Logic is the anatomy of thought. John Locke ( ) This sentence is false.
|
|
|
- Reynard McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Logic is the anatomy of thought. John Locke ( ) This sentence is false. I know that I know nothing. anonymous Plato (In Apology, Plato relates that Socrates accounts for his seeming wiser than any other person because he does not imagine that he knows what he does not know.) Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 75 / 133
2 Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators Note that these shorthand operators are not available in languages such as Matlab, R, and Python. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 76 / 133
3 Example int x = 1; 3 System.out.println(x); // output 1 4 x = x + 1; 5 System.out.println(x); // output 2 6 x += 2; 7 System.out.println(x); // output 4 8 x++; // equivalent to x += 1 and x = x System.out.println(x); // output Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 77 / 133
4 The compound assignment operators are also useful for char values. 1 For example, char s = a ; 3 System.out.println(s); // output a 4 s += 1; 5 System.out.println(s); // output b 6 s++; 7 System.out.println(s); // output c Contribution by Mr. Edward Wang (Java265) on May 1, Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 78 / 133
5 ++x vs. x++ The expression ++x first increments the value of x and then returns x. Instead, the expression x++ first returns the value of x and then increments itself. For example, int x = 1; 3 int y = ++x; 4 System.out.println(y); // output 2; aka preincrement 5 System.out.println(x); // output int w = 1; 8 int z = w++; 9 System.out.println(z); // output 1; aka postincrement 10 System.out.println(w); // output We will use these notations very often. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 79 / 133
6 Operator Precedence 2 2 See Table3-10 in YDL, p Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 80 / 133
7 Using Parentheses Parentheses are used in expressions to change the natural order of precedence among the operators. One always evaluates the expression inside of parentheses first. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 81 / 133
8 Scanner Objects It is not convenient to modify the source code and recompile it for a different radius. Reading from the console enables the program to receive an input from the user. A Scanner object provides some input methods, say the input received from the keyboard or the files. Java uses System.in to refer to the standard input device, by default, the keyboard. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 82 / 133
9 Example: Reading Input From The Console Write a program which receives a number as input, and outputs the area of the circle. 1 import java.util.scanner; Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 4 System.out.println("Enter r?"); 5 // input 6 int r = input.nextint(); 7 // algorithm 8 double area = r r 3.14; 9 // output 10 System.out.println(area); 11 input.close(); Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 83 / 133
10 In the listing, Line 3 is to create a Scanner object by the new operator, as an agent between the keyboard and your program. Note that all objects are resided in the heap of the memory. To control this object, its memory address is then assigned to the variable input which is a variable in the stack of memory. So the variable input is a reference. We will discuss the objects and reference variables later. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 84 / 133
11 Methods Provided by Scanner Objects 3 3 See Table 2-1 in YDL, p. 38. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 85 / 133
12 Example: Mean and Standard Deviation Write a program which calculates the mean and the standard deviation of 3 numbers. The mean of 3 numbers is given by x = ( 3 i=1 x i Also, the resulting standard deviation is given by S = 3 i=1 (x i x) 2. 3 You may use these two methods: Math.pow(double x, double y) for x y Math.sqrt(double x) for x See more methods within Math class. ) /3. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 86 / 133
13 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 System.out.println("a =?"); 4 double a = input.nextdouble(); 5 System.out.println("b =?"); 6 double b = input.nextdouble(); 7 System.out.println("c =?"); 8 double c = input.nextdouble(); 9 10 double mean = (a + b + c) / 3; 11 double std = Math.sqrt((Math.pow(a mean, 2) + 12 Math.pow(b mean, 2) + 13 Math.pow(c mean, 2)) / 3); System.out.println("mean = " + mean); 16 System.out.println("std = " + std); Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 87 / 133
14 1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 88 / 133
15 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted by the following operations: Sequential statements: execute instructions in order. Selection: first check if the predetermined condition is satisfied, then execute the corresponding instruction. Repetition: repeat the execution of some instructions until the criterion fails. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 89 / 133
16 Note that they are involved with each other generally. For example, recall how to find the maximum in the input list? Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 90 / 133
17 Selections One-way if statements Two-way if-else statements Nested if statements Multiway if-else if-else statements switch-case statements Conditional operators Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 91 / 133
18 One-Way if Statements A one-way if statement executes an action if and only if the condition is true. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 92 / 133
19 if (condition) { 3 // selection body 4 } 5... The keyword if is followed by the parenthesized condition. The condition should be a boolean expression or a boolean value. It the condition is true, then the statements in the selection body will be executed once. If not, then the program won t enter the selection body and skip the whole selection body. Note that the braces can be omitted if the block contains only single statement. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 93 / 133
20 Example Write a program which receives a nonnegative number as input for the radius of a circle, and determines the area of the circle double area; 3 if (r > 0) { 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6 } 7... However, the world is not well-defined. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 94 / 133
21 Two-Way if-else Statements A two-way if-else statement decides which statements to execute based on whether the condition is true or false if (condition) { 3 // body for the true case 4 } else { 5 // body for the false case 6 } 7... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 95 / 133
