CHAPTER INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Lee Shaw
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION The base slide set from which most slide sets in this course were created was originally created by Donald W. Smith of TechNeTrain.com Final Draft Oct. 15, 2011
2 » Names!» Your Job» What is my (whole) job?» Teaching philosophies» Syllabus (and grading) Day One Agenda» What is Computer Science?» And what it is not» Learning Computer Programming» Like learning a musical instrument
3 Why This Text?» My experience shows that students have trouble with the following» Interactive» Late Objects?» Well, yes. And no.
4 Research» Compilers» Networks» Security» Graphics» Music?!» Machine Learning
5 Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time and run-time errors To describe an algorithm with pseudocode In this chapter, you will learn how to write and run your first Java program. You will also learn how to diagnose and fix programming errors, and how to use pseudocode to describe an algorithm. Page 2
6 Contents Computer Programs The Anatomy of a Computer You read it The Java Programming Language Becoming Familiar with your Programming Environment Analyzing Your First Program Errors Problem Solving: Algorithm Design Page 3
7 1.1 Computer Programs A Computer Program is a sequence of instructions and decisions Computers execute very basic instructions in rapid succession Programming is the act of designing and implementing computer programs Page 4
8 Source code Java Virtual Machines Portable byte code The compiler generates byte code in a class file which can be run on any Java Virtual Machine Oracle Tutorials Page 10
9 Wait What?! Three Questions» What is this compiling thing?» Source code» Assembly code» Machine language» More on this at a later date» What is an interpreter?» How does this apply to Java?» Why so many programming languages?
10 Source code Java Virtual Machines Portable byte code The compiler generates byte code in a class file which can be run on any Java Virtual Machine Oracle Tutorials Page 10
11 The Java API The Java Platform consists of two parts: 1) Java Virtual Machine 2) Java API -- also called libraries The Application Programming Interface (API) is a huge collection of handy software packages that programmers can use: Graphics, user interface, networking, sound, database, math, and many more Page 12
12 The Java API (cont.)
13 Let s Go to the API!
14 An Example IDE Editor Output Many IDEs are designed specifically for Java programming Page 15
15 The IDE We ll Use: BlueJ
16 Your First Program Page 16
17 Source Code to Running Program The compiler generates the.class file which contains instructions for the Java Virtual machine Class files contain byte code that you cannot edit D:\temp\hello>Type HelloPrinter.class 2!! <init> ()V Code LineNumberTable main ([Ljava/lang/String;)V Hello, World! elloprinter.java Page 18
18 Organize your work Your source code is stored in.java files Create one folder per program Can be many.java files Be sure you know where your IDE stores your files! Backup your work! Backup your work to a Flash Drive, external hard drive, or network drive that is backed up nightly. Page 19
19 I Reiterate: Back Up Your Work!!!
20 1.5 Analyzing your First Program 1: Declares a class HelloPrinter -- Every Java program has one or more classes. 3: Declares a method called main -- Every Java application has exactly one main method -- Entry point where the program starts 5: Method System.out.println outputs Hello, World! -- A statement must end with a semicolon (;) Page 20
21 Syntax 1.1: The Java Program Every application has the same basic layout Add your code inside the main method Page 21
22 Calling Java Library methods Line 5 shows how to call a method from the Java API: System.out.println Code that somebody else wrote for you! Notice the dots (periods) Parenthesis surround the arguments that you pass to a method We are passing a String Hello World Note the double quotes which denote a String inside You can also print numerical values System.out.println(3 + 4); Page 22
23 » Objects» Fields (data)» Methods (functions) Wait What?!» Methods that do something (void)» Methods that give you something (types)
24 Calling Java Library methods Line 5 shows how to call a method from the Java API: System.out.println Code that somebody else wrote for you! Notice the dots (periods) Parenthesis surround the arguments that you pass to a method We are passing a String Hello World Note the double quotes which denote a String inside You can also print numerical values System.out.println(3 + 4); Page 22
25 Getting to know println The println method prints a string or a number and then starts a new line. System.out.println("Hello"); System.out.println("World! ); Hello World! println has a cousin method named print that does not print a new line. System.out.print("00"); System.out.println(3+4); A method is called by specifying the method and its agruments 007 Page 23
26
27 1.6 Errors The Two Categories of Errors: 1) Compile-time Errors Syntax Errors Spelling, Capitalization, punctuation Ordering of statements, matching of braces/parenthesis No.class file is generated by the compiler Correct first error listed, then compile again 2) Run-time Errors Logic Errors Program runs, but produces unintended results Program may crash Page 25
28 Syntax Errors What happens if you Misspell a word: System.ou.println Don t Capitalize a word system.out.println Leave out a word void Forget a Semicolon after ("Hello, World!") Don t match a curly brace? Remove line 6 Try it to see what error messages are generated Page 26
29 Logic Errors What happens if you Divide by Zero Mis-spell output System.out.println(1/0); ("Hello, Word!") Forget to output Remove line 5 Programs will compile and run The output may not be as expected Page 27
30 1.7 Problem Solving: Algorithm Design Algorithms are simply plans Detailed plans that describe the steps to solve a specific problem You already know quite a few Calculate the area of a circle Find the length of the hypotenuse of a triangle Some problems are more complex and require more steps Calculate PI to 100 decimal places Calculate the trajectory of a missile Page 28
31 Text Problem to Algorithm Given the problem: You put $10,000 into a bank account that earns 5 percent interest per year. How many years does it take for the account balance to be double the original? How would you solve it? Manual method Make a table Add lines until done Use a spreadsheet! Write a formula Per line, based on line above Page 29
