Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
|
|
|
- Melvyn Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services Redesign hardware as object-oriented Unconscious connectivity paradigm Devices interconnect automatically Minimal user intervention Wireless Personal Area Network (wpan) Small networks formed dynamically Wireless internetworking among wpans 3 4 Universal Wireless Connectivity Universal Wireless Connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate
2 5 6 Ubiquitous Computing Environment Intelligence is local and communication is universal devices Search for other compatible devices Share information about services they provide Exchange commonly defined data objects Service provision is distributed over wpan Integrated automation of Central servers Information repositories Sensors Actuators Example of Ubiquitous Computing Environment Automated integration of: PC PDA Telephone Stereo System mp3 device Global Positioning System (GPS) Coffee Pot Toaster Oven 7 8 Unconscious Connectivity Paradigm Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) Connectivity is a problem for the user Inconvenient to establish connections manually Available devices change frequently Users may not remember how to connect Devices connect automatically and dynamically Devices discover one another Devices determine when and why to connect Users do not need to remember how to connect Small network Piconet formed dynamically Short-range, Ad Hoc networks Device can belong to several Piconets simultaneously Each Piconet has One device (Primary) 1 to 7 devices (Secondary)
3 9 10 Example of The Vision User Enters hotel lobby PDA in user's pocket Connects to hotel reservations system for check in Receives key code for door Displays room number Alerts laptop in suitcase to log onto hotel server User's Laptop Downloads messages while user waits for elevator User's PDA Unlocks door of hotel room User's laptop Uploads music to audio system User's PDA Orders room service from menu user prepared on airplane Example of a Real Product Three-in-One Telephone Automatic network selection by environment: Intercom at home or in office PSTN phone when a PSTN access point is available Cellular mobile phone otherwise How is Different? Standards and Information In cellular and wlan systems: Base Stations and Mobile Stations are clearly distinct Base Stations handle services Channel access Channel allocation Traffic control Interference problems Mobile Stations are relatively simple clients In Ad Hoc networks: Communication is peer to peer No central controller Devices in area self-organize in a shared channel May be many devices in region Only a few need to communicate Mutual coordination is complex Special Interest Group (SIG) Commercial consortium founded by: Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Nokia and Toshiba Issued Specification 1.1 Basic protocol specification (1,084 pages) Generic application specification (452 pages) Standardized by IEEE 802 Committee IEEE Std Specification for Wireless Personal Area Networks (wpans) Covers only Infrastructure Layers Physical and Data Link Issues Does not address service provision
4 13 14 Problems with Specification History 1536 pages with no system overview chapter Each protocol layer is described in isolation Poor definition of states and events States and state transitions given identical names States are named after their default activity IEEE Standard is better written Provides overview Includes a formal description, written in Specification and Description Language (SDL) Designed in 1994 by Ericsson of Sweden Standard is named after Harald Blaatand "" II King of Denmark C.E. United Denmark and Norway Special Interest Group (SIG) Founded by Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Nokia and Toshiba Includes 3Com, Microsoft, Lucent and Motorola Over 2000 other companies Standard Structures Protocol Layers Services and functionality Device discovery Formation of wpans Service discovery wpan management Protocol structure and functions functions Session/Transport functions Data Link functions Physical transmission functions Generic application profiles Serial data transfer Telephony Packet services Device specific services Layer MAC Sublayer Physical Layer Mapping to OSI Functions Session/Transport Functions Data Link (LLC + MAC) Functions Physical Functions Actual Functionality