22 Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 96 / 133
23 Example Write a program which receives a number as input for the radius of a circle. If the number is nonnegative, then determine the area of the circle; otherwise, output Not a circle double area; 3 if (r > 0) { 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6 } else { 7 System.out.println("Not a circle."); 8 } 9 input.close(); 10 } Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 97 / 133
24 Nested if Statements For example, if (score >= 90) 3 System.out.println("A"); 4 else { 5 if (score >= 80) 6 System.out.println("B"); 7 else { 8 if (score >= 70) 9 System.out.println("C"); 10 else { 11 if (score >= 60) 12 System.out.println("D"); 13 else 14 System.out.println("F"); 15 } 16 } 17 } Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 98 / 133
25 Multi-Way if-else Let s redo the previous problem if (score >= 90) 3 System.out.println("A"); 4 else if (score >= 80) 5 System.out.println("B"); 6 else if (score >= 70) 7 System.out.println("C"); 8 else if (score >= 60) 9 System.out.println("D"); 10 else 11 System.out.println("F"); An if-elseif-else statement is a preferred format for multiple alternatives, in order to avoid deep indentation and make the program easy to read. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 99 / 133
26 The order of conditions may be relevant. (Why?) if ((score >= 90) && (score <= 100)) 3 else if ((score >= 80) && (score < 90)) else 6... The performance may degrade due to the order of conditions. (Why?) Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 100 / 133
27 Common Errors double area; 3 if (r > 0); 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 101 / 133
28 Example Generating random numbers Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows =? If the user answers 7, then the program reports Correct. and terminates. Otherwise, the program reports Wrong answer. The correct answer is 7. for this case. You may use Math.random() for a random value between 0.0 and 1.0, excluding themselves. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 102 / 133
29 int x = (int) (Math.random() 10); // integers int y = (int) (Math.random() 10); 4 int answer = x + y; 5 6 System.out.println(x + " + " + y + " =?"); 7 8 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 9 int z = input.nextint(); if (z == answer) 12 System.out.println("Correct."); 13 else 14 System.out.println("Wrong. Answer: " + answer); 15 input.close(); Can you extend this program for all arithmetic expressions (i.e., + )? Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 103 / 133
30 Exercise Find Max Write a program which determines the maximum value in 3 random integers whose range from 0 to 99. How many variables do we need? How to compare? How to keep the maximum value? Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 104 / 133
31 int x = (int) (Math.random() 100); 3 int y = (int) (Math.random() 100); 4 int z = (int) (Math.random() 100); 5 6 int max = x; 7 if (y > max) max = y; 8 if (z > max) max = z; 9 System.out.println("max = " + max); In this case, a scalar variable is not convenient. (Why?) So we need arrays and loops. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 105 / 133
32 switch-case Statements A switch-case structure takes actions depending on the target variable switch (target) { 3 case v1: 4 // statements 5 break; 6 case v2: case vk: 10 // statements 11 break; 12 default: 13 // statements 14 } Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 106 / 133
33 A switch-case statement is more convenient than an if statement for multiple discrete conditions. The variable target, always enclosed in parentheses, must yield a value of char, byte, short, int, or String type. The value v 1,..., and v k must have the same data type as the variable target. In each case, a break statement is a must. 4 break is used to break a construct! The default case, which is optional, can be used to perform actions when none of the specified cases matches target. Counterpart to else statements. 4 If not, there will be a fall-through behavior. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 107 / 133
34 Example // RED: 0 3 // YELLOW: 1 4 // GREEN: 2 5 int trafficlight = (int) (Math.random() 3); 6 switch (trafficlight) { 7 case 0: 8 System.out.println("Stop!!!"); 9 break; 10 case 1: 11 System.out.println("Slow down!!"); 12 break; 13 case 2: 14 System.out.println("Go!"); 15 } Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 108 / 133
35 Conditional Operators A conditional expression evaluates an expression based on the specified condition and returns a value accordingly somevar = booleanexpr? expra : exprb; 3... This is the only ternary operator in Java. If the boolean expression is evaluated true, then return expr A; otherwise, expr B. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 109 / 133
36 For example, if (num1 > num2) 3 max = num1; 4 else 5 max = num2; 6... Alternatively, one can use a conditional expression like this: max = (num1 > num2)? num1 : num2; 3... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 110 / 133
37 1 class Lecture4 { 2 3 "Loops" 4 5 } 6 7 // keywords: 8 while, do, for, break, continue Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 111 / 133
38 Loops A loop can be used to make a program execute statements repeatedly without having to code the same statements. For example, a program outputs Hello, Java. for 100 times System.out.println("Hello, Java."); 3 System.out.println("Hello, Java."); // copy and paste for 100 times 6. 7 System.out.println("Hello, Java."); 8... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 112 / 133
39 int cnt = 0; 3 while (cnt < 100) { 4 System.out.println("Hello, Java."); 5 cnt++; 6 } 7... This is a simple example to show the power of loops. In practice, any routine which repeats couples of times 5 can be done by folding them into a loop. 5 I prefer to call them patterns. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 113 / 133
40 成也迴圈, 敗也迴圈 Loops provide substantial computational power. Loops bring an efficient way of programming. Loops could consume a lot of time. 6 6 We will visit the analysis of algorithms in the end of this lecture. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 114 / 133
41 while Loops A while loop executes statements repeatedly while the condition is true while (condition) { 3 // loop body 4 } 5... The condition should be a boolean expression which determines whether or not the execution of the body occurs. If true, the loop body is executed and check the condition again. Otherwise, the entire loop terminates. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 115 / 133
42 Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 116 / 133
