Constants are named in ALL_CAPS, using upper case letters and underscores in their names.
|
|
|
- Abel Williamson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Naming conventions in Java The method signature Invoking methods All class names are capitalized Variable names and method names start with a lower case letter, but every word in the name after the first word starts with an upper case letter. Method names are followed by round brackets. Variable names are not. Constants are named in ALL_CAPS, using upper case letters and underscores in their names. Crab, World, Actor, MyWorld act(), move(10), atworldedge(), wormcount, score In the examples above, act, move and atworldedge are all methods, while wormcount and score are variables. EAST, BLACK, RED The method signature defines a method. It contains four parts: 1. The access level - usually public or private, but could be protected public void movearound() 2. The return type - int, boolean, String, public boolean atedge() double or void are the most common data public void turn( int angle ) types. 3. The name of the method. 4. The formal parameters. Invoking or calling a method involves using the method name and providing the required actual parameter values. If the method has a movearound(); void return type, then that method is a command and is if( atedge() ) { used as a separate statement in your code. If the method has a return type other than void (int, turn( 15 ); double, String or boolean) then the method is providing information which your code must use in some way.
2 How the world is measured Adding objects to the world Where is an object? The world is made up of square cells arranged to rows and columns. The world's dimensions are established in the constructor of the World subclass. Objects are added to the world by invoking the addobject method. This method has three parameters. the first is the object to be added to the world and the second and third parameters are the x and t coordinates of the location where the object is to be added to the world. The position of an object in the world is the position of the center of the object's image and is given by the methods getx (the column the object is in) and gety (the row the object is in). super( 800, 600, 1); int w = getwidth(); // w will be 800 int h = getheight(); // h will be 600 int w = getwidth(); // w will be 40 int h = getheight(); // h will be 30 // add a Crab object to the center of the world addobject( new Crab(), getwidth()/2, getheight()/2 );
3 There are two ways to make an object move: 1. The move method makes an object move in the direction it is facing. Making things move 2. The setlocation method Makes an object move in any direction, independent of where it is facing. The setlocation method ahs two parameters. the first one is the x- coordinate of the location you want the object to move to and the second parameter is the y-coordinate of the location you want the object to move to. You can make the object move left or right by subtracting or adding to its x- coordinate. You can make the object move up and down by subtracting or adding to its y-coordinate. // moves 10 cells in the direction it is facing move( 10 ); // moves to cell at column 200 and row 300 of the world setlocation( 200, 300 ); // moves the object 5 cells to the right setlocation( getx()+5, gety() );
4 Making things turn The Greenfoot classes To change that you can use the setrotation method or the turn method. 1. setrotation( int angle ) - sets the direction the object is facing to the angle parameter. 2. turn( int degree ) - turns the object from the direction it is currently facing by the number of degrees in its parameter. The Greenfoot class contains several useful methods for doing things in a Greenfoot scenario. These methods are all static methods which means they are invoked by using the class name and the method call in dot-notation. setrotation( 90 ); // face down turn( 15 ); Greenfoot.isKeyDown("left") Greenfoot.getRandomNumber(100) Greenfoot.stop();
5 Calling World methods from an Actor subclass. When the Java compiler seeing an method call in a line of your code, it looks for that method, first inside your class. If it's not there, it looks in each of your class' super classes, starting with the closest one in the class structure. If it can't find the method in any of these classes, you get an error message that says, for example, "Can not find symbol: method getwidth" In order to call methods that are in other classes you need to tell Java what class the method is in. If the method is a static method (see "The Greenfoot classes" above), you name the class, followed by a dot and the method call. If the method is non-static, then it belongs to an object, so you must reference the object, followed by a dot and the method call. So, to invoke a World method, you must get a reference to the world the object lives in using the getworld method. So, to call the getwidth method of the World class, from an Actor class, you'd use getworld().getwidth(). to invoke the same method inside the World class, you'd just use getwidth(). int x = getworld().getwidth()/2; int y = getworld().getheight()/2; getworld().addobject( new Ant(), x, y );
6 The if-statement The for-loop The if-statement allows your code to make true or false decisions and select different statements to execute based on those decisions. The for-loop is used to repeat a block of code more than once. The statement has three parts to it: 1. The initialization part declares an int variable and sets it to its initial value, usually The condition checks this variable against some condition. As long as the condition is true, the loop continues to repeat 3. The increment part, where the variable's value is changed, usually by 1. It is important to note that the for-loop automatically checks the condition before each iteration of the loop and changes the variable after every iteration of the loop. // adds a bug to the world 3% of the time int n = Greenfoot.getRandomNumber(100); if( n < 3 ) { // the bug is positioned randomly 25 cells from the top of // the world int x = Greenfoot.getRandomNumber(getWidth( )); int y = 25; addobject( new Bug(), x, y); move(); if( atworldedge() ) { turn(15); for(int r=0; r<15; r++) { // body of the loop The statements in the body of the loop will be repeated 15 times.