5 17 18 Protocol Overview Frequency Hopping Layer Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol () Host Controller Interface () Link Manager Protocol () Layer Layer User application programs User application support protocols: FTP, TCP, WAP, PPP, telephony, USB, Serial Port, etc Channel management (socket-type interface), Segmentation and Reassembly, QoS (speed, reliability, delay) Supports standard I/O hardware standards (when device is external to PC) Manages Piconet membership and link activity Manages point-to-point links, handles security, and interfaces user data to the radio links Physical data transmission (FHSS in ISM band, at 10 or 100 meter broadcast range) transmits using Frequency Hopping (FHSS) Group of RF frequencies = k MHz, for k = 0, 1,, 78 Specific Hop Sequence depends on Service Clock Device Data transmission Pseudorandom hop sequence Connection control Deterministic hop sequences Frequency Hop Sequence Train = sequence of integers {k 0, k 1, k 2,, k N } 0 k i 78, for i = 0, 1,, N N = 16 or Time Slots Frequency Hopping Clock is a 28-bit counter Upper 27 bits define Time Slot 2 Clock Cycles per Time Slot Counter creates 2 27 = 134,271,728 numbered Time Slots Counts from 0 to (then returns to 0) Packet transmission begins on a Time Slot boundary Packets may be up to 5 Time Slots in length Frequency hop on each Time Slot Unless packet is longer than 1 Slot No frequency hop during a multi-slot packet Each Time Slot is 625 µs in length (1600 slots/second) Time slot number returns to 0 every 23.3 hours f 0 f 1 f 2 f 3 f 5 f 6 f 7 t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 t 4 t 5 t 6 t 7
6 21 22 Piconet Topologies Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPAN) Piconets (from pico = ) Physical Channel Specific Frequency Hop Sequence Point-To-Multipoint Piconet One device is 1 to 7 s in active connection to master 1 to 256 s in passive connection to master Passive connection called "parked" state Point-to-Point Piconet Two devices on a common Physical Channel FHS is unique to a given Piconet device acts as client device acts as server Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPAN) Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO) Links Combination of Piconets Some devices act as in one Piconet in another Piconet Point-to-Point link between and Circuit-mode connection based on reserved slots Symmetric transmission rate Supports isochronous information like voice can support 1 to 3 SCO links to one or more s can support 1 to 3 SCO links with one 1 or 2 SCO links from different s
7 25 26 Asynchronous Connectionless Link (ACL) Connection Layers Point-to-Multipoint link Connects and all active s in Piconet Packet-mode connection Based on statistical multiplexing Uses available slots not reserved for SCO links Asynchronous and Isochronous services supported Only one ACL link between a and a channel multiplexing packet mode service packet mode service packet mode service circuit mode service C C C packet mode channel B B B packet mode channel A A A packet mode channel circuit mode channel packet mode service packet mode service packet mode service circuit mode service packet switch C B A ACL: asynchronous connectionless link packet switch circuit switch SCO: synchronous connection-oriented link circuit switch radio SCO ACL SCO ACL SCO ACL packets over radio connection Connection: synchronized frequency hop sequence radio Overview of Services and Functionality State Relationships Low Level Connection Standby communication is not active Inquiry device identifies other devices Paging Devices synchronize a physical radio link Link Establishment Devices establish digital data links High Level Connection Service Discovery Devices exchange capability information Service s open service channels over the link Power Management Operational Modes Active, Sniff, Hold, and Parked
8 29 30 Device Standby Condition Inquiry Procedures Low power state transmission system inactive Internal System Clock is running Clock must run to maintain synchronization device searches for other devices Device in Inquiry State Clock synchronization method Devices have independently running internal clocks Clock Offset = difference between 2 clock values Standby device Stores offset for device discovered by Inquiry Estimate device synchronization using stored offset device stores offset for device Synchronizes to using stored offset Maintains offset and internal clock in low power modes Device in Inquiry Scan State Device enters Inquiry State Inquiry Inquiry Inquiry Inquiry Device in Inquiry Scan State Device enters Inquiry State Inquiry Inquiry Hop Sequence (Train) Inquiring device enters Inquiry State Transmits Inquiry message Contains code for Inquiry Type General Inquiry Addressed to all devices Dedicated Inquiry Addressed to a particular class of devices Printers, telephones, etc Inquiry message repeated 16 times during 32 Time Slots Each transmission at a different frequency Listens for s in alternate Time Slots f 0 f 1... f 14 f 15 t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 t 28 t 29 t 30 t 31 Two defined frequency Inquiry Trains A and B Each Train repeated 256 times Enough time to collect all Inquiry s Total time required for Inquiry is 32 time slots 2 Trains 256 attempts 625 μsec seconds = Train attempt Inquiry time slot Inquiry
