Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet
|
|
|
- Melanie Morrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on the ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet Passwords, page 1 Recover Enable and Telnet Passwords, page 2 Set the Date and Time, page 7 Configure the Master Passphrase, page 9 Configure the DNS Server, page 11 Configure the Hardware Bypass and Dual Power Supply (Cisco ISA 3000), page 13 Adjust ASP (Accelerated Security Path) Performance and Behavior, page 15 Monitoring the DNS Cache, page 17 History for, page 17 Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet Passwords To set the hostname, domain name, and the enable and Telnet passwords, perform the following steps. Before You Begin Before you set the hostname, domain name, and the enable and Telnet passwords, check the following requirements: In multiple context mode, you can configure the hostname and domain name in both the system and context execution spaces. For the enable and Telnet passwords, set them in each context; they are not available in the system. When you session to the ASASM from the switch in multiple context mode, the ASASM uses the login password you set in the admin context. To change from the system to a context configuration, in the Configuration > Device List pane, double-click the context name under the active device IP address. 1
2 Recover Enable and Telnet Passwords Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Choose Configuration > Device Setup > Device Name/Password. Enter the hostname. The default hostname is ciscoasa. The hostname appears in the command line prompt, and if you establish sessions to multiple devices, the hostname helps you keep track of where you enter commands. The hostname is also used in syslog messages. For multiple context mode, the hostname that you set in the system execution space appears in the command line prompt for all contexts. The hostname that you optionally set within a context does not appear in the command line; it can be used for a banner. Enter the domain name. The default domain name is default.domain.invalid. The ASA appends the domain name as a suffix to unqualified names. For example, if you set the domain name to example.com and specify a syslog server by the unqualified name of jupiter, then the ASA qualifies the name to jupiter.example.com. Change the privileged mode (enable) password. The default password is blank. The enable password lets you enter privileged EXEC mode if you do not configure enable authentication. The enable password also lets you log into ASDM with a blank username if you do not configure HTTP authentication. a) Check the Change the privileged mode password check box. b) Enter the new password, and then confirm the new password. Set a case-sensitive password of up to 127 characters long. It can be any combination of ASCII printable characters (character codes ), with the exception of spaces and the question mark. Set the login password for Telnet access. There is no default password. The login password is used for Telnet access when you do not configure Telnet authentication. You also use this password when accessing the ASASM from the switch with the session command. a) Check the Change the password to access the console of the security appliance check box. b) Enter the old password (for a new ASA, leave this field blank), new password, then confirm the new password. The password can be up to 16 characters long. It can be any combination of ASCII printable characters (character codes ), with the exception of spaces and the question mark. Click Apply to save your changes. Recover Enable and Telnet Passwords If you forget the enable or Telnet passwords, you can recover them. The procedure differs by device type. You must perform the task using the CLI. Recover Passwords on the ASA To recover passwords for the ASA, perform the following steps: 2
3 Recover Passwords on the ASA Step 3 Step 4 Connect to the ASA console port. Power off the ASA, then power it on. After startup, press the Escape key when you are prompted to enter ROMMON mode. To update the configuration register value, enter the following command: rommon #1> confreg 0x41 Update Config Register (0x41) in NVRAM... Step 5 To set the ASA to ignore the startup configuration, enter the following command: rommon #1> confreg The ASA displays the current configuration register value, and asks whether you want to change it: Current Configuration Register: 0x Configuration Summary: boot default image from Flash ignore system configuration Do you wish to change this configuration? y/n [n]: y Step 6 Step 7 Record the current configuration register value, so you can restore it later. At the prompt, enter Y to change the value. The ASA prompts you for new values. Step 8 Accept the default values for all settings, except for the "disable system configuration?" value. Step 9 At the prompt, enter Y. 0 Reload the ASA by entering the following command: rommon #2> boot Launching BootLoader... Boot configuration file contains 1 entry. Loading disk0:/asa k8.bin... Booting...Loading... The ASA loads the default configuration instead of the startup configuration. 1 Access the privileged EXEC mode by entering the following command: ciscoasa# enable 2 3 When prompted for the password, press Enter. The password is blank. Load the startup configuration by entering the following command: ciscoasa# copy startup-config running-config 3
4 Recover Passwords on the ASA 5506-X, ASA 5508-X, and ASA 5516-X 4 Access the global configuration mode by entering the following command: ciscoasa# configure terminal 5 Change the passwords, as required, in the default configuration by entering the following commands: ciscoasa(config)# password password ciscoasa(config)# enable password password ciscoasa(config)# username name password password 6 Load the default configuration by entering the following command: ciscoasa(config)# no config-register The default configuration register value is 0x1. See the command reference for more information about the configuration register. 7 Save the new passwords to the startup configuration by entering the following command: ciscoasa(config)# copy running-config startup-config Recover Passwords on the ASA 5506-X, ASA 5508-X, and ASA 5516-X To recover passwords for the ASA 5506-X, ASA 5508-X, and ASA 5516-X perform the following steps: Step 3 Step 4 Connect to the ASA console port. Power off the ASA, then power it on. After startup, press the Escape key when you are prompted to enter ROMMON mode. To update the configuration register value, enter the following command: rommon #1> confreg 0x41 You must reset or power cycle for new config to take effect The ASA displays the current configuration register value and a list of configuration options. Record the current configuration register value, so you can restore it later. Configuration Register: 0x Configuration Summary [ 0 ] password recovery [ 1 ] display break prompt [ 2 ] ignore system configuration [ 3 ] auto-boot image in disks 4
5 Recover Passwords or Images on the ASAv [ 4 ] console baud: 9600 boot:... auto-boot index 1 image in disks Step 5 Reload the ASA by entering the following command: rommon #2> boot Launching BootLoader... Boot configuration file contains 1 entry. Loading disk0:/asa k8.bin... Booting...Loading... The ASA loads the default configuration instead of the startup configuration. Step 6 Access the privileged EXEC mode by entering the following command: ciscoasa# enable Step 7 Step 8 When prompted for the password, press Enter. The password is blank. Load the startup configuration by entering the following command: ciscoasa# copy startup-config running-config Step 9 Access the global configuration mode by entering the following command: ciscoasa# configure terminal 0 Change the passwords, as required, in the default configuration by entering the following commands: ciscoasa(config)# password password ciscoasa(config)# enable password password ciscoasa(config)# username name password password 1 Load the default configuration by entering the following command: ciscoasa(config)# no config-register The default configuration register value is 0x1. See the command reference for more information about the configuration register. 2 Save the new passwords to the startup configuration by entering the following command: ciscoasa(config)# copy running-config startup-config Recover Passwords or Images on the ASAv To recover passwords or images on the ASAv, perform the following steps: 5
6 Recover Passwords or Images on the ASAv Copy the running configuration to a backup file on the ASAv: copy running-config filename Example: ciscoasa# copy running-config backup.cfg Step 3 Restart the ASAv: reload From the GNU GRUB menu, press the down arrow, choose the <filename> with no configuration load option, then press Enter. The filename is the default boot image filename on the ASAv. The default boot image is never automatically booted through the fallback command. Then load the selected boot image. GNU GRUB version 2.0(12)4 bootflash:/asa smp-k8.bin bootflash: /asa smp-k8.bin with no configuration load Example: GNU GRUB version 2.0(12)4 bootflash: /asa smp-k8.bin with no configuration load Step 4 Copy the backup configuration file to the running configuration. copy filename running-config Example: ciscoasa (config)# copy backup.cfg running-config Step 5 Reset the password. enable password Example: ciscoasa(config)# enable password cisco123 Step 6 Save the new configuration. write memory Example: ciscoasa(config)# write memory 6
