
Index Construction 1 October, 2009 1 Vorlage: Folien von M. Schütze 1 von 43 Index Construction Hardware basics Many design decisions in information retrieval are based on hardware constraints. We begin
Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval Lecture 4: Index Construction Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards This time: Spell correction Soundex Index construction Index
Introduction to Information Retrieval Lecture 4: Index Construction Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards This time: Spell correction Soundex Index construction Index
Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval Lecture 4: Index Construction 1 Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards Spell correction Soundex a-hu hy-m n-z $m mace madden mo
Introduction to Information Retrieval Lecture 4: Index Construction 1 Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards Spell correction Soundex a-hu hy-m n-z $m mace madden mo
Information Retrieval
 Information Retrieval Suan Lee - Information Retrieval - 04 Index Construction 1 04 Index Construction - Information Retrieval - 04 Index Construction 2 Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant
Information Retrieval Suan Lee - Information Retrieval - 04 Index Construction 1 04 Index Construction - Information Retrieval - 04 Index Construction 2 Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant
index construct Overview Overview Recap How to construct index? Introduction Index construction Introduction to Recap
 to to Information Retrieval Index Construct Ruixuan Li Huazhong University of Science and Technology http://idc.hust.edu.cn/~rxli/ October, 2012 1 2 How to construct index? Computerese term document docid
to to Information Retrieval Index Construct Ruixuan Li Huazhong University of Science and Technology http://idc.hust.edu.cn/~rxli/ October, 2012 1 2 How to construct index? Computerese term document docid
3-2. Index construction. Most slides were adapted from Stanford CS 276 course and University of Munich IR course.
 3-2. Index construction Most slides were adapted from Stanford CS 276 course and University of Munich IR course. 1 Ch. 4 Index construction How do we construct an index? What strategies can we use with
3-2. Index construction Most slides were adapted from Stanford CS 276 course and University of Munich IR course. 1 Ch. 4 Index construction How do we construct an index? What strategies can we use with
Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology
 Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2014 Most slides have been adapted from: Profs. Manning, Nayak & Raghavan (CS-276, Stanford) Ch.
Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2014 Most slides have been adapted from: Profs. Manning, Nayak & Raghavan (CS-276, Stanford) Ch.
Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology
 Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Most slides have been adapted from: Profs. Manning, Nayak & Raghavan (CS-276, Stanford) Ch.
Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Most slides have been adapted from: Profs. Manning, Nayak & Raghavan (CS-276, Stanford) Ch.
Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology
 Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2017 Most slides have been adapted from: Profs. Manning, Nayak & Raghavan (CS-276, Stanford) Ch.
Index construction CE-324: Modern Information Retrieval Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2017 Most slides have been adapted from: Profs. Manning, Nayak & Raghavan (CS-276, Stanford) Ch.
Index Construction. Dictionary, postings, scalable indexing, dynamic indexing. Web Search
 Index Construction Dictionary, postings, scalable indexing, dynamic indexing Web Search 1 Overview Indexes Query Indexing Ranking Results Application Documents User Information analysis Query processing
Index Construction Dictionary, postings, scalable indexing, dynamic indexing Web Search 1 Overview Indexes Query Indexing Ranking Results Application Documents User Information analysis Query processing
Introduction to. CS276: Information Retrieval and Web Search Christopher Manning and Prabhakar Raghavan. Lecture 4: Index Construction
 Introduction to Information Retrieval CS276: Information Retrieval and Web Search Christopher Manning and Prabhakar Raghavan Lecture 4: Index Construction 1 Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures
Introduction to Information Retrieval CS276: Information Retrieval and Web Search Christopher Manning and Prabhakar Raghavan Lecture 4: Index Construction 1 Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures
Introduction to Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval CS276: Information Retrieval and Web Search Pandu Nayak and Prabhakar Raghavan Hamid Rastegari Lecture 4: Index Construction Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures
Introduction to Information Retrieval CS276: Information Retrieval and Web Search Pandu Nayak and Prabhakar Raghavan Hamid Rastegari Lecture 4: Index Construction Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures
Introduc)on to. CS60092: Informa0on Retrieval
 Introduc)on to CS60092: Informa0on Retrieval Ch. 4 Index construc)on How do we construct an index? What strategies can we use with limited main memory? Sec. 4.1 Hardware basics Many design decisions in
Introduc)on to CS60092: Informa0on Retrieval Ch. 4 Index construc)on How do we construct an index? What strategies can we use with limited main memory? Sec. 4.1 Hardware basics Many design decisions in
Information Retrieval
 Introduction to CS3245 Lecture 5: Index Construction 5 CS3245 Last Time Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards Spelling correction Soundex a-hu hy-m n-z $m mace madden mo among amortize
Introduction to CS3245 Lecture 5: Index Construction 5 CS3245 Last Time Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards Spelling correction Soundex a-hu hy-m n-z $m mace madden mo among amortize
Introduction to Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 4: Index Construction Hinrich Schütze, Christina Lioma Institute for Natural Language Processing, University of Stuttgart 2010-05-04
Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 4: Index Construction Hinrich Schütze, Christina Lioma Institute for Natural Language Processing, University of Stuttgart 2010-05-04
Information Retrieval
 Introduction to CS3245 Lecture 5: Index Construction 5 Last Time Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards Spelling correction Soundex a-hu hy-m n-z $m mace madden mo among amortize on abandon
Introduction to CS3245 Lecture 5: Index Construction 5 Last Time Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards Spelling correction Soundex a-hu hy-m n-z $m mace madden mo among amortize on abandon
Index Construction. Slides by Manning, Raghavan, Schutze
 Introduction to Information Retrieval ΕΠΛ660 Ανάκτηση Πληροφοριών και Μηχανές Αναζήτησης ης Index Construction ti Introduction to Information Retrieval Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant
Introduction to Information Retrieval ΕΠΛ660 Ανάκτηση Πληροφοριών και Μηχανές Αναζήτησης ης Index Construction ti Introduction to Information Retrieval Plan Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant
CSCI 5417 Information Retrieval Systems Jim Martin!