9 33 34 Inquiry Scan Inquiry 1 Devices periodically enter Inquiry Scan State Enter from Standby State or Connected State Active SCO links are maintained Active ACL links are suspended Device listens for Inquiry message packets Listens at just one frequency Chosen from Inquiry Train A or B Particular frequency depends on device address Responding device Leaves Inquiry Scan State Enters Inquiry State Sends Inquiry contains FHS Packet Lower Address Portion (LAP) Lower 24 bits of 48-bit full hardware address Frequency Hop Synchronization (FHS) Value of internal clock in responding device Listens in Inquiry Scan State for at least 32 Time Slots Covers both A and B frequency trains Inquiry 2 Paging Procedures Inquiring Device Receives FHS Packet from responding device Calculates clock offset Clock Offset = master clock - received FHS clock Virtual Clock = clock + offset Stores device address and clock offset Builds database of devices and virtual clocks Uses database information when connecting to device Devices use stored FSH packet from other devices Devices synchronize on a physical radio link Paging device becomes Piconet Device enters Paging State Device enters State FHS Device in Scan State Device enters State ACK Connected Poll Null Connected
10 37 38 Paging Paging Device has database of stored FHS Packets Received and Stored during Inquiry State Database includes 24-bit Lower Address Portion (LAP) Clock Offset for each device Device initiates connection as Chooses device from database to be Calculates Device Access Code (DAC) Long code derived from LAP 68 bits (for short ID packet) or 72 bits (if followed by a header) Used for addressing, timing synchronization, DC-offset compensation Estimates when enters Scan State Based on stored Clock Offset for device May be totally wrong and not yet synchronized FHS ACK Poll Null transmits message message length is 1 time slot repeated on all Scan frequencies Hop Frequency Trains Two 16-frequency Trains (A and B) Calculated from stored Device Address Transmission starts at estimated listening frequency Each Train is repeated up to 128 times waits for between Trains Train stopped if response is received f 0 f 1 f 2... f 14 f 15 t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 t 14 t 15 FHS ACK Poll Null Scan 1 Device periodically enters Scan State Enters from Standby State or Connection State Responds as device listens for Messages Addressed to its Device Access Code (DAC) Listens at unique Scan frequency fk One frequency from Train Calculated from Device Address Listens to entire Train Does not respond in Scan State Must not interrupt Train receives Message FHS ACK Poll Null Device leaves Scan State Enters State Sends Message On unique frequency f k = Scan frequency f k+1 = frequency Transmitted in time slot k+1 provides with s unique Scan frequency f 0 f 1 f 2 f k f k+1 f 15 t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 t k t k+1 t 15 listens for Paging on f k is short packet ID packet containing 68-bit DAC sends on f k+1 f k+1 t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 t k t k+1 t 15 FHS ACK Poll Null
11 receives Message Synchronizes to listening frequency Received on frequency f k+1 Transmits next packet to on frequency f k+2 Enters State sends FHS packet to on frequency f k+2 Provides with Lower Address Portion (LAP) stores clock offset for now synchronized to Assigns Active Member Address 3-bit AM_ADDR 7 active slaves per Piconet FHS ACK responds to ACK (ID packet) with Poll Packet Addressed to s Active Member Address responds with Null Packet (header only) If Procedure is successful Paging is finished and are in Connected State Synchronized on a radio link Otherwise, Paging has failed Error procedures are followed FHS ACK acknowledges FHS with ACK (ID packet) Poll Null Poll Null Connection Modes Digital Link Establishment Connected devices may establish digital links Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO) Link Point-to-Point circuit-mode connection sends Link Manager Protocol () Request to set up ACL Accepts or Rejects link Asynchronous Connectionless Link (ACL) Point-to-Multipoint Packet-mode connection may request to exchange roles (become ) Connected Connect Request Connected may Accept or Reject Linked Accept Linked
