Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
|
|
|
- Diane Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 v WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining MODRAT hydrologic data for sub-basins and hydraulic structures. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required Components Hydrologic Models Time minutes Page 1 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
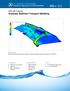
2 1 Introduction Getting Started Creating a Topologic Tree Schematic MODRAT Job Control Schematic Tree Numbering Editing MODRAT Input Parameters Editing Basin Data Editing Reach Parameters Running a MODRAT 2.0 Simulation Adding a Diversion (Flow Split) Renumbering to Include Diversion Defining the Diversion Running MODRAT with Diversion Adding a Detention Basin Defining a Detention Basin Defining the Outlet Pipe and Spillway Running MODRAT with Diversion Control Structures Running MODRAT Conclusion Introduction The Modified Rational (MODRAT) model developed by the Los Angeles County Department of Public Works (LACDPW) can be set up and run using the Hydrologic Modeling Module in WMS. This module allows MODRAT simulation of a watershed without requiring GIS or digital terrain data. The following steps demonstrate setting up a topologic tree or schematic representation of the watershed of Palmer Canyon (Figure 1), entering necessary parameters, and executing a MODRAT simulation. Figure 1 Palmer Canyon watershed Page 2 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
3 2 Getting Started Starting WMS new at the beginning of each tutorial is recommended. This resets the data, display options, and other WMS settings to the defaults. To do this: 1. If necessary, launch WMS. 2. If WMS is already running, press Ctrl-N or select File New to ensure that the program settings are restored to the default state. 3. A dialog may appear asking to save changes. Click No to clear all data. The graphics window of WMS should refresh to show an empty space. 3 Creating a Topologic Tree Schematic A topologic tree is a simple schematic that shows the connectivity of drainage areas (basins) with outlets (confluence points) and reaches (stream segment). The schematic can be built in the Hydrologic Modeling Module. 1. Switch to the Hydrologic Modeling Module. 2. Select MODRAT in the Model drop-down list to make MODRAT the active model in WMS (Figure 2). Figure 2 Model drop-down with MODRAT selected For the following steps, basins can be created by selecting Tree Add Basin and outlets can be created by selecting Tree Add Outlet. The keyboard shortcuts for these are B and O (respectively), which greatly speeds up this process. The steps below will use the shortcuts, grouping several at a time to speed up the process even further. 3. Press O, B, O. This creates the main watershed outlet, attaches a drainage area to the active outlet point, and adds a reach and outlet upstream from the active outlet point. 4. Press B, O, B, B. This creates another basin, another outlet point, and two basins attached to that outlet point. 5. Press O, B, O, B. 6. Press B, O, B. The main line in the Palmer Canyon watershed has been completed. Now create a tributary line. 7. Using the Select outlet tool, select 4C. 8. Press O, B, O. 9. Press B, O, B. This creates a second outlet and reach attached to the selected outlet point. The rest of the watershed is then created and the schematic is now complete (Figure 3). The connectivity Page 3 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
4 of basins, reaches, and outlets is now established, so it is now possible to assign MODRAT input parameters to the watershed. Figure 3 Schematic for Palmer Canyon watershed 4 MODRAT Job Control The MODRAT Job Control dialog allows for specifying input and output filenames, simulation duration, and storm frequency. 1. Select MODRAT Job Control to bring up the MODRAT Job Control 2. In the left section, select MODRAT Select 2 from the Run time drop-down. 4. Select 25 year from the Frequency drop-down. 5. In the Filenames section, enter Palmer1 as the Prefix and click Update. Note that the Output files prefix updated. 6. In the Input section, enter palmer_rain.dat in the Rain field. WMS saves the rainfall input data to this filename. 7. Click Browse to the right of the Soil field to bring up the Open 8. Select WMS Data Sets (*.dat) from the Files of type drop-down. Page 4 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
5 9. Browse to the MODRAT\MODRAT\ directory and select sgr_soilx_71.dat. 10. Click Open to exit the Open The pathway to the selected DAT file should appear in the Soil field now. WMS imports the soil data from this file. This soil file contains data for the San Gabriel River watershed where Palmer Canyon is located. 11. Click OK to close the MODRAT Job Control 5 Schematic Tree Numbering The MODRAT model requires that a watershed model be numbered sequentially in operational order from upstream to downstream. The order in which hydrologic units are processed depends on model numbering. WMS automatically numbers the tree. 1. Using the Select basin tool, select the top right basin. This indicates to WMS in the next step that this is the upstream end of the main line of the watershed. 2. Select MODRAT Number Tree to bring up the MODRAT Renumber 3. Click OK to start numbering with location/lateral of 1A, close the MODRAT Renumber dialog, and open the Select a lateral The numbering process prompts to Select a lateral" for each of the basins at a confluence. Notice that WMS zooms into the outlet point labeled 14AB and its surrounding outlet points. The first one is the one on the left. 4. Select B from the wide drop-down to assign the basin on the left to the "B" lateral of the watershed. 5. Click OK to reload the Select a lateral dialog for the basin on the right. 6. Select A from the wide drop-down to assign the right basin to the "A" lateral of the watershed. 7. Click OK to close the Select a lateral 8. Frame the project. The numbering is now complete. Note that the basin selected when the numbering was initiated is now 1A. The main line is met by Line B at the 16AB confluence (outlet) point (Figure 4). The numbers now indicate the order in which the units will be processed by MODRAT. Before proceeding, save the WMS project. 1. Select File Save As to bring up the Save As 2. Select WMS XMDF Project File (*.wms) from the Save as type drop-down. 3. Enter PalmerCyn25.wms as the File name. 4. Click Save to save the project under the new name and close the Save As WMS saves the project to a set of WMS project files. The WMS file is an index file and contains other information that instructs WMS to load all the files associated with the project when opening the project at a later time. Page 5 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