32 Text Problem to Algorithm Steps You put $10,000 into a bank account that earns 5 percent interest per year. How many years does it take for the account balance to be double the original? Break it into steps Start with a year value of 0 and a balance of $10,000 Repeat the following while the balance is less than $20,000 Add 1 to the year value Multiply the balance by 1.05 (5% increase) Report the final year value as the answer Page 30
33 Pseudocode Text Problem to Pseudocode Half-way between natural language and a programming language Modified Steps Set the year value of 0 Set the balance to $10,000 While the balance is less than $20,000 Add 1 to the year value Multiply the balance by 1.05 Report the final year value as the answer Pseudocode is an informal description of a sequence of steps for solving a problem This can be translated into Java fairly easily Page 31
34 Algorithm Defined An algorithm describes a sequence of steps that is: Unambiguous Do not require assumptions Uses precise instructions Executable Can be carried out in practice Terminating Will eventually come to an end Page 32
35 Steps: Algorithm to Pseudocode You have the choice of buying two cars. One is more fuel efficient than the other, but also more expensive. You know the price and fuel efficiency (in miles per gallon, mpg) of both cars. You plan to keep the car for ten years. Which car is the better deal? 1. Determine the inputs and outputs From the problem statement: price1, price2, mpg1, mpg2 2. Break down the problem into smaller tasks Calculate total cost for each car 3. Describe each subtask as pseudocode total cost = purchase price + operating cost 4. Test your pseudocode with example input Page 33
36 Summary: Java Java was originally designed for programming consumer devices, but it was first successfully used to write Internet applets. Java was designed to be safe and portable, benefiting both Internet users and students. Java programs are distributed as instructions for a virtual machine, making them platformindependent. Java has a very large set of libraries. Focus on learning those parts of libraries that you need for your programming projects. Page 35
37 Summary: Java Set aside some time to become familiar with the programming environment that you will use for your class work. An editor is a program for entering and modifying text, such as a Java program. Java is case sensitive. You must be careful about distinguishing between upper and lowercase letters. The Java compiler translates source code into class files that contain instructions for the Java virtual machine. Page 36
38 Summary: Java Classes are the fundamental building blocks of Java programs. Every Java application contains a class with a main method. When the application starts, the instructions in the main method are executed. Each class contains declarations of methods. Each method contains a sequence of instructions. A method is called by specifying the method and its parameters. A string is a sequence of characters enclosed in quotation marks. Page 37
39 Summary: Errors and Pseudocode A compile-time error is a violation of the programming language rules that is detected by the compiler. A run-time error causes a program to take an action that the programmer did not intend. Pseudocode is an informal description of a sequence of steps for solving a problem. An algorithm for solving a problem is a sequence of steps that is unambiguous, executable, and terminating. Page 38
Chapter Goals. Contents INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time and run-time
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time and run-time
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION. Final Draft Oct. 15, Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com. Copyright 2013 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com Final Draft Oct. 15, 2011 Chapter Goals q To learn about computers and programming q To compile and run your first Java program q To recognize
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com Final Draft Oct. 15, 2011 Chapter Goals q To learn about computers and programming q To compile and run your first Java program q To recognize
Chapter Goals. Contents. 1.1 Computer Programs
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time and run-time errors To describe an algorithm with pseudocode
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time and run-time errors To describe an algorithm with pseudocode
Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT
 Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT Outline In this chapter you will learn: About computer hardware, software and programming How to write and execute
Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT Outline In this chapter you will learn: About computer hardware, software and programming How to write and execute
ICOM 4015: Advanced Programming
 ICOM 4015: Advanced Programming Lecture 1 Reading: Chapter One: Introduction Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter Goals To understand the activity of programming To learn about the architecture of computers
ICOM 4015: Advanced Programming Lecture 1 Reading: Chapter One: Introduction Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter Goals To understand the activity of programming To learn about the architecture of computers
Chapter 1 - Introduction. Copyright 2014 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. 1
 Chapter 1 - Introduction Copyright 2014 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. 1 Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time
Chapter 1 - Introduction Copyright 2014 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. 1 Chapter Goals To learn about computers and programming To compile and run your first Java program To recognize compile-time
Chapter One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT
 Chapter One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT Chapter Goals In this chapter you will earn: About computer hardware, so8ware and programming How to write
Chapter One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT Chapter Goals In this chapter you will earn: About computer hardware, so8ware and programming How to write
Which statement regarding computer programs is correct? Which statement best describes a computer program?
