What is a personal area network?
|
|
|
- Tamsyn Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wireless Personal Area Networks David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Slides 16 Wireless Networks Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs) Cellular Networks : GSM, cdmaone (IS-95), UMTS, cdma2000 EV-DO Satellite Networks: Iridium, Globalstar, GPS, etc. Wireless Metro Area Networks (WMANs) IEEE WiMAX Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) IEEE , a, b, g, etc. (infrastructure, ad hoc, sensor) Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) IEEE (Bluetooth), IrDa, Zigbee, 6LowWPAN, proprietary sensor, etc. 2 What is a personal area network? Origins in the BodyLAN project initiated by BBN in the early 1990s for military Networking personal devices around a solider Now networking devices around an individual sensors, cameras, handheld computers, audio devices, cell phone, printers, etc. Goal was smart technology that self configures, recognizes other units within range and provides on the fly communications Universal short-range wireless capability Use band available globally for unlicensed users Low powered medium data rate 4
2 Bandwidth versus Range PANs digital video a/g IrDA digital camera HIPERLAN b hi-fi audio mp3 player LAN Bluetooth applications keyboard Zigbee serial connection mouse remote control Distance in meters 5 Applications of WPANs Cable Replacement (a) Ad hoc connectivity (b) PSTN or the Internet Access to wired network (c) 6 Bluetooth Much of the WPAN focus today is around Bluetooth Originated by Ericsson, Nokia, IBM, Toshiba, Intel formed a WPAN special interest group (SIG) 1998 Named after King of Denmark and Norway Kong Harald Blaatand (Bluetooth), Specifies the complete system from the radio level up to the application level Protocol stack is partly in hardware and partly in software running on a microprocessor Embedded devices Low power Low cost Uses ISM band of spectrum 7
3 IEEE Started in 1997 as a sub-group of IEEE Focused on WPANS Initial functional requirements Low power devices Range of 0-10m Low data rates ( kbps) Small sizes (0.5 cubic inches) Low cost Multiple l networks in the same area Up to 16 separate devices in a PAN IEEE Took over Bluetooth standardization in 2000 Today over 2500 companies as Bluetooth SIG members Built-in Bluetooth chip shipped in more than 100 million cellular phones and laptops last year Several millions of other communication devices Cameras, headsets, microphones, keyboards etc. 8 IEEE today Task Group 1 ( ) PHY and MAC layer design for wirelessly connecting devices entering a personal operating space (POS) POS is a 10m space around a person who is stationary or in motion Task Group 2 ( ) Coexistence of WLANs and WPANs Interoperability between a WLAN and WPAN device Task Group 3 ( ) Higher data rates (> 20 Mbps) (Kodak, Cisco, Motorola) Multimedia applications like digital imaging and video UWB radios WiMedia protocol stack at higher layers Task Group 4 ( ) Low data rates and ultra low power/complexity devices for sensor networking Home automation, smart tags, interactive toys, location tracking, etc. Zigbee is now part of this group 9 Bluetooth Protocol Architecture Bluetooth architecture has three types of protocols 1. Core protocols Radio Baseband Link manager protocol (LMP) Logical link control and adaptation protocol (L2CAP) Service discovery protocol (SDP) 2. Cable replacement and Telephony protocols RFCOMM Telephony control specification binary (TCS BIN) 3. Adopted protocols PPP TCP/UDP/IP WAP Etc. 10
4 Example Protocol Stack Other WAP Applications Service Discovery SDP Telephony TCS TCP/UDP IP RFCOMM PPP Audio L2CAP = Logical Link Control and Adaptation Host Controller Interface Baseband Bluetooth Radio LMP = Link Mgt. 11 Bluetooth RF and Baseband Layers Operates in the same 2.4 GHz bands as IEEE b Channels are 1MHz wide (79 or 23 channels depending on country) Modulation : GFSK at 1Mbps on air Version 2.0 Enhanced Data Rate 2-level - GFSK : 2Mbps rate Error control depends on connection and rate either 1/3 convolutional coded FEC, 2/3 FEC ARQ Single chip implementation < $5 a chip 12 Employs frequency hopping spread spectrum Reduce interference with other devices Bluetooth FHSS Pseudorandom hopping 1600 hops/sec- time slot is defined as 625 microseconds Packet 1-5 time slots long TDD up/downlink System is FH/FDMA/TDD 13
5 Bluetooth Architecture Master Scattered ad-hoc topology called a ``scatter-net A cell or piconet is defined by a Master device The master controls the frequency hopping sequence The master also controls the transmission within its piconet using a TDMA structure There is NO contention within a piconet There is interference between piconets in the same geographic space 14 Bluetooth Architecture (2) Master Master/ A B A device can belong to several piconets A device can be the master of only one piconet A device can be the master of one piconet and slave of another piconet or a slave in different piconets 15 Bluetooth Architecture (3) The Master device is the device that initiates an exchange of data The device is a device that responds to the Master s use the frequency hopping pattern specified by the Master A slave can transmit ONLY in response to a Master A Master device can simultaneously control seven slave devices and might have up to 200 slave devices in a piconet Multiple piconets in the same geographic space interfere with each other FH-SS is used so multiple piconets can coexist in same space 16