12 45 46 Service Discovery Service Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) Invoked when Connection State established Opens Channel on ACL link SDP (client) Queries SDP (server) about available services Maintains database of services available from slaves SDP (server) Provides service information SPD specifies Database structure Service codes s identify service providers using SDP Packet-oriented applications Open channels on ACL link Channels use a source/destination port session structure One connection-oriented application Can open a channel on SCO link SCO channel transfers raw data Channels are a time division sharing of ACL link Predefined Services Active Mode Defined through the Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) Telephony Control Protocol Specification (TCS) Serial Data communication WAP Object Exchange Protocol Support (TCP/IP, PPP, , ) Full power mode Units actively communicate and s transmit in alternate slots transmits in every even numbered slot The addressed transmits in the next odd numbered slot Transmissions from keep all s synchronized
13 49 50 Sniff Mode Hold Mode A low power mode for Listening activity of the is reduced listens for transmissions Only at fixed intervals T sniff At the offset Slot D sniff For N sniff Time Slots SCO links may remain active ACL link is put on hold may enter sleep mode Device keeps its Active Member Address Extra capacity can be used for Scanning Paging Inquiring Communicating in another Piconet and agree on hold interval After hold interval returns to Active Mode Park Mode Protocol Layers Very low power mode gives up its 3-bit Active Member Address gets 8-bit Parked Member Address Used by to Unpark a slave 8-bit Access Request Address Used by to ask to Unpark it Layer MAC Sublayer Functions Session/Transport Functions Data Link (LLC + MAC) Functions stays synchronized to the channel Physical Layer Physical Functions Mapping to OSI Actual Functionality
14 53 54 Layer User programs Networking clients Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) Client/Server architecture Server maintains database of provided services Client may query specific service or all services Telephony Control Protocol Specification (TCS) RFCOMM parallel and serial port emulation Interfaces May invoke Profile for protocol support May request channel in ACL link from May request SCO channel from Network Protocol Emulation TCP/IP, PPP, FTP, WAP, OBEX Transaction oriented Object Exchange Similar to HTTP Request channel in ACL link from Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol Protocol Multiplexing Divides ACL links into channels One channel per service between two devices packet header contains the service s channel number Segmentation and Reassembly (SAR) accepts packets 0 to 64 KB packet SDU is 0 to 2745 bits QoS Management Peak bandwidth Latency Delay variation 2 Unreliable session-type service No error checking Relies on for error control, security and packet ordering Establishes a separate Signaling Channel Connection request Configuration Disconnection Echo (for testing) Transaction Oriented Receives request from upper layer Performs actions Returns responses to upper layer usually invokes service from
15 57 58 Link Manager Protocol () Manages ACL link establishment state Transaction process with baseband Handles Link configuration (hopping sequence for each Piconet) Juggles participation in multiple Piconets (and their hop sequences) Manages Inquiry and Paging Transaction process with baseband Attaches/detaches s (by ) Exchanges / roles Manages low power modes: Hold, Sniff, Park Manages Security functions Authentication of devices Packet Header contains Addresses (Device, Active Member, Access Code) Reliability Parameters (SEQ, ACK, HEC, Flow Control) invokes services from Layer Performs frequency hopping (one Piconet at a time) Lower level encryption (generates encryption keys) Performs services for Inquiry and Paging Link establishment Connection establishment (SCO/ACL) Clock synchronization Address discovery Error correction Data whitening Forwards data to Layer (one Piconet at a time) Performs physical transmission/reception Transmission Frequencies k MHz, where k= 0,1,...,78 Actual k value is determined by Deterministic Frequency Hopping Trains for Management Pseudo-random Frequency Hopping Trains for data transmission Transmitter Power 0 dbm (1 mw) for 10 m transmission range 20 dbm (100 mw) for 100 m range Host Controller Interface For external transmitter modules Host data sent to via I/O port Serial port, parallel port, or USB High level stack, Profiles, Runs under host OS Low level stack,, Runs in external hardware Host Controller Interface () Interfaces I/O port driver to Standard software driver operates I/O port for the OS
