Built-in data types. public static void main(string [] args) logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science
|
|
|
- Lisa Butler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Built-in data types logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science
2 Variables Overview Allows us to store and compute on data For now we'll be using basic Java data types String, int, double, boolean, char Variables in Java must be declared including type! Converting between different basic types Types of errors Runtime, compile Random numbers Allow us to simulate random events Needed for loops assignment 2
3 Variables Variables and data types Stores information your program needs Each has a unique name Each has a specific type Java built-in type what it stores example values operations String sequence of characters "Hello world!" "I love this!" concatenate char characters 'a', 'b', '!' compare int integer values double floating-point values e8 boolean truth values true false add, subtract, multiply, divide, remainder add, subtract, multiply, divide and, or, not 3
4 int a; a = 10; int b; b = 7; int c = a + b; Some definitions Declaration statement I'm going to need an integer and let's call it a NOTE: in Java you are required to declare a variable before using it! Variable name Whenever I say a, I mean the value stored in a Literal I want the value 10 Assignment statement Variable b gets the literal value 7 = in CS is not the same as = in math! Combined declaration and assignment Make me an integer variable called c and assign it the value obtained by adding together a and b 4
5 String data type Text A sequence of characters Double quote around the characters Concatenation using the + operator String firstname = "Keith"; String lastname = "Vertanen"; String fullname = firstname + " " + lastname; String favnumber = "42"; System.out.println(fullName + "'s favorite number is " + favnumber); Keith Vertanen's favorite number is 42 5
6 Characters char data type Holds a single character Single apostrophe, e.g. 'a', 'z' public class CharExample public static void main(string [] args) char ch1 = 'y'; char ch2 = 'o'; String result = "" + ch1; result = result + ch2; result = result + ch2; result = result + ch2; Double quotes with nothing in between, an empty String } } System.out.println(result); % java CharExample yooo 6
7 int data type Integers An integer value between and Between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647 Operations: add subtract multiply divide remainder + - * / % example result comment Watch out for this! / is integer division if both sides are integers! 10 * / 7 1 integer division, no fractional part 10 % 7 3 remainder after dividing by 7 10 / 0 runtime error, you can't divide an integer by 0! 7
8 int data type Integers Normal rules of mathematical precedence e.g. multiplication/division before addition/subtraction Use ()'s to force a different order of calculation example result comment * 2 24 multiplication comes before addition (10 + 7) * 2 34 ()'s force addition to occur first 10 / integer division result is 1 which is added to (10-7) (7-2) 5 8
9 double data type Floating-point numbers Floating-point number (as specified by IEEE 754) Operations: add subtract multiply divide + - * / example result / / / 0.0 Infinity 0.0 / / 0.0 NaN 9
10 boolean data type Either true or false Booleans Controls logic and flow of control in programs Operations: logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Note: two symbols for logical AND and OR, not one! 10
11 boolean data type Booleans logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&!!a Is a set to false? a && b Are both a and b set to true? a b Is either a or b (or both) set to true? a!a true false false true a b a && b a b false false false false false true false true true false false true true true true true 11
12 Comparisons Given two numbers return a boolean operator meaning true example false example == equal 7 == 7 7 == 8!= not equal 7!= 8 7!= 7 < less than 7 < 8 8 < 7 <= less than or equal 7 <= 7 8 <= 7 > greater than 8 > 7 7 > 8 >= greater than or equal 8 >= 2 8 >= 10 Is the sum of a, b and c equal to 0? (a + b + c) == 0 Is grade in the B range? (grade >= 80.0) && (grade < 90.0) Is sumitems an even number? (sumitems % 2) == 0 12
13 Leap year example Years divisible by 4 but not by 100 leap year Years divisible by 400 leap year public class LeapYear public static void main(string [] args) int year = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); boolean isleapyear; // Leap year if divisible by 4 but not by 100 isleapyear = (year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100!= 0); } } // But also leap year if divisible by 400 isleapyear = isleapyear (year % 400 == 0); System.out.println(isLeapYear); % java LeapYear 2000 true 13