 CSCI 5417 Information Retrieval Systems Jim Martin! Lecture 4 9/1/2011 Today Finish up spelling correction Realistic indexing Block merge Single-pass in memory Distributed indexing Next HW details 1 Query
CSCI 5417 Information Retrieval Systems Jim Martin! Lecture 4 9/1/2011 Today Finish up spelling correction Realistic indexing Block merge Single-pass in memory Distributed indexing Next HW details 1 Query
Introduction to Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 4: Index Construction Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2014-04-16 Schütze:
Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 4: Index Construction Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2014-04-16 Schütze:
Introduction to Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 4: Index Construction Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2014-04-16 1/54 Overview
Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 4: Index Construction Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2014-04-16 1/54 Overview
Informa(on Retrieval
 Introduc*on to Informa(on Retrieval CS276: Informa*on Retrieval and Web Search Pandu Nayak and Prabhakar Raghavan Lecture 4: Index Construc*on Plan Last lecture: Dic*onary data structures Tolerant retrieval
Introduc*on to Informa(on Retrieval CS276: Informa*on Retrieval and Web Search Pandu Nayak and Prabhakar Raghavan Lecture 4: Index Construc*on Plan Last lecture: Dic*onary data structures Tolerant retrieval
CSE 7/5337: Information Retrieval and Web Search Index construction (IIR 4)
 CSE 7/5337: Information Retrieval and Web Search Index construction (IIR 4) Michael Hahsler Southern Methodist University These slides are largely based on the slides by Hinrich Schütze Institute for Natural
CSE 7/5337: Information Retrieval and Web Search Index construction (IIR 4) Michael Hahsler Southern Methodist University These slides are largely based on the slides by Hinrich Schütze Institute for Natural
INDEX CONSTRUCTION 1
 1 INDEX CONSTRUCTION PLAN Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards Spell correction Soundex a-hu hy-m n-z $m mace madden This time: mo among amortize Index construction on
1 INDEX CONSTRUCTION PLAN Last lecture: Dictionary data structures Tolerant retrieval Wildcards Spell correction Soundex a-hu hy-m n-z $m mace madden This time: mo among amortize Index construction on
PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval
 PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval http://www.fi.muni.cz/~sojka/pv211 IIR 4: Index construction Handout version Petr Sojka, Hinrich Schütze et al. Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University,
PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval http://www.fi.muni.cz/~sojka/pv211 IIR 4: Index construction Handout version Petr Sojka, Hinrich Schütze et al. Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University,
Introduction to Information Retrieval (Manning, Raghavan, Schutze)
 Introduction to Information Retrieval (Manning, Raghavan, Schutze) Chapter 3 Dictionaries and Tolerant retrieval Chapter 4 Index construction Chapter 5 Index compression Content Dictionary data structures
Introduction to Information Retrieval (Manning, Raghavan, Schutze) Chapter 3 Dictionaries and Tolerant retrieval Chapter 4 Index construction Chapter 5 Index compression Content Dictionary data structures
Index construc-on. Friday, 8 April 16 1
 Index construc-on Informa)onal Retrieval By Dr. Qaiser Abbas Department of Computer Science & IT, University of Sargodha, Sargodha, 40100, Pakistan qaiser.abbas@uos.edu.pk Friday, 8 April 16 1 4.1 Index
Index construc-on Informa)onal Retrieval By Dr. Qaiser Abbas Department of Computer Science & IT, University of Sargodha, Sargodha, 40100, Pakistan qaiser.abbas@uos.edu.pk Friday, 8 April 16 1 4.1 Index
Index Construction Introduction to Information Retrieval INF 141/ CS 121 Donald J. Patterson
 Index Construction Introduction to Information Retrieval INF 141/ CS 121 Donald J. Patterson Content adapted from Hinrich Schütze http://www.informationretrieval.org Index Construction Overview Introduction
Index Construction Introduction to Information Retrieval INF 141/ CS 121 Donald J. Patterson Content adapted from Hinrich Schütze http://www.informationretrieval.org Index Construction Overview Introduction
Document Representation : Quiz
 Document Representation : Quiz Q1. In-memory Index construction faces following problems:. (A) Scaling problem (B) The optimal use of Hardware resources for scaling (C) Easily keep entire data into main
Document Representation : Quiz Q1. In-memory Index construction faces following problems:. (A) Scaling problem (B) The optimal use of Hardware resources for scaling (C) Easily keep entire data into main
Index Construction Introduction to Information Retrieval INF 141 Donald J. Patterson
 Index Construction Introduction to Information Retrieval INF 141 Donald J. Patterson Content adapted from Hinrich Schütze http://www.informationretrieval.org Index Construction Overview Introduction Hardware
Index Construction Introduction to Information Retrieval INF 141 Donald J. Patterson Content adapted from Hinrich Schütze http://www.informationretrieval.org Index Construction Overview Introduction Hardware