43 Example Write a program which sums up all integers from 1 to 100. In math, the question can be written as: sum = But this form is not doable in the machine. 7 7 We need to develop computational thinking. Read or Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 117 / 133
44 Normally, the machine executes the instructions sequentially. So one needs to decompose the math equation into several steps, like: int sum = 0; 3 sum = sum + 1; 4 sum = sum + 2; sum = sum + 100; 9... It is obvious that many similar statements can be found. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 118 / 133
45 Using a while loop, the program can be rearranged as follows: int sum = 0; 3 int i = 1; 4 while (i <= 100) { 5 sum = sum + i; 6 ++i; 7 } 8... You should guarantee that the loop will terminate as expected. In practice, the number of loop steps (iterations) is unknown until the input data is given. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 119 / 133
46 Malfunctioned Loops It is really easy to make an infinite loop while (true); 3... The common errors of the loops are: never start never stop not complete exceed the expected number of iterations Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 120 / 133
47 Example Write a program which asks the sum of two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until correct Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random() 10); 4 int y = (int) (Math.random() 10); 5 int ans = x + y; 6 7 System.out.println(x + " + " + y + " =? "); 8 int z = input.nextint(); 9 10 while (z!= ans) { 11 System.out.println("Try again? "); 12 z = input.nextint(); 13 } 14 System.out.println("Correct."); 15 input.close(); Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 121 / 133
48 Loop Design Strategy Writing a correct loop is not an easy task for novice programmers. Consider 3 steps when writing a loop: Find the pattern: identify the statements that need to be repeated. Wrap by loops: put these statements in the loop. Set the continuation condition: translate the criterion from the real world problem into computational conditions. 8 8 Not unique. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 122 / 133
49 Sentinel-Controlled Loops Another common technique for controlling a loop is to designate a special value when reading and processing a set of values. This special input value, known as a sentinel value, signifies the end of the loop. For example, the operating systems and the GUI apps. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 123 / 133
50 Example: Cashier Problem Write a program which sums over positive integers from consecutive inputs and then outputs the sum when the input is nonpositive int total = 0; 3 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 4 5 System.out.println("Enter price?"); 6 int price = input.nextint(); 7 while (price > 0) { 8 total += price; 9 System.out.println("Enter price?"); 10 price = input.nextint(); 11 // These two lines above repeat Line 3 and 4?! 12 } System.out.println("Total = " + total); 15 input.close(); Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 124 / 133
51 do-while Loops A do-while loop is similar to a while loop except that it does execute the loop body first and then checks the loop continuation condition do { 3 // loop body 4 } while (condition); // Do not miss the semicolon! 5... Note that there is a semicolon at the end of the do-while loop. The do-while loops are also called posttest loops, in contrast to while loops, which are pretest loops. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 125 / 133
52 Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 126 / 133
53 Example (Revisted) Write a program which sums over positive integers from consecutive inputs and then outputs the sum when the input is nonpositive int total = 0, price = 0; 3 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 4 5 do { 6 total += price; 7 System.out.println("Enter price?"); 8 price = input.nextint(); 9 } while (price > 0); System.out.println("Total = " + total); 12 input.close(); Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 127 / 133
54 for Loops A for loop generally uses a variable to control how many times the loop body is executed for (init action; condition; increment) { 3 // loop body 4 } 5... init-action: declare and initialize a variable condition: set a criterion for loop continuation increment: how the variable changes after each iteration Note that these terms are separated by semicolons. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 128 / 133
55 Sum from 1 to 100 Example Write a program which sums from 1 to int sum = 0; 3 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; ++i) 4 sum = sum + i; 5... Compared to the while version, int sum = 0; 3 int i = 1; 4 while (i <= 100) { 5 sum = sum + i; 6 ++i; 7 } 8... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 129 / 133
56 Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 130 / 133
57 Example: Selection Resided in Loop Display all even numbers Write a program which displays all even numbers smaller than 100. An even number is an integer of the form x = 2k, where k is an integer. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 131 / 133
58 You may use the modular operator (%) for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { 3 if (i % 2 == 0) System.out.println(i); 4 } 5... Also consider this alternative: for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) { 3 System.out.println(i); 4 } 5... How about odd numbers? Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 132 / 133
59 Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 9 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 9 See Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 133
Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators
 Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators Note that these shorthand operators are not available in languages such as Matlab and R. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 76 / 141 Example 1... 2 int x = 1; 3 System.out.println(x);
Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators Note that these shorthand operators are not available in languages such as Matlab and R. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 76 / 141 Example 1... 2 int x = 1; 3 System.out.println(x);
Scanner Objects. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 82 / 133
 Scanner Objects It is not convenient to modify the source code and recompile it for a different radius. Reading from the console enables the program to receive an input from the user. A Scanner object
Scanner Objects It is not convenient to modify the source code and recompile it for a different radius. Reading from the console enables the program to receive an input from the user. A Scanner object
++x vs. x++ We will use these notations very often.
