17 Hello world 18 Type: String: literal 19 Standard API: System: out.println() 20 Hello world 21 Statement 22 Statement: simple statements are ended w
|
|
|
- Ambrose Golden
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs are divided into classes 7 Class: public class 8 Class: definition 9 Hello world 10 Method: main method: programs contain a main method 11 Method: main method: is public 12 Method: main method: is static 13 Method: main method: is void 14 Method: main method: is the program starting point 15 Command line arguments: program arguments are passed to main 16 Method: main method: always has the same heading 0-0
2 17 Hello world 18 Type: String: literal 19 Standard API: System: out.println() 20 Hello world 21 Statement 22 Statement: simple statements are ended with a semi-colon 23 Hello world 24 The full HelloWorld code 25 Trying it 26 Coursework: HelloWorld in French 27 Section 3: Example:Hello world with a syntactic error 28 Aim 29 Error 30 Error: syntactic error 33 Hello world with a syntactic error 34 Trying it 35 Type: String: literal: must be ended on the same line 36 Trying it 0-1
3 37 Coursework: Fortune syntactic errors 38 Section 4: Example:Hello world with a semantic error 39 Aim 40 Error: semantic error 42 Error: compile time error 43 Hello world with a semantic error 44 Trying it 45 Coursework: ManchesterWeather semantic errors 46 Section 5: Example:Hello solar system 47 Aim 48 Execution: sequential execution 49 Hello solar system 50 Trying it 51 Coursework: HelloFamily 52 Section 6: Example:Hello solar system with a run time error 53 Aim 54 Error: run time error 55 Hello solar system with a run time error 0-2
4 56 Trying it 57 Trying it 58 Trying it 59 Coursework: Quote run time errors 60 Section 7: Example:Hello anyone 61 Aim 62 Command line arguments: program arguments are accessed by inde 63 Type: String: concatenation 64 Hello anyone 65 Trying it 66 Trying it 67 Trying it 68 Trying it 69 Trying it 70 Coursework: FlatterMe 71 Section 8: Example:Hello anyone with a logical error 72 Aim 73 Error: logical error 0-3
5 74 Hello anyone with a logical error 75 Trying it 76 Coursework: Birthday logical errors 77 Section 9: Hello solar system, looking at the layout 78 Aim 79 Code clarity: layout 81 Hello solar system, looking at the layout 82 Code clarity: layout: indentation 84 Coursework: Limerick layout 85 Concepts covered in this chapter 0-4
6 Title Java Just in Time John Latham October 25, 2017 October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 1(0/0)
7 Chapter 2 Sequential execution and program errors October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 2(0/0)
8 Chapter aims Introduce some very basic Java concepts. Especially sequential execution. Look at kinds of errors we can have in programs. Because you will make errors! You don t need to be afraid of them they are part of the programming experience! October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 3(0/0)
9 Section 2 Example: Hello world October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 4(0/0)
10 Aim AIM: To introduce some very basic Java concepts, including the main method and System.out.println(). October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 5(0/0)
11 Class: programs are divided into classes Program source text separated into pieces called classes. Each piece (usually) stored in separate file. File name is name of class, with.java appended. E.g. HelloWorld in HelloWorld.java. One reason for dividing makes management easier program maybe thousands of lines. Another reason: make sharing between programs easier software reuse helps productivity. Every program has at least one class. Its name reflects intention of the program. Convention: class names start with upper case letter. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 6(0/0)
12 Class: public class A class declared public can be accessed from anywhere in the running Java environment; in particular the virtual machine can access it. Source text starts with reserved word public. A reserved word is part of the Java language e.g. cannot have a program called public. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 7(0/0)
13 Class: definition After public we write reserved word class, then name, then left brace ({), body of text and finally closing right brace (}). public class MyFabulousProgram {... Lots of stuff here. } October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 8(0/0)
14 Hello world The heading for our HelloWorld class. 001: public class HelloWorld Then the opening bracket. 002: { October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 9(0/0)
15 Method: main method: programs contain a main method All Java programs contain a section of code called main. This is where the computer will start to execute the program. Sections of code are called methods contain instructions how to do something. The main method always starts with following heading. public static void main(string[] args) October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 10(0/0)
16 Method: main method: is public The main method starts with reserved word public so virtual machine has access to it. public October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 11(0/0)
17 Method: main method: is static The main method has reserved word static. Thus is allowed to be used in the static context. A context is an allocation of computer memory for the program and data, etc.. The virtual machine creates the static context when program is loaded. A dynamic context is a kind of allocation of memory made during run of the program. Main method must be able to run in the static context else program could not be started! public static October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 12(0/0)
18 Method: main method: is void A method might calculate and return some result if so we state this in its heading. E.g. method might calculate square root of a number, and return the answer as a number. If it does not we write reserved word void. Void means without contents. The main method does not return a value. public static void October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 13(0/0)
19 Method: main method: is the program starting point The program starting part main method is always called main it is main part of program. public static void main October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 14(0/0)
20 Command line arguments: program arguments are passed to main Programs can be given command line arguments. So can Java programs. Program arguments are list of text strings. In Java, String[] means list of strings. Must give a name for this list, usually args so we can refer to given data from within program if needed. public static void main(string[] args) October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 15(0/0)
21 Method: main method: always has the same heading Java program main methods always have this heading: public static void main(string[] args) Even if we do not intend to use command line arguments. Typical single class program looks like: public class MyFabulousProgram { public static void main(string[] args) {... Stuff here to perform the task. } } October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 16(0/0)
22 Hello world Back to HelloWorld : public static void main(string[] args) 004: { October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 17(0/0)
23 Type: String: literal A string literal is a fixed piece of text to be used as data. We enclose text in double quotes: "This is a fixed piece of text data -- a string literal" Might be used as a message to the user. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 18(0/0)
