Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN
|
|
|
- Nicholas Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN Cisco IOS software offers two solutions to send virtual asynchronous traffic over ISDN: Using International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) Recommendation V.120, which allows for reliable transport of synchronous, asynchronous, or bit transparent data over ISDN bearer channels. Using ITU-T Recommendation X.75, which allows a system with an ISDN terminal adapter supporting asynchronous traffic over Link Access Procedure, Balanced (LAPB) to call into a router and establish an asynchronous PPP session. This method of asynchronous traffic transmission is also called ISDN Link Access Procedure, Balanced-Terminal Adapter (LAPB-TA). A virtual asynchronous interface (also known as vty-async) is created on demand to support calls that enter the router through a nonphysical interface. For example, asynchronous character stream calls terminate or land on nonphysical interfaces. These types of calls include inbound Telnet, local-area transport (LAT), PPP over character-oriented protocols (such as V.120 or X.25), and LAPB-TA and packet assembler/disassembler (PAD) calls. Virtual asynchronous interfaces are not user configurable; rather, they are dynamically created and torn down on demand. A virtual asynchronous line is used to access a virtual asynchronous interface. Refer to the section Virtual Asynchronous Interfaces in the chapter Overview of Dial Interfaces, Controllers, and Lines in this publication for more overview information about virtual asynchronous interfaces. Refer to the section Enabling Asynchronous Functions on Virtual Terminal Lines in the chapter Configuring Protocol Translation and Virtual Asynchronous Devices in the Cisco IOS Terminal Services Configuration Guide, for additional virtual asynchronous interface configuration information. This chapter describes how to configure virtual asynchronous traffic over ISDN lines. It includes the following main sections: Recommendation V.120 Overview How to Configure V.120 Access Configuration Example for V.120 ISDN LAPB-TA Overview How to Configure ISDN LAPB-TA Configuration Example for ISDN LAPB-TA DC-197
2 Recommendation V.120 Overview Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN To identify the hardware platform or software image information associated with a feature, use the Feature Navigator on Cisco.com to search for information about the feature or refer to the software release notes for a specific release. For more information, see the Identifying Supported Platforms section in the Using Cisco IOS Software chapter. For a complete description of the commands in this chapter, refer to the Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Reference. To locate documentation of other commands that appear in this chapter, use the command reference master index or search online. Recommendation V.120 Overview The V-series recommendations are ITU-T standards dealing with data communications over telephone networks. V.120 allows for reliable transport of synchronous, asynchronous, or bit transparent data over ISDN bearer channels. Cisco provides three V.120 support features for terminal adapters that do not send the low-layer compatibility fields or bearer capability V.120 information: Answer all incoming calls as V.120 Static configuration used when all remote users have asynchronous terminals and need to connect with a vty on the router. Automatically detect V.120 encapsulation Encapsulation dynamically detected and set. Enable V.120 Support for Asynchronous Access over ISDN. For terminal adapters that send the low-layer compatibility or bearer capability V.120 information, mixed V.120 and ISDN calls are supported. No special configuration is required. How to Configure V.120 Access To configure V.120 access, perform the tasks in the following sections: Configuring Answering of All Incoming Calls as V.120 (Required) Configuring Automatic Detection of Encapsulation Type (Required) Enabling V.120 Support for Asynchronous Access over ISDN (Required) See the section Configuration Example for V.120 at the end of this chapter for an example of how to configure V.120 access. Configuring Answering of All Incoming Calls as V.120 This V.120 support feature allows users to connect using an asynchronous terminal over ISDN terminal adapters with V.120 support to a vty on the router, much like a direct asynchronous connection. Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 11.1, this feature supports incoming calls only. When all the remote users have asynchronous terminals and call in to a router through an ISDN terminal adapter that uses V.120 encapsulation but does not send the low-layer compatibility or bearer capability V.120 information, you can configure the interface to answer all calls as V.120. Such calls are connected with an available vty on the router. DC-198
3 Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN How to Configure V.120 Access To configure an ISDN BRI or PRI interface to answer all incoming calls as V.120, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode: Step 1 Step 2 Cisco 4000 series routers only Router(config)# interface bri number or Cisco 7200 series routers only Router(config)# interface bri slot/port Router(config)# interface serial e1 controller-number:15 or Configures the ISDN BRI interface and begins interface configuration mode. Configures the ISDN PRI D channel and begins interface configuration mode. Router(config)# interface serial t1 controller-number:23 Step 3 Router(config-if)# isdn all-incoming-calls-v120 Configures the interface to answer all calls as V.120. Configuring Automatic Detection of Encapsulation Type If an ISDN call does not identify the call type in the lower-layer compatibility fields and is using an encapsulation that is different from the one configured on the interface, the interface can change its encapsulation type dynamically. This feature enables interoperation with ISDN terminal adapters that use V.120 encapsulation but do not signal V.120 in the call setup message. An ISDN interface that by default answers a call as synchronous serial with PPP encapsulation can change its encapsulation and answer such calls. Automatic detection is attempted for the first 10 seconds after the link is established or the first 5 packets exchanged over the link, whichever is first. To enable automatic detection of V.120 encapsulation, use the following command in interface configuration mode: Router(config-if)# autodetect encapsulation v120 Enables automatic detection of encapsulation type on the specified interface. You can specify one or more encapsulations to detect. Cisco IOS software currently supports automatic detection of PPP and V.120 encapsulations. Enabling V.120 Support for Asynchronous Access over ISDN You can optionally configure a router to support asynchronous access over ISDN by globally enabling PPP on vty lines. Asynchronous access is then supported over ISDN from the ISDN terminal to the vty session on the router. DC-199
