Lab: Supplying Inputs to Programs
|
|
|
- Imogen Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Steven Zeil May 25, 2013 Contents 1 Running the Program 2 2 Supplying Standard Input 4 3 Command Line Parameters 4 1
2 In this lab, we will look at some of the different ways that basic I/O information can be supplied to a running program. Probably most of the programs you have written and tested so far have been text-interactive. They were designed to print out a prompt on the screen (cout) requesting a single piece of data. Then they would read that info from the keyboard (cin). Then they would prompt for another piece of input, read another, and so on. cout << " Enter a number between 1 and 10: " << flush ; int k ; cin >> k ; while ( k < 1 k > 10) cout << " Try again : " << flush ; cin >> k ; cout << "Thanks! " << endl ; Enter a number between 1 and 10: 12 Try again : 9 Thanks! It s rare for a useful program to actually work that way. If we really want interaction with the human operator, we would expect some sort of Graphic User Interface (GUI) with windows, pop-up dialog boxes, etc. We re not ready to start writing in that style yet. On the other hand, a lot of very useful programs are not designed to be interactive at all. They take their inputs from files, from other programs, and from parameters specified when the program is launched, and they send their output to files or other programs. If you are going to write these kinds of programs, you need to know how to control their inputs and outputs so that you can execute and test them. 1 Running the Program 1. Run Code::Blocks and create a new project named "io_lab" with the following function: #include <iostream > #include <string > using namespace std ; int main ( int argc, char ** argv ) cout << "Now reading from standard in " << endl ; s t r i n g l i n e ; g e t l i n e ( cin, l i n e ) ; while ( cin ) cout << " I saw : " << l i n e << endl ; CS333 2
3 g e t l i n e ( cin, l i n e ) ; return 0 ; Compile. Run the program using the Code::Blocks blue arrow icon. When the program says it is reading from standard in, type some lines of text. Watch as it echoes your input. This program reads until it encounters the end of input (a.k.a. end of file). How do you indicate this when you are typing? In Windows, type Ctrl-Z. In Unix/Linux, type Ctrl-D. In both cases, you should really only do this at the start of a new line of input. 2. Now we are going to look at a few other ways to launch that program. Open up Windows Explorer ("My Computer") and navigate to the folder where you have stored this project. You should see a bin folder and, inside that, a Debug folder. In there, you will find your executable, io_lab.exe. Double-click on that to run the program. A command window will open in which you can interact with the program. It will close when you signal end of input. 3. Now right-click on that file and drag it somewhere (a convenient folder, or your desktop). You should see an option to create a shortcut. Choose that. Double-click the shortcut to launch the program. Leave that shortcut and the folder showing your executable program where you can get to them easily. We ll be using them again later. 4. Click the Windows Start button, select "Run...", and type "cmd". This opens a command window. cd to the folder where your executable resides. The cd and pwd commands work the same way in Windows as they do in Unix (and you did do the required assignment in CS252 before today s lab, right?), except that Windows uses a backslash \ instead of a forward slash / to separate directories. The Windows command dir is the closest equivalent of the Unix ls. To switch to a different drive in Windows, give a command consisting of the drive letter followed by a colon. For example, if you stored your project on a USB flash drive that installed itself as drive E, the command is E : Once you have cd d all the way to the directory containing your executable, you can run it by typing the file name: lab2.exe. Try that. CS333 3
4 2 Supplying Standard Input When you are testing and debugging a program, you often want to run the same input through it, over and over, as you work to fix the bugs. This can be rather tiresome if you have to actually type it out, over and over each time. It s also easy to make mistakes so that you don t quite run the tests the way you intended. 1. Run the program again, using any of the launch techniques we tried earlier. This time, instead of typing your input, copy a few lines of text from this web page (or from any file you have handy.) to the clipboard. Paste it to your running program - left click on the small box in the upper-left corner of the command window, then select edit -> paste. In practice, you can use any text editor to create files of test input data, then use copy-and-paste to feed them to your program. This includes both NotePad and, perhaps more conveniently, the Code::Blocks editor, which can certainly be used to create text files with names that don t end in.h or.cpp. Use the end-of-input character to close out the program. 2. Using the Code::Blocks editor, or notepad, or any convenient text editor, create a plain text file testdata.txt in the same directory where you have your executable. Be sure you use a text editor, not a word processor. We want a file of plain text, not the binary codes that word processors use to store fancy formatting. It doesn t matter what you put into the file - your name and address, a few lines from your favorite song, whatever. Make sure that you hit enter/return at the end of the last line. OK, now let s say we want to use the text in that file as input to test our program We could use the copy-and-paste technique. But when we are running from the command line, there s another option. Go to your cmd window and run your program like this: lab2 < testdata. t x t You should see the program print out all the text from your file. The < character in the command is used to request redirection of the input. The program is still reading from cin, but now the data going to cin is being supplied from the file named after the < instead of from the keyboard. Redirection is a technique used heavily in Unix, and is covered in more detail in CS252. But even in Windows, it is very useful for testing programs that read large amounts of data from standard in. 3 Command Line Parameters The main function receives two parameters. These are traditionally called argc and argv, although those aren t the most descriptive of names. These are used to supply command-line options to the program. 1. Let s add a few lines to the program: CS333 4
5 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main (int argc, char** argv) cout << "This program received " << argc << " command parameters." << endl; for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) cout << "argv[" << i << "] is " << argv[i] << endl; cout << "Now reading from standard in" << endl; string line; getline (cin, line); while (cin) cout << "I saw: " << line << endl; getline (cin, line); return 0; Compile and run the program. Note the new output. argv is an array of C-strings (character arrays). Each item in this array is one item from the command-line. argc tells you how many things are in this array. 2. Go to your cmd window and run the program like this: io_ lab a b cdef Notice that your command line has 4 items (including the name of the program itself), and the output shows that the argv array has the same 4 items (the program name might be altered slightly, but the others are given exactly). Stop the program and run it again like this: io_ lab "a b" cdef Notice that the quotes can be used to group together a string that includes blanks, turning it into a single entry in the command parameter array. 3. A lot of Windows programs accept command line parameters, though you may not realize this if you always launch them by double clicking on shortcuts or selecting them from the Start menu. CS333 5