6 Bluetooth Device Address Each Bluetooth device has a 48 bit IEEE 802 MAC address Called the Bluetooth Device Address (BD_ADDR) This MAC address is split into three parts The Non-significant Address Part (NAP) Used for encryption seed The Upper Address part (UAP) Used for error correction seed initialization and FH sequence generation The Lower Address Part (LAP) Used for FH sequence generation Additional address fields are used once in a piconet Active member address Address valid as long as device is active slave in a piconet Parked member address Address valid as long as a device is a parked slave in a piconet 17 Bluetooth connections Synchronous connection-oriented (SCO) link Circuit-switched periodic single-slot packet assignment Symmetric 64 kbps full-duplex Up to three simultaneous links from master Asynchronous connection-less (ACL) link Packet data Variable packet size (1-5 slots) Asymmetric bandwidth point to multipoint Maximum Asymmetric rate: kbps (57.6 kbps return channel) Symmetric data rates: kbps FEC/ARQ used for error control 18 Bluetooth Power Control Three classes of devices exist Class 1: 100 mw (20 dbm) (~100m) Class 2: 2.5 mw (4 dbm) (~10m) Class 3: 1 mw (0 dbm) (~1m) Mixture of devices can exist in a piconet Range of devices is subject to their class Mandatory power control is implemented Steps of 2 db to 8 db Only the power required for adequate RSS is to be used Based on feedback (closed loop) using link management protocol control commands 19
7 Clock Synchronization Each Bluetooth device has a free running clock called the native clock or CLKN A Master device uses its CLKN for timing A device determines an offset from its own CLKN to synchronize to the Master The Master also uses an offset to determine the slave s clock to establish an initial connection with a slave 20 Discovering Bluetooth Devices A device wishes to discover what Bluetooth devices exist in its vicinity and what services they offer Performs an inquiry procedure It transmits a series of inquiry packets on different frequencies and awaits a response Devices scanning for inquiries use a sliding window to detect such inquiries If an inquiry i is detected t d by a scanning device it responds with a frequency hop synchronization (FHS) packet that enables completion of a successful connection FHS contains ID and clock info If collision occurs on inquiry device implement random backoff and retries Connection is established Device that initiates connection is master in resulting piconet 21 Paging a device Paging is similar to inquiry except that the slave address is known clock/frequency hopping pattern is known The page packet is transmitted at the expected frequency of the slave The Master sends a page train with a duration of 10 ms covering 16 frequency hops, repeat if necessary The listens for its own device access code (DAC) for the duration of a scan window The sends a slave response when its own DAC is heard The Master sends a master response The responds to the master with its own DAC using the Master s clock included in FHS packet 22
8 Bluetooth connection states Standby Standby Connecting Inquiry Page Transmit Connected Active Sniff Hold Park Low power modes 23 Connection States (2) Standby (default) Waiting to join a piconet Inquire Discover device within range or find out unknown destination address Page Establish actual connection using device access code (DAC) Connected Actively on a piconet (master or slave) Park/Hold/Sniff (Low-power connected states) Hold mode stops traffic for a specified period of time Sniff mode reduces traffic to periodic sniff slots Park mode gives up its active member address and ceases to be a member of the piconet Active Unit participates on channel master schedule transmisisons 24 Service Discovery After inquiry or paging an ACL or SCO is set up SCO is used for telephony or audio connection If ACL connection, the Master sets up an L2CAP connection with the slave L2CAP is logical link control layer Responsible for segmenting and reassembling data packets L2CAP allows several protocols to be multiplexed l over it using a Protocol and Service Multiplexer (PSM) number emulates serial port The master s service discovery client can use SDP to obtain the services that slave devices within the piconet can offer The Master can then decide what slave devices to communicate with and what services to employ 25
9 Service Discovery After inquiry or paging an ACL or SCO is set up SCO is used for telephony or audio If ACL connection, the Master sets up an L2CAP connection with the slave L2CAP is logical link control layer Responsible for segmenting and reassembling data packets L2CAP allows several protocols to be multiplexed l over it using a Protocol and Service Multiplexor (PSM) number emulates serial port The master s service discovery client can use SDP to obtain the services that slave devices within the piconet can offer The Master can then decide what slave devices to communicate with and what services to employ 26 Link Manager The Link manager manages the following operations Attaching slaves to the piconet Allocates an active member address to a slave Breaks connections to slaves Establishes SCO or ACL links Changes the connection state of devices (like sniff, park or hold) Uses the Link Management Protocol (LMP) to connect between devices 28 Comments A device can be part of several piconets simultaneously (scatternet) This implies that the device should maintain multiple sets of clocks and timers and switch between them The throughput of the device is substantially reduced compared to what it might have if connected to a single piconet Audio part of Bluetooth specifies different codecs Supports A-law and μ-law for PCM Also supports DPCM RFCOMM (Radio Frequency Virtual Communications Port Emulation) Similar to RS-232 serial connections No handoffs between piconets for mobile users 29
