Chapter 8 Structuring System Logic Requirements
|
|
|
- Jack Martin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 8 Structuring System Logic Requirements 168 Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 8 Structuring System Logic Requirements 1. Which of the following is not a logic model? c. sequence diagram d. data flow diagrams 2. Which of the following is a modified version of the English language useful for representing the logic in information system processes? b. COBOL c. Unified Modeling Language d. pseudocode 3. A modeling technique that allows you to represent a set of conditions and the actions that follow from them in a tabular format best describes: a. data flow diagram b. decision table c. flowchart d. Structured English 4. Techniques used for modeling process decision logic include: a. sequence diagrams c. Structured English 5. In the analysis phase, logic modeling: a. will be complete and reasonably detailed, but it will also be generic in that it will not reflect the structure or syntax of a particular programming language b. should not be complete and detailed; it will be generic in that it will not reflect the structure or syntax of a particular programming language c. should be complete and detailed, reflecting the structure and syntax of a particular programming language d. should be complete and reflect the physical aspects of the system 6. Modeling a system s logic is part of: a. requirements determination b. requirements structuring c. alternative generation and selection d. logical design 7. The deliverables for logic modeling include: a. a Structured English representation of process logic b. state-transition diagrams c. decision table representation
2 Chapter 8 Structuring System: Logic Modeling A modified form of the English language used to specify the logic of information system processes defines: b. shorthand c. decision logic d. state-transition diagram 9. Which of the following is a difference between Structured English and pseudocode? is a communication technique between programmers and systems analysts. b. Pseudocode is a communication technique between analysts and users. c. Structured English resembles spoken English; pseudocode resembles a programming language. d. Actually, Structured English and pseudocode are synonymous terms. 10. In a decision table, a condition whose value does not affect which actions are taken for two or more rules is referred to as a(n): a. indifferent condition b. static condition c. fixed condition d. flexible condition 11. A decision table is simplified by: a. removing extended entries b. removing any rules with impossible actions c. removing simple entries d. removing any rules with static actions 12. Which of the following uses a format for a process description that mimics the format usually used in programming languages. a. state-transition diagram b. Structured English c. decision table d. sequence diagram 13. It is possible to use Structured English to represent all of the following processes typical of structured programming except for: a. sequence b. conditional statements c. decision points d. repetition 14. When converting conditions and actions to sequential statements, Structured English: a. is superior to decision tables and decision trees b. and decision trees are viewed as being the best techniques c. is rated the third best d. is rated second best 15. For checking consistency and completeness, Structured English was rated as: a. the best technique b. the second best technique c. the third best technique d. not very useful
3 Chapter 8 Structuring System Logic Requirements For checking consistency and completeness, decision tables: a. were rated as second best when compared with Structured English and decision trees b. were rated best when compared with Structured English and decision trees c. were rated third best when compared with Structured English and decision trees d. tied with decision trees as the best technique 17. For which of the following criteria are decision tables rated best when compared to Structured English? a. checking consistency and completeness b. making decisions c. portraying simple problems d. none of the above 18. For which of the following criteria are Structured English rated best when compared to decision tables? a. portraying complex logic b. more compact c. easier to manipulate 19. For which of the following criteria were decision tables rated good when compared to Structured English? a. more compact b. easier to manipulate c. portraying complex logic 20. Which of the following is a true statement? a. Decision tables can be checked for completeness, consistency, and degree of redundancy. b. The pioneers of structured analysis and design thought decision tables were best for portraying complex logic. c. The pioneers of structured analysis and design thought Structured English was better for simpler problems. d. All of the above.
4 Chapter 8 Structuring System: Logic Modeling 171 Answers 1. Which of the following is not a logic model? c. sequence diagram d. data flow diagrams Answer: d Difficulty: Med Reference: p Which of the following is a modified version of the English language useful for representing the logic in information system processes? b. COBOL c. Unified Modeling Language d. pseudocode Answer: a Difficulty: Med Reference: p A modeling technique that allows you to represent a set of conditions and the actions that follow from them in a tabular format best describes: a. data flow diagram b. decision table c. flowchart d. Structured English Answer: b Difficulty: Med Reference: p Techniques used for modeling process decision logic include: a. sequence diagrams c. Structured English Answer: d Difficulty: Med Reference: p In the analysis phase, logic modeling: a. will be complete and reasonably detailed, but it will also be generic in that it will not reflect the structure or syntax of a particular programming language b. should not be complete and detailed; it will be generic in that it will not reflect the structure or syntax of a particular programming language c. should be complete and detailed, reflecting the structure and syntax of a particular programming language d. should be complete and reflect the physical aspects of the system Answer: a Difficulty: Hard Reference: p. 254
5 Chapter 8 Structuring System Logic Requirements Modeling a system s logic is part of: a. requirements determination b. requirements structuring c. alternative generation and selection d. logical design Answer: b Difficulty: Med Reference: p The deliverables for logic modeling include: a. a Structured English representation of process logic b. state-transition diagrams c. decision table representation Answer: d Difficulty: Med Reference: p A modified form of the English language used to specify the logic of information system processes defines: b. shorthand c. decision logic d. state-transition diagram Answer: a Difficulty: Med Reference: p Which of the following is a difference between Structured English and pseudocode? is a communication technique between programmers and systems analysts. b. Pseudocode is a communication technique between analysts and users. c. Structured English resembles spoken English; pseudocode resembles a programming language. d. Actually, Structured English and pseudocode are synonymous terms. Answer: c Difficulty: Med Reference: p In a decision table, a condition whose value does not affect which actions are taken for two or more rules is referred to as a(n): a. indifferent condition b. static condition c. fixed condition d. flexible condition Answer: a Difficulty: Med Reference: p A decision table is simplified by: a. removing extended entries b. removing any rules with impossible actions c. removing simple entries d. removing any rules with static actions Answer: b Difficulty: Med Reference: p. 260