6 Figure 4 Schematic after renumbering 6 Editing MODRAT Input Parameters Input parameters for each basin and reach must be defined for the watershed. The following sections demonstrate entering required data for basins and reaches and setting output preferences for each hydrologic unit. 6.1 Editing Basin Data Each basin (drainage area) must have data associated with it to be successfully simulated by MODRAT. 1. Select MODRAT Edit Parameters to bring up the MODRAT Parameters 2. Select All from the Show drop-down. 3. In the Temporal distribution column in the All row, click Define to open the XY Series Editor This is where the rainfall temporal distribution (time vs. cumulative rainfall percentage) is specified. Page 6 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
7 4. Click Import to bring up the Open file 5. Select XY Series File (*.xys) from the Files of type drop-down. 6. Select LACDPWStorm-4thday.xys and click Open to import the file and exit the Open file The LACDPW curve will appear in the spreadsheet/plot window (Figure 5). Figure 5 LACDPW curve 7. Click OK to assign this curve to all basins and close the XY Series Editor 8. In the All row, scroll to the right and select Hydrograph (*.hyf) and WMS plot file (*.sol) from the drop-down in the Hydrograph Output column. The input for one of the basins in the Palmer Canyon watershed has been completed. Now define the rest of the data for all basins: 9. In an external spreadsheet program, open the modrat-schematic.xls file in the MODRAT\MODRAT\ directory. 10. Copy the values in the Area (ac) column of the Basin Data table. 11. In WMS, in the MODRAT Parameters dialog, paste the values into the Area (ac) column. Be sure to paste the values to the first white cell in the column. 12. Repeat steps for the Tc (min), Soil type, Impervious %, and Rainfall depth (n) columns. 13. When finished, click OK to close the MODRAT Parameters The basin parameters for all drainage areas should now be entered for the simulation. Now is a good time to save the project. 14. Save the project 6.2 Editing Reach Parameters Each reach must have data associated with it to be successfully simulated by MODRAT. Reaches are selected in WMS by clicking on an outlet (confluence) point. The parameters for that point and the channel downstream from that point to the next can be edited. Page 7 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
8 1. Using the Select outlet tool, select outlet 2A. 2. Select MODRAT Edit Parameters to bring up the MODRAT Parameters 3. Select All from the Show drop-down. 4. Scroll all the way to the right to the Hydrograph Output column, and select Hydrograph (*.hyf) and WMS plot file (*.sol) from the drop-down on the All row. 5. In an external spreadsheet program, open the modrat-schematic.xls file in the MODRAT\MODRAT\ directory. 6. Copy from modrat-schematic.xls the values in the Length (ft) column of the Reach Parameters table. 7. In WMS, paste the values into the Length (ft) column in the MODRAT Parameters Be sure to paste the values into the first white cell of the column. 8. Repeat steps 6-7 for the Slope (ft/ft), Routing type, and Manning s n columns. 9. When finished, click OK to close the MODRAT Parameters The input parameters for all reaches should now be entered for the simulation. Save this data to the working project file. 10. Save the project. 7 Running a MODRAT 2.0 Simulation All the data required to run a simulation is now ready. To make sure there are no omissions in the data, WMS will perform a model check. 1. Select MODRAT Check Simulation to bring up the MODRAT Model Check Notice that there are two possible errors in the MODRAT model for outlet 20A. Because this is the watershed outlet, there is no reach downstream to define. 2. Click Done to exit the MODRAT Model Check The model checker is a simple way to verify that needed data has not been omitted. It does not verify that the model is correct, but that all the data needed to run the simulation is in place. To execute the MODRAT simulation, do the following: 3. Select MODRAT Run Simulation to bring up the MODRAT Run Options 4. Click Browse to bring up the Select MODRAT Input File Name 5. Browse to the MODRAT\MODRAT\ directory for the tutorial. 6. Enter Palmer1.lac as the File name and click Save to close the Select MODRAT Input File Name 7. Turn on Save file before run. Page 8 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
9 8. Click OK to open the Model Wrapper dialog and start the simulation. 9. Once MODRAT finishes, turn on Read solution on exit and click Close to import the solution and close the Model Wrapper The resulting hydrographs will be imported and a small hydrograph plot will appear next to each basin and outlet (Figure 6). Figure 6 Hydrographs generated for each basin and outlet 10. Using the Select hydrograph tool, double-click on the hydrograph icon next to outlet 20A to bring up the Hydrograph 11. Review the hydrograph plot. Notice that peak flow, time to peak, and volume are reported both below the title and in legend of the plot. 12. Hold the Shift key and double-click on the hydrograph icon next to outlet 16AB to bring up a new Hydrograph 13. Notice that both hydrographs are plotted on the same axes. 14. Close both plot windows by clicking on the in the upper right corner of each window. 15. Select File Edit File to bring up the Open 16. Select Palmer1.out and click Open to exit the Open dialog and open the View Data File If the Never ask this again option has previously been checked, this dialog will not appear. If this is the case, skip to step 18. Page 9 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
