Lesson 2: First Java Programs
|
|
|
- Godwin Austin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 2: First Java Programs
2 Lesson 2: First Java Programs Objectives: Discuss why Java is an important programming language. Explain the Java virtual machine and byte code. Choose a user interface style. Describe the structure of a simple Java program.
3 Lesson 2: First Java Programs Objectives: Write a simple program. Edit, compile, and run a program using a Java development environment. Format a program to give a pleasing, consistent appearance. Understand compile-time errors. Write a graphics program.
4 Lesson 2: First Java Programs - Applet - Assignment operator - Byte code - DOS development environment - Graphical user interface (GUI) - Hacking - Import statement - Integrated development environment (IDE) - Interpreter Vocabulary: - Java virtual machine(jvm) - Just-in-time compilation (JIT) - Panel - Panes - Parameter - Source code - Statement - Terminal I/O interface - Variable
5 2.1 Why Java? Java is the fastest growing programming language in the world. Java is a modern object-oriented programming language. Java has benefited by learning from the less desirable features of early objectoriented programming languages.
6 2.1 Why Java? Java is ideal for distributed, network-based applications. Secure: Virus-free, tamper-free systems. Robust: Supports development of programs that do not overwrite memory. Portable: Yields programs that can be run on different computer types.
7 2.1 Why Java? Java is ideally suited to develop distributed, network-based applications because it: Enables the construction of virus-free, tamper-free systems (security) Supports the development of programs that do not overwrite memory (robust) Yields programs that can be run on different types of computers without change (portable)
8 2.1 Why Java? Java supports advanced programming concepts such as threads. A thread is a process that can run concurrently with other processes. Java resembles C++, the world s most popular industrial strength programming language. Java however, runs more slowly than most modern programming languages because it is interpreted.
9 2.2 The Java Virtual Machine and Byte Code Java compilers translate Java into pseudomachine language called java byte code. To run java byte code on a particular computer, a Java virtual machine (JVM) must be installed.
10 2.2 The Java Virtual Machine and Byte Code A Java virtual machine is a program that runs like a computer. It is called an interpreter. Disadvantage: Runs more slowly than an actual computer To combat slower processing, some JVMs translate code when first encountered. This is known as just-in-time compilation (JIT).
11 2.2 The Java Virtual Machine and Byte Code Advantages: Portability. Any computer can run an interpreter. This makes byte code portable. Applets. Applets are small Java programs already translated into byte code. Applets run in a JVM incorporated in a web browser Applets can be decorative (like animated characters on a web page.) Applets can be practical (like continuous streams of stock market quotes.) Security. It is possible to limit the capabilities of a Java program since it runs inside a virtual machine.
12 2.2 The Java Virtual Machine and Byte Code Advantages: - JVMs are getting faster. Using JIT (just-in-time) compilations, which translate byte code into machine language.
13 2.3 Choosing a User Interface Style There are two types of user interfaces available to use to create Java programs. Graphical User Interface (GUI) Terminal I/O interface Figure 2-1 illustrates both interfaces used to create the same program.
14 2.3 Choosing a User Interface Style Graphical user interface (GUI)
15 2.3 Choosing a User Interface Style Terminal I/O user interface
16 2.3 Choosing a User Interface Style There are 3 reasons for beginning with terminal I/O: It is easier to implement than a GUI There are programming situations that require terminal I/O Terminal-oriented programs are similar in structure to programs that process files of sequentially organized data. (What is learned here is easily transferred to that setting.)
17 2.4 HelloWorld Figure 2-2 displays the results of a small Java program, entitled HelloWorld
18 2.4 HelloWorld A program is a sequence of instructions for a computer. The following is the bulk of instructions, or source code, for the HelloWorld program.
19 2.4 HelloWorld The Explanation: System.out is an object that displays characters in a terminal window. println is the message being sent to the object. The quotations indicate what is to be displayed. Semicolons mark the end of each statement. The characters between the parentheses are the parameters. The period (.) is the method selector operator. Sending messages to objects always takes the following form: <name of object>.<name of message>(<parameters>)
20 2.4 HelloWorld The Larger Framework: The program must be embedded in several lines of code, such as: Program comments are in green, reserved words in blue, and code in black.
21 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute Figure 2-3 illustrates the edit, compile and execute steps.
22 Edit 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute The programmer uses a word processor or editor to enter the source code. Save it as a text file with the extension.java. Compile The programmer invokes the Java language compiler. Translates the source code into Java byte code. Execute The programmer instructs the JVM to load the byte code into memory and execute. The user and program can now interact.