7 Disable Password Recovery Disable Password Recovery Note You cannot disable password recovery on the ASAv. To disable password recovery to ensure that unauthorized users cannot use the password recovery mechanism to compromise the ASA, perform the following steps. Before You Begin On the ASA, the no service password-recovery command prevents you from entering ROMMON mode with the configuration intact. When you enter ROMMON mode, the ASA prompts you to erase all Flash file systems. You cannot enter ROMMON mode without first performing this erasure. If you choose not to erase the Flash file system, the ASA reloads. Because password recovery depends on using ROMMON mode and maintaining the existing configuration, this erasure prevents you from recovering a password. However, disabling password recovery prevents unauthorized users from viewing the configuration or inserting different passwords. In this case, to restore the system to an operating state, load a new image and a backup configuration file, if available. The service password-recovery command appears in the configuration file for information only. When you enter the command at the CLI prompt, the setting is saved in NVRAM. The only way to change the setting is to enter the command at the CLI prompt. Loading a new configuration with a different version of the command does not change the setting. If you disable password recovery when the ASA is configured to ignore the startup configuration at startup (in preparation for password recovery), then the ASA changes the setting to load the startup configuration as usual. If you use failover, and the standby unit is configured to ignore the startup configuration, then the same change is made to the configuration register when the no service passwordrecovery command replicates to the standby unit. Disable password recovery. no service password-recovery Example: ciscoasa (config)# no service password-recovery Set the Date and Time Note Do not set the date and time for the ASASM or the Firepower 9300 ASA security module; they receive these settings from the host device. 7
8 Set the Date and Time Using an NTP Server Set the Date and Time Using an NTP Server NTP is used to implement a hierarchical system of servers that provide a precisely synchronized time among network systems. This kind of accuracy is required for time-sensitive operations, such as validating CRLs, which include a precise time stamp. You can configure multiple NTP servers. The ASA chooses the server with the lowest stratum a measure of how reliable the data is. Time derived from an NTP server overrides any time set manually. Before You Begin In multiple context mode, you can set the time in the system configuration only. Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Step 7 Step 8 Step Choose Configuration > Device Setup > System Time > NTP. Click Add to display the Add NTP Server Configuration dialog box. Enter the NTP server IP address. Check the Preferred check box to set this server as a preferred server. NTP uses an algorithm to determine which server is the most accurate and synchronizes to it. If servers are of similar accuracy, then the preferred server is used. However, if a server is significantly more accurate than the preferred one, the ASA uses the more accurate one. Choose the interface from the drop-down list. This setting specifies the outgoing interface for NTP packets. If the interface is blank, then the ASA uses the default admin context interface according to the routing table. Choose None (the default interface) for stability to change the admin context (and the available interfaces). Choose the key number from the drop-down list. This setting specifies the key ID for this authentication key, which enables you to use MD5 authentication to communicate with the NTP server. The NTP server packets must also use this key ID. If you have previously configured a key ID for another server, you can select it from the list; otherwise, enter a number between 1 and Check the Trusted check box to set this authentication key as a trusted key, which is required for authentication to succeed. Enter the key value to set the authentication key, which is a string that can be up to 32 characters long. Reenter the key value to make sure that you enter it correctly twice. Click OK. Check the Enable NTP authentication check box to turn on NTP authentication. Click Apply to save your changes. Set the Date and Time Manually To set the date and time manually, perform the following steps: Before You Begin In multiple context mode, you can set the time in the system configuration only. 8
9 Configure the Master Passphrase Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Choose Configuration > Device Setup > System Time > Clock. Choose the time zone from the drop-down list. This setting specifies the time zone as GMT plus or minus the appropriate number of hours. If you select the Eastern Time, Central Time, Mountain Time, or Pacific Time zone, then the time adjusts automatically for daylight savings time, from 2:00 a.m. on the second Sunday in March to 2:00 a.m. on the first Sunday in November. Note Changing the time zone on the ASA may drop the connection to intelligent SSMs. Click the Date drop-down list to display a calendar. Then find the correct date using the following methods: Click the name of the month to display a list of months, then click the desired month. The calendar updates to that month. Click the year to change the year. Use the up and down arrows to scroll through the years, or enter a year in the entry field. Click the arrows to the right and left of the month and year to scroll the calendar forward and backward one month at a time. Click a day on the calendar to set the date. Enter the time manually in hours, minutes, and seconds. Click Update Display Time to update the time shown in the bottom right corner of the ASDM pane. The current time updates automatically every ten seconds. Configure the Master Passphrase The master passphrase allows you to securely store plain text passwords in encrypted format and provides a key that is used to universally encrypt or mask all passwords, without changing any functionality. Features that use the master passphrase include the following: OSPF EIGRP VPN load balancing VPN (remote access and site-to-site) Failover AAA servers Logging Shared licenses 9
10 Add or Change the Master Passphrase Add or Change the Master Passphrase To add or change the master passphrase, perform the following steps. Before You Begin This procedure will only be accepted in a secure session, for example by console, SSH, or ASDM via HTTPS. If failover is enabled but no failover shared key is set, an error message appears if you change the master passphrase, informing you that you must enter a failover shared key to protect the master passphrase changes from being sent as plain text. Choose Configuration > Device Management > High Availability > Failover, enter any character in the Shared Key field or 32 hexadecimal numbers (0-9A-Fa-f) if a failover hexadecimal key is selected, except a backspace. Then click Apply. Enabling or changing password encryption in Active/Standby failover causes a write standby, which replicates the active configuration to the standby unit. Without this replication, the encrypted passwords on the standby unit will differ even though they use the same passphrase; configuration replication ensures that the configurations are the same. For Active/Active failover, you must manually enter write standby. A write standby can cause traffic interruption in Active/Active mode, because the configuration is cleared on the secondary unit before the new configuration is synced. You should make all contexts active on the primary ASA using the failover active group 1 and failover active group 2 commands, enter write standby, and then restore the group 2 contexts to the secondary unit using the no failover active group 2 command. Step 3 Step 4 Choose one of the following options: In single context mode, choose Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > Master Passphrase. In multiple context mode, choose Configuration > Device Management > Device Administration > Master Passphrase. Check the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) password encryption check box. If no master passphrase is in effect, a warning message appears when you click Apply. You can click OK or Cancel to continue. If you later disable password encryption, all existing encrypted passwords are left unchanged, and as long as the master passphrase exists, the encrypted passwords will be decrypted, as required by the application. Check the Change the encryption master passphrase check box to enable you to enter and confirm your new master passphrases. By default, they are disabled. Your new master passphrase must be between 8 and 128 characters long. If you are changing an existing passphrase, you must enter the old passphrase before you can enter a new one. Leave the New and Confirm master passphrase fields blank to delete the master passphrase. Click Apply. 10
11 Disable the Master Passphrase Disable the Master Passphrase Disabling the master passphrase reverts encrypted passwords into plain text passwords. Removing the passphrase might be useful if you downgrade to a previous software version that does not support encrypted passwords. Before You Begin You must know the current master passphrase to disable it. This procedure works only in a secure session; that is, by Telnet, SSH, or ASDM via HTTPS. To disable the master passphrase, perform the following steps: Choose one of the following options: In single context mode, choose Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > Master Passphrase. In multiple context mode, choose Configuration > Device Management > Device Administration > Master Passphrase. Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Check the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) password encryption check box. If no master passphrase is in effect, a warning statement appears when you click Apply. Click OK or Cancel to continue. Check the Change the encryption master passphrase check box. Enter the old master passphrase in the Old master passphrase field. You must provide the old master passphrase to disable it. Leave the New master passphrase and the Confirm master passphrase fields empty. Click Apply. Configure the DNS Server You need to configure DNS servers so that the ASA can resolve host names to IP addresses. You also must configure DNS servers to use fully qualified domain names (FQDN) network objects in access rules. Some ASA features require use of a DNS server to access external servers by domain name; for example, the Botnet Traffic Filter feature requires a DNS server to access the dynamic database server and to resolve entries in the static database. Other features, such as the ping or traceroute command, let you enter a name that you want to ping or traceroute, and the ASA can resolve the name by communicating with a DNS server. Many SSL VPN and certificate commands also support names. 11