14 Java is strongly typed Type conversion Helps protect you from mistakes (aka "bugs") public class TypeExample0 public static void main(string [] args) int ordertotal = 0; double costitem = 29.95; ordertotal = costitem * 1.06; System.out.println("total=" + ordertotal); } } % javac TypeExample0.java TypeExample0.java:7: possible loss of precision found : double required: int ordertotal = costitem * 1.06; ^ 14
15 Type conversion Converting from one type to another: Manually using a cast A cast is accomplished by putting a type inside ()'s Casting to int drops fractional part Does not round! public class TypeExample1 public static void main(string [] args) int ordertotal = 0; double costitem = 29.95; ordertotal = (int) (costitem * 1.06); } } System.out.println("total=" + ordertotal); % java TypeExample1 total=31 15
16 Automatic conversion Numeric types: Type conversion If no loss of precision automatic promotion public class TypeExample2 public static void main(string [] args) double ordertotal = 0.0; int costitem = 30; ordertotal = costitem * 1.06; System.out.println("total=" + ordertotal); } } % java TypeExample2 total=
17 Automatic conversion Type conversion String concatenation using the + operator converts numeric types to also be a String public class TypeExample3 public static void main(string [] args) double costitem = 29.95; String message = "The widget costs "; message = message + costitem; message = message + "!"; System.out.println(message); } } % java TypeExample3 The widget costs 29.95! 17
18 args array public static void main(string [] args) Program input comes in as Strings from command line (for now) % java CostCalc bananas To buy 12 bananas you will need $2.52 identifier meaning value type args[0] 1 st thing on command line after Java class name "bananas" String args[1] 2 nd thing on command line "12" String args[2] 3 rd thing on command line after Java class "0.21" String args.length # of things on command line 3 int 18
19 Static methods Java has lots of helper methods Things that take value(s) and return a result e.g. Math functions e.g. Type conversion: String int String double e.g. Random number generation For now, we'll stick to static methods Live in some particular Java class e.g. Math, Integer or Double Call using class name followed by dot 19
20 Converting text to a numeric type method description Integer.parseInt(String a) converts text a into an int Double.parseDouble(String a) convert text a into a double public class CostCalc public static void main(string [] args) String product = args[0]; int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); double cost = Double.parseDouble(args[2]); double total = qty * cost; System.out.print("To buy " + qty); System.out.print(" " + product); System.out.println(" you will need $" + total); } } % java CostCalc elections 2 1e6 To buy 2 elections you will need $
21 Different types of errors: runtime runtime error % java CostCalc apples 6-10 To buy 6 apples you will need $-60.0 % java CostCalc apples 6 foo Exception in thread "main" java.lang.numberformatexception: For input string: "foo" at sun.misc.floatingdecimal.readjavaformatstring (FloatingDecimal.java:1222) at java.lang.double.parsedouble(double.java:510) at CostCalc.main(ArgsExample.java:7) % java CostCalc apples Exception in thread "main" java.lang.numberformatexception: For input string: "6.1" at java.lang.numberformatexception.forinputstring (NumberFormatException.java:48) at java.lang.integer.parseint(integer.java:458) at java.lang.integer.parseint(integer.java:499) at CostCalc.main(ArgsExample.java:6) % java CostCalc apples Exception in thread "main" java.lang.numberformatexception: For input string: "6.0" at java.lang.numberformatexception.forinputstring (NumberFormatException.java:48) at java.lang.integer.parseint(integer.java:458) at java.lang.integer.parseint(integer.java:499) at CostCalc.main(ArgsExample.java:6) 21
22 Different types of errors: compile time public class CostCalc public static void main(string [] args) String product = args[0]; int qty = args[1]; double cost = args[2]; double total = qty * cost; compile time error System.out.print("To buy " + qty); System.out.print(" " + product); System.out.println(" you will need $" + total); } } % javac CostCalc.java CostCalc.java:6: incompatible types found : java.lang.string required: int int qty = args[1]; ^ CostCalc.java:7: incompatible types found required: double double cost 2 errors : java.lang.string = args[2]; ^ 22
23 Randomness Simulate roll of two 6-sided dice Generate two random #'s between 1 and 6 Math.random() number in [0, 1.0) e.g. 0.0, 0.312, Math.random()*6 number in [0, 6.0) e.g. 0.0, 1.872, (Math.random()*6)+1 number in [1, 7.0) e.g. 1.0, 2.872, (int)(math.random()*6)+1 number in set 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} e.g. 1, 2,
