Using Classes and Objects
|
|
|
- Sharon Snow
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using Classes and Objects CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website:
2 Today Creating Objects The String Class The Random and Math Classes The Java API class library
3 Declaring Variables, revisited Examples of variable declarations: int count = 0; double mpg; String title; Graphics page; Color aquamarine; Scanner scan; A class name can be used as a type to declare an object reference variable The object itself must be created separately
4 Creating Objects We have already seen something like this: Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in); This calls the Scanner constructor, which is a special method that sets up the object Variable refers to a Scanner object
5 Creating Objects Generally, we use the new operator to create an object Creating an object is called instantiation An object is an instance of a particular class title = new String ("Java Software Solutions"); This calls the String constructor, which is a special method that sets up the object
6 The String Class is SPECIAL! Because strings are so common, we don't have to use the new operator to create a String object title = "Java Software Solutions" This is special syntax that works only for strings Each string literal (enclosed in double quotes) represents a String object
7 Invoking Methods We've seen that once an object has been instantiated, we can use the dot operator to invoke its methods ans = scan.nextline(); numchars = title.length(); Jargon alert: A method invocation can be thought of as asking an object to perform a service
8 Chapter 3: Using Classes and Objects We can create more interesting programs using predefined classes and related objects Chapter 3 focuses on: object creation and object references the String class and its methods the Java API class library the Random and Math classes formatting output enumerated types wrapper classes graphical components and containers labels and images
9 Next Creating Objects The String Class The Random and Math Classes The Java API class library
10 String Indexes The characters in a string are indexed by their position. "Hello" Position 0 Position 4
11 Example: Using String methods String a = "stuff "; String b = a.concat ("more stuff"); String c = a.touppercase(); String d = b.replace ('r', 'v'); String e = b.substring (2, 7); char letter = c.charat(3); int num = a.length(); int comp = a.compareto(b); [a >> b? (use lexicographic order: positive if a>>b, zero if equal, negative if a<<b)] List of some String methods: textbook page 119
12 //******************************************************************** // StringMutation.java Author: Lewis/Loftus // // Demonstrates the use of the String class and its methods. //******************************************************************** public class StringMutation { // // Prints a string and various mutations of it. // public static void main (String[] args) { String phrase = "Change is inevitable"; String mutation1, mutation2, mutation3, mutation4; continued System.out.println ("Original string: \"" + phrase + "\""); System.out.println ("Length of string: " + phrase.length()); mutation1 = phrase.concat (", except from vending machines."); mutation2 = mutation1.touppercase(); mutation3 = mutation2.replace ('E', 'X'); mutation4 = mutation3.substring (3, 30); See StringMutation.java
13 continued // Print each mutated string System.out.println ("Mutation #1: " + mutation1); System.out.println ("Mutation #2: " + mutation2); System.out.println ("Mutation #3: " + mutation3); System.out.println ("Mutation #4: " + mutation4); } } System.out.println ("Mutated length: " + mutation4.length()); See StringMutation.java
14 Output Original string: "Change is inevitable" Length continued of string: 20 Mutation #1: Change is inevitable, except from vending machines. Mutation // #2: Print CHANGE each mutated IS INEVITABLE, string EXCEPT FROM VENDING MACHINES. Mutation System.out.println #3: CHANGX IS INXVITABLX, ("Mutation #1: XXCXPT " + mutation1); FROM VXNDING MACHINXS. Mutation System.out.println #4: NGX IS INXVITABLX, ("Mutation XXCXPT #2: " + F mutation2); Mutated System.out.println length: 27 ("Mutation #3: " + mutation3); System.out.println ("Mutation #4: " + mutation4); } } System.out.println ("Mutated length: " + mutation4.length());
15 Quick Check What output is produced by the following? String str = "Space, the final frontier."; System.out.println (str.length()); System.out.println (str.substring(7)); System.out.println (str.touppercase()); System.out.println (str.length()); 26 the final frontier. SPACE, THE FINAL FRONTIER. 26
16 Today Creating Objects The String Class The Random and Math Classes The Java API class library
17 The Random Class The Random class is part of the java.util package, so we need to import it: import java.util.random; It provides methods that generate pseudorandom numbers
18 Example: Using Random methods Random rand = new Random(); int a = rand.nextint(); // int range[ ] int b = rand.nextint(4); // int range [0,1,2,3] float c = rand.nextfloat(); //float range [0,1) int d = rand.nextint(4) + 1; //random [1,2,3,4] List of some Random methods: page 126 See RandomNumbers.java
19 Quick Check Given a Random object named gen, what range of values are produced by the following expressions? gen.nextint(25) gen.nextint(6) + 1 gen.nextint(100) + 10 gen.nextint(50) gen.nextint(10) 5 gen.nextint(22) + 12 Range 0 to 24 1 to 6 10 to to to 4 12 to 33