16 61 62 Host Controller Interface Operation Review of the Connection Process 1 Low Level Connection Initiated and managed by layer Device Discovery Inquiry Device A initiates Inquiry Inquiry Scan Device B listens for Inquiry packets Inquiry Device B receives Inquiry and sends Inquiry packet Connection Paging device s device Scan device listens for Paging Paging s synchronizes clock and hopping sequence Devices are now Connected in a Piconet Link Establishment opens an ACL link over the Piconet Connection informs SDP of the ACL link Review of the Connection Process 2 Security Features High Level Connection SDP (in Layer) requests a Channel (in the ACL link) from maps a Channel over the ACL link for SDP SDP client formulates Service Query Query is Fragmented by and sent to addresses query to device and sends to formulates transmission frame and sends to Layer Layer broadcasts s open Channels over the ACL link Telephony s use TCS (based on Q.921) to request SCO directly from Fast frequency hopping Low transmit power (range <= 10m) Authentication of remote device based on link key (128 Bit) May be performed in both directions Encryption of payload data Stream cipher algorithm ( 128 Bit) Affects all traffic on a link Initialization PIN entry by user
17 65 66 Synchronization Profile Headset Profile IrOBEX IrMC AT Commands RFCOMM RFCOMM Audio Stream ACL SCO ACL SCO LAN Access Point Profile PPP RFCOMM Earpiece Philips Semiconductor VWS Integrated Circuits processor (VWS26002) Ceramic Multi-chip RF module (PBA 31301) External Flash memory NiMh or Lithium ion battery Talk time ~4 hours Size weight 75g, 15cc ACL SCO
18 69 70 Philips Semiconductor VWS26003 Philips Semiconductor VWS26003 VWS26002 processor ARM7 TDMI 32-bit embedded RISC processor 72 kbytes internal SRAM 4 kbytes internal ROM 4 kbytes internal SRAM instruction cache Timers and watchdog. 8 general purpose PIO pins. Voice Codec PBA Frequency Module Software Point to Point Protocol stack Systems or NiMh or Li Ion battery Single Chip Device Controller Typical Earpiece Organization Philips PCD87750E MTP = Multiple Time Programmable ROM EBC = Ericsson Core CVSD = Continuously Variable Slope Delta modulation SPI = Security Parameter Index
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
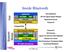 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic
 Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Introducing Bluetooth
 Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Chapter 1 Introducing Bluetooth In This Chapter From the beginning, Bluetooth technology was intended to hasten the convergence of voice and data to handheld devices, such as cellular telephones and portable
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech. Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, 7.1
 Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
System Level Analysis of the Bluetooth standard
 System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
System Level Analysis of the standard Massimo Conti, Daniele Moretti Università Politecnica delle Marche, via Brecce Bianche, I-60131, Ancona, Italy Abstract The SystemC modules of the Link Manager Layer
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY
 Bachelor s Thesis (UAS) Information Technology Networking and Programming 2011 IDAHOSA AKHANOLU IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY i BACHELOR S THESIS (UAS) ABSTRACT TURKU UNIVERSITY OF
Bachelor s Thesis (UAS) Information Technology Networking and Programming 2011 IDAHOSA AKHANOLU IMPLEMENTATION AND SECURITY OF BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY i BACHELOR S THESIS (UAS) ABSTRACT TURKU UNIVERSITY OF
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE W.lan.4
 Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Security. Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011
 Security Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011 What is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is an open standard for short-range radio frequency (RF) communication. Bluetooth technology is used primarily to establish
Security Nelli Gordon and Sean Vakili May 10 th 2011 What is Bluetooth? Bluetooth is an open standard for short-range radio frequency (RF) communication. Bluetooth technology is used primarily to establish
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Wireless Local Area Network. Internet Protocol Suite
 Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Objectives of the Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Master. Slave. Master. Slaves. TCP/IP Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology. Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3
 / Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
/ Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
Delivering Voice over IEEE WLAN Networks
 Delivering Voice over IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks Al Petrick, Jim Zyren, Juan Figueroa Harris Semiconductor Palm Bay Florida Abstract The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard was developed primarily for packet
Delivering Voice over IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks Al Petrick, Jim Zyren, Juan Figueroa Harris Semiconductor Palm Bay Florida Abstract The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard was developed primarily for packet
What is a personal area network?