12 Configure the DNS Server Note The ASA has limited support for using the DNS server, depending on the feature. Before You Begin Make sure that you configure the appropriate routing and access rules for any interface on which you enable DNS domain lookup so you can reach the DNS server. Choose Configuration > Device Management > DNS > DNS Client. Choose one of the following options in the DNS Setup area: Configure one DNS server group This option defines the servers in the DefaultDNS group. Configure multiple DNS server groups With this option, you should still configure the DefaultDNS group, which is the only one used for FQDN network object name resolution. Keep DefaultDNS as the active group. But you can also create additional groups for use in remote access SSL VPN group policies. Even if you configure the DefaultDNS group only, you must select this option if you want to alter the timeout and other characteristics used with the group. Step 3 If you select Configure one DNS server group, configure the servers in the DefaultDNS group. a) In Primary DNS Server, enter the IP address of the DNS server that should be used whenever it is available. For this server and each secondary server, optionally specify the interface_name through which the ASA communicates with the server. If you do not specify the interface, the ASA checks the data routing table; if there are no matches, it then checks the management-only routing table. b) Click Add to add secondary DNS servers. You can add up to six DNS servers. The ASA tries each DNS server in order until it receives a response. Use the Move Up/Move Down buttons to put the servers in priority order. c) Enter a DNS domain name appended to the hostname if it is not fully-qualified. Step 4 If you select Configure multiple DNS server groups, define the server group properties. a) Click Add to create a new group, or select a group and click Edit. The DefaultDNS group is always listed. b) Configure the group properties. Server IP Address to Add, Source Interface Enter the IP address of a DNS server and click Add>>. For each server, optionally specify the interface_name through which the ASA communicates with the server. If you do not specify the interface, the ASA checks the management-only routing table; if there are no matches, it then checks the data routing table. You can add up to six DNS servers. The ASA tries each DNS server in order until it receives a response. Use the Move Up/Move Down buttons to put the servers in priority order. Timeout The number of seconds, from 1 to 30, to wait before trying the next DNS server. The default is 2 seconds. Each time the ASA retries the list of servers, this timeout doubles. Retries The number of times, from 0 to 10, to retry the list of DNS servers when the ASA does not receive a response. 12
13 Configure the Hardware Bypass and Dual Power Supply (Cisco ISA 3000) Expire Entry Timer (DefaultDNS or active group only) The number of minutes after a DNS entry expires (that is, the TTL has passed) that the entry is removed from the DNS lookup table. Removing an entry requires that the table be recompiled, so frequent removals can increase the processing load on the device. Because some DNS entries can have very short TTL (as short as three seconds), you can use this setting to virtually extend the TTL. The default is 1 minute (that is, the entry is removed one minute after the TTL has passed). The range is 1 to minutes. This option is used when resolving FQDN network objects only. Poll Timer (DefaultDNS or active group only) The time, in minutes, of the polling cycle used to resolve FQDN network/host objects to IP addresses. FQDN objects are resolved only if they are used in a firewall policy. The timer determines the maximum time between resolutions; the DNS entry's time-to-live (TTL) value is also used to determine when to update to IP address resolution, so individual FQDNs might be resolved more frequently than the polling cycle. The default is 240 (four hours). The range is 1 to minutes. Domain Name The domain name appended to the hostname if it is not fully-qualified. Step 5 Step 6 Step 7 c) Click OK. d) If you have multiple groups, you can change the one used for DNS requests by selecting it and clicking Set Active. Ensure that at DNS lookup is enabled on at least one interface. In the DNS Lookup interface list, below the DNS server group table, click in the DNS Enabled column and select True to enable lookup on the interface. If you do not enable DNS lookup on an interface, then the DNS server Source Interface or the interface found using the routing table cannot be used. (Optional) Check the Enable DNS Guard on all interfaces check box to enforce one DNS response per query. You can also set DNS Guard when configuring DNS inspection. For a given interface, the DNS Guard setting configured in DNS inspection takes precedence over this global setting. By default, DNS inspection is enabled on all interfaces with DNS Guard enabled. Click Apply to save your changes. Configure the Hardware Bypass and Dual Power Supply (Cisco ISA 3000) You can enable the hardware bypass so that traffic continues to flow between an interface pair during a power outage. Supported interface pairs are copper GigabitEthernet 1/1 & 1/2; and GigabitEthernet 1/3 & 1/4. When the hardware bypass is active, no firewall functions are in place, so make sure you understand the risks of allowing traffic through. For dual power supplies in the ISA 3000, you can establish dual power supplies as the expected configuration in the ASA OS. If one power supply fails, the ASA issues an alarm. By default, the ASA expects a single power supply and won't issue an alarm as long as it includes one working power supply. Before You Begin Hardware Bypass 13
14 Configure the Hardware Bypass and Dual Power Supply (Cisco ISA 3000) This feature is only available on the Cisco ISA 3000 appliance. If you have a fiber Ethernet model, only the copper Ethernet pair (GigabitEthernet 1/1 & 1/2) supports hardware bypass. We suggest that you disable TCP sequence randomization (as described in this procedure). If randomization is enabled (the default), then when the hardware bypass is activated, TCP sessions will need to be re-established. By default, the ISA 3000 rewrites the initial sequence number (ISN) of TCP connections passing through it to a random number. When the hardware bypass is activated, the ISA 3000 is no longer in the data path and does not translate the sequence numbers; the receiving client receives an unexpected sequence number and drops the connection. Even with TCP sequence randomization disabled, some TCP connections will have to be re-established because of the link that is temporarily down during the switchover. When the hardware bypass is deactivated and traffic resumes going through the ISA 3000 data path, some existing TCP sessions need to be re-established because of the link that is temporarily down during the switchover. Cisco TrustSec connections on hardware bypass interfaces are dropped when hardware bypass is activated. When the ISA 3000 powers on and hardware bypass is deactivated, the connections are renegotiated. When the ISA 3000 loses power and goes into hardware bypass mode, only the above interface pairs can communicate; when using the default configuration, inside1 <---> inside2, and outside1 <---> outside2 can no longer communicate. Any existing connections between these interfaces will be lost. Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Step 7 To configure hardware bypass, choose Configuration > Device Management > Hardware Bypass. Configure the hardware bypass to activate for each interface pair by checking the Enable Bypass during Power Down check box. (Optional) Configure each interface pair to remain in hardware bypass mode after the power comes back and the appliance boots up by checking the Stay in Bypass after Power Up check box. When the hardware bypass is deactivated, there is a brief connection interruption as the ASA takes over the flows. In this case, you need to manually turn off the hardware bypass when you are ready; this option lets you control when the brief interruption occurs. For an interface pair, manually activate or deactivate the hardware bypass by checking the Bypass Immediately check box. (Optional) Configure the hardware bypass to remain active until after the ASA FirePOWER module boots up by checking the Stay in Bypass Mode until after the ASA Firepower Module Boots Up check box. You must enable hardware bypass without the Stay in Bypass after Power Up option for the boot delay to operate. Without this option, the hardware bypass is likely to become inactive before the ASA FirePOWER module finishes booting up. This scenario can cause traffic to be dropped if you configured the module to fail-close, for example. Click Apply. Disable TCP randomization. This example shows how to disable randomization for all traffic by adding the setting to the default configuration. a) Choose Configuration > Firewall > Service Policy. b) Select the sfrclass rule, and click Edit. c) Click Rule Actions, and then click Connection Settings. 14
15 Adjust ASP (Accelerated Security Path) Performance and Behavior Step 8 d) Uncheck the Randomize Sequence Number check box. e) Click OK, and then Apply. To establish dual power supplies as the expected configuration, choose Configuration > Device Management > Power Supply, check the Enable Redundant Power Supply check box, and click Apply. This screen also shows the available power supplies. Adjust ASP (Accelerated Security Path) Performance and Behavior The ASP is an implementation layer that puts your policies and configurations into action. It is not of direct interest except during troubleshooting with the Cisco Technical Assistance Center. However, there are a few behaviors related to performance and reliability that you can adjust. Choose a Rule Engine Transactional Commit Model By default, when you change a rule-based policy (such as access rules), the changes become effective immediately. However, this immediacy comes with a slight cost in performance. The performance cost is more noticeable for very large rule lists in a high connections-per-second environment, for example, when you change a policy with 25,000 rules while the ASA is handling 18,000 connections per second. The performance is affected because the rule engine compiles rules to enable faster rule lookup. By default, the system also searches uncompiled rules when evaluating a connection attempt so that new rules can be applied; because the rules are not compiled, the search takes longer. You can change this behavior so that the rule engine uses a transactional model when implementing rule changes, continuing to use the old rules until the new rules are compiled and ready for use. With the transactional model, performance should not drop during the rule compilation. The following table clarifies the behavioral difference. Model Before Compilation During Compilation After Compilation Default Matches old rules. Match new rules. Matches new rules. (The rate for connections per second decreases.) Transactional Matches old rules. Match old rules. Matches new rules. (The rate for connections per second is unaffected.) An additional benefit of the transactional model is that, when replacing an ACL on an interface, there is no gap between deleting the old ACL and applying the new one. This feature reduces the chances that acceptable connections may be dropped during the operation. 15