20 //******************************************************************** // RandomNumbers.java Author: Lewis/Loftus // // Demonstrates the creation of pseudo-random numbers using the // Random class. //******************************************************************** import java.util.random; public class RandomNumbers { // // Generates random numbers in various ranges. // public static void main (String[] args) { Random generator = new Random(); int num1; float num2; continued num1 = generator.nextint(); System.out.println ("A random integer: " + num1); num1 = generator.nextint(10); System.out.println ("From 0 to 9: " + num1); See RandomNumbers.java
21 continued num1 = generator.nextint(10) + 1; System.out.println ("From 1 to 10: " + num1); num1 = generator.nextint(15) + 20; System.out.println ("From 20 to 34: " + num1); num1 = generator.nextint(20) - 10; System.out.println ("From -10 to 9: " + num1); num2 = generator.nextfloat(); System.out.println ("A random float (between 0-1): " + num2); } } num2 = generator.nextfloat() * 6; // 0.0 to num1 = (int)num2 + 1; System.out.println ("From 1 to 6: " + num1); See RandomNumbers.java
22 continued Sample Run A random integer: num1 = generator.nextint(10) + 1; System.out.println From 0 to 9: ("From 0 1 to 10: " + num1); From 1 to 10: 3 num1 = From generator.nextint(15) 20 34: ; System.out.println From -10 to ("From 9: to 34: " + num1); A random float (between 0-1): num1 = From generator.nextint(20) 1 6: 3-10; System.out.println ("From -10 to 9: " + num1); num2 = generator.nextfloat(); System.out.println ("A random float (between 0-1): " + num2); } } num2 = generator.nextfloat() * 6; // 0.0 to num1 = (int)num2 + 1; System.out.println ("From 1 to 6: " + num1); See RandomNumbers.java
23 Quick Check Given a Random object named gen, write an expression that produces a random integer in the following ranges: Range 0 to 12 1 to to to 0 gen.nextint(13) gen.nextint(20) + 1 gen.nextint(6) + 15 gen.nextint(11) 10
24 Example: counting snake eyes Random gen = new Random(); int trial = 1, count = 0; // Roll two dice 100,000 times and count how many // times you roll snake eyes, i.e., two 1 s. while (trial < ) { } die1 = gen.nextint(6) + 1; die2 = gen.nextint(6) + 1; if (die1 == 1 && die2 == 1) count++; // snake eyes trial++;
25 The Math Class The Math class contains methods that perform various mathematical functions These include: absolute value square root exponentiation trigonometric functions value = Math.cos(90) + Math.sqrt(delta);
26 The Math Class is special! The Math class is part of the java.lang package No need to import anything! The methods of the Math class are static methods (also called class methods) Static methods are invoked through the class name Do not need to create a Math object value = Math.cos(90) + Math.sqrt(delta); See Quadratic.java
27 //******************************************************************** // Quadratic.java Author: Lewis/Loftus // // Demonstrates the use of the Math class to perform a calculation // based on user input. //******************************************************************** import java.util.scanner; public class Quadratic { // // Determines the roots of a quadratic equation. // public static void main (String[] args) { int a, b, c; // ax^2 + bx + c double discriminant, root1, root2; continued Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in); System.out.print ("Enter the coefficient of x squared: "); a = scan.nextint(); See Quadratic.java
28 continued System.out.print ("Enter the coefficient of x: "); b = scan.nextint(); System.out.print ("Enter the constant: "); c = scan.nextint(); // Use the quadratic formula to compute the roots. // Assumes a positive discriminant. discriminant = Math.pow(b, 2) - (4 * a * c); root1 = ((-1 * b) + Math.sqrt(discriminant)) / (2 * a); root2 = ((-1 * b) - Math.sqrt(discriminant)) / (2 * a); } } System.out.println ("Root #1: " + root1); System.out.println ("Root #2: " + root2); See Quadratic.java
29 continued Sample Run Enter the coefficient of x squared: 3 System.out.print ("Enter the coefficient of x: "); b = scan.nextint(); Enter the coefficient of x: 8 Enter the constant: 4 System.out.print Root #1:("Enter the constant: "); c = scan.nextint(); Root #2: -2.0 // Use the quadratic formula to compute the roots. // Assumes a positive discriminant. discriminant = Math.pow(b, 2) - (4 * a * c); root1 = ((-1 * b) + Math.sqrt(discriminant)) / (2 * a); root2 = ((-1 * b) - Math.sqrt(discriminant)) / (2 * a); } } System.out.println ("Root #1: " + root1); System.out.println ("Root #2: " + root2); See Quadratic.java
30 Class Libraries A class library is a collection of classes that we can use when developing programs The Java standard class library is part of any Java development environment Its classes are not part of the Java language per se, but we rely on them heavily Various classes we've already used (System, Scanner, String) are part of the Java standard class library
31 The Java API The Java class library is sometimes referred to as the Java API API stands for Application Programming Interface Clusters of related classes are sometimes referred to as specific APIs: The Swing API The Database API
32 The Java API Get comfortable navigating the online Java API documentation
