Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word. Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
|
|
|
- Candace Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5 Methods Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection Statements Chapter 4 Loops Chapter 5 Methods in Chapter 19 Recursion Chapter 6 Arrays Chapter 23 Algorithm Efficiency and Sorting 1
2 Objectives To declare methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( ). To use method overloading and know ambiguous overloading ( 5.5). To determine the scope of local variables ( 5.6). To know how to use the methods in the Math class ( 5.8). To group classes into packages ( 5.11 Optional). 2
3 Introducing Methods A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. Define a method Invoke a method method header method body modifier return value type method name formal parameters public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; parameter list if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; return value return result; int z = max(x, y); actual parameters (arguments) 3
4 Introducing Methods, cont. Method signature is the combination of the method name and the parameter list. The variables defined in the method header are known as formal parameters. When a method is invoked, you pass a value to the parameter. This value is referred to as actual parameter or argument. 4
5 Introducing Methods, cont. A method may return a value. The returnvaluetype is the data type of the value the method returns. If the method does not return a value, the returnvaluetype is the keyword void. For example, the returnvaluetype in the main method is void. 5
6 animation Calling Methods, cont. pass the value of i pass the value of j public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; return result; public class TestMax{ public static void main(string [] args){ public static int max(int num1, int num2) { This program demonstrates calling a method max to return the largest of the int values TestMax 6
7 Call Stacks Space required for the main method k: j: 2 i: 5 Space required for the max method result: 5 num2: 2 num1: 5 Space required for the main method k: j: 2 i 5 Space required for the main method k: 5 j: 2 i: 5 i: 5 Stack is empty The main method The max method is The max method is is invoked. invoked. finished i and the return value is sent to k. The main method is finished. i Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
8 animation Trace Call Stack i is declared and initialized public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; i: 5 if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; The main method is invoked. return result; Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
9 animation Trace Call Stack j is declared and initialized public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; The main method is invoked. j: 2 i: 5 return result; Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
10 animation Trace Call Stack Declare k public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); Space required for the public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; main method k: j: 2 i: 5 if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; The main method is invoked. return result; Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
11 animation Trace Call Stack Invoke max(i, j) public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); Space required for the public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; main method k: j: 2 i: 5 if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; The main method is invoked. return result; Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
12 animation Trace Call Stack pass the values of i and j to num1 and num2 public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; num2: 2 num1: 5 Space required for the main method k: j: 2 i: 5 return result; The max method is invoked. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
13 animation Trace Call Stack pass the values of i and j to num1 and num2 public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; result: num2: 2 num1: 5 Space required for the main method k: j: 2 i: 5 return result; The max method is invoked. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
14 animation Trace Call Stack (num1 > num2) istrue public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; result: num2: 2 num1: 5 Space required for the main method k: j: 2 i: 5 return result; The max method is invoked. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
15 animation Trace Call Stack Assign num1 to result public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; Space required for the max method result: 5 num2: 2 num1: 5 Space required for the main method k: j: 2 i: 5 return result; The max method is invoked. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
16 animation Trace Call Stack Return result and assign it to k public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; Space required for the max method result: 5 num2: 2 num1: 5 Space required for the main method k:5 j: 2 i: 5 return result; The max method is invoked. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
17 animation Trace Call Stack Execute print statement public static void main(string[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; int k = max(i, j); System.out.println( "The maximum between " + i + " and " + j + " is " + k); Space required for the public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; main method k:5 j: 2 i: 5 if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; The main method is invoked. return result; Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
18 CAUTION A return statement is required for a nonvoid method. The following method is logically correct, but it has a compilation error, because the Java compiler thinks it possible that this method does not return any value. public static int sign(int n) { if (n > 0) return 1; else if (n == 0) return 0; else if (n < 0) return 1; //compile error should be public static int sign(int n) { if (n > 0) return 1; else if (n == 0) return 0; else return 1; To fix this problem, delete if (n<0) in the code. ในเมธอดแบบ void ม statement return ได หร อไม? 18
19 Void method with return public class Test { public static void main(string[] args) { int num= TestMax.max(2,20); System.out.println(num); printgrade(-78.5); public static void printgrade(double score) { if (score < 0 score > 100){ System.out.println("Invalid score"); return; if (score>=90.0) System.out.println("A"); else if (score >=80.0) System.out.println("B"); else if (score >=70.0) 0) System.out.println( println("c"); else if (score >=60.0) System.out.println("D"); else System.out.println("F"); Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Sixth Edition, (c) 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