10 Bluetooth Packet Fields Access code used for timing synchronization, offset compensation, paging, and inquiry Header used to identify packet type, packet numbering, slave address, error checking info and control info Payload contains user voice, data or both and payload header, if present 30 Baseband Frame Format General packet format Access code Payload Voice field: fixed length, 240 bits Data field: Payload header, body, CRC <Header: single-slot vs. multi-slot packets> 31 Packet Header Fields AM_ADDR contains active mode address of one of the slaves Type identifies type of packet Flow 1-bit flow control ARQN 1-bit acknowledgment SEQN 1-bit sequential numbering schemes Header error control (HEC) 8-bit error detection code 32
11 Security Master Due to low radio range security threat must be in very close range Link Management Protocol layer of Bluetooth provides security and encryption services Security in piconet involves identifying device itself, not who is using device Three security mode in Bluetooth Level 1: No security Level 2: Service-level security is established after connection is made Level 3: Link-level security is performed before a connection is made 33 Authentication Authentication involves verifying that a device should be allowed to join piconet Bluetooth uses a challengeresponse strategy to confirm that other device knows a shared identical secret key Secret key entered as PIN by hand Version 1.1 improves authentication process by first confirming roles of master and slave before generating response number 35 Encryption Encoding communications ensures that transmissions cannot be intercepted and decoded Three encryption modes Encryption Mode 1 Nothing is encrypted Encryption Mode 2 Traffic from master to one slave is encrypted, but traffic from master to multiple slaves is not Encryption Mode 3 All traffic is encrypted Uses variable bit key (64 is default value) 36
12 State of Bluetooth Bluetooth shipped in over a 1 Billion devices Bluetooth challenges Reduce Cost ~$5 a port vs cable Conflicts with other devices in radio spectrum Limited security Most of the focus in the standards group is on other tasks IEEE for low power, low data rate, cheap, WPANs (Zigbee) IEEE Mesh Networking WPANs IEEE for high data rate WPANs (WiMedia) a focus is Ultra WideBand (UWB) WPANs Standard Focus on low data rates/low power/moderate range/low complexity devices for WPAN sensor networks Took over Zigbee interest group work Data rates of 250 kb/s, 40 kb/s and 20 kb/s. Distances meters Star or Peer-to-Peer operation. Support for low latency devices. Full handshake protocol for transfer reliability. Very Low power consumption multi-year battery based lifetime Frequency Bands of Operation 16 channels in the 2.4GHz ISM* band 10 channels in the 915MHz ISM band 1 channel in the European 868MHz band. Early applications: home/factory monitoring, medical monitoring 38 ZigBee Stack Architecture 39
13 IEEE Frequency Bands 868MHz / 915MHz PHY Channel 0 Channels MHz MHz 902 MHz 928 MHz BPSK 20Kbps BPSK 40 Kbps 2.4 GHz PHY Channels MHz 2.4 GHz OQPSK 250Kbps Slide courtesy Joe Dvorak, Motorola GHz 40 IEEE PHY Packet Structure PHY Packet Fields Preamble (32 bits) synchronization Start of Packet Delimiter (8 bits) PHY Header (8 bits) PSDU length PSDU (0 to 1016 bits) Data field Preamble Start of Packet Delimiter PHY Header PHY Service Data Unit (PSDU) 6 Octets Octets Courtesy Joe Dvorak, Motorola 41 IEEE Device Classes Three Device Classes Full function device (FFD) Any topology Can maintain connection to multiple devices Talks to any other device PAN Coordinator (PANC) FFD responsible for starting and maintaining networks First FFD powered on in a area becomes PANC Reduced function device (RFD) Limited to star topology Talks only to a network coordinator Can not be a relay for other RFD or FFD Very simple implementation expect to transmit 0.1%-2% of the time long battery life 42
14 IEEE Topologies PAN Coordinator Master/slave Full function device Reduced function device 43 IEEE Topologies Clustered stars: basically a tree composed of multiple stars Note backbone/trunk of tree made up of FFDs Full function device Communications flow Reduced function device 44 IEEE MAC Overview Payload MAC Layer MAC Header (MHR) MAC Service Data Unit (MSDU) MAC Footer (MFR) PHY Layer Synch. Header (SHR) PHY Header (PHR) MAC Protocol Data Unit (MPDU) PHY Service Data Unit (PSDU) Uses bit static MAC addresses 4 Types of MAC Frames: Data Frame Beacon Frame from PANC defines timeslots Acknowledgment Frame MAC Command Frame CSMA/CA is used except for synchronous traffic which get guaranteed time slots Joe Dvorak, Motorola 45
15 IEEE MAC Periodic data Application defined rate (e.g. sensors) Intermittent data Application/external stimulus defined rate (e.g. light switch) Repetitive low latency data Allocation of time slots (e.g. mouse) Security Three modes: 1. Unsecured 2. Access control list mode devices only communicated with stored list of addresses 3. Secured mode Symmetric key for authentication and encryption with 4,6,8,12, 14 octets length key options Frame/message integrity (checksum like security feature) Sequential freshness frames numbered 46 Typical ZigBee-Enabled Device Design Typical design consist of RF IC and 8-bit microprocessor with peripherals connected to an application sensor or actuators 47 Wireless Technology Comparison Chart 3-6 μa deep sleep 0.2 μa 34KB /14KB Energy consumption typically support 2 packets per sec for > 1 year on AA battery 48