6 Go to any empty spot on your desktop, right-click and select New->Shortcut. For the "location of the item", enter: explorer Click Next, give the shortcut any convenient name, and click Finish. Now double-click on your new shortcut to run it. "explorer" is the program that Windows uses to show you your folders. By default, it shows the folder "My Documents". But we can change that with a command-line parameter. Right-click on your shortcut, select properties, and to the "Target" line add a space and then the characters "c:". Save this and then run your shortcut again. Notice that the command parameter ("c:") controls which folder is displayed. The lesson here is that even Windows programs that will probably never be invoked directly from a command line will, nonetheless, often benefit from the ability to handle command-line parameters. Now let s return to the shortcut you created earlier. Right-click on the shortcut and select "properties". The "target" entry holds the same thing you might have typed in the cmd window. Try appending some command line parameters onto the end, click OK to save the changes, then launch the program by double-clicking the shortcut. The output should reflect your new command parameters. 4. When you run your own programs from inside Code::Blocks, you can also supply command-line parameters. This is particularly important if you want to use its built-in debugger to find bugs in a program that is designed to take information from the command line. In the Code::Blocks Project menu, select "Select programs arguments...". In the "Program Arguments" box, enter a few lines of text. Run the program. You ll see that each line is treated as one command line parameter. 5. Some programs get all their input directly from their command line parameters. For example, the expr program on most Unix systems works like a calculator: > expr > But one of the most common uses of command-line parameters is to supply file names to programs so that it will know from where to take its inputs and put its outputs. For example, change the io_lab program to #include <iostream > #include <fstream > #include <string > using namespace std ; CS333 6
7 int main ( int argc, char ** argv ) ifstream input ( argv [ 1 ] ) ; ofstream output ( argv [ 2 ] ) ; cout << " This program received " << argc << " command parameters. " << endl ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < argc ; ++ i ) cout << " argv [ " << i << " ] i s " << argv [ i ] << endl ; cout << "Now reading from " << argv [ 1 ] << endl ; cout << " and writing to " << argv [ 2 ] << endl ; s t r i n g l i n e ; g e t l i n e ( input, l i n e ) ; while ( input ) output << " I saw : " << l i n e << endl ; g e t l i n e ( input, l i n e ) ; return 0 ; In your cmd window, run the program as io_lab testdata. t x t output. t x t Then open output.txt in any text editor (including the Code::Blocks editor) to view the output. As you progress through the semester, you will be working on programs that take their inputs from a variety of sources. Try to remember that you have many options on how you supply your test inputs, whether you work entirely inside Code::Blocks or work directly at the command line. CS333 7
CS101 Linux Shell Handout
 CS101 Linux Shell Handout Introduction This handout is meant to be used as a quick reference to get a beginner level hands on experience to using Linux based systems. We prepared this handout assuming
CS101 Linux Shell Handout Introduction This handout is meant to be used as a quick reference to get a beginner level hands on experience to using Linux based systems. We prepared this handout assuming
Unit 10. Linux Operating System
 1 Unit 10 Linux Operating System 2 Linux Based on the Unix operating system Developed as an open-source ("free") alternative by Linux Torvalds and several others starting in 1991 Originally only for Intel
1 Unit 10 Linux Operating System 2 Linux Based on the Unix operating system Developed as an open-source ("free") alternative by Linux Torvalds and several others starting in 1991 Originally only for Intel
ENCM 339 Fall 2017: Editing and Running Programs in the Lab
 page 1 of 8 ENCM 339 Fall 2017: Editing and Running Programs in the Lab Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary September 2017 Introduction This document is a
page 1 of 8 ENCM 339 Fall 2017: Editing and Running Programs in the Lab Steve Norman Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Calgary September 2017 Introduction This document is a
Unit 13. Linux Operating System Debugging Programs
 1 Unit 13 Linux Operating System Debugging Programs COMPILATION 2 3 Editors "Real" developers use editors designed for writing code No word processors!! You need a text editor to write your code Eclipse,
1 Unit 13 Linux Operating System Debugging Programs COMPILATION 2 3 Editors "Real" developers use editors designed for writing code No word processors!! You need a text editor to write your code Eclipse,
Text File I/O. #include <iostream> #include <fstream> using namespace std; int main() {
 Text File I/O We can use essentially the same techniques we ve been using to input from the keyboard and output to the screen and just apply them to files instead. If you want to prepare input data ahead,
Text File I/O We can use essentially the same techniques we ve been using to input from the keyboard and output to the screen and just apply them to files instead. If you want to prepare input data ahead,
Lab 1: Introduction to C++
 CPSC 221, Jan-Apr 2017 Lab 1 1/5 Lab 1: Introduction to C++ This is an introduction to C++ through some simple activities. You should also read the C++ Primer in your textbook, and practice as much as
CPSC 221, Jan-Apr 2017 Lab 1 1/5 Lab 1: Introduction to C++ This is an introduction to C++ through some simple activities. You should also read the C++ Primer in your textbook, and practice as much as
CS354 gdb Tutorial Written by Chris Feilbach
 CS354 gdb Tutorial Written by Chris Feilbach Purpose This tutorial aims to show you the basics of using gdb to debug C programs. gdb is the GNU debugger, and is provided on systems that
CS354 gdb Tutorial Written by Chris Feilbach Purpose This tutorial aims to show you the basics of using gdb to debug C programs. gdb is the GNU debugger, and is provided on systems that
Linux Tutorial #1. Introduction. Login to a remote Linux machine. Using vim to create and edit C++ programs
 Linux Tutorial #1 Introduction The Linux operating system is now over 20 years old, and is widely used in industry and universities because it is fast, flexible and free. Because Linux is open source,
Linux Tutorial #1 Introduction The Linux operating system is now over 20 years old, and is widely used in industry and universities because it is fast, flexible and free. Because Linux is open source,
C++ Support Classes (Data and Variables)
 C++ Support Classes (Data and Variables) School of Mathematics 2018 Today s lecture Topics: Computers and Programs; Syntax and Structure of a Program; Data and Variables; Aims: Understand the idea of programming
C++ Support Classes (Data and Variables) School of Mathematics 2018 Today s lecture Topics: Computers and Programs; Syntax and Structure of a Program; Data and Variables; Aims: Understand the idea of programming
clicking on the on the New
 ECCS 1611 Programming 1 Dr. Estell Lab 1 Introduction to C++ Programming using Visual Studio 2010 Today s lab is meant as an introduction, both to the development system that you will be using this semester
ECCS 1611 Programming 1 Dr. Estell Lab 1 Introduction to C++ Programming using Visual Studio 2010 Today s lab is meant as an introduction, both to the development system that you will be using this semester
1) Log on to the computer using your PU net ID and password.