20 Reuse Methods from Other Classes NOTE: One of the benefits of methods is for reuse. The max method can be invoked from any class besides TestMax. If you create a new class Test, you can invoke the max method using ClassName.methodName() e.g., TestMax.max() public class TestMax{ public static int max(int num1, int num2) { int result; if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else result = num2; return result; public class Test{ public static void main (String [] args){ int num = TestMax.max(2,20); System.out.println(num); 20
21 Passing Parameters public static void nprintln(int m, int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) System.out.println(m); Suppose you invoke the method using nprintln(5, 5); What is the output? Suppose you invoke the method using nprintln(15, Computer Science ); What is the output? Suppose you invoke the method using nprintln(15, 6, 5.6); What is the output? The arguments must match the parameter in order, number, and compatible type as defined in the method signature --int to double is ok. 21
22 public class TestPassByValue { /** Main method */ public static void main(string[] args) { // Declare and initialize variables int num1 = 1; int num2 = 2; System.out.println("Before invoking the swap method, num1 is " + num1 + " and num2 is " + num2); // Invoke the swap method to attempt to swap two variables swap(num1, num2); System.out.println("After invoking the swap method, num1 is " + num1 + " and num2 is " + num2); /** Swap two variables */ public static void swap(int n1, int n2) { // Swap n1 with n2 int temp = n1; n1 = n2; n2 = temp; System.out.println("\t\tAfter swapping n1 is " + n1 + " n2 is " + n2); 1 pass-by-value TestPassByValue 22
23 Pass by Value, cont. The values of num1 and num2 are passed to n1 and n2. Executing swap does not affect num1 and num2. Space required for the swap method temp: n2: 2 n1: 1 Space required for the main method num2: 2 num1: 1 Space required for the main method num2: 2 num1: 1 Space required for the main method num2: 2 num1: 1 Stack is empty The main method The swap method The swap method The main method is invoked is invoked is finished is finished Primitive type เป นแบบ เปนแบบ pass-by-value 23
24 Overloading Methods Two methods have the same name but different parameter lists within one class. Order, number, data type Overload method must thave different parameter lists and cannot overload methods based on different modifiers or return types //Listing 5.3 Overloading the max Method public static double max(double num1, double num2) { if (num1 > num2) return num1; else return num2; public static ti void m(int n, double d ) { public static void m(double d, int n){ public static int m(double d, int m){//no TestMethodOverloading ComputeTaxWithMethod 24
25 Ambiguous Invocation Sometimes there may be two or more possible matches for an invocation of a method, but the compiler cannot determine the most specific match. This is referred to as ambiguous invocation. Ambiguous invocation is a compilation error. 25
26 Ambiguous Invocation: compile error 1 public class AmbiguousOverloading { 2 public static void main(string[] args) { 3 System.out.println(max(1, 2)); public static ti double max(int num1, double num2) { 7 if (num1 > num2) 8 return num1; 9 else 10 return rn num2; public static double max(double num1, int num2) { 14 if (num1 > num2) return num1; else return num2; max(1, 5.6); max(6.7, 2); 26
27 Scope of Local Variables A local variable: a variable defined inside a method. Scope: the part of the program where the variable can be referenced. The scope of a local variable starts from its declaration and continues to the end of the block that contains the variable. A local variable must be declared before it can be used. 27
28 Scope of Local Variables, cont. You can declare a local variable with the same name multiple times in different nonnesting blocks in a method, but you cannot declare a local variable twice in nested blocks. for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (int i = 0; ; i < 10; ; j++) { 28
29 Scope of Local Variables, cont. A variable declared in the initial action part of a for loop header has its scope in the entire loop. Bt But a variable ibl declared dinside id a for loop body has its scope limited in the loop body from its declaration and to the end of the block that contains the variable. The scope of i The scope of j public static void method1() {.. for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {.. int j;... 29
30 Scope of Local Variables, cont. It is fine to declare i in two non-nesting blocks public static void method1() { int x = 1; int y = 1; for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { x += i; for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { y += i; It is wrong to declare i in two nesting blocks public static void method2() { int i = 1; int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) sum += i; 30
31 Scope of Local Variables, cont. // With errors public static ti void incorrectmethod() th { int x = 1; int y = 1; for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { int x = 0;//error x += i; 31
32 Class constants: PI E Class methods: The Math Class Trigonometric Methods Exponent Methods Rounding Methods min, max, abs, and random Methods 32
33 View java.lang.math Documentation You can view the complete documentation for the Math class online from 33
34 Eclipse Optional How to Set JavaDoc in Eclipse 1.Window Preference 2.แล วเล อก jre6 ป ม Edit 3.เล อกไฟล 3.เลอกไฟล rt.jar กดป ม กดป ม Javadoc Location 4. Browse ไปท directory ท ไฟล javadoc นามสก ล.zip และ browse ไปท path docs/api 34
35 Trigonometric Methods sin(double a) cos(double a) tan(double a) acos(double a) asin(double a) atan(double a) Examples: Math.sin(0) returns 0.0 Math.sin(Math.PI / 6) returns 0.5 Math.sin(Math.PI / 2) returns 1.0 Math.cos(0) returns 1.0 Math.cos(Math.PI / 6) returns Math.cos(Math.PI / 2) returns 0 ส งเกตการใช งาน 35
36 Exponent Methods exp(double a) Examples: Returns e raised to the power of a. log(double a) Returns the natural logarithm of a. log10(double a) Returns the 10-based logarithm of a. pow(double a, double b) Returns a raised to the power of b. Math.exp(1) returns 2.71 Math.log(2.71) returns 1.0 Math.pow(2, 3) returns 8.0 Math.pow(3, 2) returns 9.0 Math.pow(3.5, 2.5) returns Math.sqrt(4) returns 2.0 Math.sqrt(10.5) returns 3.24 sqrt(double a) Returns the square root of a. ส งเกตการใช งาน 36
37 Rounding Methods static double ceil(double x) x rounded up to its nearest integer. This integer is returned as a double value. static double floor(double x) x is rounded down to its nearest integer. This integer is returned as a double value. double rint(double x) x is rounded to its nearest integer. If x is equally close to two integers, the even one is returned as a double. int round(float x) Return (int)math.floor(x+0.5). long round(double x) Return (long)math.floor(x+0.5). 37
