Android CardView Tutorial
|
|
|
- Alberta Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Android CardView Tutorial by Kapil - Wednesday, April 13, YouTube Video We have already discussed about RecyclerView in the following tutorial Listing Items using RecyclerView and shown a recyclerview example in android studio. Today we will discuss about Android CardView in Android SDK which was introduced with the android material design through the support v7 library. We will show you how Android CardView can be implemented in a RecyclerView list. After reading this article you should feel comfortable creating Lists and Cards view in your android app. Android CardView provides a more advanced and flexible way of implementing complex and custom listview with more functionality that is required nowadays for our apps. We would be creating an Android CardView Example List app, where we will list 7 wonders of Modern World along with a Like Button and a Share Button. On clicking the Like Button it will get highlighted and show a message. Clicking the Share Button will provide you options to share the photo of the Item you clicked. After completion, the app would look like as shown in the video. (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle ).push({); Pre-requisites 1. Android Studio installed on your PC (Unix or Windows). You can learn how to install it here. 2. A real time android device (Smartphone or Tablet) configured with Android Studio.. 3. Before proceeding we advice you to go through the Recycler View tutorial at the following link => Listing Items using RecyclerView. Since we won't be repeating the concepts described in earlier above post. Creating a New Project 1. Open Android Studio and create a new project Android CardView Tutorial and company domain application.example.com (We have used our own company domain i.e androidtutorialpoint.com. Similarly you can use yours). 2. Click Next and choose Min SDK, we have kept the default value. Again Click Next and Choose Blank Activity. 1 / 15
2 3. Choose the Activity as MainActivity and click next. 4. Leave all other things as default and Click Finish. A new project will be created and gradle will resolve all the dependencies. We would be listing wonders of the world so create a new WonderModel. class which will have all the field as well getter,setter methods required for a wonder. Add the following code to the class WonderModel. package com.androidtutorialpoint.cardviewtutorial; public class WonderModel { String cardname; int imageresourceid; int isfav; int isturned; public int getisturned() { return isturned; public void setisturned(int isturned) { this.isturned = isturned; public int getisfav() { return isfav; public void setisfav(int isfav) { this.isfav = isfav; public String getcardname() { return cardname; public void setcardname(string cardname) { this.cardname = cardname; public int getimageresourceid() { return imageresourceid; 2 / 15
3 public void setimageresourceid(int imageresourceid) { this.imageresourceid = imageresourceid; Adding Support Library for RecyclerView Add the following code to the App Level build.gradle compile 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:23.1.1' compile 'com.android.support:cardview-v7:23.1.1' Now, Gradle will sync your project and add the dependencies. Add a RecyclerView 1. Create a layout file by Right-clicking on the res/layout directory and selectingnew? Layout resource file. Name the file fragment_card. and click OK to create the file.open the file add the following code. fragment_card. <RelativeLayout ns:android=" ns:tools=" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingbottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingleft="@dimen/activity_left_margin" android:paddingright="@dimen/activity_right_margin" android:paddingtop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".myactivity"> <android.support.v7.widget.recyclerview android:id="@+id/cardview" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </RelativeLayout> Let's create a layout file. Create a new Layout resource file name it recycle_items. and paste the following code. 3 / 15
4 recycle_items. <android.support.v7.widget.cardview ns:android=" ns:card_view=" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="5dp" card_view:cardcornerradius="4dp"> <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:weightsum="4"> <LinearLayout android:layout_height="0dip" android:layout_weight="3.2" android:orientation="vertical"> <FrameLayout android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"> <ImageView android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_gravity="center" android:scaletype="centercrop" /> <LinearLayout android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="left bottom" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView 4 / 15
5 android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:padding="16dp" android:textcolor="#ffffff" android:textstyle="bold" /> </LinearLayout> </FrameLayout> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_height="0dip" android:layout_weight="0.8" android:gravity="center right" android:orientation="horizontal"> <ImageView /> <ImageView /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout> </android.support.v7.widget.cardview> The layout is pretty much self explanatory, We have used a combination of LinearLayout and FrameLayout's to generate a beautiful Android Carview layout. We have an ImageView for the android cardview background and a TextView for the displaying the name of the place. Then we have used another LinearLayout for rendering the Like and Share buttons. Adding The Functionality 1. Create a new fragment, name it CardFragment. and add the following code. Let's use arrays to store the name and ImageId for each 7 wonders. We have already added 5 / 15
6 the photos of the places to the drawable folder. You can download the code by clicking on the Download Now Button provided at the top. CardFragment. String Wonders = {"Chichen Itza","Christ the Redeemer","Great Wall of China","Machu Picchu","Petra","Taj Mahal","Colosseum"; int Images = {R.drawable.chichen_itza,R.drawable.christ_the_redeemer,R.drawable.grea t_wall_of_china,r.drawable.machu_picchu,r.drawable.petra,r.drawable.taj_mahal,r.dra wable.colosseum; 2. In the oncreate() method we use the initializelist() method to initialize the ArrayList in Android Cardview which will be passed to the Adapter later. public void oncreate(@nullable Bundle savedinstancestate) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate); initializelist(); getactivity().settitle("7 Wonders of the Modern World"); Following is the implementation of the intializelist() method. Add this method after the oncreate() method in the file. public void initializelist() { listitems.clear(); for(int i =0;i<7;i++){ WonderModel item = new WonderModel(); item.setcardname(wonders[i]); item.setimageresourceid(images[i]); item.setisfav(0); item.setisturned(0); listitems.add(item); 6 / 15
7 3. A view Holder is required to hold on to the views, so add the following code. public class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { public TextView titletextview; public ImageView coverimageview; public ImageView likeimageview; public ImageView shareimageview; public MyViewHolder(View v) { super(v); titletextview = (TextView) v.findviewbyid(r.id.titletextview); coverimageview = (ImageView) v.findviewbyid(r.id.coverimageview); likeimageview = (ImageView) v.findviewbyid(r.id.likeimageview); shareimageview = (ImageView) v.findviewbyid(r.id.shareimageview); likeimageview.setonclicklistener(new View.OnClickListener() { public void onclick(view v) { int id = (int)likeimageview.gettag(); if( id == R.drawable.ic_like){ likeimageview.settag(r.drawable.ic_liked); likeimageview.setimageresource(r.drawable.ic_liked); Toast.makeText(getActivity(),titleTextView.getText()+" added to favourites",toast.length_short).show(); else{ likeimageview.settag(r.drawable.ic_like); likeimageview.setimageresource(r.drawable.ic_like); Toast.makeText(getActivity(),titleTextView.getText()+" removed from favourites",toast.length_short).show(); ); shareimageview.setonclicklistener(new View.OnClickListener() { public void onclick(view v) { 7 / 15