23 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute Development environments: Unix standard text editor command line activation of compiler and JVM DOS, using Microsoft Windows and NT OS notepad text editor command line activation of compiler and JVM from a DOS window Integrated development environment, using Windows, NT, or MAC OS Examples: Symantec s Visual Café, Microsoft s Visual J++, NetBeans, or Borland s J Builder
24 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute Unix or Linux Standard text editor Free Microsoft Windows Integrated development environment (IDE) Notepad and DOS window BlueJ, Eclipse, or JGrasp Free Not free, but combines editor, compiler, debugger, and JVM
25 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute Preparing your development environment: Create a directory, open a terminal window, use the cd command to move to your new directory Open notepad, create the file HelloWorld.java, type in the lines of code Save the file, go back to the terminal window, compile the program Run the program
26 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute The program as typed into Notepad
27 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute The following figures illustrate the steps necessary for preparing your development environment.
28 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute Compile-Time Errors: Mistakes detected by the compiler are called syntax errors or compile-time errors. Typos made when editing. Compiler prints a list of errors in the terminal window.
29 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute Readability: Programs may be maintained by other people. Layout affects readability. Use indentation, blank lines, and spaces.
30 2.5 Edit, Compile, and Execute
31 2.6 Temperature Conversion View the program s source code: import java.util.scanner; public class Convert { public static void main (String [ ] args) { Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); // This allows the user // to enter data from // the keyboard double fahrenheit; // The temperature in // Fahrenheit double celsius; // The temperature in // Celsius System.out.print( Enter degrees Fahrenheit: ); fahrenheit = reader.readdouble(); celsius = (Fahrenheit 32.0) * 5.0 / 9.0; System.out.print( The equivalent in Celsius is ); System.out.println(celsius); }
32 2.6 Temperature Conversion The following is an explanation of the program code: Import statement Instantiate or create an object Declare the variables Position the cursor after Enter degrees Fahrenheit Assignment operators Assignment statements are evaluated Print text (and position the cursor) Print the value of the variable Statement to prevent the terminal window from disappearing from the display (optional, only needed with certain development environments)
33 2.6 Temperature Conversion Temperature conversion program reads user input and performs computations. The first line of code is an import statement. Variables for Fahrenheit and Celsius. Assignment statements use an operator such as *, /, +, and -.
34 2.6 Temperature Conversion Variables and objects used in the conversion program.
35 2.7 Graphics and GUIs: Windows and Panels A Simple Application Window: Graphics and GUI programs in Java can be stand-alone applications or applets. Consistent features: Title bar with controls (maximize, zoom, etc.) Width and height can be resized Code for application windows is in the class Jframe. JFrame responds to messages to set the title bar and window size.
36 2.7 Graphics and GUIs: Windows and Panels Some commonly used JFrame methods
37 2.7 Graphics and GUIs: Windows and Panels Panels and Colors: A Jframe has a container or pane to fill with objects. A panel is a rectangle used to display objects such a shapes and images. Panes are panels that contain related objects such as images and widgets. Colors in most computer system use RGB. Red, green, blue Values 0-255
38 2.7 Graphics and GUIs: Windows and Panels Layout Managers and Multiple Panels: Each container object uses a layout manager to control panel placement. BorderLayout class allows arrangement of up to five objects. North, south, east, west, center GridLayout uses rows and columns to arrange objects.
39 Summary In this chapter, you learned: Java is the fastest growing programming language in the world. It is secure, robust, and portable. It is also similar to C++, the world s most popular programming language.
40 Summary The Java compiler translates Java into a pseudomachine language called Java byte code. Byte code can be run on any computer that has a Java virtual machine installed. The Java virtual machine (JVM) is a program that behaves like a computer an interpreter. Java programs include variables, arithmetic expressions, statements, objects, messages, and methods.
41 Summary Three basic steps in the coding process are editing, compiling, and running a program using a Java development environment. Programmers should pay attention to a program s format to ensure readability.
42 Summary Java programs accomplish many tasks by sending messages to objects. Examples are sending text to the terminal window for output and receiving input data from the keyboard. There are several user interface styles, among them terminal based and graphical based.
