clicker question Comments Using comments Topic 3 static Methods and Structured Programming
|
|
|
- Rebecca Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topic 3 static Methods and Structured Programming "The cleaner and nicer the program, the faster it's going to run. And if it doesn't, it'll be easy to make it fast." -Joshua Bloch clicker question What is the name of the method that is called when a Java program starts? A. main B. static C. void D. println E. class Based on slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from 2 Comments comment: A note written in source code by the programmer to describe or clarify the code. Comments are not executed when your program runs. Syntax: comment text, on one line or, comment text; may span multiple lines Examples: Using comments Where to place comments: at the top of each file (a "comment header") at the start of every method (seen later) to explain complex pieces of code Comments are useful for: Understanding larger, more complex programs. Multiple programmers working together, who 3 must understand each other's code. 4
2 Comments example Program Hygiene - a.ka. Style 5 Provide a structure to the program Eliminate redundant code Use spaces judiciously and consistently Indent properly Follow the naming conventions Use comments to describe code behavior Follow a brace style Good software follows a style guide See links on assignment page 6 Google C++ Style Guide Google C++ Style Guide 7 8
3 Why Worry About Program Hygiene? Computer Scientists and Software developers spend as much time maintaining code as they do creating new code You should spend time on thinking and coding. You should NOT be wasting time looking for that missing closing brace. 9 Algorithms algorithm: A list of steps for solving a problem. Example algorithm: "Bake sugar cookies" Mix the dry ingredients. Cream the butter and sugar. Beat in the eggs. Stir in the dry ingredients. Set the oven temperature. Set the timer. Place the cookies into the oven. Allow the cookies to bake. Mix ingredients for frosting Problems with algorithms lack of structure: Many small steps; tough to remember. redundancy: Consider making a double batch... Mix the dry ingredients. Cream the butter and sugar. Beat in the eggs. Stir in the dry ingredients. Set the oven temperature. Set the timer. Place the first batch of cookies into the oven. Allow the cookies to bake. Set the oven temperature. Set the timer. Place the second batch of cookies into the oven. Allow the cookies to bake. Mix ingredients for frosting Structured algorithms structured algorithm: Split solution into coherent tasks. 1 Make the cookie batter. Mix the dry ingredients. Cream the butter and sugar. Beat in the eggs. Stir in the dry ingredients. 2 Bake the cookies. Set the oven temperature. Set the timer. Place the cookies into the oven. Allow the cookies to bake. 3 Add frosting and sprinkles. Mix the ingredients for the frosting. Spread frosting and sprinkles onto the cookies
4 Removing redundancy A well-structured algorithm can describe repeated tasks with less redundancy. A program with redundancy 1 Make the cookie batter. Mix the dry ingredients.... 2a Bake the cookies (first batch). Set the oven temperature. Set the timer.... 2b Bake the cookies (second batch). 3 Decorate the cookies Static methods static method: A named group of statements. denotes the structure of a program eliminates redundancy by code reuse Building complex systems is hard Some of the most complex systems are software systems procedural decomposition: dividing a problem into methods a way to manage complexity Writing a static method is like adding a new command to Java
5 Using static methods 1. Design the algorithm. Look at the structure, and which commands are repeated. Decide what are the important overall tasks. Good programmers do this BEFORE writing any code Design of an algorithm 2. Declare (write down) the methods. Arrange statements into groups and give each group a name. 3. Call (run) the methods. The program's method executes the other methods to perform the overall task Gives your method a name so it can be executed Syntax: <statement> <statement>... <statement> Example: Declaring a method <name> Syntax: <name> Calling a method Executes the method's code You can call the same method many times if you like. Example: Output: 19 20
6 Program with static method Final cookie program Output: Summary: Why methods? Makes code easier to read by capturing the structure of the program should be a good summary of the program Summary: Why methods? Eliminate redundancy Note: necessarily mean worse code!!! 23 24
7 Methods calling methods Control flow When a method is called, the program's execution... "jumps" into that method, executing its statements, then "jumps" back to the point where the method was called. Output: How many lines of output with visible characaters does the following program produce? Drawing complex figures with static methods reading: 1.5 (Ch. 1 Case Study: ) A. 3 B. 4 C. 8 D. 12 E. 20
8 Static methods question Write a program to print these figures. Development strategy Program version 1 Development strategy
9 Output structure Program version Program version 2, cont'd. Development strategy
10 Output redundancy Program version Program version 3, cont'd. 39
Topic 3 static Methods and Structured Programming
 Topic 3 static Methods and Structured Programming "The cleaner and nicer the program, the faster it's going to run. And if it doesn't, it'll be easy to make it fast." -Joshua Bloch Based on slides by Marty
Topic 3 static Methods and Structured Programming "The cleaner and nicer the program, the faster it's going to run. And if it doesn't, it'll be easy to make it fast." -Joshua Bloch Based on slides by Marty
Recap: Structure of a Java program CS 112 Introduction to Programming. A Foundation for Programming Why Introduce Static Methods?