33 Packages For purposes of accessing them, classes in the Java API are organized into packages Package java.lang java.applet java.awt javax.swing java.net java.util javax.xml.parsers Purpose General support Creating applets for the web Graphics and graphical user interfaces Additional graphics capabilities Network communication Utilities XML document processing
34 The import Declaration Without importing a class, you could use its fully qualified name java.util.scanner Or you can import the class, and then use just the class name import java.util.scanner; Or import all classes in a particular package (use the * wildcard character) import java.util.*;
35 The import Declaration All classes of the java.lang package are imported automatically into all programs It's as if all programs contain the following line: import java.lang.*; That's why we didn't have to import the System or String classes explicitly in earlier programs The Scanner class, on the other hand, is part of the java.util package, and therefore must be imported
36 Homework Read Sections Always do all self-review exercises when you review material Do Exercises EX Many of the slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying Java Software solutions, 7 th edition by Lewis and Loftus. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Using Classes and Objects. Chapter
 Using Classes and Objects 3 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Using Classes and Objects To create
Using Classes and Objects 3 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Using Classes and Objects To create
Using Classes and Objects
 Using Classes and Objects CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ The
Using Classes and Objects CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ The
CSCI 2010 Principles of Computer Science. Basic Java Programming. 08/09/2013 CSCI Basic Java 1
 CSCI 2010 Principles of Computer Science Basic Java Programming 1 Today s Topics Using Classes and Objects object creation and object references the String class and its methods the Java standard class
CSCI 2010 Principles of Computer Science Basic Java Programming 1 Today s Topics Using Classes and Objects object creation and object references the String class and its methods the Java standard class
Using Classes and Objects
 Using Classes and Objects The Java class library or Java API (Application Programming Interface) CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Using Classes and Objects The Java class library or Java API (Application Programming Interface) CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Objectives of CS 230. Java portability. Why ADTs? 8/18/14
 http://cs.wellesley.edu/~cs230 Objectives of CS 230 Teach main ideas of programming Data abstraction Modularity Performance analysis Basic abstract data types (ADTs) Make you a more competent programmer
http://cs.wellesley.edu/~cs230 Objectives of CS 230 Teach main ideas of programming Data abstraction Modularity Performance analysis Basic abstract data types (ADTs) Make you a more competent programmer
Chapter 3 Using Classes and Objects
 Chapter 3 Using Classes and Objects Java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design Seventh Edition John Lewis William Loftus Using Classes and Objects We can create more interesting programs using
Chapter 3 Using Classes and Objects Java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design Seventh Edition John Lewis William Loftus Using Classes and Objects We can create more interesting programs using
Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes
 Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes Quick review of last lecture September 8, 2006 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2006 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev
Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes Quick review of last lecture September 8, 2006 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2006 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev
Using Classes and Objects Chapters 3 Creating Objects Section 3.1 The String Class Section 3.2 The Scanner Class Section 2.6
 Using Classes and Objects Chapters 3 Creating Objects Section 3.1 The String Class Section 3.2 The Scanner Class Section 2.6 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Creating
Using Classes and Objects Chapters 3 Creating Objects Section 3.1 The String Class Section 3.2 The Scanner Class Section 2.6 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Creating
Data Representation Classes, and the Java API
 Data Representation Classes, and the Java API CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: http://www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Data Representation Classes, and the Java API CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: http://www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Chapter 3 Using Classes and Objects
 Chapter 3 Using Classes and Objects Java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design Seventh Edition John Lewis William Loftus Using Classes and Objects We can create more interesting programs using
Chapter 3 Using Classes and Objects Java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design Seventh Edition John Lewis William Loftus Using Classes and Objects We can create more interesting programs using
Packages & Random and Math Classes