6 Chapter 8 Structuring System: Logic Modeling Which of the following uses a format for a process description that mimics the format usually used in programming languages. a. state-transition diagram b. Structured English c. decision table d. sequence diagram Answer: b Difficulty: Med Reference: p It is possible to use Structured English to represent all of the following processes typical of structured programming except for: a. sequence b. conditional statements c. decision points d. repetition Answer: c Difficulty: Med Reference: p When converting conditions and actions to sequential statements, Structured English: a. is superior to decision tables and decision trees b. and decision trees are viewed as being the best techniques c. is rated the third best d. is rated second best Answer: b Difficulty: Med Reference: p For checking consistency and completeness, Structured English was rated as: a. the best technique b. the second best technique c. the third best technique d. not very useful Answer: c Difficulty: Med Reference: p For checking consistency and completeness, decision tables: a. were rated as second best when compared with Structured English and decision trees b. were rated best when compared with Structured English and decision trees c. were rated third best when compared with Structured English and decision trees d. tied with decision trees as the best technique Answer: d Difficulty: Hard Reference: p For which of the following criteria are decision tables rated best when compared to Structured English? a. checking consistency and completeness b. making decisions c. portraying simple problems d. none of the above Answer: a Difficulty: Med Reference: p. 262
7 Chapter 8 Structuring System Logic Requirements For which of the following criteria are Structured English rated best when compared to decision tables? a. portraying complex logic b. more compact c. easier to manipulate Answer: d Difficulty: Med Reference: p For which of the following criteria were decision tables rated good when compared to Structured English? a. more compact b. easier to manipulate c. portraying complex logic Answer: d Difficulty: Med Reference: p Which of the following is a true statement? a. Decision tables can be checked for completeness, consistency, and degree of redundancy. b. The pioneers of structured analysis and design thought decision tables were best for portraying complex logic. c. The pioneers of structured analysis and design thought Structured English was better for simpler problems. d. All of the above. Answer: d Difficulty: Med Reference: p. 262
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A process has a: 1) A) pronoun label B) noun phrase label C) verb phrase label D) adjective
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A process has a: 1) A) pronoun label B) noun phrase label C) verb phrase label D) adjective
Programming Languages and Program Development Life Cycle Fall Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102
 Programming Languages and Program Development Life Cycle Fall 2016 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102 Outline The most common approaches to program design and development
Programming Languages and Program Development Life Cycle Fall 2016 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies CSD 102 Outline The most common approaches to program design and development
Introduction to Computer Programming/Handout 01 Page 1 of 13
 Introduction to Computer Programming/Handout 01 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Learning Objectives... 2 Program... 2 Programmer... 2 Programming Language... 2 Types of Languages...
Introduction to Computer Programming/Handout 01 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Learning Objectives... 2 Program... 2 Programmer... 2 Programming Language... 2 Types of Languages...
SNS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING,
 SNS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, COIMBATORE Department of Computer Science and Engineering QUESTION BANK(PART A) GE8151 - PROBLEM SOLVING AND PYTHON PROGRAMMING TWO MARKS UNIT-I 1. What is computer? Computers
SNS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, COIMBATORE Department of Computer Science and Engineering QUESTION BANK(PART A) GE8151 - PROBLEM SOLVING AND PYTHON PROGRAMMING TWO MARKS UNIT-I 1. What is computer? Computers
ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING. Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University
 ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University Lecture 03: Program Development Life Cycle Readings: Not Covered in Textbook Program Development
ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University Lecture 03: Program Development Life Cycle Readings: Not Covered in Textbook Program Development
A Quick Review of Chapter 1
 A Quick Review of Chapter 1 The core of computing is algorithms Algorithm A well-ordered collection of unambiguous and effectively computable operations that, when executed, produces a result and halts
A Quick Review of Chapter 1 The core of computing is algorithms Algorithm A well-ordered collection of unambiguous and effectively computable operations that, when executed, produces a result and halts
(Murlidhar Group of Institutions,Bhavnagar Road, Rajkot) by:-assit. Prof. Vijay Vora (SOOADM) MCA-III
 Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
Technology in Action. Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy. Eleventh Edition. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Eleventh Edition Technology in Action Chapter 8 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming 2 Topics Understanding Software Programming The Importance
Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Eleventh Edition Technology in Action Chapter 8 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming 2 Topics Understanding Software Programming The Importance
Algorithm: 1. Introduction
 Algorithm 1 Algorithm: a finite set of instructions that specify a sequence of operations to be carried out in order to solve a specific problem or class of problems. [Zwass] Properties of algorithms:
Algorithm 1 Algorithm: a finite set of instructions that specify a sequence of operations to be carried out in order to solve a specific problem or class of problems. [Zwass] Properties of algorithms:
Problem Solving and Program Design - Chapter 1. Cory L. Strope
 Problem Solving and Program Design - Chapter 1 Cory L. Strope Overview of Computers and Programming Computer Hardware Computer Software Software Development (Problem Solving) Pseudocode Flowchart Intro.
Problem Solving and Program Design - Chapter 1 Cory L. Strope Overview of Computers and Programming Computer Hardware Computer Software Software Development (Problem Solving) Pseudocode Flowchart Intro.