7 Collision Detection Detecting the edges of the word This method has one parameter, the class of objects you're looking for. It returns any object of that type whose image is intersecting the object's image. If no object is intersecting this object's image, the method returns a null pointer. You can use this fact to determine if an object is intersecting this object: An object is close to the top and left edges of the world when its x or y coordinate gets close to 0. It is close to the left or bottom edge when its x or y coordinate is close o the width or height of the world, respectively. Actor thing = getoneintersectingobject(thing.class); if( thing!= null ) { if( getx() < 5 ) { if( gety() < 5 ) { if( getx() > getworld().getwidth()-5 ) { if( gety() > getworld().getheight()-5 ) {
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot
 Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot Defining Methods 1 Copyright 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights Overview This lesson covers the following topics: Describe effective placement of methods
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot Defining Methods 1 Copyright 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights Overview This lesson covers the following topics: Describe effective placement of methods
Greenfoot! Introducing Java With Games And Simulations. Workshop material. Wombats. Object Orientation. Asteroids, Ants and other creatures.
 Greenfoot! Introducing Java With Games And Simulations Michael Kölling University of Kent Birmingham, June 2009 Workshop material Download and install Greenfoot: www.greenfoot.org Wombats. Download the
Greenfoot! Introducing Java With Games And Simulations Michael Kölling University of Kent Birmingham, June 2009 Workshop material Download and install Greenfoot: www.greenfoot.org Wombats. Download the
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot
 Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot Using Randomization and Understanding Dot Notation and Constructors 1 Copyright 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights Overview This lesson covers the following
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot Using Randomization and Understanding Dot Notation and Constructors 1 Copyright 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights Overview This lesson covers the following
asteroids-day 3 Class Space
 Class Space // (World, Actor, GreenfootImage, Greenfoot and MouseInfo) import greenfoot.*; * Space -- something for rockets to fly in. * * @author Prof. Carl B. Struck * @version November 2010 public class
Class Space // (World, Actor, GreenfootImage, Greenfoot and MouseInfo) import greenfoot.*; * Space -- something for rockets to fly in. * * @author Prof. Carl B. Struck * @version November 2010 public class
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot
 Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot Working with Source Code and Documentation 1 Copyright 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights Objectives This lesson covers the following topics: Demonstrate
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot Working with Source Code and Documentation 1 Copyright 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights Objectives This lesson covers the following topics: Demonstrate
Chapter Two: Classes and Objects
 Chapter Two: Classes and Objects Section 1: Real Objects Versus Virtual Objects Computer games do not have to match reality. In them we can violate the rules of physics (or make up our own), pigs can fly
Chapter Two: Classes and Objects Section 1: Real Objects Versus Virtual Objects Computer games do not have to match reality. In them we can violate the rules of physics (or make up our own), pigs can fly
Improving the Crab more sophisticated programming
 CHAPTER 3 Improving the Crab more sophisticated programming topics: concepts: random behavior, keyboard control, sound dot notation, random numbers, defining methods, comments In the previous chapter,
CHAPTER 3 Improving the Crab more sophisticated programming topics: concepts: random behavior, keyboard control, sound dot notation, random numbers, defining methods, comments In the previous chapter,
Session 1 Welcome to Greenfoot & Code Breaker Authored by Brian Cullen
 Session 1 Welcome to Greenfoot & Code Breaker Authored by Brian Cullen (bcullen@rossettschool.co.uk) (c) Copyright 2011 Computing At School. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Session 1 Welcome to Greenfoot & Code Breaker Authored by Brian Cullen (bcullen@rossettschool.co.uk) (c) Copyright 2011 Computing At School. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Assignment 4: Dodo gets smarter
 Assignment 4: Dodo gets smarter Algorithmic Thinking and Structured Programming (in Greenfoot) 2017 Renske Smetsers-Weeda & Sjaak Smetsers 1 Contents Introduction 1 Learning objectives 1 Instructions 1
Assignment 4: Dodo gets smarter Algorithmic Thinking and Structured Programming (in Greenfoot) 2017 Renske Smetsers-Weeda & Sjaak Smetsers 1 Contents Introduction 1 Learning objectives 1 Instructions 1
Improving the crab: more sophisticated programming
 Chapter 3 Improving the crab: more sophisticated programming topics: concepts: random behavior, keyboard control, sound dot notation, random numbers, defining methods, comments In the previous chapter,
Chapter 3 Improving the crab: more sophisticated programming topics: concepts: random behavior, keyboard control, sound dot notation, random numbers, defining methods, comments In the previous chapter,
Critters. Critter #2 Attack.ROAR Attack.POUNCE Attack.SCRATCH. Critter #1
 Critters This assignment was co-created by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp. This program focuses on classes, objects, and inheritance. You will write the following files: Ant.java, Bird.java, Crab.java, FireAnt.java,
Critters This assignment was co-created by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp. This program focuses on classes, objects, and inheritance. You will write the following files: Ant.java, Bird.java, Crab.java, FireAnt.java,
Session 4 Starting the Air Raid Game
 Session 4 Starting the Air Raid Game Authored by Brian Cullen (bcullen@rossettschool.co.uk/@mrbcullen) (c) Copyright 2011 Computing At School. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Session 4 Starting the Air Raid Game Authored by Brian Cullen (bcullen@rossettschool.co.uk/@mrbcullen) (c) Copyright 2011 Computing At School. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
JAVA MOCK TEST JAVA MOCK TEST II
 http://www.tutorialspoint.com JAVA MOCK TEST Copyright tutorialspoint.com This section presents you various set of Mock Tests related to Java Framework. You can download these sample mock tests at your
http://www.tutorialspoint.com JAVA MOCK TEST Copyright tutorialspoint.com This section presents you various set of Mock Tests related to Java Framework. You can download these sample mock tests at your