10 17. Select the desired text editor from the Open with drop-down and click OK to close the View Data File dialog and open the file in the selected text editor. 18. When done reviewing the output data, close the text editor by clicking the in the top right corner and return to WMS. 19. Clear the results by selecting Hydrographs Delete All. This successfully completes this simple simulation with MODRAT. There are many other options in MODRAT not included in this simple model. The following sections will present two of those options: detention basins and diversions. 8 Adding a Diversion (Flow Split) The flow in a line of a MODRAT model can be split using a diversion in WMS. The diverted flow can be routed and returned to a downstream location in the model, if desired. To split flow at one location in the model, do the following: 1. Using the Select outlet tool, select outlet 14B. 2. Select Tree Add Diversion. WMS will insert the diversion. 3. Click on the outlet named 20A. 4. Select Tree Retrieve Diversion. Note that the diversion arrow returns to the outlet named 20A (Figure 7). Figure 7 Diversion from 14B to 20A 8.1 Renumbering to Include Diversion Since a diversion has been added to the model, renumber the model to include this new diversion in the numbering scheme. 1. Using the Select basin tool, select sub-basin 1A (most upstream on the right branch). 2. Select MODRAT Number Tree to bring up the MODRAT Renumber Page 10 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
11 3. Click OK to start numbering with location/lateral of 1A, close the MODRAT Renumber dialog, and open the Select a lateral 4. Select B from the wide drop-down to assign basin 15B to the "B" lateral of the watershed. 5. Click OK to reload the Select a lateral dialog for the basin on the right. 6. Select A from the wide drop-down to assign basin 8A to the "A" lateral of the watershed. 7. Click OK to close the Select a lateral 8. Frame the project. Notice that the diversion basin has been numbered 15C (it may be difficult to see due to the hydrograph icon), and the stream from 14BC to 21AC has been renumbered (Figure 8). Figure 8 Renumbered section 8.2 Defining the Diversion Now that the location and return have been defined, instruct MODRAT how to split the flow and route it in the diversion channel. 1. Using the Select outlet tool, double-click outlet 14BC to bring up the MODRAT Parameters 2. To the right of Display, turn on Relief Drains. 3. Scroll to the right to the Relief drain type column and select Drain Capacity from the drop-down menu. 4. Enter in the Flow rate column. Page 11 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
12 This is the maximum flow allowed in the main channel. Flow above this rate will be diverted. 5. Click OK to exit the MODRAT Parameters 6. Using the Select diversion tool, double-click diversion 15C to bring up the MODRAT Parameters 7. In the spreadsheet on the 15C row, enter in the Length column. 8. Enter 0.05 in the Slope column. 9. Select Circular pipe from the Routing type drop-down. 10. Enter in the Manning s n column. 11. Enter 3.0 in the Size column. This is the diameter of the pipe. 12. Scroll to the right and select Hydrograph (*.hyf) and WMS plot file (*.hyf) in the Hydrograph output column. 13. Click OK to exit the MODRAT Parameters 14. Save the project. 8.3 Running MODRAT with Diversion The diversion is now complete. Now re-run the simulation to see the effects of the diversion. 1. Select MODRAT Job Control to bring up the MODRAT Job Control 2. In the Filenames section, enter Palmer2 as the Prefix and click Update. 3. Click OK to close the MODRAT Job Control 4. Select MODRAT Run Simulation to bring up the MODRAT Run Options 5. Click Browse to bring up the Select MODRAT Input File Name 6. Enter Palmer2.lac as the File name and click Save to close the Select MODRAT Input File Name 7. Turn on Save file before run and click OK to close the MODRAT Run Options dialog and bring up the Model Wrapper 8. Once MODRAT is finished, turn on Read solution on exit and click Close to exit the Model Wrapper The resulting hydrographs will be imported and a small hydrograph plot will appear next to each basin and outlet. 9. Using the Select hydrograph tool, double-click on the hydrograph icon next to outlet 14BC to bring up the Hydrograph 10. Note that the hydrograph peak is cut off at cfs. 11. Double-click on the hydrograph icon next to diversion 15C. Page 12 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
13 12. Compare the two hydrographs, and notice that the one for 15C appears to be a continuation of the one for 14BC (Figure 9). 13. Close all Hydrograph dialogs by clicking the in the upper right corner of each window. 14. Clear the hydrograph results by selecting Hydrographs Delete All. Figure 9 Hydrographs for 14BC (left) and 15C (right) 9 Adding a Detention Basin A detention basin can be placed at any outlet point, routing incoming flow through that structure with MODRAT. In this model, define a detention basin at the watershed outlet (the mouth of Palmer Canyon). 1. Using the Select outlet tool, double-click outlet 21AC to bring up the MODRAT Parameters 2. To the right of Display, turn on Reservoir Routing. 3. Scroll to the right and check the box on the 21AC row in the Reservoir routing column. 4. Click the Define button in the Reservoir column to bring up the Detention Basin Hydrograph Routing 5. Click Define to bring up the Storage Capacity Input 9.1 Defining a Detention Basin Now define a hypothetical detention basin from approximate geometric parameters. WMS can compute a storage capacity curve for a rectangular basin. A pre-computed storage capacity curve should also be entered. 1. In the Storage capacity section, select Known Geometry. 2. Enter as the Length. 3. Enter as the Width. 4. Enter 20.0 as the Depth. Page 13 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