43 THE END
Chapter 2 First Java Programs
 First Java Programs Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives Why is Java an important programming language? What is the Java virtual machine and byte code? What are
First Java Programs Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives Why is Java an important programming language? What is the Java virtual machine and byte code? What are
Full file at
 Ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Java bears a superficial resemblance to C++. 2. Java is ideally suited to developing distributed, network-based applications. 3. Java
Ch02 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Java bears a superficial resemblance to C++. 2. Java is ideally suited to developing distributed, network-based applications. 3. Java
1. Java is the fastest growing programming language in the world.
 Chapter 2 First Java Programs TRUE/FALSE 1. Java is the fastest growing programming language in the world. T PTS: 1 REF: 31 2. Java programs cannot be run on different types of computers unless code changes
Chapter 2 First Java Programs TRUE/FALSE 1. Java is the fastest growing programming language in the world. T PTS: 1 REF: 31 2. Java programs cannot be run on different types of computers unless code changes
Chapter 3 Syntax, Errors, and Debugging. Fundamentals of Java
 Chapter 3 Syntax, Errors, and Debugging Objectives Construct and use numeric and string literals. Name and use variables and constants. Create arithmetic expressions. Understand the precedence of different
Chapter 3 Syntax, Errors, and Debugging Objectives Construct and use numeric and string literals. Name and use variables and constants. Create arithmetic expressions. Understand the precedence of different
C++ Spring Break Packet 11 The Java Programming Language
 C++ Spring Break Packet 11 The Java Programming Language! Programmers write instructions in various programming languages, some directly understandable by computers and others requiring intermediate translation
C++ Spring Break Packet 11 The Java Programming Language! Programmers write instructions in various programming languages, some directly understandable by computers and others requiring intermediate translation
Introduction to OOP Using Java Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 1 1 Introduction to OOP Using Java 2 Introduction Sun s implementation called the Java Development Kit (JDK) Object-Oriented Programming Java is language of choice for networked applications Java Enterprise
1 1 Introduction to OOP Using Java 2 Introduction Sun s implementation called the Java Development Kit (JDK) Object-Oriented Programming Java is language of choice for networked applications Java Enterprise
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview of computer hardware and software, programs and compilers Introduce program design and objectoriented programming Overview of the Java programming
Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview of computer hardware and software, programs and compilers Introduce program design and objectoriented programming Overview of the Java programming
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview of computer hardware and software, programs and compilers the Java programming language Example program Hardware and Software Computer systems
Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview of computer hardware and software, programs and compilers the Java programming language Example program Hardware and Software Computer systems
COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Introduction to Java. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics: Why Program? Computer Systems: Hardware and
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics: Why Program? Computer Systems: Hardware and
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Java
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Java Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics:
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Java Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics:
8/23/2014. Chapter Topics. Introduction. Java History. Why Program? Java Applications and Applets. Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Java
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Java Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics:
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Java Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects Fifth Edition by Tony Gaddis Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics:
CHAPTER 1. Introduction to JAVA Programming
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to JAVA Programming What java is Java is high level You can use java to write computer applications that computes number,process words,play games,store data, etc. History of Java.
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to JAVA Programming What java is Java is high level You can use java to write computer applications that computes number,process words,play games,store data, etc. History of Java.
9/11/08 (c) 2008 Matthew J. Rutherford Class (c) 2008 Matthew J. Rutherford Class
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 ISBN 0136130887 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved 7 Hardware and Software
1 2 3 4 5 6 Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 ISBN 0136130887 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All Rights Reserved 7 Hardware and Software
Introduction to Computers and Java. Objectives. Outline. Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich.
 Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives! Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives! Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives! Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives! Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives Overview computer
Introduction to JAVA Programming Language
 Introduction to JAVA Programming Language Lecture 2 Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof 1 Origins of the Java Language Patrick Naughton and Jonathan Payne at Sun Microsystems developed a Web browser that
Introduction to JAVA Programming Language Lecture 2 Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof 1 Origins of the Java Language Patrick Naughton and Jonathan Payne at Sun Microsystems developed a Web browser that
12/22/11. Java How to Program, 9/e. Help you get started with Eclipse and NetBeans integrated development environments.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Introduction to Computers and Java. Objectives. Outline. Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich.
 Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java Harald Gall, Prof. Dr. Institut für Informatik Universität Zürich http://seal.ifi.uzh.ch 2008 W. Savitch, F.M. Carrano, Pearson Prentice Hall Objectives Overview computer
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Objectives overview computer hardware and software introduce program design and object-oriented programming overview the Java programming language
Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Objectives overview computer hardware and software introduce program design and object-oriented programming overview the Java programming language
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Give one example where you might wish to use a three dimensional array
 CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
Introduction to Software Development (ISD) David Weston and Igor Razgon
 Introduction to Software Development (ISD) David Weston and Igor Razgon Autumn term 2013 Course book The primary book supporting the ISD module is: Java for Everyone, by Cay Horstmann, 2nd Edition, Wiley,
Introduction to Software Development (ISD) David Weston and Igor Razgon Autumn term 2013 Course book The primary book supporting the ISD module is: Java for Everyone, by Cay Horstmann, 2nd Edition, Wiley,
Getting Started with Java. Atul Prakash
 Getting Started with Java Atul Prakash Running Programs C++, Fortran, Pascal Python, PHP, Ruby, Perl Java is compiled into device-independent code and then interpreted Source code (.java) is compiled into
Getting Started with Java Atul Prakash Running Programs C++, Fortran, Pascal Python, PHP, Ruby, Perl Java is compiled into device-independent code and then interpreted Source code (.java) is compiled into
Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators
 www.thestudycampus.com Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.3 Modifying Your First Java Program 2.4 Displaying
www.thestudycampus.com Introduction to Java Applications; Input/Output and Operators 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.3 Modifying Your First Java Program 2.4 Displaying
Introduction to Java
 Introduction to Java What Java is: A tool for programming well Portable across any hardware platform that has a JVM interpreter Relatively easy to learn if you have a good foundation An object-oriented
Introduction to Java What Java is: A tool for programming well Portable across any hardware platform that has a JVM interpreter Relatively easy to learn if you have a good foundation An object-oriented
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
COMP Computer Basics. Yi Hong May 13, 2015
 COMP 110-001 Computer Basics Yi Hong May 13, 2015 Today Hardware and memory Programs and compiling Your first program 2 Before Programming Need to know basics of a computer Understand what your program
COMP 110-001 Computer Basics Yi Hong May 13, 2015 Today Hardware and memory Programs and compiling Your first program 2 Before Programming Need to know basics of a computer Understand what your program
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Laying Out Components. What is Widget Layout?
 Laying Out Components Interior Design for GUIs What is Widget Layout? Positioning widgets in their container (typically a JPanel or a JFrame s content pane) Basic idea: each widget has a size and position
Laying Out Components Interior Design for GUIs What is Widget Layout? Positioning widgets in their container (typically a JPanel or a JFrame s content pane) Basic idea: each widget has a size and position
What is Widget Layout? Laying Out Components. Resizing a Window. Hierarchical Widget Layout. Interior Design for GUIs
 What is Widget Layout? Laying Out Components Positioning widgets in their container (typically a JPanel or a JFrame s content pane) Basic idea: each widget has a size and position Main problem: what if
What is Widget Layout? Laying Out Components Positioning widgets in their container (typically a JPanel or a JFrame s content pane) Basic idea: each widget has a size and position Main problem: what if
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview computer hardware and software Introduce program design and objectoriented programming Overview the java
Walter Savitch Frank M. Carrano Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Objectives Overview computer hardware and software Introduce program design and objectoriented programming Overview the java
Java Programming Lecture 6
 Java Programming Lecture 6 Alice E. Fischer Feb 15, 2013 Java Programming - L6... 1/32 Dialog Boxes Class Derivation The First Swing Programs: Snow and Moving The Second Swing Program: Smile Swing Components
Java Programming Lecture 6 Alice E. Fischer Feb 15, 2013 Java Programming - L6... 1/32 Dialog Boxes Class Derivation The First Swing Programs: Snow and Moving The Second Swing Program: Smile Swing Components
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise
 COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
CPS109 Lab 1. i. To become familiar with the Ryerson Computer Science laboratory environment.
 CPS109 Lab 1 Source: Partly from Big Java lab1, by Cay Horstmann. Objective: i. To become familiar with the Ryerson Computer Science laboratory environment. ii. To obtain your login id and to set your
CPS109 Lab 1 Source: Partly from Big Java lab1, by Cay Horstmann. Objective: i. To become familiar with the Ryerson Computer Science laboratory environment. ii. To obtain your login id and to set your
Outline. Introduction to Java. What Is Java? History. Java 2 Platform. Java 2 Platform Standard Edition. Introduction Java 2 Platform
 Outline Introduction to Java Introduction Java 2 Platform CS 3300 Object-Oriented Concepts Introduction to Java 2 What Is Java? History Characteristics of Java History James Gosling at Sun Microsystems
Outline Introduction to Java Introduction Java 2 Platform CS 3300 Object-Oriented Concepts Introduction to Java 2 What Is Java? History Characteristics of Java History James Gosling at Sun Microsystems
Command-Line Applications. GUI Libraries GUI-related classes are defined primarily in the java.awt and the javax.swing packages.
 1 CS257 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 14: Graphical User Interfaces Command-Line Applications 2 The programs we've explored thus far have been text-based applications A Java application is
1 CS257 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 14: Graphical User Interfaces Command-Line Applications 2 The programs we've explored thus far have been text-based applications A Java application is
CMSC 150 LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE HELLO WORLD
 CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE
Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Introduction to Java Programming
 Introduction to Java Programming Lecture 1 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 1/9/2017 Main Components of a computer CPU - Central Processing Unit: The brain of the computer ISA - Instruction Set Architecture: the specific
Introduction to Java Programming Lecture 1 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 1/9/2017 Main Components of a computer CPU - Central Processing Unit: The brain of the computer ISA - Instruction Set Architecture: the specific
Java Programming Constructs Java Programming 2 Lesson 1
 Java Programming Constructs Java Programming 2 Lesson 1 Course Objectives Welcome to OST's Java 2 course! In this course, you'll learn more in-depth concepts and syntax of the Java Programming language.