16 Enable ASP Load Balancing Tip If you enable the transactional model for a rule type, syslogs to mark the beginning and the end of the compilation are generated. These syslogs are numbered through Use the following procedure to enable the transactional commit model for the rule engine. Choose Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > Rule Engine and select the desired options: Access group Access rules applied globally or to interfaces. NAT Network address translation rules. Enable ASP Load Balancing The ASP load balancing mechanism helps avoid the following issues: Overruns caused by sporadic traffic spikes on flows Overruns caused by bulk flows oversubscribing specific interface receive rings Overruns caused by relatively heavily overloaded interface receive rings, in which a single core cannot sustain the load. ASP load balancing allows multiple cores to work simultaneously on packets that were received from a single interface receive ring. If the system drops packets, and the show cpu command output is far less than 100%, then this feature may help your throughput if the packets belong to many unrelated connections. Choose Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > ASP Load Balancing, then check the EnableASP load balancing check box. Check the Dynamically enable or disable ASP load balancing based on traffic monitoring check box to enable ASP load balancing automatically. Before You Begin The automatic option is not available on the ASAv; you must manually enable or disable ASP load balancing. Command or Action To enable the automatic switching on and off of ASP load balancing, choose Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > ASP Load Balancing, and check the Dynamically enable or disable ASP load balancing based on traffic monitoring check box. Purpose This option is not available on the ASAv; you must manually enable or disable ASP load balancing. 16
17 Monitoring the DNS Cache Command or Action To manually enable or disable ASP load balancing, check or uncheck the Enable ASP load balancing check box. Purpose When you manually enable ASP load balancing, it is enabled until you manually disable it, even if you also have the Dynamic option enabled. Manually disabling ASP load balancing applies only if you manually enabled ASP load blancing. If you also enabled the Dynamic option, then the system reverts to automatically enabling or disabling ASP load balancing. Monitoring the DNS Cache The ASA provides a local cache of DNS information from external DNS queries that are sent for certain clientless SSL VPN and certificate commands. Each DNS translation request is first looked for in the local cache. If the local cache has the information, the resulting IP address is returned. If the local cache can not resolve the request, a DNS query is sent to the various DNS servers that have been configured. If an external DNS server resolves the request, the resulting IP address is stored in the local cache with its corresponding hostname. See the following command for monitoring the DNS cache: show dns-hosts History for This command shows the DNS cache, which includes dynamically learned entries from a DNS server as well as manually entered name and IP addresses using the name command. Feature Name Master Passphrase Password Encryption Visibility Platform Releases 8.3(1) 8.4(1) Description We introduced this feature. The master passphrase allows you to securely store plain text passwords in encrypted format and provides a key that is used to universally encrypt or mask all passwords, without changing any functionality. We introduced the following screens: Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > Master Passphrase Configuration > Device Management > Device Administration > Master Passphrase We modified the show password encryption command. 17
18 History for Feature Name Removal of the default Telnet password Automatic ASP Load Balancing ISA 3000 hardware bypass Dual power supply support for the ISA 3000 Platform Releases 9.0(2)/9.1(2) 9.3(2) 9.4(1.225) 9.6(1) Description To improve security for management access to the ASA, the default login password for Telnet was removed; you must manually set the password before you can log in using Telnet. Note The login password is only used for Telnet if you do not configure Telnet user authentication. Previously, when you cleared the password, the ASA restored the default of cisco. Now when you clear the password, the password is removed. The login password is also used for Telnet sessions from the switch to the ASASM (see the session command). For initial ASASM access, you must use the service-module session command, until you set a login password. We did not modify any ASDM screens. You can now enable automatic switching on and off of the ASP load balancing feature. Note The automatic feature is not supported on the ASAv; only manual enabling and disabling is supported. We modified the following screen: Configuration > Device Management > Advanced > ASP Load Balancing The ISA 3000 supports a hardware bypass function to allow traffic to continue flowing through the appliance when there is a loss of power. We introduced the following screen: Configuration > Device Management > Hardware Bypass This feature is not available in Version 9.5(1). For dual power supplies in the ISA 3000, you can establish dual power supplies as the expected configuration in the ASA OS. If one power supply fails, the ASA issues an alarm. By default, the ASA expects a single power supply and won't issue an alarm as long as it includes one working power supply. We introduced the following screen: Configuration > Device Management > Power Supply 18
19 History for Feature Name Longer password support for local username and enable passwords (up to 127 characters) Platform Releases 9.6(1) Description You can now create local username and enable passwords up to 127 characters (the former limit was 32). When you create a password longer than 32 characters, it is stored in the configuration using a PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2) hash. Shorter passwords continue to use the MD5-based hashing method. We modified the following screens: Configuration > Device Setup > Device Name/Password > Enable Password Configuration > Device Management > Users/AAA > User Accounts > Add/Edit User Account > Identity 19
20 History for 20
Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet
 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on the ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet Passwords, page 1
This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on the ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet Passwords, page 1
Configuring the Hostname, Domain Name, Passwords, and Other Basic Settings
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Hostname, Domain Name, Passwords, and Other Basic Settings This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASA 1000V that are typically required for a functioning
CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Hostname, Domain Name, Passwords, and Other Basic Settings This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASA 1000V that are typically required for a functioning
Troubleshooting. Testing Your Configuration CHAPTER
 82 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the ASA and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 82-1 Reloading the ASA, page 82-8 Performing Password Recovery, page
82 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the ASA and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 82-1 Reloading the ASA, page 82-8 Performing Password Recovery, page
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Troubleshooting the Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 43 This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the security appliance, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 43-1 Reloading the Security Appliance, page 43-6 Performing
CHAPTER 43 This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the security appliance, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 43-1 Reloading the Security Appliance, page 43-6 Performing
Getting Started. Access the Console for the Command-Line Interface. Access the Appliance Console
 This chapter describes how to get started with your Cisco ASA. Access the Console for the Command-Line Interface, on page 1 Configure ASDM Access, on page 9 Start ASDM, on page 15 Factory Default Configurations,
This chapter describes how to get started with your Cisco ASA. Access the Console for the Command-Line Interface, on page 1 Configure ASDM Access, on page 9 Start ASDM, on page 15 Factory Default Configurations,
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Multiple Context Mode
 This chapter describes how to configure multiple security contexts on the Cisco ASA. About Security Contexts, page 1 Licensing for, page 12 Prerequisites for, page 13 Guidelines for, page 14 Defaults for,
This chapter describes how to configure multiple security contexts on the Cisco ASA. About Security Contexts, page 1 Licensing for, page 12 Prerequisites for, page 13 Guidelines for, page 14 Defaults for,
Licenses: Product Authorization Key Licensing
 A license specifies the options that are enabled on a given Cisco ASA. This document describes product authorization key (PAK) licenses for all physical ASAs. For the ASAv, see Licenses: Smart Software
A license specifies the options that are enabled on a given Cisco ASA. This document describes product authorization key (PAK) licenses for all physical ASAs. For the ASAv, see Licenses: Smart Software
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces.