 1 of 21 5/27/17, 8:21 PM Book Big Java, Early Objects Edition 6 Introduction 1. Which statement best describes a computer program? A. A program is a sequence of comments. B. A program can dece what task
1 of 21 5/27/17, 8:21 PM Book Big Java, Early Objects Edition 6 Introduction 1. Which statement best describes a computer program? A. A program is a sequence of comments. B. A program can dece what task
Programming Environments
 Programming Environments There are several ways of crea/ng a computer program Using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Using a text editor You should use the method you are most comfortable with.
Programming Environments There are several ways of crea/ng a computer program Using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Using a text editor You should use the method you are most comfortable with.
Computer Hardware. Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus. Key Hardware Components 12/17/2013
 Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus Chapter 1 Notes Computer Hardware Key Hardware Components CPU central processing unit Input / Output devices Main memory (RAM) Secondary storage devices: Hard drive
Java Software Solutions Lewis & Loftus Chapter 1 Notes Computer Hardware Key Hardware Components CPU central processing unit Input / Output devices Main memory (RAM) Secondary storage devices: Hard drive
From Algorithms to Architecture....a lightning introduction to computer architecture
 From Algorithms to Architecture...a lightning introduction to computer architecture Implementing Algorithms Now have a methodology for going from problem to program Next develop a mental model of a device
From Algorithms to Architecture...a lightning introduction to computer architecture Implementing Algorithms Now have a methodology for going from problem to program Next develop a mental model of a device
Introduction to Software Development (ISD) David Weston and Igor Razgon
 Introduction to Software Development (ISD) David Weston and Igor Razgon Autumn term 2013 Course book The primary book supporting the ISD module is: Java for Everyone, by Cay Horstmann, 2nd Edition, Wiley,
Introduction to Software Development (ISD) David Weston and Igor Razgon Autumn term 2013 Course book The primary book supporting the ISD module is: Java for Everyone, by Cay Horstmann, 2nd Edition, Wiley,
Software and Programming 1
 Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 17 January 2019 SP1-Lab1-2018-19.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 17 January 2019 SP1-Lab1-2018-19.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Welcome to CSE 142! Whitaker Brand. University of Washington, Winter 2018
 Welcome to CSE 142! Whitaker Brand University of Washington, Winter 2018 1 What is computer science? computers? science? programming? late lonely nights in front of the computer? ALGORITHMIC THINKING al
Welcome to CSE 142! Whitaker Brand University of Washington, Winter 2018 1 What is computer science? computers? science? programming? late lonely nights in front of the computer? ALGORITHMIC THINKING al
Chapter Goals. Chapter One: Introduction. Prerequisites. What Is Programming?