Java Programming Constructs Java Programming 2 Lesson 1 Course Objectives Welcome to OST's Java 2 course! In this course, you'll learn more in-depth concepts and syntax of the Java Programming language.
2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators
 Page 1 of 6 [Page 56] 2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators A condition is an expression that can be either true or false. This section introduces a simple version of Java's if statement
Page 1 of 6 [Page 56] 2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators A condition is an expression that can be either true or false. This section introduces a simple version of Java's if statement
IT151: Introduction to Programming (java)
 IT151: Introduction to Programming (java) Programming Basics Program A set of instructions that a computer uses to do something. Programming / Develop The act of creating or changing a program Programmer
IT151: Introduction to Programming (java) Programming Basics Program A set of instructions that a computer uses to do something. Programming / Develop The act of creating or changing a program Programmer
Goals. Java - An Introduction. Java is Compiled and Interpreted. Architecture Neutral & Portable. Compiled Languages. Introduction to Java
 Goals Understand the basics of Java. Introduction to Java Write simple Java Programs. 1 2 Java - An Introduction Java is Compiled and Interpreted Java - The programming language from Sun Microsystems Programmer
Goals Understand the basics of Java. Introduction to Java Write simple Java Programs. 1 2 Java - An Introduction Java is Compiled and Interpreted Java - The programming language from Sun Microsystems Programmer
Eclipse Tutorial. For Introduction to Java Programming By Y. Daniel Liang
 Eclipse Tutorial For Introduction to Java Programming By Y. Daniel Liang This supplement covers the following topics: Getting Started with Eclipse Choosing a Perspective Creating a Project Creating a Java
Eclipse Tutorial For Introduction to Java Programming By Y. Daniel Liang This supplement covers the following topics: Getting Started with Eclipse Choosing a Perspective Creating a Project Creating a Java
Chapter 3 Intro to Java
 Chapter 3 Intro to Java Introducing Java Barrett Computer Science Designing Technology Solutions 1 2 Key Terminology - OS Operating System 3 Why Program in Java? Java is an Object Oriented Programming
Chapter 3 Intro to Java Introducing Java Barrett Computer Science Designing Technology Solutions 1 2 Key Terminology - OS Operating System 3 Why Program in Java? Java is an Object Oriented Programming
MEAP Edition Manning Early Access Program Get Programming with Java Version 1
 MEAP Edition Manning Early Access Program Get Programming with Java Version 1 Copyright 2018 Manning Publications For more information on this and other Manning titles go to www.manning.com welcome First,
MEAP Edition Manning Early Access Program Get Programming with Java Version 1 Copyright 2018 Manning Publications For more information on this and other Manning titles go to www.manning.com welcome First,
CS 315 Software Design Homework 1 First Sip of Java Due: Sept. 10, 11:30 PM
 CS 315 Software Design Homework 1 First Sip of Java Due: Sept. 10, 11:30 PM Objectives The objectives of this assignment are: to get your first experience with Java to become familiar with Eclipse Java
CS 315 Software Design Homework 1 First Sip of Java Due: Sept. 10, 11:30 PM Objectives The objectives of this assignment are: to get your first experience with Java to become familiar with Eclipse Java
Learning objectives. The Java Environment. Java timeline (cont d) Java timeline. Understand the basic features of Java
 Learning objectives The Java Environment Understand the basic features of Java What are portability and robustness? Understand the concepts of bytecode and interpreter What is the JVM? Learn few coding
Learning objectives The Java Environment Understand the basic features of Java What are portability and robustness? Understand the concepts of bytecode and interpreter What is the JVM? Learn few coding
Text User Interfaces. Keyboard IO plus
 Text User Interfaces Keyboard IO plus User Interface and Model Model: objects that solve problem at hand. User interface: interacts with user getting input from user giving output to user reporting on
Text User Interfaces Keyboard IO plus User Interface and Model Model: objects that solve problem at hand. User interface: interacts with user getting input from user giving output to user reporting on
Computer Hardware. Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus. Key Hardware Components 12/17/2013
 Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus Chapter 1 Notes Computer Hardware Key Hardware Components CPU central processing unit Input / Output devices Main memory (RAM) Secondary storage devices: Hard drive
Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus Chapter 1 Notes Computer Hardware Key Hardware Components CPU central processing unit Input / Output devices Main memory (RAM) Secondary storage devices: Hard drive
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java. What is a Computer? A Bit of History
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java CS170 Introduction to Computer Science 1 What is a Computer? A machine that manipulates data according to a list of instructions Consists of hardware
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java CS170 Introduction to Computer Science 1 What is a Computer? A machine that manipulates data according to a list of instructions Consists of hardware
Identifiers. Identifiers are the words a programmer uses in a program Some identifiers are already defined. Some are made up by the programmer:
 C1 D6 Obj: cont. 1.3 and 1.4, to become familiar with identifiers and to understand how programming languages work HW: p.51 #1.8 1.9 (Short Answers) Chapter 1 Test in two class days!! Do Now: How is the