24 Standard API: System: out.println() Simplest way to print a message on standard output: System.out.println("This text will appear on standard output"); System is a class in Java s application programming interface (API). Inside System there is a thing called out. This has a method called println. Overall is called System.out.println. It takes a string in its brackets displays it on the standard output. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 19(0/0)
25 Hello world Back to HelloWorld : System.out.println("Hello world!"); Observe semi-colon... October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 20(0/0)
26 Statement A command that makes computer perform a task is a statement. E.g. System.out.println("I will output whatever I am told to") October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 21(0/0)
27 Statement: simple statements are ended with a semi-colon All simple Java statements must end with semi-colon. a rule of the Java language syntax. Coffee time: Can you think of a reason why Java insists on the programmer putting a semi-colon at the end of statements? October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 22(0/0)
28 Hello world Back to HelloWorld : } 007: } October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 23(0/0)
29 The full HelloWorld code 001: public class HelloWorld 002: { 003: public static void main(string[] args) 004: { 005: System.out.println("Hello world!"); 006: } 007: } October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 24(0/0)
30 Trying it We create source code and compile it. $ ls -l HelloWorld.java Console Input / Output -rw jtl jtl 117 Mar 26 20:09 HelloWorld.java $ javac HelloWorld.java $ ls -l HelloWorld.* -rw jtl jtl 426 Mar 26 20:09 HelloWorld.class -rw jtl jtl 117 Mar 26 20:09 HelloWorld.java $ _ Run We run program to get message on standard output. Console Input / Output $ java HelloWorld Hello world! $ _ Run October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 25(0/0)
31 Coursework: HelloWorld in French (Summary only) Write a program to greet the whole world, in French! October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 26(0/0)
32 Section 3 Example: Hello world with a syntactic error October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 27(0/0)
33 Aim AIM: To introduce the principle of program errors, in particularsyntacticerrors. Wealsoseethatastringliteralmust be ended on the same line its starts on. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 28(0/0)
34 Error To err is Human... when you write source code you will get some things wrong. Lots of rules of Java to obey for a valid program. Being new to it you will break these rules. Even seasoned Java programmers make errors. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 29(0/0)
35 Error: syntactic error When we break syntax rules of Java we have a syntactic error. E.g. omitting closing bracket, semi-colon... Similar to grammatical error in natural language. E.g. sign strapped to back of a poodle... October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 30(0/0)
36 Error: syntactic error My other dog an Alsatian. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 31(0/0)
37 Error: syntactic error The compiler gives error messages for syntactic errors. Watch out: compiler can get confused... October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 32(0/0)
38 Hello world with a syntactic error 001: public class HelloWorld 002: { 003: public static void main(string[] args) 004: { 005: System.out.println("Hello world!); 006: } 007: } Coffee time: Can you spot the syntactic error? October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 33(0/0)
39 Trying it Console Input / Output $ javac HelloWorld.java HelloWorld.java:5: unclosed string literal System.out.println("Hello world!); ˆ HelloWorld.java:5: ; expected System.out.println("Hello world!); ˆ HelloWorld.java:7: reached end of file while parsing } ˆ 3 errors $ _ Run Error messages from compiler can look very scary. Read carefully observe the parts... October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 34(0/0)
40 Type: String: literal: must be ended on the same line In Java string literals must end on same line they start on. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 35(0/0)
41 Trying it Coffee time: What has caused the other error message(s)? October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 36(0/0)
42 Coursework: Fortune syntactic errors (Summary only) Take a given program that has syntactic errors in it, and get it working. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 37(0/0)
43 Section 4 Example: Hello world with a semantic error October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 38(0/0)
44 Aim AIM: To introduce semantic errors and note that these and syntactic errors are compile time errors. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 39(0/0)
45 Error: semantic error A semantic error we obey syntax rules but write something with no meaning (semantics). E.g. another sign, another poodle... October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 40(0/0)
46 Error: semantic error My other dog is a Porsche. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 41(0/0)
47 Error: compile time error Java syntactic errors and semantic errors are detected by compiler. Collectively called compile time errors. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 42(0/0)
48 Hello world with a semantic error 001: public class HelloWorld 002: { 003: public static void main(text[] args) 004: { 005: System.out.println("Hello world!"); 006: } 007: } Coffee time: Can you spot the semantic error? October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 43(0/0)
49 Trying it $ javac HelloWorld.java Console Input / Output HelloWorld.java:3: cannot find symbol symbol : class Text location: class HelloWorld public static void main(text[] args) ˆ 1 error $ _ Run A little cryptic? Read carefully. You ll get used to it. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 44(0/0)
50 Coursework: ManchesterWeather semantic errors (Summary only) Take a given program that has semantic errors in it, and get it working. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 45(0/0)
51 Section 5 Example: Hello solar system October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 46(0/0)
52 Aim AIM: To introduce the principle of sequential execution. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 47(0/0)
53 Execution: sequential execution Programs have many statements in a list. Usually placed on separate lines enhance human readability. Java doesn t care about layout we should. Statements in a list are executed one after the other. Actually compiler turns each into byte codes. The virtual machine executes each collection of byte codes in turn. Known as sequential execution. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 48(0/0)
54 Hello solar system 001: public class HelloSolarSystem 002: { 003: public static void main(string[] args) 004: { 005: System.out.println("Hello Mercury!"); 006: System.out.println("Hello Venus!"); 007: System.out.println("Hello Earth!"); 008: System.out.println("Hello Mars!"); 009: System.out.println("Hello Jupiter!"); 010: System.out.println("Hello Saturn!"); 011: System.out.println("Hello Uranus!"); 012: System.out.println("Hello Neptune!"); 013: System.out.println("Goodbye Pluto!"); 014: } 015: } October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 49(0/0)
55 Trying it Console Input / Output $ javac HelloSolarSystem.java $ java HelloSolarSystem Hello Mercury! Hello Venus! Hello Earth! Hello Mars! Hello Jupiter! Hello Saturn! Hello Uranus! Hello Neptune! Goodbye Pluto! $ _ Run October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 50(0/0)
56 Coursework: HelloFamily (Summary only) Write a program to greet some of your family. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 51(0/0)
57 Section 6 Example: Hello solar system with a run time error October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 52(0/0)
58 Aim AIM: To introduce the principle of run time errors. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 53(0/0)
59 Error: run time error Errors detected when the program is run are run time errors. Java calls them exceptions. Messages can look very cryptic? Read carefully, get used to them. E.g. Exception in thread "main" java.lang.nosuchmethoderror: main Best clue: look either side of the colon (:). October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 54(0/0)
60 Hello solar system with a run time error 001: public class HelloSolarSystem 002: { 003: public static void Main(String[] args) 004: { 005: System.out.println("Hello Mercury!"); 006: System.out.println("Hello Venus!"); 007: System.out.println("Hello Earth!"); 008: System.out.println("Hello Mars!"); 009: System.out.println("Hello Jupiter!"); 010: System.out.println("Hello Saturn!"); 011: System.out.println("Hello Uranus!"); 012: System.out.println("Hello Neptune!"); 013: System.out.println("Goodbye Pluto!"); 014: } 015: } Coffee time: What will cause a run time error? October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 55(0/0)
61 Trying it It compiles okay. Console Input / Output $ javac HelloSolarSystem.java $ _ Run But when we run it... Console Input / Output $ java HelloSolarSystem Exception in thread "main" java.lang.nosuchmethoderror: main $ _ Run The virtual machine says our program has no main method. Called it Main instead of main! October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 56(0/0)
62 Trying it Another example run time error. Console Input / Output $ java HelloMum Exception in thread "main" java.lang.noclassdeffounderror: HelloMum $ _ Run October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 57(0/0)
63 Trying it Coffee time: Imagine a version of HelloSolarSystem, called HelloSolarSystemNoArgs, with a lower case m on main, but String[] args has been omitted. Explain the following. Console Input / Output $ javac HelloSolarSystemNoArgs.java $ java HelloSolarSystemNoArgs Exception in thread "main" java.lang.nosuchmethoderror: main $ _ Run October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 58(0/0)
64 Coursework: Quote run time errors (Summary only) Take a given program that has run time errors in it, and get it working. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 59(0/0)
65 Section 7 Example: Hello anyone October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 60(0/0)
66 Aim AIM: To introduce the principle of making Java programs perform a variation of their task based on command line arguments, which can be accessed via an index. We also meet string concatenation. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 61(0/0)
67 Command line arguments: program arguments are accessed by index The command line arguments given to main method a list of strings from the command line. Each has integer index, starting from zero. To access one, use its index in square brackets. E.g. args[0] is first command line argument. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 62(0/0)
68 Type: String: concatenation The + operator gives concatenation of two strings. E.g. "Hello " + "world" has same value as "Hello world". (Note where space came from.) Most useful with one or more variable values. E.g. "Hello " + args[0] E.g. System.out.println("Hello " + args[0]) Coffee time: When might we concatenate two string literals? October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 63(0/0)
69 Hello anyone 001: public class HelloAnyone 002: { 003: public static void main(string[] args) 004: { 005: System.out.println("Hello " + args[0]); 006: } 007: } October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 64(0/0)
70 Trying it Console Input / Output $ javac HelloAnyone.java $ java HelloAnyone John Hello John $ java HelloAnyone Lizzy Hello Lizzy $ _ Run What if no argument? Console Input / Output $ java HelloAnyone Exception in thread "main" java.lang.arrayindexoutofboundsexception: 0 at HelloAnyone.main(HelloAnyone.java:5) $ _ Run Observe source name and line number. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 65(0/0)
71 Trying it What if name contains space? Console Input / Output $ java HelloAnyone "John Latham" Hello John Latham $ java HelloAnyone John Latham Hello John $ _ Run Empty string? Console Input / Output $ java HelloAnyone "" Hello $ _ Run October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 66(0/0)
72 Trying it D:\JJIT\Example 2.7>dir HelloAnyone.java Volume in drive D is DATA Volume Serial Number is 5C90 0C33 Directory of D:\JJIT\Example /03/ : HelloAnyone.java 1 File(s) 130 bytes 0 Dirs(s) 8,389,459,968 bytes free D:\JJIT\Example 2.7>javac HelloAnyone.java D:\JJIT\Example 2.7>dir HelloAnyone.* Volume in drive D is DATA Volume Serial Number is 5C90 0C33 Directory of D:\JJIT\Example /03/ : HelloAnyone.java 26/03/ : HelloAnyone.class 2 File(s) 716 bytes 0 Dirs(s) 8,389,459,968 bytes free D:\JJIT\Example 2.7>java HelloAnyone "John Latham" Hello John Latham D:\JJIT\Example 2.7>_ October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 67(0/0)
73 Trying it October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 68(0/0)
74 Trying it October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 69(0/0)
75 Coursework: FlatterMe (Summary only) Write a program to say how wonderful the user is. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 70(0/0)
76 Section 8 Example: Hello anyone with a logical error October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 71(0/0)
77 Aim AIM: To introduce the principle of logical errors. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 72(0/0)
78 Error: logical error Most tricky kind of error logical error. No help from compiler, nor virtual machine. Code is meaningful to Java. But program does not do what we want! Java is too stupid to know that. Subtle ones slip through our testing. i.e. bugs. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 73(0/0)
79 Hello anyone with a logical error 001: public class HelloAnyone 002: { 003: public static void main(string[] args) 004: { 005: System.out.println("Hello + args[0]"); 006: } 007: } Coffee time: Can you spot the logical error? October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 74(0/0)
80 Trying it Compiles and runs without error. Console Input / Output $ javac HelloAnyone.java $ java HelloAnyone John Hello + args[0] $ _ Run October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 75(0/0)
81 Coursework: Birthday logical errors (Summary only) Take a given program that has logical errors in it, and get it working. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 76(0/0)
82 Section 9 Hello solar system, looking at the layout October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 77(0/0)
83 Aim AIM: To begin to explore the decisions behind the way we lay out the source code for a program. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 78(0/0)
84 Code clarity: layout Java doesn t care about layout white space must separate symbols that would be one symbol otherwise. E.g. public void would be publicvoid. Could put program on one line, minimum space. public class HelloSolarSystem{public static void main(string[]args){system.out.println("hello Mercu Or split just to fit on page. public class HelloSolarSystem{public static void main(string[]args){ System.out.println("Hello Mercury!");System.out.println( "Hello Venus!");System.out.println("Hello Earth!");System.out.println ("Hello Mars!");System.out.println("Hello Jupiter!");System.out. println("hello Saturn!");System.out.println("Hello Uranus!");System. out.println("hello Neptune!");System.out.println("Goodbye Pluto!");}} October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 79(0/0)
85 Code clarity: layout Layout important for human reader. Take pride in making your work most readable. Split lines in good places. Use indentation to show structure. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 80(0/0)
86 Hello solar system, looking at the layout 001: public class HelloSolarSystem 002: { 003: public static void main(string[] args) 004: { 005: System.out.println("Hello Mercury!"); 006: System.out.println("Hello Venus!"); 007: System.out.println("Hello Earth!"); 008: System.out.println("Hello Mars!"); 009: System.out.println("Hello Jupiter!"); 010: System.out.println("Hello Saturn!"); 011: System.out.println("Hello Uranus!"); 012: System.out.println("Hello Neptune!"); 013: System.out.println("Goodbye Pluto!"); 014: } 015: } New line after class heading. New line plus indentation 2 or3spaces formainmethod. New line, same indentation. More indentation, each statement on own line. Line up with opening braces. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 81(0/0)
87 Code clarity: layout: indentation A class contains nested structures: class has heading and body body has main method main method has heading and body body has statements. Use indentation to show structure the more nested, the more space. Be consistent: always same number of spaces per nesting two or three is good. don t use tabs! Opening and closing braces have same indentation. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 82(0/0)
88 Code clarity: layout: indentation Some people prefer this style subjectively less clear? public class HelloWorld { } public static void main(string[] args) { } System.out.println("Hello world!"); October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 83(0/0)
89 Coursework: Limerick layout (Summary only) Take a given program and lay it out properly. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 84(0/0)
90 Concepts covered in this chapter Each book chapter ends with a list of concepts covered in it. Each concept has with it a self-test question, and a page reference to where it was covered. Please use these to check your understanding before we start the next chapter. October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 85(0/0)
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs ar
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs are divided into classes 7 Class: public class 8 Class:
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs are divided into classes 7 Class: public class 8 Class:
17 Statement: assignment statement: assigning an expression value 18 Age next year 19 Type: String: conversion: from int 21 Age next year 22 The full
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 3: Types, variables and expressions 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Age next year 5 Aim 6 Design: hard coding 7 Age next year 8 Type 9 Type: int 10 Variable 11 Variable:
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 3: Types, variables and expressions 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Age next year 5 Aim 6 Design: hard coding 7 Age next year 8 Type 9 Type: int 10 Variable 11 Variable:
Introduction to Java. Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords
 Introduction to Java Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords Program Errors Syntax Runtime Logic Procedural Decomposition Methods Flow of Control
Introduction to Java Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords Program Errors Syntax Runtime Logic Procedural Decomposition Methods Flow of Control
Java Bytecode (binary file)
 Java is Compiled Unlike Python, which is an interpreted langauge, Java code is compiled. In Java, a compiler reads in a Java source file (the code that we write), and it translates that code into bytecode.
Java is Compiled Unlike Python, which is an interpreted langauge, Java code is compiled. In Java, a compiler reads in a Java source file (the code that we write), and it translates that code into bytecode.
A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to
 A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to perform some task. A simple enough idea, but for the computer to make any use of the instructions, they must be written in a form
A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to perform some task. A simple enough idea, but for the computer to make any use of the instructions, they must be written in a form
CS 177 Recitation. Week 1 Intro to Java
 CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
17 GUI API: Container 18 Hello world with a GUI 19 GUI API: JLabel 20 GUI API: Container: add() 21 Hello world with a GUI 22 GUI API: JFrame: setdefau
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 13: Graphical user interfaces 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world with a GUI 5 Aim 6 Hello world with a GUI 7 Hello world with a GUI 8 Package: java.awt and
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 13: Graphical user interfaces 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world with a GUI 5 Aim 6 Hello world with a GUI 7 Hello world with a GUI 8 Package: java.awt and
Mobile App:IT. Methods & Classes
 Mobile App:IT Methods & Classes WHAT IS A METHOD? - A method is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method's name. -
Mobile App:IT Methods & Classes WHAT IS A METHOD? - A method is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method's name. -
Class 1: Homework. Intro to Computer Science CSCI-UA.0101 New York University Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2017
 Intro to Computer Science CSCI-UA.0101 New York University Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2017 1 1. Please obtain a copy of Introduction to Java Programming, 11th (or 10th) Edition, Brief
Intro to Computer Science CSCI-UA.0101 New York University Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2017 1 1. Please obtain a copy of Introduction to Java Programming, 11th (or 10th) Edition, Brief
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming Homework 1 It is due this coming Sunday
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 3: SEP. 13TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Reading Assignment Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming Homework 1 It is due this coming Sunday
Lecture 2. COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall M. Jason Hinek Carleton University
 Lecture 2 COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall 2013 M. Jason Hinek Carleton University today s agenda a quick look back (last Thursday) assignment 0 is posted and is due this Friday at 2pm Java compiling
Lecture 2 COMP1406/1006 (the Java course) Fall 2013 M. Jason Hinek Carleton University today s agenda a quick look back (last Thursday) assignment 0 is posted and is due this Friday at 2pm Java compiling
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science. Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style
 CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style c 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 4 : Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style c 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 4 : Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming
Chapter Two Bonus Lesson: JavaDoc
 We ve already talked about adding simple comments to your source code. The JDK actually supports more meaningful comments as well. If you add specially-formatted comments, you can then use a tool called
We ve already talked about adding simple comments to your source code. The JDK actually supports more meaningful comments as well. If you add specially-formatted comments, you can then use a tool called
COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Introduction to Java. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
Lab # 2. For today s lab:
 1 ITI 1120 Lab # 2 Contributors: G. Arbez, M. Eid, D. Inkpen, A. Williams, D. Amyot 1 For today s lab: Go the course webpage Follow the links to the lab notes for Lab 2. Save all the java programs you
1 ITI 1120 Lab # 2 Contributors: G. Arbez, M. Eid, D. Inkpen, A. Williams, D. Amyot 1 For today s lab: Go the course webpage Follow the links to the lab notes for Lab 2. Save all the java programs you
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Variables and Output Statement Lecture 03 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives ü Declare and assign values to variable ü How to use eclipse ü What
Programming with Java Variables and Output Statement Lecture 03 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives ü Declare and assign values to variable ü How to use eclipse ü What
Program Development. Program Development. A Foundation for Programming. Program Development
 Program Development Program Development Ada Lovelace Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 11, 2010 8:48 AM 2 A Foundation
Program Development Program Development Ada Lovelace Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 11, 2010 8:48 AM 2 A Foundation
Who and what can help? Inf1-OP. Lecturer: Timothy Hospedales TA: Natalia Zon
 Who and what can help? Inf1-OP Lecturer: Timothy Hospedales TA: Natalia Zon Course Overview Web: http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/ courses/inf1/op/ Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita
Who and what can help? Inf1-OP Lecturer: Timothy Hospedales TA: Natalia Zon Course Overview Web: http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/ courses/inf1/op/ Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita
Inf1-OP. Course Overview. Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein. February 26, School of Informatics
 Inf1-OP Course Overview Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics February 26, 2018 Administrative Stuff Who to contact for help? Lecturer: Volker
Inf1-OP Course Overview Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics February 26, 2018 Administrative Stuff Who to contact for help? Lecturer: Volker
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE
 CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
Lecture Notes CPSC 224 (Spring 2012) Today... Java basics. S. Bowers 1 of 8
 Today... Java basics S. Bowers 1 of 8 Java main method (cont.) In Java, main looks like this: public class HelloWorld { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); Q: How
Today... Java basics S. Bowers 1 of 8 Java main method (cont.) In Java, main looks like this: public class HelloWorld { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); Q: How
Introduction Basic elements of Java
 Software and Programming I Introduction Basic elements of Java Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Module Information Time: Thursdays in the Spring term Lectures: MAL B04: 2
Software and Programming I Introduction Basic elements of Java Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Module Information Time: Thursdays in the Spring term Lectures: MAL B04: 2
Java Foundations: Unit 3. Parts of a Java Program
 Java Foundations: Unit 3 Parts of a Java Program class + name public class HelloWorld public static void main( String[] args ) System.out.println( Hello world! ); A class creates a new type, something
Java Foundations: Unit 3 Parts of a Java Program class + name public class HelloWorld public static void main( String[] args ) System.out.println( Hello world! ); A class creates a new type, something
40 Absolute difference 42 Trying it 43 Trying it 44 Concepts covered in this chapter 0-2
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 4: Conditional execution 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Oldest spouse 1 5 Aim 6 Execution: conditional execution 7 Expression: boolean 8 Expression: boolean: relational
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 4: Conditional execution 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Oldest spouse 1 5 Aim 6 Execution: conditional execution 7 Expression: boolean 8 Expression: boolean: relational
An overview of Java, Data types and variables
 An overview of Java, Data types and variables Lecture 2 from (UNIT IV) Prepared by Mrs. K.M. Sanghavi 1 2 Hello World // HelloWorld.java: Hello World program import java.lang.*; class HelloWorld { public
An overview of Java, Data types and variables Lecture 2 from (UNIT IV) Prepared by Mrs. K.M. Sanghavi 1 2 Hello World // HelloWorld.java: Hello World program import java.lang.*; class HelloWorld { public
Inf1-OOP. Textbooks. Who and What. Organisational issues. Why Java? Course Overview. Hello, World! in Java
 Organisational issues Inf1-OOP Course Overview Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 11, 2014 Why Java? Hello, World! in Java Built-in Types Integers Floating-Point
Organisational issues Inf1-OOP Course Overview Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 11, 2014 Why Java? Hello, World! in Java Built-in Types Integers Floating-Point
Java Just in Time: task questions
 Java Just in Time: task questions John Latham October 24, 2017 Contents 1 Chapter 1 Introduction 4 1.6 Section / task 1.6 Our first Java program..................... 4 1.7 Section / task 1.7 Our second
Java Just in Time: task questions John Latham October 24, 2017 Contents 1 Chapter 1 Introduction 4 1.6 Section / task 1.6 Our first Java program..................... 4 1.7 Section / task 1.7 Our second
Basic Programming Language Syntax
 Java Created in 1990 by Sun Microsystems. Free compiler from Sun, commercial from many vendors. We use free (Sun) Java on UNIX. Compiling and Interpreting...are processes of translating a high-level programming
Java Created in 1990 by Sun Microsystems. Free compiler from Sun, commercial from many vendors. We use free (Sun) Java on UNIX. Compiling and Interpreting...are processes of translating a high-level programming
Lesson 04: Our First Java Program (W01D4
 Lesson 04: Our First Java Program (W01D4) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro Lesson 04: Our First Java Program (W01D4 Do Now Start a terminal shell. From there, issue these commands
Lesson 04: Our First Java Program (W01D4) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro Lesson 04: Our First Java Program (W01D4 Do Now Start a terminal shell. From there, issue these commands
Inf1-OOP. Textbooks. Who and What. Organizational Issues. Why Java? Course Overview. Hello, World! in Java. Ewan Klein, Perdita Stevens
 Organizational Issues Inf1-OOP Course Overview Ewan Klein, Perdita Stevens School of Informatics January 12, 2013 Why Java? Hello, World! in Java Built-in Types Integers Floating-Point Numbers Type Conversion
Organizational Issues Inf1-OOP Course Overview Ewan Klein, Perdita Stevens School of Informatics January 12, 2013 Why Java? Hello, World! in Java Built-in Types Integers Floating-Point Numbers Type Conversion
Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 04 Demonstration 1 So, we have learned about how to run Java programs
Programming in Java Prof. Debasis Samanta Department of Computer Science Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 04 Demonstration 1 So, we have learned about how to run Java programs
Program Fundamentals
 Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
Welcome to CSE 142! Zorah Fung University of Washington, Spring Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1: Introduction; Basic Java Programs
 Welcome to CSE 142! Zorah Fung University of Washington, Spring 2015 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1: Introduction; Basic Java Programs reading: 1.1-1.3 1 What is computer science? computers?
Welcome to CSE 142! Zorah Fung University of Washington, Spring 2015 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1: Introduction; Basic Java Programs reading: 1.1-1.3 1 What is computer science? computers?
3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS)
 GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION 15 3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS) GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION Checklist: The most recent version of Java SE Development
GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION 15 3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS) GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION Checklist: The most recent version of Java SE Development
Title. Java Just in Time. John Latham. October 25, October 25, 2017 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 1(0/0)
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 6: Control statements nested in loops 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Film certificate age checking the whole queue 5 Aim 6 Statement: statements can be nested within
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 6: Control statements nested in loops 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Film certificate age checking the whole queue 5 Aim 6 Statement: statements can be nested within
Getting Started with Java. Atul Prakash
 Getting Started with Java Atul Prakash Running Programs C++, Fortran, Pascal Python, PHP, Ruby, Perl Java is compiled into device-independent code and then interpreted Source code (.java) is compiled into
Getting Started with Java Atul Prakash Running Programs C++, Fortran, Pascal Python, PHP, Ruby, Perl Java is compiled into device-independent code and then interpreted Source code (.java) is compiled into
Get JAVA. I will just tell you what I did (on January 10, 2017). I went to:
 Get JAVA To compile programs you need the JDK (Java Development Kit). To RUN programs you need the JRE (Java Runtime Environment). This download will get BOTH of them, so that you will be able to both
Get JAVA To compile programs you need the JDK (Java Development Kit). To RUN programs you need the JRE (Java Runtime Environment). This download will get BOTH of them, so that you will be able to both
CS 11 java track: lecture 1
 CS 11 java track: lecture 1 Administrivia need a CS cluster account http://www.cs.caltech.edu/ cgi-bin/sysadmin/account_request.cgi need to know UNIX www.its.caltech.edu/its/facilities/labsclusters/ unix/unixtutorial.shtml
CS 11 java track: lecture 1 Administrivia need a CS cluster account http://www.cs.caltech.edu/ cgi-bin/sysadmin/account_request.cgi need to know UNIX www.its.caltech.edu/its/facilities/labsclusters/ unix/unixtutorial.shtml
Welcome to CSE 142! Whitaker Brand. University of Washington, Winter 2018
 Welcome to CSE 142! Whitaker Brand University of Washington, Winter 2018 1 What is computer science? computers? science? programming? late lonely nights in front of the computer? ALGORITHMIC THINKING al
Welcome to CSE 142! Whitaker Brand University of Washington, Winter 2018 1 What is computer science? computers? science? programming? late lonely nights in front of the computer? ALGORITHMIC THINKING al
Computer Hardware. Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus. Key Hardware Components 12/17/2013
 Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus Chapter 1 Notes Computer Hardware Key Hardware Components CPU central processing unit Input / Output devices Main memory (RAM) Secondary storage devices: Hard drive
Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus Chapter 1 Notes Computer Hardware Key Hardware Components CPU central processing unit Input / Output devices Main memory (RAM) Secondary storage devices: Hard drive
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics. COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction
 CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
Code Ninjas: Introduction to Computer Science. Macomb Science Olympiad Presented by Swati Dharia
 Code Ninjas: Introduction to Computer Science Macomb Science Olympiad Presented by Swati Dharia Intro to Java Programming The three basic steps required to get a simple program running. As with any application,
Code Ninjas: Introduction to Computer Science Macomb Science Olympiad Presented by Swati Dharia Intro to Java Programming The three basic steps required to get a simple program running. As with any application,
BIT Java Programming. Sem 1 Session 2011/12. Chapter 2 JAVA. basic
 BIT 3383 Java Programming Sem 1 Session 2011/12 Chapter 2 JAVA basic Objective: After this lesson, you should be able to: declare, initialize and use variables according to Java programming language guidelines
BIT 3383 Java Programming Sem 1 Session 2011/12 Chapter 2 JAVA basic Objective: After this lesson, you should be able to: declare, initialize and use variables according to Java programming language guidelines
Administrative Stuff. Inf1-OP. Additional help? Who to contact for help? Course Overview
 nf1-op Course Overview Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein Administrative Stuff School of nformatics February 26, 2018 Who to contact for help? Additional help? Lecturer:
nf1-op Course Overview Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein Administrative Stuff School of nformatics February 26, 2018 Who to contact for help? Additional help? Lecturer:
Pace University. Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1
 Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Creating a Program in JCreator. JCreator is then used to create our program. But the first step is to create a new file.
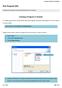 First Program (02) Creating a Java program and understanding the basic concepts. Creating a Program in JCreator It is usually a good idea to create a folder where you re going to save your Java programs.
First Program (02) Creating a Java program and understanding the basic concepts. Creating a Program in JCreator It is usually a good idea to create a folder where you re going to save your Java programs.
Lec 3. Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables
 Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Learn about cutting-edge research over lunch with cool profs January 18-22, 2015 11:30
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Learn about cutting-edge research over lunch with cool profs January 18-22, 2015 11:30
1 Introduction Java, the beginning Java Virtual Machine A First Program BlueJ Raspberry Pi...
 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Java, the beginning.......................... 3 1.2 Java Virtual Machine........................ 4 1.3 A First Program........................... 4 1.4 BlueJ.................................
Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Java, the beginning.......................... 3 1.2 Java Virtual Machine........................ 4 1.3 A First Program........................... 4 1.4 BlueJ.................................
C02: Overview of Software Development and Java
 CISC 3120 C02: Overview of Software Development and Java Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 08/31/2017 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Recap and issues Brief introduction
CISC 3120 C02: Overview of Software Development and Java Hui Chen Department of Computer & Information Science CUNY Brooklyn College 08/31/2017 CUNY Brooklyn College 1 Outline Recap and issues Brief introduction
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Midterm Exams on 4 th of June (12:35 14:35) Room allocation will be announced soon
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Midterm Exams on 4 th of June (12:35 14:35) Room allocation will be announced soon
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015 Assignment Due Date Assignment 1 is now due on Tuesday, Jan 20 th, 11:59pm. Quiz 1 is
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2015 Assignment Due Date Assignment 1 is now due on Tuesday, Jan 20 th, 11:59pm. Quiz 1 is
Goals. Java - An Introduction. Java is Compiled and Interpreted. Architecture Neutral & Portable. Compiled Languages. Introduction to Java
 Goals Understand the basics of Java. Introduction to Java Write simple Java Programs. 1 2 Java - An Introduction Java is Compiled and Interpreted Java - The programming language from Sun Microsystems Programmer
Goals Understand the basics of Java. Introduction to Java Write simple Java Programs. 1 2 Java - An Introduction Java is Compiled and Interpreted Java - The programming language from Sun Microsystems Programmer
12/22/11. Java How to Program, 9/e. Help you get started with Eclipse and NetBeans integrated development environments.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java: Comment Text. Introduction. Concepts
 Java: Comment Text Introduction Comment text is text included in source code that is ignored by the compiler and does not cause any machine-language object code to be generated. It is written into the
Java: Comment Text Introduction Comment text is text included in source code that is ignored by the compiler and does not cause any machine-language object code to be generated. It is written into the
How to make a "hello world" program in Java with Eclipse *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m43473 1 How to make a "hello world" program in Java with Eclipse * Hannes Hirzel Based on How to make a "hello world" program in Java. by Rodrigo Rodriguez This work is produced by
OpenStax-CNX module: m43473 1 How to make a "hello world" program in Java with Eclipse * Hannes Hirzel Based on How to make a "hello world" program in Java. by Rodrigo Rodriguez This work is produced by
G52PGP. Lecture oo3 Java (A real object oriented language)
 G52PGP Lecture oo3 Java (A real object oriented language) 1 Last lecture Associating functions with data into objects is an alternative way to decompose a program Can then consider each object on its own
G52PGP Lecture oo3 Java (A real object oriented language) 1 Last lecture Associating functions with data into objects is an alternative way to decompose a program Can then consider each object on its own
Software and Programming 1
 Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 17 January 2019 SP1-Lab1-2018-19.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 17 January 2019 SP1-Lab1-2018-19.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Outline. Overview. Control statements. Classes and methods. history and advantage how to: program, compile and execute 8 data types 3 types of errors
 Outline Overview history and advantage how to: program, compile and execute 8 data types 3 types of errors Control statements Selection and repetition statements Classes and methods methods... 2 Oak A
Outline Overview history and advantage how to: program, compile and execute 8 data types 3 types of errors Control statements Selection and repetition statements Classes and methods methods... 2 Oak A
Building Java Programs. Introduction to Programming and Simple Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Introduction to Programming and Simple Java Programs 1 A simple Java program public class Hello { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello, world!"); code
Building Java Programs Introduction to Programming and Simple Java Programs 1 A simple Java program public class Hello { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello, world!"); code
Title. Java Just in Time. John Latham. November 5, November 5, 2018 Java Just in Time - John Latham Page 1(0/0)
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 9: Consolidation of concepts so far 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Java concepts 5 Aim 6 Java concepts 7 Type: long 8 Type: short 9 Type: byte 10 Type: char 11 Type: char:
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 9: Consolidation of concepts so far 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Java concepts 5 Aim 6 Java concepts 7 Type: long 8 Type: short 9 Type: byte 10 Type: char 11 Type: char:
Interpreted vs Compiled. Java Compile. Classes, Objects, and Methods. Hello World 10/6/2016. Python Interpreted. Java Compiled
 Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
1007 Imperative Programming Part II
 Agenda 1007 Imperative Programming Part II We ve seen the basic ideas of sequence, iteration and selection. Now let s look at what else we need to start writing useful programs. Details now start to be
Agenda 1007 Imperative Programming Part II We ve seen the basic ideas of sequence, iteration and selection. Now let s look at what else we need to start writing useful programs. Details now start to be
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise
 COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
COMP 110 Project 1 Programming Project Warm-Up Exercise Creating Java Source Files Over the semester, several text editors will be suggested for students to try out. Initially, I suggest you use JGrasp,
Kickstart Intro to Java Part I
 Kickstart Intro to Java Part I COMP346/5461 - Operating Systems Revision 1.6 February 9, 2004 1 Topics Me, Myself, and I Why Java 1.2.*? Setting Up the Environment Buzz about Java Java vs. C++ Basic Java
Kickstart Intro to Java Part I COMP346/5461 - Operating Systems Revision 1.6 February 9, 2004 1 Topics Me, Myself, and I Why Java 1.2.*? Setting Up the Environment Buzz about Java Java vs. C++ Basic Java
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java by Vlad Costel Ungureanu for Learn Stuff Programming Languages A programming language is a formal constructed language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly
Getting started with Java by Vlad Costel Ungureanu for Learn Stuff Programming Languages A programming language is a formal constructed language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly
Review Chapters 1 to 4. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Department of Computer Science University of Pretoria. Introduction to Computer Science COS 151
 Department of Computer Science University of Pretoria Introduction to Computer Science COS 151 Practical 1 16 February 2018 1 Plagiarism Policy The Department of Computer Science considers plagiarism as
Department of Computer Science University of Pretoria Introduction to Computer Science COS 151 Practical 1 16 February 2018 1 Plagiarism Policy The Department of Computer Science considers plagiarism as
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 05 / 31 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / Comments? recap and some more details about variables, and if / else statements do lab work
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 05 / 31 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / Comments? recap and some more details about variables, and if / else statements do lab work
CSE 142 Su 04 Computer Programming 1 - Java. Objects
 Objects Objects have state and behavior. State is maintained in instance variables which live as long as the object does. Behavior is implemented in methods, which can be called by other objects to request
Objects Objects have state and behavior. State is maintained in instance variables which live as long as the object does. Behavior is implemented in methods, which can be called by other objects to request
Programs, Statements, Variables
 Programs, Statements, Variables Wolfgang Schreiner Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC) Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria Wolfgang.Schreiner@risc.jku.at http://www.risc.jku.at Wolfgang
Programs, Statements, Variables Wolfgang Schreiner Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC) Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria Wolfgang.Schreiner@risc.jku.at http://www.risc.jku.at Wolfgang
CS11 Java. Fall Lecture 1
 CS11 Java Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! 8 Lectures Slides posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 7-8 Lab Assignments Made available on Mondays Due one week later Monday, 12 noon
CS11 Java Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! 8 Lectures Slides posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 7-8 Lab Assignments Made available on Mondays Due one week later Monday, 12 noon
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
Chapter 2 Author Notes
 Chapter 2 Author Notes Good Programming Practice 2.1 Every program should begin with a comment that explains the purpose of the program, the author and the date and time the program was last modified.
Chapter 2 Author Notes Good Programming Practice 2.1 Every program should begin with a comment that explains the purpose of the program, the author and the date and time the program was last modified.
1. Download the JDK 6, from
 1. Install the JDK 1. Download the JDK 6, from http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/widget/jdk6.jsp. 2. Once the file is completed downloaded, execute it and accept the license agreement. 3. Select the
1. Install the JDK 1. Download the JDK 6, from http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/widget/jdk6.jsp. 2. Once the file is completed downloaded, execute it and accept the license agreement. 3. Select the
Programming Language Concepts: Lecture 2
 Programming Language Concepts: Lecture 2 Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute madhavan@cmi.ac.in http://www.cmi.ac.in/~madhavan/courses/pl2011 PLC 2011, Lecture 2, 6 January 2011 Classes and
Programming Language Concepts: Lecture 2 Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute madhavan@cmi.ac.in http://www.cmi.ac.in/~madhavan/courses/pl2011 PLC 2011, Lecture 2, 6 January 2011 Classes and
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Java Basics
 WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics
 CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Prerequisites These are the topics that I assume that you have already seen: Variables Boolean expressions
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Prerequisites These are the topics that I assume that you have already seen: Variables Boolean expressions
TOPIC 2 INTRODUCTION TO JAVA AND DR JAVA
 1 TOPIC 2 INTRODUCTION TO JAVA AND DR JAVA Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia Approach by M. Guzdial and B. Ericson, and instructor materials prepared
1 TOPIC 2 INTRODUCTION TO JAVA AND DR JAVA Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia Approach by M. Guzdial and B. Ericson, and instructor materials prepared
Arrays. Lecture 9 COP 3014 Fall October 16, 2017
 Arrays Lecture 9 COP 3014 Fall 2017 October 16, 2017 Array Definition An array is an indexed collection of data elements of the same type. Indexed means that the array elements are numbered (starting at
Arrays Lecture 9 COP 3014 Fall 2017 October 16, 2017 Array Definition An array is an indexed collection of data elements of the same type. Indexed means that the array elements are numbered (starting at
BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I
![BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I](/thumbs/81/83968367.jpg) BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
5/3/2006. Today! HelloWorld in BlueJ. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont.
 Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Chapter 2: Programming Concepts
 Chapter 2: Programming Concepts Objectives Students should Know the steps required to create programs using a programming language and related terminology. Be familiar with the basic structure of a Java
Chapter 2: Programming Concepts Objectives Students should Know the steps required to create programs using a programming language and related terminology. Be familiar with the basic structure of a Java
1B1a Programming I Getting Started
 1B1a Programming I Getting Started Agenda Definitions. What is programming? What is Java? Writing your first program. Classes and Objects. 1 2 Reading You should be reading chapters 1 & 2 of the text book.
1B1a Programming I Getting Started Agenda Definitions. What is programming? What is Java? Writing your first program. Classes and Objects. 1 2 Reading You should be reading chapters 1 & 2 of the text book.
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter Scope Introduce the Java programming language Program compilation and execution Problem solving in general The software development process Overview of object-oriented principles
Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter Scope Introduce the Java programming language Program compilation and execution Problem solving in general The software development process Overview of object-oriented principles
CHAPTER 2 Java Fundamentals
 CHAPTER 2 Java Fundamentals Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 2 discusses the following main topics: The Parts of a Java Program The print and println Methods, and
CHAPTER 2 Java Fundamentals Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 2 discusses the following main topics: The Parts of a Java Program The print and println Methods, and
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba. (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Introduction To Java. Chapter 1. Origins of the Java Language. Origins of the Java Language. Objects and Methods. Origins of the Java Language
 Chapter 1 Getting Started Introduction To Java Most people are familiar with Java as a language for Internet applications We will study Java as a general purpose programming language The syntax of expressions
Chapter 1 Getting Started Introduction To Java Most people are familiar with Java as a language for Internet applications We will study Java as a general purpose programming language The syntax of expressions
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types and
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types and
A Foundation for Programming
 Program Development Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 2/17/11 7:35 AM! A Foundation for Programming any program you
Program Development Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 2/17/11 7:35 AM! A Foundation for Programming any program you
CMSC 150 LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE HELLO WORLD
 CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 8: SEP. 29TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 8: SEP. 29TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Prepare the Weekly Quiz The weekly quiz is for the knowledge we learned in the previous week (both the
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 8: SEP. 29TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Prepare the Weekly Quiz The weekly quiz is for the knowledge we learned in the previous week (both the
The compiler is spewing error messages.
 Appendix B Debugging There are a few different kinds of errors that can occur in a program, and it is useful to distinguish between them in order to track them down more quickly. Compile-time errors are
Appendix B Debugging There are a few different kinds of errors that can occur in a program, and it is useful to distinguish between them in order to track them down more quickly. Compile-time errors are
PROGRAMMING STYLE. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 PROGRAMMING STYLE Fundamentals of Computer Science I Documentation and Style: Outline Meaningful Names Comments Indentation Named Constants Whitespace Compound Statements Documentation and Style Most programs
PROGRAMMING STYLE Fundamentals of Computer Science I Documentation and Style: Outline Meaningful Names Comments Indentation Named Constants Whitespace Compound Statements Documentation and Style Most programs
Introduction to JAVA
 Java A001 Hello World Let's study the entire program below: Introduction to JAVA // The "A001" class. import java.awt.*; public class A001 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello
Java A001 Hello World Let's study the entire program below: Introduction to JAVA // The "A001" class. import java.awt.*; public class A001 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
INFO Object-Oriented Programming
 INFO0062 - Object-Oriented Programming Exercise session #1 - Basic Java programs Jean-François Grailet University of Liège Faculty of Applied Sciences Academic Year 2017-2018 Creating a simple Java program
INFO0062 - Object-Oriented Programming Exercise session #1 - Basic Java programs Jean-François Grailet University of Liège Faculty of Applied Sciences Academic Year 2017-2018 Creating a simple Java program
Java Programming Fundamentals - Day Instructor: Jason Yoon Website:
 Java Programming Fundamentals - Day 1 07.09.2016 Instructor: Jason Yoon Website: http://mryoon.weebly.com Quick Advice Before We Get Started Java is not the same as javascript! Don t get them confused
Java Programming Fundamentals - Day 1 07.09.2016 Instructor: Jason Yoon Website: http://mryoon.weebly.com Quick Advice Before We Get Started Java is not the same as javascript! Don t get them confused