Object Declaration. <class name>: the name of the class to which the object belongs <object name>: the name of the object (any valid identifier)
 Object Declaration Every object used must be declared Syntax: ; : the name of the class to which the object belongs : the name of the object (any valid
Object Declaration Every object used must be declared Syntax: ; : the name of the class to which the object belongs : the name of the object (any valid
Java Primer 1: Types, Classes and Operators
 Java Primer 1 3/18/14 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Java Primer 1: Types,
Java Primer 1 3/18/14 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Java Primer 1: Types,
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot
 Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot Using Loops, Variables, and Strings 1 Copyright 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights Overview This lesson covers the following topics: Create a while loop
Creating Java Programs with Greenfoot Using Loops, Variables, and Strings 1 Copyright 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights Overview This lesson covers the following topics: Create a while loop
Some client code. output. subtype polymorphism As dynamic binding occurs the behavior (i.e., methods) follow the objects. Squarer
 public class Base { protected int theint = 100; System.out.println( theint ); public class Doubler extends Base { System.out.println( theint*2 ); public class Tripler extends Base { System.out.println(
public class Base { protected int theint = 100; System.out.println( theint ); public class Doubler extends Base { System.out.println( theint*2 ); public class Tripler extends Base { System.out.println(
CS112 Lecture: Working with Numbers
 CS112 Lecture: Working with Numbers Last revised January 30, 2008 Objectives: 1. To introduce arithmetic operators and expressions 2. To expand on accessor methods 3. To expand on variables, declarations
CS112 Lecture: Working with Numbers Last revised January 30, 2008 Objectives: 1. To introduce arithmetic operators and expressions 2. To expand on accessor methods 3. To expand on variables, declarations
3.1 Class Declaration
 Chapter 3 Classes and Objects OBJECTIVES To be able to declare classes To understand object references To understand the mechanism of parameter passing To be able to use static member and instance member
Chapter 3 Classes and Objects OBJECTIVES To be able to declare classes To understand object references To understand the mechanism of parameter passing To be able to use static member and instance member
Abstract Class. Lecture 21. Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof
 Abstract Class Lecture 21 Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof 1 Abstract Class Abstract class is a class with one or more abstract methods. The abstract method Method signature without implementation
Abstract Class Lecture 21 Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof 1 Abstract Class Abstract class is a class with one or more abstract methods. The abstract method Method signature without implementation
3. Java - Language Constructs I
 Educational Objectives 3. Java - Language Constructs I Names and Identifiers, Variables, Assignments, Constants, Datatypes, Operations, Evaluation of Expressions, Type Conversions You know the basic blocks
Educational Objectives 3. Java - Language Constructs I Names and Identifiers, Variables, Assignments, Constants, Datatypes, Operations, Evaluation of Expressions, Type Conversions You know the basic blocks
CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM
 CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM This assignment focuses on classes and objects. Turn in Ant.java, Bird.java, Hippo.java, Vulture.java,
CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM This assignment focuses on classes and objects. Turn in Ant.java, Bird.java, Hippo.java, Vulture.java,
CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2014 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 Java OO (Object Orientation) 2 Python and Matlab have objects and classes. Strong-typing nature of
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2014 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 Java OO (Object Orientation) 2 Python and Matlab have objects and classes. Strong-typing nature of
9/19/2018 Programming Data Structures. Polymorphism And Abstract
 9/19/2018 Programming Data Structures Polymorphism And Abstract 1 In-class assignment: deadline noon!! 2 Overview: 4 main concepts in Object-Oriented Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping the
9/19/2018 Programming Data Structures Polymorphism And Abstract 1 In-class assignment: deadline noon!! 2 Overview: 4 main concepts in Object-Oriented Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping the
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 20, 2014 Abstract
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 20, 2014 Abstract
CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL 2017 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 CMS VideoNote.com, PPT slides, DrJava 2 CMS. Visit course webpage, click Links, then CMS for 2110.
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL 2017 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 CMS VideoNote.com, PPT slides, DrJava 2 CMS. Visit course webpage, click Links, then CMS for 2110.
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract
Critter #1 Attack.ROAR random winner #2 wins #1 wins Attack.POUNCE #1 wins random winner #2 wins Attack.SCRATCH #2 wins #1 wins random winner
 CSE 142, Winter 2016 Programming Assignment #8: Critters (40 points) Due: Tuesday, March 8, 2016, 11:30 PM (Husky must be submitted on time to be in tournament in class on Friday, March 11) This assignment
CSE 142, Winter 2016 Programming Assignment #8: Critters (40 points) Due: Tuesday, March 8, 2016, 11:30 PM (Husky must be submitted on time to be in tournament in class on Friday, March 11) This assignment
CSE 113 A. Announcements - Lab
 CSE 113 A February 21-25, 2011 Announcements - Lab Lab 1, 2, 3, 4; Practice Assignment 1, 2, 3, 4 grades are available in Web-CAT look under Results -> Past Results and if looking for Lab 1, make sure
CSE 113 A February 21-25, 2011 Announcements - Lab Lab 1, 2, 3, 4; Practice Assignment 1, 2, 3, 4 grades are available in Web-CAT look under Results -> Past Results and if looking for Lab 1, make sure
CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2017 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 CMS VideoNote.com, PPT slides, DrJava, Book 2 CMS available. Visit course webpage, click Links, then
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2017 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 CMS VideoNote.com, PPT slides, DrJava, Book 2 CMS available. Visit course webpage, click Links, then
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-3: Encapsulation; Homework 8 (Critters) reading: 8.3-8.4 Encapsulation reading: 8.4 2 Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding implementation details from clients.
Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-3: Encapsulation; Homework 8 (Critters) reading: 8.3-8.4 Encapsulation reading: 8.4 2 Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding implementation details from clients.
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Interface Abstract data types Version of January 26, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes are meant
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Interface Abstract data types Version of January 26, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes are meant
COMP 401 Fall Recitation 6: Inheritance
 COMP 401 Fall 2017 Recitation 6: Inheritance Agenda Brief Review of Inheritance Examples of extending existing classes Exercises and Quiz 2 High-level Classes are Abstract Data Types We can define a set
COMP 401 Fall 2017 Recitation 6: Inheritance Agenda Brief Review of Inheritance Examples of extending existing classes Exercises and Quiz 2 High-level Classes are Abstract Data Types We can define a set
ISY00245 Principles of Programming. Module 7
 ISY00245 Principles of Programming Module 7 Module 7 Loops and Arrays Introduction This week we have gone through some of the concepts in your lecture, and will be putting them in to practice (as well
ISY00245 Principles of Programming Module 7 Module 7 Loops and Arrays Introduction This week we have gone through some of the concepts in your lecture, and will be putting them in to practice (as well
Lecture 3. Lecture
 True Object-Oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Static Object-Oriented Programming Reference Variables Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111, 114-115 Riley: 5.1, 5.2 D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design
True Object-Oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Static Object-Oriented Programming Reference Variables Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111, 114-115 Riley: 5.1, 5.2 D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design
Outline. Inheritance. Abstract Classes Interfaces. Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism.
 Outline Inheritance Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism Abstract Classes Interfaces 1 OOP Principles Encapsulation Methods and data are combined in classes Not
Outline Inheritance Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism Abstract Classes Interfaces 1 OOP Principles Encapsulation Methods and data are combined in classes Not
Inheritance Systems. Merchandise. Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress 9.1.1
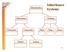 Merchandise Inheritance Systems Electronics Clothing Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress Digital Analog 9.1.1 Another AcademicDisciplines Hierarchy Mathematics Engineering Algebra Probability Geometry
Merchandise Inheritance Systems Electronics Clothing Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress Digital Analog 9.1.1 Another AcademicDisciplines Hierarchy Mathematics Engineering Algebra Probability Geometry
Java How to Program, 10/e. Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Java How to Program, 10/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Each class you create becomes a new type that can be used to declare variables and create objects. You can declare new classes as needed;
Java How to Program, 10/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Each class you create becomes a new type that can be used to declare variables and create objects. You can declare new classes as needed;
Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Objects and Methods Performing Actions and Using Object Methods Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Objects and Methods Duration: 00:01:14 Hi Folks. This is the CS 170, Java Programming
CS 170 Java Programming 1 Objects and Methods Performing Actions and Using Object Methods Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Objects and Methods Duration: 00:01:14 Hi Folks. This is the CS 170, Java Programming
Enums. In this article from my free Java 8 course, I will talk about the enum. Enums are constant values that can never be changed.
 Enums Introduction In this article from my free Java 8 course, I will talk about the enum. Enums are constant values that can never be changed. The Final Tag To display why this is useful, I m going to
Enums Introduction In this article from my free Java 8 course, I will talk about the enum. Enums are constant values that can never be changed. The Final Tag To display why this is useful, I m going to
CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2018 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 Homework HW1 2 The answers you handed in at the end of lecture 1 showed mass confusion! Perhaps 80%
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 SPRING 2018 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 Homework HW1 2 The answers you handed in at the end of lecture 1 showed mass confusion! Perhaps 80%
Object oriented programming. Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: Ch: 3
 Object oriented programming Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: http://www.masses.ir/lectures/oops2017sut Ch: 3 1 In this slide We follow: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/index.html Trail: Learning
Object oriented programming Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: http://www.masses.ir/lectures/oops2017sut Ch: 3 1 In this slide We follow: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/index.html Trail: Learning
JFrame In Swing, a JFrame is similar to a window in your operating system
 JFrame In Swing, a JFrame is similar to a window in your operating system All components will appear inside the JFrame window Buttons, text labels, text fields, etc. 5 JFrame Your GUI program must inherit
JFrame In Swing, a JFrame is similar to a window in your operating system All components will appear inside the JFrame window Buttons, text labels, text fields, etc. 5 JFrame Your GUI program must inherit
Practice Midterm 1. Problem Points Score TOTAL 50
 CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
Chapter 9 Worksheet. public class AntHill extends Actor { private int ants = 0; private int maxants = 40; private Counter foodcounter;
 public class AntHill extends Actor { private int ants = 0; private int maxants = 40; private Counter foodcounter; public AntHill() { public AntHill(int numberofants) { maxants = numberofants; if(ants
public class AntHill extends Actor { private int ants = 0; private int maxants = 40; private Counter foodcounter; public AntHill() { public AntHill(int numberofants) { maxants = numberofants; if(ants
CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Java
CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Java
About Technocamps. We go around schools and show you lots of interesting stuff! We also do things we call bootcamps during holidays!