 CS 150 Lab Logging on: 1) Log on to the computer using your PU net ID and password. Connecting to Winter: Winter is the computer science server where all your work will be stored. Remember, after you log
CS 150 Lab Logging on: 1) Log on to the computer using your PU net ID and password. Connecting to Winter: Winter is the computer science server where all your work will be stored. Remember, after you log
The QuickCalc BASIC User Interface
 The QuickCalc BASIC User Interface Running programs in the Windows Graphic User Interface (GUI) mode. The GUI mode is far superior to running in the CONSOLE mode. The most-used functions are on buttons,
The QuickCalc BASIC User Interface Running programs in the Windows Graphic User Interface (GUI) mode. The GUI mode is far superior to running in the CONSOLE mode. The most-used functions are on buttons,
Starting to Program in C++ (Basics & I/O)
 Copyright by Bruce A. Draper. 2017, All Rights Reserved. Starting to Program in C++ (Basics & I/O) On Tuesday of this week, we started learning C++ by example. We gave you both the Complex class code and
Copyright by Bruce A. Draper. 2017, All Rights Reserved. Starting to Program in C++ (Basics & I/O) On Tuesday of this week, we started learning C++ by example. We gave you both the Complex class code and
My First Command-Line Program
 1. Tutorial Overview My First Command-Line Program In this tutorial, you re going to create a very simple command-line application that runs in a window. Unlike a graphical user interface application where
1. Tutorial Overview My First Command-Line Program In this tutorial, you re going to create a very simple command-line application that runs in a window. Unlike a graphical user interface application where
Lab 1 Introduction to UNIX and C
 Name: Lab 1 Introduction to UNIX and C This first lab is meant to be an introduction to computer environments we will be using this term. You must have a Pitt username to complete this lab. NOTE: Text
Name: Lab 1 Introduction to UNIX and C This first lab is meant to be an introduction to computer environments we will be using this term. You must have a Pitt username to complete this lab. NOTE: Text
Getting started with UNIX/Linux for G51PRG and G51CSA
 Getting started with UNIX/Linux for G51PRG and G51CSA David F. Brailsford Steven R. Bagley 1. Introduction These first exercises are very simple and are primarily to get you used to the systems we shall
Getting started with UNIX/Linux for G51PRG and G51CSA David F. Brailsford Steven R. Bagley 1. Introduction These first exercises are very simple and are primarily to get you used to the systems we shall
Today in CS162. External Files. What is an external file? How do we save data in a file? CS162 External Data Files 1
 Today in CS162 External Files What is an external file? How do we save data in a file? CS162 External Data Files 1 External Files So far, all of our programs have used main memory to temporarily store
Today in CS162 External Files What is an external file? How do we save data in a file? CS162 External Data Files 1 External Files So far, all of our programs have used main memory to temporarily store
Laboratory Assignment #4 Debugging in Eclipse CDT 1
 Lab 4 (10 points) November 20, 2013 CS-2301, System Programming for Non-majors, B-term 2013 Objective Laboratory Assignment #4 Debugging in Eclipse CDT 1 Due: at 11:59 pm on the day of your lab session
Lab 4 (10 points) November 20, 2013 CS-2301, System Programming for Non-majors, B-term 2013 Objective Laboratory Assignment #4 Debugging in Eclipse CDT 1 Due: at 11:59 pm on the day of your lab session
Using the Xcode Debugger
 g Using the Xcode Debugger J Objectives In this appendix you ll: Set breakpoints and run a program in the debugger. Use the Continue program execution command to continue execution. Use the Auto window
g Using the Xcode Debugger J Objectives In this appendix you ll: Set breakpoints and run a program in the debugger. Use the Continue program execution command to continue execution. Use the Auto window
C++ for Everyone, 2e, Cay Horstmann, Copyright 2012 John Wiley and Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Using a Debugger WE5.
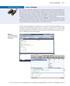 Using a Debugger WE5 W o r k E D E x a m p l e 5.2 Using a Debugger As you have undoubtedly realized by now, computer programs rarely run perfectly the first time. At times, it can be quite frustrating
Using a Debugger WE5 W o r k E D E x a m p l e 5.2 Using a Debugger As you have undoubtedly realized by now, computer programs rarely run perfectly the first time. At times, it can be quite frustrating
Configuring Ubuntu to Code for the OmniFlash or OmniEP
 Configuring Ubuntu to Code for the OmniFlash or OmniEP Table of Contents Introduction...2 Assumptions...2 Getting Started...2 Getting the Cross Compiler for ARM...2 Extracting the contents of the compressed
Configuring Ubuntu to Code for the OmniFlash or OmniEP Table of Contents Introduction...2 Assumptions...2 Getting Started...2 Getting the Cross Compiler for ARM...2 Extracting the contents of the compressed
FILE ORGANIZATION. GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn
 FILE ORGANIZATION GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn PRINCIPLES OF FILE ORGANIZATION PAGE 03 Organization Trees Creating Categories FILES AND FOLDERS PAGE 05 Creating Folders Saving
FILE ORGANIZATION GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn PRINCIPLES OF FILE ORGANIZATION PAGE 03 Organization Trees Creating Categories FILES AND FOLDERS PAGE 05 Creating Folders Saving
Installing and Using Dev-C++
 Installing and Using Dev-C++ 1. Installing Dev-C++ Orwell Dev-C++ is a professional C++ IDE, but not as big and complex as Visual Studio. It runs only on Windows; both Windows 7 and Windows 8 are supported.
Installing and Using Dev-C++ 1. Installing Dev-C++ Orwell Dev-C++ is a professional C++ IDE, but not as big and complex as Visual Studio. It runs only on Windows; both Windows 7 and Windows 8 are supported.