24 Randomness Simulate roll of two 6-sided dice Generate two random #'s between 1 and 6 public class TwoDice public static void main(string [] args) int dice1 = (int) (Math.random() * 6) + 1; int dice2 = (int) (Math.random() * 6) + 1; int sum = dice1 + dice2; } } System.out.println(dice1 + " + " + dice2 + " = " + sum); % java TwoDice = 7 % java TwoDice = 7 % java TwoDice = 2 24
25 Type conversion quiz Automatic: no loss of precision int will convert to a double if need be double cannot automatically convert to int Manual: cast or using a method expression resulting type resulting value (int) Math.round(3.6) 2 * * (int) 3.0 (int) 2 *
26 Type conversion quiz Automatic: no loss of precision int will convert to a double if need be double cannot automatically convert to int Manual: cast or using a method expression resulting type resulting value (int) int 3 Math.round(3.6) long 4 2 * 3.0 double * (int) 3.0 int 6 (int) 2 * 3.0 double
27 String conversion quiz String conversion, using: Integer.parseInt() Double.parseDouble() expression resulting type resulting value Integer.parseInt("30") Double.parseDouble("30") Integer.parseInt("30.1") Double.parseDouble("30.1") Integer.parseInt("$30") Double.parseDouble(3.14) 27
28 String conversion quiz String conversion, using: Integer.parseInt() Double.parseDouble() expression resulting type resulting value Integer.parseInt("30") int 30 Double.parseDouble("30") double 30.0 Integer.parseInt("30.1") (runtime error, can't parse as int) Double.parseDouble("30.1") double 30.1 Integer.parseInt("$30") Double.parseDouble(3.14) (runtime error, can't parse as int) (compile (runtime error, 3.14 not a String) 28
29 String concatenation quiz + is addition for numeric types + is concatenation for String type numeric types convert to String if needed Strings never (automatically) go back to number expression resulting type resulting value "testing " "3.1" "2" + " + " + "3" "66" 29
30 String concatenation quiz + is addition for numeric types + is concatenation for String type numeric types convert to String if needed Strings never (automatically) go back to number expression resulting type resulting value "testing " String "testing 123" "3.1" String " " "2" + " + " + "3" String "2 + 3" "66" String "666" 30
31 Variables Summary Allows us to store and compute on data String, int, double, boolean, char Boolean operators for logic and program flow control (more on this next time!) Type conversion Automatic e.g. int converting itself to a double Explicit via cast or method call Important! Cause of many, many, many software bugs 31
Built-in data types. logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! public static void main(string [] args)
![Built-in data types. logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! public static void main(string [] args) Built-in data types. logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! public static void main(string [] args)](/thumbs/72/67635764.jpg) Built-in data types logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Variables Variables and data types Stores
Built-in data types logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Variables Variables and data types Stores
Variables and data types
 Survivor: CSCI 135 Variables Variables and data types Stores information your program needs Each has a unique name Each has a specific type Java built-in type what it stores example values operations String
Survivor: CSCI 135 Variables Variables and data types Stores information your program needs Each has a unique name Each has a specific type Java built-in type what it stores example values operations String
MODULE 02: BASIC COMPUTATION IN JAVA
 MODULE 02: BASIC COMPUTATION IN JAVA Outline Variables Naming Conventions Data Types Primitive Data Types Review: int, double New: boolean, char The String Class Type Conversion Expressions Assignment
MODULE 02: BASIC COMPUTATION IN JAVA Outline Variables Naming Conventions Data Types Primitive Data Types Review: int, double New: boolean, char The String Class Type Conversion Expressions Assignment
DATA TYPES AND EXPRESSIONS
 DATA TYPES AND EXPRESSIONS Outline Variables Naming Conventions Data Types Primitive Data Types Review: int, double New: boolean, char The String Class Type Conversion Expressions Assignment Mathematical
DATA TYPES AND EXPRESSIONS Outline Variables Naming Conventions Data Types Primitive Data Types Review: int, double New: boolean, char The String Class Type Conversion Expressions Assignment Mathematical
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
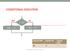 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 5/20/2013 9:37:22 AM Why Programming? Why programming? Need
1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 5/20/2013 9:37:22 AM Why Programming? Why programming? Need
! Widely available. ! Widely used. ! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs. ! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.
 Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features.! Widely available.! Widely used.! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs.! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.! No perfect
Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features.! Widely available.! Widely used.! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs.! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.! No perfect
BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I
![BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I](/thumbs/81/83968367.jpg) BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
1/16/12. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. A Foundation for Programming. (Spring 2012) Lecture #4: Built-in Types of Data. The Computer s View
 1/16/12 A Foundation for Programming CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) any program you might want to write Lecture #4: Built-in Types of Data objects Zhong Shao methods and classes graphics,
1/16/12 A Foundation for Programming CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) any program you might want to write Lecture #4: Built-in Types of Data objects Zhong Shao methods and classes graphics,
Lecture 2: Intro to Java
 Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features. Widely available. Widely used. Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs. Embraces full set of modern abstractions. 2 Why Java? Why Java? Java
Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features. Widely available. Widely used. Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs. Embraces full set of modern abstractions. 2 Why Java? Why Java? Java
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 1/29/11 6:37 AM! Why Programming? Why programming? Need to
1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 1/29/11 6:37 AM! Why Programming? Why programming? Need to
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? Idealized computer. "Please simulate the motion of a system of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton's laws of motion and gravity." 1.1 Your First Program Prepackaged software solutions.
Why Programming? Idealized computer. "Please simulate the motion of a system of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton's laws of motion and gravity." 1.1 Your First Program Prepackaged software solutions.
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what to do. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton s laws of motion and gravity. Prepackaged software
Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what to do. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton s laws of motion and gravity. Prepackaged software
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program 1 Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies,
1.1 Your First Program 1 Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies,
1.1 Your First Program! Naive ideal. Natural language instructions.
 Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. 1.1 Your First Program Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. 1.1 Your First Program Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring
 Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring 2016 1 Review of Java Basics Data Types Arrays NEW: multidimensional
Michele Van Dyne Museum 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II, Spring 2016 1 Review of Java Basics Data Types Arrays NEW: multidimensional
Conditionals, Loops, and Style. Control flow thus far. if statement. Control flow. Common branching statement Evaluate a boolean expression
 Conditionals, Loops, and Style Control flow thus far yes no x > y? max = x; max = y; public class ArgsExample time 0 String product = args[0]; time 1 int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); time 2 double
Conditionals, Loops, and Style Control flow thus far yes no x > y? max = x; max = y; public class ArgsExample time 0 String product = args[0]; time 1 int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); time 2 double
Conditionals, Loops, and Style
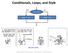 Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Lecture 2: Intro to Java
 Why Programming? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Idealized computer. "Please simulate the motion of a system of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton's laws of motion and gravity." Prepackaged software solutions.
Why Programming? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Idealized computer. "Please simulate the motion of a system of N heavenly bodies, subject to Newton's laws of motion and gravity." Prepackaged software solutions.
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject
Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 self-check: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #1 2 Data types type: A category or set of data
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 self-check: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #1 2 Data types type: A category or set of data
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Data and expressions reading: 2.1 self-check: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #1 Copyright
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education Data and expressions reading: 2.1 self-check: 1-4 videos: Ch. 2 #1 Copyright
A human being should be able to change a diaper, plan an invasion, butcher a hog, conn a ship, design a building, write a sonnet, balance accounts,
 A human being should be able to change a diaper, plan an invasion, butcher a hog, conn a ship, design a building, write a sonnet, balance accounts, build a wall, set a bone, comfort the dying, take orders,
A human being should be able to change a diaper, plan an invasion, butcher a hog, conn a ship, design a building, write a sonnet, balance accounts, build a wall, set a bone, comfort the dying, take orders,
1.1 Your First Program
 A human being should be able to change a diaper, plan an invasion, butcher a hog, conn a ship, design a building, write a sonnet, balance accounts, build a wall, set a bone, comfort the dying, take orders,