Higher Computing Science Software Design and Development - Programming Summary Notes
 Higher Computing Science Software Design and Development - Programming Summary Notes Design notations A design notation is the method we use to write down our program design. Pseudocode is written using
Higher Computing Science Software Design and Development - Programming Summary Notes Design notations A design notation is the method we use to write down our program design. Pseudocode is written using
Managing Change and Complexity
 Managing Change and Complexity The reality of software development Overview Some more Philosophy Reality, representations and descriptions Some more history Managing complexity Managing change Some more
Managing Change and Complexity The reality of software development Overview Some more Philosophy Reality, representations and descriptions Some more history Managing complexity Managing change Some more
ITEC102 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES
 ITEC102 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 5 ALGORITHMS AND FLOW CHARTS EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF COMPUTING AND TECHNOLOGY Aim of the course Aim of this course to have information about,
ITEC102 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES LECTURE 5 ALGORITHMS AND FLOW CHARTS EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF COMPUTING AND TECHNOLOGY Aim of the course Aim of this course to have information about,
Chapter 2: Algorithm Discovery and Design. Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Fourth Edition
 Chapter 2: Algorithm Discovery and Design Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Fourth Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about Representing algorithms Examples of algorithmic problem
Chapter 2: Algorithm Discovery and Design Invitation to Computer Science, C++ Version, Fourth Edition Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about Representing algorithms Examples of algorithmic problem
C++ Programming Language Lecture 2 Problem Analysis and Solution Representation
 C++ Programming Language Lecture 2 Problem Analysis and Solution Representation By Ghada Al-Mashaqbeh The Hashemite University Computer Engineering Department Program Development Cycle Program development
C++ Programming Language Lecture 2 Problem Analysis and Solution Representation By Ghada Al-Mashaqbeh The Hashemite University Computer Engineering Department Program Development Cycle Program development
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER AND PROGRAMMING
 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER AND PROGRAMMING Computer programming BTI 10202 Compiled by SIA CHEE KIONG DEPARTMENT OF MATERIAL AND DESIGN ENGINEERING FACULTY OF MECHANICAL AND MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER AND PROGRAMMING Computer programming BTI 10202 Compiled by SIA CHEE KIONG DEPARTMENT OF MATERIAL AND DESIGN ENGINEERING FACULTY OF MECHANICAL AND MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING
Chapter 1: An Overview of Computers and Logic
 Chapter 1: An Overview of Computers and Logic Programming Logic and Design, Third Edition Comprehensive Objectives After studying Chapter 1, you should be able to: Understand computer components and operations
Chapter 1: An Overview of Computers and Logic Programming Logic and Design, Third Edition Comprehensive Objectives After studying Chapter 1, you should be able to: Understand computer components and operations
1) What is the first step of the system development life cycle (SDLC)? A) Design B) Analysis C) Problem and Opportunity Identification D) Development
 Technology In Action, Complete, 14e (Evans et al.) Chapter 10 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming 1) What is the first step of the system development life cycle (SDLC)? A) Design B) Analysis C) Problem
Technology In Action, Complete, 14e (Evans et al.) Chapter 10 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming 1) What is the first step of the system development life cycle (SDLC)? A) Design B) Analysis C) Problem
Outline. Program development cycle. Algorithms development and representation. Examples.
 Outline Program development cycle. Algorithms development and representation. Examples. 1 Program Development Cycle Program development cycle steps: Problem definition. Problem analysis (understanding).
Outline Program development cycle. Algorithms development and representation. Examples. 1 Program Development Cycle Program development cycle steps: Problem definition. Problem analysis (understanding).
BIL101E: Introduction to Computers and Information systems Lecture 8
 BIL101E: Introduction to Computers and Information systems Lecture 8 8.1 Algorithms 8.2 Pseudocode 8.3 Control Structures 8.4 Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators 8.5 The if Selection Structure
BIL101E: Introduction to Computers and Information systems Lecture 8 8.1 Algorithms 8.2 Pseudocode 8.3 Control Structures 8.4 Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators 8.5 The if Selection Structure
REPRESENTING ALGORITHMS. REPRESENTING ALGORITHMS IB DP Computer science Standard Level ICS3U
 C A N A D I A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L S C H O O L O F H O N G K O N G 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Representing Algorithms algorithm should be clear, precise, and unambiguous one possibility is to use the
C A N A D I A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L S C H O O L O F H O N G K O N G 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Representing Algorithms algorithm should be clear, precise, and unambiguous one possibility is to use the
CSc 10200! Introduction to Computing. Lecture 1 Edgardo Molina Fall 2013 City College of New York
 CSc 10200! Introduction to Computing Lecture 1 Edgardo Molina Fall 2013 City College of New York 1 Introduction to Computing Lectures: Tuesday and Thursday s (2-2:50 pm) Location: NAC 1/202 Recitation:
CSc 10200! Introduction to Computing Lecture 1 Edgardo Molina Fall 2013 City College of New York 1 Introduction to Computing Lectures: Tuesday and Thursday s (2-2:50 pm) Location: NAC 1/202 Recitation:
Programming Logic Beginning
 Programming Logic Beginning 152-101 Designing Programs and Applications Quick Links & Text References Program Design Pages 23 27 Algorithms Pages 25 26 Levels of Design Pages IOPs Pages User Interface
Programming Logic Beginning 152-101 Designing Programs and Applications Quick Links & Text References Program Design Pages 23 27 Algorithms Pages 25 26 Levels of Design Pages IOPs Pages User Interface
Programming Logic - Beginning
 Instructor s Programming Logic - Beginning Designing Programs and Applications Programming Logic - Beginning 152-101 Designing Programs and Applications Quick Links & Text References Program Design Pages
Instructor s Programming Logic - Beginning Designing Programs and Applications Programming Logic - Beginning 152-101 Designing Programs and Applications Quick Links & Text References Program Design Pages
Programming Languages and Program Development
 Programming Languages and Program Development 1 Programming Languages and How They Work Programming o Process used to create software programs Programmers o People who use programming languages to create
Programming Languages and Program Development 1 Programming Languages and How They Work Programming o Process used to create software programs Programmers o People who use programming languages to create
Discovering Computers Chapter 13 Programming Languages and Program Development
 Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 13 Programming Languages and Program Development Chapter 13 Objectives Differentiate between machine and assembly languages Identify and discuss the purpose of procedural
Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 13 Programming Languages and Program Development Chapter 13 Objectives Differentiate between machine and assembly languages Identify and discuss the purpose of procedural
Unit II. (i) Computer Programming Languages
 Unit II. (i) Computer Programming Languages Need of a computer programming language: A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a computer. Thousands of different
Unit II. (i) Computer Programming Languages Need of a computer programming language: A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a computer. Thousands of different
IDENTIFY WAYS OF REPRESENTING ALGORITHMS.
