Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 4. Dr Nick Hayward
|
|
|
- Leo Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward
2 XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files, data storage, data exchange... XML is a simple, very flexible text format used for the description of marked-up electronic content XML is classified as extensible because allows user to define markup elements e.g. elements for a document, project, domain... XML is a meta-language a means of formally describing a language e.g. a markup language XML useful for sharing data abstraction of data and presentation document reuse... XML provides a basic syntax
3 XML - recap - origins XML emerged as a way to overcome the shortcomings of its two predecessors Standard Generalised Markup Language (SGML) HyperText Markup Language (HTML) HTML is too limited, while SGML is too complex XML is software and hardware independent light and simple tool for carrying information XML helps science, industries, companies specify how to store specific data store data in a machine compatible form allows applications to run on any platform easily import and process this data...
4 XML - recap - usage XML has some important characteristics extensible so it does not contain a fixed set of tags documents must be well-formed according to a strict set of rules may be formally validated using DTDs or XML Schemas HTML documents can contain errors (and often do) mdern browsers will still render the pages as well as possible XML focuses on the meaning of data, not its presentation XML is not a replacement for HTML XML is used to transport data HTML is used to format and display the data for the Web &c.
5 XML - syntax XML is a formal specification for markup languages formal language specifications have an associated syntax an XML document consists of the following: a prolog includes XML declaration optional reference to external structuring documents the body consisting of a number of elements which may also contain attributes prolog is the declaration informs the machine that the document &c. is XML includes any relevant additional information such as the encoding... other components may be inserted in the prolog associated schemas (either DTDs or XML Schema) or attached stylesheets (in CSS or XSL) in the body elements are organized in a hierarchical structure (a tree) one root element (Document element) all other elements within the root
6 XML - example structure xml <?xml version="1.0" standalone='yes'?> <library> <book category="non-fiction"> <title>the Discovery of the Tomb of Tutankhamen</title> <author>howard Carter</author> <year>1923</year> </book> </library> tree /library -book ---title ---author ---year
7 XML - structure - elements <library> <book category="non-fiction"> <title>the Discovery of the Tomb of Tutankhamen</title> <author>howard Carter</author> <year>1923</year> </book> </library> XML element everything from start to end tag inclusive of the tags element can contain other elements text attributes or a mix of all of the above... example listing - a bit of fun
8 XML - structure - elements - naming rules There are some naming rules for use with XML elements, e.g. elements can contain letters, numbers, and other characters elements cannot start with a number or punctuation character elements cannot start with the letters xml (or XML, or Xml, etc) elements cannot contain spaces
9 XML - structure - elements - best practices There are also some best practices for use with XML elements, e.g. make element names descriptive and easy to read try to avoid hyphenated words some software may perceive this as a subtraction try to avoid using a. period some software may perceive this as a defined property... e.g. property of an object... avoid colons in the element name reserved for the namespace in an XML document
10 XML - structure - elements - extensible XML elements are also extensible extend an element and it should not break an application XML is extensible not a fixed format like HTML XML is a metalanguage a language for describing other languages describe your own languages, e.g. RDF, SVG... list of XML markup languages
11 XML - structure - attributes <book type="print">hannibal's Footsteps</book> additional information about the element attribute values must be quoted double or single quotes "
12 XML - structure - attribute usage some of the problems with using attributes include, attributes cannot contain multiple values (elements can) attributes cannot contain tree structures (elements can) attributes are not easily expandable (for future changes) metadata is a common use of attributes for the element content e.g. an id or reference number
13 XML - structure - attribute vs element different discussions amongst various scientific and technical communities when and why to encode information into attributes or as content in elements there is not a prescribed or specific rule for this choice the choice will often depend on the developer or designer domain influence as well company practice and preferences parser or tools for transforming XML... using attributes at all is often a matter of choice and expediency e.g. what's the difference between the following? <title><primary>the Discovery of the Tomb of Tutankhamen</primary></title> or <title type="primary">the Discovery of the Tomb of Tutankhamen</title>