Efficiency. Efficiency: Indexing. Indexing. Efficiency Techniques. Inverted Index. Inverted Index (COSC 488)
 Efficiency Efficiency: Indexing (COSC 488) Nazli Goharian nazli@cs.georgetown.edu Difficult to analyze sequential IR algorithms: data and query dependency (query selectivity). O(q(cf max )) -- high estimate-
Efficiency Efficiency: Indexing (COSC 488) Nazli Goharian nazli@cs.georgetown.edu Difficult to analyze sequential IR algorithms: data and query dependency (query selectivity). O(q(cf max )) -- high estimate-
Reuters collection example (approximate # s)
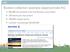 BSBI Reuters collection example (approximate # s) 800,000 documents from the Reuters news feed 200 terms per document 400,000 unique terms number of postings 100,000,000 BSBI Reuters collection example
BSBI Reuters collection example (approximate # s) 800,000 documents from the Reuters news feed 200 terms per document 400,000 unique terms number of postings 100,000,000 BSBI Reuters collection example
Introduction to Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 5: Index Compression Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2014-04-17 1/59 Overview
Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 5: Index Compression Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2014-04-17 1/59 Overview
Information Retrieval
 Information Retrieval Suan Lee - Information Retrieval - 05 Index Compression 1 05 Index Compression - Information Retrieval - 05 Index Compression 2 Last lecture index construction Sort-based indexing
Information Retrieval Suan Lee - Information Retrieval - 05 Index Compression 1 05 Index Compression - Information Retrieval - 05 Index Compression 2 Last lecture index construction Sort-based indexing
Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval CS3245 Information Retrieval Lecture 6: Index Compression 6 Last Time: index construction Sort- based indexing Blocked Sort- Based Indexing Merge sort is effective
Introduction to Information Retrieval CS3245 Information Retrieval Lecture 6: Index Compression 6 Last Time: index construction Sort- based indexing Blocked Sort- Based Indexing Merge sort is effective
Building an Inverted Index
 Building an Inverted Index Algorithms Memory-based Disk-based (Sort-Inversion) Sorting Merging (2-way; multi-way) 2 Memory-based Inverted Index Phase I (parse and read) For each document Identify distinct
Building an Inverted Index Algorithms Memory-based Disk-based (Sort-Inversion) Sorting Merging (2-way; multi-way) 2 Memory-based Inverted Index Phase I (parse and read) For each document Identify distinct
Lecture 3 Index Construction and Compression. Many thanks to Prabhakar Raghavan for sharing most content from the following slides
 Lecture 3 Index Construction and Compression Many thanks to Prabhakar Raghavan for sharing most content from the following slides Recap of the previous lecture Tokenization Term equivalence Skip pointers
Lecture 3 Index Construction and Compression Many thanks to Prabhakar Raghavan for sharing most content from the following slides Recap of the previous lecture Tokenization Term equivalence Skip pointers
Index construc-on. Friday, 8 April 16 1
 Index construc-on Informa)onal Retrieval By Dr. Qaiser Abbas Department of Computer Science & IT, University of Sargodha, Sargodha, 40100, Pakistan qaiser.abbas@uos.edu.pk Friday, 8 April 16 1 4.3 Single-pass
Index construc-on Informa)onal Retrieval By Dr. Qaiser Abbas Department of Computer Science & IT, University of Sargodha, Sargodha, 40100, Pakistan qaiser.abbas@uos.edu.pk Friday, 8 April 16 1 4.3 Single-pass
Developing MapReduce Programs
 Cloud Computing Developing MapReduce Programs Dell Zhang Birkbeck, University of London 2017/18 MapReduce Algorithm Design MapReduce: Recap Programmers must specify two functions: map (k, v) * Takes
Cloud Computing Developing MapReduce Programs Dell Zhang Birkbeck, University of London 2017/18 MapReduce Algorithm Design MapReduce: Recap Programmers must specify two functions: map (k, v) * Takes
Web Information Retrieval. Lecture 4 Dictionaries, Index Compression
 Web Information Retrieval Lecture 4 Dictionaries, Index Compression Recap: lecture 2,3 Stemming, tokenization etc. Faster postings merges Phrase queries Index construction This lecture Dictionary data
Web Information Retrieval Lecture 4 Dictionaries, Index Compression Recap: lecture 2,3 Stemming, tokenization etc. Faster postings merges Phrase queries Index construction This lecture Dictionary data
Administrative. Distributed indexing. Index Compression! What I did last summer lunch talks today. Master. Tasks
 Administrative Index Compression! n Assignment 1? n Homework 2 out n What I did last summer lunch talks today David Kauchak cs458 Fall 2012 adapted from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/handouts/lecture5-indexcompression.ppt
Administrative Index Compression! n Assignment 1? n Homework 2 out n What I did last summer lunch talks today David Kauchak cs458 Fall 2012 adapted from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/handouts/lecture5-indexcompression.ppt
EECS 395/495 Lecture 3 Scalable Indexing, Searching, and Crawling