14 5. Enter 1.0 as the Side slope. The Base Elevation is assumed to be on-grade at the outlet location for this tutorial, so it does not need to be set. 6. Click OK to close the Storage Capacity Input dialog and bring up the Detention Basin Analysis 9.2 Defining the Outlet Pipe and Spillway Now define a low-level outlet pipe and spillway (weir) for outlet structures and WMS will compute the elevation-discharge relationship automatically. In addition to standpipes and weirs, low-level outlets can be defined, or a pre-computed elevation-discharge relationship can be entered. 1. Click Define Outflow Discharges to bring up the Elevation Discharge Input 2. Click Add Riser to add a riser ( Riser 1 ) to the Discharges section. 3. In the Parameter section, select Circular from the Opening Shape Type dropdown. 4. Enter 4.90 as the Opening Diameter. 5. Enter 1.0 as the Height above Base Elev to Bottom of Opening. 6. Click Add Weir to add a weir ( Weir 2 ) to the Discharges section. 7. Enter 50.0 as the Weir length. 8. Enter 17.0 as the Height above Base Elev. 9. Click OK to close the Elevation Discharge Input 10. Click OK to close the Detention Basin Analysis The curves should be plotted in the Detention Basin Hydrograph Routing dialog (Figure 10). Figure 10 Reservoir Storage-Elevation-Discharge Page 14 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
15 11. Click OK to close the Detention Basin Hydrograph Routing 12. Click OK to exit the MODRAT Parameters window. A detention facility has now been defined that has an outlet pipe and a spillway for control structures. The incoming hydrograph to this outlet point will be routed through the detention facility before being routed downstream and combined with the hydrographs of other basins. 9.3 Running MODRAT with Diversion Control Structures To re-run the simulation and see the effects, do the following: 1. Select MODRAT Job Control to bring up the MODRAT Job Control 2. In the Filenames section, enter Palmer3 as the Prefix and click Update. 3. Click OK to close the MODRAT Job Control 4. Select MODRAT Run Simulation to bring up the MODRAT Run Options 5. Click Browse to bring up the Select MODRAT Input File Name 6. Enter Palmer3.lac as the File name and click Save to close the Select MODRAT Input File Name 7. Turn on Save file before run. 8. Click OK to close the MODRAT Run Options dialog, open the Model Wrapper dialog, and start the simulation. 9. Once MODRAT finishes, turn on Read solution on exit and click Close to import the solution and close the Model Wrapper The resulting hydrographs will be imported and a small hydrograph plot will appear next to each basin and outlet. Note that there are two hydrograph icons near 21AC. 10. Using the Select hydrograph tool, select one of them, then hold Shift wile double-clicking the other to open the Hydrograph Notice that both are plotted together on the same plot. Both hydrographs will be plotted in a new window (Figure 11). Note the effects of the detention basin on the incoming hydrograph. When selecting multiple hydrographs, view all the selected hydrographs in a single plot by selecting Display Open Hydrograph Plot. 11. When done reviewing the Hydrograph dialog, close it by clicking the in the top right corner. 12. Clear all the hydrograph results by selecting Hydrographs Delete All. 13. Save the project. Page 15 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
16 Figure 11 Both hydrographs at outlet 21AC 10 Running MODRAT 1.0 This section is optional as it discusses how to run a simulation using the older MODRAT 1.0 version of MODRAT that uses the 4-day storm approach instead of a continuous simulation approach To run MODRAT 1.0, some Job Control items and precipitation input for the basins in the model must be entered and edited. 1. Select MODRAT Job Control to bring up the MODRAT Job Control 2. In the left section, select MODRAT. 3. Select Days: 4 from the Time period drop-down. 4. In the Filenames section, enter Palmer4 as the Prefix and click Update. 5. Click OK to close the MODRAT Job Control 6. Select MODRAT Edit Parameters to bring up the MODRAT Parameters 7. Select Basins from the Type drop-down. 8. Select All from the Show drop-down. 9. In the All row of the Temporal distribution column, click Define to bring up the XY Series Editor 10. Click Import to bring up the Open File 11. Select LACDPWStorm1500min.xys and click Open to exit the Open File The LACDPWStormSeries1500min curve will appear in the spreadsheet/plot window (Figure 12). Page 16 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
17 Figure 12 LACDPWStormSeries1500min curve plot 12. Click OK to close the XY Series Editor dialog and assign this curve to all basins. Note that the rainfall depths entered do not need to be changed due to running a 4th day simulation with MODRAT 2.0. These depths correspond to a 24 hour design storm and are appropriate with the 1500 min. curve used with MODRAT Click OK to close the MODRAT Parameters 14. Select MODRAT Run Simulation to bring up the MODRAT Run Options 15. Click Browse to bring up the Select MODRAT Input File Name 16. Enter Palmer4.lac as the File name and click Save to close the Select MODRAT Input File Name 17. Turn on Save file before run and click OK to close the MODRAT Run Options dialog and bring up the Model Wrapper 18. Once MODRAT 1.0 finishes, turn on Read solution on exit and click Close to exit the Model Wrapper dialog and import the solutions. The resulting hydrographs will be imported and a small hydrograph plot will appear next to each basin and outlet. Feel free to review the hydrographs as desired. 11 Conclusion This concludes the tutorial. Key concepts discussed and demonstrated include some of the options available for using the MODRAT model in WMS. Feel free to continue experimenting with the different options to become familiar with all the capabilities in WMS for doing MODRAT simulations. Page 17 of 17 Aquaveo 2018
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define a basic MODRAT model using
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model Objectives Delineate a watershed from a DEM and derive many of the MODRAT input parameters
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model Objectives Delineate a watershed from a DEM and derive many of the MODRAT input parameters
Watershed Modeling Rational Method Interface. Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface Objectives Learn how to model urban areas using the Rational method, including how to compute rainfall intensity,
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface Objectives Learn how to model urban areas using the Rational method, including how to compute rainfall intensity,
Watershed Modeling HEC-HMS Interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins.