14 XML - structure - attribute usage XML attributes are normally used to describe elements provide additional information about elements metadata (data about data) commonly stored as attributes data stored as elements styles and patterns of usage will also develop with experience often informed by best practices in a given domain or community e.g. <library> <book category="non-fiction"> <title type="primary">the Discovery of the Tomb of Tutankhamen</title> <author>howard Carter</author> <year>1923</year> </book> </library>
15 XML - test 1 Think about how you might encode the following information: a car a sports team 2 Musical CDs including each song per album per CD (e.g. each album has 5 songs)
16 XML - test 1 - example solution <?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso "?> <vehicle> <car id="1" type="compact" manufacturer="ford"> <model>focus</model> <variant>hatchback</variant> <doors>5</doors> <trim>sport</trim> <colour>black</colour> <year>2014</year> <fuel>unleaded</fuel> <transmission>manual</transmission> </car> <boat id="1" type="motor" manufacturer="princess">... </boat> </vehicle> demo
17 XML - test 2
18 XML - test 2 - example solution <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <novel> <page no="198"> <line no="1"> <title align="centre" style="underline" colour="black">to the Lighthouse</t </line> <line no="2" type="empty"></line> <para no="1"> <line no="3">(here Mr. Carmichael, who was reading</line> </para> <line no="6"> <section align="centre" style="heading" colour="blue">3</section> </line>... <line no="11"><rend style="highlight" colour="green">green</rend>...</line>... </page> </novel> demo
19 XML - processing instructions an XML document can also contain processing instructions processing instructions encode application-specific data e.g. document declaration which opens every XML document each instruction is enclosed in <? and?> delimiters the target identifies the application an application should ignore unrecognised processing instructions processing instructions allow a developer to enter directives not part of the XML document's content instructions are passed up to different ad-hoc applications
20 XML - entities an XML document can use also entities similar to macros for programmers or aliases for more complex functions a single entity name can replace lots of text e.g. <!ENTITY editor "yvaine"> an entity can be recalled in the content of the document e.g. &editor; use in an XML document, e.g. <person>the editor's name is &editor;</person>
21 XML - CDATA we may also use CDATA elements in an XML document a CDATA element tells the XML parser not to interpret or parse characters the content may now be parsed even though it contains a character as part of an instruction... parser expects an entity <editors><![cdata[tristan & yvaine]]></editors>
22 XML - namespaces - intro in XML, element names are defined by developers different organisations may use the same tag and then markup content with different semantics XML also designed to enable interoperability and data exchange method to combine XML sources without ambiguity namespaces designed to provide uniquely named elements and attributes as defined by the W3C a namespace is a collection of XML elements and attributes identified by an Internationalised Resource Identifier (IRI) often referred to as an XML vocabulary
23 XML - namespaces - usage namespaces are declared as an attribute of an element using the xmlns name attribute in an element's start tag not mandatory to declare namespaces only at the root element may be declared at any element in the XML document namespace scope: begins at the element where it has been declared applies to the entire content of that element unless overridden by another namespace declaration <editor xmlns:editor=" /> a namespace declaration has the following syntax, e.g. xmlns:prefix="uri"
24 XML - namespaces - structure URI is a string of characters, which identifies an Internet Resource most common URI is the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) a less common type of URI is the Uniform Resource Name (URN) e.g. urn:isbn: a specific namespace identifies a collection of names a collection of element names e.g. standard XHTML a collection of attribute names e.g. XLink a namespace can collect names of properties e.g. FOAF (Friend of a Friend) dictionary of named properties and classes uses W3C's RDF technology a namespace may describe a set of functions e.g. the XPath Data Model
25 XML - rendering - css styling XML was created to structure content, not to display it for users &c. render XML with styles in a browser a CSS stylesheet can be applied similar to HTML files CSS is a language used to describe the presentation of a document a document written in a markup language e.g. SVG has its own CSS properties and values... CSS document is basically constituted by a set of rules a ruleset consists of two parts: a selector and a declaration property and a value, e.g. selector {property1:value; property2:value;} selector is a reference to the element to be rendered declaration defines applied styles, effects...
26 Image - CSS Syntax CSS Syntax
27 XML - rendering - css stylesheets with XML documents attach external stylesheets using xml-stylesheet processing instruction add to the prolog of the XML document, e.g. <?xml-stylesheet href= style.css type= text/css?> there can be multiple XML stylesheet processing instructions possible to attach multiple stylesheets to an XML document possible attributes are type - specific type, e.g. text/css medium - display medium type, e.g. print, screen... title - specify local name, a title...