 Greenfoot About Technocamps We go around schools and show you lots of interesting stuff! We also do things we call bootcamps during holidays! Pre-day Questionnaires This is a Computer What do computers
Greenfoot About Technocamps We go around schools and show you lots of interesting stuff! We also do things we call bootcamps during holidays! Pre-day Questionnaires This is a Computer What do computers
Chapter 24. Graphical Objects The GraphicalObject Class
 290 Chapter 24 Graphical Objects The simple graphics we saw earlier created screen artifacts. A screen artifact is simply an image drawn on the screen (viewport), just as a picture can be drawn on a whiteboard.
290 Chapter 24 Graphical Objects The simple graphics we saw earlier created screen artifacts. A screen artifact is simply an image drawn on the screen (viewport), just as a picture can be drawn on a whiteboard.
Assignment 6: Dodo keeps getting smarter
 Assignment 6: Dodo keeps getting smarter Algorithmic Thinking and Structured Programming (in Greenfoot) c 2015 Renske Smetsers-Weeda & Sjaak Smetsers Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
Assignment 6: Dodo keeps getting smarter Algorithmic Thinking and Structured Programming (in Greenfoot) c 2015 Renske Smetsers-Weeda & Sjaak Smetsers Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba. (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba Laboratory Session: Exercises on classes Analogy to help you understand classes and their contents. Suppose you want to drive a car and make it go faster by pressing down
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba Laboratory Session: Exercises on classes Analogy to help you understand classes and their contents. Suppose you want to drive a car and make it go faster by pressing down
CSE 8B Programming Assignments Spring Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3:
 PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENT 3: Read Savitch: Chapter 7 Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3: ShapeP3.java PointP3.java CircleP3.java RectangleP3.java TriangleP3.java
PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENT 3: Read Savitch: Chapter 7 Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3: ShapeP3.java PointP3.java CircleP3.java RectangleP3.java TriangleP3.java
Weiss Chapter 1 terminology (parenthesized numbers are page numbers)
 Weiss Chapter 1 terminology (parenthesized numbers are page numbers) assignment operators In Java, used to alter the value of a variable. These operators include =, +=, -=, *=, and /=. (9) autoincrement
Weiss Chapter 1 terminology (parenthesized numbers are page numbers) assignment operators In Java, used to alter the value of a variable. These operators include =, +=, -=, *=, and /=. (9) autoincrement
CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: David Joseph Ola Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 4 questions
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: David Joseph Ola Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 4 questions
12/22/11. Java How to Program, 9/e. public must be stored in a file that has the same name as the class and ends with the.java file-name extension.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Covered in this chapter Classes Objects Methods Parameters double primitive type } Create a new class (GradeBook) } Use it to create an object.
Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Covered in this chapter Classes Objects Methods Parameters double primitive type } Create a new class (GradeBook) } Use it to create an object.
Reviewing OO Concepts
 Reviewing OO Concepts Users want to draw circles onto the display canvas. public class Circle { // more code here SWEN-261 Introduc2on to So3ware Engineering Department of So3ware Engineering Rochester
Reviewing OO Concepts Users want to draw circles onto the display canvas. public class Circle { // more code here SWEN-261 Introduc2on to So3ware Engineering Department of So3ware Engineering Rochester
CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL 2018 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 Homework HW1 2 The answers you handed in at the end of lecture 1 showed mass confusion! Perhaps 80%
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL 2018 Lecture 2: Objects and classes in Java http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110 Homework HW1 2 The answers you handed in at the end of lecture 1 showed mass confusion! Perhaps 80%
Chapter 6: Inheritance
 Chapter 6: Inheritance EECS 1030 moodle.yorku.ca State of an object final int WIDTH = 3; final int HEIGTH = 4; final int WEIGHT = 80; GoldenRectangle rectangle = new GoldenRectangle(WIDTH, HEIGHT, WEIGHT);
Chapter 6: Inheritance EECS 1030 moodle.yorku.ca State of an object final int WIDTH = 3; final int HEIGTH = 4; final int WEIGHT = 80; GoldenRectangle rectangle = new GoldenRectangle(WIDTH, HEIGHT, WEIGHT);
Data Structures. Data structures. Data structures. What is a data structure? Simple answer: a collection of data equipped with some operations.