8 Uri imageuri = Uri.parse(ContentResolver.SCHEME_ANDROID_RESOURCE + "://" + getresources().getresourcepackagename(coverimageview.getid()) + '/' + "drawable" + '/' + getresources().getresourceentryname((int)coverimageview.gettag())); Intent shareintent = new Intent(); shareintent.setaction(intent.action_send); shareintent.putextra(intent.extra_stream,imageuri); shareintent.settype("image/jpeg"); startactivity(intent.createchooser(shareintent, getresources().gettext(r.string.send_to))); ); The above code extends the RecyclerView.ViewHolder class and references the ImageView and the TextViews for each view it will be holding. It also has setonclicklistener() attached to the likeimageview and the shareimageview. On clicking the like button the state of the button is toggled and it shows a corresponding message that it has added/removed the item to/from favourites. In the OnClick() for the shareimageview an Intent is fired that shows an option to share the image of the place you have selected. 4. Next, extend the RecyclerView.Adapter class, this adapter is link between the RecyclerView and the data which we want to list. It creates required ViewHolders and also binds the ViewHolder to data from the WonderModel class. It has three main methods: 1. oncreateviewholder() : Inflates the layout and creates a new view Holder. 2. onbindviewhodler() : Binds the data to the view holder. 3. getitemcount() : returns the size of the data to be dispalyed. Use the following code to create a MyAdapter. public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyViewHolder> { private ArrayList<WonderModel> list; public MyAdapter(ArrayList<WonderModel> Data) { 8 / 15
9 list = Data; public MyViewHolder oncreateviewholder(viewgroup parent,int viewtype) { // create a new view View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.recycle_items, parent, false); MyViewHolder holder = new MyViewHolder(view); return holder; public void onbindviewholder(final MyViewHolder holder, int position) { holder.titletextview.settext(list.get(position).getcardname()); holder.coverimageview.setimageresource(list.get(position).getimageresourceid()); holder.coverimageview.settag(list.get(position).getimageresourceid()); holder.likeimageview.settag(r.drawable.ic_like); public int getitemcount() { return list.size(); 5. In the oncreateview() method of the CardFragment., we reference the RecyclerView that was added in the layout file. We create a new LinearLayoutManager and later set the RecyclerView to use it. The purpose of the LayoutManager is to handle the positioning of the list items and scrolling behaviour. public View oncreateview(layoutinflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedinstancestate) { View view = inflater.inflate(r.layout.fragment_card, container, false); MyRecyclerView = (RecyclerView) view.findviewbyid(r.id.cardview); MyRecyclerView.setHasFixedSize(true); LinearLayoutManager MyLayoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(getActivity()); MyLayoutManager.setOrientation(LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL); 9 / 15
10 if (listitems.size() > 0 & MyRecyclerView!= null) { MyRecyclerView.setAdapter(new MyAdapter(listitems)); MyRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(MyLayoutManager); return view; Here is the completed CardFragment. file. CardFragment. package com.androidtutorialpoint.cardviewtutorial; import android.content.contentresolver; import android.content.intent; import android.net.uri; import android.os.bundle; import android.support.annotation.nullable; import android.support.v4.app.fragment; import android.support.v7.widget.linearlayoutmanager; import android.support.v7.widget.recyclerview; import android.support.v7.widget.toolbar; import android.view.layoutinflater; import android.view.view; import android.view.viewgroup; import android.widget.imageview; import android.widget.textview; import android.widget.toast; import.util.arraylist; public class CardFragment extends Fragment { ArrayList<WonderModel> listitems = new ArrayList<>(); RecyclerView MyRecyclerView; String Wonders = {"Chichen Itza","Christ the Redeemer","Great Wall of China","Machu Picchu","Petra","Taj Mahal","Colosseum"; int Images = {R.drawable.chichen_itza,R.drawable.christ_the_redeemer,R.drawable.grea t_wall_of_china,r.drawable.machu_picchu,r.drawable.petra,r.drawable.taj_mahal,r.dra wable.colosseum; public void oncreate(@nullable Bundle savedinstancestate) { 10 / 15
11 super.oncreate(savedinstancestate); initializelist(); getactivity().settitle("7 Wonders of the Modern World"); public View oncreateview(layoutinflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedinstancestate) { View view = inflater.inflate(r.layout.fragment_card, container, false); MyRecyclerView = (RecyclerView) view.findviewbyid(r.id.cardview); MyRecyclerView.setHasFixedSize(true); LinearLayoutManager MyLayoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(getActivity()); MyLayoutManager.setOrientation(LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL); if (listitems.size() > 0 & MyRecyclerView!= null) { MyRecyclerView.setAdapter(new MyAdapter(listitems)); MyRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(MyLayoutManager); return view; public void onactivitycreated(bundle savedinstancestate) { super.onactivitycreated(savedinstancestate); public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyViewHolder> { private ArrayList<WonderModel> list; public MyAdapter(ArrayList<WonderModel> Data) { list = Data; public MyViewHolder oncreateviewholder(viewgroup parent,int viewtype) { // create a new view View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.recycle_items, parent, false); MyViewHolder holder = new MyViewHolder(view); return holder; public void onbindviewholder(final MyViewHolder holder, int position) { 11 / 15
12 holder.titletextview.settext(list.get(position).getcardname()); holder.coverimageview.setimageresource(list.get(position).getimageresourceid()); holder.coverimageview.settag(list.get(position).getimageresourceid()); holder.likeimageview.settag(r.drawable.ic_like); public int getitemcount() { return list.size(); public class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { public TextView titletextview; public ImageView coverimageview; public ImageView likeimageview; public ImageView shareimageview; public MyViewHolder(View v) { super(v); titletextview = (TextView) v.findviewbyid(r.id.titletextview); coverimageview = (ImageView) v.findviewbyid(r.id.coverimageview); likeimageview = (ImageView) v.findviewbyid(r.id.likeimageview); shareimageview = (ImageView) v.findviewbyid(r.id.shareimageview); likeimageview.setonclicklistener(new View.OnClickListener() { public void onclick(view v) { int id = (int)likeimageview.gettag(); if( id == R.drawable.ic_like){ likeimageview.settag(r.drawable.ic_liked); likeimageview.setimageresource(r.drawable.ic_liked); Toast.makeText(getActivity(),titleTextView.getText()+" added to favourites",toast.length_short).show(); else{ likeimageview.settag(r.drawable.ic_like); likeimageview.setimageresource(r.drawable.ic_like); Toast.makeText(getActivity(),titleTextView.getText()+" removed from favourites",toast.length_short).show(); 12 / 15