28 XML - rendering - css stylesheets example XML <?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?> <library> <title>example with CSS</title> <body>body in the library...</body> </library> XML & CSS stylesheet <?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?> <?xml-stylesheet href="style1.css" type="text/css"?> <library> <title>example with CSS</title> <body>body in the library...</body> </library> XML document is still visible to the browser - i.e. data open and accessible tags rendered and styled with CSS
29 XML - viewing examples view without styling in a web browser, editor... demo render with CSS by associating a stylesheet with a given XML file demo transform the document using XSLT access, query and manipulate XML using JavaScript parse XML using PHP, render HTML, manipulate with JavaScript, and style with CSS demo 1 - TEI Parser simple demo 2 - TEI Parser full Winchester XML
30 Demos TEI Parser - simple TEI Parser - full XML Basic - cars XML Basic - literary text XML Basic - CD catalogue XML Basic - CD catalogue with CSS XML Sample - Winchester
31 Resources MDN - CSS W3C - CSS W3 Schools - CSS list of XML markup languages
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 4. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2017 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2017 - Week 4 Dr Nick Hayward XML - recap first version of XML became a W3C Recommendation in 1998 a useful format for data storage and exchange config files,
XML. Jonathan Geisler. April 18, 2008
 April 18, 2008 What is? IS... What is? IS... Text (portable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) Extensible (valuable for future)
April 18, 2008 What is? IS... What is? IS... Text (portable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) Extensible (valuable for future)
XML: Introduction. !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... Directive... 9:11
 !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
!important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 7 XML
 Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 2. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2017 - Week 2 Dr Nick Hayward Digitisation - textual considerations comparable concerns with music in textual digitisation density of data is still a concern
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2017 - Week 2 Dr Nick Hayward Digitisation - textual considerations comparable concerns with music in textual digitisation density of data is still a concern
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
7.1 Introduction. extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML
 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
Introduction to XML. XML: basic elements
 Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
The XML Metalanguage
 The XML Metalanguage Mika Raento mika.raento@cs.helsinki.fi University of Helsinki Department of Computer Science Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage p.1/442 2003-09-15 Preliminaries Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage
The XML Metalanguage Mika Raento mika.raento@cs.helsinki.fi University of Helsinki Department of Computer Science Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage p.1/442 2003-09-15 Preliminaries Mika Raento The XML Metalanguage
XML. Objectives. Duration. Audience. Pre-Requisites
 XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or remote-live attendance.
 XML Programming Duration: 5 Days Price: $2795 *California residents and government employees call for pricing. Discounts: We offer multiple discount options. Click here for more info. Delivery Options:
XML Programming Duration: 5 Days Price: $2795 *California residents and government employees call for pricing. Discounts: We offer multiple discount options. Click here for more info. Delivery Options:
Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or via remote-live attendance.
 XML Programming Duration: 5 Days US Price: $2795 UK Price: 1,995 *Prices are subject to VAT CA Price: CDN$3,275 *Prices are subject to GST/HST Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or
XML Programming Duration: 5 Days US Price: $2795 UK Price: 1,995 *Prices are subject to VAT CA Price: CDN$3,275 *Prices are subject to GST/HST Delivery Options: Attend face-to-face in the classroom or
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
Chapter 1: Getting Started. You will learn:
 Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2017 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid= 2465 1
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2017 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid= 2465 1
Structured documents
 Structured documents An overview of XML Structured documents Michael Houghton 15/11/2000 Unstructured documents Broadly speaking, text and multimedia document formats can be structured or unstructured.
Structured documents An overview of XML Structured documents Michael Houghton 15/11/2000 Unstructured documents Broadly speaking, text and multimedia document formats can be structured or unstructured.