Spring CS Homework 12 p. 1. CS Homework 12
 Spring 2018 - CS 111 - Homework 12 p. 1 Deadline 11:59 pm on Friday, May 4, 2018 Purpose CS 111 - Homework 12 To practice with sentinel- and question-controlled loops, file input and file output, and writing
Spring 2018 - CS 111 - Homework 12 p. 1 Deadline 11:59 pm on Friday, May 4, 2018 Purpose CS 111 - Homework 12 To practice with sentinel- and question-controlled loops, file input and file output, and writing
14 - Multiple Files and Folders Dragging and dropping File name collisions revisited
 14 - Multiple Files and Folders In the last lesson, we saw how to use the context menu or the ribbon to copy and move files on our hard drive. In this lesson, we will review and build on those skills as
14 - Multiple Files and Folders In the last lesson, we saw how to use the context menu or the ribbon to copy and move files on our hard drive. In this lesson, we will review and build on those skills as
CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015)
 CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015) First Name: Last Name: NetID: Completing this lab assignment is very important and you must have a CS 1110 course consultant tell CMS that you did the work. (Correctness
CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015) First Name: Last Name: NetID: Completing this lab assignment is very important and you must have a CS 1110 course consultant tell CMS that you did the work. (Correctness
Using Windows 7 Explorer By Len Nasman, Bristol Village Computer Club
 By Len Nasman, Bristol Village Computer Club Understanding Windows 7 Explorer is key to taking control of your computer. If you have ever created a file and later had a hard time finding it, or if you
By Len Nasman, Bristol Village Computer Club Understanding Windows 7 Explorer is key to taking control of your computer. If you have ever created a file and later had a hard time finding it, or if you
Installing and Using Xcode
 Installing and Using Xcode 1. Installing Xcode Xcode is a professional C++ IDE for the Mac. This is Apple s IDE for Mac and ios software. Note that while the IDE itself is free, it may require the latest
Installing and Using Xcode 1. Installing Xcode Xcode is a professional C++ IDE for the Mac. This is Apple s IDE for Mac and ios software. Note that while the IDE itself is free, it may require the latest
Laboratory 1 Semester 1 11/12
 CS2106 National University of Singapore School of Computing Laboratory 1 Semester 1 11/12 MATRICULATION NUMBER: In this lab exercise, you will get familiarize with some basic UNIX commands, editing and
CS2106 National University of Singapore School of Computing Laboratory 1 Semester 1 11/12 MATRICULATION NUMBER: In this lab exercise, you will get familiarize with some basic UNIX commands, editing and
CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) First Name: Last Name: NetID:
 CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2016sp/labs/lab01/lab01.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: Goals. Learning a computer language is a lot like learning
CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2016sp/labs/lab01/lab01.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: Goals. Learning a computer language is a lot like learning
Software Design & Programming I
 Software Design & Programming I Starting Out with C++ (From Control Structures through Objects) 7th Edition Written by: Tony Gaddis Pearson - Addison Wesley ISBN: 13-978-0-132-57625-3 Chapter 3 Introduction
Software Design & Programming I Starting Out with C++ (From Control Structures through Objects) 7th Edition Written by: Tony Gaddis Pearson - Addison Wesley ISBN: 13-978-0-132-57625-3 Chapter 3 Introduction
Lab 8. Follow along with your TA as they demo GDB. Make sure you understand all of the commands, how and when to use them.
 Lab 8 Each lab will begin with a recap of last lab and a brief demonstration by the TAs for the core concepts examined in this lab. As such, this document will not serve to tell you everything the TAs
Lab 8 Each lab will begin with a recap of last lab and a brief demonstration by the TAs for the core concepts examined in this lab. As such, this document will not serve to tell you everything the TAs
Week 5: Files and Streams
 CS319: Scientific Computing (with C++) Week 5: and Streams 9am, Tuesday, 12 February 2019 1 Labs and stuff 2 ifstream and ofstream close a file open a file Reading from the file 3 Portable Bitmap Format
CS319: Scientific Computing (with C++) Week 5: and Streams 9am, Tuesday, 12 February 2019 1 Labs and stuff 2 ifstream and ofstream close a file open a file Reading from the file 3 Portable Bitmap Format
Introduction to Lab Sessions
 Introduction to Lab Sessions PRO1 Josep Carmona, Lluís Padró Introduction Programació 1 -- Dept. CS, UPC 2 Introduction In this course we will learn to write programs that run in commandline mode (i.e.
Introduction to Lab Sessions PRO1 Josep Carmona, Lluís Padró Introduction Programació 1 -- Dept. CS, UPC 2 Introduction In this course we will learn to write programs that run in commandline mode (i.e.
CHAPTER 1 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Finding Your Way in the Inventor Interface
 CHAPTER 1 Finding Your Way in the Inventor Interface COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL Understanding Inventor s interface behavior Opening existing files Creating new files Modifying the look and feel of Inventor Managing
CHAPTER 1 Finding Your Way in the Inventor Interface COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL Understanding Inventor s interface behavior Opening existing files Creating new files Modifying the look and feel of Inventor Managing
CS 2400 Laboratory Assignment #1: Exercises in Compilation and the UNIX Programming Environment (100 pts.)