 EECS 395/495 Lecture 3 Scalable Indexing, Searching, and Crawling Doug Downey Based partially on slides by Christopher D. Manning, Prabhakar Raghavan, Hinrich Schütze Announcements Project progress report
EECS 395/495 Lecture 3 Scalable Indexing, Searching, and Crawling Doug Downey Based partially on slides by Christopher D. Manning, Prabhakar Raghavan, Hinrich Schütze Announcements Project progress report
Text Analytics. Index-Structures for Information Retrieval. Ulf Leser
 Text Analytics Index-Structures for Information Retrieval Ulf Leser Content of this Lecture Inverted files Storage structures Phrase and proximity search Building and updating the index Using a RDBMS Ulf
Text Analytics Index-Structures for Information Retrieval Ulf Leser Content of this Lecture Inverted files Storage structures Phrase and proximity search Building and updating the index Using a RDBMS Ulf
Recap: lecture 2 CS276A Information Retrieval
 Recap: lecture 2 CS276A Information Retrieval Stemming, tokenization etc. Faster postings merges Phrase queries Lecture 3 This lecture Index compression Space estimation Corpus size for estimates Consider
Recap: lecture 2 CS276A Information Retrieval Stemming, tokenization etc. Faster postings merges Phrase queries Lecture 3 This lecture Index compression Space estimation Corpus size for estimates Consider
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 29: an Introduction to Virtual Memory Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Virtual memory used to protect applications
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 29: an Introduction to Virtual Memory Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Virtual memory used to protect applications
Advance Indexing. Limock July 3, 2014
 Advance Indexing Limock July 3, 2014 1 Papers 1) Gurajada, Sairam : "On-line index maintenance using horizontal partitioning." Proceedings of the 18th ACM conference on Information and knowledge management.
Advance Indexing Limock July 3, 2014 1 Papers 1) Gurajada, Sairam : "On-line index maintenance using horizontal partitioning." Proceedings of the 18th ACM conference on Information and knowledge management.
Text Analytics. Index-Structures for Information Retrieval. Ulf Leser
 Text Analytics Index-Structures for Information Retrieval Ulf Leser Content of this Lecture Inverted files Storage structures Phrase and proximity search Building and updating the index Using a RDBMS Ulf
Text Analytics Index-Structures for Information Retrieval Ulf Leser Content of this Lecture Inverted files Storage structures Phrase and proximity search Building and updating the index Using a RDBMS Ulf
Course work. Today. Last lecture index construc)on. Why compression (in general)? Why compression for inverted indexes?
 Course work Introduc)on to Informa(on Retrieval Problem set 1 due Thursday Programming exercise 1 will be handed out today CS276: Informa)on Retrieval and Web Search Pandu Nayak and Prabhakar Raghavan
Course work Introduc)on to Informa(on Retrieval Problem set 1 due Thursday Programming exercise 1 will be handed out today CS276: Informa)on Retrieval and Web Search Pandu Nayak and Prabhakar Raghavan
CS60092: Informa0on Retrieval
 Introduc)on to CS60092: Informa0on Retrieval Sourangshu Bha1acharya Last lecture index construc)on Sort- based indexing Naïve in- memory inversion Blocked Sort- Based Indexing Merge sort is effec)ve for
Introduc)on to CS60092: Informa0on Retrieval Sourangshu Bha1acharya Last lecture index construc)on Sort- based indexing Naïve in- memory inversion Blocked Sort- Based Indexing Merge sort is effec)ve for
Information Retrieval. Lecture 2 - Building an index
 Information Retrieval Lecture 2 - Building an index Seminar für Sprachwissenschaft International Studies in Computational Linguistics Wintersemester 2007 1/ 40 Overview Introduction Introduction Boolean
Information Retrieval Lecture 2 - Building an index Seminar für Sprachwissenschaft International Studies in Computational Linguistics Wintersemester 2007 1/ 40 Overview Introduction Introduction Boolean
Index Compression. David Kauchak cs160 Fall 2009 adapted from:
 Index Compression David Kauchak cs160 Fall 2009 adapted from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/handouts/lecture5-indexcompression.ppt Administrative Homework 2 Assignment 1 Assignment 2 Pair programming?
Index Compression David Kauchak cs160 Fall 2009 adapted from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/handouts/lecture5-indexcompression.ppt Administrative Homework 2 Assignment 1 Assignment 2 Pair programming?
Map-Reduce. Marco Mura 2010 March, 31th
 Map-Reduce Marco Mura (mura@di.unipi.it) 2010 March, 31th This paper is a note from the 2009-2010 course Strumenti di programmazione per sistemi paralleli e distribuiti and it s based by the lessons of
Map-Reduce Marco Mura (mura@di.unipi.it) 2010 March, 31th This paper is a note from the 2009-2010 course Strumenti di programmazione per sistemi paralleli e distribuiti and it s based by the lessons of
Indexing. CS6200: Information Retrieval. Index Construction. Slides by: Jesse Anderton
 Indexing Index Construction CS6200: Information Retrieval Slides by: Jesse Anderton Motivation: Scale Corpus Terms Docs Entries A term incidence matrix with V terms and D documents has O(V x D) entries.