 ++x vs. x++ The expression ++x first increments the value of x and then returns x. Instead, the expression x++ first returns the value of x and then increments itself. For example, 1... 2 int x = 1; 3
++x vs. x++ The expression ++x first increments the value of x and then returns x. Instead, the expression x++ first returns the value of x and then increments itself. For example, 1... 2 int x = 1; 3
1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 88 / 133
 1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 88 / 133 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted
1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 88 / 133 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted
1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 89 / 137
 1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 89 / 137 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted
1 class Lecture3 { 2 3 "Selections" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords 8 if, else, else if, switch, case, default Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 89 / 137 Flow Controls The basic algorithm (and program) is constituted
Example. Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression.
 Generating random numbers Example Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows 2 + 5 =? If the user answers 7, then
Generating random numbers Example Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows 2 + 5 =? If the user answers 7, then
Example. Generating random numbers. Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression.
 Example Generating random numbers Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows 2 + 5 =? If the user answers 7, then
Example Generating random numbers Write a program which generates 2 random integers and asks the user to answer the math expression. For example, the program shows 2 + 5 =? If the user answers 7, then
Common Errors double area; 3 if (r > 0); 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 101 / 141
 Common Errors 2 double area; 3 if (r > 0); 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 101 / 141 Generating random numbers Example Write a program which generates
Common Errors 2 double area; 3 if (r > 0); 4 area = r r 3.14; 5 System.out.println(area); 6... Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 101 / 141 Generating random numbers Example Write a program which generates
switch-case Statements
 switch-case Statements A switch-case structure takes actions depending on the target variable. 2 switch (target) { 3 case v1: 4 // statements 5 break; 6 case v2: 7. 8. 9 case vk: 10 // statements 11 break;
switch-case Statements A switch-case structure takes actions depending on the target variable. 2 switch (target) { 3 case v1: 4 // statements 5 break; 6 case v2: 7. 8. 9 case vk: 10 // statements 11 break;
IEEE Floating-Point Representation 1
 IEEE Floating-Point Representation 1 x = ( 1) s M 2 E The sign s determines whether the number is negative (s = 1) or positive (s = 0). The significand M is a fractional binary number that ranges either
IEEE Floating-Point Representation 1 x = ( 1) s M 2 E The sign s determines whether the number is negative (s = 1) or positive (s = 0). The significand M is a fractional binary number that ranges either
Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators
 Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators Note that these shorthand operators are not available in languages such as Matlab and R. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 76 / 172 Example 1... 2 int x = 1; 3 System.out.println(x);
Arithmetic Compound Assignment Operators Note that these shorthand operators are not available in languages such as Matlab and R. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 76 / 172 Example 1... 2 int x = 1; 3 System.out.println(x);
Data Types. 1 You cannot change the type of the variable after declaration. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 52 / 87
 Data Types Java is a strongly-typed 1 programming language. Every variable has a type. Also, every (mathematical) expression has a type. There are two categories of data types: primitive data types, and
Data Types Java is a strongly-typed 1 programming language. Every variable has a type. Also, every (mathematical) expression has a type. There are two categories of data types: primitive data types, and
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45
Example. Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct.