 1 Introduction 1 CS 2400 Laboratory Assignment #1: Exercises in Compilation and the UNIX Programming Environment (100 pts.) This laboratory is intended to give you some brief experience using the editing/compiling/file
1 Introduction 1 CS 2400 Laboratory Assignment #1: Exercises in Compilation and the UNIX Programming Environment (100 pts.) This laboratory is intended to give you some brief experience using the editing/compiling/file
First C or C++ Lab Paycheck-V1.0 Using Microsoft Visual Studio
 C & C++ LAB ASSIGNMENT #1 First C or C++ Lab Paycheck-V1.0 Using Microsoft Visual Studio Copyright 2013 Dan McElroy Paycheck-V1.0 The purpose of this lab assignment is to enter a C or C++ into Visual Studio
C & C++ LAB ASSIGNMENT #1 First C or C++ Lab Paycheck-V1.0 Using Microsoft Visual Studio Copyright 2013 Dan McElroy Paycheck-V1.0 The purpose of this lab assignment is to enter a C or C++ into Visual Studio
1 Installation (briefly)
 Jumpstart Linux Bo Waggoner Updated: 2014-09-15 Abstract A basic, rapid tutorial on Linux and its command line for the absolute beginner. Prerequisites: a computer on which to install, a DVD and/or USB
Jumpstart Linux Bo Waggoner Updated: 2014-09-15 Abstract A basic, rapid tutorial on Linux and its command line for the absolute beginner. Prerequisites: a computer on which to install, a DVD and/or USB
Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse
 Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse Step Zero: Select workspace 1. Upon launching eclipse, we are ask to chose a workspace: 2. We select a new workspace directory (e.g., C:\Courses ): 3. We accept the
Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse Step Zero: Select workspace 1. Upon launching eclipse, we are ask to chose a workspace: 2. We select a new workspace directory (e.g., C:\Courses ): 3. We accept the
Program Organization and Comments
 C / C++ PROGRAMMING Program Organization and Comments Copyright 2013 Dan McElroy Programming Organization The layout of a program should be fairly straight forward and simple. Although it may just look
C / C++ PROGRAMMING Program Organization and Comments Copyright 2013 Dan McElroy Programming Organization The layout of a program should be fairly straight forward and simple. Although it may just look
The Command Shell. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 The Command Shell Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Starting the Command Shell Locally Remote Host Directory Structure Moving around the directories Displaying File Contents Compiling and Running
The Command Shell Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Starting the Command Shell Locally Remote Host Directory Structure Moving around the directories Displaying File Contents Compiling and Running
Introduction to Unix and Linux. Workshop 1: Directories and Files
 Introduction to Unix and Linux Workshop 1: Directories and Files Genomics Core Lab TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY CORPUS CHRISTI Anvesh Paidipala, Evan Krell, Kelly Pennoyer, Chris Bird Genomics Core Lab Informatics
Introduction to Unix and Linux Workshop 1: Directories and Files Genomics Core Lab TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY CORPUS CHRISTI Anvesh Paidipala, Evan Krell, Kelly Pennoyer, Chris Bird Genomics Core Lab Informatics
Operating System Interaction via bash
 Operating System Interaction via bash bash, or the Bourne-Again Shell, is a popular operating system shell that is used by many platforms bash uses the command line interaction style generally accepted
Operating System Interaction via bash bash, or the Bourne-Again Shell, is a popular operating system shell that is used by many platforms bash uses the command line interaction style generally accepted
I/O Streams and Standard I/O Devices (cont d.)
 Chapter 3: Input/Output Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn what a stream is and examine input and output streams Explore how to read data from the standard input device Learn how to use predefined
Chapter 3: Input/Output Objectives In this chapter, you will: Learn what a stream is and examine input and output streams Explore how to read data from the standard input device Learn how to use predefined
Tutorial 2: Compiling and Running C++ Source Code
 Tutorial 2: Compiling and Running C++ Source Code 1. Log in to your UNIX account as you did during the first tutorial. 2. Click on the desktop with the left mouse button and consider the menu that appears
Tutorial 2: Compiling and Running C++ Source Code 1. Log in to your UNIX account as you did during the first tutorial. 2. Click on the desktop with the left mouse button and consider the menu that appears
Easy Windows Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files
 Easy Windows 98-3 - Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files Page 1 of 11 Easy Windows 98-3 - Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files Task 1: Opening Folders Folders contain files, programs, or other
Easy Windows 98-3 - Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files Page 1 of 11 Easy Windows 98-3 - Working with Disks, Folders, - and Files Task 1: Opening Folders Folders contain files, programs, or other
Check the Desktop development with C++ in the install options. You may want to take 15 minutes to try the Hello World C++ tutorial:
 CS262 Computer Vision OpenCV 3 Configuration with Visual Studio 2017 Prof. John Magee Clark University Install Visual Studio 2017 Community Check the Desktop development with C++ in the install options.
CS262 Computer Vision OpenCV 3 Configuration with Visual Studio 2017 Prof. John Magee Clark University Install Visual Studio 2017 Community Check the Desktop development with C++ in the install options.
Lab 2: Linux/Unix shell
 Lab 2: Linux/Unix shell Comp Sci 1585 Data Structures Lab: Tools for Computer Scientists Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 What is a shell? What is a shell? login is a program that logs users in to a computer. When
Lab 2: Linux/Unix shell Comp Sci 1585 Data Structures Lab: Tools for Computer Scientists Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 What is a shell? What is a shell? login is a program that logs users in to a computer. When
2 Getting Started. Getting Started (v1.8.6) 3/5/2007
 2 Getting Started Java will be used in the examples in this section; however, the information applies to all supported languages for which you have installed a compiler (e.g., Ada, C, C++, Java) unless
2 Getting Started Java will be used in the examples in this section; however, the information applies to all supported languages for which you have installed a compiler (e.g., Ada, C, C++, Java) unless
File Management Tutorial
 Just a reminder... Files: any individual item on your computer that contains data. E.g. document, photo, spreadsheet, email, PowerPoint, etc. File Management Tutorial Folders: containers for your files
Just a reminder... Files: any individual item on your computer that contains data. E.g. document, photo, spreadsheet, email, PowerPoint, etc. File Management Tutorial Folders: containers for your files
Computer Basics: Step-by-Step Guide (Session 2)
 Table of Contents Computer Basics: Step-by-Step Guide (Session 2) ABOUT PROGRAMS AND OPERATING SYSTEMS... 2 THE WINDOWS 7 DESKTOP... 3 TWO WAYS TO OPEN A PROGRAM... 4 DESKTOP ICON... 4 START MENU... 5
Table of Contents Computer Basics: Step-by-Step Guide (Session 2) ABOUT PROGRAMS AND OPERATING SYSTEMS... 2 THE WINDOWS 7 DESKTOP... 3 TWO WAYS TO OPEN A PROGRAM... 4 DESKTOP ICON... 4 START MENU... 5
Windows XP. A Quick Tour of Windows XP Features
 Windows XP A Quick Tour of Windows XP Features Windows XP Windows XP is an operating system, which comes in several versions: Home, Media, Professional. The Windows XP computer uses a graphics-based operating
Windows XP A Quick Tour of Windows XP Features Windows XP Windows XP is an operating system, which comes in several versions: Home, Media, Professional. The Windows XP computer uses a graphics-based operating