Indexing Index Construction CS6200: Information Retrieval Slides by: Jesse Anderton Motivation: Scale Corpus Terms Docs Entries A term incidence matrix with V terms and D documents has O(V x D) entries.
Algorithm Performance Factors. Memory Performance of Algorithms. Processor-Memory Performance Gap. Moore s Law. Program Model of Memory I
 Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval Boolean retrieval Basic assumptions of Information Retrieval Collection: Fixed set of documents Goal: Retrieve documents with information that is relevant to the user
Introduction to Information Retrieval Boolean retrieval Basic assumptions of Information Retrieval Collection: Fixed set of documents Goal: Retrieve documents with information that is relevant to the user
Chapter 3 - Memory Management
 Chapter 3 - Memory Management Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 3 - Memory Management 1 / 222 1 A Memory Abstraction: Address Spaces The Notion of an Address Space Swapping
Chapter 3 - Memory Management Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 3 - Memory Management 1 / 222 1 A Memory Abstraction: Address Spaces The Notion of an Address Space Swapping
INFO 4300 / CS4300 Information Retrieval. slides adapted from Hinrich Schütze s, linked from
 INFO 4300 / CS4300 Information Retrieval slides adapted from Hinrich Schütze s, linked from http://informationretrieval.org/ IR 6: Index Compression Paul Ginsparg Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 15 Sep
INFO 4300 / CS4300 Information Retrieval slides adapted from Hinrich Schütze s, linked from http://informationretrieval.org/ IR 6: Index Compression Paul Ginsparg Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 15 Sep
L9: Storage Manager Physical Data Organization
 L9: Storage Manager Physical Data Organization Disks and files Record and file organization Indexing Tree-based index: B+-tree Hash-based index c.f. Fig 1.3 in [RG] and Fig 2.3 in [EN] Functional Components
L9: Storage Manager Physical Data Organization Disks and files Record and file organization Indexing Tree-based index: B+-tree Hash-based index c.f. Fig 1.3 in [RG] and Fig 2.3 in [EN] Functional Components
Distributed computing: index building and use
 Distributed computing: index building and use Distributed computing Goals Distributing computation across several machines to Do one computation faster - latency Do more computations in given time - throughput
Distributed computing: index building and use Distributed computing Goals Distributing computation across several machines to Do one computation faster - latency Do more computations in given time - throughput
Map Reduce. Yerevan.
 Map Reduce Erasmus+ @ Yerevan dacosta@irit.fr Divide and conquer at PaaS 100 % // Typical problem Iterate over a large number of records Extract something of interest from each Shuffle and sort intermediate
Map Reduce Erasmus+ @ Yerevan dacosta@irit.fr Divide and conquer at PaaS 100 % // Typical problem Iterate over a large number of records Extract something of interest from each Shuffle and sort intermediate
Data-analysis and Retrieval Boolean retrieval, posting lists and dictionaries
 Data-analysis and Retrieval Boolean retrieval, posting lists and dictionaries Hans Philippi (based on the slides from the Stanford course on IR) April 25, 2018 Boolean retrieval, posting lists & dictionaries
Data-analysis and Retrieval Boolean retrieval, posting lists and dictionaries Hans Philippi (based on the slides from the Stanford course on IR) April 25, 2018 Boolean retrieval, posting lists & dictionaries
Preview. Memory Management
 Preview Memory Management With Mono-Process With Multi-Processes Multi-process with Fixed Partitions Modeling Multiprogramming Swapping Memory Management with Bitmaps Memory Management with Free-List Virtual
Preview Memory Management With Mono-Process With Multi-Processes Multi-process with Fixed Partitions Modeling Multiprogramming Swapping Memory Management with Bitmaps Memory Management with Free-List Virtual
CS122 Lecture 3 Winter Term,
 CS122 Lecture 3 Winter Term, 2017-2018 2 Record-Level File Organization Last time, finished discussing block-level organization Can also organize data files at the record-level Heap file organization A
CS122 Lecture 3 Winter Term, 2017-2018 2 Record-Level File Organization Last time, finished discussing block-level organization Can also organize data files at the record-level Heap file organization A
LECTURE 12. Virtual Memory
 LECTURE 12 Virtual Memory VIRTUAL MEMORY Just as a cache can provide fast, easy access to recently-used code and data, main memory acts as a cache for magnetic disk. The mechanism by which this is accomplished
LECTURE 12 Virtual Memory VIRTUAL MEMORY Just as a cache can provide fast, easy access to recently-used code and data, main memory acts as a cache for magnetic disk. The mechanism by which this is accomplished
INFO 4300 / CS4300 Information Retrieval. slides adapted from Hinrich Schütze s, linked from
 INFO 4300 / CS4300 Information Retrieval slides adapted from Hinrich Schütze s, linked from http://informationretrieval.org/ IR 7: Scores in a Complete Search System Paul Ginsparg Cornell University, Ithaca,
INFO 4300 / CS4300 Information Retrieval slides adapted from Hinrich Schütze s, linked from http://informationretrieval.org/ IR 7: Scores in a Complete Search System Paul Ginsparg Cornell University, Ithaca,
CS399 New Beginnings. Jonathan Walpole
 CS399 New Beginnings Jonathan Walpole Memory Management Memory Management Memory a linear array of bytes - Holds O.S. and programs (processes) - Each cell (byte) is named by a unique memory address Recall,
CS399 New Beginnings Jonathan Walpole Memory Management Memory Management Memory a linear array of bytes - Holds O.S. and programs (processes) - Each cell (byte) is named by a unique memory address Recall,
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Memory - Paging. Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1
 Memory - Paging Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1 Physical Frame Allocation How do we allocate physical memory across multiple processes? What if Process A needs to evict a page from Process
Memory - Paging Copyright : University of Illinois CS 241 Staff 1 Physical Frame Allocation How do we allocate physical memory across multiple processes? What if Process A needs to evict a page from Process