 Example Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct. 1... 2 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random()
Example Write a program which sums two random integers and lets the user repeatedly enter a new answer until it is correct. 1... 2 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 3 int x = (int) (Math.random()
Values in 2 s Complement
 Values in 2 s Complement Java uses an encoding known as 2 s complement 1, which means that negative numbers are represented by inverting 2 all of the bits in a value, then adding 1 to the result. For example,
Values in 2 s Complement Java uses an encoding known as 2 s complement 1, which means that negative numbers are represented by inverting 2 all of the bits in a value, then adding 1 to the result. For example,
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1
 Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
Example: Monte Carlo Simulation 1 Write a program which conducts a Monte Carlo simulation to estimate π. 1 See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/monte_carlo_method. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 133 / 149
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture4 { 2 3 "Loops" / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 125 / 207
![1 class Lecture4 { 2 3 Loops / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 125 / 207 1 class Lecture4 { 2 3 Loops / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 125 / 207](/thumbs/77/74823043.jpg) 1 class Lecture4 { 2 3 "Loops" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 125 / 207 Loops A loop can be used to make a program execute statements repeatedly without having
1 class Lecture4 { 2 3 "Loops" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 125 / 207 Loops A loop can be used to make a program execute statements repeatedly without having
Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections. Motivating Examples (1.2) Learning Outcomes. EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018
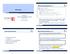 Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1 import java.util.scanner; 2 public class ComputeArea { 3 public static void main(string[] args)
Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1 import java.util.scanner; 2 public class ComputeArea { 3 public static void main(string[] args)
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Selections. EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Selections EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes The Boolean Data Type if Statement Compound vs. Primitive Statement Common Errors
Selections EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes The Boolean Data Type if Statement Compound vs. Primitive Statement Common Errors
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
Introduction to OOP with Java. Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017
 Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Eng. Mohammed S. Abdualal
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 3 Selections
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 3 Selections
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 5 Control Structures II: Repetition Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use: o Counter-controlled
Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them.
 Dec. 9 Loops Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them. What is a loop? What are the three loops in Java? What do control structures do?
Dec. 9 Loops Please answer the following questions. Do not re-code the enclosed codes if you have already completed them. What is a loop? What are the three loops in Java? What do control structures do?
Wentworth Institute of Technology. Engineering & Technology WIT COMP1000. Simple Control Flow: if-else statements
 WIT COMP1000 Simple Control Flow: if-else statements Control Flow Control flow is the order in which program statements are executed So far, all of our programs have been executed straight-through from
WIT COMP1000 Simple Control Flow: if-else statements Control Flow Control flow is the order in which program statements are executed So far, all of our programs have been executed straight-through from
Exercise (Revisited)
 Exercise (Revisited) Redo the cashier problem by using an infinite loop with a break statement. 1... 2 while (true) { 3 System.out.println("Enter price?"); 4 price = input.nextint(); 5 if (price
Exercise (Revisited) Redo the cashier problem by using an infinite loop with a break statement. 1... 2 while (true) { 3 System.out.println("Enter price?"); 4 price = input.nextint(); 5 if (price
Computer Programming I - Unit 5 Lecture page 1 of 14
 page 1 of 14 I. The while Statement while, for, do Loops Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly. The while statement is one of three looping statements
page 1 of 14 I. The while Statement while, for, do Loops Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly. The while statement is one of three looping statements
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
CompSci 125 Lecture 11
 CompSci 125 Lecture 11 switch case The? conditional operator do while for Announcements hw5 Due 10/4 p2 Due 10/5 switch case! The switch case Statement Consider a simple four-function calculator 16 buttons:
CompSci 125 Lecture 11 switch case The? conditional operator do while for Announcements hw5 Due 10/4 p2 Due 10/5 switch case! The switch case Statement Consider a simple four-function calculator 16 buttons:
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Elementary Programming
 Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Learn ingredients of elementary programming: data types [numbers, characters, strings] literal
Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Learn ingredients of elementary programming: data types [numbers, characters, strings] literal
L o o p s. for(initializing expression; control expression; step expression) { one or more statements }
 L o o p s Objective #1: Explain the importance of loops in programs. In order to write a non trivial computer program, you almost always need to use one or more loops. Loops allow your program to repeat
L o o p s Objective #1: Explain the importance of loops in programs. In order to write a non trivial computer program, you almost always need to use one or more loops. Loops allow your program to repeat
Tester vs. Controller. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Compile Time vs. Run Time
 Tester vs. Controller Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG For effective illustrations, code examples will mostly be written in the form of a tester
Tester vs. Controller Elementary Programming EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG For effective illustrations, code examples will mostly be written in the form of a tester
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #3. Selections
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #3
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #3
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types
 Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Repetition, Looping. While Loop
 Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Variables and Assignments
 Variables and Assignments ˆ A variable is used to keep a value or values. ˆ A box which contains something. ˆ In most languages, a statement looks like var = expression, where var is a variable and expression
Variables and Assignments ˆ A variable is used to keep a value or values. ˆ A box which contains something. ˆ In most languages, a statement looks like var = expression, where var is a variable and expression
Chapter 3. Selections
 Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Development Process
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations
 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1. Name SOLUTION
 CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1 Name SOLUTION Page Points Score 2 15 3 8 4 18 5 10 6 7 7 7 8 14 9 11 10 10 Total 100 1 P age 1. Program Traces (41 points, 50 minutes)
CIS 1068 Program Design and Abstraction Spring2016 Midterm Exam 1 Name SOLUTION Page Points Score 2 15 3 8 4 18 5 10 6 7 7 7 8 14 9 11 10 10 Total 100 1 P age 1. Program Traces (41 points, 50 minutes)
Chapter 3. More Flow of Control. Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Chapter 3 More Flow of Control Overview 3.1 Using Boolean Expressions 3.2 Multiway Branches 3.3 More about C++ Loop Statements 3.4 Designing Loops Slide 3-3 Flow Of Control Flow of control refers to the
Chapter 3 More Flow of Control Overview 3.1 Using Boolean Expressions 3.2 Multiway Branches 3.3 More about C++ Loop Statements 3.4 Designing Loops Slide 3-3 Flow Of Control Flow of control refers to the
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #6. Loops
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #6
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #6
1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 "Methods" / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199
![1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 Methods / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199 1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 Methods / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199](/thumbs/77/74905821.jpg) 1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 "Methods" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199 Methods 2 Methods can be used to define reusable code, and organize
1 class Lecture5 { 2 3 "Methods" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 5 in YDL 9 [1] Ch. 20 in YDL 0 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 176 / 199 Methods 2 Methods can be used to define reusable code, and organize
CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING. Lectures 7&8
 CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING Lectures 7&8 Hopefully the Programming Assignment #1 released by tomorrow REVIEW The switch statement is an alternative way of writing what? How do you end a case in
CS 302: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING Lectures 7&8 Hopefully the Programming Assignment #1 released by tomorrow REVIEW The switch statement is an alternative way of writing what? How do you end a case in
Iteration: Intro. Two types of loops: 1. Pretest Condition precedes body Iterates 0+ times. 2. Posttest Condition follows body Iterates 1+ times
 Iteration: Intro Two types of loops: 1. Pretest Condition precedes body Iterates 0+ times 2. Posttest Condition follows body Iterates 1+ times 1 Iteration: While Loops Pretest loop Most general loop construct
Iteration: Intro Two types of loops: 1. Pretest Condition precedes body Iterates 0+ times 2. Posttest Condition follows body Iterates 1+ times 1 Iteration: While Loops Pretest loop Most general loop construct
Computational Expression
 Computational Expression Conditionals Janyl Jumadinova 10 October, 2018 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 10 October, 2018 1 / 16 Computational Thinking: a problem solving process Decomposition
Computational Expression Conditionals Janyl Jumadinova 10 October, 2018 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 10 October, 2018 1 / 16 Computational Thinking: a problem solving process Decomposition
Programming for Experimental Research. Flow Control
 Programming for Experimental Research Flow Control FLOW CONTROL In a simple program, the commands are executed one after the other in the order they are typed. Many situations require more sophisticated
Programming for Experimental Research Flow Control FLOW CONTROL In a simple program, the commands are executed one after the other in the order they are typed. Many situations require more sophisticated
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Chapter 3 Selections. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Chapter 3 Selections Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Compile Time vs. Run Time. Learning Outcomes
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will be defined within the
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will be defined within the
Introduction to Java Applications
 2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
More on control structures
 Lecture slides for: Chapter 5 More on control structures Java Actually: A Comprehensive Primer in Programming Khalid Azim Mughal, Torill Hamre, Rolf W. Rasmussen Cengage Learning, 2008. ISBN: 978-1-844480-933-2
Lecture slides for: Chapter 5 More on control structures Java Actually: A Comprehensive Primer in Programming Khalid Azim Mughal, Torill Hamre, Rolf W. Rasmussen Cengage Learning, 2008. ISBN: 978-1-844480-933-2
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #2. Elementary Programming
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word. Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
 Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch
 Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
St. Edmund Preparatory High School Brooklyn, NY
 AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
AP Computer Science Mr. A. Pinnavaia Summer Assignment St. Edmund Preparatory High School Name: I know it has been about 7 months since you last thought about programming. It s ok. I wouldn t want to think
Flow of Control. Chapter 3 Part 3 The Switch Statement
 Flow of Control Chapter 3 Part 3 The Switch Statement Agenda Hw 03 comments Review of Ch03 - Parts 1 & 2 Conditional operator I/O of boolean values The switch statement Random numbers Methods with arguments
Flow of Control Chapter 3 Part 3 The Switch Statement Agenda Hw 03 comments Review of Ch03 - Parts 1 & 2 Conditional operator I/O of boolean values The switch statement Random numbers Methods with arguments
Problem Solving With Loops
 To appreciate the value of loops, take a look at the following example. This program will calculate the average of 10 numbers input by the user. Without a loop, the three lines of code that prompt the
To appreciate the value of loops, take a look at the following example. This program will calculate the average of 10 numbers input by the user. Without a loop, the three lines of code that prompt the
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch.