 Packages & Random and Math Classes Quick review of last lecture September 6, 2006 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2006 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev Objects Classes An object
Packages & Random and Math Classes Quick review of last lecture September 6, 2006 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2006 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev Objects Classes An object
Learning objectives: Objects and Primitive Data. Introduction to Objects. A Predefined Object. The print versus the println Methods
 CSI1102 Introduction to Software Design Chapter 2: Objects and Primitive Data Learning objectives: Objects and Primitive Data Introducing objects and their properties Predefined objects: System.out Variables
CSI1102 Introduction to Software Design Chapter 2: Objects and Primitive Data Learning objectives: Objects and Primitive Data Introducing objects and their properties Predefined objects: System.out Variables
We now start exploring some key elements of the Java programming language and ways of performing I/O
 We now start exploring some key elements of the Java programming language and ways of performing I/O This week we focus on: Introduction to objects The String class String concatenation Creating objects
We now start exploring some key elements of the Java programming language and ways of performing I/O This week we focus on: Introduction to objects The String class String concatenation Creating objects
ECE 122. Engineering Problem Solving with Java
 ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 4 Creating and Using Objects Outline Problem: How do I create multiple objects from a class Java provides a number of built-in classes for us Understanding
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 4 Creating and Using Objects Outline Problem: How do I create multiple objects from a class Java provides a number of built-in classes for us Understanding
ECE 122. Engineering Problem Solving with Java
 ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 4 Creating and Using Objects Outline Problem: How do I create multiple objects from a class Java provides a number of built-in classes for us Understanding
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 4 Creating and Using Objects Outline Problem: How do I create multiple objects from a class Java provides a number of built-in classes for us Understanding
Chap. 3. Creating Objects The String class Java Class Library (Packages) Math.random() Reading for this Lecture: L&L,
 Chap. 3 Creating Objects The String class Java Class Library (Packages) Math.random() Reading for this Lecture: L&L, 3.1 3.6 1 From last time: Account Declaring an Account object: Account acct1 = new Account
Chap. 3 Creating Objects The String class Java Class Library (Packages) Math.random() Reading for this Lecture: L&L, 3.1 3.6 1 From last time: Account Declaring an Account object: Account acct1 = new Account
A variable is a name for a location in memory A variable must be declared
 Variables A variable is a name for a location in memory A variable must be declared, specifying the variable's name and the type of information that will be held in it data type variable name int total;
Variables A variable is a name for a location in memory A variable must be declared, specifying the variable's name and the type of information that will be held in it data type variable name int total;
COMP 202. Built in Libraries and objects. CONTENTS: Introduction to objects Introduction to some basic Java libraries string
 COMP 202 Built in Libraries and objects CONTENTS: Introduction to objects Introduction to some basic Java libraries string COMP 202 Objects and Built in Libraries 1 Classes and Objects An object is an
COMP 202 Built in Libraries and objects CONTENTS: Introduction to objects Introduction to some basic Java libraries string COMP 202 Objects and Built in Libraries 1 Classes and Objects An object is an
Chapter 4. Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings
 Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings 1 Outline 1. Java Class Library 2. Class Math 3. Character Data Type 4. Class String 5. printf Statement 2 1. Java Class Library A class library
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings 1 Outline 1. Java Class Library 2. Class Math 3. Character Data Type 4. Class String 5. printf Statement 2 1. Java Class Library A class library
Selection Statements and operators
 Selection Statements and operators CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection Statements and operators CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Selection and Repetition Revisited
 Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection Statements and operators
 Selection Statements and operators CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection Statements and operators CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection and Repetition
 Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Designing Classes. Where do objects come from? Where do objects come from? Example: Account datatype. Dr. Papalaskari 1
 Designing Classes Where do objects come from? CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Designing Classes Where do objects come from? CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Where do objects come from? Good question!