Information Retrieval. Danushka Bollegala
 Information Retrieval Danushka Bollegala Anatomy of a Search Engine Document Indexing Query Processing Search Index Results Ranking 2 Document Processing Format detection Plain text, PDF, PPT, Text extraction
Information Retrieval Danushka Bollegala Anatomy of a Search Engine Document Indexing Query Processing Search Index Results Ranking 2 Document Processing Format detection Plain text, PDF, PPT, Text extraction
Information Retrieval
 Information Retrieval Natural Language Processing: Lecture 12 30.11.2017 Kairit Sirts Homework 4 things that seemed to work Bidirectional LSTM instead of unidirectional Change LSTM activation to sigmoid
Information Retrieval Natural Language Processing: Lecture 12 30.11.2017 Kairit Sirts Homework 4 things that seemed to work Bidirectional LSTM instead of unidirectional Change LSTM activation to sigmoid
Memory Management. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College February 27, 2018
 Memory Management Kevin Webb Swarthmore College February 27, 2018 Today s Goals Shifting topics: different process resource memory Motivate virtual memory, including what it might look like without it
Memory Management Kevin Webb Swarthmore College February 27, 2018 Today s Goals Shifting topics: different process resource memory Motivate virtual memory, including what it might look like without it
Advanced Database Systems
 Lecture IV Query Processing Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Basic Steps in Query Processing 2 Query Optimization Many equivalent execution plans Choosing the best one Based on Heuristics, Cost Will be discussed
Lecture IV Query Processing Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Basic Steps in Query Processing 2 Query Optimization Many equivalent execution plans Choosing the best one Based on Heuristics, Cost Will be discussed
CS 31: Intro to Systems Virtual Memory. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 15, 2018
 CS 31: Intro to Systems Virtual Memory Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 15, 2018 Reading Quiz Memory Abstraction goal: make every process think it has the same memory layout. MUCH simpler for compiler
CS 31: Intro to Systems Virtual Memory Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 15, 2018 Reading Quiz Memory Abstraction goal: make every process think it has the same memory layout. MUCH simpler for compiler
Information Retrieval and Organisation
 Information Retrieval and Organisation Dell Zhang Birkbeck, University of London 2016/17 IR Chapter 01 Boolean Retrieval Example IR Problem Let s look at a simple IR problem Suppose you own a copy of Shakespeare
Information Retrieval and Organisation Dell Zhang Birkbeck, University of London 2016/17 IR Chapter 01 Boolean Retrieval Example IR Problem Let s look at a simple IR problem Suppose you own a copy of Shakespeare
CS105 Introduction to Information Retrieval
 CS105 Introduction to Information Retrieval Lecture: Yang Mu UMass Boston Slides are modified from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/ Information Retrieval Information Retrieval (IR) is finding material
CS105 Introduction to Information Retrieval Lecture: Yang Mu UMass Boston Slides are modified from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/ Information Retrieval Information Retrieval (IR) is finding material
Physical DB Issues, Indexes, Query Optimisation. Database Systems Lecture 13 Natasha Alechina
 Physical DB Issues, Indexes, Query Optimisation Database Systems Lecture 13 Natasha Alechina In This Lecture Physical DB Issues RAID arrays for recovery and speed Indexes and query efficiency Query optimisation
Physical DB Issues, Indexes, Query Optimisation Database Systems Lecture 13 Natasha Alechina In This Lecture Physical DB Issues RAID arrays for recovery and speed Indexes and query efficiency Query optimisation
More on Address Translation. CS170 Fall T. Yang Some of slides from UCB CS162 by Kubiatowicz
 More on Address Translation CS170 Fall 2018. T. Yang Some of slides from UCB CS162 by Kubiatowicz Topics Review of last lecture on pagetable based address translation One-level page table Muti-level paging
More on Address Translation CS170 Fall 2018. T. Yang Some of slides from UCB CS162 by Kubiatowicz Topics Review of last lecture on pagetable based address translation One-level page table Muti-level paging
Big Data Management and NoSQL Databases
 NDBI040 Big Data Management and NoSQL Databases Lecture 2. MapReduce Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. holubova@ksi.mff.cuni.cz http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~holubova/ndbi040/ Framework A programming model
NDBI040 Big Data Management and NoSQL Databases Lecture 2. MapReduce Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. holubova@ksi.mff.cuni.cz http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~holubova/ndbi040/ Framework A programming model
Persistent Storage - Datastructures and Algorithms
 Persistent Storage - Datastructures and Algorithms 1 / 21 L 03: Virtual Memory and Caches 2 / 21 Questions How to access data, when sequential access is too slow? Direct access (random access) file, how
Persistent Storage - Datastructures and Algorithms 1 / 21 L 03: Virtual Memory and Caches 2 / 21 Questions How to access data, when sequential access is too slow? Direct access (random access) file, how
Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
 CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [HADOOP/HDFS] Trying to have your cake and eat it too Each phase pines for tasks with locality and their numbers on a tether Alas within a phase, you get one,
CS 455: INTRODUCTION TO DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [HADOOP/HDFS] Trying to have your cake and eat it too Each phase pines for tasks with locality and their numbers on a tether Alas within a phase, you get one,
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Recap Paged MMU: Two main Issues Translation speed can be slow TLB Table size is big Multi-level page table
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 Recap Paged MMU: Two main Issues Translation speed can be slow TLB Table size is big Multi-level page table
CS 138: Google. CS 138 XVII 1 Copyright 2016 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved.