C1 D6 Obj: cont. 1.3 and 1.4, to become familiar with identifiers and to understand how programming languages work HW: p.51 #1.8 1.9 (Short Answers) Chapter 1 Test in two class days!! Do Now: How is the
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba. (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java 1 Objectives To understand computer basics, programs, and operating systems ( 1.2 1.4). To describe the relationship between Java and the World Wide
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java 1 Objectives To understand computer basics, programs, and operating systems ( 1.2 1.4). To describe the relationship between Java and the World Wide
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
CT 229. CT229 Lecture Notes. Labs. Tutorials. Lecture Notes. Programming II CT229. Objectives for CT229. IT Department NUI Galway
 Lecture Notes CT 229 Programming II Lecture notes, Sample Programs, Lab Assignments and Tutorials will be available for download at: http://www.nuigalway.ie/staff/ted_scully/ct229/ Lecturer: Dr Ted Scully
Lecture Notes CT 229 Programming II Lecture notes, Sample Programs, Lab Assignments and Tutorials will be available for download at: http://www.nuigalway.ie/staff/ted_scully/ct229/ Lecturer: Dr Ted Scully
Getting Started (1.8.7) 9/2/2009
 2 Getting Started For the examples in this section, Microsoft Windows and Java will be used. However, much of the information applies to other operating systems and supported languages for which you have
2 Getting Started For the examples in this section, Microsoft Windows and Java will be used. However, much of the information applies to other operating systems and supported languages for which you have
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter Scope Introduce the Java programming language Program compilation and execution Problem solving in general The software development process Overview of object-oriented principles
Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter Scope Introduce the Java programming language Program compilation and execution Problem solving in general The software development process Overview of object-oriented principles
2 Getting Started. Getting Started (v1.8.6) 3/5/2007
 2 Getting Started Java will be used in the examples in this section; however, the information applies to all supported languages for which you have installed a compiler (e.g., Ada, C, C++, Java) unless
2 Getting Started Java will be used in the examples in this section; however, the information applies to all supported languages for which you have installed a compiler (e.g., Ada, C, C++, Java) unless
Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 04 Demonstration 1 So, we have learned about how to run Java programs
Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 04 Demonstration 1 So, we have learned about how to run Java programs
Lab # 2. For today s lab:
 1 ITI 1120 Lab # 2 Contributors: G. Arbez, M. Eid, D. Inkpen, A. Williams, D. Amyot 1 For today s lab: Go the course webpage Follow the links to the lab notes for Lab 2. Save all the java programs you
1 ITI 1120 Lab # 2 Contributors: G. Arbez, M. Eid, D. Inkpen, A. Williams, D. Amyot 1 For today s lab: Go the course webpage Follow the links to the lab notes for Lab 2. Save all the java programs you
The NetBeans IDE is a big file --- a minimum of around 30 MB. After you have downloaded the file, simply execute the file to install the software.
 Introduction to Netbeans This document is a brief introduction to writing and compiling a program using the NetBeans Integrated Development Environment (IDE). An IDE is a program that automates and makes
Introduction to Netbeans This document is a brief introduction to writing and compiling a program using the NetBeans Integrated Development Environment (IDE). An IDE is a program that automates and makes
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Java Basics
 WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
The Computer System. Hardware = Physical Computer. Software = Computer Programs. People = End Users & Programmers. people
 The Computer System Hardware = Physical Computer The equipment associated with a computer system. hardware software people The set of instructions that tell a computer what to do. Use the power of the
The Computer System Hardware = Physical Computer The equipment associated with a computer system. hardware software people The set of instructions that tell a computer what to do. Use the power of the
An Introduction to Software Engineering. David Greenstein Monta Vista High School
 An Introduction to Software Engineering David Greenstein Monta Vista High School Software Today Software Development Pre-1970 s - Emphasis on efficiency Compact, fast algorithms on machines with limited
An Introduction to Software Engineering David Greenstein Monta Vista High School Software Today Software Development Pre-1970 s - Emphasis on efficiency Compact, fast algorithms on machines with limited
Programming. Syntax and Semantics
 Programming For the next ten weeks you will learn basic programming principles There is much more to programming than knowing a programming language When programming you need to use a tool, in this case
Programming For the next ten weeks you will learn basic programming principles There is much more to programming than knowing a programming language When programming you need to use a tool, in this case
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
 Chapter Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java. Introduction Java is the Internet program language Why Java? The answer is that Java enables user to deploy applications on the Internet for servers,
Chapter Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java. Introduction Java is the Internet program language Why Java? The answer is that Java enables user to deploy applications on the Internet for servers,