 Recap: Structure of a Java program CS 112 Introduction to Programming A class: - has a name, defined in a file with same name Convention we follow: capitalize each English word - starts with {, and ends
Recap: Structure of a Java program CS 112 Introduction to Programming A class: - has a name, defined in a file with same name Convention we follow: capitalize each English word - starts with {, and ends
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #6: Static Methods and Decomposition Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #6: Static Methods and Decomposition Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1-2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 2 Recall: structure, syntax class: a program public class name { public static void main(string[] args) { statement; statement;...
Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1-2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 2 Recall: structure, syntax class: a program public class name { public static void main(string[] args) { statement; statement;...
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) 2 Recall: structure, syntax class: a program public class
Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) 2 Recall: structure, syntax class: a program public class
CSc 110, Spring Lecture 2: Functions. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 2: Functions Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Review From last lecture: print, strings, escape sequences. What is the output of the following statement?
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 2: Functions Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Review From last lecture: print, strings, escape sequences. What is the output of the following statement?
Building Java Programs
 Comments Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1-2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 comment: A note written in source code by the programmer to describe or clarify the code. Comments are not executed
Comments Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1-2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 comment: A note written in source code by the programmer to describe or clarify the code. Comments are not executed
Static Methods & Decomposition
 Static Methods & Decomposition Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 1 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Warm Up Questions What
Static Methods & Decomposition Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 1 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Warm Up Questions What
CSc 110, Autumn Lecture 2: Functions
 CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 2: Functions Escape sequences escape sequence: A special sequence of characters used to represent certain special characters in a string. \t tab character \n new line character
CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 2: Functions Escape sequences escape sequence: A special sequence of characters used to represent certain special characters in a string. \t tab character \n new line character
Entering the world of Javatar
 Entering the world of Javatar Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Compiling/running programs 1. Write
Entering the world of Javatar Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Compiling/running programs 1. Write
Lecture 1: Basic Java Syntax
 Lecture 1: Basic Java Syntax Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Java Terminology class: (a) A module or program
Lecture 1: Basic Java Syntax Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Java Terminology class: (a) A module or program
CSE 142, Summer 2015
 CSE 142, Summer 2015 Lecture 2: Static Methods Expressions reading: 1.4 2.1 The Mechanical Turk 2 Escape Characters System.out.println( ab\ \\\\\\/\td ); Output: ab \\\/ d 3 Algorithms algorithm: A list
CSE 142, Summer 2015 Lecture 2: Static Methods Expressions reading: 1.4 2.1 The Mechanical Turk 2 Escape Characters System.out.println( ab\ \\\\\\/\td ); Output: ab \\\/ d 3 Algorithms algorithm: A list
CSE 142, Summer 2014
 CSE 142, Summer 2014 Lecture 2: Static Methods Expressions reading: 1.4 2.1 Algorithms algorithm: A list of steps for solving a problem. Example algorithm: "Bake sugar cookies" Mix the dry ingredients.
CSE 142, Summer 2014 Lecture 2: Static Methods Expressions reading: 1.4 2.1 Algorithms algorithm: A list of steps for solving a problem. Example algorithm: "Bake sugar cookies" Mix the dry ingredients.