16 IETF effort on IEEE sensor networks 6LowWPAN Transmission of IPV6 Packets over networks IETF RFC 4994 Compresses IPV6 header, TCP, ICMP, UDP to fit frame format Uses link local IPV6 addresses for local communication - PAN ID maps to IPV6 prefix Fragmentation of IP packets to fit byte MTU Supports link-layer mesh routing under IP topology Allows IP routing over a mesh of nodes Pros/Cons IP is the standard internetworking protocol IPV6 is still not widely deployed Energy effects? WPANS High Data Rate WPANs Applications WiMedia Alliance Multimedia Streaming audio and video Interactive audio and video Data PDAs, PCs, printers Projectors USB wireless transfer Digital imaging Still image and video Camera to kiosk 50 High Speed WPANs (Mbps) Data Rate m Short 4m Distance Fast download Room-range High-definition Quality of service, streaming (WPAN) technology for transmitting data Quickly Cost-effectively With low power consumption 10m a/b/g/n Data Networking.11n promises 100m 1 Bluetooth Range (m) Source: Texas Instruments 51
17 Requirements Data rate and Range: 22 Mbps ~100m, Mbps ~50m, 480 Mbps ~2-3m QoS capable Security Quick join/unjoin j i Basic security/authentication Low power, cost, size, complexity Piconet, not network connectivity Connect up to 256 devices in a Piconet 52 Qualities of the MAC PAN Coordinator (PNC) Device (DEV) topology PNC assigns time for connections Commands go to and come from the PNC. Communication is peer-to-peer Quality of Service TDMA architecture with guaranteed time slots (GTSs) Security and Authentication No Security Mode Security Mode uses AES with 128 bit key Security Key for encryption key distribution Authentication Key for Challenge/Response auth. 53 Basic structure is the superframe 3 parts to the superframe Beacon Contention Access Period (CAP) Contention Free Period (CFP) CFP has GTSs and MTSs 54
18 Access methods Beacon TDMA, only sent by the PNC CAP (Contention Access Period) CSMA/CA, types of data and commands can be restricted by PNC PNC can replace the CAP with management time slots (MTSs) using slotted-aloha access. CFP (Contention Free Period) TDMA, assigned by the PNC GTSs are unidirectional 55 PNC selection/handover Alternate coordinators (ACs) broadcast capabilities Based on criteria, best AC is chosen and becomes the PNC PNC begins to issue beacon PNC hands over task if more capable AC joins the piconet Exception only if security policy is verified 56 Features Commands supported: PNC selection and handover Association and disassociation Information request commands Repeater service Power management commands Device information Retransmission Request and modify GTS allocations MAC Support Peer Discovery Multi-rate support Repeater service Dynamic channel selection Power management Transmit power control 57
19 Physical Layer Characteristics 2.4 GHz band Unlicensed operation 15 MHz RF bandwidth 3 or 4 non-overlapping channels Similar to for coexistence 5 data rates Mbps with multi-bit symbols and coding Use Trellis Coded Modulation (TCM) for coding Modulation Coding Data rate Sensitivity QPSK 8 state TCM 11 Mb/s -82 dbm DQPSk None 22 Mb/s -75 dbm 16-QAM 8 state TCM 33 Mb/s -74 dbm 32-QAM 8 state TCM 44 Mb/s -71 dbm 64-QAM 8 state TCM 55 Mb/s -68 dbm 58 Physical Layer Characteristics also for US Spectrum GHz band with ultra wideband radios (UWB) FCC requires minimum 500 MHz use for UWB Spectrum divided into fourteen 528 MHz bands Data rate Mbps with OFDM OFDM with 128 subcarriers in a band similar to a/g Current radios use a group three frequencies as a mulit-band channel that is Multi-Band OFDM is used Band Group #6 59 WPANs WPANS Growing number applications and type/range of devices IEEE standardization of several different scenarios/applications Bluetooth th sensors (Zigbee, 6loWPAN) higher data rate WPANs including UWB Cost, power, support for application development current issues 60
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering
 Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Jean Parrend ENRNG3076 : Oral presentation BEng Computer and Communications Engineering 1 Origin 2 Purpose : Create a cable replacement standard for personal area network Handle simultaneously both data
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #7: Medium Access Control WPAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Bluetooth Page 2 Spring 2013 CS 795/895 - Wireless Networked
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
MOBILE COMPUTING. Jan-May,2012. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
WPAN: Bluetooth MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com EM Spectrum ISM band 902 928 Mhz 2.4 2.4835 Ghz 5.725 5.85 Ghz LF MF
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
12/2/09. Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing. Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! Bluetooth Overview"
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Bluetooth Networking" George Roussos! g.roussos@dcs.bbk.ac.uk! Bluetooth Overview" A cable replacement technology! Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz! Frequency
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
WPAN-like Systems. UWB Ultra Wide Band. IrDA Infrared Data Association. Bluetooth. Z-Wave. WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network
 WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
WPAN-like Systems WPAN Wireless Personal Area Network PAN: Personal Area Network. Small, within a few meters. WPAN: Wireless PAN. Mostly short-range, low-power, lowrate networks. More or less self-organizing.