 Chapter Goals To understand the activity of programming To learn about the architecture of computers To learn about machine code and high level programming languages To become familiar with your computing
Chapter Goals To understand the activity of programming To learn about the architecture of computers To learn about machine code and high level programming languages To become familiar with your computing
Lesson 1A - First Java Program HELLO WORLD With DEBUGGING examples. By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2015
 Lesson 1A - First Java Program HELLO WORLD With DEBUGGING examples By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2015 Table of Contents Objectives Hello World Lesson Sequence Compile Errors Lexical
Lesson 1A - First Java Program HELLO WORLD With DEBUGGING examples By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2015 Table of Contents Objectives Hello World Lesson Sequence Compile Errors Lexical
Introduction to JAVA
 Java A001 Hello World Let's study the entire program below: Introduction to JAVA // The "A001" class. import java.awt.*; public class A001 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello
Java A001 Hello World Let's study the entire program below: Introduction to JAVA // The "A001" class. import java.awt.*; public class A001 { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello
Define a method vs. calling a method. Chapter Goals. Contents 1/21/13
 CHAPTER 2 Define a method vs. calling a method Line 3 defines a method called main Line 5 calls a method called println, which is defined in the Java library You will learn later how to define your own
CHAPTER 2 Define a method vs. calling a method Line 3 defines a method called main Line 5 calls a method called println, which is defined in the Java library You will learn later how to define your own
Module 1: Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
 Module 1: Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Module 1: Introduction to Java page 1 Objectives To review Program Design and Problem-Solving Techniques To describe the relationship between Java
Module 1: Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Module 1: Introduction to Java page 1 Objectives To review Program Design and Problem-Solving Techniques To describe the relationship between Java
2/9/2012. Chapter One: Introduction. Chapter Goals
 Chapter One: Introduction Chapter Goals To understand the activity of programming To learn about the architecture of computers To learn about machine code and high level programming languages To become
Chapter One: Introduction Chapter Goals To understand the activity of programming To learn about the architecture of computers To learn about machine code and high level programming languages To become
Lab # 2. For today s lab:
 1 ITI 1120 Lab # 2 Contributors: G. Arbez, M. Eid, D. Inkpen, A. Williams, D. Amyot 1 For today s lab: Go the course webpage Follow the links to the lab notes for Lab 2. Save all the java programs you
1 ITI 1120 Lab # 2 Contributors: G. Arbez, M. Eid, D. Inkpen, A. Williams, D. Amyot 1 For today s lab: Go the course webpage Follow the links to the lab notes for Lab 2. Save all the java programs you
Java Bytecode (binary file)
 Java is Compiled Unlike Python, which is an interpreted langauge, Java code is compiled. In Java, a compiler reads in a Java source file (the code that we write), and it translates that code into bytecode.
Java is Compiled Unlike Python, which is an interpreted langauge, Java code is compiled. In Java, a compiler reads in a Java source file (the code that we write), and it translates that code into bytecode.
Introduction to Java Applications
 2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Object-Oriented Programming
 Object-Oriented Programming Java Syntax Program Structure Variables and basic data types. Industry standard naming conventions. Java syntax and coding conventions If Then Else Case statements Looping (for,
Object-Oriented Programming Java Syntax Program Structure Variables and basic data types. Industry standard naming conventions. Java syntax and coding conventions If Then Else Case statements Looping (for,
4 Programming Fundamentals. Introduction to Programming 1 1
 4 Programming Fundamentals Introduction to Programming 1 1 Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student should be able to: Identify the basic parts of a Java program Differentiate among Java literals,
4 Programming Fundamentals Introduction to Programming 1 1 Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student should be able to: Identify the basic parts of a Java program Differentiate among Java literals,
The name of our class will be Yo. Type that in where it says Class Name. Don t hit the OK button yet.
 Mr G s Java Jive #2: Yo! Our First Program With this handout you ll write your first program, which we ll call Yo. Programs, Classes, and Objects, Oh My! People regularly refer to Java as a language that
Mr G s Java Jive #2: Yo! Our First Program With this handout you ll write your first program, which we ll call Yo. Programs, Classes, and Objects, Oh My! People regularly refer to Java as a language that
BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I
![BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I](/thumbs/81/83968367.jpg) BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
Welcome to Python 3. Some history
 Python 3 Welcome to Python 3 Some history Python was created in the late 1980s by Guido van Rossum In December 1989 is when it was implemented Python 3 was released in December of 2008 It is not backward
Python 3 Welcome to Python 3 Some history Python was created in the late 1980s by Guido van Rossum In December 1989 is when it was implemented Python 3 was released in December of 2008 It is not backward
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG
 CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Assignments Reading Assignment: Chapter 3: Introduction to Parameters and Objects The Class 10 Exercise
CS/IT 114 Introduction to Java, Part 1 FALL 2016 CLASS 10: OCT. 6TH INSTRUCTOR: JIAYIN WANG 1 Notice Assignments Reading Assignment: Chapter 3: Introduction to Parameters and Objects The Class 10 Exercise
Software and Programming 1
 Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 11 January 2018 SP1-Lab1-2017-18.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Software and Programming 1 Lab 1: Introduction, HelloWorld Program and use of the Debugger 11 January 2018 SP1-Lab1-2017-18.pptx Tobi Brodie (tobi@dcs.bbk.ac.uk) 1 Module Information Lectures: Afternoon
Interpreted vs Compiled. Java Compile. Classes, Objects, and Methods. Hello World 10/6/2016. Python Interpreted. Java Compiled
 Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Java Programming Fundamentals - Day Instructor: Jason Yoon Website:
 Java Programming Fundamentals - Day 1 07.09.2016 Instructor: Jason Yoon Website: http://mryoon.weebly.com Quick Advice Before We Get Started Java is not the same as javascript! Don t get them confused