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site I hope to have a course web site up on Blackboard soon However, I am using the following site all semester to allow
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site I hope to have a course web site up on Blackboard soon However, I am using the following site all semester to allow
Introduction to Computer Programming
 Introduction to Computer Programming Getting Started: An Introduction to Programming in Java What Is Programming? Computers cannot do all the wonderful things that we expect without instructions telling
Introduction to Computer Programming Getting Started: An Introduction to Programming in Java What Is Programming? Computers cannot do all the wonderful things that we expect without instructions telling
Procedural decomposition using static methods
 Algorithms Procedural decomposition using static methods Recall: An algorithm is a list of steps for solving a problem. What is the algorithm to bake sugar cookies? 1 2 The Bake sugar cookies algorithm
Algorithms Procedural decomposition using static methods Recall: An algorithm is a list of steps for solving a problem. What is the algorithm to bake sugar cookies? 1 2 The Bake sugar cookies algorithm
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1-1: Introduction; Basic Java Programs reading: 1.1-1.3 self-check: #1-14 exercises: #1-4 What is CSE? Computer Science Study of computation (information processing)
Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1-1: Introduction; Basic Java Programs reading: 1.1-1.3 self-check: #1-14 exercises: #1-4 What is CSE? Computer Science Study of computation (information processing)
Building Java Programs Chapter 1
 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Introduction to Java Programming Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. What is computer science? Computer Science The study of theoretical foundations of information
Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Introduction to Java Programming Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. What is computer science? Computer Science The study of theoretical foundations of information
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming These lecture notes are copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges, 2007. They may not be rehosted, sold, or modified without expressed
Building Java Programs Chapter 1: Introduction to Java Programming These lecture notes are copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges, 2007. They may not be rehosted, sold, or modified without expressed
CSE 201 Java Programming I. Smart Coding School website:
 CSE 201 Java Programming I Smart Coding School website: http://www.smartcodingschool.com Definition: A named group of statements public static void methodname() { statements Usage: 1. denotes the structure
CSE 201 Java Programming I Smart Coding School website: http://www.smartcodingschool.com Definition: A named group of statements public static void methodname() { statements Usage: 1. denotes the structure
Building Java Programs Chapter 1
 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Introduction to Java Programming Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. The CS job market 160,000 140,000 120,000 100,000 80,000 60,000 PhD Master's Bachelor's
Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Introduction to Java Programming Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. The CS job market 160,000 140,000 120,000 100,000 80,000 60,000 PhD Master's Bachelor's
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 6: Parameters. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 6: Parameters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Promoting reuse Programmers build increasingly complex applications Enabled by existing building blocks, e.g.
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 6: Parameters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Promoting reuse Programmers build increasingly complex applications Enabled by existing building blocks, e.g.
Topic 7 parameters. Based on slides from Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from
 Topic 7 parameters "We're flooding people with information. We need to feed it through a processor. A human must turn information into intelligence or knowledge. We've tended to forget that no computer
Topic 7 parameters "We're flooding people with information. We need to feed it through a processor. A human must turn information into intelligence or knowledge. We've tended to forget that no computer
Topic 6 loops, figures, constants
 Topic 6 loops, figures, constants "Complexity has and will maintain a strong fascination for many people. It is true that we live in a complex world and strive to solve inherently complex problems, which
Topic 6 loops, figures, constants "Complexity has and will maintain a strong fascination for many people. It is true that we live in a complex world and strive to solve inherently complex problems, which
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 5: Parameters and Scope reading: 3.1 i's scope Scope scope: The part of a program where a variable exists. From its declaration to the end of the { braces A variable
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 5: Parameters and Scope reading: 3.1 i's scope Scope scope: The part of a program where a variable exists. From its declaration to the end of the { braces A variable
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-1: Parameters reading: 3.1 (I think this is a made up language like Visual Basic but not quite.) 2 Promoting reuse Programmers build increasingly complex applications
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-1: Parameters reading: 3.1 (I think this is a made up language like Visual Basic but not quite.) 2 Promoting reuse Programmers build increasingly complex applications
Building Java Programs. Introduction to Java Programming
 Building Java Programs Introduction to Java Programming 1 What is java? Developed by Sun Microsystems (James Gosling) A general-purpose object-oriented language Based on C/C++ Designed for easy Web/Internet
Building Java Programs Introduction to Java Programming 1 What is java? Developed by Sun Microsystems (James Gosling) A general-purpose object-oriented language Based on C/C++ Designed for easy Web/Internet
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-1: Parameters reading: 3.1 self-check: #1-6 exercises: #1-3 videos: Ch. 3 #1 Redundant recipes Recipe for baking 20 cookies: Mix the following ingredients in
Building Java Programs Chapter 3 Lecture 3-1: Parameters reading: 3.1 self-check: #1-6 exercises: #1-3 videos: Ch. 3 #1 Redundant recipes Recipe for baking 20 cookies: Mix the following ingredients in
A Unicorn Named Sparkle Word Search. A New Friend for Sparkle Coloring Sheet. A Unicorn Named Sparkle s First Christmas Coloring Sheet
 Table of Contents Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Pages 8 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Name Tags A Unicorn Named Sparkle Word Search Draw and Name Your Unicorn Connect
Table of Contents Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Pages 8 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Name Tags A Unicorn Named Sparkle Word Search Draw and Name Your Unicorn Connect
Topic 4 Expressions and variables
 Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Java Static Methods. Recap: Decomposition Example. Recap: Static Method Example
 Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
Introduction to Computer Programming concepts using StarLogo TNG
 Introduction to Computer Programming concepts using StarLogo TNG Overview In this class, we will use the StarLogo TNG language to introduce basic concepts used in computer programs. Learning Objectives
Introduction to Computer Programming concepts using StarLogo TNG Overview In this class, we will use the StarLogo TNG language to introduce basic concepts used in computer programs. Learning Objectives
Recap: Assignment as an Operator CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 Recap: Assignment as an Operator CS 112 Introduction to Programming q You can consider assignment as an operator, with a (Spring 2012) lower precedence than the arithmetic operators First the expression
Recap: Assignment as an Operator CS 112 Introduction to Programming q You can consider assignment as an operator, with a (Spring 2012) lower precedence than the arithmetic operators First the expression
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #7: Variable Scope, Constants, and Loops Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #7: Variable Scope, Constants, and Loops Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
Topic 27 classes and objects, state and behavior
 Topic 27 classes and objects, state and behavior "A 'class' is where we teach an 'object' to behave." -Rich Pattis Copyright Pearson Education, 2010 Based on slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from
Topic 27 classes and objects, state and behavior "A 'class' is where we teach an 'object' to behave." -Rich Pattis Copyright Pearson Education, 2010 Based on slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand
 COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us From this site you can click on the COSC-236
COSC 236 Section 101 Computer Science 1 -- Prof. Michael A. Soderstrand COSC 236 Web Site You will always find the course material at: http://www.class-notes.us From this site you can click on the COSC-236
Introduction to Java. Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords
 Introduction to Java Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords Program Errors Syntax Runtime Logic Procedural Decomposition Methods Flow of Control
Introduction to Java Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords Program Errors Syntax Runtime Logic Procedural Decomposition Methods Flow of Control
The diagram below is only partially complete. Use the terms in the word list to complete the empty boxes. Make dinner
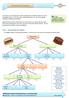 Decomposing Problems As we have seen, decomposition means breaking down a difficult problem into more manageable pieces. A common way to tackle this process is to use a tree diagram showing increasing
Decomposing Problems As we have seen, decomposition means breaking down a difficult problem into more manageable pieces. A common way to tackle this process is to use a tree diagram showing increasing
Topic 9 More Graphics. Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from
 Topic 9 More Graphics Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ Clicker Question What happens if a graphics object is used to draw a shape that exceeds the
Topic 9 More Graphics Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ Clicker Question What happens if a graphics object is used to draw a shape that exceeds the
Array Basics: Outline. Creating and Accessing Arrays. Creating and Accessing Arrays. Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7)
 Array Basics: Outline Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7) TOPICS Array Basics Arrays in Classes and Methods Programming with Arrays Searching and Sorting Arrays Multi-Dimensional Arrays Static Variables and Constants
Array Basics: Outline Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7) TOPICS Array Basics Arrays in Classes and Methods Programming with Arrays Searching and Sorting Arrays Multi-Dimensional Arrays Static Variables and Constants
Introduction Jan. 22, Ch 1
 Introduction Jan. 22, Ch 1 Object Oriented Main focus is on objects and how they interact (represented by me as boxes) Reusable groups of actions (verbs) between objects are called functions (squiggly
Introduction Jan. 22, Ch 1 Object Oriented Main focus is on objects and how they interact (represented by me as boxes) Reusable groups of actions (verbs) between objects are called functions (squiggly
COMPUTATIONAL THINKING
 Computational Concepts sequence loops parallelism events conditionals operators variables lists COMPUTATIONAL THINKING PROGRAMMING AS PROBLEM SOLVING Computational Practices incremental/iterative testing/debugging
Computational Concepts sequence loops parallelism events conditionals operators variables lists COMPUTATIONAL THINKING PROGRAMMING AS PROBLEM SOLVING Computational Practices incremental/iterative testing/debugging
Critters. Critter #2 Attack.ROAR Attack.POUNCE Attack.SCRATCH. Critter #1
 Critters This assignment was co-created by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp. This program focuses on classes, objects, and inheritance. You will write the following files: Ant.java, Bird.java, Crab.java, FireAnt.java,
Critters This assignment was co-created by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp. This program focuses on classes, objects, and inheritance. You will write the following files: Ant.java, Bird.java, Crab.java, FireAnt.java,
ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING. Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University
 ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University Lecture 02: Algorithms Readings: Not Covered in Textbook Problem Solving Process System Design:
ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University Lecture 02: Algorithms Readings: Not Covered in Textbook Problem Solving Process System Design:
Graded Project. HTML Coding
 Graded Project HTML Coding OVERVIEW 1 INSTRUCTIONS 1 SUBMITTING YOUR PROJECT 17 Contents iii HTML Coding OVERVIEW After completing the exercises for your HTML Coding study guide, you re now ready to complete
Graded Project HTML Coding OVERVIEW 1 INSTRUCTIONS 1 SUBMITTING YOUR PROJECT 17 Contents iii HTML Coding OVERVIEW After completing the exercises for your HTML Coding study guide, you re now ready to complete
2.9 Modularization. Department of CSE,Coimbatore
 2.9 Modularization Objectives To understand how algorithms are modularized. To learn how smaller units can be made flexible through the use of formal parameters. To understand the characteristics of well-defined
2.9 Modularization Objectives To understand how algorithms are modularized. To learn how smaller units can be made flexible through the use of formal parameters. To understand the characteristics of well-defined
Lab 1: Introduction to Java
 Lab 1: Introduction to Java Welcome to the first CS15 lab! In the reading, we went over objects, methods, parameters and how to put all of these things together into Java classes. It's perfectly okay if
Lab 1: Introduction to Java Welcome to the first CS15 lab! In the reading, we went over objects, methods, parameters and how to put all of these things together into Java classes. It's perfectly okay if
QUIZ. What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables?