1 Introduction Java, the beginning Java Virtual Machine A First Program BlueJ Raspberry Pi...
 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Java, the beginning.......................... 3 1.2 Java Virtual Machine........................ 4 1.3 A First Program........................... 4 1.4 BlueJ.................................
Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Java, the beginning.......................... 3 1.2 Java Virtual Machine........................ 4 1.3 A First Program........................... 4 1.4 BlueJ.................................
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Lecture Notes. System.out.println( Circle radius: + radius + area: + area); radius radius area area value
 Lecture Notes 1. Comments a. /* */ b. // 2. Program Structures a. public class ComputeArea { public static void main(string[ ] args) { // input radius // compute area algorithm // output area Actions to
Lecture Notes 1. Comments a. /* */ b. // 2. Program Structures a. public class ComputeArea { public static void main(string[ ] args) { // input radius // compute area algorithm // output area Actions to
Introduction Basic elements of Java
 Software and Programming I Introduction Basic elements of Java Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Module Information Time: Thursdays in the Spring term Lectures: MAL B04: 2
Software and Programming I Introduction Basic elements of Java Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Module Information Time: Thursdays in the Spring term Lectures: MAL B04: 2
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
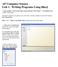 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java. Lecture 1 COP 3252 Summer May 16, 2017
 Introduction to Java Lecture 1 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 16, 2017 The Java Language Java is a programming language that evolved from C++ Both are object-oriented They both have much of the same syntax Began
Introduction to Java Lecture 1 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 16, 2017 The Java Language Java is a programming language that evolved from C++ Both are object-oriented They both have much of the same syntax Began
Chapter. Focus of the Course. Object-Oriented Software Development. program design, implementation, and testing
 Introduction 1 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Focus of the Course Object-Oriented Software Development
Introduction 1 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Focus of the Course Object-Oriented Software Development
Chapter 3. Selections
 Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Programming with Java
 Java-At-A-Glance Widely used, high-level programming language Programming with Java Developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995 (which was acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2010) An object-oriented programming
Java-At-A-Glance Widely used, high-level programming language Programming with Java Developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995 (which was acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2010) An object-oriented programming
Lesson 01 Introduction
 Lesson 01 Introduction MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Lecturer in Management & IT M.Sc. In IS (SLIIT), PGD in IS (SLIIT), BBA (Hons.) Spl. in IS (SEUSL), MCP Programs Computer
Lesson 01 Introduction MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Lecturer in Management & IT M.Sc. In IS (SLIIT), PGD in IS (SLIIT), BBA (Hons.) Spl. in IS (SEUSL), MCP Programs Computer
Resizing a Window. COSC 3461: Module 5B. What is Widget Layout? Size State Transitions. What is Widget Layout? Hierarchical Widget Layout.