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces.
Using the Startup Wizard
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes the Startup wizard and how to use it to configure your sensor. It contains the following sections: Startup Wizard Introduction Window, page 3-1 Setting up the Sensor, page
CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes the Startup wizard and how to use it to configure your sensor. It contains the following sections: Startup Wizard Introduction Window, page 3-1 Setting up the Sensor, page
Cisco Expressway Cluster Creation and Maintenance
 Cisco Expressway Cluster Creation and Maintenance Deployment Guide Cisco Expressway X8.6 July 2015 Contents Introduction 4 Prerequisites 5 Upgrading an X8.n cluster to X8.6 6 Prerequisites 6 Upgrade Expressway
Cisco Expressway Cluster Creation and Maintenance Deployment Guide Cisco Expressway X8.6 July 2015 Contents Introduction 4 Prerequisites 5 Upgrading an X8.n cluster to X8.6 6 Prerequisites 6 Upgrade Expressway
AAA and the Local Database
 This chapter describes authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA, pronounced triple A ). AAA is a a set of services for controlling access to computer resources, enforcing policies, assessing
This chapter describes authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA, pronounced triple A ). AAA is a a set of services for controlling access to computer resources, enforcing policies, assessing
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces. 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces. 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Setting Up the Sensor
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides information for setting up the sensor. This chapter contains the following sections: Understanding Initialization, page 4-1 Configuring Network Settings, page 4-1 Configuring
CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides information for setting up the sensor. This chapter contains the following sections: Understanding Initialization, page 4-1 Configuring Network Settings, page 4-1 Configuring
GSS Administration and Troubleshooting
 CHAPTER 9 GSS Administration and Troubleshooting This chapter covers the procedures necessary to properly manage and maintain your GSSM and GSS devices, including login security, software upgrades, GSSM
CHAPTER 9 GSS Administration and Troubleshooting This chapter covers the procedures necessary to properly manage and maintain your GSSM and GSS devices, including login security, software upgrades, GSSM
Cisco TelePresence VCS Cluster Creation and Maintenance
 Cisco TelePresence VCS Cluster Creation and Maintenance Deployment Guide Cisco VCS X8.5 Cisco TMS 13.2 or later December 2014 Contents Introduction 4 Prerequisites 5 Upgrading an X7.1 or later cluster
Cisco TelePresence VCS Cluster Creation and Maintenance Deployment Guide Cisco VCS X8.5 Cisco TMS 13.2 or later December 2014 Contents Introduction 4 Prerequisites 5 Upgrading an X7.1 or later cluster
Management Access. Configure Management Remote Access. Configure ASA Access for ASDM, Telnet, or SSH
 This chapter describes how to access the Cisco ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, and how to create login banners. Configure
This chapter describes how to access the Cisco ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, and how to create login banners. Configure
High Availability Options
 , on page 1 Load Balancing, on page 2 Distributed VPN Clustering, Load balancing and Failover are high-availability features that function differently and have different requirements. In some circumstances
, on page 1 Load Balancing, on page 2 Distributed VPN Clustering, Load balancing and Failover are high-availability features that function differently and have different requirements. In some circumstances
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
 Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Identity Firewall. About the Identity Firewall
 This chapter describes how to configure the ASA for the. About the, on page 1 Guidelines for the, on page 7 Prerequisites for the, on page 9 Configure the, on page 10 Monitoring the, on page 16 History
This chapter describes how to configure the ASA for the. About the, on page 1 Guidelines for the, on page 7 Prerequisites for the, on page 9 Configure the, on page 10 Monitoring the, on page 16 History
ASACAMP - ASA Lab Camp (5316)
 ASACAMP - ASA Lab Camp (5316) Price: $4,595 Cisco Course v1.0 Cisco Security Appliance Software v8.0 Based on our enhanced FIREWALL and VPN courses, this exclusive, lab-based course is designed to provide
ASACAMP - ASA Lab Camp (5316) Price: $4,595 Cisco Course v1.0 Cisco Security Appliance Software v8.0 Based on our enhanced FIREWALL and VPN courses, this exclusive, lab-based course is designed to provide
CISCO EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CISCO 642-618 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 642-618 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 39.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 642-618 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: Deploying Cisco
CISCO 642-618 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 642-618 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 39.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 642-618 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: Deploying Cisco
New Features for ASA Version 9.0(2)
 FIREWALL Features New Features for ASA Version 9.0(2) Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) Software Release 9.0 is the latest release of the software that powers the Cisco ASA family. The same core
FIREWALL Features New Features for ASA Version 9.0(2) Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) Software Release 9.0 is the latest release of the software that powers the Cisco ASA family. The same core
Licenses: Smart Software Licensing (ASAv, ASA on Firepower)
 Licenses: Smart Software Licensing (ASAv, ASA on Firepower) Cisco Smart Software Licensing lets you purchase and manage a pool of licenses centrally. Unlike product authorization key (PAK) licenses, smart
Licenses: Smart Software Licensing (ASAv, ASA on Firepower) Cisco Smart Software Licensing lets you purchase and manage a pool of licenses centrally. Unlike product authorization key (PAK) licenses, smart
Logging. About Logging. This chapter describes how to log system messages and use them for troubleshooting.