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
Amarjeet Singh. February 7, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
Amarjeet Singh February 7, 2012 References Bluetooth Protocol Architecture v.1 www.bluetooth.org http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/bluetooth/ Slides from last class uploaded on the course website
[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]
![[A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY]](/thumbs/74/69742987.jpg) 2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
2011 [A SHORT REPORT ON BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY] By Ram Kumar Bhandari 1. Introduction Bluetooth Technology A Technical Report Bluetooth is a short-ranged wire-less communication technology implementing the
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Bluetooth. The Bluetooth Vision. Universal Wireless Connectivity. Universal Wireless Connectivity
 1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
1 2 The Vision Universal wireless connectivity Replace existing cables with radio Connect systems that have been separate Ubiquitous computing environment Intelligent devices performing distributed services
Bluetooth. Quote of the Day. "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson. Stephen Carter March 19, 2002
 Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
Bluetooth Stephen Carter March 19, 2002 Quote of the Day "I don't have to be careful, I've got a gun. -Homer Simpson 1 About Bluetooth Developed by a group called Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG),
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 12 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
LECTURE 10. Wireless Local Area Networks and Bluetooth
 1 LECTURE 10 Wireless Local Area Networks and Bluetooth Wireless LANs 2 Local Area Ubiquitous WiFi Others HIPERLAN? Bluetooth based WLANs IR WLANs Started as extensions to wired LANs Still extensions to
1 LECTURE 10 Wireless Local Area Networks and Bluetooth Wireless LANs 2 Local Area Ubiquitous WiFi Others HIPERLAN? Bluetooth based WLANs IR WLANs Started as extensions to wired LANs Still extensions to
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
 WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES Bluetooth, ZigBee and ANT Thomas Aasebø OVERVIEW What are wireless sensor networks? What are personal area networks? What are these networks typically used for? Bluetooth, ZigBee
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism. Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09
 Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
Solving the Interference Problem due to Wireless LAN for Bluetooth Transmission Using a Non- Collaborative Mechanism Yun-Ming, Chiu 2005/6/09 Outline Overview Survey of Bluetooth Structure of Bluetooth
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
 BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
BLUETOOTH Amita Tiwari IIIrd Semester amitaasct@gmail.com Sunil Kumar IIIrd Semester sunilasct@gmail.com ALL SAINTS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL ABSTRACT Blue tooth is a standard developed by a group
WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS
 3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
3 WIRELESS-NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES/PROTOCOLS Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of
Wireless Local Area Network. Internet Protocol Suite
 Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Wireless Local Area Network Internet Protocol Suite Application layer File transfer protocol Telnet Hypertext transfer protocol Transport layer Network layer Host-tonetwork layer User datagram protocol
Embedded Systems. 8. Communication
 Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Embedded Systems 8. Communication Lothar Thiele 8-1 Contents of Course 1. Embedded Systems Introduction 2. Software Introduction 7. System Components 10. Models 3. Real-Time Models 4. Periodic/Aperiodic
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T )
 Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Computer Networks II Advanced Features (T-110.5111) Bluetooth, PhD Assistant Professor DCS Research Group Based on slides previously done by Matti Siekkinen, reused with permission For classroom use only,
Bluetooth. Basic idea
 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement of IrDA Embedded in other devices,
Outline. TWR Module. Different Wireless Protocols. Section 7. Wireless Communication. Wireless Communication with
 Section 7. Wireless Communication Outline Wireless Communication with 802.15.4/Zigbee Protocol Introduction to Freescale MC12311 802.15.4/Zigbee Protocol TWR-12311 Module TWR-MC12311 Smart Radio Features
Section 7. Wireless Communication Outline Wireless Communication with 802.15.4/Zigbee Protocol Introduction to Freescale MC12311 802.15.4/Zigbee Protocol TWR-12311 Module TWR-MC12311 Smart Radio Features
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE
 CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
CHAPTER 3 BLUETOOTH AND IEEE 802.15 These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial work
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth ( ) Zigbee ( ) Renato Lo Cigno
 Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
Ah-Hoc, PAN, WSN,... Introduction Bluetooth (802.15.1) Zigbee (802.15.4) Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/ Ad-Hoc Networks Built by the userse themselves to support specific (in time, space, applications)
AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE
 Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Wireless Technology AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. References 2 The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Modulation. Propagation. Typical frequency bands
 References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
References Wireless Technology 2 AT THE END OF THIS SECTION, YOU SHOULD HAVE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE UNDERLYING WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES. The physical layer provides mechanical, electrical, l functional,
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance
 Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Sensor Application for Museum Guidance Radka Dimitrova a a TU,Dresden, Germany, e-mail: dimitrova@ifn.et.tu-dresden.de Abstract - This article examines the conditions for successful communication and power
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Wireless Sensor Networks 11th Lecture 29.11.2006 Christian Schindelhauer schindel@informatik.uni-freiburg.de 1 Bluetooth in WSN? There are several commercially available MAC protocol/products Wi-Fi Bluetooth
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth
 Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Redes Inalámbricas Tema 2.B Wireless PANs: Bluetooth Bluetooh Acknowledgments: Foo Chun Choong, Ericsson Research / Cyberlab Singapore, and Open Source Software Lab, ECE Dept, NUS Máster de Ingeniería
Structure of the Lecture
 Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Structure of the Lecture Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: GSM, GPRS, UMTS Satellites
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Introduction to IEEE
 Introduction to IEEE 802.15.4 Marcos Rubinstein IEEE 802.15.4 Short range, low bit rate, low power consumption Home Automotive Industrial applications Games Metering 1 PHY speeds 250 kbps 40 kbps 20 kbps.