![1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 Elementray Programming / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 Elementray Programming / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch.](/thumbs/88/115141835.jpg) 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 41 / 68 Example Given the radius
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 41 / 68 Example Given the radius
3chapter C ONTROL S TATEMENTS. Objectives
 3chapter C ONTROL S TATEMENTS Objectives To understand the flow of control in selection and loop statements ( 3.2 3.7). To use Boolean expressions to control selection statements and loop statements (
3chapter C ONTROL S TATEMENTS Objectives To understand the flow of control in selection and loop statements ( 3.2 3.7). To use Boolean expressions to control selection statements and loop statements (
REPETITION CONTROL STRUCTURE LOGO
 CSC 128: FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER PROBLEM SOLVING REPETITION CONTROL STRUCTURE 1 Contents 1 Introduction 2 for loop 3 while loop 4 do while loop 2 Introduction It is used when a statement or a block of
CSC 128: FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER PROBLEM SOLVING REPETITION CONTROL STRUCTURE 1 Contents 1 Introduction 2 for loop 3 while loop 4 do while loop 2 Introduction It is used when a statement or a block of
Object-oriented programming. and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018
 Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
Arrays. ˆ An array, is a linear data structure consisting of a collection of elements, each identified by one array index. ˆ For math, arrays could be
 Arrays ˆ An array, is a linear data structure consisting of a collection of elements, each identified by one array index. ˆ For math, arrays could be ˆ row vectors: u R 1 n for any positive integer n ˆ
Arrays ˆ An array, is a linear data structure consisting of a collection of elements, each identified by one array index. ˆ For math, arrays could be ˆ row vectors: u R 1 n for any positive integer n ˆ
Programming Basics. Digital Urban Visualization. People as Flows. ia
 Programming Basics Digital Urban Visualization. People as Flows. 28.09.2015 ia zuend@arch.ethz.ch treyer@arch.ethz.ch Programming? Programming is the interaction between the programmer and the computer.
Programming Basics Digital Urban Visualization. People as Flows. 28.09.2015 ia zuend@arch.ethz.ch treyer@arch.ethz.ch Programming? Programming is the interaction between the programmer and the computer.
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
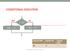 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Loops and Expression Types
 Software and Programming I Loops and Expression Types Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Outline The while, for and do Loops Sections 4.1, 4.3 and 4.4 Variable Scope Section
Software and Programming I Loops and Expression Types Roman Kontchakov / Carsten Fuhs Birkbeck, University of London Outline The while, for and do Loops Sections 4.1, 4.3 and 4.4 Variable Scope Section
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations. CONTENTS: The while and for statements
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming With Iterations CONTENTS: The while and for statements Introduction (1) Suppose we want to write a program to be used in cash registers in stores to compute the amount of money
Introduction to Computer Science, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya. Lectures Control Structures
 Introduction to Computer Science, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya Lectures 3.1 3.2 Control Structures Control Structures, Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya, www.intro2cs.com slide 1 Control structures A program
Introduction to Computer Science, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya Lectures 3.1 3.2 Control Structures Control Structures, Shimon Schocken IDC Herzliya, www.intro2cs.com slide 1 Control structures A program
Review. Primitive Data Types & Variables. String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > <= >= == int, long float, double boolean char
 Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Motivations. Chapter 3: Selections and Conditionals. Relational Operators 8/31/18. Objectives. Problem: A Simple Math Learning Tool
 Chapter 3: Selections and Conditionals CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius in Listing 2.2, ComputeAreaWithConsoleInput.java, the program
Chapter 3: Selections and Conditionals CS1: Java Programming Colorado State University Motivations If you assigned a negative value for radius in Listing 2.2, ComputeAreaWithConsoleInput.java, the program
5.1. Chapter 5: The Increment and Decrement Operators. The Increment and Decrement Operators. The Increment and Decrement Operators
 Chapter 5: 5.1 Looping The Increment and Decrement Operators The Increment and Decrement Operators The Increment and Decrement Operators ++ is the increment operator. It adds one to a variable. val++;
Chapter 5: 5.1 Looping The Increment and Decrement Operators The Increment and Decrement Operators The Increment and Decrement Operators ++ is the increment operator. It adds one to a variable. val++;
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing. Objectives: Examples: Text-printing program. CSC 209 JAVA I
 AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
AL GHURAIR UNIVERSITY College of Computing CSC 209 JAVA I week 2- Arithmetic and Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators Objectives: To use arithmetic operators. The precedence of arithmetic
Chapter 3: Operators, Expressions and Type Conversion
 101 Chapter 3 Operators, Expressions and Type Conversion Chapter 3: Operators, Expressions and Type Conversion Objectives To use basic arithmetic operators. To use increment and decrement operators. To
101 Chapter 3 Operators, Expressions and Type Conversion Chapter 3: Operators, Expressions and Type Conversion Objectives To use basic arithmetic operators. To use increment and decrement operators. To
Java. Programming: Chapter Objectives. Why Is Repetition Needed? Chapter 5: Control Structures II. Program Design Including Data Structures
 Chapter 5: Control Structures II Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use count-controlled,
Chapter 5: Control Structures II Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Learn about repetition (looping) control structures Explore how to construct and use count-controlled,
Prof. Navrati Saxena TA: Rochak Sachan
 JAVA Prof. Navrati Saxena TA: Rochak Sachan Operators Operator Arithmetic Relational Logical Bitwise 1. Arithmetic Operators are used in mathematical expressions. S.N. 0 Operator Result 1. + Addition 6.