 This chapter describes how to log system messages and use them for troubleshooting. About, page 1 Guidelines for, page 7 Configure, page 8 Monitoring the Logs, page 26 History for, page 29 About System
This chapter describes how to log system messages and use them for troubleshooting. About, page 1 Guidelines for, page 7 Configure, page 8 Monitoring the Logs, page 26 History for, page 29 About System
Managing CX Devices in Multiple Device Mode
 Tip Device inventory management applies to PRSM in Multiple Device mode only. If you are configuring a CX device through a direct connection to the device, you do not need to add the device to the inventory
Tip Device inventory management applies to PRSM in Multiple Device mode only. If you are configuring a CX device through a direct connection to the device, you do not need to add the device to the inventory
through ftp-map Commands
 CHAPTER 12 12-1 email Chapter 12 email To include the indicated email address in the Subject Alternative Name extension of the certificate during enrollment, use the email command in crypto ca trustpoint
CHAPTER 12 12-1 email Chapter 12 email To include the indicated email address in the Subject Alternative Name extension of the certificate during enrollment, use the email command in crypto ca trustpoint
User Identity Sources
 The following topics describe Firepower System user identity sources, which are sources for user awareness. These users can be controlled with identity and access control policies: About, on page 1 The
The following topics describe Firepower System user identity sources, which are sources for user awareness. These users can be controlled with identity and access control policies: About, on page 1 The
Software and Configurations
 This chapter describes how to manage the Cisco ASA software and configurations. Upgrade the Software, page 1 Use the ROMMON to Load an Image, page 1 Upgrade the ROMMON Image (ASA 5506-X, 5508-X, and 5516-X),
This chapter describes how to manage the Cisco ASA software and configurations. Upgrade the Software, page 1 Use the ROMMON to Load an Image, page 1 Upgrade the ROMMON Image (ASA 5506-X, 5508-X, and 5516-X),
Overview. ACE Appliance Device Manager Overview CHAPTER
 1 CHAPTER This section contains the following: ACE Appliance Device Manager, page 1-1 Logging Into ACE Appliance Device Manager, page 1-3 Changing Your Account Password, page 1-4 ACE Appliance Device Manager
1 CHAPTER This section contains the following: ACE Appliance Device Manager, page 1-1 Logging Into ACE Appliance Device Manager, page 1-3 Changing Your Account Password, page 1-4 ACE Appliance Device Manager
Chapter 4. Network Security. Part II
 Chapter 4 Network Security Part II CCNA4-1 Chapter 4-2 Introducing Network Security Securing Cisco Routers CCNA4-2 Chapter 4-2 Router Security Issues The Role of Routers in Network Security: Router security
Chapter 4 Network Security Part II CCNA4-1 Chapter 4-2 Introducing Network Security Securing Cisco Routers CCNA4-2 Chapter 4-2 Router Security Issues The Role of Routers in Network Security: Router security
Deploying Cisco ASA Firewall Features (FIREWALL) v1.0. Global Knowledge European Remote Labs Instructor Guide
 Deploying Cisco ASA Firewall Features (FIREWALL) v1.0 Global Knowledge European Remote Labs Instructor Guide Revision Draft 0.2 11/03/2011 1. Contents 1. Contents.2 2. Introduction.3 3. Remote Labs Topology,
Deploying Cisco ASA Firewall Features (FIREWALL) v1.0 Global Knowledge European Remote Labs Instructor Guide Revision Draft 0.2 11/03/2011 1. Contents 1. Contents.2 2. Introduction.3 3. Remote Labs Topology,
Maintenance Tasks. About A/B Partition CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 4 These topics describe the Chassis Manager maintenance tasks: About A/B Partition, page 4-1 Configuring Basic System Information, page 4-2 Configuring System Global Settings, page 4-4 Configuring
CHAPTER 4 These topics describe the Chassis Manager maintenance tasks: About A/B Partition, page 4-1 Configuring Basic System Information, page 4-2 Configuring System Global Settings, page 4-4 Configuring
Chapter 10 Lab B: Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDM
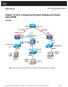 Chapter 10 Lab B: Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of Fast Ethernet interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992
Chapter 10 Lab B: Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of Fast Ethernet interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992
Multiple Context Mode
 This chapter describes how to configure multiple security contexts on the Cisco ASA. About Security Contexts, page 1 Licensing for, page 13 Prerequisites for, page 14 Guidelines for, page 14 Defaults for,
This chapter describes how to configure multiple security contexts on the Cisco ASA. About Security Contexts, page 1 Licensing for, page 13 Prerequisites for, page 14 Guidelines for, page 14 Defaults for,
Getting Started. About the ASA for Firepower How the ASA Works with the Firepower 2100
 This chapter describes how to deploy the ASA on the Firepower 2100 in your network, and how to perform initial configuration. About the ASA for Firepower 2100, page 1 Connect the Interfaces, page 4 Power
This chapter describes how to deploy the ASA on the Firepower 2100 in your network, and how to perform initial configuration. About the ASA for Firepower 2100, page 1 Connect the Interfaces, page 4 Power
Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2
 Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2 The Cisco Network Analysis Module (NAM) is an integrated module that enables network managers
Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2 The Cisco Network Analysis Module (NAM) is an integrated module that enables network managers
Cisco ASA 5500 LAB Guide
 INGRAM MICRO Cisco ASA 5500 LAB Guide Ingram Micro 4/1/2009 The following LAB Guide will provide you with the basic steps involved in performing some fundamental configurations on a Cisco ASA 5500 series
INGRAM MICRO Cisco ASA 5500 LAB Guide Ingram Micro 4/1/2009 The following LAB Guide will provide you with the basic steps involved in performing some fundamental configurations on a Cisco ASA 5500 series
Setting Up the Sensor
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter contains procedures for the setting up the sensor, such as changing sensor initialization information, adding and deleting users, configuring time and setting up NTP, creating a
CHAPTER 4 This chapter contains procedures for the setting up the sensor, such as changing sensor initialization information, adding and deleting users, configuring time and setting up NTP, creating a
Configuring Management Access
 37 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to access the ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, how to create login banners, and how
37 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to access the ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, how to create login banners, and how
Cisco - ASA Lab Camp v9.0
 Cisco - ASA Lab Camp v9.0 Code: 0007 Lengt h: 5 days URL: View Online Based on our enhanced SASAC v1.0 and SASAA v1.2 courses, this exclusive, lab-based course, provides you with your own set of equipment
Cisco - ASA Lab Camp v9.0 Code: 0007 Lengt h: 5 days URL: View Online Based on our enhanced SASAC v1.0 and SASAA v1.2 courses, this exclusive, lab-based course, provides you with your own set of equipment
Multiple Context Mode
 This chapter describes how to configure multiple security contexts on the Cisco ASA. About Security Contexts About Security Contexts, on page 1 Licensing for, on page 10 Prerequisites for, on page 12 Guidelines
This chapter describes how to configure multiple security contexts on the Cisco ASA. About Security Contexts About Security Contexts, on page 1 Licensing for, on page 10 Prerequisites for, on page 12 Guidelines
Access Rules. Controlling Network Access
 This chapter describes how to control network access through or to the ASA using access rules. You use access rules to control network access in both routed and transparent firewall modes. In transparent
This chapter describes how to control network access through or to the ASA using access rules. You use access rules to control network access in both routed and transparent firewall modes. In transparent
Management Access. Configure Management Remote Access. Configure SSH Access. Before You Begin
 This chapter describes how to access the Cisco ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, and how to create login banners. Configure
This chapter describes how to access the Cisco ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, and how to create login banners. Configure
User and System Administration
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter provides information about performing user and system administration tasks and generating diagnostic information for obtaining technical assistance. The top-level Admin window displays
CHAPTER 2 This chapter provides information about performing user and system administration tasks and generating diagnostic information for obtaining technical assistance. The top-level Admin window displays
Configuring DNS Sticky
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to configure a GSS to support Domain Name System (DNS) stickiness to answer requests received from client D-proxies. The GSS supports DNS sticky both locally and globally
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to configure a GSS to support Domain Name System (DNS) stickiness to answer requests received from client D-proxies. The GSS supports DNS sticky both locally and globally
Identity Firewall. About the Identity Firewall. This chapter describes how to configure the ASA for the Identity Firewall.
 This chapter describes how to configure the ASA for the. About the, page 1 Guidelines for the, page 7 Prerequisites for the, page 9 Configure the, page 10 Collect User Statistics, page 19 Examples for
This chapter describes how to configure the ASA for the. About the, page 1 Guidelines for the, page 7 Prerequisites for the, page 9 Configure the, page 10 Collect User Statistics, page 19 Examples for
Overview of the Cisco NCS Command-Line Interface
 CHAPTER 1 Overview of the Cisco NCS -Line Interface This chapter provides an overview of how to access the Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) command-line interface (CLI), the different command modes,
CHAPTER 1 Overview of the Cisco NCS -Line Interface This chapter provides an overview of how to access the Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) command-line interface (CLI), the different command modes,
Maintenance Tasks CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 5 These topics describe the Maintenance tasks of Element Manager: Viewing Basic System Information, page 5-2 Configuring Basic System Information, page 5-4 Configuring Date and Time Properties,
CHAPTER 5 These topics describe the Maintenance tasks of Element Manager: Viewing Basic System Information, page 5-2 Configuring Basic System Information, page 5-4 Configuring Date and Time Properties,
Getting Started. Getting Started with Your Platform Model. Factory Default Configurations CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface, configure the firewall mode, and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: with Your Platform
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface, configure the firewall mode, and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: with Your Platform
Management Access. Configure Management Remote Access. Configure SSH Access. Before You Begin
 This chapter describes how to access the Cisco ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, and how to create login banners. Configure
This chapter describes how to access the Cisco ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, and how to create login banners. Configure
DoS Attacks Malicious Code Attacks Device Hardening Social Engineering The Network Security Wheel
 CCNA4 Chapter 4 * DoS Attacks DoS attacks are the most publicized form of attack and also among the most difficult to eliminate. DoS attacks prevent authorized people from using a service by consuming
CCNA4 Chapter 4 * DoS Attacks DoS attacks are the most publicized form of attack and also among the most difficult to eliminate. DoS attacks prevent authorized people from using a service by consuming
Remote Access VPN. Remote Access VPN Overview. Licensing Requirements for Remote Access VPN
 Remote Access virtual private network (VPN) allows individual users to connect to your network from a remote location using a laptop or desktop computer connected to the Internet. This allows mobile workers
Remote Access virtual private network (VPN) allows individual users to connect to your network from a remote location using a laptop or desktop computer connected to the Internet. This allows mobile workers
Command-Line Interfaces
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the CLIs you use to configure the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Accessing the Switch CLI, page 2-1 Performing Command-Line
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the CLIs you use to configure the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Accessing the Switch CLI, page 2-1 Performing Command-Line
CISCO ASA FIREWALL FUNDAMENTALS 3 RD EDITION
 CISCO ASA FIREWALL FUNDAMENTALS 3 RD EDITION EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW TO CONFIGURE AND IMPLEMENT THE BEST FIREWALL IN THE MARKET WRITTEN BY: HARRIS ANDREA MSC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE
CISCO ASA FIREWALL FUNDAMENTALS 3 RD EDITION EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW TO CONFIGURE AND IMPLEMENT THE BEST FIREWALL IN THE MARKET WRITTEN BY: HARRIS ANDREA MSC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE
Maintenance Tasks CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 5 These topics describe the Maintenance tasks of Element Manager: Viewing Basic System Information, page 5-2 Configuring Basic System Information, page 5-3 Configuring Date and Time Properties,
CHAPTER 5 These topics describe the Maintenance tasks of Element Manager: Viewing Basic System Information, page 5-2 Configuring Basic System Information, page 5-3 Configuring Date and Time Properties,
Managing GSS Devices from the GUI
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure and manage your Global Site Selector Manager (GSSM) and Global Site Selector (GSS) devices from the primary GSSM graphical user interface. It includes
CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure and manage your Global Site Selector Manager (GSSM) and Global Site Selector (GSS) devices from the primary GSSM graphical user interface. It includes
Viewing System Status, page 404. Backing Up and Restoring a Configuration, page 416. Managing Certificates for Authentication, page 418
 This chapter describes how to maintain the configuration and firmware, reboot or reset the security appliance, manage the security license and digital certificates, and configure other features to help
This chapter describes how to maintain the configuration and firmware, reboot or reset the security appliance, manage the security license and digital certificates, and configure other features to help
Platform Settings for Classic Devices
 The following topics explain Firepower platform settings and how to configure them on Classic devices: Introduction to Firepower Platform Settings, page 1 Configuring Firepower Platform Settings, page
The following topics explain Firepower platform settings and how to configure them on Classic devices: Introduction to Firepower Platform Settings, page 1 Configuring Firepower Platform Settings, page
Failover for High Availability in the Public Cloud
 This chapter describes how to configure Active/Backup failover to accomplish high availability of the Cisco ASAv in a public cloud environment, such as Microsoft Azure. About Failover in the Public Cloud,
This chapter describes how to configure Active/Backup failover to accomplish high availability of the Cisco ASAv in a public cloud environment, such as Microsoft Azure. About Failover in the Public Cloud,
GRP Redundant Processor Support
 GRP Redundant Processor Support Feature Summary The GRP redundant processor feature allows you to install two gigabit route processors (GRPs) in a Cisco 12000 series router. One GRP functions as the primary
GRP Redundant Processor Support Feature Summary The GRP redundant processor feature allows you to install two gigabit route processors (GRPs) in a Cisco 12000 series router. One GRP functions as the primary
Device Management Basics
 The following topics describe how to manage devices in the Firepower System: The Device Management Page, on page 1 Remote Management Configuration, on page 2 Adding Devices to the Firepower Management
The following topics describe how to manage devices in the Firepower System: The Device Management Page, on page 1 Remote Management Configuration, on page 2 Adding Devices to the Firepower Management
Skills Assessment Student Training
 Skills Assessment Student Training Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (6 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (33 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure Switch
Skills Assessment Student Training Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (6 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (33 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure Switch
Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Initial Configuration for the Switch
 Options for Initial Configuration, page 1 Configuring the Switch Using the Web User Interface, page 1 Configuring the Switch Using the CLI, page 4 Configuring the Switch in the ROMMON Mode, page 12 Options
Options for Initial Configuration, page 1 Configuring the Switch Using the Web User Interface, page 1 Configuring the Switch Using the CLI, page 4 Configuring the Switch in the ROMMON Mode, page 12 Options
eigrp log-neighbor-warnings through functions Commands
 CHAPTER 12 eigrp log-neighbor-warnings through functions Commands 12-1 eigrp log-neighbor-changes Chapter 12 eigrp log-neighbor-changes To enable the logging of EIGRP neighbor adjacency changes, use the
CHAPTER 12 eigrp log-neighbor-warnings through functions Commands 12-1 eigrp log-neighbor-changes Chapter 12 eigrp log-neighbor-changes To enable the logging of EIGRP neighbor adjacency changes, use the
Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure switch-based authentication on the switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. This chapter consists
CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure switch-based authentication on the switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. This chapter consists
Cisco Expressway Cluster Creation and Maintenance
 Cisco Expressway Cluster Creation and Maintenance Deployment Guide First Published: December 2009 Last Updated: April 2017 Cisco Expressway X8.9.2 Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com Contents Preface 3 Change
Cisco Expressway Cluster Creation and Maintenance Deployment Guide First Published: December 2009 Last Updated: April 2017 Cisco Expressway X8.9.2 Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com Contents Preface 3 Change
Configuring Security with Passwords, Privileges, and Logins
 Configuring Security with Passwords, Privileges, and Logins Cisco IOS based networking devices provide several features that can be used to implement basic security for CLI sessions using only the operating
Configuring Security with Passwords, Privileges, and Logins Cisco IOS based networking devices provide several features that can be used to implement basic security for CLI sessions using only the operating
Configuring the Management Interface and Security
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Management Interface and Security Revised: February 15, 2011, Introduction This module describes how to configure the physical management interfaces (ports) as well as the various
CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Management Interface and Security Revised: February 15, 2011, Introduction This module describes how to configure the physical management interfaces (ports) as well as the various
Configuring Cisco Prime NAM
 Cisco SRE NAM has an internal Gigabit Ethernet interface and an external interface. You can use either interface for Prime NAM management traffic such as the NAM web GUI, telnet or ssh, but not both. You
Cisco SRE NAM has an internal Gigabit Ethernet interface and an external interface. You can use either interface for Prime NAM management traffic such as the NAM web GUI, telnet or ssh, but not both. You
Command-Line Interfaces
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the CLIs you use to configure the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Accessing the Switch CLI, page 2-2 Performing Command-Line
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the CLIs you use to configure the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Accessing the Switch CLI, page 2-2 Performing Command-Line
Firepower Threat Defense Cluster for the Firepower 4100/9300
 Firepower Threat Defense Cluster for the Firepower 4100/9300 Clustering lets you group multiple Firepower Threat Defense units together as a single logical device. Clustering is only supported for the
Firepower Threat Defense Cluster for the Firepower 4100/9300 Clustering lets you group multiple Firepower Threat Defense units together as a single logical device. Clustering is only supported for the
Using Cisco IOS XE Software
 This chapter describes the basics of using the Cisco IOS XE software and includes the following section: Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console, on page 1 Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console Before
This chapter describes the basics of using the Cisco IOS XE software and includes the following section: Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console, on page 1 Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console Before
Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server
 CHAPTER 4 Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server This chapter describes how to configure the GSS, primary GSSM, or standby GSSM as a client of a Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
CHAPTER 4 Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server This chapter describes how to configure the GSS, primary GSSM, or standby GSSM as a client of a Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
System Management Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9400 Switches)
 System Management Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9400 Switches) First Published: 2017-07-31 Last Modified: 2017-11-03 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman
System Management Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9400 Switches) First Published: 2017-07-31 Last Modified: 2017-11-03 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman
Configuring TACACS+ Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for TACACS+
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for TACACS+, page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure TACACS+, page 7 Monitoring TACACS+, page 16 Finding Feature Information Your software
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for TACACS+, page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure TACACS+, page 7 Monitoring TACACS+, page 16 Finding Feature Information Your software
Configuring Stateful Interchassis Redundancy
 The Stateful Interchassis Redundancy feature enables you to configure pairs of devices to act as backups for each other. This module describes conceptual information about and tasks for configuring stateful
The Stateful Interchassis Redundancy feature enables you to configure pairs of devices to act as backups for each other. This module describes conceptual information about and tasks for configuring stateful
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
Configuring Cisco TelePresence Manager
 CHAPTER 3 Revised: November 27, 2006, First Published: November 27, 2006 Contents Introduction, page 3-1 System Configuration Tasks, page 3-2 Security Settings, page 3-3 Database, page 3-4 Room Phone UI,
CHAPTER 3 Revised: November 27, 2006, First Published: November 27, 2006 Contents Introduction, page 3-1 System Configuration Tasks, page 3-2 Security Settings, page 3-3 Database, page 3-4 Room Phone UI,
Cluster creation and maintenance
 Cluster creation and maintenance Cisco TelePresence Deployment Guide Cisco VCS X6.1 Cisco TMS 12.6 or later D14367.08 May 2011 Contents Contents Document revision history... 5 Introduction... 6 Prerequisites...