 QUIZ What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables? Solution QUIZ Source: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17349387/scope-of-macros-in-c Solution The C/C++ preprocessor substitutes mechanically,
QUIZ What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables? Solution QUIZ Source: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17349387/scope-of-macros-in-c Solution The C/C++ preprocessor substitutes mechanically,
LN #6 & 7 (2 Hrs) Modularization 1 & 2 CTPS Department of CSE,Coimbatore
 LN #6 & 7 (2 Hrs) Modularization 1 & 2 CTPS 2018 Objectives To understand how algorithms are modularized. To learn how smaller units can be made flexible through the use of formal parameters. To understand
LN #6 & 7 (2 Hrs) Modularization 1 & 2 CTPS 2018 Objectives To understand how algorithms are modularized. To learn how smaller units can be made flexible through the use of formal parameters. To understand
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE
 CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
12/22/11. Java How to Program, 9/e. Help you get started with Eclipse and NetBeans integrated development environments.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops These lecture notes are copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges, 2007. They may not be rehosted, sold, or modified without expressed
Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops These lecture notes are copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges, 2007. They may not be rehosted, sold, or modified without expressed
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Coding Standards
 CS 251 Intermediate Programming Coding Standards Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Fall 2018 CS-251 Coding Standards All projects and labs must follow the great and hallowed CS-251 coding standards.
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Coding Standards Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Fall 2018 CS-251 Coding Standards All projects and labs must follow the great and hallowed CS-251 coding standards.
QUIZ. Source:
 QUIZ Source: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17349387/scope-of-macros-in-c Ch. 4: Data Abstraction The only way to get massive increases in productivity is to leverage off other people s code. That
QUIZ Source: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17349387/scope-of-macros-in-c Ch. 4: Data Abstraction The only way to get massive increases in productivity is to leverage off other people s code. That
CS 152 Computer Programming Fundamentals Coding Standards
 CS 152 Computer Programming Fundamentals Coding Standards Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Fall 2018 CS-152 Coding Standards All projects and labs must follow the great and hallowed CS-152 coding
CS 152 Computer Programming Fundamentals Coding Standards Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Fall 2018 CS-152 Coding Standards All projects and labs must follow the great and hallowed CS-152 coding
Identifiers. Identifiers are the words a programmer uses in a program Some identifiers are already defined. Some are made up by the programmer:
 C1 D6 Obj: cont. 1.3 and 1.4, to become familiar with identifiers and to understand how programming languages work HW: p.51 #1.8 1.9 (Short Answers) Chapter 1 Test in two class days!! Do Now: How is the
C1 D6 Obj: cont. 1.3 and 1.4, to become familiar with identifiers and to understand how programming languages work HW: p.51 #1.8 1.9 (Short Answers) Chapter 1 Test in two class days!! Do Now: How is the
Welcome to Python! If you re the type of person who wants to know
 In This Chapter The history of Python What people use Python for Chapter 1 Introducing Python Useful concepts for Python programming Welcome to Python! If you re the type of person who wants to know what
In This Chapter The history of Python What people use Python for Chapter 1 Introducing Python Useful concepts for Python programming Welcome to Python! If you re the type of person who wants to know what
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 18: Classes and Objects reading: 8.1-8.2 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) 2 File output reading: 6.4-6.5 3 Output to files PrintStream:
Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 18: Classes and Objects reading: 8.1-8.2 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) 2 File output reading: 6.4-6.5 3 Output to files PrintStream:
Topic 8 graphics. -mgrimes, Graphics problem report 134
 Topic 8 graphics "What makes the situation worse is that the highest level CS course I've ever taken is cs4, and quotes from the graphics group startup readme like 'these paths are abstracted as being
Topic 8 graphics "What makes the situation worse is that the highest level CS course I've ever taken is cs4, and quotes from the graphics group startup readme like 'these paths are abstracted as being
CS 170 Java Programming 1. Week 5: Procedures and Functions
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 5: Procedures and Functions What s the Plan? Topic 1: More on graphical objects Creating your own custom Turtle types Introducing media, pictures and sounds Topic 2: Decomposition:
CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 5: Procedures and Functions What s the Plan? Topic 1: More on graphical objects Creating your own custom Turtle types Introducing media, pictures and sounds Topic 2: Decomposition:
COMP Summer 2015 (A01) Jim (James) Young jimyoung.ca
 COMP 1010- Summer 2015 (A01) Jim (James) Young young@cs.umanitoba.ca jimyoung.ca Hello! James (Jim) Young young@cs.umanitoba.ca jimyoung.ca office hours T / Th: 17:00 18:00 EITC-E2-582 (or by appointment,
COMP 1010- Summer 2015 (A01) Jim (James) Young young@cs.umanitoba.ca jimyoung.ca Hello! James (Jim) Young young@cs.umanitoba.ca jimyoung.ca office hours T / Th: 17:00 18:00 EITC-E2-582 (or by appointment,
 WELCOME TO CS 24! Problem Solving with Computers-II https://ucsb-cs24-s18.github.io/ Read the syllabus. Know what s required. Know how to get help. Enrollment status: 117/105 2 About me Diba Mirza (diba@ucsb.edu)
WELCOME TO CS 24! Problem Solving with Computers-II https://ucsb-cs24-s18.github.io/ Read the syllabus. Know what s required. Know how to get help. Enrollment status: 117/105 2 About me Diba Mirza (diba@ucsb.edu)
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming. Lecture 2 Decomposition and Static Methods ( 1.4)
 CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 2 Decomposition and Static Methods ( 1.4) Outline Structure and redundancy in algorithms Static methods Procedural decomposition 9/16/2011 CIS 110
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 2 Decomposition and Static Methods ( 1.4) Outline Structure and redundancy in algorithms Static methods Procedural decomposition 9/16/2011 CIS 110
Algorithms: The recipe for computation
 Algorithms: The recipe for computation 2A What is an algorithm? 15-105 Principles of Computation, Carnegie Mellon University - CORTINA 1 Algorithms An algorithm is a precise rule (or set of rules) specifying
Algorithms: The recipe for computation 2A What is an algorithm? 15-105 Principles of Computation, Carnegie Mellon University - CORTINA 1 Algorithms An algorithm is a precise rule (or set of rules) specifying
Chapter Two: Classes and Objects
 Chapter Two: Classes and Objects Section 1: Real Objects Versus Virtual Objects Computer games do not have to match reality. In them we can violate the rules of physics (or make up our own), pigs can fly
Chapter Two: Classes and Objects Section 1: Real Objects Versus Virtual Objects Computer games do not have to match reality. In them we can violate the rules of physics (or make up our own), pigs can fly
Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum
 Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Questions to consider
Advanced if/else & Cumulative Sum Subset of the Supplement Lesson slides from: Building Java Programs, Chapter 4 by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp (http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ ) Questions to consider
Boolean evaluation and if statements. Making decisions in programs
 Boolean evaluation and if statements Making decisions in programs Goals By the end of this lesson you will be able to: Understand Boolean logic values Understand relational operators Understand if and
Boolean evaluation and if statements Making decisions in programs Goals By the end of this lesson you will be able to: Understand Boolean logic values Understand relational operators Understand if and
Chapter 2. Designing a Program. Input, Processing, and Output Fall 2016, CSUS. Chapter 2.1
 Chapter 2 Input, Processing, and Output Fall 2016, CSUS Designing a Program Chapter 2.1 1 Algorithms They are the logic on how to do something how to compute the value of Pi how to delete a file how to
Chapter 2 Input, Processing, and Output Fall 2016, CSUS Designing a Program Chapter 2.1 1 Algorithms They are the logic on how to do something how to compute the value of Pi how to delete a file how to
CSc 110, Autumn Lecture 30: Methods. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 30: Methods Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Why objects? Primitive types don't model complex concepts well Cost is a float. What's a person? Classes are
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 30: Methods Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Why objects? Primitive types don't model complex concepts well Cost is a float. What's a person? Classes are
Functions: Decomposition And Code Reuse
 Programming: problem decomposition into functions 1 Functions: Decomposition And Code Reuse This section of notes shows you how to write functions that can be used to: decompose large problems, and to
Programming: problem decomposition into functions 1 Functions: Decomposition And Code Reuse This section of notes shows you how to write functions that can be used to: decompose large problems, and to
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs A Back to Basics Approach Stuart Reges I Marty Stepp University ofwashington Preface 3 Chapter 1 Introduction to Java Programming 25 1.1 Basic Computing Concepts 26 Why Programming?