Install & First Time Setup Guide
 cs@cyberonic.com CONTENTS www.cyberonic.com Install & First Time Setup Guide Cyberonic Development Team December 10, 2013 This guide should help you install and set-up the CMS software for use with a pre-configured
cs@cyberonic.com CONTENTS www.cyberonic.com Install & First Time Setup Guide Cyberonic Development Team December 10, 2013 This guide should help you install and set-up the CMS software for use with a pre-configured
Getting Started with Python and the PyCharm IDE
 New York University School of Continuing and Professional Studies Division of Programs in Information Technology Getting Started with Python and the PyCharm IDE Please note that if you already know how
New York University School of Continuing and Professional Studies Division of Programs in Information Technology Getting Started with Python and the PyCharm IDE Please note that if you already know how
Getting Started (1.8.7) 9/2/2009
 2 Getting Started For the examples in this section, Microsoft Windows and Java will be used. However, much of the information applies to other operating systems and supported languages for which you have
2 Getting Started For the examples in this section, Microsoft Windows and Java will be used. However, much of the information applies to other operating systems and supported languages for which you have
Power users are all about shortcuts,
 Fun With The Command Prompt Power users are all about shortcuts, workarounds, and customizations, and the Command Prompt is the most powerful utility on your PC for performing these. There s almost nothing
Fun With The Command Prompt Power users are all about shortcuts, workarounds, and customizations, and the Command Prompt is the most powerful utility on your PC for performing these. There s almost nothing
CSCI 161: Introduction to Programming I Lab 1b: Hello, World (Eclipse, Java)
 Goals - to learn how to compile and execute a Java program - to modify a program to enhance it Overview This activity will introduce you to the Java programming language. You will type in the Java program
Goals - to learn how to compile and execute a Java program - to modify a program to enhance it Overview This activity will introduce you to the Java programming language. You will type in the Java program
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Fall Programming Assignment 1 (updated 9/16/2017)
 UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Fall 2017 Programming Assignment 1 (updated 9/16/2017) Introduction The purpose of this programming assignment is to give you
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Fall 2017 Programming Assignment 1 (updated 9/16/2017) Introduction The purpose of this programming assignment is to give you
Reading: Managing Files in Windows XP
 Student Resource 13.4a Reading: Managing Files in Windows XP Directions: All recent versions of Windows (XP, Vista, Windows 7) have fairly similar ways of managing files, but their graphic user interfaces
Student Resource 13.4a Reading: Managing Files in Windows XP Directions: All recent versions of Windows (XP, Vista, Windows 7) have fairly similar ways of managing files, but their graphic user interfaces
Overview. - General Data Types - Categories of Words. - Define Before Use. - The Three S s. - End of Statement - My First Program
 Overview - General Data Types - Categories of Words - The Three S s - Define Before Use - End of Statement - My First Program a description of data, defining a set of valid values and operations List of
Overview - General Data Types - Categories of Words - The Three S s - Define Before Use - End of Statement - My First Program a description of data, defining a set of valid values and operations List of
Chapter 1 - What s in a program?
 Chapter 1 - What s in a program? I. Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) a. You should be able to use Input-Process-Output charts to define basic processes in a programming module. b. You should be able to
Chapter 1 - What s in a program? I. Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) a. You should be able to use Input-Process-Output charts to define basic processes in a programming module. b. You should be able to
My First iphone App. 1. Tutorial Overview
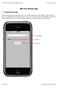 My First iphone App 1. Tutorial Overview In this tutorial, you re going to create a very simple application on the iphone or ipod Touch. It has a text field, a label, and a button. You can type your name
My First iphone App 1. Tutorial Overview In this tutorial, you re going to create a very simple application on the iphone or ipod Touch. It has a text field, a label, and a button. You can type your name
Turns your Wallbox into a Complete Jukebox
 JukeMP3 Wallbox Controller Turns your Wallbox into a Complete Jukebox JukeMP3 Features: 1. The JukeMP3 kit includes everything you need to turn your wallbox into a complete jukebox, except speakers and
JukeMP3 Wallbox Controller Turns your Wallbox into a Complete Jukebox JukeMP3 Features: 1. The JukeMP3 kit includes everything you need to turn your wallbox into a complete jukebox, except speakers and
Chapter 14 Sequential Access Files
 Chapter 14 Sequential Access Files Objectives Create file objects Open a sequential access file Determine whether a sequential access file was opened successfully Write data to a sequential access file
Chapter 14 Sequential Access Files Objectives Create file objects Open a sequential access file Determine whether a sequential access file was opened successfully Write data to a sequential access file
Using LINUX a BCMB/CHEM 8190 Tutorial Updated (1/17/12)
 Using LINUX a BCMB/CHEM 8190 Tutorial Updated (1/17/12) Objective: Learn some basic aspects of the UNIX operating system and how to use it. What is UNIX? UNIX is the operating system used by most computers
Using LINUX a BCMB/CHEM 8190 Tutorial Updated (1/17/12) Objective: Learn some basic aspects of the UNIX operating system and how to use it. What is UNIX? UNIX is the operating system used by most computers
1. Make the recordings. 2. Transfer the recordings to your computer
 Making recordings and burning them to CD can be done in four steps: 1. Make the recordings 2. Transfer them to your computer 3. Edit them 4. Copy the edited files to itunes 1. Make the recordings Turn
Making recordings and burning them to CD can be done in four steps: 1. Make the recordings 2. Transfer them to your computer 3. Edit them 4. Copy the edited files to itunes 1. Make the recordings Turn
Lab 1 Introduction to UNIX and C
 Name: Lab 1 Introduction to UNIX and C This first lab is meant to be an introduction to computer environments we will be using this term. You must have a Pitt username to complete this lab. The doc is
Name: Lab 1 Introduction to UNIX and C This first lab is meant to be an introduction to computer environments we will be using this term. You must have a Pitt username to complete this lab. The doc is
For this class we are going to create a file in Microsoft Word. Open Word on the desktop.
 File Management Windows 10 What is File Management? As you use your computer and create files you may need some help in storing and retrieving those files. File management shows you how to create, move,
File Management Windows 10 What is File Management? As you use your computer and create files you may need some help in storing and retrieving those files. File management shows you how to create, move,
Scientific Computing
 Scientific Computing Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Lecture 1, September 22, 2014 Outline Course Overview Programming Basics The C++ Programming Language Outline Course
Scientific Computing Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Lecture 1, September 22, 2014 Outline Course Overview Programming Basics The C++ Programming Language Outline Course
The first thing we ll need is some numbers. I m going to use the set of times and drug concentration levels in a patient s bloodstream given below.