 v. 11.0 HEC-HMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial HEC-HMS Learn how to create multiple sub-basins using HEC-HMS Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins. Prerequisite
v. 11.0 HEC-HMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial HEC-HMS Learn how to create multiple sub-basins using HEC-HMS Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins. Prerequisite
Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Rational Design
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD Data Setup an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using CAD data with inlet and pipe information Objectives Learn to define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD Data Setup an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using CAD data with inlet and pipe information Objectives Learn to define
Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files
 WMS 10.1 Tutorial v. 10.1 Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files Set up an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using common file types such
WMS 10.1 Tutorial v. 10.1 Storm Drain Modeling Defining HY-12 Storm Drain Networks with Shapefiles and LandXML files Set up an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using common file types such
Watershed Modeling Maricopa Predictive HEC-1 Model. Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling HEC-1 Interface Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v. 8.4 Prerequisite Tutorials Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Time minutes
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
v Water Distribution System Modeling Working with WMS Tutorials Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Water Distribution System Modeling Working with EPANET Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Objectives Open shapefiles containing the geometry and attributes of EPANET
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Water Distribution System Modeling Working with EPANET Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Objectives Open shapefiles containing the geometry and attributes of EPANET
Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how to define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how to define
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v Introduction to WMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Prerequisite Tutorials None Required Components Data Map
 s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define data for and run a rational method model for a watershed in Orange County.
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
v Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how
Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
Water Distribution System Modeling EPANET. Import an existing water distribution model and modify link and node parameters within WMS
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Water Distribution System Modeling EPANET Hydraulic Model Import an existing water distribution model and modify link and node parameters within WMS Objectives View an existing
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Water Distribution System Modeling EPANET Hydraulic Model Import an existing water distribution model and modify link and node parameters within WMS Objectives View an existing
v Prerequisite Tutorials GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow GSSHA WMS Basics Creating Feature Objects and Mapping their Attributes to the 2D Grid
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions Objectives Learn techniques for using various additional boundary conditions with the Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial SRH-2D Additional Boundary Conditions Objectives Learn techniques for using various additional boundary conditions with the Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional
Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v Prerequisite Tutorials None Time minutes Required Components Hydrologic Models
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Orange County Rational Method Build and run a rational method analysis based on methods in the Orange County (California) hydrology manual Objectives Completing
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Orange County Rational Method Build and run a rational method analysis based on methods in the Orange County (California) hydrology manual Objectives Completing
WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model Objectives Learn how to add hydraulic channel routing to your GSSHA model and how to define channel properties. Learn how
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model Objectives Learn how to add hydraulic channel routing to your GSSHA model and how to define channel properties. Learn how
v Introduction to WMS Become familiar with the WMS interface WMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 s v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Read files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Read files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
Introduction to Bentley PondPack
 Introduction to Bentley PondPack CE 365K Hydraulic Engineering Design Prepared by Cassandra Fagan and David Maidment Spring 2015 Contents Goals of the Tutorial... 1 Procedure... 1 (1) Opening Bentley PondPack...
Introduction to Bentley PondPack CE 365K Hydraulic Engineering Design Prepared by Cassandra Fagan and David Maidment Spring 2015 Contents Goals of the Tutorial... 1 Procedure... 1 (1) Opening Bentley PondPack...
WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results Objectives This tutorial demonstrates different ways of
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results Objectives This tutorial demonstrates different ways of
WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results Objectives This tutorial demonstrates different ways
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results Objectives This tutorial demonstrates different ways
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform Setup a basic distributed MODClark model using the WMS interface Objectives In this
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform Setup a basic distributed MODClark model using the WMS interface Objectives In this
SMS v Simulations. SRH-2D Tutorial. Time. Requirements. Prerequisites. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will demonstrate the process of creating a new SRH-2D simulation from an existing simulation. This workflow is very useful when adding new features
SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will demonstrate the process of creating a new SRH-2D simulation from an existing simulation. This workflow is very useful when adding new features
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling DEM Delineation Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Read a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Read a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009)
 Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009) This tutorial demonstrates the usability of xpswmm and xpstorm for simulating detention basins in urban areas. This fictitious example includes the use
Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009) This tutorial demonstrates the usability of xpswmm and xpstorm for simulating detention basins in urban areas. This fictitious example includes the use
Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data Learn how to delineate sub-basins and compute soil losses for Orange County (California) hydrologic modeling Objectives
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data Learn how to delineate sub-basins and compute soil losses for Orange County (California) hydrologic modeling Objectives
SMS v Obstructions. SRH-2D Tutorial. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of creating and defining in-stream obstructions within an SRH-2D model. The SRH-2D Simulations tutorial should have been completed
SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of creating and defining in-stream obstructions within an SRH-2D model. The SRH-2D Simulations tutorial should have been completed
Tutorial Hydrodynamics in sewers
 Tutorial Hydrodynamics in sewers September 2007 3.9230.00 Tutorial Hydrodynamics in sewers September 2007 Tutorial Hydrodynamics in sewers 3.9230.00 September 2007 Contents 1 Tutorial Hydrodynamics in
Tutorial Hydrodynamics in sewers September 2007 3.9230.00 Tutorial Hydrodynamics in sewers September 2007 Tutorial Hydrodynamics in sewers 3.9230.00 September 2007 Contents 1 Tutorial Hydrodynamics in
Building a new model in wspg2010
 Building a new model in wspg2010 The Water Surface Profile Gradient 2010 (wspg2010 by XP Software) model is a hydraulic analysis system that computes and plots uniform and non-uniform steady flow water
Building a new model in wspg2010 The Water Surface Profile Gradient 2010 (wspg2010 by XP Software) model is a hydraulic analysis system that computes and plots uniform and non-uniform steady flow water
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS
 Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk SSA
 Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk Josh Kehs, P.E. Autodesk, Inc. CI4541 Learning Objectives At the end of this class, you will be able to: Model
Ducks on the Pond: Stormwater Management Basin Analysis Using AutoCAD Civil 3D and Autodesk Josh Kehs, P.E. Autodesk, Inc. CI4541 Learning Objectives At the end of this class, you will be able to: Model
WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and bank
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and bank
WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HEC-RAS Analysis Learn how to setup a basic HEC-RAS analysis using WMS Objectives Learn how to build cross sections, stream centerlines, and
Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D.
 SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial SRH-2D SRH-2D Sediment Transport
SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to perform unsteady sediment transport simulations in SRH-2D. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial SRH-2D SRH-2D Sediment Transport
This loads a preset standard set of data appropriate for Malaysian modeling projects.
 XP Software On-Site Detention (OSD) Example Step 1 Open xpswmm2010 program Or from Start menu select Programs XPS - then select xpswmm2010 Select Create From Template Save file, e.g. Filename.xp The program
XP Software On-Site Detention (OSD) Example Step 1 Open xpswmm2010 program Or from Start menu select Programs XPS - then select xpswmm2010 Select Create From Template Save file, e.g. Filename.xp The program
Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD
 Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD Workshop Overview In this workshop you will use StormCAD to analyze an existing storm sewer system. You will add a parking
Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD Workshop Overview In this workshop you will use StormCAD to analyze an existing storm sewer system. You will add a parking
This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional (SRH-2D) simulation. Requirements
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
SMS v SRH-2D Tutorials Obstructions. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.3 SRH-2D Tutorials Obstructions Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of creating and defining in-stream obstructions within an SRH-2D model. The SRH-2D Simulations tutorial should
SMS v. 12.3 SRH-2D Tutorials Obstructions Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of creating and defining in-stream obstructions within an SRH-2D model. The SRH-2D Simulations tutorial should
WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Applications Analyzing the Effects of Land Use Change (Part - I) Model land use changes using GSSHA
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Applications Analyzing the Effects of Land Use Change (Part - I) Model land use changes using GSSHA Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to model and compare the effects
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Applications Analyzing the Effects of Land Use Change (Part - I) Model land use changes using GSSHA Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to model and compare the effects
v SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Prerequisites None Time minutes Requirements Map Module Mesh Module Scatter Module Generic Model SRH-2D
 v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Objectives This lesson will teach you how to prepare an unstructured mesh, run the SRH-2D numerical engine and view the results all within SMS. You will start by reading
v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Objectives This lesson will teach you how to prepare an unstructured mesh, run the SRH-2D numerical engine and view the results all within SMS. You will start by reading
MODFLOW STR Package The MODFLOW Stream (STR) Package Interface in GMS
 v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial The MODFLOW Stream (STR) Package Interface in GMS Objectives Learn how to create a model containing STR-type streams. Create a conceptual model of the streams using arcs and orient
v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial The MODFLOW Stream (STR) Package Interface in GMS Objectives Learn how to create a model containing STR-type streams. Create a conceptual model of the streams using arcs and orient
SMS v Weir Flow. SRH-2D Tutorial. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of using a weir boundary condition (BC) within SRH-2D to model an overflow weir near a bridge structure. The Simulations tutorial
SMS v. 12.2 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of using a weir boundary condition (BC) within SRH-2D to model an overflow weir near a bridge structure. The Simulations tutorial
WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM Objectives Learn how to delineate a watershed
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM Objectives Learn how to delineate a watershed
SMS v Culvert Structures with HY-8. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Culvert Structures with HY-8 Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D coupled with the Federal Highway Administrations HY-8 culvert analysis
SMS v. 12.1 SRH-2D Tutorial Culvert Structures with HY-8 Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D coupled with the Federal Highway Administrations HY-8 culvert analysis
v TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics SMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
Linear Routing: Floodrouting. HEC-RAS Introduction. Brays Bayou. Uniform Open Channel Flow. v = 1 n R2/3. S S.I. units
 Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM Objectives Learn how to delineate a watershed
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM Objectives Learn how to delineate a watershed
v TUFLOW FV SMS 13.0 Tutorial Requirements Time Prerequisites Objectives
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates creating a simple model of a short section of river using the SMS TUFLOW FV interface. A mesh for an inbank area of a river will be built,
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates creating a simple model of a short section of river using the SMS TUFLOW FV interface. A mesh for an inbank area of a river will be built,
Appendix E-1. Hydrology Analysis
 Appendix E-1 Hydrology Analysis July 2016 HYDROLOGY ANALYSIS For Tentative Tract 20049 City of Chino Hills County of San Bernardino Prepared For: 450 Newport Center Drive, Suite 300 Newport Beach, CA 92660
Appendix E-1 Hydrology Analysis July 2016 HYDROLOGY ANALYSIS For Tentative Tract 20049 City of Chino Hills County of San Bernardino Prepared For: 450 Newport Center Drive, Suite 300 Newport Beach, CA 92660
This tutorial introduces the HEC-RAS model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the HEC-RAS software.