38 min, max, and abs max(a, b)and min(a, b) Returns the maximum or minimum of two parameters. abs(a) Returns the absolute value of the parameter. random() Returns a random double value in the range [0.0, 1.0). Examples: Math.max(2, 3) returns 3 Math.max(2.5, 3) returns 3.0 Math.min(2.5, 3.6) returns 2.5 Math.abs( abs(-2) returns 2 Math.abs(-2.1) returns 2.1 ส งเกตการใช งาน 38
39 The random Method Generates a random double value greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than 1.0 (0 <= Math.random() < 1.0). double ran = Math.random() *1.0; Examples: (int)(math.random() * 10) 50 + (int)(math.random() * 50) Returns a random integer between 0 and 9. Returns a random integer between 50 and 99. In general, a + Math.random() * b Returns a random number between a and a + b, excluding a + b. 39
40 Optional Package There are three reasons for using packages: 1. To avoid naming conflicts. When you develop reusable classes to be shared by other programmers, naming conflicts often occur. To prevent this, put your classes into packages so that they can be referenced through package names. 2. To distribute software conveniently. Packages group related classes so that they can be easily distributed. 3. To protect classes. Packages provide protection so that the protected members of the classes are accessible to the classes in the same package, but not to the external classes. 40
41 Java Platform, Standard Edition 6 API Specification System, String java.lang JOptionPane javax.swing import import javax.swing. JOptionPane; import javax.swing.*; java.lang ไม ต อง import Demo with Java API 41
42 Package-Naming Conventions Packages are hierarchical, and you can have packages within packages. For example, java.lang.math indicates that Math is a class in the package lang and that lang is a package in the package java. Levels of nesting can be used to ensure the uniqueness of package names. Choosing a unique name is important because your package may be used on the Internet by other programs. Java designers recommend that you use your Internet domain name in reverse order as a package prefix. Since Internet domain names are unique, this prevents naming conflicts. Suppose you want to create a package named mypackage on a host machine with the Internet domain name prenhall.com. To follow the naming convention, you would name the entire package com.prenhall.mypackage. By convention, package names are all in lowercase. 42
43 Package Directories Java expects one-to-one mapping of the package name and the file system directory structure. For the package named com.prenhall.mypackage, you must create a directory, as shown in the figure. In other words, a package is actually a directory that contains the bytecode of the classes. com.prenhall.mypackage hll Format.class 43
44 Putting Classes into Packages Every class in Java belongs to a package. The class is added to the package when it is compiled. All the classes that you have used so far in this book were placed in the current directory (a default package) when the Java source programs were compiled. To put a class in a specific package, you need to add the following line as the first statement in the program: package packagename; Ex.. package mylib; public class A{ เวลาใช งานโดยคลาสอ นๆ import mylib.a; public class Test{.. temp mylib A.class 44
45 Listing 5.8 Putting Classes into Packages Problem This example creates a class named Format and places it in the package com.prenhall.mypackage. The Format class contains the format(number, numofdecimaldigits) method that returns a new number with the specified number of digits after the decimal point. For example, format( , 2) returns 10.34, and format( , 3) returns Solution 1. Create Format.java as follows and save it into c:\book\com\prenhall\mypackage. // Format.java: Format number. //ช อไฟล ช อเด ยวก บคลาสท เป น public package com.prenhall.mypackage; public class Format { public static double format( double number, int numofdecimaldigits) { return Math.round(number * Math.pow(10, numofdecimaldigits)) / Math.pow(10, numofdecimaldigits); 2. Compile Format.java. Make sure Format.class is in c:\book\com\prenhall\mypackage. -c:\book>javac Format.java :หล งจากน นสร างไดเรกทอร ตามช อ package แล วย ายไฟล ไปใส เอง -c:\book>javac Format.java d. :สร างไดเรกทอร ตามช อ :สรางไดเรกทอรตามชอ package ให อ ตโนม ต ใหอตโนมต ตอจากไดเรกทอรปจจ บน ต อจากไดเรกทอร ป จจบ น 45
46 Setting classpath Environment Format.class The com directory does not thave to be the root tdirectory. In order for Java to know where your package is in the file system, you must modify the environment variable classpath so that it points to the directory in which your package resides. Suppose the com directory is under c:\book. The following line adds c:\book into the classpath: classpath=.;c:\book; The period (.) indicating the current directory is always in classpath. The directory c:\book is in classpath so that you can use the package com.prenhall.mypackage in the program. 46
47 Using Classes from Packages There are two ways to use classes from a package. One way is to use the fully qualified name of the class. For example, the fully qualified name for JOptionPane is javax.swing.joptionpane., For Format in the preceding example, it is com.prenhall.mypackage.format. This is convenient if the class is used a few times in the program. The other way is to use the import statement. For example, to import all the classes in the javax.swing package, you can use import javax.swing.*; An import that uses a * is called an import on demand declaration. You can also import a specific class. For example, this statement imports javax.swing.joptionpane: import javax.swing.joptionpane; The information for the classes in an imported package is not read in at compile time or runtime unless the class is used in the program. The import statement simply tells the compiler where to locate the classes. 47
48 Listing 5.9 Using Packages Problem This example shows a program that uses the Format class in the com.prenhall.mypackage.mypackage package. Solution 1. Create TestFormatClass.java as follows and save it into c:\book. The following code gives the solution to the problem. // TestFormatClass.java: Demonstrate using the Format class import com.prenhall.mypackage.format; public class TestFormatClass tcl { /** Main method */ public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println(Format.format( , ( 2)); System.out.println(Format.format( , 3)); 48
Chapter 5 Methods. Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk
 Chapter 5 Methods Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk ١ Introducing Methods A method is a collection of statements that
Chapter 5 Methods Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk ١ Introducing Methods A method is a collection of statements that
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( ). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug,
 1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. rights reserved. 0132130807 2 1 Problem int sum =
Chapter 5 Methods rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. rights reserved. 0132130807 2 1 Problem int sum =
Chapter 5 Methods. Modifier returnvaluetype methodname(list of parameters) { // method body; }
 Chapter 5 Methods 5.1 Introduction A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. You will learn how to: o create your own mthods with or without return values,
Chapter 5 Methods 5.1 Introduction A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. You will learn how to: o create your own mthods with or without return values,
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions
 Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Ninth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I
 CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
CS115 Principles of Computer Science
 CS115 Principles of Computer Science Chapter 5 Methods Prof. Joe X. Zhou Department of Computer Science CS115 Methods.1 Re: Objectives in Loops Sequence and selection aside, we need repetition (loops)
CS115 Principles of Computer Science Chapter 5 Methods Prof. Joe X. Zhou Department of Computer Science CS115 Methods.1 Re: Objectives in Loops Sequence and selection aside, we need repetition (loops)
COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1. Instructor: Parisa Rashidi
 COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1 Instructor: Parisa Rashidi Chapter 4 Loops for while do-while Last Week Chapter 5 Methods Input arguments Output Overloading Code reusability Scope of
COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1 Instructor: Parisa Rashidi Chapter 4 Loops for while do-while Last Week Chapter 5 Methods Input arguments Output Overloading Code reusability Scope of
Opening Problem. Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively.
 Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Opening Problem. Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively.
 Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Lecture 5: Methods CS2301
 Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Announcements. PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6. Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am
 Announcements PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6 Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am Room TBD Scope: Lecture 1 to Lecture 9 (Chapters 1 to 6 of text) You may bring a sheet of paper (A4, both sides) Tutoring
Announcements PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6 Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am Room TBD Scope: Lecture 1 to Lecture 9 (Chapters 1 to 6 of text) You may bring a sheet of paper (A4, both sides) Tutoring
12. Numbers. Java. Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini
 12. Numbers Java Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Numeric Type Conversions Math Class References Numeric Type Conversions Numeric Data Types (Review) Numeric Type Conversions Consider
12. Numbers Java Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Numeric Type Conversions Math Class References Numeric Type Conversions Numeric Data Types (Review) Numeric Type Conversions Consider
JAVA Programming Concepts
 JAVA Programming Concepts M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and Information Technology University of Jeddah, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@uj.edu.sa Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10,
JAVA Programming Concepts M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and Information Technology University of Jeddah, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@uj.edu.sa Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10,
Benefits of Methods. Chapter 5 Methods
 Chapter 5 Methods Benefits of Methods Write a method once and reuse it anywhere. Information hiding: hide the implementation from the user Reduce complexity 1 4 Motivating Example Often we need to find
Chapter 5 Methods Benefits of Methods Write a method once and reuse it anywhere. Information hiding: hide the implementation from the user Reduce complexity 1 4 Motivating Example Often we need to find
Chapter 6 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited
 Chapter 6 Methods Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from
Chapter 6 Methods Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from
Chapter 6: Methods. Objectives 9/21/18. Opening Problem. Problem. Problem. Solution. CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University
 Opening Problem Chapter 6: Methods Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Original slides by Daniel Liang
Opening Problem Chapter 6: Methods Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Original slides by Daniel Liang
CS5000: Foundations of Programming. Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University
 CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Mathematical Functions Java provides many useful methods in the Math class for performing common mathematical
CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Mathematical Functions Java provides many useful methods in the Math class for performing common mathematical
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings
 Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Motivations Suppose you need to estimate
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, Global Edition. Pearson Education Limited 2015 1 Motivations Suppose you need to estimate
Methods. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Methods CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Opening Problem Find multiple sums of integers: - from 1 to 10, - from 20 to 30, - from 35 to 45,... 2
Methods CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Opening Problem Find multiple sums of integers: - from 1 to 10, - from 20 to 30, - from 35 to 45,... 2
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Static methods Remember the main method header? public static void
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Lecture #6-7 Methods
 Lecture #6-7 s 1. a. group of statements designed to perform a specific function b. may be reused many times i. in a particular program or ii. in multiple programs 2. Examples from the Java Library a.
Lecture #6-7 s 1. a. group of statements designed to perform a specific function b. may be reused many times i. in a particular program or ii. in multiple programs 2. Examples from the Java Library a.
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java
 CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture IX: Methods Introduction method: construct for grouping statements together to
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture IX: Methods Introduction method: construct for grouping statements together to
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Methods
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Methods Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Methods Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #7. Methods
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #7
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #7
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Methods
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Methods Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Methods Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java
 CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture X: Methods II Passing Arguments Passing Arguments methods can accept outside information
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture X: Methods II Passing Arguments Passing Arguments methods can accept outside information
INTRODUCTION TO C++ FUNCTIONS. Dept. of Electronic Engineering, NCHU. Original slides are from
 INTRODUCTION TO C++ FUNCTIONS Original slides are from http://sites.google.com/site/progntut/ Dept. of Electronic Engineering, NCHU Outline 2 Functions: Program modules in C Function Definitions Function
INTRODUCTION TO C++ FUNCTIONS Original slides are from http://sites.google.com/site/progntut/ Dept. of Electronic Engineering, NCHU Outline 2 Functions: Program modules in C Function Definitions Function
Chapter 4. Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings
 Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings 1 Outline 1. Java Class Library 2. Class Math 3. Character Data Type 4. Class String 5. printf Statement 2 1. Java Class Library A class library
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings 1 Outline 1. Java Class Library 2. Class Math 3. Character Data Type 4. Class String 5. printf Statement 2 1. Java Class Library A class library
int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) sum += i; System.out.println("Sum from 1 to 10 is " + sum);
 problem METHODS www.thestudycampus.com 5.1 Introduction Suppose that you need to find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to45, respectively. You may write the code as follows:
problem METHODS www.thestudycampus.com 5.1 Introduction Suppose that you need to find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to45, respectively. You may write the code as follows:
Advanced Computer Programming
 Programming in the Large I: Methods (Subroutines) 188230 Advanced Computer Programming Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Department of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
Programming in the Large I: Methods (Subroutines) 188230 Advanced Computer Programming Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Department of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
Methods. Eng. Mohammed Abdualal
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 8 Methods
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 8 Methods
Functions. Prof. Indranil Sen Gupta. Dept. of Computer Science & Engg. Indian Institute t of Technology Kharagpur. Introduction
 Functions Prof. Indranil Sen Gupta Dept. of Computer Science & Engg. Indian Institute t of Technology Kharagpur Programming and Data Structure 1 Function Introduction A self-contained program segment that
Functions Prof. Indranil Sen Gupta Dept. of Computer Science & Engg. Indian Institute t of Technology Kharagpur Programming and Data Structure 1 Function Introduction A self-contained program segment that
Methods (Deitel chapter 6)
 Methods (Deitel chapter 6) 1 Plan 2 Introduction Program Modules in Java Math-Class Methods Method Declarations Argument Promotion Java API Packages Random-Number Generation Scope of Declarations Methods
Methods (Deitel chapter 6) 1 Plan 2 Introduction Program Modules in Java Math-Class Methods Method Declarations Argument Promotion Java API Packages Random-Number Generation Scope of Declarations Methods
Methods (Deitel chapter 6)
 1 Plan 2 Methods (Deitel chapter ) Introduction Program Modules in Java Math-Class Methods Method Declarations Argument Promotion Java API Packages Random-Number Generation Scope of Declarations Methods
1 Plan 2 Methods (Deitel chapter ) Introduction Program Modules in Java Math-Class Methods Method Declarations Argument Promotion Java API Packages Random-Number Generation Scope of Declarations Methods
Functions. Functions are everywhere in C. Pallab Dasgupta Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc & Engg INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR
 1 Functions Functions are everywhere in C Pallab Dasgupta Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc & Engg INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR Introduction Function A self-contained program segment that carries
1 Functions Functions are everywhere in C Pallab Dasgupta Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc & Engg INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR Introduction Function A self-contained program segment that carries
Module 4: Characters, Strings, and Mathematical Functions
 Module 4: Characters, Strings, and Mathematical Functions Objectives To solve mathematics problems by using the methods in the Math class ( 4.2). To represent characters using the char type ( 4.3). To
Module 4: Characters, Strings, and Mathematical Functions Objectives To solve mathematics problems by using the methods in the Math class ( 4.2). To represent characters using the char type ( 4.3). To
Expressions and operators
 Mathematical operators and expressions The five basic binary mathematical operators are Operator Operation Example + Addition a = b + c - Subtraction a = b c * Multiplication a = b * c / Division a = b
Mathematical operators and expressions The five basic binary mathematical operators are Operator Operation Example + Addition a = b + c - Subtraction a = b c * Multiplication a = b * c / Division a = b
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word. and Java. Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations
 Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter p 1 Introduction to Computers, p, Programs, g, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter p 1 Introduction to Computers, p, Programs, g, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
Lecture 2:- Functions. Introduction
 Lecture 2:- Functions Introduction A function groups a number of program statements into a unit and gives it a name. This unit can then be invoked from other parts of the program. The most important reason
Lecture 2:- Functions Introduction A function groups a number of program statements into a unit and gives it a name. This unit can then be invoked from other parts of the program. The most important reason
DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY
 DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY REPEAT EXAMINATIONS 2008 MODULE: Object-oriented Programming I - EE219 COURSE: B.Eng. in Electronic Engineering (Year 2 & 3) B.Eng. in Information Telecomms Engineering (Year 2 &
DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY REPEAT EXAMINATIONS 2008 MODULE: Object-oriented Programming I - EE219 COURSE: B.Eng. in Electronic Engineering (Year 2 & 3) B.Eng. in Information Telecomms Engineering (Year 2 &
Primitive Data Types: Intro
 Primitive Data Types: Intro Primitive data types represent single values and are built into a language Java primitive numeric data types: 1. Integral types (a) byte (b) int (c) short (d) long 2. Real types
Primitive Data Types: Intro Primitive data types represent single values and are built into a language Java primitive numeric data types: 1. Integral types (a) byte (b) int (c) short (d) long 2. Real types
Top-down programming design
 1 Top-down programming design Top-down design is a programming style, the mainstay of traditional procedural languages, in which design begins by specifying complex pieces and then dividing them into successively
1 Top-down programming design Top-down design is a programming style, the mainstay of traditional procedural languages, in which design begins by specifying complex pieces and then dividing them into successively
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program 1 Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies,
1.1 Your First Program 1 Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies,
Lecture 05: Methods. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
 Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY
 DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATIONS 2007 MODULE: Object Oriented Programming I - EE219 COURSE: B.Eng. in Electronic Engineering B.Eng. in Information Telecommunications Engineering B.Eng.
DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATIONS 2007 MODULE: Object Oriented Programming I - EE219 COURSE: B.Eng. in Electronic Engineering B.Eng. in Information Telecommunications Engineering B.Eng.
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
Activity 4: Methods. Content Learning Objectives. Process Skill Goals
 Activity 4: Methods Java programs are organized into classes, each of which has one or more methods, each of which has one or more statements. Writing methods allows you to break down a complex program
Activity 4: Methods Java programs are organized into classes, each of which has one or more methods, each of which has one or more statements. Writing methods allows you to break down a complex program
Expanded Guidelines on Programming Style and Documentation
 Page 1 of 5 Expanded Guidelines on Programming Style and Documentation Introduction Introduction to Java Programming, 5E Y. Daniel Liang liang@armstrong.edu Programming style deals with the appearance
Page 1 of 5 Expanded Guidelines on Programming Style and Documentation Introduction Introduction to Java Programming, 5E Y. Daniel Liang liang@armstrong.edu Programming style deals with the appearance
A Foundation for Programming
 2.1 Functions A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
2.1 Functions A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
The Math Class. Using various math class methods. Formatting the values.
 The Math Class Using various math class methods. Formatting the values. The Math class is used for mathematical operations; in our case some of its functions will be used. In order to use the Math class,
The Math Class Using various math class methods. Formatting the values. The Math class is used for mathematical operations; in our case some of its functions will be used. In order to use the Math class,
Using Free Functions
 Chapter 3 Using Free Functions 3rd Edition Computing Fundamentals with C++ Rick Mercer Franklin, Beedle & Associates Goals Evaluate some mathematical and trigonometric functions Use arguments in function
Chapter 3 Using Free Functions 3rd Edition Computing Fundamentals with C++ Rick Mercer Franklin, Beedle & Associates Goals Evaluate some mathematical and trigonometric functions Use arguments in function
Java, Arrays and Functions Recap. CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University
 Java, Arrays and Functions Recap CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse260 1 Objectives Refresh information from CSE160 2 3 How Data is Stored? What
Java, Arrays and Functions Recap CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse260 1 Objectives Refresh information from CSE160 2 3 How Data is Stored? What
CT 229 Java Syntax Continued
 CT 229 Java Syntax Continued 06/10/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Due Date for current lab assignment : Oct 8 th Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given in the assignment
CT 229 Java Syntax Continued 06/10/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments Due Date for current lab assignment : Oct 8 th Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given in the assignment
M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s
 M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s Objective #1: Call methods. Methods are reusable sections of code that perform actions. Many methods come from classes that are built into the Java language. For
M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s Objective #1: Call methods. Methods are reusable sections of code that perform actions. Many methods come from classes that are built into the Java language. For
1.1 Your First Program! Naive ideal. Natural language instructions.
 Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. 1.1 Your First Program Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
Why Programming? Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. 1.1 Your First Program Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of these heavenly bodies, subject
Lecture 1 Java SE Programming
 Lecture 1 Java SE Programming presentation Java Programming Software App Development Assoc. Prof. Cristian Toma Ph.D. D.I.C.E/D.E.I.C Department of Economic Informatics & Cybernetics www.dice.ase.ro cristian.toma@ie.ase.ro
Lecture 1 Java SE Programming presentation Java Programming Software App Development Assoc. Prof. Cristian Toma Ph.D. D.I.C.E/D.E.I.C Department of Economic Informatics & Cybernetics www.dice.ase.ro cristian.toma@ie.ase.ro
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Assignments Reading Assignment: Chapter 3: Introduction to Parameters and Objects The Class 10 Exercise
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Assignments Reading Assignment: Chapter 3: Introduction to Parameters and Objects The Class 10 Exercise
Supplement D: Expanded Guidelines on Programming Style and Documentation
 Page 1 of 5 Introduction Supplement D: Expanded Guidelines on Programming Style and Documentation For Introduction to Java Programming Y. Daniel Liang mailto:liang@armstrong.edu Programming style deals
Page 1 of 5 Introduction Supplement D: Expanded Guidelines on Programming Style and Documentation For Introduction to Java Programming Y. Daniel Liang mailto:liang@armstrong.edu Programming style deals
Recapitulate CSE160: Java basics, types, statements, arrays and methods
 Recapitulate CSE160: Java basics, types, statements, arrays and methods CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse260 1 Objectives Refresh information from
Recapitulate CSE160: Java basics, types, statements, arrays and methods CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse260 1 Objectives Refresh information from
Java Methods. Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer May 23, 2017
 Java Methods Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 23, 2017 Java Methods In Java, the word method refers to the same kind of thing that the word function is used for in other languages. Specifically, a method
Java Methods Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 23, 2017 Java Methods In Java, the word method refers to the same kind of thing that the word function is used for in other languages. Specifically, a method
Functions. Autumn Semester 2009 Programming and Data Structure 1. Courtsey: University of Pittsburgh-CSD-Khalifa
 Functions Autumn Semester 2009 Programming and Data Structure 1 Courtsey: University of Pittsburgh-CSD-Khalifa Introduction Function A self-contained program segment that carries out some specific, well-defined
Functions Autumn Semester 2009 Programming and Data Structure 1 Courtsey: University of Pittsburgh-CSD-Khalifa Introduction Function A self-contained program segment that carries out some specific, well-defined
The Math Class (Outsource: Math Class Supplement) Random Numbers. Lab 06 Math Class
 The (Outsource: Supplement) The includes a number of constants and methods you can use to perform common mathematical functions. A commonly used constant found in the Math class is Math.PI which is defined
The (Outsource: Supplement) The includes a number of constants and methods you can use to perform common mathematical functions. A commonly used constant found in the Math class is Math.PI which is defined
1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4'
 Practice questions: 1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4' 2. Will System.out.println((char)4) display 4? a. Yes b. No 3. The expression "Java
Practice questions: 1. Which of the following is the correct expression of character 4? a. 4 b. "4" c. '\0004' d. '4' 2. Will System.out.println((char)4) display 4? a. Yes b. No 3. The expression "Java
Programmierpraktikum
 Programmierpraktikum Claudius Gros, SS2012 Institut für theoretische Physik Goethe-University Frankfurt a.m. 1 of 22 10/25/2012 09:08 AM Java - Basic Data Types 2 of 22 10/25/2012 09:08 AM primitive data
Programmierpraktikum Claudius Gros, SS2012 Institut für theoretische Physik Goethe-University Frankfurt a.m. 1 of 22 10/25/2012 09:08 AM Java - Basic Data Types 2 of 22 10/25/2012 09:08 AM primitive data
Outline. Overview. Control statements. Classes and methods. history and advantage how to: program, compile and execute 8 data types 3 types of errors
 Outline Overview history and advantage how to: program, compile and execute 8 data types 3 types of errors Control statements Selection and repetition statements Classes and methods methods... 2 Oak A
Outline Overview history and advantage how to: program, compile and execute 8 data types 3 types of errors Control statements Selection and repetition statements Classes and methods methods... 2 Oak A
Methods CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal
 Methods CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what a method is in Java Understand Java s Math Class and how to use it Learn the syntax of method construction Learn both void methods
Methods CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what a method is in Java Understand Java s Math Class and how to use it Learn the syntax of method construction Learn both void methods
Methods CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Methods CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what a method is in Java Understand Java s Math Class and how to use it Learn the syntax of method construction Learn both void methods
Methods CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what a method is in Java Understand Java s Math Class and how to use it Learn the syntax of method construction Learn both void methods
Functions. x y z. f (x, y, z) Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing)
 2.1 Functions Functions Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing) Return one output value Input Arguments x y z f Return Value f (x, y, z)
2.1 Functions Functions Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing) Return one output value Input Arguments x y z f Return Value f (x, y, z)
CISC-124. This week we continued to look at some aspects of Java and how they relate to building reliable software.
 CISC-124 20180129 20180130 20180201 This week we continued to look at some aspects of Java and how they relate to building reliable software. Multi-Dimensional Arrays Like most languages, Java permits
CISC-124 20180129 20180130 20180201 This week we continued to look at some aspects of Java and how they relate to building reliable software. Multi-Dimensional Arrays Like most languages, Java permits
public class Foo { private int var; public int Method1() { // var accessible anywhere here } public int MethodN() {
 Scoping, Static Variables, Overloading, Packages In this lecture, we will examine in more detail the notion of scope for variables. We ve already indicated that variables only exist within the block they
Scoping, Static Variables, Overloading, Packages In this lecture, we will examine in more detail the notion of scope for variables. We ve already indicated that variables only exist within the block they
Object Oriented Methods : Deeper Look Lecture Three
 University of Babylon Collage of Computer Assistant Lecturer : Wadhah R. Baiee Experience has shown that the best way to develop and maintain a large program is to construct it from small, simple pieces,
University of Babylon Collage of Computer Assistant Lecturer : Wadhah R. Baiee Experience has shown that the best way to develop and maintain a large program is to construct it from small, simple pieces,
1.1 Your First Program
 Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject
Why Programming? 1.1 Your First Program Why programming? Need to tell computer what you want it to do. Naive ideal. Natural language instructions. Please simulate the motion of N heavenly bodies, subject