 Designing Classes CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Where do objects
Designing Classes CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Where do objects
Introduction to Java (All the Basic Stuff)
 Introduction to Java (All the Basic Stuff) Learning Objectives Java's edit-compile-run loop Basics of object-oriented programming Classes objects, instantiation, methods Primitive types Math expressions
Introduction to Java (All the Basic Stuff) Learning Objectives Java's edit-compile-run loop Basics of object-oriented programming Classes objects, instantiation, methods Primitive types Math expressions
Selection and Repetition Revisited
 Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Designing Classes CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Where do objects
Designing Classes CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Where do objects
Introduction to Arrays
 Introduction to Arrays CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some
Introduction to Arrays CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Designing Classes CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Where do objects
Designing Classes CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Where do objects
2: Basics of Java Programming
 2: Basics of Java Programming CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
2: Basics of Java Programming CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
CS101 Algorithms and Programming I
 CS101 Algorithms and Programming I Week 3 24/06/2013 1 Outline Using Classes and Objects Creating Objects The String Class The Character Class The Random Class The Math Classes Formatting Output Reading
CS101 Algorithms and Programming I Week 3 24/06/2013 1 Outline Using Classes and Objects Creating Objects The String Class The Character Class The Random Class The Math Classes Formatting Output Reading
Selection and Repetition
 Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Selection and Repetition Revisited CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
CSC 1051 Villanova University. CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Course website:
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Algorithms CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Algorithms CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Object-Based Programming. Programming with Objects
 ITEC1620 Object-Based Programming g Lecture 8 Programming with Objects Review Sequence, Branching, Looping Primitive datatypes Mathematical operations Four-function calculator Scientific calculator Don
ITEC1620 Object-Based Programming g Lecture 8 Programming with Objects Review Sequence, Branching, Looping Primitive datatypes Mathematical operations Four-function calculator Scientific calculator Don
Java Basic Introduction, Classes and Objects SEEM
 Java Basic Introduction, Classes and Objects SEEM 3460 1 Java A programming language specifies the words and symbols that we can use to write a program A programming language employs a set of rules that
Java Basic Introduction, Classes and Objects SEEM 3460 1 Java A programming language specifies the words and symbols that we can use to write a program A programming language employs a set of rules that
Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life
 Introduction Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Source: http://xkcd.com/627/
Introduction Java I/O and Control Structures Algorithms in everyday life CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Source: http://xkcd.com/627/
Java Bootcamp - Villanova University. CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Arrays CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying Java Software Solutions
Arrays CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying Java Software Solutions
Java I/O and Control Structures
 Java I/O and Control Structures CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying
Java I/O and Control Structures CSC 2014 Java Bootcamp Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Some slides in this presentation are adapted from the slides accompanying
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination October 7, Name:
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 7, 2013 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 7, 2013 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces
Java Basic Introduction, Classes and Objects SEEM
 Java Basic Introduction, Classes and Objects SEEM 3460 1 Java A programming language specifies the words and symbols that we can use to write a program A programming language employs a set of rules that
Java Basic Introduction, Classes and Objects SEEM 3460 1 Java A programming language specifies the words and symbols that we can use to write a program A programming language employs a set of rules that
Computational Expression
 Computational Expression, Math Class, Wrapper Classes Janyl Jumadinova 18 February, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 18 February, 2019 1 / 8 The Random class is part of the java.util package
Computational Expression, Math Class, Wrapper Classes Janyl Jumadinova 18 February, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 18 February, 2019 1 / 8 The Random class is part of the java.util package
Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs
 Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination October 6, Name:
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 6, 2016 Name: Question Value Score 1 20 2 20 3 20 4 20 5 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided. If you make a
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 6, 2016 Name: Question Value Score 1 20 2 20 3 20 4 20 5 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided. If you make a
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Algorithms CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/f13/ Some slides in
Algorithms CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/f13/ Some slides in
Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs
 Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova
Algorithms in everyday life. Algorithms. Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs
 Data and Algorithms Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs Algorithms in everyday life CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari
Data and Algorithms Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs Algorithms in everyday life CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari
Name: Checked: Access the Java API at the link above. Why is it abbreviated to Java SE (what does the SE stand for)?