Building Java Programs A Back to Basics Approach Stuart Reges I Marty Stepp University ofwashington Preface 3 Chapter 1 Introduction to Java Programming 25 1.1 Basic Computing Concepts 26 Why Programming?
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Basics. CSCI 161 Introduction to Programming I
 Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Basics CSCI 161 Introduction to Programming I Overview Chapter 8 in the textbook Building Java Programs, by Reges & Stepp. Review of OOP History and Terms Discussion of
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Basics CSCI 161 Introduction to Programming I Overview Chapter 8 in the textbook Building Java Programs, by Reges & Stepp. Review of OOP History and Terms Discussion of
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 3: Expressions, Variables and Loops. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 3: Expressions, Variables and Loops Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Data and expressions 2 Data types Internally, computers store everything as 1s and
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 3: Expressions, Variables and Loops Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Data and expressions 2 Data types Internally, computers store everything as 1s and
CS 351 Design of Large Programs Coding Standards
 CS 351 Design of Large Programs Coding Standards Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 CS-351 Coding Standards All projects and labs must follow the great and hallowed CS-351 coding standards.
CS 351 Design of Large Programs Coding Standards Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 CS-351 Coding Standards All projects and labs must follow the great and hallowed CS-351 coding standards.
Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types
 Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set
Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set
Two figures that have the exact same shape, but not necessarily the exact same size, are called similar
 Similar and Congruent Figures Lesson 2.3 Two figures that have the exact same shape, but not necessarily the exact same size, are called similar figures. The parts of similar figures that match are called
Similar and Congruent Figures Lesson 2.3 Two figures that have the exact same shape, but not necessarily the exact same size, are called similar figures. The parts of similar figures that match are called
Object-Oriented Programming in Processing
 Object-Oriented Programming in Processing Object-Oriented Programming We ve (kinda) been doing this since Day 1: Python is a deeply object oriented language Most of the data types we were using (strings,
Object-Oriented Programming in Processing Object-Oriented Programming We ve (kinda) been doing this since Day 1: Python is a deeply object oriented language Most of the data types we were using (strings,
Java Programming. What is a program? Programs Recipes. Programs as Recipes 8/16/12. Pancakes In one bowl. mix: 1½ cup flour
 What is a program? Java Programming CS 160, Fall Semester 2012 TOPICS Computer Programs Using Eclipse Program Program Components Definition: a sequence of instructions telling a computer what to do Analogy:
What is a program? Java Programming CS 160, Fall Semester 2012 TOPICS Computer Programs Using Eclipse Program Program Components Definition: a sequence of instructions telling a computer what to do Analogy:
Variables One More (but not the last) Time with feeling
 1 One More (but not the last) Time with feeling All variables have the following in common: a name a type ( int, float, ) a value an owner We can describe variables in terms of: who owns them ( Processing
1 One More (but not the last) Time with feeling All variables have the following in common: a name a type ( int, float, ) a value an owner We can describe variables in terms of: who owns them ( Processing
Java Basics. Object Orientated Programming in Java. Benjamin Kenwright
 Java Basics Object Orientated Programming in Java Benjamin Kenwright Outline Essential Java Concepts Syntax, Grammar, Formatting, Introduce Object-Orientated Concepts Encapsulation, Abstract Data, OO Languages,
Java Basics Object Orientated Programming in Java Benjamin Kenwright Outline Essential Java Concepts Syntax, Grammar, Formatting, Introduce Object-Orientated Concepts Encapsulation, Abstract Data, OO Languages,
Ch. 10: Name Control
 Ch. 10: Name Control Static elements from C The static keyword was overloaded in C before people knew what the term overload meant, and C++ has added yet another meaning. The underlying concept with all
Ch. 10: Name Control Static elements from C The static keyword was overloaded in C before people knew what the term overload meant, and C++ has added yet another meaning. The underlying concept with all
CS 106A, Lecture 5 Booleans and Control Flow
 CS 106A, Lecture 5 Booleans and Control Flow suggested reading: Java Ch. 3.4-4.6 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5
CS 106A, Lecture 5 Booleans and Control Flow suggested reading: Java Ch. 3.4-4.6 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5
Functions: Decomposition And Code Reuse
 Functions: Decomposition And Code Reuse This section of notes shows you how to write functions that can be used to: decompose large problems, and to reduce program size by creating reusable sections. Tip
Functions: Decomposition And Code Reuse This section of notes shows you how to write functions that can be used to: decompose large problems, and to reduce program size by creating reusable sections. Tip
Slide Set 1. for ENCM 339 Fall Steve Norman, PhD, PEng. Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary
 Slide Set 1 for ENCM 339 Fall 2016 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary September 2016 ENCM 339 Fall 2016 Slide Set 1 slide 2/43
Slide Set 1 for ENCM 339 Fall 2016 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary September 2016 ENCM 339 Fall 2016 Slide Set 1 slide 2/43
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Learn about cutting-edge research over lunch with cool profs January 18-22, 2015 11:30
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Java basics and our first Java program! Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Learn about cutting-edge research over lunch with cool profs January 18-22, 2015 11:30
CSE 142/143 Unofficial Style Guide
 CSE 142/143 Unofficial Style Guide Below, things in GREEN are GOOD; things in RED are to be AVOIDED. Commenting Comment well. Follow the commenting rules for header, method, field, and inside-method comments
CSE 142/143 Unofficial Style Guide Below, things in GREEN are GOOD; things in RED are to be AVOIDED. Commenting Comment well. Follow the commenting rules for header, method, field, and inside-method comments
Topic 5 for loops and nested loops
 Topic 5 for loops and nested loops Always to see the general in the particular is the very foundation of genius. -Arthur Schopenhauer Based on slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/
Topic 5 for loops and nested loops Always to see the general in the particular is the very foundation of genius. -Arthur Schopenhauer Based on slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/
Chapter 2 Author Notes
 Chapter 2 Author Notes Good Programming Practice 2.1 Every program should begin with a comment that explains the purpose of the program, the author and the date and time the program was last modified.
Chapter 2 Author Notes Good Programming Practice 2.1 Every program should begin with a comment that explains the purpose of the program, the author and the date and time the program was last modified.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba. (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether, Ph.D.
 Topic 21 https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66702 arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether,
Topic 21 https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=66702 arrays - part 1 My methods are really methods of working and thinking; this is why they have crept in everywhere anonymously. Emmy Noether,
Building Java Programs. Introduction to Programming and Simple Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Introduction to Programming and Simple Java Programs 1 A simple Java program public class Hello { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello, world!"); code
Building Java Programs Introduction to Programming and Simple Java Programs 1 A simple Java program public class Hello { public static void main(string[] args) { System.out.println("Hello, world!"); code
Designing Forms in Access
 Designing Forms in Access This document provides basic techniques for designing, creating, and using forms in Microsoft Access. Opening Comments about Forms A form is a database object that you can use
Designing Forms in Access This document provides basic techniques for designing, creating, and using forms in Microsoft Access. Opening Comments about Forms A form is a database object that you can use
CS 106A, Lecture 3 Problem-solving with Karel
 CS 106A, Lecture 3 Problem-solving with Karel suggested reading: Karel, Ch. 5-6 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5
CS 106A, Lecture 3 Problem-solving with Karel suggested reading: Karel, Ch. 5-6 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5
University of Washington, CSE 190 M Homework Assignment 9: Remember the Cow (To-Do List)
 University of Washington, CSE 190 M Homework Assignment 9: Remember the Cow (To-Do List) In this assignment you will write a small yet complete "Web 2.0" application that includes user login sessions,
University of Washington, CSE 190 M Homework Assignment 9: Remember the Cow (To-Do List) In this assignment you will write a small yet complete "Web 2.0" application that includes user login sessions,
1 Getting used to Python
 1 Getting used to Python We assume you know how to program in some language, but are new to Python. We'll use Java as an informal running comparative example. Here are what we think are the most important
1 Getting used to Python We assume you know how to program in some language, but are new to Python. We'll use Java as an informal running comparative example. Here are what we think are the most important
COMP 102: Computers and Computing
 COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 5: What is Programming? Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html Motivation The advantage of a computer
COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 5: What is Programming? Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html Motivation The advantage of a computer
Mobile App:IT. Methods & Classes
 Mobile App:IT Methods & Classes WHAT IS A METHOD? - A method is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method's name. -
Mobile App:IT Methods & Classes WHAT IS A METHOD? - A method is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method's name. -
Homework Assignment 2: Java Console and Graphics
 SSEA August 2016 Cynthia Lee CS106A Homework Assignment 2: Java Console and Graphics Based on past assignments created by Marty Stepp, Mehran Sahami, Keith Schwarz, Eric Roberts, Stuart Reges, and others.
SSEA August 2016 Cynthia Lee CS106A Homework Assignment 2: Java Console and Graphics Based on past assignments created by Marty Stepp, Mehran Sahami, Keith Schwarz, Eric Roberts, Stuart Reges, and others.
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