 IDENTIFY WAYS OF REPRESENTING ALGORITHMS. OBJECTIVES: Identify ways of representing algorithms: Content Representation of algorithms as Pseudocode or Flowcharts; use of flow chart symbols: input/output
IDENTIFY WAYS OF REPRESENTING ALGORITHMS. OBJECTIVES: Identify ways of representing algorithms: Content Representation of algorithms as Pseudocode or Flowcharts; use of flow chart symbols: input/output
Chapter 8 Algorithms 1
 Chapter 8 Algorithms 1 Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define an algorithm and relate it to problem solving. Define three construct and describe their use in algorithms.
Chapter 8 Algorithms 1 Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define an algorithm and relate it to problem solving. Define three construct and describe their use in algorithms.
FLOW CHART AND PSEUDO CODE
 FLOW CHART AND PSEUDO CODE Flowchart A Flowchart is a pictorial representation of an algorithm. The First flowchart is made by John Von Newman in 1945. It is a symbolic diagram of operation sequence, dataflow,
FLOW CHART AND PSEUDO CODE Flowchart A Flowchart is a pictorial representation of an algorithm. The First flowchart is made by John Von Newman in 1945. It is a symbolic diagram of operation sequence, dataflow,
Pseudo Code and Flow Charts. Chapter 1 Lesson 2
 Pseudo Code and Flow Charts Chapter 1 Lesson 2 Pseudocode Using Pseudocode Statements and Flowchart Symbols English-like representation of the logical steps it takes to solve a problem Flowchart Pictorial
Pseudo Code and Flow Charts Chapter 1 Lesson 2 Pseudocode Using Pseudocode Statements and Flowchart Symbols English-like representation of the logical steps it takes to solve a problem Flowchart Pictorial
At the top of the every document that you create (word processing or source files) include:
 General Read through the Background section below, then copy and paste the questions out of the Assignment section into your word processor and answer the questions. Turn in the questions using the instructions
General Read through the Background section below, then copy and paste the questions out of the Assignment section into your word processor and answer the questions. Turn in the questions using the instructions
Simply Java Programming: An Application Driven, Tutorial
 Simply Java Programming: An Application Driven, Tutorial st Approach, 1 Edition 2004 Georgia Competency-Based Curriculum Frameworks, Career & Technical Education, Information Technology, Programming and
Simply Java Programming: An Application Driven, Tutorial st Approach, 1 Edition 2004 Georgia Competency-Based Curriculum Frameworks, Career & Technical Education, Information Technology, Programming and
Gaddis: Starting Out with Alice Test Bank Chapter Two 1 Chapter Two
 Gaddis: Starting Out with Alice Test Bank Chapter Two 1 Chapter Two MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the name of the default world method that automatically runs when an Alice program is executed? a. the first
Gaddis: Starting Out with Alice Test Bank Chapter Two 1 Chapter Two MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the name of the default world method that automatically runs when an Alice program is executed? a. the first
COMSC-051 Java Programming Part 1. Part-Time Instructor: Joenil Mistal
 COMSC-051 Java Programming Part 1 Part-Time Instructor: Joenil Mistal Chapter 5 5 Controlling the Flow of Your Program Control structures allow a programmer to define how and when certain statements will
COMSC-051 Java Programming Part 1 Part-Time Instructor: Joenil Mistal Chapter 5 5 Controlling the Flow of Your Program Control structures allow a programmer to define how and when certain statements will
1. Introduction to Programming
 Computer Science I CS 135 1. Introduction to Programming René Doursat Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Fall 2005 Computer Science I CS 135 0. Course Presentation
Computer Science I CS 135 1. Introduction to Programming René Doursat Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Fall 2005 Computer Science I CS 135 0. Course Presentation
Computer Languages, Algorithms and Program Development. How do computers know what we want them to do?
 Computer Languages, Algorithms and Program Development How do computers know what we want them to do? Communicating with a Computer Communication cycle One complete unit of communication. An idea to be
Computer Languages, Algorithms and Program Development How do computers know what we want them to do? Communicating with a Computer Communication cycle One complete unit of communication. An idea to be
Technology in Action. Chapter Topics. Scope creep occurs when: 3/20/2013. Information Systems include all EXCEPT the following:
 Technology in Action Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Chapter 10 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming Ninth Edition Chapter Topics Understanding software programming Life
Technology in Action Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Chapter 10 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming Ninth Edition Chapter Topics Understanding software programming Life
An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition. Chapter 2 Beginning the Problem-Solving Process
 An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition Chapter 2 Beginning the Problem-Solving Process Objectives Explain the problem-solving process used to create a computer program Analyze a problem
An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition Chapter 2 Beginning the Problem-Solving Process Objectives Explain the problem-solving process used to create a computer program Analyze a problem
Software Design. Levels in Design Process. Design Methodologies. Levels..
 Design Software Design Design activity begins with a set of requirements Design done before the system is implemented Design is the intermediate language between requirements and code Moving from problem
Design Software Design Design activity begins with a set of requirements Design done before the system is implemented Design is the intermediate language between requirements and code Moving from problem
Problem Solving Footer Text 10/30/2015 1
 Problem Solving Footer Text 10/30/2015 1 Learning Outcome List five (5) steps in problem solving Identify input, process and output from a given problem. 8.2.2 Define algorithm. Solve a given problem using
Problem Solving Footer Text 10/30/2015 1 Learning Outcome List five (5) steps in problem solving Identify input, process and output from a given problem. 8.2.2 Define algorithm. Solve a given problem using
Engineering program development. Edited by Péter Vass
 Engineering program development Edited by Péter Vass Introduction Question: Why engineering program development may be useful for a PhD student in Earth Sciences? Counter-argument: In these days a wide
Engineering program development Edited by Péter Vass Introduction Question: Why engineering program development may be useful for a PhD student in Earth Sciences? Counter-argument: In these days a wide
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE1. Lecture 2: Algorithmic Problem Solving
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE1 Lecture 2: Algorithmic Problem Solving Agenda 2 Problem Solving Techniques Pseudocode Algorithm Flow charts Examples How People Solve Problems 3 A Problem exists when what
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE1 Lecture 2: Algorithmic Problem Solving Agenda 2 Problem Solving Techniques Pseudocode Algorithm Flow charts Examples How People Solve Problems 3 A Problem exists when what
SOFTWARE ANALYSIS & DESIGN TOOLS
 SOFTWARE ANALYSIS & DESIGN TOOLS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/software_engineering/software_analysis_design_tools.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Software analysis and design includes all activities,
SOFTWARE ANALYSIS & DESIGN TOOLS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/software_engineering/software_analysis_design_tools.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Software analysis and design includes all activities,
Programming & Computers
 Programming & Computers CS1110 - Kaminski CS1110 focus 1. Problem solving Understand problem & requirements (I P O) Design modular program Design algorithms Code solution Test & debug 2. Programming PP
Programming & Computers CS1110 - Kaminski CS1110 focus 1. Problem solving Understand problem & requirements (I P O) Design modular program Design algorithms Code solution Test & debug 2. Programming PP
An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition. Chapter 7 The Repetition Structure
 An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition Chapter 7 The Repetition Structure Objectives Differentiate between a pretest loop and a posttest loop Include a pretest loop in pseudocode Include
An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition Chapter 7 The Repetition Structure Objectives Differentiate between a pretest loop and a posttest loop Include a pretest loop in pseudocode Include
Tutorial 4 Creating Forms and Reports
 Tutorial 4 Creating Forms and Reports Microsoft Access 2013 Objectives Session 4.1 Create a form using the Form Wizard Apply a theme to a form Add a picture to a form Change the color of text on a form
Tutorial 4 Creating Forms and Reports Microsoft Access 2013 Objectives Session 4.1 Create a form using the Form Wizard Apply a theme to a form Add a picture to a form Change the color of text on a form
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers
 Objectives Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers To review basic computer systems concepts To be able to understand the different computing environments and their components To review the history of computer
Objectives Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers To review basic computer systems concepts To be able to understand the different computing environments and their components To review the history of computer
Last Updated: 08/28/09. Imaging Concepts
 Last Updated: 08/28/09 Imaging Concepts Table of Contents What is a Folder?... 3 What is a File?... 4 What is an Image?... 4 How to collaborate while processing files?... 4 What is a File Type?... 5 How
Last Updated: 08/28/09 Imaging Concepts Table of Contents What is a Folder?... 3 What is a File?... 4 What is an Image?... 4 How to collaborate while processing files?... 4 What is a File Type?... 5 How
Homework #2. If (your ID number s last two digits % 6) = 0: 6, 12, 18
 2005/Sep/19 1 Homework #2 Chapter 1: Exercises 7, 9 with modifications: for Exercise 7.a: 20 and 32 are changed as your ID number s last two digits and 60. for Exercise 9: 47x25 are change as 47x(your
2005/Sep/19 1 Homework #2 Chapter 1: Exercises 7, 9 with modifications: for Exercise 7.a: 20 and 32 are changed as your ID number s last two digits and 60. for Exercise 9: 47x25 are change as 47x(your
2.2 (a) Statement, subroutine, procedure, function, parameter, loop
 Chapter 2.2: The structure of procedural programs 2.2 (a) Statement, subroutine, procedure, function, parameter, loop Procedural programs are ones in which instructions are executed in the order defined
Chapter 2.2: The structure of procedural programs 2.2 (a) Statement, subroutine, procedure, function, parameter, loop Procedural programs are ones in which instructions are executed in the order defined
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
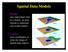 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Algorithms. Chapter 8. Objectives After studying this chapter, students should be able to:
 Objectives After studying this chapter, students should be able to: Chapter 8 Algorithms Define an algorithm and relate it to problem solving. Define three construct and describe their use in algorithms.
Objectives After studying this chapter, students should be able to: Chapter 8 Algorithms Define an algorithm and relate it to problem solving. Define three construct and describe their use in algorithms.
Chapter 5: Algorithms
 Chapter 5 Algorithms By: J. Brookshear Modified by: Yacoub Sabatin, BEng, MSc Chapter 5: Algorithms 5.1 The Concept of an Algorithm 5.2 Algorithm Representation 5.3 Algorithm Discovery 5.4 Iterative Structures
Chapter 5 Algorithms By: J. Brookshear Modified by: Yacoub Sabatin, BEng, MSc Chapter 5: Algorithms 5.1 The Concept of an Algorithm 5.2 Algorithm Representation 5.3 Algorithm Discovery 5.4 Iterative Structures
Activity Robot Behaviors and Writing Pseudocode
 Activity 2.3.2 Robot Behaviors and Writing Pseudocode Introduction A behavior is anything your robot does: turning on a single motor is a behavior, moving forward is a behavior, tracking a line is a behavior,
Activity 2.3.2 Robot Behaviors and Writing Pseudocode Introduction A behavior is anything your robot does: turning on a single motor is a behavior, moving forward is a behavior, tracking a line is a behavior,
EE414 Embedded Systems Ch 9. State Machines
 EE414 Embedded Systems Ch 9. State Machines Byung Kook Kim School of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Outline State Machine Model 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Models vs.