Well-formed XML Documents
 Well-formed XML Documents Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Agenda Types of XML documents Why Well-formed XML Documents
Well-formed XML Documents Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Agenda Types of XML documents Why Well-formed XML Documents
W3C XML XML Overview
 Overview Jaroslav Porubän 2008 References Tutorials, http://www.w3schools.com Specifications, World Wide Web Consortium, http://www.w3.org David Hunter, et al.: Beginning, 4th Edition, Wrox, 2007, 1080
Overview Jaroslav Porubän 2008 References Tutorials, http://www.w3schools.com Specifications, World Wide Web Consortium, http://www.w3.org David Hunter, et al.: Beginning, 4th Edition, Wrox, 2007, 1080
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Representing Web Data: XML
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
Information Systems. XML Essentials. Nikolaj Popov
 Information Systems XML Essentials Nikolaj Popov Research Institute for Symbolic Computation Johannes Kepler University of Linz, Austria popov@risc.uni-linz.ac.at Outline Introduction Basic Syntax Well-Formed
Information Systems XML Essentials Nikolaj Popov Research Institute for Symbolic Computation Johannes Kepler University of Linz, Austria popov@risc.uni-linz.ac.at Outline Introduction Basic Syntax Well-Formed
XML & Related Languages
 Unit 1 1 Introduction: XML XML = extensible Markup Language the universal format for structured documents and data on the Web. www.w3c.org/xml simple, very flexible text format derived from SGML (ISO 8879).
Unit 1 1 Introduction: XML XML = extensible Markup Language the universal format for structured documents and data on the Web. www.w3c.org/xml simple, very flexible text format derived from SGML (ISO 8879).
TASC Consulting Technical Writing Courseware Training
 Understanding XML Aruna Panangipally TASC Consulting Technical Writing Courseware Training Session Outline Why should a technical writer know XML? The Beginning Understanding markup languages Origins of
Understanding XML Aruna Panangipally TASC Consulting Technical Writing Courseware Training Session Outline Why should a technical writer know XML? The Beginning Understanding markup languages Origins of
Web Standards Mastering HTML5, CSS3, and XML
 Web Standards Mastering HTML5, CSS3, and XML Leslie F. Sikos, Ph.D. orders-ny@springer-sbm.com www.springeronline.com rights@apress.com www.apress.com www.apress.com/bulk-sales www.apress.com Contents
Web Standards Mastering HTML5, CSS3, and XML Leslie F. Sikos, Ph.D. orders-ny@springer-sbm.com www.springeronline.com rights@apress.com www.apress.com www.apress.com/bulk-sales www.apress.com Contents
Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda
 NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
CSS, Cascading Style Sheets
 CSS, Cascading Style Sheets HTML was intended to define the content of a document This is a heading This is a paragraph This is a table element Not how they look (aka style)
CSS, Cascading Style Sheets HTML was intended to define the content of a document This is a heading This is a paragraph This is a table element Not how they look (aka style)
A tutorial report for SENG Agent Based Software Engineering. Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far. XML Tutorial.
 A tutorial report for SENG 609.22 Agent Based Software Engineering Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far XML Tutorial Yanan Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Calgary
A tutorial report for SENG 609.22 Agent Based Software Engineering Course Instructor: Dr. Behrouz H. Far XML Tutorial Yanan Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Calgary
Introduction to XML. Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
 Introduction to XML Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://gear.kku.ac.th/~krunapon/xmlws 1 Topics p What is XML? p Why XML? p Where does XML
Introduction to XML Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://gear.kku.ac.th/~krunapon/xmlws 1 Topics p What is XML? p Why XML? p Where does XML
extensible Markup Language (XML) Basic Concepts
 (XML) Basic Concepts Giuseppe Della Penna Università degli Studi di L Aquila dellapenna@univaq.it http://www.di.univaq.it/gdellape This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
(XML) Basic Concepts Giuseppe Della Penna Università degli Studi di L Aquila dellapenna@univaq.it http://www.di.univaq.it/gdellape This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Solutions. a. Yes b. No c. Cannot be determined without the DTD. d. Schema. 9. Explain the term extensible. 10. What is an attribute?