Introduction to IEEE 802.15.4 Marcos Rubinstein IEEE 802.15.4 Short range, low bit rate, low power consumption Home Automotive Industrial applications Games Metering 1 PHY speeds 250 kbps 40 kbps 20 kbps.
Bluetooth. Renato Lo Cigno
 Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Bluetooth Renato Lo Cigno www.dit.unitn.it/locigno/teaching ...Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs- NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare:
Communication Systems. WPAN: Bluetooth. Page 1
 Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Communication Systems WPAN: Bluetooth Page 1 Outline Historical perspective Piconet Scatternet Lattency modes Applications Page 2 Bluetooth Bluetooth (BT) wireless technology is a short-range communications
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE W.lan.4
 Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
Wireless LANs & PANs Case Study: Bluetooth & IEEE802.15 W.lan.4 Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, China Dr.W.Shu@ECE University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA W.wan.4-2 PANs: Bluetooth
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee. Dmitri A. Moltchanov kurssit/elt-53306/
 WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
WPAN/WBANs: ZigBee Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/ kurssit/elt-53306/ IEEE 802.15 WG breakdown; ZigBee Comparison with other technologies; PHY and MAC; Network
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI
 Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Implementing A Bluetooth Stack on UEFI Tony C.S. Lo Senior Manager American Megatrends Inc. presented by UEFI Plugfest October 2014 Agenda Introduction Bluetooth Architecture UEFI Bluetooth Stack Summary
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Wireless Personal Area Networks
 CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
CE 477 Wireless and obile Networks Wireless ersonal Area Networks Bluetooth CE 477 User cenarios Architecture rotocol tack IEEE 802.15.1 and IEEE 802.15.2 IEEE 802.15.4 (Low-Rate Wireless ersonal Area
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
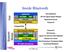 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Message acknowledgement and an optional beacon. Channel Access is via Carrier Sense Multiple Access with
 ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
ZigBee IEEE 802.15.4 Emerging standard for low-power wireless monitoring and control Scale to many devices Long lifetime is important (contrast to Bluetooth) 10-75m range typical Designed for industrial
Davide Quaglia Assistant CS depart University of Verona, Italy
 Emad Ebeid Ph.D. student @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy EmadSamuelMalki.Ebeid@univr.it Davide Quaglia Assistant Professor @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy Davide.Quaglia@univr.it 2 1 ZigBee
Emad Ebeid Ph.D. student @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy EmadSamuelMalki.Ebeid@univr.it Davide Quaglia Assistant Professor @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy Davide.Quaglia@univr.it 2 1 ZigBee
MOBILE COMPUTING. Bluetooth 9/20/15. CSE 40814/60814 Fall Basic idea
 OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
OBILE COUTING CE 40814/60814 Fall 2015 Bluetooth Basic idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting computer and peripherals, handheld devices, DAs, cell phones replacement
ZigBee/ David Sanchez Sanchez.