 Wireless Personal Area Networks David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Slides 16 Wireless Networks Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs)
Wireless Personal Area Networks David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Slides 16 Wireless Networks Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs)
TELEPHONY CONTROL PROTOCOL SPECIFICATION
 Part F:3 TELEPHONY CONTROL PROTOCOL SPECIFICATION TCS Binary This document describes the Bluetooth Telephony Control protocol Specification Binary (TCS Binary), using a bit-oriented protocol. This protocol
Part F:3 TELEPHONY CONTROL PROTOCOL SPECIFICATION TCS Binary This document describes the Bluetooth Telephony Control protocol Specification Binary (TCS Binary), using a bit-oriented protocol. This protocol
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for informatikk. Monitoring Bluetooth network topology. Cand Scient Thesis. Fredrik Borg
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for informatikk Monitoring Bluetooth network topology Cand Scient Thesis Fredrik Borg February 1, 2002 II Foreword This thesis is a part of my cand.scient. degree in Communication
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for informatikk Monitoring Bluetooth network topology Cand Scient Thesis Fredrik Borg February 1, 2002 II Foreword This thesis is a part of my cand.scient. degree in Communication
Rab Nawaz Jadoon (Assistant Professor) Department of Computer Science COMSATS University, Abbottabad, Pakistan
 Rab Nawaz Jadoon (Assistant Professor) Department of Computer Science COMSATS University, Abbottabad, Pakistan rabnawaz@ciit.net.pk 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 History... 3 1.2 Bluetooth
Rab Nawaz Jadoon (Assistant Professor) Department of Computer Science COMSATS University, Abbottabad, Pakistan rabnawaz@ciit.net.pk 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 History... 3 1.2 Bluetooth
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Wireless Protocols Overview
 Sami Kiminki Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science sami.kiminki@aalto.fi September 22, 2011 Introduction A primer for wireless IoT topics Brief overview on
Sami Kiminki Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science sami.kiminki@aalto.fi September 22, 2011 Introduction A primer for wireless IoT topics Brief overview on
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8
 ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
A Guide. Wireless Network Library Bluetooth
 A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications
 Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Efficient Multicast Schemes for Mobile Multiparty Gaming Applications P6-6th semester 2006 Group 681 - ComNet Aalborg University 9th March 2006 Institut for elektroniske systemer Fr. Bajers Vej 7 Telefon
Chapter 5. Wireless PANs
 Chapter 5 Wireless PANs 5.1 Introduction Introduction of Wireless PANs (WPANs) has caused the latest revolution in the area of wireless technologies. WPANs are short to very short-range (from a couple
Chapter 5 Wireless PANs 5.1 Introduction Introduction of Wireless PANs (WPANs) has caused the latest revolution in the area of wireless technologies. WPANs are short to very short-range (from a couple
Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth
 Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth Pravin Bhagwat Networking Research Group AT&T Labs - Research pravin@acm.org ACM Mobicom 2000 Half day tutorial Aug 06, 2000 Boston, MA Bluetooth A cable replacement
Personal Area Networking over Bluetooth Pravin Bhagwat Networking Research Group AT&T Labs - Research pravin@acm.org ACM Mobicom 2000 Half day tutorial Aug 06, 2000 Boston, MA Bluetooth A cable replacement
Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Delhi. Lecture 26 Networked Embedded Systems III
 Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Delhi Lecture 26 Networked Embedded Systems III Today, we shall look at wireless networks which are intended for usage in
Embedded Systems Dr. Santanu Chaudhury Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Delhi Lecture 26 Networked Embedded Systems III Today, we shall look at wireless networks which are intended for usage in