 Lab 5 Name: Checked: Objectives: Learn about the Java API Practice using Math, Random, String, and other classes from the Java API Practice writing code to do basic String processing Preparation: Complete
Lab 5 Name: Checked: Objectives: Learn about the Java API Practice using Math, Random, String, and other classes from the Java API Practice writing code to do basic String processing Preparation: Complete
Name: Checked: Access the Java API at the link above. Why is it abbreviated to Java SE (what does the SE stand for)?
 Lab 6 Name: Checked: Objectives: Learn about the Java API Test code snippets interactively to explore data representation and casts Practice using Math, Random, String, and other classes from the Java
Lab 6 Name: Checked: Objectives: Learn about the Java API Test code snippets interactively to explore data representation and casts Practice using Math, Random, String, and other classes from the Java
I/O Streams. program. Standard I/O. File I/O: Setting up streams from files. program. File I/O and Exceptions. Dr. Papalaskari 1
 File I/O and Exceptions CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I I/O Streams Programs read information from input streams and write information to output streams Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department
File I/O and Exceptions CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I I/O Streams Programs read information from input streams and write information to output streams Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 25, Name: KEY A
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 25, 2016 Name: KEY A Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 25, 2016 Name: KEY A Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
Chapter. Let's explore some other fundamental programming concepts
 Data and Expressions 2 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Data and Expressions Let's explore some
Data and Expressions 2 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Data and Expressions Let's explore some
File I/O and Exceptions
 File I/O and Exceptions CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some
File I/O and Exceptions CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some
Designing Classes. Where do objects come from? Where do objects come from? Example: Account datatype. Dr. Papalaskari 1
 Designing Classes Where do objects come from? CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Designing Classes Where do objects come from? CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Classes and Objects Part 1
 COMP-202 Classes and Objects Part 1 Lecture Outline Object Identity, State, Behaviour Class Libraries Import Statement, Packages Object Interface and Implementation Object Life Cycle Creation, Destruction
COMP-202 Classes and Objects Part 1 Lecture Outline Object Identity, State, Behaviour Class Libraries Import Statement, Packages Object Interface and Implementation Object Life Cycle Creation, Destruction
ECE 122. Engineering Problem Solving with Java
 ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 5 Anatomy of a Class Outline Problem: How do I build and use a class? Need to understand constructors A few more tools to add to our toolbox Formatting
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 5 Anatomy of a Class Outline Problem: How do I build and use a class? Need to understand constructors A few more tools to add to our toolbox Formatting
Algorithms and Conditionals
 Algorithms and Conditionals CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Algorithms and Conditionals CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Arrays, Part 3: Multidimensional arrays
 Arrays, Part 3: Multidimensional arrays CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Arrays, Part 3: Multidimensional arrays CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
class declaration Designing Classes part 2 Getting to know classes so far Review Next: 3/18/13 Driver classes:
 Designing Classes part 2 CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Getting to know classes so far Predefined classes from the Java API. Defining classes of our own: Driver classes: Account Transactions
Designing Classes part 2 CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Getting to know classes so far Predefined classes from the Java API. Defining classes of our own: Driver classes: Account Transactions
Lecture 3: Variables and assignment
 Lecture 3: Variables and assignment CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Lecture 3: Variables and assignment CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Last Class CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Last Class CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Algorithms in everyday life. Algorithms. Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs
 Data and Algorithms Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs Algorithms in everyday life CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari
Data and Algorithms Algorithms and Java basics: pseudocode, variables, assignment, and interactive programs Algorithms in everyday life CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari
Anatomy of a Class Encapsulation Anatomy of a Method
 Writing Classes Writing Classes We've been using predefined classes. Now we will learn to write our own classes to define objects Chapter 4 focuses on: class definitions instance data encapsulation and
Writing Classes Writing Classes We've been using predefined classes. Now we will learn to write our own classes to define objects Chapter 4 focuses on: class definitions instance data encapsulation and
I/O Streams. program. Standard I/O. File I/O: Setting up streams from files. program. File I/O and Exceptions. Dr. Papalaskari 1
 File I/O and Exceptions CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I I/O Streams Programs read information from input streams and write information to output streams Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department
File I/O and Exceptions CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I I/O Streams Programs read information from input streams and write information to output streams Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department
I/O Streams. program. Standard I/O. File I/O: Setting up streams from files. program. File I/O and Exceptions. Dr. Papalaskari 1
 File I/O and Exceptions CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I I/O Streams Programs read information from input streams and write information to output streams Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department
File I/O and Exceptions CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I I/O Streams Programs read information from input streams and write information to output streams Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing. Objectives: Examples: Text-printing program. CSC 209 JAVA I
 AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
Iterators and File Input
 Iterators and File Input CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some
Iterators and File Input CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
 Graphics & Applets CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Back to Chapter
Graphics & Applets CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Back to Chapter
Chapter 4: Writing Classes
 Chapter 4: Writing Classes Java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design Sixth Edition by Lewis & Loftus Writing Classes We've been using predefined classes. Now we will learn to write our own
Chapter 4: Writing Classes Java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design Sixth Edition by Lewis & Loftus Writing Classes We've been using predefined classes. Now we will learn to write our own
Lab 3: Work with data (IV)
 CS2370.03 Java Programming Spring 2005 Dr. Zhizhang Shen Background Lab 3: Work with data (IV) In this lab, we will go through a series of exercises to learn some basics of working with data, including
CS2370.03 Java Programming Spring 2005 Dr. Zhizhang Shen Background Lab 3: Work with data (IV) In this lab, we will go through a series of exercises to learn some basics of working with data, including
Review Chapters 1 to 4. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination October 9, Name: KEY
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 9, 2014 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination October 9, 2014 Name: KEY Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the
Basics of Java Programming variables, assignment, and input
 Basics of Java Programming variables, assignment, and input CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Basics of Java Programming variables, assignment, and input CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Improved algorithm. Java code. Control flow and conditionals CSC 1051 Villanova University. Dr Papalaskari 1. Java Programè Algorithm
 , conditionals, boolean expressions, block statements, nested statements CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course
, conditionals, boolean expressions, block statements, nested statements CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course
CSC Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 25, Name:
 CSC 1051-001 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 25, 2016 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the
CSC 1051-001 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 25, 2016 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the
Java code. Updated program. Control flow and conditionals CSC 1051 Villanova University. Dr Papalaskari 1. Java Programè Algorithm. Improved algorithm
 Control flow, conditionals, boolean expressions, block statements, nested statements CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
Control flow, conditionals, boolean expressions, block statements, nested statements CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
Designing Classes part 2
 Designing Classes part 2 CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Getting
Designing Classes part 2 CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Getting
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
Welcome to the Using Objects lab!