A human being should be able to change a diaper, plan an invasion, butcher a hog, conn a ship, design a building, write a sonnet, balance accounts, build a wall, set a bone, comfort the dying, take orders,
Static methods. Not actually a valid Java static method. Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen
 Static methods http://xkcd.com/221/ Not actually a valid Java static method Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen One big main(): Programs thus far public class DiceRolling public static void
Static methods http://xkcd.com/221/ Not actually a valid Java static method Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen One big main(): Programs thus far public class DiceRolling public static void
COMP-202 Unit 2: Java Basics. CONTENTS: Using Expressions and Variables Types Strings Methods
 COMP-202 Unit 2: Java Basics CONTENTS: Using Expressions and Variables Types Strings Methods Assignment 1 Assignment 1 posted on WebCt and course website. It is due May 18th st at 23:30 Worth 6% Part programming,
COMP-202 Unit 2: Java Basics CONTENTS: Using Expressions and Variables Types Strings Methods Assignment 1 Assignment 1 posted on WebCt and course website. It is due May 18th st at 23:30 Worth 6% Part programming,
Data and Variables. Data Types Expressions. String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators. Operators Precedence
 Data and Variables Data Types Expressions Operators Precedence String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators Review class All code in a java file is written in a class public
Data and Variables Data Types Expressions Operators Precedence String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators Review class All code in a java file is written in a class public
Lecture 2. COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall M. Jason Hinek Carleton University
 Lecture 2 COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall 2013 M. Jason Hinek Carleton University today s agenda a quick look back (last Thursday) assignment 0 is posted and is due this Friday at 2pm Java compiling
Lecture 2 COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall 2013 M. Jason Hinek Carleton University today s agenda a quick look back (last Thursday) assignment 0 is posted and is due this Friday at 2pm Java compiling
CSCI 135 Final Fall Problem Points Score Total 100
 CSCI 135 Final Fall 2011 Name: This exams consists of 11 problems on the following 14 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam. No calculators, computers, or
CSCI 135 Final Fall 2011 Name: This exams consists of 11 problems on the following 14 pages. You may use your two- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam. No calculators, computers, or
A foundation for programming. Classes and objects. Overview. Java primitive types. Primitive types Creating your own data types
 Classes and objects A foundation for programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build even bigger programs and reuse code http://www.flickr.com/photos/vermegrigio/5923415248/
Classes and objects A foundation for programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build even bigger programs and reuse code http://www.flickr.com/photos/vermegrigio/5923415248/
Inf1-OOP. Textbooks. Who and What. Organizational Issues. Why Java? Course Overview. Hello, World! in Java. Ewan Klein, Perdita Stevens
 Organizational Issues Inf1-OOP Course Overview Ewan Klein, Perdita Stevens School of Informatics January 12, 2013 Why Java? Hello, World! in Java Built-in Types Integers Floating-Point Numbers Type Conversion
Organizational Issues Inf1-OOP Course Overview Ewan Klein, Perdita Stevens School of Informatics January 12, 2013 Why Java? Hello, World! in Java Built-in Types Integers Floating-Point Numbers Type Conversion
JAVA Programming Fundamentals
 Chapter 4 JAVA Programming Fundamentals By: Deepak Bhinde PGT Comp.Sc. JAVA character set Character set is a set of valid characters that a language can recognize. It may be any letter, digit or any symbol
Chapter 4 JAVA Programming Fundamentals By: Deepak Bhinde PGT Comp.Sc. JAVA character set Character set is a set of valid characters that a language can recognize. It may be any letter, digit or any symbol
Inf1-OOP. Textbooks. Who and What. Organisational issues. Why Java? Course Overview. Hello, World! in Java
 Organisational issues Inf1-OOP Course Overview Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 11, 2014 Why Java? Hello, World! in Java Built-in Types Integers Floating-Point
Organisational issues Inf1-OOP Course Overview Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 11, 2014 Why Java? Hello, World! in Java Built-in Types Integers Floating-Point
Who and what can help? Inf1-OP. Lecturer: Timothy Hospedales TA: Natalia Zon
 Who and what can help? Inf1-OP Lecturer: Timothy Hospedales TA: Natalia Zon Course Overview Web: http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/ courses/inf1/op/ Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita
Who and what can help? Inf1-OP Lecturer: Timothy Hospedales TA: Natalia Zon Course Overview Web: http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/ courses/inf1/op/ Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 2 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 3 The computer s view Internally, computers store everything as 1 s and 0
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 2 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 3 The computer s view Internally, computers store everything as 1 s and 0
COMP 110/L Lecture 13. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 110/L Lecture 13 Kyle Dewey Outline char, charat() Command-line arguments and arrays Array access Array length Array update Integer.parseInt char, charat() char Represents a single character char
COMP 110/L Lecture 13 Kyle Dewey Outline char, charat() Command-line arguments and arrays Array access Array length Array update Integer.parseInt char, charat() char Represents a single character char