4 Configuration Example for V.120 Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN To enable asynchronous protocol features on vty lines, use the following command in global configuration mode: Router(config)# vty-async Configures all vty lines to support asynchronous protocol features. This task enables PPP on vty lines on a global basis on the router. If you prefer instead to configure PPP on a per-vty basis, use the translate command, which is described in the Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Reference. Configuration Example for V.120 The following example configures BRI 0 to call and receive calls from two sites, to use PPP encapsulation on outgoing calls, and to use Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) authentication on incoming calls. This example also enables BRI 0 to configure itself dynamically to answer calls that use V.120 but that do not signal V.120 in the call setup message. interface bri 0 encapsulation ppp autodetect encapsulation v120 no keepalive dialer map ip name EB1 234 dialer map ip name EB2 456 dialer-group 1 ppp authentication chap ISDN LAPB-TA Overview To carry asynchronous traffic over ISDN, your system must be able to convert that traffic and forward it over synchronous connections. This process can be implemented by the V.120 protocol, which carries asynchronous traffic over ISDN. However, several countries in Europe (Germany, Switzerland, and some Eastern European countries) use LAPB as the protocol to forward their asynchronous traffic over synchronous connections. Your system, therefore, must be able to recognize and accept calls from these asynchronous/synchronous conversion devices. LAPB-TA performs that function. (LAPB is sometimes referred to as X.75, because LAPB is the link layer specified in the ITU-T X.75 recommendation for carrying asynchronous traffic over ISDN.) LAPB-TA allows devices that use LAPB instead of the V.120 protocol to communicate with routers on the Cisco 3600 and 5300 series. LAPB supports both local CHAP authentication and external RADIUS authorization on the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server. Before configuring ISDN LAPB-TA in your network, observe these restrictions: LAPB-TA does not currently support the ability to set a maximum frame size per user. Outbound LAPB-TA calls are not supported. DC-200
5 Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN How to Configure ISDN LAPB-TA PPP over LAPB-TA (and V.120) connections impose a greater overhead on the router than synchronous PPP over ISDN. The number of simultaneous sessions can be limited by dedicating a pool of virtual terminals to these protocols and limiting the number of virtual terminals in the pool. Multilink PPP compression is not supported. How to Configure ISDN LAPB-TA ISDN LAPB-TA is supported on the Cisco 3600 and Cisco 5300 series routers that meet the following additional requirements: A virtual terminal must be configured for incoming LAPB-TA. If no appropriately configured virtual terminals are available, the incoming call will be cleared. ISDN, LAPB, and PPP must be running to configure LAPB-TA. The Cisco IOS software must include the vty-async global configuration command, which must be configured before you can run asynchronous PPP traffic over a LAPB-TA connection. If an interface is already configured for V.120, only the following two additional configuration commands are required on the interface because V.120 and LAPB-TA sessions are configured in a similar way: Use the autodetect encapsulation command to enable autodetection of LAPB-TA connections. Use the transport input command to list LAPB-TA as an acceptable transport on a specific router. Perform the following required task to configure LAPB-TA: To configure ISDN LAPB-TA, use the following commands beginning in global configuration command mode: (required). Procedures for verifying the configuration are found in the section Verifying ISDN LAPB-TA later in this chapter. The section Configuration Example for ISDN LAPB-TA at the end of this chapter provides configuration examples. To configure ISDN LAPB-TA, use the following commands beginning in global configuration command mode: Step 1 Router(config)# vty-async Creates a virtual asynchronous interface. Step 2 Router(config)# vty-async virtual-template 1 Applies virtual template to the virtual asynchronous interface. Step 3 Router(config)# interface virtual-template 1 Creates a virtual interface template and enters interface configuration mode. Step 4 Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered Ethernet0 Assigns an IP address to the virtual interface template. Step 5 Router(config-if)# encapsulation ppp Enables encapsulation on the virtual interface template. Step 6 Router(config-if)# no peer default ip address Disables an IP address from a pool to the device connecting to the virtual access interface Step 7 Router(config-if)# ppp authentication chap Enables the CHAP protocol for PPP authentication. Step 8 Router(config-if)# Exits to global configuration mode. DC-201
6 How to Configure ISDN LAPB-TA Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN Step 9 Router(config)# username user1 password home Specifies CHAP password to be used to authenticate calls from caller user1. Step 10 Router(config)# interface Serial0:236 Enters interface configuration mode for a D-channel serial interface. 1 Step 11 Router(config-if)# encapsulation ppp Configures PPP encapsulation as the default. Step 12 Router(config-if)# dialer-group 1 Specifies the dialer group belonging to the interface. Step 13 Router(config-if)# ppp authentication chap Enables the CHAP protocol for PPP authentication. Step 14 Router(config-if)# autodetect encapsulation lapb-ta Enables autodetect encapsulation for LAPB-TA protocols. Step 15 Router(config)# line vty 0 32 Configures a range of 32 vty lines starting with vty0. Step 16 Router(config-line)# transport input telnet lapb-ta Defines which protocol to use to connect to a specific line of the access server. 1. The D channel is the signaling channel. Verifying ISDN LAPB-TA Enter the show running configuration command to verify that LAPB-TA is configured. The following output shows LAPB-TA enabled for serial interface 0:23: Router# show running configuration Building configuration... Current configuration:! version 12.0 service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime service timestamps log datetime msec localtime no service password-encryption service udp-small-servers service tcp-small-servers! hostname Router...(output omitted) interface Serial0:23 description ENG PBX BRI num.:81063 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast encapsulation ppp no ip route-cache dialer pool-member 1 autodetect encapsulation ppp lapb-ta isdn switch-type primary-5ess no peer default ip address no fair-queue no cdp enable ppp authentication chap...(output omitted)! end DC-202