13 ); shareimageview.setonclicklistener(new View.OnClickListener() { public void onclick(view v) { Uri imageuri = Uri.parse(ContentResolver.SCHEME_ANDROID_RESOURCE + "://" + getresources().getresourcepackagename(coverimageview.getid()) + '/' + "drawable" + '/' + getresources().getresourceentryname((int)coverimageview.gettag())); Intent shareintent = new Intent(); shareintent.setaction(intent.action_send); shareintent.putextra(intent.extra_stream,imageuri); shareintent.settype("image/jpeg"); startactivity(intent.createchooser(shareintent, getresources().gettext(r.string.send_to))); ); public void initializelist() { listitems.clear(); for(int i =0;i<7;i++){ WonderModel item = new WonderModel(); item.setcardname(wonders[i]); item.setimageresourceid(images[i]); item.setisfav(0); item.setisturned(0); listitems.add(item); 6. Next, we will be hosting CardFragment in the MainActivity. Open MainActivity. and add the following code. 13 / 15
14 MainActivity package com.androidtutorialpoint.cardviewtutorial; import android.os.bundle; import android.support.v4.app.fragment; import android.support.v4.app.fragmentmanager; import android.support.v7.app.appcompatactivity; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate); setcontentview(r.layout.activity_main); FragmentManager fm = getsupportfragmentmanager(); Fragment fragment = fm.findfragmentbyid(r.id.fragmentcontainer); if (fragment == null) { fragment = new CardFragment(); ; fm.begintransaction().add(r.id.fragmentcontainer, fragment).commit(); The layout file for MainActivity i.e. activity_main. consists of a FrameLayout as a fragmentcontainer. activity_main. <? version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout ns:android=" ns:tools=" android:id="@+id/fragmentcontainer" android:layout_height="match_parent" 14 / 15
15 Powered by TCPDF ( Android CardView Tutorial tools:context=".mainactivity"> </FrameLayout> Run the App and you should see a scrollable List of 7 Wonders of the world. Try scrolling through and clicking Like or Share to share the photo. So our Android Cardview Tutorial is complete. Please comment in case you have any doubts or suggestions. (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle ).push({); What's Next We hope this tutorial will help you getting started with RecyclerView and CardView on Android. You can reuse the cards to create beautiful apps that have a list interface. We will soon be covering more such tutorials. Till then stay tuned and don't forget to subscribe our blog for latest android tutorials. Also do Like our Facebook Page or Add us on Twitter. Click on the Download Now button to download the full code. PDF generated by Kalin's PDF Creation Station 15 / 15
05. RecyclerView and Styles
 05. RecyclerView and Styles 08.03.2018 1 Agenda Intents Creating Lists with RecyclerView Creating Cards with CardView Application Bar Menu Styles and Themes 2 Intents 3 What is Intent? An Intent is an
05. RecyclerView and Styles 08.03.2018 1 Agenda Intents Creating Lists with RecyclerView Creating Cards with CardView Application Bar Menu Styles and Themes 2 Intents 3 What is Intent? An Intent is an
Android Navigation Drawer for Sliding Menu / Sidebar
 Android Navigation Drawer for Sliding Menu / Sidebar by Kapil - Tuesday, December 15, 2015 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/material-design/android-navigation-drawer-for-sliding-menusidebar/ YouTube
Android Navigation Drawer for Sliding Menu / Sidebar by Kapil - Tuesday, December 15, 2015 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/material-design/android-navigation-drawer-for-sliding-menusidebar/ YouTube
Fragment Example Create the following files and test the application on emulator or device.
 Fragment Example Create the following files and test the application on emulator or device. File: AndroidManifest.xml
Fragment Example Create the following files and test the application on emulator or device. File: AndroidManifest.xml
CSE 660 Lab 3 Khoi Pham Thanh Ho April 19 th, 2015
 CSE 660 Lab 3 Khoi Pham Thanh Ho April 19 th, 2015 Comment and Evaluation: This lab introduces us about Android SDK and how to write a program for Android platform. The calculator is pretty easy, everything
CSE 660 Lab 3 Khoi Pham Thanh Ho April 19 th, 2015 Comment and Evaluation: This lab introduces us about Android SDK and how to write a program for Android platform. The calculator is pretty easy, everything
Android JSON Parsing Tutorial
 Android JSON Parsing Tutorial by Kapil - Thursday, May 19, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/networking/json-parsing-tutorial-android/ YouTube Video JSON(JavaScript Object Notation), is a language
Android JSON Parsing Tutorial by Kapil - Thursday, May 19, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/networking/json-parsing-tutorial-android/ YouTube Video JSON(JavaScript Object Notation), is a language
Fragments. Lecture 11
 Fragments Lecture 11 Situational layouts Your app can use different layouts in different situations Different device type (tablet vs. phone vs. watch) Different screen size Different orientation (portrait
Fragments Lecture 11 Situational layouts Your app can use different layouts in different situations Different device type (tablet vs. phone vs. watch) Different screen size Different orientation (portrait
Intents. Your first app assignment
 Intents Your first app assignment We will make this. Decidedly lackluster. Java Code Java Code XML XML Preview XML Java Code Java Code XML Buttons that work
Intents Your first app assignment We will make this. Decidedly lackluster. Java Code Java Code XML XML Preview XML Java Code Java Code XML Buttons that work
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING Application Tip: Managing Screen Orientation
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Managing Screen Orientation ORIENTATIONS Portrait Landscape Reverse portrait Reverse landscape ON REVERSE PORTRAIT Android: all four orientations are
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Managing Screen Orientation ORIENTATIONS Portrait Landscape Reverse portrait Reverse landscape ON REVERSE PORTRAIT Android: all four orientations are
M.A.D ASSIGNMENT # 2 REHAN ASGHAR BSSE 15126
 M.A.D ASSIGNMENT # 2 REHAN ASGHAR BSSE 15126 Submitted to: Sir Waqas Asghar MAY 23, 2017 SUBMITTED BY: REHAN ASGHAR Intent in Android What are Intent? An Intent is a messaging object you can use to request
M.A.D ASSIGNMENT # 2 REHAN ASGHAR BSSE 15126 Submitted to: Sir Waqas Asghar MAY 23, 2017 SUBMITTED BY: REHAN ASGHAR Intent in Android What are Intent? An Intent is a messaging object you can use to request
Open Lecture Mobile Programming. Intro to Material Design
 Open Lecture Mobile Programming Intro to Material Design Agenda Introduction to Material Design Applying a Material Theme Toolbar/Action Bar Navigation Drawer RecyclerView CardView Support Design Widgets/Tools
Open Lecture Mobile Programming Intro to Material Design Agenda Introduction to Material Design Applying a Material Theme Toolbar/Action Bar Navigation Drawer RecyclerView CardView Support Design Widgets/Tools
Adapter.
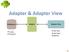 1 Adapter An Adapter object acts as a bridge between an AdapterView and the underlying data for that view The Adapter provides access to the data items The Adapter is also responsible for making a View
1 Adapter An Adapter object acts as a bridge between an AdapterView and the underlying data for that view The Adapter provides access to the data items The Adapter is also responsible for making a View
Mobile Application Development Lab [] Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator.