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site I have decided to keep this site for the whole semester I still hope to have blackboard up and running, but you
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site I have decided to keep this site for the whole semester I still hope to have blackboard up and running, but you
Eng. Mohammed S. Abdualal
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 3 Selections
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 3 Selections
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
Lesson 5: Introduction to the Java Basics: Java Arithmetic THEORY. Arithmetic Operators
 Lesson 5: Introduction to the Java Basics: Java Arithmetic THEORY Arithmetic Operators There are four basic arithmetic operations: OPERATOR USE DESCRIPTION + op1 + op2 Adds op1 and op2 - op1 + op2 Subtracts
Lesson 5: Introduction to the Java Basics: Java Arithmetic THEORY Arithmetic Operators There are four basic arithmetic operations: OPERATOR USE DESCRIPTION + op1 + op2 Adds op1 and op2 - op1 + op2 Subtracts
CIS133J. Working with Numbers in Java
 CIS133J Working with Numbers in Java Contents: Using variables with integral numbers Using variables with floating point numbers How to declare integral variables How to declare floating point variables
CIS133J Working with Numbers in Java Contents: Using variables with integral numbers Using variables with floating point numbers How to declare integral variables How to declare floating point variables
Java Foundations: Introduction to Program Design & Data Structures, 4e John Lewis, Peter DePasquale, Joseph Chase Test Bank: Chapter 2
 Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 topics: introduction to java, part 1
 topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
Program Fundamentals
 Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
Inf1-OP. Course Overview. Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein. February 26, School of Informatics
 Inf1-OP Course Overview Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics February 26, 2018 Administrative Stuff Who to contact for help? Lecturer: Volker
Inf1-OP Course Overview Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics February 26, 2018 Administrative Stuff Who to contact for help? Lecturer: Volker
Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Java basics: Compilation vs Interpretation Program structure Statements Values Variables Types Operators and Expressions
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Java basics: Compilation vs Interpretation Program structure Statements Values Variables Types Operators and Expressions
Full file at
 Java Programming, Fifth Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Using Data within a Program At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Teaching Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics Additional
Java Programming, Fifth Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Using Data within a Program At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Teaching Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics Additional
Topic 4 Expressions and variables
 Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types
 Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set
Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Building Java Programs. Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Declaration and Memory
 Declaration and Memory With the declaration int width; the compiler will set aside a 4-byte (32-bit) block of memory (see right) The compiler has a symbol table, which will have an entry such as Identifier
Declaration and Memory With the declaration int width; the compiler will set aside a 4-byte (32-bit) block of memory (see right) The compiler has a symbol table, which will have an entry such as Identifier
Chapter 2 Using Data. Instructor s Manual Table of Contents. At a Glance. Overview. Objectives. Teaching Tips. Quick Quizzes. Class Discussion Topics
 Java Programming, Sixth Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Using Data At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Teaching Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics Additional Projects Additional
Java Programming, Sixth Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Using Data At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Teaching Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics Additional Projects Additional
Visual Programming. Lecture 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals
 Visual Programming Lecture 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Outline Lecture 1 Review More types Methods Conditionals 2 Outline Lecture 1 Review More types
Visual Programming Lecture 2: More types, Methods, Conditionals Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Outline Lecture 1 Review More types Methods Conditionals 2 Outline Lecture 1 Review More types
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
Interpreted vs Compiled. Java Compile. Classes, Objects, and Methods. Hello World 10/6/2016. Python Interpreted. Java Compiled
 Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
COMP 250: Java Programming I. Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette
 COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch.
![1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 Elementray Programming / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 Elementray Programming / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch.](/thumbs/88/115141835.jpg) 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 41 / 68 Example Given the radius
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 41 / 68 Example Given the radius
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
Lecture #6-7 Methods
 Lecture #6-7 s 1. a. group of statements designed to perform a specific function b. may be reused many times i. in a particular program or ii. in multiple programs 2. Examples from the Java Library a.
Lecture #6-7 s 1. a. group of statements designed to perform a specific function b. may be reused many times i. in a particular program or ii. in multiple programs 2. Examples from the Java Library a.