 ZigBee/802.15.4 David Sanchez Sanchez david.sanchezs@upf.edu Lecture Overview 1. Introduction and motivation to ZigBee 2. ZigBee/802.15.4 specification 1. Definitions 2. MAC communication modes 3. Network
ZigBee/802.15.4 David Sanchez Sanchez david.sanchezs@upf.edu Lecture Overview 1. Introduction and motivation to ZigBee 2. ZigBee/802.15.4 specification 1. Definitions 2. MAC communication modes 3. Network
Wireless LANs/data networks
 RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
RADIO SYSTEMS - ETIN15 Lecture no: 12 Wireless LANs/data networks Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2016-05-03 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Centralized and
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech. Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, 7.1
 Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
Bluetooth Bluetooth Basics Bluetooth and Linux Bluetooth at AG Tech Dr.-Ing. H. Ritter, http://www.hartmut-ritter.de/ 7.1 I. Bluetooth Idea Universal radio interface for ad-hoc wireless connectivity Interconnecting
ZIGBEE. Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS
 ZIGBEE Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS OUTLINE ZIGBEE AND APPLICATIONS IEEE 802.15.4 PROTOCOL ZIGBEE PROTOCOL ZIGBEE ALLIANCE ZIGBEE APPLICATIONS PHYSICAL LAYER MAC LAYER ZIGBEE
ZIGBEE Erkan Ünal CSE 401 SPECIAL TOPICS IN COMPUTER NETWORKS OUTLINE ZIGBEE AND APPLICATIONS IEEE 802.15.4 PROTOCOL ZIGBEE PROTOCOL ZIGBEE ALLIANCE ZIGBEE APPLICATIONS PHYSICAL LAYER MAC LAYER ZIGBEE
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
A Guide. Wireless Network Library Bluetooth
 A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
A Guide to the Wireless Network Library Conforming to Standard v1.1 SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive,
Bluetooth Tutorial. Bluetooth Introduction. Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Bluetooth Tutorial Bluetooth strives to remove the never ending maze of wires which provide a communication link between different electronic devices, through a short range wireless solution. Consider
Electromagnetic Spectrum (3kHz 300GHz)
 Wireless Communication Serial communication Allocated a frequency of operation Could be a range of frequencies Regulated by FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in US Unfortunately, allocations are
Wireless Communication Serial communication Allocated a frequency of operation Could be a range of frequencies Regulated by FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in US Unfortunately, allocations are
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8
 ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 26 September 2016 HW#3 was posted Announcements note the warnings you were getting on toupper()
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Objectives of the Bluetooth Technology
 Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
Bluetooth Origin of the name Harald I Bleutooth (in Danish, Harald Blåtand) (b. c. 910 d. c. 987), king of Denmark was credited with the first unification of Denmark and Norway Ericsson, inspired on the
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK
 1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
Seminar: Mobile Systems. Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht
 Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Zigbee protocol stack overview
 Zigbee protocol stack overview 2018 ASSUMPTIONS FOR USING THIS TEACHING MATERIAL DSR and OTSL takes no responsibility about the problem which occurs as a result of applying the technical information written
Zigbee protocol stack overview 2018 ASSUMPTIONS FOR USING THIS TEACHING MATERIAL DSR and OTSL takes no responsibility about the problem which occurs as a result of applying the technical information written
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN)
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander Schill http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8
 MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic
 Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Dominique Chomienne & Michel Eftimakis NewLogic Bluetooth is a trademark owned by the Bluetooth SIG, and licenced to NewLogic Page 1 Tutorial Agenda Bluetooth Marketing view Bluetooth network topology
Extending or Interconnecting LANS. Physical LAN segment. Virtual LAN. Forwarding Algorithm 11/9/15. segments. VLAN2, Port3. VLAN1, Port1.
 Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Physical LAN segment q Hosts connected on the same physical LAN segment q Same subnet; L2 forwarding q ARP (IPè MAC) L2 frame (S, D), send q Scale? Extending or Interconnecting LANS q q q Why not just
Module 5. Embedded Communications. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Module 5 Embedded Communications Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 27 Wireless Communication Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would
Wireless and WiFi. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Emad Ebeid Ph.D. CS depart University of Verona, Italy
 Emad Ebeid Ph.D. student @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy EmadSamuelMalki.Ebeid@univr.it Davide Quaglia Assistant Professor @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy Davide.Quaglia@univr.it 2 1 ZigBee
Emad Ebeid Ph.D. student @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy EmadSamuelMalki.Ebeid@univr.it Davide Quaglia Assistant Professor @ CS depart University of Verona, Italy Davide.Quaglia@univr.it 2 1 ZigBee
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System
 Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Feasibility of a Bluetooth Based Structural Health Monitoring Telemetry System Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Uchil, Vilas; Kosbar, Kurt Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Lecture Objectives. Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs. Agenda (1) Agenda (2) Wireless Spectrum (1)
 Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Lecture Objectives Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 1 Wireless Environment and Wireless LANs Discuss the impact of the wireless environment on networks Explain the concept of spread spectrum,
Topic 2b Wireless MAC. Chapter 7. Wireless and Mobile Networks. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach
 Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU
 Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Evropský sociální fond Praha & EU: Investujeme do vaší budoucnosti MI-BPS (Wireless Networks) FIT - CTU Alex Moucha Lecture 8 - Piconets, Scatternets, Bluetooth, Zigbee 1 Piconet an ad-hoc network linking
Mobile Communications
 Mobile Communications Wireless Personal Area Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto 1 IEEE Standards 2 IEEE 802.15.4 Wireless PAN (Sensor Networks) 3 Information Current
Mobile Communications Wireless Personal Area Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto 1 IEEE Standards 2 IEEE 802.15.4 Wireless PAN (Sensor Networks) 3 Information Current
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
ZigBee & Wireless Sensor Networks Case Study: ZigBee & IEEE S.rou.2. ZigBee Solution. What is ZigBee?