![Mobile Application Development Lab [] Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. Mobile Application Development Lab [] Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator.](/thumbs/96/129287620.jpg) Simple Android Application for Native Calculator Aim: To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. Procedure: Creating a New project: Open Android Stdio and then click on File -> New
Simple Android Application for Native Calculator Aim: To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. Procedure: Creating a New project: Open Android Stdio and then click on File -> New
Android Volley Tutorial
 Android Volley Tutorial by Kapil - Monday, May 16, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/networking/android-volley-tutorial/ YouTube Video Volley is an HTTP library developed by Google to ease networking
Android Volley Tutorial by Kapil - Monday, May 16, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/networking/android-volley-tutorial/ YouTube Video Volley is an HTTP library developed by Google to ease networking
Arrays of Buttons. Inside Android
 Arrays of Buttons Inside Android The Complete Code Listing. Be careful about cutting and pasting.
Arrays of Buttons Inside Android The Complete Code Listing. Be careful about cutting and pasting.
android-espresso #androidespresso
 android-espresso #androidespresso Table of Contents About 1 Chapter 1: Getting started with android-espresso 2 Remarks 2 Examples 2 Espresso setup instructions 2 Checking an Options Menu items (using Spoon
android-espresso #androidespresso Table of Contents About 1 Chapter 1: Getting started with android-espresso 2 Remarks 2 Examples 2 Espresso setup instructions 2 Checking an Options Menu items (using Spoon
Android Apps Development for Mobile and Tablet Device (Level I) Lesson 2
 Workshop 1. Compare different layout by using Change Layout button (Page 1 5) Relative Layout Linear Layout (Horizontal) Linear Layout (Vertical) Frame Layout 2. Revision on basic programming skill - control
Workshop 1. Compare different layout by using Change Layout button (Page 1 5) Relative Layout Linear Layout (Horizontal) Linear Layout (Vertical) Frame Layout 2. Revision on basic programming skill - control
Appendix A : Android Studio Code For Android
 Appendix A : Android Studio Code For Android Monitoring : ` public Pubnub pubnub; public static final String PUBLISH_KEY = "pub-c-798bd0f6-540b-48af-9e98-7d0028a5132a"; public static final String SUBSCRIBE_KEY
Appendix A : Android Studio Code For Android Monitoring : ` public Pubnub pubnub; public static final String PUBLISH_KEY = "pub-c-798bd0f6-540b-48af-9e98-7d0028a5132a"; public static final String SUBSCRIBE_KEY
ActionBar. import android.support.v7.app.actionbaractivity; public class MyAppBarActivity extends ActionBarActivity { }
 Android ActionBar import android.support.v7.app.actionbaractivity; public class MyAppBarActivity extends ActionBarActivity { Layout, activity.xml
Android ActionBar import android.support.v7.app.actionbaractivity; public class MyAppBarActivity extends ActionBarActivity { Layout, activity.xml
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING UI Specification: Approaches
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 UI Specification: Approaches UIS: APPROACHES Programmatic approach: UI elements are created inside the application code Declarative approach: UI elements are listed
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 UI Specification: Approaches UIS: APPROACHES Programmatic approach: UI elements are created inside the application code Declarative approach: UI elements are listed
Practical 1.ListView example
 Practical 1.ListView example In this example, we show you how to display a list of fruit name via ListView. Android Layout file File : res/layout/list_fruit.xml
Practical 1.ListView example In this example, we show you how to display a list of fruit name via ListView. Android Layout file File : res/layout/list_fruit.xml
MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 3. Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE AUGUST 25, SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept.
 MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 3 Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE 7 15126 AUGUST 25, 2017 SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept. MainActivity.java File package com.example.tutorialspoint; import android.manifest;
MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 3 Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE 7 15126 AUGUST 25, 2017 SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept. MainActivity.java File package com.example.tutorialspoint; import android.manifest;
Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB)
 Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB) In this exercise, we will create a simple Android application that uses IBM Bluemix Cloudant NoSQL DB. The application
Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB) In this exercise, we will create a simple Android application that uses IBM Bluemix Cloudant NoSQL DB. The application
Our First Android Application
 Mobile Application Development Lecture 04 Imran Ihsan Our First Android Application Even though the HelloWorld program is trivial in introduces a wealth of new ideas the framework, activities, manifest,
Mobile Application Development Lecture 04 Imran Ihsan Our First Android Application Even though the HelloWorld program is trivial in introduces a wealth of new ideas the framework, activities, manifest,
M.A.D Assignment # 1
 Submitted by: Rehan Asghar Roll no: BSSE (7) 15126 M.A.D Assignment # 1 Submitted to: Sir Waqas Asghar Submitted by: M. Rehan Asghar 4/25/17 Roll no: BSSE 7 15126 XML Code: Calculator Android App
Submitted by: Rehan Asghar Roll no: BSSE (7) 15126 M.A.D Assignment # 1 Submitted to: Sir Waqas Asghar Submitted by: M. Rehan Asghar 4/25/17 Roll no: BSSE 7 15126 XML Code: Calculator Android App
Android Programs Day 5
 Android Programs Day 5 //Android Program to demonstrate the working of Options Menu. 1. Create a New Project. 2. Write the necessary codes in the MainActivity.java to create OptionMenu. 3. Add the oncreateoptionsmenu()
Android Programs Day 5 //Android Program to demonstrate the working of Options Menu. 1. Create a New Project. 2. Write the necessary codes in the MainActivity.java to create OptionMenu. 3. Add the oncreateoptionsmenu()
Mobile Computing Fragments
 Fragments APM@FEUP 1 Fragments (1) Activities are used to define a full screen interface and its functionality That s right for small screen devices (smartphones) In bigger devices we can have more interface
Fragments APM@FEUP 1 Fragments (1) Activities are used to define a full screen interface and its functionality That s right for small screen devices (smartphones) In bigger devices we can have more interface
Fragments. Lecture 10
 Fragments Lecture 10 Situa2onal layouts Your app can use different layouts in different situa2ons Different device type (tablet vs. phone vs. watch) Different screen size Different orienta2on (portrait
Fragments Lecture 10 Situa2onal layouts Your app can use different layouts in different situa2ons Different device type (tablet vs. phone vs. watch) Different screen size Different orienta2on (portrait
Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts
 Introduction to Android Application Development, Android Essentials, Fifth Edition Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts Chapter 8 Overview Create user interfaces in Android by defining resource files or
Introduction to Android Application Development, Android Essentials, Fifth Edition Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts Chapter 8 Overview Create user interfaces in Android by defining resource files or
 Statistics http://www.statista.com/topics/840/smartphones/ http://www.statista.com/topics/876/android/ http://www.statista.com/statistics/271774/share-of-android-platforms-on-mobile-devices-with-android-os/
Statistics http://www.statista.com/topics/840/smartphones/ http://www.statista.com/topics/876/android/ http://www.statista.com/statistics/271774/share-of-android-platforms-on-mobile-devices-with-android-os/
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING Application Tip: Switching UIs
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2015-16 Application Tip: Switching UIs THE PROBLEM How to switch from one UI to another Each UI is associated with a distinct class that controls it Solution shown: two UIs,
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2015-16 Application Tip: Switching UIs THE PROBLEM How to switch from one UI to another Each UI is associated with a distinct class that controls it Solution shown: two UIs,
ListView Containers. Resources. Creating a ListView
 ListView Containers Resources https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/listview.html https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/listview.html Creating a ListView A ListView is a
ListView Containers Resources https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/listview.html https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/listview.html Creating a ListView A ListView is a
Hello World. Lesson 1. Android Developer Fundamentals. Android Developer Fundamentals. Layouts, and. NonCommercial
 Hello World Lesson 1 This work is licensed This under work a Creative is is licensed Commons under a a Attribution-NonCommercial Creative 4.0 Commons International Attribution- License 1 NonCommercial
Hello World Lesson 1 This work is licensed This under work a Creative is is licensed Commons under a a Attribution-NonCommercial Creative 4.0 Commons International Attribution- License 1 NonCommercial
Android Application Model I
 Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Reading: Big Nerd Ranch Guide, Chapters 3, 5 (Activities);
Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Reading: Big Nerd Ranch Guide, Chapters 3, 5 (Activities);
Basic GUI elements - exercises
 Basic GUI elements - exercises https://developer.android.com/studio/index.html LIVE DEMO Please create a simple application, which will be used to calculate the area of basic geometric figures. To add
Basic GUI elements - exercises https://developer.android.com/studio/index.html LIVE DEMO Please create a simple application, which will be used to calculate the area of basic geometric figures. To add
Diving into Android. By Jeroen Tietema. Jeroen Tietema,
 Diving into Android By Jeroen Tietema Jeroen Tietema, 2015 1 Requirements 4 Android SDK 1 4 Android Studio (or your IDE / editor of choice) 4 Emulator (Genymotion) or a real device. 1 See https://developer.android.com
Diving into Android By Jeroen Tietema Jeroen Tietema, 2015 1 Requirements 4 Android SDK 1 4 Android Studio (or your IDE / editor of choice) 4 Emulator (Genymotion) or a real device. 1 See https://developer.android.com
Dynamically Create Admob Banner and Interstitial Ads
 Dynamically Create Admob Banner and Interstitial Ads activity_main.xml file 0 0 0
Dynamically Create Admob Banner and Interstitial Ads activity_main.xml file 0 0 0
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING Application Tip: Saving State
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Saving State THE PROBLEM How to save the state (of a UI, for instance) so that it survives even when the application is closed/killed The state should
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Saving State THE PROBLEM How to save the state (of a UI, for instance) so that it survives even when the application is closed/killed The state should
Tip Calculator. xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
 Tip Calculator activity_main.xml
Tip Calculator activity_main.xml
Android Workshop: Model View Controller ( MVC):
 Android Workshop: Android Details: Android is framework that provides java programmers the ability to control different aspects of smart devices. This interaction happens through the Android SDK (Software
Android Workshop: Android Details: Android is framework that provides java programmers the ability to control different aspects of smart devices. This interaction happens through the Android SDK (Software
Mobile Development Lecture 10: Fragments
 Mobile Development Lecture 10: Fragments Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Elgayyar.weebly.com Situational Layouts Your app can use different layout in different situations: different device type
Mobile Development Lecture 10: Fragments Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Elgayyar.weebly.com Situational Layouts Your app can use different layout in different situations: different device type
Tablets have larger displays than phones do They can support multiple UI panes / user behaviors at the same time
 Tablets have larger displays than phones do They can support multiple UI panes / user behaviors at the same time The 1 activity 1 thing the user can do heuristic may not make sense for larger devices Application
Tablets have larger displays than phones do They can support multiple UI panes / user behaviors at the same time The 1 activity 1 thing the user can do heuristic may not make sense for larger devices Application
User Interface Development. CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr.
 User Interface Development CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Outline UI Support in Android Fragments 2 UI Support in the Android
User Interface Development CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Outline UI Support in Android Fragments 2 UI Support in the Android
When programming in groups of people, it s essential to version the code. One of the most popular versioning tools is git. Some benefits of git are:
 ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 1.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 preparations Read through this document carefully. In order to pass lab 2, you will need to understand the topics presented in
ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 1.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 preparations Read through this document carefully. In order to pass lab 2, you will need to understand the topics presented in
Android SQLite Database Tutorial - CRUD Operations
 Android SQLite Database Tutorial - CRUD Operations by Kapil - Monday, March 21, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/storage/android-sqlite-database-tutorial/ YouTube Video Android SQLite Introduction
Android SQLite Database Tutorial - CRUD Operations by Kapil - Monday, March 21, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/storage/android-sqlite-database-tutorial/ YouTube Video Android SQLite Introduction
Android Application Model I. CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr.
 Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Framework Support (e.g. Android) 2 Framework Capabilities
Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Framework Support (e.g. Android) 2 Framework Capabilities
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING UI and Android
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 UI and Android STANDARD GESTURES (1/2) UI classes inheriting from View allow to set listeners that respond to basic gestures. Listeners are defined by suitable interfaces.
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 UI and Android STANDARD GESTURES (1/2) UI classes inheriting from View allow to set listeners that respond to basic gestures. Listeners are defined by suitable interfaces.
ANDROID USER INTERFACE
 1 ANDROID USER INTERFACE Views FUNDAMENTAL UI DESIGN Visual interface element (controls or widgets) ViewGroup Contains multiple widgets. Layouts inherit the ViewGroup class Activities Screen being displayed
1 ANDROID USER INTERFACE Views FUNDAMENTAL UI DESIGN Visual interface element (controls or widgets) ViewGroup Contains multiple widgets. Layouts inherit the ViewGroup class Activities Screen being displayed
LAMPIRAN PROGRAM. public class Listdata_adiktif extends ArrayAdapter<ModelData_adiktif> {
 1 LAMPIRAN PROGRAM JAVA Listdata_adiktif.java package com.example.win.api.adapter; import android.content.context; import android.support.annotation.nonnull; import android.view.layoutinflater; import
1 LAMPIRAN PROGRAM JAVA Listdata_adiktif.java package com.example.win.api.adapter; import android.content.context; import android.support.annotation.nonnull; import android.view.layoutinflater; import
Fragments were added to the Android API in Honeycomb, API 11. The primary classes related to fragments are: android.app.fragment
 FRAGMENTS Fragments An activity is a container for views When you have a larger screen device than a phone like a tablet it can look too simple to use phone interface here. Fragments Mini-activities, each
FRAGMENTS Fragments An activity is a container for views When you have a larger screen device than a phone like a tablet it can look too simple to use phone interface here. Fragments Mini-activities, each
Android/Java Lightning Tutorial JULY 30, 2018
 Android/Java Lightning Tutorial JULY 30, 2018 Java Android uses java as primary language Resource : https://github.mit.edu/6178-2017/lec1 Online Tutorial : https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/inde
Android/Java Lightning Tutorial JULY 30, 2018 Java Android uses java as primary language Resource : https://github.mit.edu/6178-2017/lec1 Online Tutorial : https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/inde
Programming with Android: Introduction. Layouts. Luca Bedogni. Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna
 Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Uniersità di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and a View is reaction
Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Uniersità di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and a View is reaction
CSE 660 Lab 7. Submitted by: Arumugam Thendramil Pavai. 1)Simple Remote Calculator. Server is created using ServerSocket class of java. Server.
 CSE 660 Lab 7 Submitted by: Arumugam Thendramil Pavai 1)Simple Remote Calculator Server is created using ServerSocket class of java Server.java import java.io.ioexception; import java.net.serversocket;
CSE 660 Lab 7 Submitted by: Arumugam Thendramil Pavai 1)Simple Remote Calculator Server is created using ServerSocket class of java Server.java import java.io.ioexception; import java.net.serversocket;
UI Fragment.
 UI Fragment 1 Contents Fragments Overviews Lifecycle of Fragments Creating Fragments Fragment Manager and Transactions Adding Fragment to Activity Fragment-to-Fragment Communication Fragment SubClasses
UI Fragment 1 Contents Fragments Overviews Lifecycle of Fragments Creating Fragments Fragment Manager and Transactions Adding Fragment to Activity Fragment-to-Fragment Communication Fragment SubClasses
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.internet"/>
 Chapter 11 Playing Video 11.1 Introduction We have discussed how to play audio in Chapter 9 using the class MediaPlayer. This class can also play video clips. In fact, the Android multimedia framework
Chapter 11 Playing Video 11.1 Introduction We have discussed how to play audio in Chapter 9 using the class MediaPlayer. This class can also play video clips. In fact, the Android multimedia framework
Java & Android. Java Fundamentals. Madis Pink 2016 Tartu
 Java & Android Java Fundamentals Madis Pink 2016 Tartu 1 Agenda» Brief background intro to Android» Android app basics:» Activities & Intents» Resources» GUI» Tools 2 Android» A Linux-based Operating System»
Java & Android Java Fundamentals Madis Pink 2016 Tartu 1 Agenda» Brief background intro to Android» Android app basics:» Activities & Intents» Resources» GUI» Tools 2 Android» A Linux-based Operating System»
More Effective Layouts
 More Effective Layouts In past weeks, we've looked at ways to make more effective use of the presented display (e.g. elastic layouts, and separate layouts for portrait and landscape), as well as autogenerating
More Effective Layouts In past weeks, we've looked at ways to make more effective use of the presented display (e.g. elastic layouts, and separate layouts for portrait and landscape), as well as autogenerating
10.1 Introduction. Higher Level Processing. Word Recogniton Model. Text Output. Voice Signals. Spoken Words. Syntax, Semantics, Pragmatics
 Chapter 10 Speech Recognition 10.1 Introduction Speech recognition (SR) by machine, which translates spoken words into text has been a goal of research for more than six decades. It is also known as automatic
Chapter 10 Speech Recognition 10.1 Introduction Speech recognition (SR) by machine, which translates spoken words into text has been a goal of research for more than six decades. It is also known as automatic
Android Layout Types
 Android Layout Types Android Linear Layout Android LinearLayout is a view group that aligns all children in either vertically or horizontally. android:divider - This is drawable to use as a vertical divider
Android Layout Types Android Linear Layout Android LinearLayout is a view group that aligns all children in either vertically or horizontally. android:divider - This is drawable to use as a vertical divider
MATERIAL DESIGN. Android Elective Course 4th Semester. June 2016 Teacher: Anders Kristian Børjesson. Ovidiu Floca
 MATERIAL DESIGN Android Elective Course 4th Semester June 2016 Teacher: Anders Kristian Børjesson Ovidiu Floca 1 CONTENTS 2 Introduction... 2 3 Problem Definition... 2 4 Method... 2 5 Planning... 3 6 Watching
MATERIAL DESIGN Android Elective Course 4th Semester June 2016 Teacher: Anders Kristian Børjesson Ovidiu Floca 1 CONTENTS 2 Introduction... 2 3 Problem Definition... 2 4 Method... 2 5 Planning... 3 6 Watching
Graphical User Interfaces
 Graphical User Interfaces Some suggestions Avoid displaying too many things Well-known anti-patterns Display useful content on your start screen Use action bars to provide consistent navigation Keep your
Graphical User Interfaces Some suggestions Avoid displaying too many things Well-known anti-patterns Display useful content on your start screen Use action bars to provide consistent navigation Keep your
MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 2. Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE AUGUST 25, SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept.
 MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 2 Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE 7 15126 AUGUST 25, 2017 SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept. Android Widgets There are given a lot of android widgets with simplified
MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 2 Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE 7 15126 AUGUST 25, 2017 SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept. Android Widgets There are given a lot of android widgets with simplified
Create Parent Activity and pass its information to Child Activity using Intents.
 Create Parent Activity and pass its information to Child Activity using Intents. /* MainActivity.java */ package com.example.first; import android.os.bundle; import android.app.activity; import android.view.menu;
Create Parent Activity and pass its information to Child Activity using Intents. /* MainActivity.java */ package com.example.first; import android.os.bundle; import android.app.activity; import android.view.menu;
Getting Started. Dr. Miguel A. Labrador Department of Computer Science & Engineering
 Getting Started Dr. Miguel A. Labrador Department of Computer Science & Engineering labrador@csee.usf.edu http://www.csee.usf.edu/~labrador 1 Goals Setting up your development environment Android Framework
Getting Started Dr. Miguel A. Labrador Department of Computer Science & Engineering labrador@csee.usf.edu http://www.csee.usf.edu/~labrador 1 Goals Setting up your development environment Android Framework
COMP4521 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS SOFTWARE
 COMP4521 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS SOFTWARE LAB 1: DEVELOPING SIMPLE APPLICATIONS FOR ANDROID INTRODUCTION Android is a mobile platform/os that uses a modified version of the Linux kernel. It was initially developed
COMP4521 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS SOFTWARE LAB 1: DEVELOPING SIMPLE APPLICATIONS FOR ANDROID INTRODUCTION Android is a mobile platform/os that uses a modified version of the Linux kernel. It was initially developed
Android Specifics. Jonathan Diehl (Informatik 10) Hendrik Thüs (Informatik 9)
 Android Specifics Jonathan Diehl (Informatik 10) Hendrik Thüs (Informatik 9) Android Specifics ArrayAdapter Preferences Widgets Jonathan Diehl, Hendrik Thüs 2 ArrayAdapter Jonathan Diehl, Hendrik Thüs
Android Specifics Jonathan Diehl (Informatik 10) Hendrik Thüs (Informatik 9) Android Specifics ArrayAdapter Preferences Widgets Jonathan Diehl, Hendrik Thüs 2 ArrayAdapter Jonathan Diehl, Hendrik Thüs
Developing Android Applications Introduction to Software Engineering Fall Updated 1st November 2015
 Developing Android Applications Introduction to Software Engineering Fall 2015 Updated 1st November 2015 Android Lab 3 & Midterm Additional Concepts No Class Assignment 2 Class Plan Android : Additional
Developing Android Applications Introduction to Software Engineering Fall 2015 Updated 1st November 2015 Android Lab 3 & Midterm Additional Concepts No Class Assignment 2 Class Plan Android : Additional
StoppUhr. <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="start1"
 StoppUhr
StoppUhr
Android Basics. Android UI Architecture. Android UI 1
 Android Basics Android UI Architecture Android UI 1 Android Design Constraints Limited resources like memory, processing, battery à Android stops your app when not in use Primarily touch interaction à
Android Basics Android UI Architecture Android UI 1 Android Design Constraints Limited resources like memory, processing, battery à Android stops your app when not in use Primarily touch interaction à
Data Persistence. Chapter 10
 Chapter 10 Data Persistence When applications create or capture data from user inputs, those data will only be available during the lifetime of the application. You only have access to that data as long
Chapter 10 Data Persistence When applications create or capture data from user inputs, those data will only be available during the lifetime of the application. You only have access to that data as long
Screen Slides. The Android Studio wizard adds a TextView to the fragment1.xml layout file and the necessary code to Fragment1.java.
 Screen Slides References https://developer.android.com/training/animation/screen-slide.html https://developer.android.com/guide/components/fragments.html Overview A fragment can be defined by a class and
Screen Slides References https://developer.android.com/training/animation/screen-slide.html https://developer.android.com/guide/components/fragments.html Overview A fragment can be defined by a class and
android:layout_margintop="5dp" > <EditText android:layout_width="210dp"
 activity_main.xml
activity_main.xml
Android Development Community. Let s do Material Design
 Let s do Material Design Agenda Introduction to Material Design Toolbar Navigation Drawer SwipeRefreshLayout RecyclerView Floating Action Button CardView Toolbar - Lives in package android.support.v7.widget
Let s do Material Design Agenda Introduction to Material Design Toolbar Navigation Drawer SwipeRefreshLayout RecyclerView Floating Action Button CardView Toolbar - Lives in package android.support.v7.widget
Android HelloWorld - Example. Tushar B. Kute,
 Android HelloWorld - Example Tushar B. Kute, http://tusharkute.com Anatomy of Android Application Anatomy of Android Application Java This contains the.java source files for your project. By default, it
Android HelloWorld - Example Tushar B. Kute, http://tusharkute.com Anatomy of Android Application Anatomy of Android Application Java This contains the.java source files for your project. By default, it
Android Application Development. By : Shibaji Debnath
 Android Application Development By : Shibaji Debnath About Me I have over 10 years experience in IT Industry. I have started my career as Java Software Developer. I worked in various multinational company.
Android Application Development By : Shibaji Debnath About Me I have over 10 years experience in IT Industry. I have started my career as Java Software Developer. I worked in various multinational company.
ANDROID PROGRAMS DAY 3
 ANDROID PROGRAMS DAY 3 //Android project to navigate from first page to second page using Intent Step 1: Create a new project Step 2: Enter necessary details while creating project. Step 3: Drag and drop
ANDROID PROGRAMS DAY 3 //Android project to navigate from first page to second page using Intent Step 1: Create a new project Step 2: Enter necessary details while creating project. Step 3: Drag and drop
Workshop. 1. Create a simple Intent (Page 1 2) Launch a Camera for Photo Taking
 Workshop 1. Create a simple Intent (Page 1 2) Launch a Camera for Photo Taking 2. Create Intent with Parsing Data (Page 3 8) Making Phone Call and Dial Access Web Content Playing YouTube Video 3. Create
Workshop 1. Create a simple Intent (Page 1 2) Launch a Camera for Photo Taking 2. Create Intent with Parsing Data (Page 3 8) Making Phone Call and Dial Access Web Content Playing YouTube Video 3. Create
 LAMPIRAN 1 LAMPIRAN 2 SCREENSHOOT LAMPIRAN 3 LISTING FILE JAVA CLASS 1. main_activity.java packagecom.example.sig.sigrs; import android.content.intent; import android.net.uri; import android.support.v7.app.appcompatactivity;
LAMPIRAN 1 LAMPIRAN 2 SCREENSHOOT LAMPIRAN 3 LISTING FILE JAVA CLASS 1. main_activity.java packagecom.example.sig.sigrs; import android.content.intent; import android.net.uri; import android.support.v7.app.appcompatactivity;
Android App Development. Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology
 Android App Development Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology Android Operating System Created by Android, Inc. Bought by Google in 2005. First Android Device released in 2008 Based
Android App Development Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology Android Operating System Created by Android, Inc. Bought by Google in 2005. First Android Device released in 2008 Based
1. Location Services. 1.1 GPS Location. 1. Create the Android application with the following attributes. Application Name: MyLocation
 1. Location Services 1.1 GPS Location 1. Create the Android application with the following attributes. Application Name: MyLocation Project Name: Package Name: MyLocation com.example.mylocation 2. Put
1. Location Services 1.1 GPS Location 1. Create the Android application with the following attributes. Application Name: MyLocation Project Name: Package Name: MyLocation com.example.mylocation 2. Put
Sizing and Positioning
 CS 193A Layout This document is copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stanford Computer Science. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License. All rights reserved. Sizing and Positioning How does the
CS 193A Layout This document is copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stanford Computer Science. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License. All rights reserved. Sizing and Positioning How does the
MVC Apps Basic Widget Lifecycle Logging Debugging Dialogs
 Overview MVC Apps Basic Widget Lifecycle Logging Debugging Dialogs Lecture: MVC Model View Controller What is an App? Android Activity Lifecycle Android Debugging Fixing Rotations & Landscape Layouts Localization
Overview MVC Apps Basic Widget Lifecycle Logging Debugging Dialogs Lecture: MVC Model View Controller What is an App? Android Activity Lifecycle Android Debugging Fixing Rotations & Landscape Layouts Localization
Vienos veiklos būsena. Theory
 Vienos veiklos būsena Theory While application is running, we create new Activities and close old ones, hide the application and open it again and so on, and Activity can process all these events. It is
Vienos veiklos būsena Theory While application is running, we create new Activities and close old ones, hide the application and open it again and so on, and Activity can process all these events. It is
Mobile Application Development Android
 Mobile Application Development Android Lecture 2 MTAT.03.262 Satish Srirama satish.srirama@ut.ee Android Lecture 1 -recap What is Android How to develop Android applications Run & debug the applications
Mobile Application Development Android Lecture 2 MTAT.03.262 Satish Srirama satish.srirama@ut.ee Android Lecture 1 -recap What is Android How to develop Android applications Run & debug the applications
Agenda. Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen
 Gill Cleeren Agenda Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen Lists and navigation Navigating from master to detail Optimizing the application Preparing
Gill Cleeren Agenda Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen Lists and navigation Navigating from master to detail Optimizing the application Preparing
Creating a Custom ListView
 Creating a Custom ListView References https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html#adapterviews Overview The ListView in the previous tutorial creates a TextView object for each
Creating a Custom ListView References https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html#adapterviews Overview The ListView in the previous tutorial creates a TextView object for each
Android development. Outline. Android Studio. Setting up Android Studio. 1. Set up Android Studio. Tiberiu Vilcu. 2.
 Outline 1. Set up Android Studio Android development Tiberiu Vilcu Prepared for EECS 411 Sugih Jamin 15 September 2017 2. Create sample app 3. Add UI to see how the design interface works 4. Add some code
Outline 1. Set up Android Studio Android development Tiberiu Vilcu Prepared for EECS 411 Sugih Jamin 15 September 2017 2. Create sample app 3. Add UI to see how the design interface works 4. Add some code
Android UI Development
 Android UI Development Android UI Studio Widget Layout Android UI 1 Building Applications A typical application will include: Activities - MainActivity as your entry point - Possibly other activities (corresponding
Android UI Development Android UI Studio Widget Layout Android UI 1 Building Applications A typical application will include: Activities - MainActivity as your entry point - Possibly other activities (corresponding
Create new Android project in Android Studio Add Button and TextView to layout Learn how to use buttons to call methods. Modify strings.
 Hello World Lab Objectives: Create new Android project in Android Studio Add Button and TextView to layout Learn how to use buttons to call methods. Modify strings.xml What to Turn in: The lab evaluation
Hello World Lab Objectives: Create new Android project in Android Studio Add Button and TextView to layout Learn how to use buttons to call methods. Modify strings.xml What to Turn in: The lab evaluation
Building MyFirstApp Android Application Step by Step. Sang Shin Learn with Passion!
 Building MyFirstApp Android Application Step by Step. Sang Shin www.javapassion.com Learn with Passion! 1 Disclaimer Portions of this presentation are modifications based on work created and shared by
Building MyFirstApp Android Application Step by Step. Sang Shin www.javapassion.com Learn with Passion! 1 Disclaimer Portions of this presentation are modifications based on work created and shared by
PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE)
 PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE) Network Connection Web Service K Candra Brata andra.course@gmail.com Mobille App Lab 2015-2016 Network Connection http://developer.android.com/training/basics/network-ops/connecting.html
PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE) Network Connection Web Service K Candra Brata andra.course@gmail.com Mobille App Lab 2015-2016 Network Connection http://developer.android.com/training/basics/network-ops/connecting.html
Tabel mysql. Kode di PHP. Config.php. Service.php
 Tabel mysql Kode di PHP Config.php Service.php Layout Kode di Main Activity package com.example.mini.webandroid; import android.app.progressdialog; import android.os.asynctask; import android.support.v7.app.appcompatactivity;
Tabel mysql Kode di PHP Config.php Service.php Layout Kode di Main Activity package com.example.mini.webandroid; import android.app.progressdialog; import android.os.asynctask; import android.support.v7.app.appcompatactivity;
COMP61242: Task /04/18
 COMP61242: Task 2 1 16/04/18 1. Introduction University of Manchester School of Computer Science COMP61242: Mobile Communications Semester 2: 2017-18 Laboratory Task 2 Messaging with Android Smartphones
COMP61242: Task 2 1 16/04/18 1. Introduction University of Manchester School of Computer Science COMP61242: Mobile Communications Semester 2: 2017-18 Laboratory Task 2 Messaging with Android Smartphones
Laying Out Controls in Containers
 CHAPTER 3 Laying Out Controls in Containers A container is a view used to contain other views. Android offers a collection of view classes that act as containers for views. These container classes are
CHAPTER 3 Laying Out Controls in Containers A container is a view used to contain other views. Android offers a collection of view classes that act as containers for views. These container classes are
TextView. A label is called a TextView. TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input
 1 UI Components 2 UI Components 3 A label is called a TextView. TextView TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input - - - - - - -
1 UI Components 2 UI Components 3 A label is called a TextView. TextView TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input - - - - - - -
Adaptation of materials: dr Tomasz Xięski. Based on presentations made available by Victor Matos, Cleveland State University.
 Creating dialogs Adaptation of materials: dr Tomasz Xięski. Based on presentations made available by Victor Matos, Cleveland State University. Portions of this page are reproduced from work created and
Creating dialogs Adaptation of materials: dr Tomasz Xięski. Based on presentations made available by Victor Matos, Cleveland State University. Portions of this page are reproduced from work created and
TextView Control. EditText Control. TextView Attributes. android:id - This is the ID which uniquely identifies the control.
 A TextView displays text to the user. TextView Attributes TextView Control android:id - This is the ID which uniquely identifies the control. android:capitalize - If set, specifies that this TextView has
A TextView displays text to the user. TextView Attributes TextView Control android:id - This is the ID which uniquely identifies the control. android:capitalize - If set, specifies that this TextView has
API Guide for Gesture Recognition Engine. Version 2.0
 API Guide for Gesture Recognition Engine Version 2.0 Table of Contents Gesture Recognition API... 3 API URI... 3 Communication Protocol... 3 Getting Started... 4 Protobuf... 4 WebSocket Library... 4 Project
API Guide for Gesture Recognition Engine Version 2.0 Table of Contents Gesture Recognition API... 3 API URI... 3 Communication Protocol... 3 Getting Started... 4 Protobuf... 4 WebSocket Library... 4 Project
Multiple devices. Use wrap_content and match_parent Use RelativeLayout/ConstraintLayout Use configuration qualifiers
 Multiple devices Multiple devices Use wrap_content and match_parent Use RelativeLayout/ConstraintLayout Use configuration qualifiers Create a new directory in your project's res/ and name it using the
Multiple devices Multiple devices Use wrap_content and match_parent Use RelativeLayout/ConstraintLayout Use configuration qualifiers Create a new directory in your project's res/ and name it using the
List-Based Widgets: Lists, Grids, and Scroll Views
 Lesson 5 List-Based Widgets: Lists, Grids, and Scroll Views Victor Matos Cleveland State University Portions of this page are reproduced from work created and shared by Google and used according to terms
Lesson 5 List-Based Widgets: Lists, Grids, and Scroll Views Victor Matos Cleveland State University Portions of this page are reproduced from work created and shared by Google and used according to terms

 Lampiran Program : Res - Layout Activity_main.xml
Lampiran Program : Res - Layout Activity_main.xml