Classes. Classes as Code Libraries. Classes as Data Structures. Classes/Objects/Interfaces (Savitch, Various Chapters)
 Classes Classes/Objects/Interfaces (Savitch, Various Chapters) TOPICS Classes Public versus Private Static Data Static Methods Interfaces Classes are the basis of object-oriented (OO) programming. They
Classes Classes/Objects/Interfaces (Savitch, Various Chapters) TOPICS Classes Public versus Private Static Data Static Methods Interfaces Classes are the basis of object-oriented (OO) programming. They
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 5/20/2013 9:37:22 AM Why Programming? Why programming? Need
1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 5/20/2013 9:37:22 AM Why Programming? Why programming? Need
Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x );
![Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x ); Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x );](/thumbs/82/85488895.jpg) Chapter 5 Methods Sections Pages Review Questions Programming Exercises 5.1 5.11 142 166 1 18 2 22 (evens), 30 Method Example 1. This is of a main() method using a another method, f. public class FirstMethod
Chapter 5 Methods Sections Pages Review Questions Programming Exercises 5.1 5.11 142 166 1 18 2 22 (evens), 30 Method Example 1. This is of a main() method using a another method, f. public class FirstMethod
Advanced Object Concepts
 Understanding Blocks Blocks - Appears within any class or method, the code between a pair of curly braces Outside block- The first block, begins immediately after the method declaration and ends at the
Understanding Blocks Blocks - Appears within any class or method, the code between a pair of curly braces Outside block- The first block, begins immediately after the method declaration and ends at the
CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I
 CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science department Lecture 7&8: Methods Lecture Contents What is a method? Static methods Declaring and using methods Parameters Scope of declaration Overloading
CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science department Lecture 7&8: Methods Lecture Contents What is a method? Static methods Declaring and using methods Parameters Scope of declaration Overloading
CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE
 CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE Computer Science Department Lecture 3: C# language basics Lecture Contents 2 C# basics Conditions Loops Methods Arrays Dr. Amal Khalifa, Spr 2015 3 Conditions and
CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE Computer Science Department Lecture 3: C# language basics Lecture Contents 2 C# basics Conditions Loops Methods Arrays Dr. Amal Khalifa, Spr 2015 3 Conditions and
! Widely available. ! Widely used. ! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs. ! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.
 Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features.! Widely available.! Widely used.! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs.! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.! No perfect
Why Java? Lecture 2: Intro to Java Java features.! Widely available.! Widely used.! Variety of automatic checks for mistakes in programs.! Embraces full set of modern abstractions. Caveat.! No perfect
Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes
 Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes Quick review of last lecture September 8, 2006 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2006 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev
Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes Quick review of last lecture September 8, 2006 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2006 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev
Classes. Classes as Code Libraries. Classes as Data Structures
 Classes Classes/Objects/Interfaces (Savitch, Various Chapters) TOPICS Classes Public versus Private Static Data Static Methods Interfaces Classes are the basis of object-oriented (OO) programming. They
Classes Classes/Objects/Interfaces (Savitch, Various Chapters) TOPICS Classes Public versus Private Static Data Static Methods Interfaces Classes are the basis of object-oriented (OO) programming. They
Chapter 3 Selections. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Using Java Classes Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
Using Java Classes 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Strings I/O (using Scanner) Loops, Conditionals, Scope Math Class (random) Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 The Math Class The Math class
CHAPTER 4 MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS, CHARACTERS, STRINGS
 CHAPTER 4 MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS, CHARACTERS, STRINGS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS Java
CHAPTER 4 MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS, CHARACTERS, STRINGS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS Java
Functions. Lab 4. Introduction: A function : is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation.
 Lab 4 Functions Introduction: A function : is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. The following is its format: type name ( parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements
Lab 4 Functions Introduction: A function : is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. The following is its format: type name ( parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements
1.1 Your First Program
 1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 1/29/11 6:37 AM! Why Programming? Why programming? Need to
1.1 Your First Program Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2010 1/29/11 6:37 AM! Why Programming? Why programming? Need to
Methods CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal
 Methods CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what a method is in Java Understand Java s Math Class Learn the syntax of method construction Learn both void methods and methods that
Methods CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand what a method is in Java Understand Java s Math Class Learn the syntax of method construction Learn both void methods and methods that
Chapter 5 - Methods Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
 1 Chapter 5 - Methods 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 Introduction Modules Small pieces of a problem e.g., divide and conquer Facilitate design, implementation, operation and maintenance
1 Chapter 5 - Methods 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 Introduction Modules Small pieces of a problem e.g., divide and conquer Facilitate design, implementation, operation and maintenance
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings
 Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings 4.1 Introduction The focus of this chapter is to introduce mathematical functions, characters, string objects, and use them to develop programs.
Chapter 4 Mathematical Functions, Characters, and Strings 4.1 Introduction The focus of this chapter is to introduce mathematical functions, characters, string objects, and use them to develop programs.
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
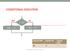 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
x++ vs. ++x x=y++ x=++y x=0; a=++x; b=x++; What are the values of a, b, and x?
 x++ vs. ++x x=y++ x=++y x=0; a=++x; b=x++; What are the values of a, b, and x? x++ vs. ++x public class Plus{ public static void main(string []args){ int x=0; int a=++x; System.out.println(x); System.out.println(a);
x++ vs. ++x x=y++ x=++y x=0; a=++x; b=x++; What are the values of a, b, and x? x++ vs. ++x public class Plus{ public static void main(string []args){ int x=0; int a=++x; System.out.println(x); System.out.println(a);