 Graphing in Excel featuring Excel 2007 1 A spreadsheet can be a powerful tool for analyzing and graphing data, but it works completely differently from the graphing calculator that you re used to. If you
Graphing in Excel featuring Excel 2007 1 A spreadsheet can be a powerful tool for analyzing and graphing data, but it works completely differently from the graphing calculator that you re used to. If you
Matlab for FMRI Module 1: the basics Instructor: Luis Hernandez-Garcia
 Matlab for FMRI Module 1: the basics Instructor: Luis Hernandez-Garcia The goal for this tutorial is to make sure that you understand a few key concepts related to programming, and that you know the basics
Matlab for FMRI Module 1: the basics Instructor: Luis Hernandez-Garcia The goal for this tutorial is to make sure that you understand a few key concepts related to programming, and that you know the basics
Strings and Streams. Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts
 Strings and Streams Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute C++, by Walter
Strings and Streams Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute C++, by Walter
INFORMATICS LABORATORY WORK #2
 KHARKIV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF RADIO ELECTRONICS INFORMATICS LABORATORY WORK #2 SIMPLE C# PROGRAMS Associate Professor A.S. Eremenko, Associate Professor A.V. Persikov 2 Simple C# programs Objective: writing
KHARKIV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF RADIO ELECTRONICS INFORMATICS LABORATORY WORK #2 SIMPLE C# PROGRAMS Associate Professor A.S. Eremenko, Associate Professor A.V. Persikov 2 Simple C# programs Objective: writing
Eclipse Environment Setup
 Eclipse Environment Setup Adapted from a document from Jeffrey Miller and the CS201 team by Shiyuan Sheng. Introduction This lab document will go over the steps to install and set up Eclipse, which is
Eclipse Environment Setup Adapted from a document from Jeffrey Miller and the CS201 team by Shiyuan Sheng. Introduction This lab document will go over the steps to install and set up Eclipse, which is
Getting Started with Visual Studio
 Getting Started with Visual Studio Visual Studio is a sophisticated but easy to use integrated development environment (IDE) for C++ (and may other languages!) You will see that this environment recognizes
Getting Started with Visual Studio Visual Studio is a sophisticated but easy to use integrated development environment (IDE) for C++ (and may other languages!) You will see that this environment recognizes
How to program with Matlab (PART 1/3)
 Programming course 1 09/12/2013 Martin SZINTE How to program with Matlab (PART 1/3) Plan 0. Setup of Matlab. 1. Matlab: the software interface. - Command window - Command history - Section help - Current
Programming course 1 09/12/2013 Martin SZINTE How to program with Matlab (PART 1/3) Plan 0. Setup of Matlab. 1. Matlab: the software interface. - Command window - Command history - Section help - Current
Introduction. Key features and lab exercises to familiarize new users to the Visual environment
 Introduction Key features and lab exercises to familiarize new users to the Visual environment January 1999 CONTENTS KEY FEATURES... 3 Statement Completion Options 3 Auto List Members 3 Auto Type Info
Introduction Key features and lab exercises to familiarize new users to the Visual environment January 1999 CONTENTS KEY FEATURES... 3 Statement Completion Options 3 Auto List Members 3 Auto Type Info
A Quick Tour GETTING STARTED WHAT S IN THIS CHAPTER?
 1 A Quick Tour WHAT S IN THIS CHAPTER? Installing and getting started with Visual Studio 2012 Creating and running your fi rst application Debugging and deploying an application Ever since software has
1 A Quick Tour WHAT S IN THIS CHAPTER? Installing and getting started with Visual Studio 2012 Creating and running your fi rst application Debugging and deploying an application Ever since software has
Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs31 More on Arithmetic Expressions The following two are equivalent:! x = x + 5;
Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs31 More on Arithmetic Expressions The following two are equivalent:! x = x + 5;
CS103L SPRING 2018 UNIT 7: FILE I/O
 CS103L SPRING 2018 UNIT 7: FILE I/O I/O STREAMS IN C++ I/O: short for input/ouput Older term from mainframe days for getting data into and out of your program C++ offers object oriented abstractions to
CS103L SPRING 2018 UNIT 7: FILE I/O I/O STREAMS IN C++ I/O: short for input/ouput Older term from mainframe days for getting data into and out of your program C++ offers object oriented abstractions to
SPSS Tutorial - How to Perform an Offline License Activation on a Windows Computer
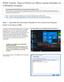 SPSS Tutorial - How to Perform an Offline License Activation on a Windows Computer Only Computers That DO NOT Have an Internet Connection Need to Do This If the computer you want to activate SPSS on does
SPSS Tutorial - How to Perform an Offline License Activation on a Windows Computer Only Computers That DO NOT Have an Internet Connection Need to Do This If the computer you want to activate SPSS on does
C++ for Java Programmers
 Basics all Finished! Everything we have covered so far: Lecture 5 Operators Variables Arrays Null Terminated Strings Structs Functions 1 2 45 mins of pure fun Introduction Today: Pointers Pointers Even
Basics all Finished! Everything we have covered so far: Lecture 5 Operators Variables Arrays Null Terminated Strings Structs Functions 1 2 45 mins of pure fun Introduction Today: Pointers Pointers Even
File Operations. Lecture 16 COP 3014 Spring April 18, 2018
 File Operations Lecture 16 COP 3014 Spring 2018 April 18, 2018 Input/Ouput to and from files File input and file output is an essential in programming. Most software involves more than keyboard input and
File Operations Lecture 16 COP 3014 Spring 2018 April 18, 2018 Input/Ouput to and from files File input and file output is an essential in programming. Most software involves more than keyboard input and
Superior University. Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115. Computing Fundamentals. Experiment No.1
 Superior University Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115 Computing Fundamentals Experiment No.1 Introduction of Compiler, Comments, Program Structure, Input Output, Data Types and Arithmetic Operators
Superior University Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115 Computing Fundamentals Experiment No.1 Introduction of Compiler, Comments, Program Structure, Input Output, Data Types and Arithmetic Operators
Learning Worksheet Fundamentals
 1.1 LESSON 1 Learning Worksheet Fundamentals After completing this lesson, you will be able to: Create a workbook. Create a workbook from a template. Understand Microsoft Excel window elements. Select
1.1 LESSON 1 Learning Worksheet Fundamentals After completing this lesson, you will be able to: Create a workbook. Create a workbook from a template. Understand Microsoft Excel window elements. Select
ENGI 1020 Introduction to Computer Programming R E Z A S H A H I D I J U L Y 2 6,