Java Programming Fundamentals - Day 1 07.09.2016 Instructor: Jason Yoon Website: http://mryoon.weebly.com Quick Advice Before We Get Started Java is not the same as javascript! Don t get them confused
A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to
 A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to perform some task. A simple enough idea, but for the computer to make any use of the instructions, they must be written in a form
A PROGRAM IS A SEQUENCE of instructions that a computer can execute to perform some task. A simple enough idea, but for the computer to make any use of the instructions, they must be written in a form
Last Time. University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu. Readings
 University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu Writing a Simple Java Program Intro to Variables Readings Your textbook is Big Java (3rd Ed). This Week s Reading: Ch 2.1-2.5, Ch
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Alan J. Hu Writing a Simple Java Program Intro to Variables Readings Your textbook is Big Java (3rd Ed). This Week s Reading: Ch 2.1-2.5, Ch
How to make a "hello world" program in Java with Eclipse *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m43473 1 How to make a "hello world" program in Java with Eclipse * Hannes Hirzel Based on How to make a "hello world" program in Java. by Rodrigo Rodriguez This work is produced by
OpenStax-CNX module: m43473 1 How to make a "hello world" program in Java with Eclipse * Hannes Hirzel Based on How to make a "hello world" program in Java. by Rodrigo Rodriguez This work is produced by
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Midterm Exams on 4 th of June (12:35 14:35) Room allocation will be announced soon
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 2: Variables, and Data Types Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Midterm Exams on 4 th of June (12:35 14:35) Room allocation will be announced soon
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics
 CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Prerequisites These are the topics that I assume that you have already seen: Variables Boolean expressions
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Prerequisites These are the topics that I assume that you have already seen: Variables Boolean expressions
Welcome to CSE 142! Zorah Fung University of Washington, Spring Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1: Introduction; Basic Java Programs
 Welcome to CSE 142! Zorah Fung University of Washington, Spring 2015 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1: Introduction; Basic Java Programs reading: 1.1-1.3 1 What is computer science? computers?
Welcome to CSE 142! Zorah Fung University of Washington, Spring 2015 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 1: Introduction; Basic Java Programs reading: 1.1-1.3 1 What is computer science? computers?
CompSci 125 Lecture 02
 Assignments CompSci 125 Lecture 02 Java and Java Programming with Eclipse! Homework:! http://coen.boisestate.edu/jconrad/compsci-125-homework! hw1 due Jan 28 (MW), 29 (TuTh)! Programming:! http://coen.boisestate.edu/jconrad/cs125-programming-assignments!
Assignments CompSci 125 Lecture 02 Java and Java Programming with Eclipse! Homework:! http://coen.boisestate.edu/jconrad/compsci-125-homework! hw1 due Jan 28 (MW), 29 (TuTh)! Programming:! http://coen.boisestate.edu/jconrad/cs125-programming-assignments!
Introduction to Java. Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords
 Introduction to Java Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords Program Errors Syntax Runtime Logic Procedural Decomposition Methods Flow of Control
Introduction to Java Java Programs Classes, Methods, and Statements Comments Strings Escape Sequences Identifiers Keywords Program Errors Syntax Runtime Logic Procedural Decomposition Methods Flow of Control
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics 1 Computer Basics Computer system: hardware + software Hardware: the physical components Software: the instructions that
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 1 Computer Basics 1 Computer Basics Computer system: hardware + software Hardware: the physical components Software: the instructions that
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering. Lecture No. #03 The Programming Cycle
 Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering Lecture No. #03 The Programming Cycle (Refer Slide Time: 00:22) Once we are understood what algorithms are, we will start
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering Lecture No. #03 The Programming Cycle (Refer Slide Time: 00:22) Once we are understood what algorithms are, we will start
Basic Programming Language Syntax
 Java Created in 1990 by Sun Microsystems. Free compiler from Sun, commercial from many vendors. We use free (Sun) Java on UNIX. Compiling and Interpreting...are processes of translating a high-level programming
Java Created in 1990 by Sun Microsystems. Free compiler from Sun, commercial from many vendors. We use free (Sun) Java on UNIX. Compiling and Interpreting...are processes of translating a high-level programming
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Development Process
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
First Java Program - Output to the Screen
 First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
First Java Program - Output to the Screen These notes are written assuming that the reader has never programmed in Java, but has programmed in another language in the past. In any language, one of the
Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution
 Unit 2, Part 1 Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Overview of the Programming Process Analysis/Specification
Unit 2, Part 1 Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Overview of the Programming Process Analysis/Specification
COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Introduction to Java. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Introduction to Java Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Key Points 1) Introduce Java, a general-purpose programming language,
Tutorial 1 CSC 201. Java Programming Concepts عؾادئماظربجمةمبادؿكدامماجلاصا
 Tutorial 1 CSC 201 Java Programming Concepts عؾادئماظربجمةمبادؿكدامماجلاصا م- م- م- م- م- Chapter 1 1. What is Java? 2. Why Learn Java? a. Java Is Platform Independent b. Java is Easy to learn 3. Programming
Tutorial 1 CSC 201 Java Programming Concepts عؾادئماظربجمةمبادؿكدامماجلاصا م- م- م- م- م- Chapter 1 1. What is Java? 2. Why Learn Java? a. Java Is Platform Independent b. Java is Easy to learn 3. Programming
Key Differences Between Python and Java
 Python Python supports many (but not all) aspects of object-oriented programming; but it is possible to write a Python program without making any use of OO concepts. Python is designed to be used interpretively.