 CS 138: Google CS 138 XVII 1 Copyright 2016 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Google Environment Lots (tens of thousands) of computers all more-or-less equal - processor, disk, memory, network interface
CS 138: Google CS 138 XVII 1 Copyright 2016 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Google Environment Lots (tens of thousands) of computers all more-or-less equal - processor, disk, memory, network interface
CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS555: Distributed Systems [Fall 2017] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/90/104368640.jpg) CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [MAPREDUCE] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Bit Torrent What is the right chunk/piece
CS 555: DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS [MAPREDUCE] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey Bit Torrent What is the right chunk/piece
MapReduce: Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters. By Stephen Cardina
 MapReduce: Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters By Stephen Cardina The Problem You have a large amount of raw data, such as a database or a web log, and you need to get some sort of derived data
MapReduce: Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters By Stephen Cardina The Problem You have a large amount of raw data, such as a database or a web log, and you need to get some sort of derived data
Chapter 9 Memory Management
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Computer-System Structures 3. Operating-System Structures 4. Processes 5. Threads 6. CPU Scheduling 7. Process Synchronization 8. Deadlocks 9. Memory Management 10. Virtual
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Computer-System Structures 3. Operating-System Structures 4. Processes 5. Threads 6. CPU Scheduling 7. Process Synchronization 8. Deadlocks 9. Memory Management 10. Virtual
Segmentation with Paging. Review. Segmentation with Page (MULTICS) Segmentation with Page (MULTICS) Segmentation with Page (MULTICS)
 Review Segmentation Segmentation Implementation Advantage of Segmentation Protection Sharing Segmentation with Paging Segmentation with Paging Segmentation with Paging Reason for the segmentation with
Review Segmentation Segmentation Implementation Advantage of Segmentation Protection Sharing Segmentation with Paging Segmentation with Paging Segmentation with Paging Reason for the segmentation with
Information Retrieval. Lecture 3 - Index compression. Introduction. Overview. Characterization of an index. Wintersemester 2007
 Information Retrieval Lecture 3 - Index compression Seminar für Sprachwissenschaft International Studies in Computational Linguistics Wintersemester 2007 1/ 30 Introduction Dictionary and inverted index:
Information Retrieval Lecture 3 - Index compression Seminar für Sprachwissenschaft International Studies in Computational Linguistics Wintersemester 2007 1/ 30 Introduction Dictionary and inverted index:
Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval Information Retrieval and Web Search Lecture 1: Introduction and Boolean retrieval Outline ❶ Course details ❷ Information retrieval ❸ Boolean retrieval 2 Course details
Introduction to Information Retrieval Information Retrieval and Web Search Lecture 1: Introduction and Boolean retrieval Outline ❶ Course details ❷ Information retrieval ❸ Boolean retrieval 2 Course details
PROCESS VIRTUAL MEMORY. CS124 Operating Systems Winter , Lecture 18
 PROCESS VIRTUAL MEMORY CS124 Operating Systems Winter 2015-2016, Lecture 18 2 Programs and Memory Programs perform many interactions with memory Accessing variables stored at specific memory locations
PROCESS VIRTUAL MEMORY CS124 Operating Systems Winter 2015-2016, Lecture 18 2 Programs and Memory Programs perform many interactions with memory Accessing variables stored at specific memory locations
PS2 out today. Lab 2 out today. Lab 1 due today - how was it?