 ENGI 1020 Introduction to Computer Programming R E Z A S H A H I D I J U L Y 2 6, 2 0 1 0 Streams and files We have already talked about the standard input stream (cin), and the standard output stream
ENGI 1020 Introduction to Computer Programming R E Z A S H A H I D I J U L Y 2 6, 2 0 1 0 Streams and files We have already talked about the standard input stream (cin), and the standard output stream
CSCI 161: Introduction to Programming I Lab 1a: Programming Environment: Linux and Eclipse
 CSCI 161: Introduction to Programming I Lab 1a: Programming Environment: Linux and Eclipse Goals - to become acquainted with the Linux/Gnome environment Overview For this lab, you will login to a workstation
CSCI 161: Introduction to Programming I Lab 1a: Programming Environment: Linux and Eclipse Goals - to become acquainted with the Linux/Gnome environment Overview For this lab, you will login to a workstation
Chapter 2. Editing And Compiling
 Chapter 2. Editing And Compiling Now that the main concepts of programming have been explained, it's time to actually do some programming. In order for you to "edit" and "compile" a program, you'll need
Chapter 2. Editing And Compiling Now that the main concepts of programming have been explained, it's time to actually do some programming. In order for you to "edit" and "compile" a program, you'll need
PYTHON YEAR 10 RESOURCE. Practical 01: Printing to the Shell KS3. Integrated Development Environment
 Practical 01: Printing to the Shell To program in Python you need the latest version of Python, which is freely available at www.python.org. Your school will have this installed on the computers for you,
Practical 01: Printing to the Shell To program in Python you need the latest version of Python, which is freely available at www.python.org. Your school will have this installed on the computers for you,
EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007
 EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn USING MICROSOFT EXCEL PAGE 03 Opening Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Features Keyboard Review Pointer Shapes
EXCEL BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2007 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites What You Will Learn USING MICROSOFT EXCEL PAGE 03 Opening Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Features Keyboard Review Pointer Shapes
Parts of this tutorial has been adapted from M. Stonebank s UNIX Tutorial for Beginners (http://www.ee.surrey.ac.uk/teaching/unix/).
 Ubuntu tutorial Parts of this tutorial has been adapted from M. Stonebank s UNIX Tutorial for Beginners (http://www.ee.surrey.ac.uk/teaching/unix/). 1 Installing Ubuntu About Ubuntu For our lab sessions
Ubuntu tutorial Parts of this tutorial has been adapted from M. Stonebank s UNIX Tutorial for Beginners (http://www.ee.surrey.ac.uk/teaching/unix/). 1 Installing Ubuntu About Ubuntu For our lab sessions
Jerry Cain Handout #5 CS 106AJ September 30, Using JSKarel
 Jerry Cain Handout #5 CS 106AJ September 30, 2017 Using JSKarel This handout describes how to download and run the JavaScript version of Karel that we ll be using for our first assignment. 1. Getting started
Jerry Cain Handout #5 CS 106AJ September 30, 2017 Using JSKarel This handout describes how to download and run the JavaScript version of Karel that we ll be using for our first assignment. 1. Getting started
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Summer 2016 Programming Assignment 1 Introduction The purpose of this
 UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Summer 2016 Programming Assignment 1 Introduction The purpose of this programming assignment is to give you some experience
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA AT OMAHA Computer Science 4500/8506 Operating Systems Summer 2016 Programming Assignment 1 Introduction The purpose of this programming assignment is to give you some experience
Where Did My Files Go? How to find your files using Windows 10
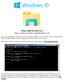 Where Did My Files Go? How to find your files using Windows 10 Have you just upgraded to Windows 10? Are you finding it difficult to find your files? Are you asking yourself Where did My Computer or My
Where Did My Files Go? How to find your files using Windows 10 Have you just upgraded to Windows 10? Are you finding it difficult to find your files? Are you asking yourself Where did My Computer or My
File I/O CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #9
 File I/O CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #9 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB I/O Data Streams and File I/O Lecture Outline An introduction to Objects and Member Functions Handling
File I/O CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #9 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB I/O Data Streams and File I/O Lecture Outline An introduction to Objects and Member Functions Handling
Outlook - an Introduction to Version 2003 Table of Contents
 Outlook - an Introduction to E-mail Version 2003 Table of Contents What is Outlook Starting Outlook The Navigation Pane Getting Help Creating and Sending a Message Using the College Exchange Directory
Outlook - an Introduction to E-mail Version 2003 Table of Contents What is Outlook Starting Outlook The Navigation Pane Getting Help Creating and Sending a Message Using the College Exchange Directory
Introduction to Personal Computing
 Introduction to Personal Computing Academic Computing Services www.ku.edu/acs Abstract: This document explains the basics of the Microsoft Windows operating system. It is intended for users who are either
Introduction to Personal Computing Academic Computing Services www.ku.edu/acs Abstract: This document explains the basics of the Microsoft Windows operating system. It is intended for users who are either
Lab 0 Introduction to the MSP430F5529 Launchpad-based Lab Board and Code Composer Studio
 ECE2049 Embedded Computing in Engineering Design Lab 0 Introduction to the MSP430F5529 Launchpad-based Lab Board and Code Composer Studio In this lab, you will be introduced to the Code Composer Studio
ECE2049 Embedded Computing in Engineering Design Lab 0 Introduction to the MSP430F5529 Launchpad-based Lab Board and Code Composer Studio In this lab, you will be introduced to the Code Composer Studio
Lutheran High North Technology The Finder
 Lutheran High North Technology shanarussell@lutheranhighnorth.org www.lutheranhighnorth.org/technology The Finder Your Mac s filing system is called the finder. In this document, we will explore different
Lutheran High North Technology shanarussell@lutheranhighnorth.org www.lutheranhighnorth.org/technology The Finder Your Mac s filing system is called the finder. In this document, we will explore different
Click Here to Begin OS X. Welcome to the OS X Basics Learning Module.
 OS X Welcome to the OS X Basics Learning Module. This module will teach you the basic operations of the OS X operating system, found on the Apple computers in the College of Technology computer labs. The
OS X Welcome to the OS X Basics Learning Module. This module will teach you the basic operations of the OS X operating system, found on the Apple computers in the College of Technology computer labs. The