 Data Structures 1 Data structures What is a data structure? Simple answer: a collection of data equipped with some operations. Examples Lists Strings... 2 Data structures In this course, we will learn
Data Structures 1 Data structures What is a data structure? Simple answer: a collection of data equipped with some operations. Examples Lists Strings... 2 Data structures In this course, we will learn
CS 1316 Exam 1 Summer 2009
 1 / 8 Your Name: I commit to uphold the ideals of honor and integrity by refusing to betray the trust bestowed upon me as a member of the Georgia Tech community. CS 1316 Exam 1 Summer 2009 Section/Problem
1 / 8 Your Name: I commit to uphold the ideals of honor and integrity by refusing to betray the trust bestowed upon me as a member of the Georgia Tech community. CS 1316 Exam 1 Summer 2009 Section/Problem
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations
 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Objects and Classes
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Objects and Classes Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Object-Oriented Thinking Chapters 1-8
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Objects and Classes Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Object-Oriented Thinking Chapters 1-8
Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap. Inheritance & Polymorphism 1
 Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap Inheritance & Polymorphism 1 Introduction! Besides composition, another form of reuse is inheritance.! With inheritance, an object can inherit behavior from another object,
Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap Inheritance & Polymorphism 1 Introduction! Besides composition, another form of reuse is inheritance.! With inheritance, an object can inherit behavior from another object,
Object Oriented Programming and Design in Java. Session 10 Instructor: Bert Huang
 Object Oriented Programming and Design in Java Session 10 Instructor: Bert Huang Announcements Homework 2 due Mar. 3rd, 11 AM two days Midterm review Monday, Mar. 8th Midterm exam Wednesday, Mar. 10th
Object Oriented Programming and Design in Java Session 10 Instructor: Bert Huang Announcements Homework 2 due Mar. 3rd, 11 AM two days Midterm review Monday, Mar. 8th Midterm exam Wednesday, Mar. 10th
Name CS/120 Sample Exam #1 -- Riley. a) Every program has syntax, which refers to the form of the code, and, which refers to the meaning of the code.
 Name CS/120 Sample Exam #1 -- Riley Please show all of your work. 1. For each part below write the term, symbols, or phrase from class that best fits the description. (Each part is worth 2 points.) a)
Name CS/120 Sample Exam #1 -- Riley Please show all of your work. 1. For each part below write the term, symbols, or phrase from class that best fits the description. (Each part is worth 2 points.) a)
AP Computer Science Homework Set 3 Class Methods
 AP Computer Science Homework Set 3 Class Methods P3A. (BlueJ) Let s upgrade your Song class from P2A. You can make a copy of project P2AProject and rename it P3AProject in your Chapter 3 folder for this
AP Computer Science Homework Set 3 Class Methods P3A. (BlueJ) Let s upgrade your Song class from P2A. You can make a copy of project P2AProject and rename it P3AProject in your Chapter 3 folder for this
Inheritance. Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L
 Inheritance Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L 9.1 9.4 1 Inheritance Inheritance allows a software developer to derive
Inheritance Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L 9.1 9.4 1 Inheritance Inheritance allows a software developer to derive
1 Shyam sir JAVA Notes
 1 Shyam sir JAVA Notes 1. What is the most important feature of Java? Java is a platform independent language. 2. What do you mean by platform independence? Platform independence means that we can write
1 Shyam sir JAVA Notes 1. What is the most important feature of Java? Java is a platform independent language. 2. What do you mean by platform independence? Platform independence means that we can write
Exam 1 Format, Concepts, What you should be able to do, and Sample Problems
 CSSE 120 Introduction to Software Development Exam 1 Format, Concepts, What you should be able to do, and Sample Problems Page 1 of 6 Format: The exam will have two sections: Part 1: Paper-and-Pencil o
CSSE 120 Introduction to Software Development Exam 1 Format, Concepts, What you should be able to do, and Sample Problems Page 1 of 6 Format: The exam will have two sections: Part 1: Paper-and-Pencil o
CS/120 Final Exam. Name
 CS/120 Final Exam Name 16 pts 1. Trace the following segment of code and to the left of each System.out.println instruction show the precise output that results when this code segment executes. java.awt.container
CS/120 Final Exam Name 16 pts 1. Trace the following segment of code and to the left of each System.out.println instruction show the precise output that results when this code segment executes. java.awt.container
Objects and Classes (1)
 Objects and Classes (1) Reading: Classes (interface, implementation, garbage collection) http://moodle.cs.man.ac.uk/course/view.php?id=81 Interface Examples Creating and using objects of existing classes
Objects and Classes (1) Reading: Classes (interface, implementation, garbage collection) http://moodle.cs.man.ac.uk/course/view.php?id=81 Interface Examples Creating and using objects of existing classes
CS 314 Exam 2 Spring
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 200 points. 2. You have
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 200 points. 2. You have
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I. Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall Office hours:
 CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Thursday 12:00 PM 2:00 PM Friday 8:30 AM 10:30 AM OR request appointment via e-mail
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Thursday 12:00 PM 2:00 PM Friday 8:30 AM 10:30 AM OR request appointment via e-mail
Java Classes & Primitive Types
 Java Classes & Primitive Types Rui Moreira Classes Ponto (from figgeom) x : int = 0 y : int = 0 n Attributes q Characteristics/properties of classes q Primitive types (e.g., char, byte, int, float, etc.)
Java Classes & Primitive Types Rui Moreira Classes Ponto (from figgeom) x : int = 0 y : int = 0 n Attributes q Characteristics/properties of classes q Primitive types (e.g., char, byte, int, float, etc.)