 6.830 Lecture 7 9/25/2017 PS2 out today. Lab 2 out today. Lab 1 due today - how was it? Project Teams Due Wednesday Those of you who don't have groups -- send us email, or hand in a sheet with just your
6.830 Lecture 7 9/25/2017 PS2 out today. Lab 2 out today. Lab 1 due today - how was it? Project Teams Due Wednesday Those of you who don't have groups -- send us email, or hand in a sheet with just your
Database Systems. November 2, 2011 Lecture #7. topobo (mit)
 Database Systems November 2, 2011 Lecture #7 1 topobo (mit) 1 Announcement Assignment #2 due today Assignment #3 out today & due on 11/16. Midterm exam in class next week. Cover Chapters 1, 2,
Database Systems November 2, 2011 Lecture #7 1 topobo (mit) 1 Announcement Assignment #2 due today Assignment #3 out today & due on 11/16. Midterm exam in class next week. Cover Chapters 1, 2,
Lecture 7. Memory Management
 Lecture 7 Memory Management 1 Lecture Contents 1. Memory Management Requirements 2. Memory Partitioning 3. Paging 4. Segmentation 2 Memory Memory is an array of words or bytes, each with its own address.
Lecture 7 Memory Management 1 Lecture Contents 1. Memory Management Requirements 2. Memory Partitioning 3. Paging 4. Segmentation 2 Memory Memory is an array of words or bytes, each with its own address.
CS370: Operating Systems [Spring 2016] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University
![CS370: Operating Systems [Spring 2016] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University CS370: Operating Systems [Spring 2016] Dept. Of Computer Science, Colorado State University](/thumbs/84/90811774.jpg) Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 7: OPERATING SYSTEMS [MEMORY MANAGEMENT] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University TLB Does the TLB work in practice? n
Frequently asked questions from the previous class survey CS 7: OPERATING SYSTEMS [MEMORY MANAGEMENT] Shrideep Pallickara Computer Science Colorado State University TLB Does the TLB work in practice? n
Recall from Tuesday. Our solution to fragmentation is to split up a process s address space into smaller chunks. Physical Memory OS.
 Paging 11/10/16 Recall from Tuesday Our solution to fragmentation is to split up a process s address space into smaller chunks. Physical Memory OS Process 3 Process 3 OS: Place Process 3 Process 1 Process
Paging 11/10/16 Recall from Tuesday Our solution to fragmentation is to split up a process s address space into smaller chunks. Physical Memory OS Process 3 Process 3 OS: Place Process 3 Process 1 Process
Princeton University. Computer Science 217: Introduction to Programming Systems. The Memory/Storage Hierarchy and Virtual Memory
 Princeton University Computer Science 27: Introduction to Programming Systems The Memory/Storage Hierarchy and Virtual Memory Goals of this Lecture Help you learn about: Locality and caching The memory
Princeton University Computer Science 27: Introduction to Programming Systems The Memory/Storage Hierarchy and Virtual Memory Goals of this Lecture Help you learn about: Locality and caching The memory
Review: Memory, Disks, & Files. File Organizations and Indexing. Today: File Storage. Alternative File Organizations. Cost Model for Analysis
 File Organizations and Indexing Review: Memory, Disks, & Files Lecture 4 R&G Chapter 8 "If you don't find it in the index, look very carefully through the entire catalogue." -- Sears, Roebuck, and Co.,
File Organizations and Indexing Review: Memory, Disks, & Files Lecture 4 R&G Chapter 8 "If you don't find it in the index, look very carefully through the entire catalogue." -- Sears, Roebuck, and Co.,
CS 138: Google. CS 138 XVI 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved.
 CS 138: Google CS 138 XVI 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Google Environment Lots (tens of thousands) of computers all more-or-less equal - processor, disk, memory, network interface
CS 138: Google CS 138 XVI 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Google Environment Lots (tens of thousands) of computers all more-or-less equal - processor, disk, memory, network interface
230 Million Tweets per day
 Tweets per day Queries per day Indexing latency Avg. query response time Earlybird - Realtime Search @twitter Michael Busch @michibusch michael@twitter.com buschmi@apache.org Earlybird - Realtime Search
Tweets per day Queries per day Indexing latency Avg. query response time Earlybird - Realtime Search @twitter Michael Busch @michibusch michael@twitter.com buschmi@apache.org Earlybird - Realtime Search
Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval CS276 Information Retrieval and Web Search Christopher Manning and Prabhakar Raghavan Lecture 1: Boolean retrieval Information Retrieval Information Retrieval (IR)
Introduction to Information Retrieval CS276 Information Retrieval and Web Search Christopher Manning and Prabhakar Raghavan Lecture 1: Boolean retrieval Information Retrieval Information Retrieval (IR)
Memory Management. Goals of Memory Management. Mechanism. Policies
 Memory Management Design, Spring 2011 Department of Computer Science Rutgers Sakai: 01:198:416 Sp11 (https://sakai.rutgers.edu) Memory Management Goals of Memory Management Convenient abstraction for programming
Memory Management Design, Spring 2011 Department of Computer Science Rutgers Sakai: 01:198:416 Sp11 (https://sakai.rutgers.edu) Memory Management Goals of Memory Management Convenient abstraction for programming
信息检索与搜索引擎 Introduction to Information Retrieval GESC1007
 信息检索与搜索引擎 Introduction to Information Retrieval GESC1007 Philippe Fournier-Viger Full professor School of Natural Sciences and Humanities philfv8@yahoo.com Spring 2019 1 Last week We have discussed about:
信息检索与搜索引擎 Introduction to Information Retrieval GESC1007 Philippe Fournier-Viger Full professor School of Natural Sciences and Humanities philfv8@yahoo.com Spring 2019 1 Last week We have discussed about:
