(12) United States Patent
|
|
|
- Jemima York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED NETWORK TO ENABLE BOTH NON-GSM CIRCUIT SERVICE AND GSM PACKET SERVICE TO THE MOBILE STATION Inventor: Satyanarayanan Ramaswamy, Wheeling, IL (US) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Schaumburg, IL (US) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 4(b) by 0 days. Appl. No.: 09/407,557 Filed: Sep. 28, 1999 Int. Cl... H04Q 7/20 U.S. Cl /445; 455/417; 455/466; 370/352 Field of Search /426, 432, 455/433,466,445, 417; 370/352, 356, 353, 354, 338 References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 6,061,346 A 5/2000 Nordman /352 6,104,929 A 8/2000 Josse et al /445 6, A * 9/2000 Frodigh et al /473 6,167,279 A * 12/2000 Chang et al /462 6, B1 * 3/2001 Lietsalmi et al /466 6,243,579 B1 6/2001 Kari /426 6, B1 * 11/2001 Nevo et al /466 6,327,256 B1 * 12/2001 Paivike et al /337 6,4,1 B1 * 7/2002 Kreppel /445 OTHER PUBLICATIONS Satya Ramaswamy, Gs Interface Stage 3 text, Sep. 29, 1998, 21 pages. Satya Ramaswamy, "Signaling Techniques and Stage 2 Procedures for 136+/GPRS, Aug. 31, 1998, 19 pages. * cited by examiner Primary Examiner-Lester G. Kincaid ASSistant Examiner Tilahun Gesesse (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Michael C. Soldner; Lawrence J. Chapa (57) ABSTRACT A non-gsm network that uses a GSM serving GPRS Support node (40) and a gateway Support node for providing packet Service to transmit a message capsule (52) containing one or more signaling messages between a mobile Station (36) and a mobile Switching center (46). The mobile station (36) constructs an uplink tunneling of messages protocol envelope (48) that includes, in addition to a uplink message capsule, information Specific to non-gsm protocols and the serving GPRS support node (40) determines a destination of the uplink message capsule based on a routing area identifier and the information specific to the non-gsm protocols. The serving GPRS Support node (40) constructs a downlink tunneling of messages protocol envelope that includes a downlink message capsule and information specific to the non-gsm protocols and transmits the downlink tunneling of messages to the mobile station (36) and the mobile Station extracts the downlink message capsule based on the infor mation specific to the non-gsm protocols. 24 Claims, 2 Drawing Sheets
2 U.S. Patent Nov. 12, 2002 Sheet 1 of 2
3 U.S. Patent Nov. 12, 2002 Sheet 2 of TON PROTOCOL ENVELOPE HEADER MESSAGE CAPSULE FI G 3 SUBFIELD 54 - TOM PROTOCOL DISCRIMINATOR 561 REMAINING LENGTH OF TOM PROTOCOL ENVELOPE HEADER NON-PUBLIC PSID/RSID 58 OTHER TIA/EIA-36 SPECIFIC INFORMATION SUBFIELD TON PROTOCOL DISCRIMINATOR REMAINING LENGTH OF TON PROTOCOL ENVELOPE HEADER OTHER TIA/EIA-56 SPECIFIC INFORMATION FI G. 6 IDENTITY TYPE IDENTITY NUMBER OF 136MM MESSAGES (M-1) LENGTH OF MESSAGE 1 (N) LENGTH OF MESSAGE 2 (N) 52 LENGTH OF MESSAGE MCN) MESSAGE MESSAGE 2 MESSAGE M FI G. 6
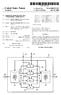
4 1 TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALING MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED NETWORK TO ENABLE BOTH NON-GSM CIRCUIT SERVICE AND GSM PACKET SERVICE TO THE MOBILE STATION FIELD OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates generally to digital cellular communication, and more particularly to non-gsm signal ing in a general packet Service based GSM network. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION A General Packet Radio Service ( GPRS ) is a packet data service used by Global System for Mobile Communi cation ( GSM') networks to enable the GSM networks to Send and receive data in an end-to-end packet transfer mode. As a result, network architecture used in a GSM network to Support packet data Service includes two pure packet net work nodes. These pure packet network nodes include a Serving GPRS Support Node ( SGSN ) that is used to perform Signaling operations, along with a Gateway GPRS Support Node ( GGSN ) used to interface with an internet protocol ("IP") network. The SGSN can also be connected to other SGSNs belonging to other service providers, which in turn can also be connected to other SGSNs, and so forth. FIG. 1 is a Schematic diagram of a packet data Service based GSM network. As illustrated in FIG. 1, in addition to a SGSN 22 and a GGSN 24, a GPRS based GSM network 20 generally includes a mobile Station 26 interconnected with a base station 28 that in turn interfaces with the SGSN 22, a mobile switching center ( MSC) 30, and a home location register ( HLR') 32 associated with the mobile Switching center 30 that is used to authenticate Service. The base station 28 receives a message sent by the mobile Station 26 and the message is transmitted from the base Station 28 to the SGSN. 22. The SGSN 22 terminates the message, processes information associated with the message to generate new signaling, and transmits the new Signaling to the mobile Switching center 30. In the same way, a message to be sent by the mobile Switching center 30 to the mobile station 26 is transmitted from the mobile Switching center 30 to the SGSN. 22. The SGSN 22 terminates the message, processes information associated with the message to generate new signaling, and transmits the new Signaling to the mobile station 26 through the base station 28. In a network system in which both the mobile Switching center 30 and the SGSN 22 operate using GSM based technology, this process of terminating the message and processing information to generate new signaling that is performed by the SGSN 22 involves processing of informa tion using a Single technology, namely GSM technology. AS a result, the termination of the message and the generation of new signaling by the SGSN 22 can be accomplished without requiring significant modification to the SGSN 22. However, operation of different, non-gsm related tech nologies within the framework of the GPRS based GSM network elements, i.e., the SGSN 22 and the GGSN 24, requires that technologies different from the GSM technol ogy be included in the GSM network 20. For example, when the mobile Switching center 30 is designed to operate within the framework of a non-gsm network, the mobile Switching center 30 utilizes technologies other than GSM technologies, and therefore the mobile switching center 30 must operate using a technology Substantially different from that of the SGSN 22 in order to provide packet services to the mobile station 26. Since the mobile station 26 can only be reached through the SGSN 22, the SGSN 22 would be required to process information using both GSM and the non-gsm technology. As a result, connecting the non-gsm mobile Switching center with the SGSN 22 becomes more complicated and requires significant modifications of the SGSN 22 and the non-gsm mobile Switching center, lim iting the extent of Signaling and non-signaling messages that can be exchanged between the mobile Station 26 and the non-gsm mobile Switching center. Therefore, what is needed is a procedure that minimizes necessary changes to the SGSN 22 and the non-gsm mobile Switching center, while enabling deployment of a wide Variety of Signaling and non-signaling message exchanges between the mobile station 26 and the mobile Switching center 30, that has minimal effects upon the operation of the SGSN. 22. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a Schematic diagram of a packet data Service based GSM network. FIG. 2 is a Schematic diagram of a signaling and data transfer interface, between a non-gsm mobile Switching center and an SGSN of a GSM network, according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3 is a table illustrating a format of a tunneling of messages protocol envelope according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 4 is a table illustrating an uplink format for a tunneling of messages protocol envelope header according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 5 is a table illustrating downlink format for a tunneling of messages protocol envelope header according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 6 is a table illustrating encapsulation of a non-gsm Signaling message. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS FIG. 2 is a Schematic diagram of a signaling and data transfer interface, between a non-gsm mobile Switching center and an SGSN in a packet service based GSM network, according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. As illustrated in FIG. 2, a packet based GSM network 34 includes a mobile station 36, a base station 38, a SGSN 40, and a GGSN 42 interconnected with a packet data network ( PDN ) 44. The SGSN 40 may also be interconnected with another SGSN 41 or with a GGSN 43 from an alternate public land mobile network ( PLMN ) 45. A mobile Station Switching center 46 that operates using non-gsm technology, such as TIA/EIA-136 technology for example, interfaces with the SGSN 40 through a gateway interface 47. According to the present invention, the gateway interface 47 is derived using a Subset of the gateway interface 47 as defined by GSM technology, and adding procedures and messages for the tunneling of non-gsm Signaling messages associated with the TLAJEIA-136 tech nology between the mobile station 36 and the mobile station Switching center 46 through the SGSN 40. It is understood that the mobile Switching center 46 may interface with other mobile Switching centers (not shown) to transmit Signaling messages from the other mobile Switching centers to the SGSN 40 through the gateway interface 47, or in the alternative, the other mobile Switching centers may interface directly with the SGSN 40 through separate gate way interfaces connecting the mobile Switching centers to the SGSN 40.
5 3 FIG. 3 is a table illustrating a format of a tunneling of messages protocol envelope according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. The tunneling of the non-gsm signaling messages between the mobile Station 36 and the mobile Station Switching center 46 through the SGSN 40 is accomplished, according to the present invention, using a combination of Specific procedures at the mobile station 36, the mobile station switching center 46, and the SGSN 40. For example, as illustrated in FIGS. 2 and 3, when one or more non-gsm messages are to be commu nicated by the mobile station 36 to the mobile Switching center 46, the mobile station 36 constructs a tunneling of messages ( TOM') protocol envelope 48 containing stan dardized information, including a protocol discriminator related to the non-gsm protocols associated with the tech nology of the mobile Switching center 46, information Specific to the protocol discriminator, along with the one or more non-gsm based messages. The TOM protocol enve lope 48 is then sent by the mobile station 36 to the SGSN 40 along a logical link control layer Service access point that is terminated at the SGSN 40. As illustrated in FIG. 3, the TOM protocol envelope 48 constructed and sent by the mobile station 36 to the SGSN 40 includes a TOM protocol envelope header 50 and a message capsule 52. The message capsule 52 contains the one or more non-gsm Signaling messages to be communi cated by the mobile station 36 to the mobile Switching center 46, and the TOM protocol envelope header 50 contains information necessary to route the message capsule 52. FIG. 4 is a table illustrating an uplink format for a tunneling of messages protocol envelope header according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention. AS illustrated in FIG. 4, the TOM protocol envelope header 50 of the TOM protocol envelope 48 includes a TOM protocol discriminator subfield 54, a remaining length of TOM pro tocol envelope header subfield 56, and non-gsm technology protocol subfields 58 related to operation protocols of the non-gsm technology, i.e., the TIA/EIA-136 technology for example. The TOM protocol discriminator subfield 54 iden tifies the protocol using tunneling of messages, which in this case is the TIA/EIA-136 protocol, and the remaining length of the TOM protocol envelope header subfield 56 indicates the number of octets following the current octet in the TOM protocol discriminator subfield 54. The non-gsm technol ogy protocol subfields 58 are specific to the type of non GSM technology involved. For example, when TIA/EIA 136 technology is involved, the non-gsm technology protocol subfields 58 include a non-public private system identifier/residential system identifier ( PSID/RSID") sub field and a subfield containing other TIA/EIA-136 specific information. Upon receiving the TOM protocol envelope 48 from the mobile station 36, the SGSN 40 determines the mobile Switching center to which the message capsule 52 contained in the TOM protocol envelope 48 is to be forwarded. This determination is made by the SGSN 40 based on a protocol discriminator located in the TOM protocol discriminator subfield 54 of the TOM protocol envelope 48 received from the mobile station 36, information in the TOM protocol envelope 48 Specific to the protocol discriminator, and a routing area identifier ( RAI ) associated with the location of the mobile station 36 obtained by the SGSN 40 upon receipt of the TOM protocol envelope 48 from the mobile station 36. For example, when the non-gsm technology used involves the TIA/EIA-136 technology, the SGSN 40 determines the mobile Switching center to receive the mes Sage capsule based on the RAI obtained upon receipt of the TOM protocol envelope 48 from the mobile station 36, a protocol discriminator indicating the TIA/EIA-136 protocol located in the TOM protocol discriminator subfield 54 of the TOM protocol envelope 48, and non-public PSID/RSID and other TIA/EIA-136 specific information contained in the non-gsm technology protocol subfields 58. The SGSN 40 then constructs an UPLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message, including the identity of the mobile station that sent the TOM protocol envelope 48, an encryp tion status indicating whether the TOM protocol envelope 48 was received from the mobile Station in an encrypted form, a priority of the message capsule 52, along with the message capsule 52. The SGSN 40 then forwards the constructed UPLINK-TUNNEL-REQUEST message to the message Switching center determined by the SGSN 40 as receiving the message. Upon receiving an UPLINK-TUNNEL-REQUEST mes sage from the SGSN 40 containing the identity of the mobile Station Sending the message capsule 52, the encryption status indicating whether the TOM protocol envelope 48 was received from the identified mobile Station in an encrypted format, the priority of the message capsule 52, and the message capsule 52, the mobile Switching center 46 extracts the message capsule 52 from the UPLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message and processes the one or more non GSM messages contained in the message capsule 52. When one or more non-gsm messages are to be com municated by the mobile Switching center 46 to the mobile station 36 that is located on the packet service based GSM network 34, and therefore can only be transmitted to the mobile station through the SGSN 40, the mobile Switching center 46 constructs a DOWNLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message with the message capsule 52 containing the one or more non-gsm messages. The DOWNLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message includes an identity of the mobile Station that is to receive the message capsule 52, an encryp tion request indicating whether the message capsule 52 is to be sent to the mobile Station in an encrypted format, the priority of the message capsule 52, along with the message capsule 52. The mobile Switching center 46 then sends the constructed DOWNLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message to the SGSN 40 associated with the mobile station 36. Upon receiving the DOWNLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message from the mobile Switching center 46, the SGSN 40 constructs a TOM protocol envelope containing the message capsule 52 received with the DOWNLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message. The SGSN 40 sends the constructed TOM protocol envelope to the mobile station identified in the DOWNLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message on an appropriate Service access point of the logical link control layer. The appropriate logical link control layer Service access point is selected by the SGSN 40 based on the priority of the message capsule 52 indicated in the DOWNLINK TUNNEL REQUEST message transmitted by the mobile Switching center 46. Logical link control layer encryption is enabled or disabled based on the encryption request infor mation contained in the DOWNLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message. The TOM protocol envelope constructed by the SGSN 40 and sent by the SGSN 40 to the mobile station 36 is similar to the TOM protocol envelope 48 constructed by the mobile station 36 and illustrated in FIG. 3. The TOM protocol envelope constructed by the SGSN 40 includes the message capsule 52 containing the one or more non-gsm signaling messages to be communicated by the mobile Switching center 46 to the mobile station 36, and the TOM protocol
6 S envelope header 50 containing information necessary to route the message capsule 52. FIG. 5 is a table illustrating a tunneling of messages protocol envelope header downlink format according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention. AS illus trated in FIG. 5, a TOM protocol envelope header constructed by the SGSN 40 and sent by the SGSN 40 to the mobile station 36 includes a TOM protocol discriminator subfield 62, a remaining length of TOM protocol envelope header subfield 64, and a non-gsm technology protocol Subfields 66, containing information Specific to the non GSM technology, such information specific to TIA/EIA-136 technology, for example. The TOM protocol discriminator Subfield 62 identifies the protocol using tunneling of messages, Such as the TIA/EIA-136 protocol, and the remaining length of TOM protocol envelope header subfield 64 indicates the number of octets following the current octet in the TOM protocol discriminator subfield 62. Upon receiving the TOM protocol envelope from the SGSN 40, a determination is made by the mobile station 36 as to whether the protocol identified by a protocol discrimi nator located in the TOM protocol discriminator subfield 62 is supported by the mobile station 36. If the identified protocol is supported by the mobile station 36, the mobile Station 36 extracts the one or more messages in the message capsule 52 from the TOM protocol envelope 48 and pro cesses the extracted one or more messages. FIG. 6 is a table illustrating encapsulation of a non-gsm Signaling message. Encapsulation of the one or more mes Sages in the message capsule 52 is specific to the non-gsm technology involved. For example, as illustrated in FIG. 6, when TIA/EIA-136 technology is involved, the message capsule 52 includes an identity type field 68 that identifies whether a mobile station identifier ( MSID") is present in the message capsule 52, and if present, identifies the type of mobile station identifier, and an identity field 70 in which the mobile station identifier is contained. Since the TIA/EIA 136 technology allows the message capsule 52 to contain one or more messages, a number of messages field 72 indicates the number of messages in the message capsule 52, and the total number of messages is one more than the value of the number of messages field 72 (M-1). Length of messages fields 74 indicate the number of octets in each message, N, to N, and message fields 76 provide octets belonging to a given message, and are padded with trailing ZeroS to the nearest octet boundary. In this way, by using the TOM protocol envelope 48 of the present invention, tunneling of the non-gsm Signaling messages between the mobile station 36 and the mobile station switching center 46 through the SGSN 40 is accom plished using a combination of Specific procedures at the mobile station 36, the mobile station switching center 46, and the SGSN 40 that are specific to information contained in the non-gsm technology. As a result, the present inven tion minimizes necessary changes to the SGSN 22 and the non-gsm mobile Switching center, while enabling deploy ment of a wide variety of Signaling and non-signaling message exchanges between the mobile Station 26 and the mobile Switching center 30, while having minimal effect upon the operation of the SGSN 22. It is understood that while a particular embodiment of the present invention has been shown and described, modifica tions may be made. For example, while the present invention has been shown and described as including TIA/EIA-136 technology as the non-gsm technology employed, the present invention may be realized using non-gsm technol ogy other than the TIA/EIA-136 technology which is intended to utilize GSM GPRS network elements to support packet data. It is therefore intended in the appended claims to cover all Such changes and modifications which fall within the true Spirit and Scope of the invention. What is claimed is: 1. A method of tunneling a message capsule, containing one or more non-gsm signaling messages, from a mobile station of a non-gsm network that uses a GSM serving GPRS Support node and a gateway GPRS Support node to provide packet Service to a one mobile Switching center of a plurality of mobile Switching centers that operate using non-gsm protocols, comprising the Steps of: constructing a tunneling of messages protocol envelope, at the mobile Station, including the message capsule and information specific to the non-gsm protocols; transmitting the tunneling of messages protocol envelope to the serving GPRS support node; determining, at the Serving GPRS Support node, that the one mobile Switching center is to receive the message capsule based on a routing area identifier corresponding to the mobile Station and the information Specific to the non-gsm protocols; and transmitting the message capsule to the one mobile Switching center. 2. The method of claim 1, wherein the tunneling of messages protocol envelope includes a tunneling of mes Sages protocol envelope header containing information nec essary to route the message capsule. 3. The method of claim 2, wherein the tunneling of messages protocol envelope header includes a tunneling of messages protocol discriminator Subfield that identifies the non-gsm protocols. 4. The method of claim 3, wherein the tunneling of messages protocol envelope header includes a remaining length of tunneling of messages protocol envelope header Subfield that indicates a number of octets following a current octet in the tunneling of messages protocol discriminator subfield, and non-gsm protocol subfields corresponding to the non-gsm protocols. 5. The method of claim 4, wherein the non-gsm proto cols are TIA/EIA-136 protocols. 6. The method of claim 5, wherein the non-gsm protocol Subfields include a non-public private System identifier/ residential system identifier subfield and a subfield contain ing other TLA/EIA-136 specific information. 7. The method of claim 6, wherein the message capsule comprises: an identity type field to identify whether a mobile station identifier is present in the message capsule, and a type of mobile station identifier in response to the mobile Station identifier being present; an identity field containing the mobile Station identifier; number of messages field indicating a total number of the One or more messages in the message capsule, a length of messages field to indicate a number of octets in each of the one or more messages, and message fields to provide octets for the one or more messages. 8. A method of tunneling a message capsule containing one or more non-gsm signaling messages from a non-gsm mobile Switching center that operates using non-gsm pro tocols to a mobile station of a non-gsm network, that uses a GSM serving GPRS Support node and a gateway GPRS Support node to provide packet Service, comprising the Steps of:
7 7 transmitting the message capsule and a mobile Station identifier corresponding to the mobile Station from the mobile Switching center to the serving GPRS Support node, constructing, at the Serving GPRS Support node, a tun neling of messages protocol envelope including the message capsule and information Specific to the non GSM protocols; and transmitting the tunneling of messages protocol envelope to the mobile station based on the mobile station identifier. 9. The method of claim 8, wherein the tunneling of messages protocol envelope includes a tunneling of mes Sages protocol envelope header containing information nec essary to route the message capsule. 10. The method of claim 9, wherein the tunneling of messages protocol envelope header includes a tunneling of messages protocol discriminator Subfield that identifies the non-gsm protocols. 11. The method of claim 10, wherein the tunneling of messages protocol envelope header includes a remaining length of tunneling of messages protocol envelope header Subfield that indicates a number of octets following a current octet in the tunneling of messages protocol discriminator subfield and a non-gsm protocol subfield corresponding to the non-gsm protocols. 12. The method of claim 11, wherein the non-gsm protocols are TIA/EIA-136 protocols. 13. The method of claim 12, wherein the non-gsm protocol subfield contains other TIA/EIA specific informa tion. 14. The method of claim 13, wherein the message capsule comprises: an identity type field to identify whether a mobile station identifier is present in the message capsule and a type of mobile station identifier in response to the mobile Station identifier being present; an identity field containing the mobile Station identifier; a number of messages field indicating a total number of the one or more messages in the message capsule, a length of messages field to indicate a number of octets in each of the one or more messages, and message fields to provide octets for the one or more messages.. A method of tunneling Signaling messages between a mobile station of a non-gsm network that uses a GSM serving GPRS Support node and a gateway GPRS support node to provide packet Service, and a plurality of mobile Switching centers that operates using non-gsm protocols, comprising the Steps of: constructing an uplink tunneling of messages protocol envelope, at the mobile Station, including an uplink message capsule containing one or more non-gsm Signaling messages and information Specific to the non-gsm protocols; transmitting the uplink tunneling of messages protocol envelope to the serving GPRS Support node; determining, at the Serving GPRS Support node, that a one mobile Switching center of the plurality of mobile Switching centers is to receive the uplink message capsule based on a routing area identifier corresponding to the mobile Station and the information Specific to the non-gsm protocols and transmitting the uplink mes Sage capsule to the mobile Switching center; transmitting a downlink message capsule, containing one or more non-gsm Signaling messages, and an identity of the mobile station, from the mobile Switching center to the serving GPRS support node; constructing, at the Serving GPRS Support node, a down link tunneling of messages protocol envelope including the downlink message capsule and information Specific to the non-gsm protocols and transmitting the down link tunneling of messages protocol envelope to the mobile Station; and determining, at the mobile station, whether the non-gsm protocols are Supported by the mobile Station based on the information specific to the non-gsm protocols contained in the downlink tunneling of messages pro tocol envelope. 16. The method of claim, wherein the uplink tunneling of messages protocol envelope and the downlink tunneling of messages protocol envelope include a tunneling of mes Sages protocol envelope header containing information nec essary to route the respective message capsule, a tunneling of messages protocol discriminator Subfield that identifies the non-gsm protocols, a remaining length of tunneling of messages protocol envelope header Subfield that indicates a number of octets following a current octet in the tunneling of messages protocol discriminator Subfield, and a non-gsm protocol subfield corresponding to the non-gsm protocols. 17. The method of claim 16, wherein the non-gsm protocols are TIA/EIA-136 protocols. 18. The method of claim 17, wherein the non-gsm protocol Subfields of the uplink tunneling of messages protocol envelope include a non-public private System identifier/residential system identifier subfield and a subfield containing other TIA/EIA-136 specific information, and the non-gsm protocol subfield of the downlink tunneling of messages protocol envelope contains TLA/EIA-136 specific information. 19. The method of claim 18, wherein the uplink message capsule and the downlink message capsule comprise: an identity type field to identify whether a mobile station identifier is present in the message capsule and a type of mobile station identifier in response to the mobile Station identifier being present; an identity field containing the mobile Station identifier; a number of messages field indicating a total number of the one or more messages in the message capsule, a length of messages field to indicate a number of octets in each of the one or more messages, and message fields to provide octets for the one or more messages. 20. A non-gsm network that uses a GSM serving GPRS Support node and a gateway GPRS Support node to provide packet Service, comprising: a mobile Station to transmit an uplink tunneling of mes Sages protocol envelope to the Serving GPRS Support node, the uplink tunneling of message protocol enve lope including an uplink message capsule, containing One or more Signaling messages constructed using non-gsm protocols, and information specific to the non-gsm protocols; and a mobile Switching center that operates using non-gsm protocols to transmit a DOWNLINK-TUNNEL REQUEST message to the serving GPRS Support node that includes a downlink message capsule, containing one or more Signaling messages constructed using the non-gsm protocols, and a mobile station identifier, wherein the serving GPRS Support node determines a destination of the uplink message capsule based on the information specific to the non-gsm protocols in
8 9 response to receiving the uplink tunneling of messages protocol envelope, and wherein the serving GPRS Support node constructs a downlink tunneling of mes Sages protocol envelope, including the downlink mes Sage capsule and information Specific to the non-gsm protocols, in response to receiving the downlink mes Sage capsule and the mobile Station identifier, and transmits the downlink tunneling of information pro tocol envelope based on the mobile station identifier. 21. The non-gsm network of claim 20, wherein the uplink tunneling of messages protocol envelope and the downlink tunneling of messages protocol envelope include a tunneling of messages protocol envelope header contain ing information necessary to route the corresponding first and Second message capsule, a tunneling of messages pro tocol discriminator Subfield that identifies the non-gsm protocols, a remaining length of tunneling of messages protocol envelope header Subfield that indicates a number of octets following a current octet in the tunneling of messages protocol discriminator subfield, and a non-gsm protocol subfield corresponding to the non-gsm protocols. 22. The non-gsm network of claim 21 wherein the non-gsm protocols are TIA/EIA-136 protocols. 23. The non-gsm network of claim 22, wherein the non-gsm protocol subfields of the uplink tunneling of 10 messages protocol envelope include a non-public private system identifier/residential system identifier subfield and a subfield containing other TIA/EIA-136 specific information, and the non-gsm protocol subfield of the downlink tunnel ing of messages protocol envelope contains TIA/EIA-136 Specific information. 24. The non-gsm network of claim 23, wherein the uplink message capsule and the downlink message capsule further comprising: an identity type field to identify whether a mobile station identifier is present in the respective first and Second message capsules and a type of mobile Station identifier in response to the mobile Station identifier being present, an identity field containing the mobile Station identifier; a number of messages field indicating a total number of the one or more messages in the message capsule, a length of messages field to indicate a number of octets in each of the one or more messages, and message fields to provide octets for the one or more messages. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].
![/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. / client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].](/thumbs/90/103929709.jpg) US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
SCSI routing table (90) and a SCSI to Fibre Channel routing table (92). The system receives a cross bus transfer of data
 US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,832,425 B2 Tomasso (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2014
 USOO8832425B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Tomasso (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2014 (54) WIDE AREA NETWORK ACCESS 2010/0017599 A1* 1/2010 Sellars et al...... 713/156 MANAGEMENT COMPUTER
USOO8832425B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Tomasso (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2014 (54) WIDE AREA NETWORK ACCESS 2010/0017599 A1* 1/2010 Sellars et al...... 713/156 MANAGEMENT COMPUTER
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
HLR/HLR-T. (12) United States Patent US 8,331,990 B2. Dec. 11, (45) Date of Patent: AUCIAUC-T. (10) Patent No.:
 USOO8331990B2 (12) United States Patent LarssOn (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD FORACTIVATING SIM CARDS (75) Inventor: Thomas Larsson, Alvsjo (SE) (73) Assignee: Giesecke
USOO8331990B2 (12) United States Patent LarssOn (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD FORACTIVATING SIM CARDS (75) Inventor: Thomas Larsson, Alvsjo (SE) (73) Assignee: Giesecke
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2
 US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,565,722 B1
 US008565722B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cheuk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) REAL TIME TRACKING AT HOME (56) References Cited NETWORK OF DATA USAGE ON ROAMING GSM NETWORK
US008565722B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Cheuk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) REAL TIME TRACKING AT HOME (56) References Cited NETWORK OF DATA USAGE ON ROAMING GSM NETWORK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(12) United States Patent Cunningham et al.
 US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
1a " " " ), Gigi Nii
 USOO8295862B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,295,862 B2 Suresh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM TO ENABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/466 COMMUNICATION THROUGHSMS (58)
USOO8295862B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,295,862 B2 Suresh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM TO ENABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/466 COMMUNICATION THROUGHSMS (58)
336w 330 FPGA / 330 MW} Compgnenf _/14 / 38 US 7,774,801 B1. Aug. 10, 2010 (56) (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: (12) United States Patent Fitkin
 US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
United States Patent (19) Finkelstein et al.
 United States Patent (19) Finkelstein et al. USOO540602A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 1995 54). METHOD FOR KEY MANAGEMENT OF POINT TO-POINT COMMUNICATIONS 75 Inventors: Louis D. Finkelstein,
United States Patent (19) Finkelstein et al. USOO540602A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 1995 54). METHOD FOR KEY MANAGEMENT OF POINT TO-POINT COMMUNICATIONS 75 Inventors: Louis D. Finkelstein,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,418,453 B1
 USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
United States Patent (19) Boltz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Boltz et al. 54 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR TIME DEFINED DELIVERY OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE MESSAGES 75 Inventors: David Boltz; David B. Westbrook, both of Garland, TeX. 73 Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Boltz et al. 54 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR TIME DEFINED DELIVERY OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE MESSAGES 75 Inventors: David Boltz; David B. Westbrook, both of Garland, TeX. 73 Assignee:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2
 US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
(SA INFORMATION) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. (19) United States ESP/AH REQUEST SA KEY MANAGEMENT FACILITY
 (19) United States US 2008O137863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0137863 A1 THOMAS (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR USING A KEY MANAGEMENT FACILITY TO NEGOTATE A
(19) United States US 2008O137863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0137863 A1 THOMAS (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR USING A KEY MANAGEMENT FACILITY TO NEGOTATE A
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,377,725 B1
 USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,446,087 B1. Lai (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002
 USOO6446087B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lai (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) SYSTEM FOR MAINTAINING THE (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Patton Boggs, LLP INTEGRITY OF APPLICATION DATA
USOO6446087B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lai (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) SYSTEM FOR MAINTAINING THE (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Patton Boggs, LLP INTEGRITY OF APPLICATION DATA
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
W15. Keung Wong, Hong Kong (HK) (21) Appl. No.: 09/875,350. (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong, Hong Kong (HK); Hoi (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,520,661 B2
 US008520661B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,520,661 B2 Strunk (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVOICE OVER 2002/0194069 A1 * 12/2002 Thakur et al.... 705/14
US008520661B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,520,661 B2 Strunk (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVOICE OVER 2002/0194069 A1 * 12/2002 Thakur et al.... 705/14
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080070528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0070528A1 Joyner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) MID-CALL FEATURES (76) Inventors: Tom Joyner, Chicago,
(19) United States US 20080070528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0070528A1 Joyner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) MID-CALL FEATURES (76) Inventors: Tom Joyner, Chicago,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent
 USOO943.2909B2 (12) United States Patent Svedevall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 30, 2016 (54) CONTROL NODE FOR A MOBILE COMMUNICATION NETWORK AND A METHOD FOR ALLOCATING RESOURCES IN
USOO943.2909B2 (12) United States Patent Svedevall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 30, 2016 (54) CONTROL NODE FOR A MOBILE COMMUNICATION NETWORK AND A METHOD FOR ALLOCATING RESOURCES IN
wo W /1997 * cited by examiner
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1
 USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1
 USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
(12) United States Patent
 USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,856,601 B1. Bell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005
 USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0059573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0059573 A1 Gong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 7, 2013 (54) MULTIPLE PARTY COMMUNICATIONS FOR Publication Classification
US 2013 0059573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0059573 A1 Gong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 7, 2013 (54) MULTIPLE PARTY COMMUNICATIONS FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2
 USOO6650589B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2 Clark (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) LOW VOLTAGE OPERATION OF STATIC 6,205,078 B1 * 3/2001 Merritt... 365/226 RANDOMACCESS
USOO6650589B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2 Clark (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) LOW VOLTAGE OPERATION OF STATIC 6,205,078 B1 * 3/2001 Merritt... 365/226 RANDOMACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100091772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/009 1772 A1 CederVallet al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010 (54) PROVIDING IPTV MULTICASTS (76) Inventors: Mats
(19) United States US 20100091772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/009 1772 A1 CederVallet al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010 (54) PROVIDING IPTV MULTICASTS (76) Inventors: Mats
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002
 US006446174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH DRAM BUS 5,969,728 A 10/1999 Dye et al...... 345/515 6,003,121 A
US006446174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH DRAM BUS 5,969,728 A 10/1999 Dye et al...... 345/515 6,003,121 A
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) Unlted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,965,995 B2 Kuo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2015
 USOO8965995B2 (12) Unlted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,965,995 B2 Kuo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2015 (54) WIRELESS STORAGE MANAGEMENT (56) References Cited SYSTEM U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
USOO8965995B2 (12) Unlted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,965,995 B2 Kuo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2015 (54) WIRELESS STORAGE MANAGEMENT (56) References Cited SYSTEM U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0049861A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0049861 A1 Cleghorn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING CONNECTIVITY
(19) United States US 2010.0049861A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0049861 A1 Cleghorn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING CONNECTIVITY
The method includes: (1) Sending, by a client, a request to
 USOO5956490A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,956,490 Buchholz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 1999 54 METHOD, CLIENT DEVICE, SERVER AND 5,742,773 4/1998 Blomfield-Brown et al... 395/200.58
USOO5956490A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,956,490 Buchholz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 1999 54 METHOD, CLIENT DEVICE, SERVER AND 5,742,773 4/1998 Blomfield-Brown et al... 395/200.58
(12) United States Patent
 US0085319B2 (12) United States Patent Jiang et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep., 2013 (54) MESSAGE PROCESSING METHOD AND SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Xiyuan Jiang, Shanghai (CN); Shukun Wang, Beijing
US0085319B2 (12) United States Patent Jiang et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep., 2013 (54) MESSAGE PROCESSING METHOD AND SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Xiyuan Jiang, Shanghai (CN); Shukun Wang, Beijing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,526,272 B1
 USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 O148568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0148568 A1 IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION DEVICE, (52) U.S. Cl. TETHERING
(19) United States US 2013 O148568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0148568 A1 IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION DEVICE, (52) U.S. Cl. TETHERING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1. Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011
 US007991882B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1 Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011 (54) COMMUNICATIONS NETWORK WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS FLOW CONTROL (75) Inventor: Robert
US007991882B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1 Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011 (54) COMMUNICATIONS NETWORK WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS FLOW CONTROL (75) Inventor: Robert
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2. Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008
 United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007
 United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
US 6,587,555 B1. Jul. 1, Cripe et al. (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73) (Us) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56)
 (12) United States Patent Cripe et al. US006587555B1 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,587,555 B1 Jul. 1, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) VIRTUAL PBX Inventors: Daniel E.
(12) United States Patent Cripe et al. US006587555B1 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,587,555 B1 Jul. 1, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) VIRTUAL PBX Inventors: Daniel E.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO8836702B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,702 B2 Yoon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) RAY TRACING CORE AND METHOD FOR (58) Field of Classification Search PROCESSING
(12) United States Patent USOO8836702B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,702 B2 Yoon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) RAY TRACING CORE AND METHOD FOR (58) Field of Classification Search PROCESSING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7370164B1 (12) United States Patent Nagarkar et al. (54) BACKUP OF VIRTUAL MACHINES FROM THE BASE MACHINE (75) Inventors: Kuldeep Sureshrao Nagarkar, Pune (IN); Sinh Dang Nguyen, Eden Prairie, MN (US);
USOO7370164B1 (12) United States Patent Nagarkar et al. (54) BACKUP OF VIRTUAL MACHINES FROM THE BASE MACHINE (75) Inventors: Kuldeep Sureshrao Nagarkar, Pune (IN); Sinh Dang Nguyen, Eden Prairie, MN (US);
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,112 B1
 USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,964,735 B2
 US008964735B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ackley (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2015 (54) TRANSLATING MEDIA ACCESS CONTROL 2010.0020806 A1 1/2010 Vahdat et al. (MAC) ADDRESSES IN A NETWORK
US008964735B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ackley (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2015 (54) TRANSLATING MEDIA ACCESS CONTROL 2010.0020806 A1 1/2010 Vahdat et al. (MAC) ADDRESSES IN A NETWORK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150334033A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0334033 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DATA TRANSMISSION METHOD AND Publication Classification RELATED
(19) United States US 20150334033A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0334033 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DATA TRANSMISSION METHOD AND Publication Classification RELATED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,614,769 B1
 USOO6614769B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Erlick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATIONS UNIT FOR SEAMLESS 6,400,946 B1 6/2002 Vazvan et al.... 455/432 (NYSEYENEYORKS
USOO6614769B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Erlick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATIONS UNIT FOR SEAMLESS 6,400,946 B1 6/2002 Vazvan et al.... 455/432 (NYSEYENEYORKS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,408,074 B1
 USOO6408074B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: LOughran (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) HARDWARE ARCHITECTURE FOR A 4.914,697 A * 4/1990 Dabbish et al.... 380/28 CONFIGURABLE CIPHER DEVICE
USOO6408074B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: LOughran (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) HARDWARE ARCHITECTURE FOR A 4.914,697 A * 4/1990 Dabbish et al.... 380/28 CONFIGURABLE CIPHER DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
United States Patent (19) Pinard et al.
 United States Patent (19) Pinard et al. US005454032A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 1995 54 METHOD OF ESTABLISHING COMMUNICATION LINK TO ONE OF MULTIPLE DEVICES ASSOCIATED WITH SINGLETELEPHONE
United States Patent (19) Pinard et al. US005454032A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 1995 54 METHOD OF ESTABLISHING COMMUNICATION LINK TO ONE OF MULTIPLE DEVICES ASSOCIATED WITH SINGLETELEPHONE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,434,614 B1. Blumenau (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002
 USOO6434614B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Blumenau () Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002 (54) TRACKING OF INTERNET 5,809,481. A 9/1998 Baron et al.... 705/14 ADVERTISEMENTS USING BANNER TAGS
USOO6434614B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Blumenau () Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002 (54) TRACKING OF INTERNET 5,809,481. A 9/1998 Baron et al.... 705/14 ADVERTISEMENTS USING BANNER TAGS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006003.1337A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0031337 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2006 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR BROADCASTING OFFERS OVER ELECTRONIC
(19) United States US 2006003.1337A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0031337 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2006 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR BROADCASTING OFFERS OVER ELECTRONIC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O232386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0232386 A1 Dong (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR ALLOWING A UICC TO MANAGE THE POPCONTEXT PARAMETHERS (76)
(19) United States US 2010O232386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0232386 A1 Dong (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR ALLOWING A UICC TO MANAGE THE POPCONTEXT PARAMETHERS (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
USOO61O1393A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,101,393. Alperovich et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2000
 USOO61O1393A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Alperovich et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2000 54 SELECTIVE ACCEPTANCE OF SHORT FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS MESSAGE SERVICE (SMS) MESSAGES INA
USOO61O1393A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Alperovich et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2000 54 SELECTIVE ACCEPTANCE OF SHORT FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS MESSAGE SERVICE (SMS) MESSAGES INA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201700854.71 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0085471 A1 Jabbari et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2017 9 (54) LABEL SWITCHED PACKET TRANSFER H04L 29/06
(19) United States US 201700854.71 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0085471 A1 Jabbari et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2017 9 (54) LABEL SWITCHED PACKET TRANSFER H04L 29/06
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,055,575 Paulsen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000
 US0055575A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Paulsen et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000 54) VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORKSYSTEM 5,550,984 8/1996 Gelb... 709/2 AND METHOD 5.835,726 11/1998 Shwed
US0055575A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Paulsen et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000 54) VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORKSYSTEM 5,550,984 8/1996 Gelb... 709/2 AND METHOD 5.835,726 11/1998 Shwed
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2
 US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