Lecture 4: The class hierarchy; static components
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL2017 Lecture 4: The class hierarchy; static components http://cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs2110 Announcements 2 A1 Due Thursday A2 Out Today Where am I? Big ideas so far. 3 Java variables
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL2017 Lecture 4: The class hierarchy; static components http://cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs2110 Announcements 2 A1 Due Thursday A2 Out Today Where am I? Big ideas so far. 3 Java variables
CS 1302 Chapter 9 (Review) Object & Classes
 CS 1302 Chapter 9 (Review) Object & Classes Reference Sections 9.2-9.5, 9.7-9.14 9.2 Defining Classes for Objects 1. A class is a blueprint (or template) for creating objects. A class defines the state
CS 1302 Chapter 9 (Review) Object & Classes Reference Sections 9.2-9.5, 9.7-9.14 9.2 Defining Classes for Objects 1. A class is a blueprint (or template) for creating objects. A class defines the state
Java Classes & Primitive Types
 Java Classes & Primitive Types Rui Moreira Classes Ponto (from figgeom) x : int = 0 y : int = 0 n Attributes q Characteristics/properties of classes q Primitive types (e.g., char, byte, int, float, etc.)
Java Classes & Primitive Types Rui Moreira Classes Ponto (from figgeom) x : int = 0 y : int = 0 n Attributes q Characteristics/properties of classes q Primitive types (e.g., char, byte, int, float, etc.)
Problem 1. Multiple Choice (choose only one answer)
 Practice problems for the Final (Tuesday, May 14 4:30-6:30pm MHP 101). The Final Exam will cover all course material. You will be expected to know the material from the assigned readings in the book, the
Practice problems for the Final (Tuesday, May 14 4:30-6:30pm MHP 101). The Final Exam will cover all course material. You will be expected to know the material from the assigned readings in the book, the
Lecture 17. For Array Class Shenanigans
 Lecture 17 For Array Class Shenanigans For or While? class WhileDemo { public static void main(string[] args){ int count = 1; while (count < 11) { System.out.println("Count is: " + count); count++; Note:
Lecture 17 For Array Class Shenanigans For or While? class WhileDemo { public static void main(string[] args){ int count = 1; while (count < 11) { System.out.println("Count is: " + count); count++; Note:
Computer Components. Software{ User Programs. Operating System. Hardware
 Computer Components Software{ User Programs Operating System Hardware What are Programs? Programs provide instructions for computers Similar to giving directions to a person who is trying to get from point
Computer Components Software{ User Programs Operating System Hardware What are Programs? Programs provide instructions for computers Similar to giving directions to a person who is trying to get from point
Please show all of your work.
 Please show all of your work. Name CS/120 Exam #2 Sample Exam 1. For each part below write the term, symbols, or phrase from class that best fits the description. (Each part is worth 2 points.) a) This
Please show all of your work. Name CS/120 Exam #2 Sample Exam 1. For each part below write the term, symbols, or phrase from class that best fits the description. (Each part is worth 2 points.) a) This
Overview. ITI Introduction to Computing II. Interface 1. Problem 1. Problem 1: Array sorting. Problem 1: Array sorting. Problem 1: Array sorting
 Overview ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Rafael Falcon and Marcel Turcotte (with contributions from R. Holte) Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Ottawa Interface Abstract
Overview ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Rafael Falcon and Marcel Turcotte (with contributions from R. Holte) Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Ottawa Interface Abstract
Assignment 4. Aggregate Objects, Command-Line Arguments, ArrayLists. COMP-202B, Winter 2011, All Sections. Due: Tuesday, March 22, 2011 (13:00)
 Assignment 4 Aggregate Objects, Command-Line Arguments, ArrayLists COMP-202B, Winter 2011, All Sections Due: Tuesday, March 22, 2011 (13:00) You MUST do this assignment individually and, unless otherwise
Assignment 4 Aggregate Objects, Command-Line Arguments, ArrayLists COMP-202B, Winter 2011, All Sections Due: Tuesday, March 22, 2011 (13:00) You MUST do this assignment individually and, unless otherwise
c) And last but not least, there are javadoc comments. See Weiss.