7 Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN Configuration Example for ISDN LAPB-TA Configuration Example for ISDN LAPB-TA The following example configures a virtual template LAPB-TA connection capable of running PPP. It assumes that you have already configured usernames and passwords for PPP authentication. vty-async vty-async virtual-template 1 interface virtual-template 1 ip unnumbered Ethernet0 encapsulation ppp no peer default ip address ppp authentication chap interface Serial0:23 autodetect encapsulation lapb-ta The following example treats the LAPB-TA and V.120 calls identically by immediately starting a PPP session without asking for username and password and relying on PPP authentication to identify the caller: vty-async vty-async virtual-template 1 interface Loopback0 ip address interface BRI3/0 encapsulation ppp autodetect encapsulation ppp lapb-ta v120 interface Virtual-Template1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 ppp authentication chap ip local pool default line vty 0 2 password <removed> login transport input telnet line vty 3 4 no login transport input lapb-ta v120 autocommand ppp neg end DC-203
8 Configuration Example for ISDN LAPB-TA Configuring Virtual Asynchronous Traffic over ISDN DC-204
Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP
 Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP Document ID: 6306 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information How V.120 Affects
Access Server Dial In IP/PPP Configuration With Dedicated V.120 PPP Document ID: 6306 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information How V.120 Affects
Configuring PPP Callback
 Configuring PPP Callback This chapter describes how to configure PPP callback for dial-on-demand routing (DDR). It includes the following main sections: PPP Callback for DDR Overview How to Configure PPP
Configuring PPP Callback This chapter describes how to configure PPP callback for dial-on-demand routing (DDR). It includes the following main sections: PPP Callback for DDR Overview How to Configure PPP
Configuring Legacy DDR Hubs
 Configuring Legacy DDR Hubs This chapter describes how to configure legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) on interfaces functioning as the hub in a hub-and-spoke network topology. It includes the following
Configuring Legacy DDR Hubs This chapter describes how to configure legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) on interfaces functioning as the hub in a hub-and-spoke network topology. It includes the following
Configuring BACP. Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Configuration Guide DC-667
 This chapter describes how to configure the Bandwidth Allocation Control Protocol (BACP), described in RFC 2125. It includes the following main sections: BACP Overview How to Configure BACP Monitoring
This chapter describes how to configure the Bandwidth Allocation Control Protocol (BACP), described in RFC 2125. It includes the following main sections: BACP Overview How to Configure BACP Monitoring
Configuring Link Fragmentation and Interleaving for Multilink PPP
 Configuring Link Fragmentation and Interleaving for Multilink PPP The Cisco IOS Link Fragmentation and Interleaving (LFI) feature uses Multilink PPP (MLP). MLP provides a method of splitting, recombining,
Configuring Link Fragmentation and Interleaving for Multilink PPP The Cisco IOS Link Fragmentation and Interleaving (LFI) feature uses Multilink PPP (MLP). MLP provides a method of splitting, recombining,
Configuring Modem Transport Support for VoIP
 Configuring Modem Transport Support for VoIP This chapter explains how to configure modem transport support for Voice over IP (VoIP) and contains the following sections: Modem Transport Support Overview,
Configuring Modem Transport Support for VoIP This chapter explains how to configure modem transport support for Voice over IP (VoIP) and contains the following sections: Modem Transport Support Overview,
Configuring X.25 on ISDN Using AO/DI
 Configuring X.25 on ISDN Using AO/DI The chapter describes how to configure the X.25 on ISDN using the Always On/Dynamic ISDN (AO/DI) feature. It includes the following main sections: AO/DI Overview How
Configuring X.25 on ISDN Using AO/DI The chapter describes how to configure the X.25 on ISDN using the Always On/Dynamic ISDN (AO/DI) feature. It includes the following main sections: AO/DI Overview How
This feature was introduced.
 Feature History Release 12.2(11)T Modification This feature was introduced. This document describes the QSIG for TCL IVR (Tool Language Interactive Voice Response) 2.0 feature in and includes the following
Feature History Release 12.2(11)T Modification This feature was introduced. This document describes the QSIG for TCL IVR (Tool Language Interactive Voice Response) 2.0 feature in and includes the following
Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts
 Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts Document ID: 23423 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Common Problems and Symptoms Idle Timeouts Interesting Traffic
Understanding and Troubleshooting Idle Timeouts Document ID: 23423 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Common Problems and Symptoms Idle Timeouts Interesting Traffic
Configuring Virtual Profiles
 Configuring Virtual Profiles This chapter describes how to configure virtual profiles for use with virtual access interfaces. It includes the following main sections: Virtual Profiles Overview How Virtual
Configuring Virtual Profiles This chapter describes how to configure virtual profiles for use with virtual access interfaces. It includes the following main sections: Virtual Profiles Overview How Virtual
L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients
 L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients The L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients feature allows mulitple Windows client to connect to an IPsec-enabled Cisco IOS Layer 2 Tunneling
L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients The L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients feature allows mulitple Windows client to connect to an IPsec-enabled Cisco IOS Layer 2 Tunneling
Terminal Services Commands translate lat
 translate lat translate lat To translate a connection request to another protocol connection type when receiving a local-area transport (LAT) request, use the translate lat command in global configuration
translate lat translate lat To translate a connection request to another protocol connection type when receiving a local-area transport (LAT) request, use the translate lat command in global configuration
PPP over Frame Relay
 The feature allows a router to establish end-to-end Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) sessions over Frame Relay. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information
The feature allows a router to establish end-to-end Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) sessions over Frame Relay. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information
Configuring Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over IPSec
 Configuring Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over IPSec Document ID: 14122 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuring Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over IPSec Document ID: 14122 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Completing an ISDN BRI Call. 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 13-1
 Completing an ISDN BRI Call 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 13-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks:? Describe the components that make up ISDN connectivity?