 v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial introduces the model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the software. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements 5.0 Mesh Module
v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial introduces the model and how it can be used to generate files for use with the software. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements 5.0 Mesh Module
SMS v Culvert Structures. SRH-2D Tutorial. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.0 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D. The Working with Simulations tutorial should have been completed before attempting this one.
SMS v. 12.0 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates the process of modeling culverts in SRH-2D. The Working with Simulations tutorial should have been completed before attempting this one.
Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface.
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements ADH Mesh Module Scatter
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements ADH Mesh Module Scatter
Cross Sections, Profiles, and Rating Curves. Viewing Results From The River System Schematic. Viewing Data Contained in an HEC-DSS File
 C H A P T E R 9 Viewing Results After the model has finished the steady or unsteady flow computations the user can begin to view the output. Output is available in a graphical and tabular format. The current
C H A P T E R 9 Viewing Results After the model has finished the steady or unsteady flow computations the user can begin to view the output. Output is available in a graphical and tabular format. The current
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1P - Designing with a Pond Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1P - Designing with a Pond Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
v Observations SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will give an overview of using the observation coverage in SMS. Observation points will be created to measure the numerical analysis with measured field
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will give an overview of using the observation coverage in SMS. Observation points will be created to measure the numerical analysis with measured field
v Basic FESWMS Analysis SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial instructs on how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15 30 minutes
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial instructs on how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15 30 minutes
v MODFLOW Transient Calibration Calibrating transient MODFLOW models GMS Tutorials Time minutes
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial MODFLOW Transient Calibration Calibrating transient MODFLOW models Objectives GMS provides a powerful suite of tools for inputting and managing transient data. These tools allow
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial MODFLOW Transient Calibration Calibrating transient MODFLOW models Objectives GMS provides a powerful suite of tools for inputting and managing transient data. These tools allow
Watershed Analysis Lab Heterogeneous, Gaged Watershed I (Northwest Branch)
 Watershed Analysis Lab Heterogeneous, Gaged Watershed I (Northwest Branch) The previous lab demonstrated the process of selecting quadrangles, specifying data types, delineating a watershed, and using
Watershed Analysis Lab Heterogeneous, Gaged Watershed I (Northwest Branch) The previous lab demonstrated the process of selecting quadrangles, specifying data types, delineating a watershed, and using
v TUFLOW FV SMS 12.2 Tutorial Time Requirements Prerequisites Objectives
 SMS 12.2 Tutorial v. 12.2 Objectives is an engine for performing 2D and 3D hydrodynamic simulations. The model solves the Non-linear Shallow Water Equations (NLSWE) on a flexible mesh using a finite-volume
SMS 12.2 Tutorial v. 12.2 Objectives is an engine for performing 2D and 3D hydrodynamic simulations. The model solves the Non-linear Shallow Water Equations (NLSWE) on a flexible mesh using a finite-volume
Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional (SRH-2D) simulation.
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial Requirements Model Map Module
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam with Seepage Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of a earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials None Required
v SMS 12.2 Tutorial Observation Prerequisites Requirements Time minutes
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Observation Objectives This tutorial will give an overview of using the observation coverage in SMS. Observation points will be created to measure the numerical analysis with
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Observation Objectives This tutorial will give an overview of using the observation coverage in SMS. Observation points will be created to measure the numerical analysis with
v Data Visualization SMS 12.3 Tutorial Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data.
 v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data. Prerequisites None Requirements GIS Module Map Module Time 30 60 minutes Page 1 of 16 Aquaveo 2017 1 Introduction...
v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import, manipulate, and view solution data. Prerequisites None Requirements GIS Module Map Module Time 30 60 minutes Page 1 of 16 Aquaveo 2017 1 Introduction...