 Welcome to the Using Objects lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 3 terms. 2. Describe reference variables and compare with primitive data type variables. 3. Draw
Welcome to the Using Objects lab! Learning Outcomes By the end of this lab: 1. Be able to define chapter 3 terms. 2. Describe reference variables and compare with primitive data type variables. 3. Draw
Control flow, conditionals, boolean expressions, block statements, nested statements. Course website:
 Control flow, conditionals, boolean expressions, block statements, nested statements CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
Control flow, conditionals, boolean expressions, block statements, nested statements CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University
Chapter 4 Classes in the Java Class Libraries
 Programming Fundamental I ACS-1903 Chapter 4 Classes in the Java Class Libraries 1 Random Random The Random class provides a capability to generate pseudorandom values pseudorandom because the stream of
Programming Fundamental I ACS-1903 Chapter 4 Classes in the Java Class Libraries 1 Random Random The Random class provides a capability to generate pseudorandom values pseudorandom because the stream of
Java Libraries. Lecture 6 CGS 3416 Fall September 21, 2015
 Java Libraries Lecture 6 CGS 3416 Fall 2015 September 21, 2015 Intro to Libraries We ve barely scratched the surface of Java, but before we proceed with programming concepts, we need to talk about the
Java Libraries Lecture 6 CGS 3416 Fall 2015 September 21, 2015 Intro to Libraries We ve barely scratched the surface of Java, but before we proceed with programming concepts, we need to talk about the
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
Method OverLoading printf method Arrays Declaring and Using Arrays Arrays of Objects Array as Parameters
 Outline Method OverLoading printf method Arrays Declaring and Using Arrays Arrays of Objects Array as Parameters Variable Length Parameter Lists split() Method from String Class Integer & Double Wrapper
Outline Method OverLoading printf method Arrays Declaring and Using Arrays Arrays of Objects Array as Parameters Variable Length Parameter Lists split() Method from String Class Integer & Double Wrapper
Class API. Class API. Constructors. CS200: Computer Science I. Module 19 More Objects
 CS200: Computer Science I Module 19 More Objects Kevin Sahr, PhD Department of Computer Science Southern Oregon University 1 Class API a class API can contain three different types of methods: 1. constructors
CS200: Computer Science I Module 19 More Objects Kevin Sahr, PhD Department of Computer Science Southern Oregon University 1 Class API a class API can contain three different types of methods: 1. constructors
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination March 1, Name: KEY A
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination March 1, 2018 Name: KEY A Question Value Score 1 20 2 20 3 20 4 20 5 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided. If you make
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination March 1, 2018 Name: KEY A Question Value Score 1 20 2 20 3 20 4 20 5 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided. If you make
Assignment 1 due Monday at 11:59pm
 Assignment 1 due Monday at 11:59pm The heart of Object-Oriented Programming (Now it gets interesting!) Reading for next lecture is Ch. 7 Focus on 7.1, 7.2, and 7.6 Read the rest of Ch. 7 for class after
Assignment 1 due Monday at 11:59pm The heart of Object-Oriented Programming (Now it gets interesting!) Reading for next lecture is Ch. 7 Focus on 7.1, 7.2, and 7.6 Read the rest of Ch. 7 for class after
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
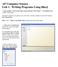 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 26, Name: Key
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 26, 2015 Name: Key Question Value 1 10 Score 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 26, 2015 Name: Key Question Value 1 10 Score 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the
Chapter. We've been using predefined classes. Now we will learn to write our own classes to define objects
 Writing Classes 4 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Writing Classes We've been using predefined
Writing Classes 4 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Writing Classes We've been using predefined
Arrays - Review. Initializer Lists. The for-each Loop. Arrays, Part 2. Dr. Papalaskari 1. CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Arrays, Part 2 Arrays - Review Declaration: double[] scores element type Instantiation: = new double[10]; CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences
Arrays, Part 2 Arrays - Review Declaration: double[] scores element type Instantiation: = new double[10]; CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination March 2, Name:
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination March 2, 2017 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 20 4 20 5 20 6 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided. If you make
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination March 2, 2017 Name: Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 20 4 20 5 20 6 20 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in the spaces provided. If you make
CompSci 125 Lecture 05. Programming Style, String Class and Literals, Static Methods, Packages
 CompSci 125 Lecture 05 Programming Style, String Class and Literals, Static Methods, Packages Homework Update HW2 Due 9/13 Programming Assignment Update p1: Traffic Applet due Sept 21 Programming Style
CompSci 125 Lecture 05 Programming Style, String Class and Literals, Static Methods, Packages Homework Update HW2 Due 9/13 Programming Assignment Update p1: Traffic Applet due Sept 21 Programming Style