Completing an ISDN BRI Call 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 13-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks:? Describe the components that make up ISDN connectivity?
Tactical Software requires that Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(9) or later be installed on the NAS to interoperate with DialOut/EZ.
 Products & Services Using Dialout/EZ with a Cisco Access Server Document ID: 23241 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Installation and Configuration Installing
Products & Services Using Dialout/EZ with a Cisco Access Server Document ID: 23241 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Installation and Configuration Installing
Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites
 Case Study 1 Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: Asynchronous
Case Study 1 Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: Asynchronous
Configuring a Cisco 827 Router Using PPPoA With CHAP and PAP
 Configuring a Cisco 827 Router Using PPPoA With CHAP and PAP Document ID: 12886 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Configure Network Diagram PPPoA Using CHAP
Configuring a Cisco 827 Router Using PPPoA With CHAP and PAP Document ID: 12886 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Configure Network Diagram PPPoA Using CHAP
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (A)
 CCNA 4 - Final Exam (A) 1. A network administrator is asked to design a system to allow simultaneous access to the Internet for 250 users. The ISP for this network can only supply five public IPs. What
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (A) 1. A network administrator is asked to design a system to allow simultaneous access to the Internet for 250 users. The ISP for this network can only supply five public IPs. What
Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy
 Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature. It includes information on the benefits of the feature, supported platforms, configuration
Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature. It includes information on the benefits of the feature, supported platforms, configuration
Configuring a Cisco 827 Router to Support PPPoE Clients, Terminating on a Cisco 6400 UAC
 Configuring a Cisco 827 Router to Support PPPoE Clients, Terminating on a Cisco 6400 UAC Document ID: 12889 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Configure Network
Configuring a Cisco 827 Router to Support PPPoE Clients, Terminating on a Cisco 6400 UAC Document ID: 12889 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Configure Network
Configuring Client-Initiated Dial-In VPDN Tunneling
 Configuring Client-Initiated Dial-In VPDN Tunneling Client-initiated dial-in virtual private dialup networking (VPDN) tunneling deployments allow remote users to access a private network over a shared
Configuring Client-Initiated Dial-In VPDN Tunneling Client-initiated dial-in virtual private dialup networking (VPDN) tunneling deployments allow remote users to access a private network over a shared
Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6
 Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6 Last Updated: July 31, 2012 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6, page 1 Information
Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6 Last Updated: July 31, 2012 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for Implementing ADSL and Deploying Dial Access for IPv6, page 1 Information
How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode
 How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode MB5000 has a configurable serial port. With this serial port, MB5000 can be used as DCE device to be connected with Cisco router s console port so that MB5000
How to configure MB5000 Serial Port Bridge mode MB5000 has a configurable serial port. With this serial port, MB5000 can be used as DCE device to be connected with Cisco router s console port so that MB5000
Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists)
 Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists) Feature History Release Modification Cisco IOS For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This chapter
Configuring Lock-and-Key Security (Dynamic Access Lists) Feature History Release Modification Cisco IOS For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This chapter
Configuring Asynchronous Serial Traffic over UDP
 Configuring Asynchronous Serial Traffic over UDP This chapter describes how to communicate with a modem using the Asynchronous Serial Traffic over UDP feature in the following main sections: UDPTN Overview
Configuring Asynchronous Serial Traffic over UDP This chapter describes how to communicate with a modem using the Asynchronous Serial Traffic over UDP feature in the following main sections: UDPTN Overview
Configuring Authentication Proxy
 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against industry standard TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication protocols.
The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against industry standard TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication protocols.
Configuring a Terminal/Comm Server
 Configuring a Terminal/Comm Server Document ID: 5466 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Cabling Design Strategy Configure Network Diagram Configurations Command Summary
Configuring a Terminal/Comm Server Document ID: 5466 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Cabling Design Strategy Configure Network Diagram Configurations Command Summary
Configuration du laboratoire par accès téléphonique (San Jose, États-Unis)
 Configuration du laboratoire par accès téléphonique (San Jose, États-Unis) Contenu Introduction Conditions préalables Conditions requises Composants utilisés Conventions Configuration Informations connexes
Configuration du laboratoire par accès téléphonique (San Jose, États-Unis) Contenu Introduction Conditions préalables Conditions requises Composants utilisés Conventions Configuration Informations connexes
Configuring Virtual Template Interfaces
 Configuring Virtual Template Interfaces Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 11.2, virtual template interfaces can be configured independently of any physical interface and applied dynamically, as needed,
Configuring Virtual Template Interfaces Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 11.2, virtual template interfaces can be configured independently of any physical interface and applied dynamically, as needed,
Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles
 Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles Document ID: 10219 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Are Dialer Profiles Right for You?
Configuring and Troubleshooting Dialer Profiles Document ID: 10219 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Are Dialer Profiles Right for You?