EE414 Embedded Systems Ch 9. State Machines Byung Kook Kim School of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Outline State Machine Model 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Models vs.
The Pivot framework: Design and Implementation
 The Pivot framework: Design and Implementation B. Stroustrup G. Dos Reis Department of Computer Science Texas A&M University Argone, 2004-08-18 p. 1 The Problem The original problem (inspiration) Poor
The Pivot framework: Design and Implementation B. Stroustrup G. Dos Reis Department of Computer Science Texas A&M University Argone, 2004-08-18 p. 1 The Problem The original problem (inspiration) Poor
Copyright 2005 Department of Computer & Information Science
 Introducing Programming Copyright 2005 Goals By the end of this lecture, you should Understand the different types of programming languages. Understand the basic procedures in a program as input, processing
Introducing Programming Copyright 2005 Goals By the end of this lecture, you should Understand the different types of programming languages. Understand the basic procedures in a program as input, processing
13/11/2017. Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515
 Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Data Flow Diagram (DFD) A graphical system model that shows all of the main requirements for an information
Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Data Flow Diagram (DFD) A graphical system model that shows all of the main requirements for an information
Chapter Twelve. Systems Design and Development
 Chapter Twelve Systems Design and Development After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the process of designing, programming, and debugging a computer program Explain why there are many
Chapter Twelve Systems Design and Development After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the process of designing, programming, and debugging a computer program Explain why there are many
Object-Oriented Modeling with UML: A Study of Developers Perceptions
 Object-Oriented Modeling with UML: A Study of Developers Perceptions Ritu Agarwal and Atish P. Sinha The object-oriented (OO) approach provides a powerful and effective environment for modeling and building
Object-Oriented Modeling with UML: A Study of Developers Perceptions Ritu Agarwal and Atish P. Sinha The object-oriented (OO) approach provides a powerful and effective environment for modeling and building
An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition. Chapter 8 More on the Repetition Structure
 An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition Chapter 8 More on the Repetition Structure Objectives Include a posttest loop in pseudocode Include a posttest loop in a flowchart Code a posttest
An Introduction to Programming with C++ Sixth Edition Chapter 8 More on the Repetition Structure Objectives Include a posttest loop in pseudocode Include a posttest loop in a flowchart Code a posttest
Course Outline. Microsoft Power BI Interactive Data Visualizations Course : 2 days Instructor Led
 Microsoft Power BI Interactive Data Visualizations Course 752550: 2 days Instructor Led ABOUT THE COURSE Microsoft Power BI transforms your company data into rich visuals that facilitate new ways of thinking
Microsoft Power BI Interactive Data Visualizations Course 752550: 2 days Instructor Led ABOUT THE COURSE Microsoft Power BI transforms your company data into rich visuals that facilitate new ways of thinking
1. Review of program specifications 2. Program design 3. Coding 4. Testing 5. Finalizing documentation
 1.1 Computer Program A computer program is a detailed set of instructions that directs a computer to perform the tasks necessary to process data into information. These instructions, usually written by
1.1 Computer Program A computer program is a detailed set of instructions that directs a computer to perform the tasks necessary to process data into information. These instructions, usually written by
Low-Level Languages. Computer Programs and Programming Languages
 Computer Programs and Programming Languages What is a computer program? Set of instructions that directs computer to perform tasks Programming used to write instructions 1 Computer Programs and Programming
Computer Programs and Programming Languages What is a computer program? Set of instructions that directs computer to perform tasks Programming used to write instructions 1 Computer Programs and Programming
4. The is a diagram that graphically depicts the steps that take place in a program. a. Program b. Flowchart c. Algorithm d. Code e.
 Gaddis: Starting Out with Programming Logic & Design Test Bank Chapter Two MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which error produces incorrect results but does not prevent the program from running? a. syntax b. logic c.
Gaddis: Starting Out with Programming Logic & Design Test Bank Chapter Two MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which error produces incorrect results but does not prevent the program from running? a. syntax b. logic c.
COP 1220 Introduction to Programming in C++ Course Justification
 Course Justification This course is a required first programming C++ course in the following degrees: Associate of Arts in Computer Science, Associate in Science: Computer Programming and Analysis; Game
Course Justification This course is a required first programming C++ course in the following degrees: Associate of Arts in Computer Science, Associate in Science: Computer Programming and Analysis; Game
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level COMPUTER SCIENCE 9608/23 Paper 2 Fundamental Problem-solving and Programming Skills May/June 2018 PRE-RELEASE
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level COMPUTER SCIENCE 9608/23 Paper 2 Fundamental Problem-solving and Programming Skills May/June 2018 PRE-RELEASE
Number System. Introduction. Decimal Numbers
 Number System Introduction Number systems provide the basis for all operations in information processing systems. In a number system the information is divided into a group of symbols; for example, 26
Number System Introduction Number systems provide the basis for all operations in information processing systems. In a number system the information is divided into a group of symbols; for example, 26
SALVO-a fourth-generation language for personal computers
 SALVO-a fourth-generation language for personal computers by MARVIN ELDER Software Automation, Inc. Dallas, Texas ABSTRACT Personal computer users are generally nontechnical people. Fourth-generation products
SALVO-a fourth-generation language for personal computers by MARVIN ELDER Software Automation, Inc. Dallas, Texas ABSTRACT Personal computer users are generally nontechnical people. Fourth-generation products
Developing Algorithms
 This scheme gives pupils a practical looking at developing algorithms firstly by looking at abstraction, decomposition and algorithmic thinking. Students then learn about the different techniques used
This scheme gives pupils a practical looking at developing algorithms firstly by looking at abstraction, decomposition and algorithmic thinking. Students then learn about the different techniques used
Computer System and programming in C
 Approaches to Problem Solving Concept of algorithm and flow charts ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS A typical programming task can be divided into two phases: Problem solving phase produce an ordered sequence
Approaches to Problem Solving Concept of algorithm and flow charts ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS A typical programming task can be divided into two phases: Problem solving phase produce an ordered sequence
Object Oriented Analysis and Design - Part2(Design)
 Object Oriented Analysis and Design - Part2(Design) Exam A QUESTION 1 Which statement is true about elements within the subsystem and public visibility? A. Only the subset of elements that define the subsystems
Object Oriented Analysis and Design - Part2(Design) Exam A QUESTION 1 Which statement is true about elements within the subsystem and public visibility? A. Only the subset of elements that define the subsystems
Introduction Objectives: 1) differentiate between high-level, low-level, and machine language; 2) explain why it is necessary to translate a program
 Introduction Objectives: 1) differentiate between high-level, low-level, and machine language; 2) explain why it is necessary to translate a program written in a high-level programming language into machine
Introduction Objectives: 1) differentiate between high-level, low-level, and machine language; 2) explain why it is necessary to translate a program written in a high-level programming language into machine
Algorithms. Abdelghani Bellaachia, CSCI 1121 Page: 1
 Algorithms 1. Objectives... 2 2. Design You Solution... 2 3. Structure of an algorithm:... 3 4. Pseudocode:... 4 5. Example... 5 6. Selection or Conditional Execution... 8 7. Looping or Iteration... 9
Algorithms 1. Objectives... 2 2. Design You Solution... 2 3. Structure of an algorithm:... 3 4. Pseudocode:... 4 5. Example... 5 6. Selection or Conditional Execution... 8 7. Looping or Iteration... 9
CS187 - Science Gateway Seminar for CS and Math
 CS187 - Science Gateway Seminar for CS and Math Fall 2013 Class 6 Sep. 19, 2013 Programming and Programming Languages Why, How and What? A programming language is a formal language (vs. natural language)
CS187 - Science Gateway Seminar for CS and Math Fall 2013 Class 6 Sep. 19, 2013 Programming and Programming Languages Why, How and What? A programming language is a formal language (vs. natural language)
ENT 189: COMPUTER PROGRAMMING. H/P: Home page:
 ENT 189: COMPUTER PROGRAMMING Dr. PAULRAJ M P, Associate Professor, School of Mechatronic Engineering, #42- Level 2, Ulu Pauh New Campus 02600-Arau. PERLIS Email: paul@unimap.edu.my H/P: 017 5103757 Home
ENT 189: COMPUTER PROGRAMMING Dr. PAULRAJ M P, Associate Professor, School of Mechatronic Engineering, #42- Level 2, Ulu Pauh New Campus 02600-Arau. PERLIS Email: paul@unimap.edu.my H/P: 017 5103757 Home
Technology in Action. Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy. Tenth Edition. Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Tenth Edition Technology in Action Chapter 8 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming 2 Chapter Topics Understanding Software Programming
Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Tenth Edition Technology in Action Chapter 8 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming 2 Chapter Topics Understanding Software Programming
8 Algorithms 8.1. Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning
 8 Algorithms 8.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning 8.2 Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define an algorithm and relate it to problem solving. Define
8 Algorithms 8.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning 8.2 Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define an algorithm and relate it to problem solving. Define
Administrativia. CS107 Introduction to Computer Science. Readings. Algorithms. Expressing algorithms
 CS107 Introduction to Computer Science Lecture 2 An Introduction to Algorithms: and Conditionals Administrativia Lab access Searles 128: Mon-Friday 8-5pm (unless class in progress) and 6-10pm Sat, Sun
CS107 Introduction to Computer Science Lecture 2 An Introduction to Algorithms: and Conditionals Administrativia Lab access Searles 128: Mon-Friday 8-5pm (unless class in progress) and 6-10pm Sat, Sun
(I m not printing out these notes! Take your own.)
 PT1420 Week 2: Software Program Design I (I m not printing out these notes! Take your own.) Today we'll be discussing designing programs: Algorithms and errors Flowcharts and pseudocode Sequence structures
PT1420 Week 2: Software Program Design I (I m not printing out these notes! Take your own.) Today we'll be discussing designing programs: Algorithms and errors Flowcharts and pseudocode Sequence structures
Enterprise Application Viewer (eav )
 Automated documentation: Program documentation JCL documentation Application documentation IMS, VSAM, Flat File Use Documentation Compliance: Sarbanes-Oxley compliance Basel II compliance HIPAA compliance
Automated documentation: Program documentation JCL documentation Application documentation IMS, VSAM, Flat File Use Documentation Compliance: Sarbanes-Oxley compliance Basel II compliance HIPAA compliance
Department of Industrial Engineering. Sharif University of Technology. Operational and enterprises systems. Exciting directions in systems
 Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology Session# 9 Contents: The role of managers in Information Technology (IT) Organizational Issues Information Technology Operational and
Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology Session# 9 Contents: The role of managers in Information Technology (IT) Organizational Issues Information Technology Operational and
STUDENT OUTLINE. Lesson 8: Structured Programming, Control Structures, if-else Statements, Pseudocode
 STUDENT OUTLINE Lesson 8: Structured Programming, Control Structures, if- Statements, Pseudocode INTRODUCTION: This lesson is the first of four covering the standard control structures of a high-level
STUDENT OUTLINE Lesson 8: Structured Programming, Control Structures, if- Statements, Pseudocode INTRODUCTION: This lesson is the first of four covering the standard control structures of a high-level
 1 Information system An information system is the combination of technology(computers) and people that enable an organization to collect data, store them, and transform them into information Data Data
1 Information system An information system is the combination of technology(computers) and people that enable an organization to collect data, store them, and transform them into information Data Data
Fundamentals of Programming. Lecture 6: Structured Development (part one)
 Fundamentals of Programming Lecture 6: Structured Development (part one) Instructor: Fatemeh Zamani f_zamani@ce.sharif.edu edu Sharif University of Technology Computer Engineering Department Outline Algorithms
Fundamentals of Programming Lecture 6: Structured Development (part one) Instructor: Fatemeh Zamani f_zamani@ce.sharif.edu edu Sharif University of Technology Computer Engineering Department Outline Algorithms
Procedural Programming
 Procedural Programming Lecture 2 - Summer Semester 2016 Control Structures Flow Charts Faculty of Engineering Institute of Computer Engineering What we know so far... Programming is only one step in program
Procedural Programming Lecture 2 - Summer Semester 2016 Control Structures Flow Charts Faculty of Engineering Institute of Computer Engineering What we know so far... Programming is only one step in program
The data in the table are arranged into 12 rows and 12 columns. The process of printing them out can be expressed in a pseudocode algorithm as
 Control structures in Java are statements that contain statements. In particular, control structures can contain control structures. You've already seen several examples of if statements inside loops,
Control structures in Java are statements that contain statements. In particular, control structures can contain control structures. You've already seen several examples of if statements inside loops,
Procedural Programming
 Procedural Programming Lecture 2 - Summer Semester 2017 Control Structures Flow Charts Faculty of Engineering Institute of Computer Engineering Practical Training REGISTRATION ends tomorrow Wednesday (26
Procedural Programming Lecture 2 - Summer Semester 2017 Control Structures Flow Charts Faculty of Engineering Institute of Computer Engineering Practical Training REGISTRATION ends tomorrow Wednesday (26
Chapter 5 Conditional and Iterative Statements. Statement are the instructions given to the computer to perform any kind of action.
 Chapter 5 Conditional and Iterative Statements Statement Statement are the instructions given to the computer to perform any kind of action. Types of Statement 1. Empty Statement The which does nothing.
Chapter 5 Conditional and Iterative Statements Statement Statement are the instructions given to the computer to perform any kind of action. Types of Statement 1. Empty Statement The which does nothing.
Registering for classes Help
 Registering for classes Help Before You Begin 1. Create your class schedule from the material provided by your campus. 2. Prepare additional schedules in the event courses on your first choice schedule
Registering for classes Help Before You Begin 1. Create your class schedule from the material provided by your campus. 2. Prepare additional schedules in the event courses on your first choice schedule
Chapter 3 Structured Program Development
 1 Chapter 3 Structured Program Development Copyright 2007 by Deitel & Associates, Inc. and Pearson Education Inc. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 3 - Structured Program Development Outline 3.1 Introduction
1 Chapter 3 Structured Program Development Copyright 2007 by Deitel & Associates, Inc. and Pearson Education Inc. All Rights Reserved. Chapter 3 - Structured Program Development Outline 3.1 Introduction
Computing and compilers
 Computing and compilers Comp Sci 1570 to Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Evaluate the difference between hardware and software Find out about the various types of software Get a high level understanding of how program
Computing and compilers Comp Sci 1570 to Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Evaluate the difference between hardware and software Find out about the various types of software Get a high level understanding of how program
Fundamentals of Programming Session 1
 Fundamentals of Programming Session 1 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2014 Sharif University of Technology Outlines Review of Course Content Grading Policy What Is
Fundamentals of Programming Session 1 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2014 Sharif University of Technology Outlines Review of Course Content Grading Policy What Is
1. Lexical Analysis Phase
 1. Lexical Analysis Phase The purpose of the lexical analyzer is to read the source program, one character at time, and to translate it into a sequence of primitive units called tokens. Keywords, identifiers,
1. Lexical Analysis Phase The purpose of the lexical analyzer is to read the source program, one character at time, and to translate it into a sequence of primitive units called tokens. Keywords, identifiers,
Invitation to Computer Science 7th Edition TEST BANK Schneider Gersting
 Invitation to Computer Science 7th Edition TEST BANK Schneider Gersting Instant download at: Invitation to Computer Science 7th Edition SOLUTIONS MANUAL Schneider Gersting Instant download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/invitation-computer-science-7th-edition-test-bankschneider-gersting/
Invitation to Computer Science 7th Edition TEST BANK Schneider Gersting Instant download at: Invitation to Computer Science 7th Edition SOLUTIONS MANUAL Schneider Gersting Instant download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/invitation-computer-science-7th-edition-test-bankschneider-gersting/
Steps to program development
 Automate processes - Programming Concepts and Design Steps to program development A computer program is a set of formal instructions, which the computer executes in order to carry out some designated task.
Automate processes - Programming Concepts and Design Steps to program development A computer program is a set of formal instructions, which the computer executes in order to carry out some designated task.
Analysing Ferret XML Reports to Estimate the Density of Copied Code
 Analysing Ferret XML Reports to Estimate the Density of Copied Code Pam Green Peter C.R. Lane Austen Rainer Sven-Bodo Scholz April 2010 Technical Report No. 501 School of Computer Science University of
Analysing Ferret XML Reports to Estimate the Density of Copied Code Pam Green Peter C.R. Lane Austen Rainer Sven-Bodo Scholz April 2010 Technical Report No. 501 School of Computer Science University of
Introduction to Programming
 Introduction to Programming Course ISI-1329 - Three Days - Instructor-Led Introduction This three-day, instructor-led course introduces students to computer programming. Students will learn the fundamental
Introduction to Programming Course ISI-1329 - Three Days - Instructor-Led Introduction This three-day, instructor-led course introduces students to computer programming. Students will learn the fundamental
CTI Short Learning Programme in Internet Development Specialist
 CTI Short Learning Programme in Internet Development Specialist Module Descriptions 2015 1 Short Learning Programme in Internet Development Specialist (10 months full-time, 25 months part-time) Computer
CTI Short Learning Programme in Internet Development Specialist Module Descriptions 2015 1 Short Learning Programme in Internet Development Specialist (10 months full-time, 25 months part-time) Computer