 CSCI 151 Spring 2010 Java Bootcamp The following notes are meant to be a quick refresher on Java. It is not meant to be a means on its own to learn Java. For that you would need a lot more detail (for
CSCI 151 Spring 2010 Java Bootcamp The following notes are meant to be a quick refresher on Java. It is not meant to be a means on its own to learn Java. For that you would need a lot more detail (for
Decaf Language Reference Manual
 Decaf Language Reference Manual C. R. Ramakrishnan Department of Computer Science SUNY at Stony Brook Stony Brook, NY 11794-4400 cram@cs.stonybrook.edu February 12, 2012 Decaf is a small object oriented
Decaf Language Reference Manual C. R. Ramakrishnan Department of Computer Science SUNY at Stony Brook Stony Brook, NY 11794-4400 cram@cs.stonybrook.edu February 12, 2012 Decaf is a small object oriented
Classes. Integer Division. Thursday, October 23, March 13, 2008
 Classes March 13, 2008 1 Integer Division private static final int FACE_SIZE = HEAD_SIZE * (4/5); WARNING! FACE_SIZE is not 80% of the HEAD_SIZE! 4 and 5 are integers 4 / 5 is integer division and results
Classes March 13, 2008 1 Integer Division private static final int FACE_SIZE = HEAD_SIZE * (4/5); WARNING! FACE_SIZE is not 80% of the HEAD_SIZE! 4 and 5 are integers 4 / 5 is integer division and results
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 03.Java Language Basics
 03.Java Language Basics http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/index.htm CS260 - Intro to Java & Android 1 What is the distinction between fields and variables? Java has the following kinds of variables: Instance
03.Java Language Basics http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/index.htm CS260 - Intro to Java & Android 1 What is the distinction between fields and variables? Java has the following kinds of variables: Instance
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II
 CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Java Support for OOP Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Object Oriented Programming (OOP) OO Principles Abstraction Encapsulation
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Java Support for OOP Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Object Oriented Programming (OOP) OO Principles Abstraction Encapsulation
Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals. By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014
 Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014 Table of Contents Objectives Definition Pointers vs containers Object vs primitives Constructors Methods Object class
Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014 Table of Contents Objectives Definition Pointers vs containers Object vs primitives Constructors Methods Object class
An introduction to Java II
 An introduction to Java II Bruce Eckel, Thinking in Java, 4th edition, PrenticeHall, New Jersey, cf. http://mindview.net/books/tij4 jvo@ualg.pt José Valente de Oliveira 4-1 Java: Generalities A little
An introduction to Java II Bruce Eckel, Thinking in Java, 4th edition, PrenticeHall, New Jersey, cf. http://mindview.net/books/tij4 jvo@ualg.pt José Valente de Oliveira 4-1 Java: Generalities A little
Topic 7: Algebraic Data Types
 Topic 7: Algebraic Data Types 1 Recommended Exercises and Readings From Haskell: The craft of functional programming (3 rd Ed.) Exercises: 5.5, 5.7, 5.8, 5.10, 5.11, 5.12, 5.14 14.4, 14.5, 14.6 14.9, 14.11,
Topic 7: Algebraic Data Types 1 Recommended Exercises and Readings From Haskell: The craft of functional programming (3 rd Ed.) Exercises: 5.5, 5.7, 5.8, 5.10, 5.11, 5.12, 5.14 14.4, 14.5, 14.6 14.9, 14.11,
CIS 120 Midterm II November 16, 2012 SOLUTIONS
 CIS 120 Midterm II November 16, 2012 SOLUTIONS 1 1. Java vs. OCaml (22 points) a. In OCaml, the proper way to check whether two string values s and t are structurally equal is: s == t s = t s.equals(t)
CIS 120 Midterm II November 16, 2012 SOLUTIONS 1 1. Java vs. OCaml (22 points) a. In OCaml, the proper way to check whether two string values s and t are structurally equal is: s == t s = t s.equals(t)
AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide
 AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide 1. A class that uses a given class X is called a client of X. 2. Private features of a class can be directly accessed only within
AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide 1. A class that uses a given class X is called a client of X. 2. Private features of a class can be directly accessed only within
Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects
 Unit 5, Part 1 Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Types of Decomposition When writing a program, it's important
Unit 5, Part 1 Classes as Blueprints: How to Define New Types of Objects Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Types of Decomposition When writing a program, it's important
An Introduction to C++
 An Introduction to C++ Introduction to C++ C++ classes C++ class details To create a complex type in C In the.h file Define structs to store data Declare function prototypes The.h file serves as the interface
An Introduction to C++ Introduction to C++ C++ classes C++ class details To create a complex type in C In the.h file Define structs to store data Declare function prototypes The.h file serves as the interface
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I
 Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Algorithmic Thinking and Structured Programming (in Greenfoot) Teachers: Renske Smetsers-Weeda Sjaak Smetsers
 Algorithmic Thinking and Structured Programming (in Greenfoot) Teachers: Renske Smetsers-Weeda Sjaak Smetsers Assignment 5: difficulties Write a method int degreesneededtoturntofacenorth( ) which returns
Algorithmic Thinking and Structured Programming (in Greenfoot) Teachers: Renske Smetsers-Weeda Sjaak Smetsers Assignment 5: difficulties Write a method int degreesneededtoturntofacenorth( ) which returns
CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL2017. Lecture 4: The class hierarchy; static components
 1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL2017 Lecture 4: The class hierarchy; static components http://cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs2110 Announcements 2 A0, HW1 due tonight Next week s recitation: loop invariants for ( ) { You
1 CS/ENGRD 2110 FALL2017 Lecture 4: The class hierarchy; static components http://cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs2110 Announcements 2 A0, HW1 due tonight Next week s recitation: loop invariants for ( ) { You
Java Bytecode (binary file)
 Java is Compiled Unlike Python, which is an interpreted langauge, Java code is compiled. In Java, a compiler reads in a Java source file (the code that we write), and it translates that code into bytecode.
Java is Compiled Unlike Python, which is an interpreted langauge, Java code is compiled. In Java, a compiler reads in a Java source file (the code that we write), and it translates that code into bytecode.
More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario
 More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario The Story So Far... Classes as collections of fields and methods. Methods can access fields, and
More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario The Story So Far... Classes as collections of fields and methods. Methods can access fields, and