Configuración del laboratorio de acceso telefónico de clientes (San José, Estados Unidos)
 Configuración del laboratorio de acceso telefónico de clientes (San José, Estados Unidos) Contenido Introducción prerrequisitos Requisitos Componentes Utilizados Convenciones Configuración Información
Configuración del laboratorio de acceso telefónico de clientes (San José, Estados Unidos) Contenido Introducción prerrequisitos Requisitos Componentes Utilizados Convenciones Configuración Información
PPP/MLP MRRU Negotiation Configuration
 PPP/MLP MRRU Negotiation Configuration The PPP/MLP MRRU Negotiation Configuration feature allows a router to send and receive frames over Multilink PPP (MLP) bundles that are larger than the default Maximum
PPP/MLP MRRU Negotiation Configuration The PPP/MLP MRRU Negotiation Configuration feature allows a router to send and receive frames over Multilink PPP (MLP) bundles that are larger than the default Maximum
Configuring Authorization
 Configuring Authorization AAA authorization enables you to limit the services available to a user. When AAA authorization is enabled, the network access server uses information retrieved from the user
Configuring Authorization AAA authorization enables you to limit the services available to a user. When AAA authorization is enabled, the network access server uses information retrieved from the user
Autosense for ATM PVCs and MUX SNAP Encapsulation
 Autosense for ATM PVCs and MUX SNAP Encapsulation The PPPoA/PPPoE Autosense for ATM PVCs feature enables a router to distinguish between incoming PPP over ATM (PPPoA) and PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) over
Autosense for ATM PVCs and MUX SNAP Encapsulation The PPPoA/PPPoE Autosense for ATM PVCs feature enables a router to distinguish between incoming PPP over ATM (PPPoA) and PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) over
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
 Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) www.ine.com PPP» Point-to-Point Protocol» Open standard» Operates in the LLC sub-layer of data link layer in OSI» Originally designed for dial-up connections (modems, ISDN,
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) www.ine.com PPP» Point-to-Point Protocol» Open standard» Operates in the LLC sub-layer of data link layer in OSI» Originally designed for dial-up connections (modems, ISDN,
Configuração do laboratório de discagem de entrada de cliente (SÃO JOSÉ, USA)
 Configuração do laboratório de discagem de entrada de cliente (SÃO JOSÉ, USA) Índice Introdução Pré-requisitos Requisitos Componentes Utilizados Convenções Configuração Informações Relacionadas Introdução
Configuração do laboratório de discagem de entrada de cliente (SÃO JOSÉ, USA) Índice Introdução Pré-requisitos Requisitos Componentes Utilizados Convenções Configuração Informações Relacionadas Introdução
ppp accounting through quit
 ppp accounting through quit ppp accounting, page 3 ppp authentication, page 5 ppp authentication ms-chap-v2, page 9 ppp authorization, page 11 ppp chap hostname, page 13 ppp chap password, page 15 ppp
ppp accounting through quit ppp accounting, page 3 ppp authentication, page 5 ppp authentication ms-chap-v2, page 9 ppp authorization, page 11 ppp chap hostname, page 13 ppp chap password, page 15 ppp
WCCPv2 and WCCP Enhancements
 WCCPv2 and WCCP Enhancements Release 12.0(11)S June 20, 2000 This feature module describes the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) Enhancements feature and includes information on the benefits of the
WCCPv2 and WCCP Enhancements Release 12.0(11)S June 20, 2000 This feature module describes the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) Enhancements feature and includes information on the benefits of the
Symbols INDEX. <cr> baud rates? command xiv. transmit line speed, configuring. buffers. XRemote size TR-224 busy-message command
 INDEX Symbols B xv baud rates? command xiv transmit line speed, configuring TR-208 buffers A XRemote size TR-224 busy-message command TR-17 absolute-timeout command TR-2 access-class (LAT) command
INDEX Symbols B xv baud rates? command xiv transmit line speed, configuring TR-208 buffers A XRemote size TR-224 busy-message command TR-17 absolute-timeout command TR-2 access-class (LAT) command
Cisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide Cisco DSL Router Acting as a PPPoE Client with a Dynamic IP Address
 Cisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide Cisco DSL Router Acting as a PPPoE Client with a Dynamic IP Address Document ID: 71118 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Cisco DSL Router Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide Cisco DSL Router Acting as a PPPoE Client with a Dynamic IP Address Document ID: 71118 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Overview encapsulation hdlc show interface show controllers show interface debug PPP
 PPP CCNA 4 Overview Explain serial communication Describe and give an example of TDM Identify the demarcation point in a WAN Describe the functions of the DTE and DCE Discuss the development of HDLC encapsulation
PPP CCNA 4 Overview Explain serial communication Describe and give an example of TDM Identify the demarcation point in a WAN Describe the functions of the DTE and DCE Discuss the development of HDLC encapsulation
Introducing ISDN ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) User-Network Interface (UNI),
 ISDN and DDR CCNA 4 Note to instructors If you have downloaded this presentation from the Cisco Networking Academy Community FTP Center, this may not be my latest version of this PowerPoint. For the latest
ISDN and DDR CCNA 4 Note to instructors If you have downloaded this presentation from the Cisco Networking Academy Community FTP Center, this may not be my latest version of this PowerPoint. For the latest
1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms
 1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms Feature History Release 12.2(2)XB Description This feature was introduced. The 1- and 2-port V.90 modem WAN interface
1- and 2-Port V.90 Modem WICs for Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 Series Multiservice Platforms Feature History Release 12.2(2)XB Description This feature was introduced. The 1- and 2-port V.90 modem WAN interface
Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing This chapter describes how to configure your communication server for dial-on-demand routing (DDR) and dial backup. For a complete description of the
C H A P T E R 7 Configuring Dial-on-Demand Routing This chapter describes how to configure your communication server for dial-on-demand routing (DDR) and dial backup. For a complete description of the
Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces
 Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces This chapter describes how to implement the Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1/E1 Interfaces with the AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 Module feature. This card provides
Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces This chapter describes how to implement the Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1/E1 Interfaces with the AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 Module feature. This card provides
pri-group timeslots pri-group timeslots range nfas_d [primary backup none] nfas_int number nfas_group group-id-number pri-group timeslots range
![pri-group timeslots pri-group timeslots range nfas_d [primary backup none] nfas_int number nfas_group group-id-number pri-group timeslots range pri-group timeslots pri-group timeslots range nfas_d [primary backup none] nfas_int number nfas_group group-id-number pri-group timeslots range](/thumbs/75/72118184.jpg) pri-group timeslots pri-group timeslots To configure Non-Facility Associated Signaling (NFAS) and specify the channels to be controlled by the primary NFAS D channel, use the pri-group timeslots command
pri-group timeslots pri-group timeslots To configure Non-Facility Associated Signaling (NFAS) and specify the channels to be controlled by the primary NFAS D channel, use the pri-group timeslots command
Number of seconds that elapse after the primary line goes down before the router activates the secondary line. The default is 0 seconds.