Cluster creation and maintenance Cisco TelePresence Deployment Guide Cisco VCS X6.1 Cisco TMS 12.6 or later D14367.08 May 2011 Contents Contents Document revision history... 5 Introduction... 6 Prerequisites...
Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server
 4 CHAPTER Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server This chapter describes how to configure the GSS, primary GSSM, or standby GSSM as a client of a Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
4 CHAPTER Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server This chapter describes how to configure the GSS, primary GSSM, or standby GSSM as a client of a Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server The authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) feature verifies the identity of, grants access to, and tracks the actions of users
CHAPTER 3 Configuring Security Features on an External AAA Server The authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) feature verifies the identity of, grants access to, and tracks the actions of users
ASDM Graphical User Interface
 This chapter describes how to use the ASDM user interface. About the ASDM User Interface, page 2 Navigate the ASDM User Interface, page 4 Menus, page 5 Toolbar, page 10 ASDM Assistant, page 11 Status Bar,
This chapter describes how to use the ASDM user interface. About the ASDM User Interface, page 2 Navigate the ASDM User Interface, page 4 Menus, page 5 Toolbar, page 10 ASDM Assistant, page 11 Status Bar,
Failover for High Availability
 This chapter describes how to configure Active/Standby or Active/Active failover to accomplish high availability of the Cisco ASA. About Failover, page 1 Licensing for Failover, page 25 Guidelines for
This chapter describes how to configure Active/Standby or Active/Active failover to accomplish high availability of the Cisco ASA. About Failover, page 1 Licensing for Failover, page 25 Guidelines for
Setting General VPN Parameters
 CHAPTER 62 The adaptive security appliance implementation of virtual private networking includes useful features that do not fit neatly into categories. This chapter describes some of these features. It
CHAPTER 62 The adaptive security appliance implementation of virtual private networking includes useful features that do not fit neatly into categories. This chapter describes some of these features. It
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
WLM1200-RMTS User s Guide
 WLM1200-RMTS User s Guide Copyright 2011, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1 WLM1200-RMTS User Guide Contents WLM1200-RMTS Publication Suite........................................ 2 WLM1200-RMTS Hardware Description....................................
WLM1200-RMTS User s Guide Copyright 2011, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1 WLM1200-RMTS User Guide Contents WLM1200-RMTS Publication Suite........................................ 2 WLM1200-RMTS Hardware Description....................................
Failover for High Availability
 This chapter describes how to configure Active/Standby or Active/Active failover to accomplish high availability of the Cisco ASA. About Failover, on page 1 Licensing for Failover, on page 25 Guidelines
This chapter describes how to configure Active/Standby or Active/Active failover to accomplish high availability of the Cisco ASA. About Failover, on page 1 Licensing for Failover, on page 25 Guidelines
User and System Administration
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter provides information about performing user and system administration tasks in Cisco Prime Network Analysis Module 5.1and generating diagnostic information for obtaining technical
CHAPTER 5 This chapter provides information about performing user and system administration tasks in Cisco Prime Network Analysis Module 5.1and generating diagnostic information for obtaining technical
This study aid describes the purpose of security contexts and explains how to enable, configure, and manage multiple contexts.
 Configuring Security Contexts Created by Bob Eckhoff This study aid describes the purpose of security contexts and explains how to enable, configure, and manage multiple contexts. Security Context Overview
Configuring Security Contexts Created by Bob Eckhoff This study aid describes the purpose of security contexts and explains how to enable, configure, and manage multiple contexts. Security Context Overview
Configuring Web-Based Authentication
 This chapter describes how to configure web-based authentication on the switch. It contains these sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Web-Based Authentication Overview, page 1 How to Configure
This chapter describes how to configure web-based authentication on the switch. It contains these sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Web-Based Authentication Overview, page 1 How to Configure
Managing Switch Stacks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Switch Stacks, page 1 Restrictions for Switch Stacks, page 2 Information About Switch Stacks, page 2 How to Configure a Switch Stack, page 14 Troubleshooting
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Switch Stacks, page 1 Restrictions for Switch Stacks, page 2 Information About Switch Stacks, page 2 How to Configure a Switch Stack, page 14 Troubleshooting
Maintaining the MGX RPM-PR
 APPENDIX A This appendix describes maintenance procedures you might need to perform as your internetworking needs change. It contains the following sections: Reading Front Panel LEDs Recovering a Lost
APPENDIX A This appendix describes maintenance procedures you might need to perform as your internetworking needs change. It contains the following sections: Reading Front Panel LEDs Recovering a Lost
Configuring TACACS+ About TACACS+
 This chapter describes how to configure the Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: About TACACS+,
This chapter describes how to configure the Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: About TACACS+,
Release Notes for Cisco ASDM Version 5.2(5)
 May 2010 This document contains release information for Cisco ASDM Version 5.2(5) on the Cisco ASA 5500. It includes the following sections: New Features, page 1 System Requirements, page 1 Upgrading ASDM,
May 2010 This document contains release information for Cisco ASDM Version 5.2(5) on the Cisco ASA 5500. It includes the following sections: New Features, page 1 System Requirements, page 1 Upgrading ASDM,
Configuring Web-Based Authentication
 CHAPTER 61 This chapter describes how to configure web-based authentication. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH and later releases support web-based authentication. Note For complete syntax and usage information
CHAPTER 61 This chapter describes how to configure web-based authentication. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH and later releases support web-based authentication. Note For complete syntax and usage information
Realms and Identity Policies
 The following topics describe realms and identity policies: Introduction:, page 1 Creating a Realm, page 5 Creating an Identity Policy, page 11 Creating an Identity Rule, page 15 Managing Realms, page
The following topics describe realms and identity policies: Introduction:, page 1 Creating a Realm, page 5 Creating an Identity Policy, page 11 Creating an Identity Rule, page 15 Managing Realms, page
UniNets CCNA Security LAB MANUAL UNiNets CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate Security LAB MANUAL UniNets CCNA LAB MANUAL
 UNiNets CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate Security LAB MANUAL Contents: UniNets CCNA Security LAB MANUAL Section 1 Securing Layer 2 Lab 1-1 Configuring Native VLAN on a Trunk Links Lab 1-2 Disabling
UNiNets CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate Security LAB MANUAL Contents: UniNets CCNA Security LAB MANUAL Section 1 Securing Layer 2 Lab 1-1 Configuring Native VLAN on a Trunk Links Lab 1-2 Disabling