 COSC 3461: Module 5B Resizing a Window Widgets II What has changed? scrollbar added menu has wrapped toolbar modified (buttons lost) 2 What is Widget Layout? Size State Transitions Recall: each widget
COSC 3461: Module 5B Resizing a Window Widgets II What has changed? scrollbar added menu has wrapped toolbar modified (buttons lost) 2 What is Widget Layout? Size State Transitions Recall: each widget
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.1 Introduction ( none ) Section 2.2 First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.1 Introduction ( none ) Section 2.2 First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler
First Java Program - Output to the Screen
 First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
CSI Lab 02. Tuesday, January 21st
 CSI Lab 02 Tuesday, January 21st Objectives: Explore some basic functionality of python Introduction Last week we talked about the fact that a computer is, among other things, a tool to perform high speed
CSI Lab 02 Tuesday, January 21st Objectives: Explore some basic functionality of python Introduction Last week we talked about the fact that a computer is, among other things, a tool to perform high speed
Eng. Mohammed S. Abdualal
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2124) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 1 Introduction
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2124) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 1 Introduction
What is Widget Layout? COSC 3461 User Interfaces. Hierarchical Widget Layout. Resizing a Window. Module 5 Laying Out Components
 COSC User Interfaces Module 5 Laying Out Components What is Widget Layout? Positioning widgets in their container (typically a JPanel or a JFrame s content pane) Basic idea: each widget has a size and
COSC User Interfaces Module 5 Laying Out Components What is Widget Layout? Positioning widgets in their container (typically a JPanel or a JFrame s content pane) Basic idea: each widget has a size and
Introduction to Java Applications
 2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
4 WORKING WITH DATA TYPES AND OPERATIONS
 WORKING WITH NUMERIC VALUES 27 4 WORKING WITH DATA TYPES AND OPERATIONS WORKING WITH NUMERIC VALUES This application will declare and display numeric values. To declare and display an integer value in
WORKING WITH NUMERIC VALUES 27 4 WORKING WITH DATA TYPES AND OPERATIONS WORKING WITH NUMERIC VALUES This application will declare and display numeric values. To declare and display an integer value in
Pace University. Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1
 Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition
 SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition Hosted by The School of Computer Science, University of Windsor WORKSHOP I [ Overview of the Java/Eclipse
SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition Hosted by The School of Computer Science, University of Windsor WORKSHOP I [ Overview of the Java/Eclipse
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Development Process
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 2: SEP. 8TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 2: SEP. 8TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Class Website http://www.cs.umb.edu/~jane/cs114/ Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 2: SEP. 8TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Class Website http://www.cs.umb.edu/~jane/cs114/ Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming
NetBeans Tutorial. For Introduction to Java Programming By Y. Daniel Liang. This tutorial applies to NetBeans 6, 7, or a higher version.
 NetBeans Tutorial For Introduction to Java Programming By Y. Daniel Liang This tutorial applies to NetBeans 6, 7, or a higher version. This supplement covers the following topics: Getting Started with
NetBeans Tutorial For Introduction to Java Programming By Y. Daniel Liang This tutorial applies to NetBeans 6, 7, or a higher version. This supplement covers the following topics: Getting Started with
BlueJ Demo. Topic 1: Basic Java. 1. Sequencing. Features of Structured Programming Languages
 Topic 1: Basic Java Plan: this topic through next Friday (5 lectures) Required reading on web site I will not spell out all the details in lecture! BlueJ Demo BlueJ = Java IDE (Interactive Development
Topic 1: Basic Java Plan: this topic through next Friday (5 lectures) Required reading on web site I will not spell out all the details in lecture! BlueJ Demo BlueJ = Java IDE (Interactive Development
CONTENTS: Compilation Data and Expressions COMP 202. More on Chapter 2
 CONTENTS: Compilation Data and Expressions COMP 202 More on Chapter 2 Programming Language Levels There are many programming language levels: machine language assembly language high-level language Java,
CONTENTS: Compilation Data and Expressions COMP 202 More on Chapter 2 Programming Language Levels There are many programming language levels: machine language assembly language high-level language Java,
Chapter 2: Programming Concepts
 Chapter 2: Programming Concepts Objectives Students should Know the steps required to create programs using a programming language and related terminology. Be familiar with the basic structure of a Java
Chapter 2: Programming Concepts Objectives Students should Know the steps required to create programs using a programming language and related terminology. Be familiar with the basic structure of a Java
Week 2: Data and Output
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 2: Data and Output Learning to speak Java Types, Values and Variables Output Objects and Methods What s the Plan? Topic I: A little review IPO, hardware, software and Java
CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 2: Data and Output Learning to speak Java Types, Values and Variables Output Objects and Methods What s the Plan? Topic I: A little review IPO, hardware, software and Java
B.V. Patel Institute of BMC & IT, UTU 2014
 BCA 3 rd Semester 030010301 - Java Programming Unit-1(Java Platform and Programming Elements) Q-1 Answer the following question in short. [1 Mark each] 1. Who is known as creator of JAVA? 2. Why do we
BCA 3 rd Semester 030010301 - Java Programming Unit-1(Java Platform and Programming Elements) Q-1 Answer the following question in short. [1 Mark each] 1. Who is known as creator of JAVA? 2. Why do we
Chapter 1 - Introduction. Copyright 2014 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. 1
 Chapter 1 - Introduction Copyright 2014 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. 1 Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time
Chapter 1 - Introduction Copyright 2014 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. 1 Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time
USING THE OOSIML/JAVA COMPILER. With the Command Window
 USING THE OOSIML/JAVA COMPILER With the Command Window On Windows Operating System José M. Garrido Department of Computer Science December 2017 College of Computing and Software Engineering Kennesaw State
USING THE OOSIML/JAVA COMPILER With the Command Window On Windows Operating System José M. Garrido Department of Computer Science December 2017 College of Computing and Software Engineering Kennesaw State