JAVA Prof. Navrati Saxena TA: Rochak Sachan Operators Operator Arithmetic Relational Logical Bitwise 1. Arithmetic Operators are used in mathematical expressions. S.N. 0 Operator Result 1. + Addition 6.
Chapter 3 Selection Statements
 Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
ECE 122. Engineering Problem Solving with Java
 ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 10 For Loops and Arrays Outline Problem: How can I perform the same operations a fixed number of times? Considering for loops Performs same operations
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Lecture 10 For Loops and Arrays Outline Problem: How can I perform the same operations a fixed number of times? Considering for loops Performs same operations
Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups:
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
Controls Structure for Repetition
 Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 5 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15
 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Event-based Programming Misc. Java Operator Precedence Java Formatting
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Event Based Programming Lecture 06 - September 17, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda Event-based Programming Misc. Java Operator Precedence Java Formatting
AP Programming - Chapter 6 Lecture
 page 1 of 21 The while Statement, Types of Loops, Looping Subtasks, Nested Loops I. The while Statement Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly.
page 1 of 21 The while Statement, Types of Loops, Looping Subtasks, Nested Loops I. The while Statement Note: Loop - a control structure that causes a sequence of statement(s) to be executed repeatedly.
Loops. EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Loops EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Understand about Loops : Motivation: Repetition of similar actions Two common loops: for and while Primitive
Loops EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Understand about Loops : Motivation: Repetition of similar actions Two common loops: for and while Primitive
Repetition Structures
 Repetition Structures Chapter 5 Fall 2016, CSUS Introduction to Repetition Structures Chapter 5.1 1 Introduction to Repetition Structures A repetition structure causes a statement or set of statements
Repetition Structures Chapter 5 Fall 2016, CSUS Introduction to Repetition Structures Chapter 5.1 1 Introduction to Repetition Structures A repetition structure causes a statement or set of statements
Loops and Files. Chapter 04 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz
 Loops and Files Chapter 04 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Chapter Topics o The Increment and Decrement Operators o The while Loop o Shorthand Assignment Operators o The do-while
Loops and Files Chapter 04 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Chapter Topics o The Increment and Decrement Operators o The while Loop o Shorthand Assignment Operators o The do-while
Computer Programming. Basic Control Flow - Loops. Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons
 Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Lecture 3 Tao Wang 1
 Lecture 3 Tao Wang 1 Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Arithmetic operations Variables and declaration statements Program input using the cin object Common programming errors C++ for Engineers
Lecture 3 Tao Wang 1 Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Arithmetic operations Variables and declaration statements Program input using the cin object Common programming errors C++ for Engineers
Introduction. C provides two styles of flow control:
 Introduction C provides two styles of flow control: Branching Looping Branching is deciding what actions to take and looping is deciding how many times to take a certain action. Branching constructs: if
Introduction C provides two styles of flow control: Branching Looping Branching is deciding what actions to take and looping is deciding how many times to take a certain action. Branching constructs: if
Chapter 4 Introduction to Control Statements
 Introduction to Control Statements Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives 2 How do you use the increment and decrement operators? What are the standard math methods?
Introduction to Control Statements Fundamentals of Java: AP Computer Science Essentials, 4th Edition 1 Objectives 2 How do you use the increment and decrement operators? What are the standard math methods?
CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE
 CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE Computer Science Department Lecture 3: C# language basics Lecture Contents 2 C# basics Conditions Loops Methods Arrays Dr. Amal Khalifa, Spr 2015 3 Conditions and
CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE Computer Science Department Lecture 3: C# language basics Lecture Contents 2 C# basics Conditions Loops Methods Arrays Dr. Amal Khalifa, Spr 2015 3 Conditions and
Loops. EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Loops EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Understand about Loops : Motivation: Repetition of similar actions Two common loops: for
Loops EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes Understand about Loops : Motivation: Repetition of similar actions Two common loops: for