Python Python supports many (but not all) aspects of object-oriented programming; but it is possible to write a Python program without making any use of OO concepts. Python is designed to be used interpretively.
AP Computer Science A: Java Programming
 AP Computer Science A: Java Programming Zheng-Liang Lu Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University APcomSci 297 Spring 2018 Class Information Instructor: Zheng-Liang
AP Computer Science A: Java Programming Zheng-Liang Lu Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University APcomSci 297 Spring 2018 Class Information Instructor: Zheng-Liang
CS11 Java. Fall Lecture 1
 CS11 Java Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! 8 Lectures Slides posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 7-8 Lab Assignments Made available on Mondays Due one week later Monday, 12 noon
CS11 Java Fall 2006-2007 Lecture 1 Welcome! 8 Lectures Slides posted on CS11 website http://www.cs.caltech.edu/courses/cs11 7-8 Lab Assignments Made available on Mondays Due one week later Monday, 12 noon
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba. (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba (C) 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Java application A computer program that executes when you use the java command to launch the Java Virtual Machine
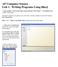
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Chapter 2 Author Notes
 Chapter 2 Author Notes Good Programming Practice 2.1 Every program should begin with a comment that explains the purpose of the program, the author and the date and time the program was last modified.
Chapter 2 Author Notes Good Programming Practice 2.1 Every program should begin with a comment that explains the purpose of the program, the author and the date and time the program was last modified.
Creating a Program in JCreator. JCreator is then used to create our program. But the first step is to create a new file.
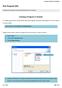 First Program (02) Creating a Java program and understanding the basic concepts. Creating a Program in JCreator It is usually a good idea to create a folder where you re going to save your Java programs.
First Program (02) Creating a Java program and understanding the basic concepts. Creating a Program in JCreator It is usually a good idea to create a folder where you re going to save your Java programs.
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
CSE 142. Lecture 1 Course Introduction; Basic Java. Portions Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education
 CSE 142 Lecture 1 Course Introduction; Basic Java Welcome Today: Course mechanics A little about computer science & engineering (CSE) And how this course relates Java programs that print text 2 Handouts
CSE 142 Lecture 1 Course Introduction; Basic Java Welcome Today: Course mechanics A little about computer science & engineering (CSE) And how this course relates Java programs that print text 2 Handouts
3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS)
 GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION 15 3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS) GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION Checklist: The most recent version of Java SE Development
GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION 15 3 CREATING YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION (USING WINDOWS) GETTING STARTED: YOUR FIRST JAVA APPLICATION Checklist: The most recent version of Java SE Development
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
12/22/11. Java How to Program, 9/e. Help you get started with Eclipse and NetBeans integrated development environments.
 Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Java How to Program, 9/e Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. } Java application programming } Use tools from the JDK to compile and run programs. } Videos at www.deitel.com/books/jhtp9/ Help you get started
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
5/3/2006. Today! HelloWorld in BlueJ. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont.
 Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics. COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction
 CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
CMSC 150 LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE HELLO WORLD
 CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE
CMSC 150 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH INTRODUCTION TO JAVA PROGRAMMING, LIANG (PEARSON 2014) LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION TO COURSE COMPUTER SCIENCE
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Computer Programming : C++
 The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming : C++ Experiment #1 Basics Contents Structure of a program
The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming : C++ Experiment #1 Basics Contents Structure of a program
Working with JavaScript
 Working with JavaScript Creating a Programmable Web Page for North Pole Novelties 1 Objectives Introducing JavaScript Inserting JavaScript into a Web Page File Writing Output to the Web Page 2 Objectives
Working with JavaScript Creating a Programmable Web Page for North Pole Novelties 1 Objectives Introducing JavaScript Inserting JavaScript into a Web Page File Writing Output to the Web Page 2 Objectives
CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 3* * 3 17 % 9-20 % (26 / 7) "2"
 CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 1. For each Java expression in the left hand column, indicate its value in the right hand column. Be sure to show a constant
CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 1. For each Java expression in the left hand column, indicate its value in the right hand column. Be sure to show a constant
OBJECTS AND CLASSES CHAPTER. Final Draft 10/30/2011. Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com
 CHAPTER 8 OBJECTS AND CLASSES Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com Final Draft 10/30/2011 Chapter Goals To understand the concepts of classes, objects and encapsulation To implement instance variables,
CHAPTER 8 OBJECTS AND CLASSES Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com Final Draft 10/30/2011 Chapter Goals To understand the concepts of classes, objects and encapsulation To implement instance variables,
Outline. CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming. What is Computer Science? What is computer programming? What is computer science?