What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements
 Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Java Static Methods. Recap: Decomposition Example. Recap: Static Method Example
 Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
More on methods and variables. Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen
 More on methods and variables Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Terminology of a method Goal: helper method than can draw a random integer between start and end (inclusive) access modifier
More on methods and variables Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Terminology of a method Goal: helper method than can draw a random integer between start and end (inclusive) access modifier
Java Basic Programming Constructs
 Java Basic Programming Constructs /* * This is your first java program. */ class HelloWorld{ public static void main(string[] args){ System.out.println( Hello World! ); A Closer Look at HelloWorld 2 This
Java Basic Programming Constructs /* * This is your first java program. */ class HelloWorld{ public static void main(string[] args){ System.out.println( Hello World! ); A Closer Look at HelloWorld 2 This
17 Statement: assignment statement: assigning an expression value 18 Age next year 19 Type: String: conversion: from int 21 Age next year 22 The full
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 3: Types, variables and expressions 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Age next year 5 Aim 6 Design: hard coding 7 Age next year 8 Type 9 Type: int 10 Variable 11 Variable:
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 3: Types, variables and expressions 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Age next year 5 Aim 6 Design: hard coding 7 Age next year 8 Type 9 Type: int 10 Variable 11 Variable:
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
Basics of Java Programming
 Basics of Java Programming Lecture 2 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 16, 2017 Components of a Java Program statements - A statement is some action or sequence of actions, given as a command in code. A statement
Basics of Java Programming Lecture 2 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 16, 2017 Components of a Java Program statements - A statement is some action or sequence of actions, given as a command in code. A statement
1. Download the JDK 6, from
 1. Install the JDK 1. Download the JDK 6, from http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/widget/jdk6.jsp. 2. Once the file is completed downloaded, execute it and accept the license agreement. 3. Select the
1. Install the JDK 1. Download the JDK 6, from http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/widget/jdk6.jsp. 2. Once the file is completed downloaded, execute it and accept the license agreement. 3. Select the
Hello World. n Variables store information. n You can think of them like boxes. n They hold values. n The value of a variable is its current contents
 Variables in a programming language Basic Computation (Savitch, Chapter 2) TOPICS Variables and Data Types Expressions and Operators Integers and Real Numbers Characters and Strings Input and Output Variables
Variables in a programming language Basic Computation (Savitch, Chapter 2) TOPICS Variables and Data Types Expressions and Operators Integers and Real Numbers Characters and Strings Input and Output Variables
CLASSES AND OBJECTS. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 CLASSES AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Primitive types Creating your own data types Classes Objects Instance variables Instance methods Constructors Arrays of objects A Foundation
CLASSES AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Primitive types Creating your own data types Classes Objects Instance variables Instance methods Constructors Arrays of objects A Foundation
Chapter 3 Selections. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
CS 61B Data Structures and Programming Methodology. June David Sun
 CS 61B Data Structures and Programming Methodology June 25 2008 David Sun Announcements Visit 387 Soda to arrange for after hours access to Soda Hall. Computer Science Undergraduate Association event:
CS 61B Data Structures and Programming Methodology June 25 2008 David Sun Announcements Visit 387 Soda to arrange for after hours access to Soda Hall. Computer Science Undergraduate Association event:
CS 302: Introduction to Programming
 CS 302: Introduction to Programming Lectures 2-3 CS302 Summer 2012 1 Review What is a computer? What is a computer program? Why do we have high-level programming languages? How does a high-level program
CS 302: Introduction to Programming Lectures 2-3 CS302 Summer 2012 1 Review What is a computer? What is a computer program? Why do we have high-level programming languages? How does a high-level program
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below.
 C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5)
 Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5) 1. Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java a) What is a computer? b) What is a computer program? c) A bit is a binary digit 0 or 1. A byte is a sequence of 8 bits.
Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5) 1. Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java a) What is a computer? b) What is a computer program? c) A bit is a binary digit 0 or 1. A byte is a sequence of 8 bits.
CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions
 CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 1 Character Strings A character string is an object in Java,
CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 1 Character Strings A character string is an object in Java,
Data Structure and Programming Languages
 204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
204700 Data Structure and Programming Languages Jakarin Chawachat From: http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computerscience/6-092-introduction-to-programming-in-java-january-iap-2010/index.htm
CSC 1214: Object-Oriented Programming
 CSC 1214: Object-Oriented Programming J. Kizito Makerere University e-mail: jkizito@cis.mak.ac.ug www: http://serval.ug/~jona materials: http://serval.ug/~jona/materials/csc1214 e-learning environment:
CSC 1214: Object-Oriented Programming J. Kizito Makerere University e-mail: jkizito@cis.mak.ac.ug www: http://serval.ug/~jona materials: http://serval.ug/~jona/materials/csc1214 e-learning environment:
CLASSES AND OBJECTS. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 CLASSES AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Primitive types Creating your own data types Classes Objects Instance variables Instance methods Constructors Arrays of objects A Foundation
CLASSES AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Primitive types Creating your own data types Classes Objects Instance variables Instance methods Constructors Arrays of objects A Foundation
Operators and Expressions
 Operators and Expressions Conversions. Widening and Narrowing Primitive Conversions Widening and Narrowing Reference Conversions Conversions up the type hierarchy are called widening reference conversions
Operators and Expressions Conversions. Widening and Narrowing Primitive Conversions Widening and Narrowing Reference Conversions Conversions up the type hierarchy are called widening reference conversions
Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution
 Unit 2, Part 1 Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Overview of the Programming Process Analysis/Specification
Unit 2, Part 1 Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Overview of the Programming Process Analysis/Specification
Classes and objects. Chapter 2: Head First Java: 2 nd Edi4on, K. Sierra, B. Bates
 Classes and objects Chapter 2: Head First Java: 2 nd Edi4on, K. Sierra, B. Bates Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 A founda4on for programming any program you might want to
Classes and objects Chapter 2: Head First Java: 2 nd Edi4on, K. Sierra, B. Bates Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 A founda4on for programming any program you might want to
The Math Class. Using various math class methods. Formatting the values.