BASEBAND SPECIFICATION
 Core System Package [Controller volume] Part B BASEBAND SPECIFICATION This document describes the specification of the Bluetooth link controller which carries out the baseband protocols and other lowlevel
Core System Package [Controller volume] Part B BASEBAND SPECIFICATION This document describes the specification of the Bluetooth link controller which carries out the baseband protocols and other lowlevel
Lecture Computer Networks
 Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Lecture Computer Networks Networks for Multimedia
Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit M. Rabel sowie H. Hutschenreiter und T. Nau Sommersemester 2012 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen Lecture Computer Networks Networks for Multimedia
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN
 Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
Bluetooth Wireless Technology meets CAN Matthias Fuchs esd electronic system design GmbH, Hannover, Germany To access mobile and moving CAN fieldbus systems a wireless approach is often a good solution.
MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU
 Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Image acquisition and Communication
 Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
Image acquisition and Communication Developements around the ACME Fox Board E. Pamba Capo-ChiChi 1,2,G. Weisenhorn 1,J-M. Friedt 3,4 H. Guyennet 1,2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Franche-Comte
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks
 EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 10 wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Outline 2 The Medium Access Control Sublayer Bluetooth
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 10 wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Outline 2 The Medium Access Control Sublayer Bluetooth
Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies
 Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies Topics Background What is Bluetooth low energy? Basic concepts Architecture Differentiation and comparison Markets and applications Background Background
Bluetooth low energy technology Bluegiga Technologies Topics Background What is Bluetooth low energy? Basic concepts Architecture Differentiation and comparison Markets and applications Background Background
Electromagnetic Spectrum (3kHz 300GHz)
 Wireless Communication Serial communication Allocated a frequency of operation Could be a range of frequencies Regulated by FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in US Unfortunately, allocations are
Wireless Communication Serial communication Allocated a frequency of operation Could be a range of frequencies Regulated by FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in US Unfortunately, allocations are
Extending or Interconnecting LANS. Physical LAN segment. Virtual LAN. Forwarding Algorithm 11/9/15. segments. VLAN2, Port3. VLAN1, Port1.
 Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Bluetooth in Mobile Devices
 Bluetooth in Mobile Devices Vidar Rinne Mälardalen University School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Computer Science: Game Development vre03001@student.mdh.se Abstract The basic idea of Bluetooth
Bluetooth in Mobile Devices Vidar Rinne Mälardalen University School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Computer Science: Game Development vre03001@student.mdh.se Abstract The basic idea of Bluetooth
PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin
 Bluetooth solution PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin 林 lin.magic@tw.anritsu.com 0933-710-634 v.9 群 1 Bluetooth Core System Architecture 2 Bluetooth Core System Architecture_2
Bluetooth solution PCs Closed! Cell Phones Off! Marketing Assistant Manager - Magic Lin 林 lin.magic@tw.anritsu.com 0933-710-634 v.9 群 1 Bluetooth Core System Architecture 2 Bluetooth Core System Architecture_2
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN)
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Bluetooth. Bluetooth. WPAN Technologies. HomeRF. Bluetooth. Claudio Casetti. Dipartimento di Elettronica Politecnico di Torino