 This chapter describes the function and displays the syntax of each dialon-demand routing command. For more information about defaults and usage guidelines, see the corresponding chapter of the Router
This chapter describes the function and displays the syntax of each dialon-demand routing command. For more information about defaults and usage guidelines, see the corresponding chapter of the Router
QoS: Classification, Policing, and Marking on LAC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 12.4T
 QoS: Classification, Policing, and Marking on LAC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 12.4T Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com
QoS: Classification, Policing, and Marking on LAC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 12.4T Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com
Interworking Signaling Enhancements for H.323 and SIP VoIP
 Interworking Signaling Enhancements for H.323 and SIP VoIP This feature module describes enhancements to H.323 and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) signaling when interworking with ISDN, T1 channel associated
Interworking Signaling Enhancements for H.323 and SIP VoIP This feature module describes enhancements to H.323 and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) signaling when interworking with ISDN, T1 channel associated
Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings
 APPENDIX A Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings The following is a sample configuration of a Business Ready Branch. There are many permutations of feature combinations when setting up the
APPENDIX A Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings The following is a sample configuration of a Business Ready Branch. There are many permutations of feature combinations when setting up the
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B)
 CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B) 1. Identify the factors that contribute to congestion on an Ethernet LAN. (Choose three.) improper placement of enterprise level servers addition of hosts to a physical segment
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B) 1. Identify the factors that contribute to congestion on an Ethernet LAN. (Choose three.) improper placement of enterprise level servers addition of hosts to a physical segment
Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall
 Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall Document ID: 43068 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall Document ID: 43068 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Configuring RADIUS. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for RADIUS
 The RADIUS security system is a distributed client/server system that secures networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation, RADIUS clients run on Cisco devices and send authentication
The RADIUS security system is a distributed client/server system that secures networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation, RADIUS clients run on Cisco devices and send authentication
Chapter 12. AAA. Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks:
 Chapter 12. AAA 15-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Describe CiscoSecure features and operations Configure a router with AAA commands Use a
Chapter 12. AAA 15-1 Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to perform the following tasks: Describe CiscoSecure features and operations Configure a router with AAA commands Use a
ROUTER COMMANDS. BANNER: Config# banner motd # TYPE MESSAGE HERE # - # can be substituted for any character, must start and finish the message
 ROUTER COMMANDS TERMINAL CONTROLS: Config# terminal editing - allows for enhanced editing commands Config# terminal monitor - shows output on telnet session Config# terminal ip netmask-format hexadecimal
ROUTER COMMANDS TERMINAL CONTROLS: Config# terminal editing - allows for enhanced editing commands Config# terminal monitor - shows output on telnet session Config# terminal ip netmask-format hexadecimal
Configure Allied Telesyn and Cisco routers to interoperate over L2TP
 How To Configure Allied Telesyn and Cisco routers to interoperate over L2TP Introduction This document covers a range of examples on how to configure Allied Telesyn and Cisco routers to interoperate over
How To Configure Allied Telesyn and Cisco routers to interoperate over L2TP Introduction This document covers a range of examples on how to configure Allied Telesyn and Cisco routers to interoperate over
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 350-025 Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 350-025
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 350-025 Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 350-025
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Configuring PPP over ATM with NAT
 CHAPTER 4 The Cisco Secure Router 520 ADSL-over-POTS and Cisco Secure Router 520 ADSL-over-ISDN routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (PPPoA) clients and network address
CHAPTER 4 The Cisco Secure Router 520 ADSL-over-POTS and Cisco Secure Router 520 ADSL-over-ISDN routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (PPPoA) clients and network address
IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling
 IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker duplicating encrypted packets by assigning a unique sequence
IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker duplicating encrypted packets by assigning a unique sequence
Configuring Secure Shell
 Configuring Secure Shell Last Updated: October 24, 2011 The Secure Shell (SSH) feature is an application and a protocol that provides a secure replacement to the Berkeley r-tools. The protocol secures
Configuring Secure Shell Last Updated: October 24, 2011 The Secure Shell (SSH) feature is an application and a protocol that provides a secure replacement to the Berkeley r-tools. The protocol secures
The MSCHAP Version 2 feature (introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XB5) allows Cisco routers to
 The feature (introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XB5) allows Cisco routers to utilize Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol Version 2 (MSCHAP V2) authentication for PPP connections between
The feature (introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(2)XB5) allows Cisco routers to utilize Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol Version 2 (MSCHAP V2) authentication for PPP connections between
ISDN Authentication and Callback with Caller ID
 ISDN Authentication and Callback with Caller ID Document ID: 15925 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations
ISDN Authentication and Callback with Caller ID Document ID: 15925 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations
RADIUS Tunnel Attribute Extensions
 The feature allows a name to be specified (other than the default) for the tunnel initiator and the tunnel terminator in order to establish a higher level of security when setting up VPN tunneling. Finding
The feature allows a name to be specified (other than the default) for the tunnel initiator and the tunnel terminator in order to establish a higher level of security when setting up VPN tunneling. Finding
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
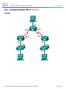 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
RADIUS Logical Line ID
 The feature, also known as the Logical Line Identification (LLID) Blocking feature enables administrators to track their customers on the basis of the physical lines on which customer calls originate.
The feature, also known as the Logical Line Identification (LLID) Blocking feature enables administrators to track their customers on the basis of the physical lines on which customer calls originate.
Configuring Security on the GGSN
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure security features on the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN), including Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA), and RADIUS. IPSec on the Cisco
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure security features on the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN), including Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA), and RADIUS. IPSec on the Cisco
Cisco CP Express Wizard
 CHAPTER1 These help topics introduce Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) wizard, describe the configurations you can perform with it, and explain the information required in each
CHAPTER1 These help topics introduce Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) wizard, describe the configurations you can perform with it, and explain the information required in each
IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling
 IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling First Published: February 28, 2005 Last Updated: March 24, 2011 Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker
IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling First Published: February 28, 2005 Last Updated: March 24, 2011 Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Enchilada Solutions
 Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Universal Port Resource Pooling for Voice and Data Services
 Universal Port Resource Pooling for Voice and Data Services Feature History Release 12.2(2)XA 12.2(2)XB1 12.2(11)T Description This feature was introduced on the Cisco AS5350 and AS5400. This feature was
Universal Port Resource Pooling for Voice and Data Services Feature History Release 12.2(2)XA 12.2(2)XB1 12.2(11)T Description This feature was introduced on the Cisco AS5350 and AS5400. This feature was
Configuring TCP Header Compression
 Configuring TCP Header Compression First Published: January 30, 2006 Last Updated: May 5, 2010 Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted.
Configuring TCP Header Compression First Published: January 30, 2006 Last Updated: May 5, 2010 Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted.
Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server
 Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server Document ID: 10384 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Network Diagram General AAA Configuration Enabling AAA Specifying
Configuring Basic AAA on an Access Server Document ID: 10384 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Network Diagram General AAA Configuration Enabling AAA Specifying
Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels
 Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configuration Problem Configuration Solution and
Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configuration Problem Configuration Solution and
Configuration Examples
 APPENDIX A This appendix shows some examples of the configuration in the Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, and Cisco 3700 series routers Cisco 2600 Series Router Configuration Example Following is
APPENDIX A This appendix shows some examples of the configuration in the Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, and Cisco 3700 series routers Cisco 2600 Series Router Configuration Example Following is
virtual-template virtual-template template-number no virtual-template Syntax Description
 VPDN Commands virtual-template virtual-template To specify which virtual template will be used to clone virtual access interfaces (VAI), use the virtual-template command in BBA group configuration mode
VPDN Commands virtual-template virtual-template To specify which virtual template will be used to clone virtual access interfaces (VAI), use the virtual-template command in BBA group configuration mode
Configuring Authentication Proxy
 Configuring Authentication Proxy Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against
Configuring Authentication Proxy Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against
Configuring RTP Header Compression
 Configuring RTP Header Compression First Published: January 30, 2006 Last Updated: July 23, 2010 Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted.
Configuring RTP Header Compression First Published: January 30, 2006 Last Updated: July 23, 2010 Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted.
SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands
 CHAPTER 15 SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands SLIP and PPP define methods of sending Internet Protocol (IP) packets over standard EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous serial lines with minimum line speeds of 1200
CHAPTER 15 SLIP and PPP Configuration Commands SLIP and PPP define methods of sending Internet Protocol (IP) packets over standard EIA/TIA-232 asynchronous serial lines with minimum line speeds of 1200
aaa max-sessions maximum-number-of-sessions The default value for aaa max-sessions command is platform dependent. Release 15.0(1)M.
 aaa max-sessions aaa max-sessions To set the maximum number of simultaneous authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) connections permitted for a user, use the aaa max-sessions command in global
aaa max-sessions aaa max-sessions To set the maximum number of simultaneous authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) connections permitted for a user, use the aaa max-sessions command in global
SSG Configuration Example
 APPENDIX A Example A-1 is a sample SSG configuration for the Cisco 10000 series router based on the topology in Figure A-1. The configuration includes AAA, PPP, SSG, and RADIUS. The SSG configuration enables
APPENDIX A Example A-1 is a sample SSG configuration for the Cisco 10000 series router based on the topology in Figure A-1. The configuration includes AAA, PPP, SSG, and RADIUS. The SSG configuration enables
DDR Routing Commands
 DDR Routing Commands This section describes the function and displays the syntax of each dial-on-demand routing (DDR) command. For more information about defaults and usage guidelines, see the corresponding
DDR Routing Commands This section describes the function and displays the syntax of each dial-on-demand routing (DDR) command. For more information about defaults and usage guidelines, see the corresponding
Passwords and Privileges Commands
 Passwords and Privileges Commands This chapter describes the commands used to establish password protection and configure privilege levels. Password protection lets you restrict access to a network or
Passwords and Privileges Commands This chapter describes the commands used to establish password protection and configure privilege levels. Password protection lets you restrict access to a network or
Configuring RTP Header Compression
 Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted. Header compression reduces network overhead and speeds up the transmission of either Real-Time
Header compression is a mechanism that compresses the IP header in a packet before the packet is transmitted. Header compression reduces network overhead and speeds up the transmission of either Real-Time
Home Agent Redundancy
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter discusses several concepts related to, how Home Agent redundancy works, and how to configure redundancy on the Cisco Mobile Wireless Home Agent. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 5 This chapter discusses several concepts related to, how Home Agent redundancy works, and how to configure redundancy on the Cisco Mobile Wireless Home Agent. This chapter includes the following
Exam : Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial. Version : DEMO
 Exam : 350-025 Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial Version : DEMO 1. What command is used to set the length of time a non-isdn interface stays down after a call has been completed or has failed and before
Exam : 350-025 Title : CCIE Service Provider Dial Version : DEMO 1. What command is used to set the length of time a non-isdn interface stays down after a call has been completed or has failed and before
PPPoE Session Limit per NAS Port
 PPPoE Session Limit per NAS Port First Published: March 17, 2003 Last Updated: February 28, 2006 The PPPoE Session Limit per NAS Port feature enables you to limit the number of PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
PPPoE Session Limit per NAS Port First Published: March 17, 2003 Last Updated: February 28, 2006 The PPPoE Session Limit per NAS Port feature enables you to limit the number of PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Configuring Authentication Proxy
 Configuring Authentication Proxy Last Updated: January 7, 2013 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against
Configuring Authentication Proxy Last Updated: January 7, 2013 The Cisco IOS Firewall Authentication Proxy feature provides dynamic, per-user authentication and authorization, authenticating users against
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Solution)
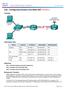 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
Configuring Dial-In Terminal Services
 Configuring Dial-In Terminal Services This chapter describes how to configure support for asynchronous character stream calls running Telnet, rlogin, local-area transport (LAT), XRemote, or TN3270. It
Configuring Dial-In Terminal Services This chapter describes how to configure support for asynchronous character stream calls running Telnet, rlogin, local-area transport (LAT), XRemote, or TN3270. It
PPPoE Client DDR Idle-Timer
 The feature supports the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) interesting traffic control list functionality of the dialer interface with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client, but also keeps original functionality
The feature supports the dial-on-demand routing (DDR) interesting traffic control list functionality of the dialer interface with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client, but also keeps original functionality
Voice over IP Q.SIG Network Transparency
 Voice over IP Q.SIG Network Transparency Feature History Release 12.0(7)T 12.1(5)XM2 Modification This feature was introduced Support was added for the Cisco AS5350 and Cisco AS5400 universal gateways.
Voice over IP Q.SIG Network Transparency Feature History Release 12.0(7)T 12.1(5)XM2 Modification This feature was introduced Support was added for the Cisco AS5350 and Cisco AS5400 universal gateways.
Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme. Topology. Objectives. Background / Scenario
 CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
Remote Access MPLS-VPNs
 First Published: August 12, 2002 Last Updated: May 4, 2009 The feature allows the service provider to offer a scalable end-to-end Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to remote users. This feature integrates
First Published: August 12, 2002 Last Updated: May 4, 2009 The feature allows the service provider to offer a scalable end-to-end Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to remote users. This feature integrates
Configuring RADIUS. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for RADIUS. Last Updated: November 2, 2012
 Configuring RADIUS Last Updated: November 2, 2012 The RADIUS security system is a distributed client/server system that secures networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation, RADIUS
Configuring RADIUS Last Updated: November 2, 2012 The RADIUS security system is a distributed client/server system that secures networks against unauthorized access. In the Cisco implementation, RADIUS
Configuring PPP over Ethernet with NAT
 CHAPTER 3 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Ethernet-to-Ethernet routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT). Multiple PCs can be connected to
CHAPTER 3 The Cisco Secure Router 520 Ethernet-to-Ethernet routers support Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) clients and network address translation (NAT). Multiple PCs can be connected to
Configuring Authorization
 The AAA authorization feature is used to determine what a user can and cannot do. When AAA authorization is enabled, the network access server uses information retrieved from the user s profile, which
The AAA authorization feature is used to determine what a user can and cannot do. When AAA authorization is enabled, the network access server uses information retrieved from the user s profile, which
Autosense of MUX/SNAP Encapsulation and PPPoA/PPPoE on ATM PVCs
 Autosense of MUX/SNAP Encapsulation and PPPoA/PPPoE on ATM PVCs Feature History for Autosense of MUX/SNAP Encapsulation and PPPoA/PPPoE on ATM PVCs Release Modification 12.2(15)B This feature was introduced.
Autosense of MUX/SNAP Encapsulation and PPPoA/PPPoE on ATM PVCs Feature History for Autosense of MUX/SNAP Encapsulation and PPPoA/PPPoE on ATM PVCs Release Modification 12.2(15)B This feature was introduced.
Cisco - Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable
 1 of 5 6/12/2001 1:43 PM Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable Contents Introduction Conventions Network Diagram Configurations Troubleshooting the Configuration
1 of 5 6/12/2001 1:43 PM Connecting Routers Back-to-Back Through the AUX Ports using a Rollover Cable Contents Introduction Conventions Network Diagram Configurations Troubleshooting the Configuration