 S.rou.2-2 Wireless Sensor Networks Case Study: ZigBee & IEEE802.15.4 S.rou.2 ZigBee & 802.15.4 ZigBee overview IEEE 802.15.4 overview ZigBee & bluetooth End Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai,
S.rou.2-2 Wireless Sensor Networks Case Study: ZigBee & IEEE802.15.4 S.rou.2 ZigBee & 802.15.4 ZigBee overview IEEE 802.15.4 overview ZigBee & bluetooth End Dr.M.Y.Wu@CSE Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai,
101seminartopics.com. Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks
 Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Bluetooth Based Smart Sensor Networks ABSTRACT Dragging the world towards wireless galaxy Various sensors are already in a broad use today as part of different devices or as standalone devices connected
Overview of Bluetooth
 Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and Bluetooth Page 1 http://developers.sun.com/techtopics/mobility/midp/articles/bluetooth1/ Dec 19, 2004 Article Wireless Application Programming with J2ME and
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks. Lecture
 Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Special Course in Computer Science: Local Networks Lecture 11 16.5.2012 Roadmap of the Course So far Basic telecom concepts General study of LANs Local Networks Ethernet Token bus Token ring ATM LAN Wi-Fi
Wireless Sensor Networks
 Wireless Sensor Networks c.buratti@unibo.it +39 051 20 93147 Office Hours: Tuesday 3 5 pm @ Main Building, third floor Credits: 6 Standard Solutions Data-rate RFID 20 cm, 10-200 kbps 100m, 11-100 Mbps
Wireless Sensor Networks c.buratti@unibo.it +39 051 20 93147 Office Hours: Tuesday 3 5 pm @ Main Building, third floor Credits: 6 Standard Solutions Data-rate RFID 20 cm, 10-200 kbps 100m, 11-100 Mbps
Communications Options for Wireless Sensor Networks. Marco Zennaro and Antoine Bagula ICTP and UWC Italy and South Africa
 Communications Options for Wireless Sensor Networks Marco Zennaro and Antoine Bagula ICTP and UWC Italy and South Africa WSN communications options When considering communications options, parameters to
Communications Options for Wireless Sensor Networks Marco Zennaro and Antoine Bagula ICTP and UWC Italy and South Africa WSN communications options When considering communications options, parameters to
Chapter 7. ZigBee (IEEE ) Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel
 Chapter 7 ZigBee (IEEE 802.15.4) Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel Outline 7.1 Introduction and Overview of IEEE 802.15.4 / ZigBee 7.2 IEEE 802.15.4: Physical Layer Protocols 7.3 IEEE 802.15.4: MAC Layer Protocols
Chapter 7 ZigBee (IEEE 802.15.4) Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel Outline 7.1 Introduction and Overview of IEEE 802.15.4 / ZigBee 7.2 IEEE 802.15.4: Physical Layer Protocols 7.3 IEEE 802.15.4: MAC Layer Protocols
Chapter 7. IEEE ZigBee. Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel
 Chapter 7 IEEE 802.15.4 ZigBee Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel Outline 7.1 Introduction and Overview of IEEE 802.15.4 / ZigBee 7.2 IEEE 802.15.4: Physical Layer Protocols 7.3 IEEE 802.15.4: MAC Layer Protocols
Chapter 7 IEEE 802.15.4 ZigBee Liang Zhao, Andreas Timm-Giel Outline 7.1 Introduction and Overview of IEEE 802.15.4 / ZigBee 7.2 IEEE 802.15.4: Physical Layer Protocols 7.3 IEEE 802.15.4: MAC Layer Protocols
Computer Networks. Wireless LANs
 Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Computer Networks Wireless LANs Mobile Communication Technology according to IEEE (examples) Local wireless networks WLAN 802.11 Personal wireless nw WPAN 802.15 WiFi 802.11a 802.11b 802.11h 802.11i/e/
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
EC Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank
 EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
EC 6802 - Wireless Networks VIII - Semester Questions Bank UNIT I PART A 1. Find out the capacity of a single IS-95 cell that uses QPSK modulation and convolutional coding 3 db < Sr < 9 db, and bandwidth
ZigBee Technology: Wireless Control that Simply Works
 ZigBee Technology: Wireless Control that Simply Works Patrick Kinney Kinney Consulting LLC Chair of IEEE 802.15.4 Task Group Secretary of ZigBee BoD Chair of ZigBee Building Automation Profile WG - 1 -
ZigBee Technology: Wireless Control that Simply Works Patrick Kinney Kinney Consulting LLC Chair of IEEE 802.15.4 Task Group Secretary of ZigBee BoD Chair of ZigBee Building Automation Profile WG - 1 -
Communication In Smart Grid -Part3
 Communication In Smart Grid -Part3 Dr.-Ing. Abdalkarim Awad 09.12.2015 Informatik 7 Rechnernetze und Kommunikationssysteme Zigbee General characteristics Data rates of 250 kbps, 20 kbps and 40kpbs. Star
Communication In Smart Grid -Part3 Dr.-Ing. Abdalkarim Awad 09.12.2015 Informatik 7 Rechnernetze und Kommunikationssysteme Zigbee General characteristics Data rates of 250 kbps, 20 kbps and 40kpbs. Star
CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei 1393
 Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 Wireless Links, WiFi, Cellular Internet Access, and Mobility Slides derived from those available on the Web site of the book Computer Networking, by Kurose
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 Wireless Links, WiFi, Cellular Internet Access, and Mobility Slides derived from those available on the Web site of the book Computer Networking, by Kurose