v TUFLOW 1D/2D SMS 11.2 Tutorial Time minutes Prerequisites TUFLOW 2D Tutorial
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is strongly recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be completed before doing
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is strongly recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be completed before doing
Creating and Delineating a Watershed from DXF Terrain Data
 Creating and Delineating a Watershed from DXF Terrain Data 1. Start up WMS. 2. Switch to the Map Module. 3. Select DXF Import. Select the DXF file to import. 4. Notice that the DXF file imports fine into
Creating and Delineating a Watershed from DXF Terrain Data 1. Start up WMS. 2. Switch to the Map Module. 3. Select DXF Import. Select the DXF file to import. 4. Notice that the DXF file imports fine into
MODFLOW UZF Package The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS Objectives This tutorial explains how to use the MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) package and compares it to
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS Objectives This tutorial explains how to use the MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) package and compares it to
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v RMA2 Steering Module SMS Tutorials Requirements Time Prerequisites Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to use revision cards for a spin down simulation in RMA2. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial RMA2 Tutorial Requirements RMA2 GFGEN Mesh Module Time 30 60 minutes
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to use revision cards for a spin down simulation in RMA2. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial RMA2 Tutorial Requirements RMA2 GFGEN Mesh Module Time 30 60 minutes
ISIS 1D. Quick Start Guide. Cost effective, integrated software solutions ch2mhill.com/isis
 ISIS 1D Quick Start Guide Cost effective, integrated software solutions 0845 094 7990 ch2mhill.com/isis softwaresupport@ch2m.com Table of Contents Overview... 3 1. Starting ISIS and Basic Concepts... 3
ISIS 1D Quick Start Guide Cost effective, integrated software solutions 0845 094 7990 ch2mhill.com/isis softwaresupport@ch2m.com Table of Contents Overview... 3 1. Starting ISIS and Basic Concepts... 3
v GMS 10.0 Tutorial UTEXAS Dam with Seepage Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials SEEP2D
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Use SEEP2D and UTEXAS to model seepage and slope stability of an earth dam Objectives Learn how to build an integrated SEEP2D/UTEXAS model in GMS. Prerequisite Tutorials SEEP2D
Tutorial 6 - Subdivision - Pre Development
 Tutorial 6 - Subdivision - Pre Development In this tutorial, you will learn about: 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 2. Using a Template Adding a Background Image and Using the Zoom Tool Creating Nodes Creating
Tutorial 6 - Subdivision - Pre Development In this tutorial, you will learn about: 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 2. Using a Template Adding a Background Image and Using the Zoom Tool Creating Nodes Creating
v SMS Tutorials SRH-2D Prerequisites Requirements SRH-2D Model Map Module Mesh Module Data files Time
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation using SMS version 11.2 or later. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial shows how to build a Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Two-Dimensional () simulation using SMS version 11.2 or later. Prerequisites SMS Overview tutorial
v MODFLOW Grid Approach Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid GMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid Objectives The grid approach to MODFLOW pre-processing is described in this tutorial. In most cases, the conceptual model approach is more powerful
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Build a MODFLOW model on a 3D grid Objectives The grid approach to MODFLOW pre-processing is described in this tutorial. In most cases, the conceptual model approach is more powerful
WMS 9.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM Objectives Learn how to delineate a watershed
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM Objectives Learn how to delineate a watershed
WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
Watershed Modeling With Feature Objects
 Watershed Modeling With Feature Objects Lesson 4 4-1 Objectives Apply the rules of feature object topology to create a drainage coverage 4-2 Work Flow This lesson covers the use of feature objects for
Watershed Modeling With Feature Objects Lesson 4 4-1 Objectives Apply the rules of feature object topology to create a drainage coverage 4-2 Work Flow This lesson covers the use of feature objects for
v Editing Elevations DEM Basics Import, view, and edit digital elevation models WMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Import, view, and edit digital elevation models Objectives Learn to import DEMs from an online database, set the display options for an imported DEM, and view and edit the DEM
v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Import, view, and edit digital elevation models Objectives Learn to import DEMs from an online database, set the display options for an imported DEM, and view and edit the DEM
GMS Tutorials MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach 2 Adding drains, wells, and recharge to MODFLOW using the conceptual model approach
 GMS Tutorials MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach I GMS 10.4 Tutorial MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach 2 Adding drains, wells, and recharge to MODFLOW using the conceptual model approach v. 10.4 Objectives
GMS Tutorials MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach I GMS 10.4 Tutorial MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach 2 Adding drains, wells, and recharge to MODFLOW using the conceptual model approach v. 10.4 Objectives
xpwspg 2010 Modeling
 xpwspg 2010 Modeling The xpwspg capability in XP s products includes building/enhancing WSPG models with GIS/CAD data and presenting models with various graphical outputs. In this tutorial, users will
xpwspg 2010 Modeling The xpwspg capability in XP s products includes building/enhancing WSPG models with GIS/CAD data and presenting models with various graphical outputs. In this tutorial, users will
Objectives Read a delineated watershed and setup and run an HSPF model for the watershed.
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Setup a basic HSPF model Objectives Read a delineated watershed and setup and run an HSPF model for the watershed. Prerequisite Tutorials Watershed Modeling DEM Delineation Watershed
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Setup a basic HSPF model Objectives Read a delineated watershed and setup and run an HSPF model for the watershed. Prerequisite Tutorials Watershed Modeling DEM Delineation Watershed