 Outline CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 1 An introduction of an introduction ( 1.1 1.3)* 1. What is computer science and computer programming? 2. Introductions and logistics 3. The
Outline CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 1 An introduction of an introduction ( 1.1 1.3)* 1. What is computer science and computer programming? 2. Introductions and logistics 3. The
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Java Basics
 WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
WIT COMP1000 Java Basics Java Origins Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s It was derived largely from the C++ programming language with several enhancements Java
Fundamentals of Programming Session 4
 Fundamentals of Programming Session 4 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2011 These slides are created using Deitel s slides, ( 1992-2010 by Pearson Education, Inc).
Fundamentals of Programming Session 4 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2011 These slides are created using Deitel s slides, ( 1992-2010 by Pearson Education, Inc).
Fundamentals of Programming. Lecture 3: Introduction to C Programming
 Fundamentals of Programming Lecture 3: Introduction to C Programming Instructor: Fatemeh Zamani f_zamani@ce.sharif.edu Sharif University of Technology Computer Engineering Department Outline A Simple C
Fundamentals of Programming Lecture 3: Introduction to C Programming Instructor: Fatemeh Zamani f_zamani@ce.sharif.edu Sharif University of Technology Computer Engineering Department Outline A Simple C
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
Using System.out.println()
 Programming Assignments Read instructions carefully Many deduction on Program 3 for items in instructions Comment your code Coding conventions 20% of program grade going forward Class #23: Characters,
Programming Assignments Read instructions carefully Many deduction on Program 3 for items in instructions Comment your code Coding conventions 20% of program grade going forward Class #23: Characters,
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
Chapter 1 Lab Algorithms, Errors, and Testing
 Chapter 1 Lab Algorithms, Errors, and Testing Lab Objectives Be able to write an algorithm Be able to compile a Java program Be able to execute a Java program using the Sun JDK or a Java IDE Be able to
Chapter 1 Lab Algorithms, Errors, and Testing Lab Objectives Be able to write an algorithm Be able to compile a Java program Be able to execute a Java program using the Sun JDK or a Java IDE Be able to
Program Fundamentals
 Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
Program Fundamentals /* HelloWorld.java * The classic Hello, world! program */ class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[ ] args) { System.out.println( Hello, world! ); } } /* HelloWorld.java
CS 11 java track: lecture 1
 CS 11 java track: lecture 1 Administrivia need a CS cluster account http://www.cs.caltech.edu/ cgi-bin/sysadmin/account_request.cgi need to know UNIX www.its.caltech.edu/its/facilities/labsclusters/ unix/unixtutorial.shtml
CS 11 java track: lecture 1 Administrivia need a CS cluster account http://www.cs.caltech.edu/ cgi-bin/sysadmin/account_request.cgi need to know UNIX www.its.caltech.edu/its/facilities/labsclusters/ unix/unixtutorial.shtml
Introduction to Computers and Java
 Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Objectives overview computer hardware and software introduce program design and object-oriented programming overview the Java programming language
Introduction to Computers and Java Chapter 1 Chapter 1 1 Objectives overview computer hardware and software introduce program design and object-oriented programming overview the Java programming language
Java Coding 3. Over & over again!