 Bluetooth Claudio Casetti Dipartimento di Elettronica Politecnico di Torino WPAN Technologies HomeRF Bluetooth Bluetooth A cable replacement technology 1 Mb/s symbol rate Range 10+ meters Single chip radio+baseband
Bluetooth Claudio Casetti Dipartimento di Elettronica Politecnico di Torino WPAN Technologies HomeRF Bluetooth Bluetooth A cable replacement technology 1 Mb/s symbol rate Range 10+ meters Single chip radio+baseband
Wireless Local Area Networks. Networks: Wireless LANs 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Bluetooth General Information White Paper
 General Information is the registered trademark of Atmel Corporation, 2325 Orchard Parkway, San Jose, CA 95131 Rev. 1993A 11/00 Introduction The wireless technology is the world s new shortrange RF transmission
General Information is the registered trademark of Atmel Corporation, 2325 Orchard Parkway, San Jose, CA 95131 Rev. 1993A 11/00 Introduction The wireless technology is the world s new shortrange RF transmission
IrDA INTEROPERABILITY
 Part F:2 IrDA INTEROPERABILITY The IrOBEX protocol is utilized by the Bluetooth technology. In Bluetooth, OBEX offers same features for applications as within the IrDA protocol hierarchy and enabling the
Part F:2 IrDA INTEROPERABILITY The IrOBEX protocol is utilized by the Bluetooth technology. In Bluetooth, OBEX offers same features for applications as within the IrDA protocol hierarchy and enabling the
By Ambuj Varshney & Akshat Logar
 By Ambuj Varshney & Akshat Logar Wireless operations permits services, such as long range communications, that are impossible or impractical to implement with the use of wires. The term is commonly used
By Ambuj Varshney & Akshat Logar Wireless operations permits services, such as long range communications, that are impossible or impractical to implement with the use of wires. The term is commonly used
Bluetooth. Acknowledgements. Based on Jochen Schiller slides. Supporting text
 BT 1 Bluetooth FEUP PR BT 2 Acknowledgements Based on Jochen chiller slides upporting text» Jochen chiller, obile Comunications, Addison-Wesley» ection 7.5 Bluetooth BT 3 Bluetooth» Universal radio interface
BT 1 Bluetooth FEUP PR BT 2 Acknowledgements Based on Jochen chiller slides upporting text» Jochen chiller, obile Comunications, Addison-Wesley» ection 7.5 Bluetooth BT 3 Bluetooth» Universal radio interface
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs. Agenda (1) Agenda (2) Wireless Spectrum (1)
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
MESHES AND CUBES: DISTRIBUTED SCATTERNET FORMATIONS FOR BLUETOOTH PERSONAL AREA NETWORKS
 MESHES AND CUBES: DISTRIBUTED SCATTERNET FORMATIONS FOR BLUETOOTH PERSONAL AREA NETWORKS By ANIRUDDHA SHRIRAM DAPTARDAR A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER
MESHES AND CUBES: DISTRIBUTED SCATTERNET FORMATIONS FOR BLUETOOTH PERSONAL AREA NETWORKS By ANIRUDDHA SHRIRAM DAPTARDAR A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY. Flavia Martelli
 Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Wireless Sensor Networks BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY Flavia Martelli flavia.martelli@unibo.it Outline Introduction Applications Architecture Topology Controller specifications: Physical Layer Link Layer Host
Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be
 IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
IEEE OEB Wireless Seminar Fremont, CA - 12/07/02 Essential Bluetooth It s everywhere you want to be Noel Baisa Technical Marketing Manager Device Connectivity Division 408-721 721-74667466 Noel.Baisa Baisa@nsc.com
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer. Computer Networks: Wireless LANs
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Lecture 16: QoS and "
 Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Securing A Bluetooth Device
 Securing A Bluetooth Device Mrs. Dhanashri D. Dhokate 1, Mr. Milind C. Butale 2, Mr. Babasaheb S. Patil 3 Assistant Professor, Information Technology, PVPIT, Budhgaon, India 1. Associate Professor, Electronics
Securing A Bluetooth Device Mrs. Dhanashri D. Dhokate 1, Mr. Milind C. Butale 2, Mr. Babasaheb S. Patil 3 Assistant Professor, Information Technology, PVPIT, Budhgaon, India 1. Associate Professor, Electronics