 The Math Class Using various math class methods. Formatting the values. The Math class is used for mathematical operations; in our case some of its functions will be used. In order to use the Math class,
The Math Class Using various math class methods. Formatting the values. The Math class is used for mathematical operations; in our case some of its functions will be used. In order to use the Math class,
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
CS 177 Spring 2010 Exam I
 CS 177 Spring 2010 Exam I There are 25 multiple choice questions. Each one is worth 4 points. The total score for the exam is 100. Answer the multiple choice questions on the bubble sheet given. Fill in
CS 177 Spring 2010 Exam I There are 25 multiple choice questions. Each one is worth 4 points. The total score for the exam is 100. Answer the multiple choice questions on the bubble sheet given. Fill in
Review: Exam 1. Your First C++ Program. Declaration Statements. Tells the compiler. Examples of declaration statements
 Review: Exam 1 9/20/06 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 Your First C++ Program 1 //*********************************************************** 2 // File name: hello.cpp 3 // Author: Shereen Khoja
Review: Exam 1 9/20/06 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 Your First C++ Program 1 //*********************************************************** 2 // File name: hello.cpp 3 // Author: Shereen Khoja
Building Java Programs Chapter 2. bug. Primitive Data and Definite Loops. Copyright (c) Pearson All rights reserved. Software Flaw.
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 bug Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. 2 An Insect Software Flaw 3 4 Bug, Kentucky Bug Eyed 5 Cheesy Movie 6 Punch Buggy
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 bug Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. 2 An Insect Software Flaw 3 4 Bug, Kentucky Bug Eyed 5 Cheesy Movie 6 Punch Buggy
Building Java Programs Chapter 2
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. bug 2 An Insect 3 Software Flaw 4 Bug, Kentucky 5 Bug Eyed 6 Cheesy Movie 7 Punch Buggy
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. bug 2 An Insect 3 Software Flaw 4 Bug, Kentucky 5 Bug Eyed 6 Cheesy Movie 7 Punch Buggy
Key Concept: all programs can be broken down to a combination of one of the six instructions Assignment Statements can create variables to represent
 Programming 2 Key Concept: all programs can be broken down to a combination of one of the six instructions Assignment Statements can create variables to represent information Input can receive information
Programming 2 Key Concept: all programs can be broken down to a combination of one of the six instructions Assignment Statements can create variables to represent information Input can receive information
Lecture 6. Assignments. Summary - Variables. Summary Program Parts 1/29/18. Reading: 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4
 Assignments Lecture 6 Complete for Project 1 Reading: 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 Summary Program Parts Summary - Variables Class Header (class name matches the file name prefix) Class Body Because this is a program,
Assignments Lecture 6 Complete for Project 1 Reading: 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 Summary Program Parts Summary - Variables Class Header (class name matches the file name prefix) Class Body Because this is a program,
Java Programming Fundamentals. Visit for more.
 Chapter 4: Java Programming Fundamentals Informatics Practices Class XI (CBSE Board) Revised as per CBSE Curriculum 2015 Visit www.ip4you.blogspot.com for more. Authored By:- Rajesh Kumar Mishra, PGT (Comp.Sc.)
Chapter 4: Java Programming Fundamentals Informatics Practices Class XI (CBSE Board) Revised as per CBSE Curriculum 2015 Visit www.ip4you.blogspot.com for more. Authored By:- Rajesh Kumar Mishra, PGT (Comp.Sc.)
Building Java Programs Chapter 2
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set of data values. Constrains the operations that can
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set of data values. Constrains the operations that can
Chapter 3 Selection Statements
 Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
Calculations, Formatting and Conversions
 Chapter 5 Calculations, Formatting and Conversions What is in This Chapter? In this chapter we discuss how to do basic math calculations as well as use some readily available Math functions in JAVA. We
Chapter 5 Calculations, Formatting and Conversions What is in This Chapter? In this chapter we discuss how to do basic math calculations as well as use some readily available Math functions in JAVA. We