 Java Coding 3 Over & over again! Repetition Java repetition statements while (condition) statement; do statement; while (condition); where for ( init; condition; update) statement; statement is any Java
Java Coding 3 Over & over again! Repetition Java repetition statements while (condition) statement; do statement; while (condition); where for ( init; condition; update) statement; statement is any Java
FUNDAMENTAL DATA TYPES
 CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL DATA TYPES Copyright 2013 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com Final Draft Oct. 15, 2011 Chapter Goals To declare and initialize variables
CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL DATA TYPES Copyright 2013 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com Final Draft Oct. 15, 2011 Chapter Goals To declare and initialize variables
Project 1. Java Control Structures 1/17/2014. Project 1 and Java Intro. Project 1 (2) To familiarize with
 Project 1 and Java Intro Sharma Chakravarthy Information Technology Laboratory (IT Lab) Computer Science and Engineering Department The University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX 76019 Email: sharma@cse.uta.edu
Project 1 and Java Intro Sharma Chakravarthy Information Technology Laboratory (IT Lab) Computer Science and Engineering Department The University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX 76019 Email: sharma@cse.uta.edu
TOPIC 2 INTRODUCTION TO JAVA AND DR JAVA
 1 TOPIC 2 INTRODUCTION TO JAVA AND DR JAVA Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia Approach by M. Guzdial and B. Ericson, and instructor materials prepared
1 TOPIC 2 INTRODUCTION TO JAVA AND DR JAVA Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia Approach by M. Guzdial and B. Ericson, and instructor materials prepared
Lecture 2: Variables and Operators. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
 Lecture 2: Variables and Operators AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda Variables Types Naming Assignment Data Types Type casting Operators Declaring Variables in Java type name; Variables
Lecture 2: Variables and Operators AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda Variables Types Naming Assignment Data Types Type casting Operators Declaring Variables in Java type name; Variables
Conditionals, Loops, and Style
 Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Variables and Typing
 Variables and Typing Christopher M. Harden Contents 1 The basic workflow 2 2 Variables 3 2.1 Declaring a variable........................ 3 2.2 Assigning to a variable...................... 4 2.3 Other
Variables and Typing Christopher M. Harden Contents 1 The basic workflow 2 2 Variables 3 2.1 Declaring a variable........................ 3 2.2 Assigning to a variable...................... 4 2.3 Other
Chapter 1. Introduction to Computers and Java Objects. Background information. » important regardless of programming language. Introduction to Java
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Java Objects Background information» important regardless of programming language Introduction to Java Chapter 1 Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Java Objects Background information» important regardless of programming language Introduction to Java Chapter 1 Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
1 Introduction Java, the beginning Java Virtual Machine A First Program BlueJ Raspberry Pi...
 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Java, the beginning.......................... 3 1.2 Java Virtual Machine........................ 4 1.3 A First Program........................... 4 1.4 BlueJ.................................
Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Java, the beginning.......................... 3 1.2 Java Virtual Machine........................ 4 1.3 A First Program........................... 4 1.4 BlueJ.................................
Math Modeling in Java: An S-I Compartment Model
 1 Math Modeling in Java: An S-I Compartment Model Basic Concepts What is a compartment model? A compartment model is one in which a population is modeled by treating its members as if they are separated
1 Math Modeling in Java: An S-I Compartment Model Basic Concepts What is a compartment model? A compartment model is one in which a population is modeled by treating its members as if they are separated
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Java Static Methods. Recap: Decomposition Example. Recap: Static Method Example
 Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
Mobile App:IT. Methods & Classes
 Mobile App:IT Methods & Classes WHAT IS A METHOD? - A method is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method's name. -
Mobile App:IT Methods & Classes WHAT IS A METHOD? - A method is a set of code which is referred to by name and can be called (invoked) at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method's name. -
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Mr. Monroe s Guide to Mastering Java Syntax
 Mr. Monroe s Guide to Mastering Java Syntax Getting Started with Java 1. Download and install the official JDK (Java Development Kit). 2. Download an IDE (Integrated Development Environment), like BlueJ.
Mr. Monroe s Guide to Mastering Java Syntax Getting Started with Java 1. Download and install the official JDK (Java Development Kit). 2. Download an IDE (Integrated Development Environment), like BlueJ.
Java Programming. Zheng-Liang Lu. Java 304 Fall Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University
 Java Programming Zheng-Liang Lu Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University Java 304 Fall 2018 Class Information Instructor: Zheng-Liang Lu Email: d00922011@ntu.edu.tw
Java Programming Zheng-Liang Lu Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University Java 304 Fall 2018 Class Information Instructor: Zheng-Liang Lu Email: d00922011@ntu.edu.tw
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java
 Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
Lecture Set 2: Starting Java 1. Java Concepts 2. Java Programming Basics 3. User output 4. Variables and types 5. Expressions 6. User input 7. Uninitialized Variables 0 This Course: Intro to Procedural
BASIC ELEMENTS OF A COMPUTER PROGRAM
 BASIC ELEMENTS OF A COMPUTER PROGRAM CSC128 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER PROBLEM SOLVING LOGO Contents 1 Identifier 2 3 Rules for naming and declaring data variables Basic data types 4 Arithmetic operators
BASIC ELEMENTS OF A COMPUTER PROGRAM CSC128 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER PROBLEM SOLVING LOGO Contents 1 Identifier 2 3 Rules for naming and declaring data variables Basic data types 4 Arithmetic operators