 Chapter 7: Information Representation Method XML Solutions Summative Assessment Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. XML was developed to overcome the limitations of the markup language. a. EDI b. SGML
Chapter 7: Information Representation Method XML Solutions Summative Assessment Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. XML was developed to overcome the limitations of the markup language. a. EDI b. SGML
Intro to XML. Borrowed, with author s permission, from:
 Intro to XML Borrowed, with author s permission, from: http://business.unr.edu/faculty/ekedahl/is389/topic3a ndroidintroduction/is389androidbasics.aspx Part 1: XML Basics Why XML Here? You need to understand
Intro to XML Borrowed, with author s permission, from: http://business.unr.edu/faculty/ekedahl/is389/topic3a ndroidintroduction/is389androidbasics.aspx Part 1: XML Basics Why XML Here? You need to understand
Introduction to XML 3/14/12. Introduction to XML
 Introduction to XML Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://gear.kku.ac.th/~krunapon/xmlws 1 Topics p What is XML? p Why XML? p Where does XML
Introduction to XML Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://gear.kku.ac.th/~krunapon/xmlws 1 Topics p What is XML? p Why XML? p Where does XML
XML: Extensible Markup Language
 XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
Data Presentation and Markup Languages
 Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
Markup Languages SGML, HTML, XML, XHTML. CS 431 February 13, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University
 Markup Languages SGML, HTML, XML, XHTML CS 431 February 13, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University Problem Richness of text Elements: letters, numbers, symbols, case Structure: words, sentences, paragraphs,
Markup Languages SGML, HTML, XML, XHTML CS 431 February 13, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University Problem Richness of text Elements: letters, numbers, symbols, case Structure: words, sentences, paragraphs,
Data Exchange. Hyper-Text Markup Language. Contents: HTML Sample. HTML Motivation. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Problems w/html
 Data Exchange Contents: Mariano Cilia / cilia@informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Origins (HTML) Schema DOM, SAX Semantic Data Exchange Integration Problems MIX Model 1 Hyper-Text Markup Language HTML Hypertext:
Data Exchange Contents: Mariano Cilia / cilia@informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Origins (HTML) Schema DOM, SAX Semantic Data Exchange Integration Problems MIX Model 1 Hyper-Text Markup Language HTML Hypertext:
Introduction to XML. An Example XML Document. The following is a very simple XML document.
 Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
UR what? ! URI: Uniform Resource Identifier. " Uniquely identifies a data entity " Obeys a specific syntax " schemename:specificstuff
 CS314-29 Web Protocols URI, URN, URL Internationalisation Role of HTML and XML HTTP and HTTPS interacting via the Web UR what? URI: Uniform Resource Identifier Uniquely identifies a data entity Obeys a
CS314-29 Web Protocols URI, URN, URL Internationalisation Role of HTML and XML HTTP and HTTPS interacting via the Web UR what? URI: Uniform Resource Identifier Uniquely identifies a data entity Obeys a
Layered approach. Data
 Layered approach (by T. Berners-Lee) The Semantic Web principles are implemented in the layers of Web technologies and standards semantics relational data Selfdescr. doc. Data Data Rules Ontology vocabulary
Layered approach (by T. Berners-Lee) The Semantic Web principles are implemented in the layers of Web technologies and standards semantics relational data Selfdescr. doc. Data Data Rules Ontology vocabulary
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 000-141 Title : XML and related technologies Vendors : IBM Version : DEMO
PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 000-141 Title : XML and related technologies Vendors : IBM Version : DEMO
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013
 Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
XML and DTD. Mario Alviano A.Y. 2017/2018. University of Calabria, Italy 1 / 28
 1 / 28 XML and DTD Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 XML syntax 3 Namespace 4 Document Type Definition (DTD) 5 Exercises Outline 3 / 28 1 Introduction
1 / 28 XML and DTD Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 XML syntax 3 Namespace 4 Document Type Definition (DTD) 5 Exercises Outline 3 / 28 1 Introduction
XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps
 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps Erik Wilde 16.7.2001 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps 1 Outline what is XML? a syntax (not a data model!) what is the data model behind XML? XML Information Set
XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps Erik Wilde 16.7.2001 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps 1 Outline what is XML? a syntax (not a data model!) what is the data model behind XML? XML Information Set
Create web pages in HTML with a text editor, following the rules of XHTML syntax and using appropriate HTML tags Create a web page that includes
 CMPT 165 INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET AND THE WORLD WIDE WEB By Hassan S. Shavarani UNIT2: MARKUP AND HTML 1 IN THIS UNIT YOU WILL LEARN THE FOLLOWING Create web pages in HTML with a text editor, following
CMPT 165 INTRODUCTION TO THE INTERNET AND THE WORLD WIDE WEB By Hassan S. Shavarani UNIT2: MARKUP AND HTML 1 IN THIS UNIT YOU WILL LEARN THE FOLLOWING Create web pages in HTML with a text editor, following
CS6501 IP Unit IV Page 1
 CS6501 Internet Programming Unit IV Part - A 1. What is PHP? PHP - Hypertext Preprocessor -one of the most popular server-side scripting languages for creating dynamic Web pages. - an open-source technology
CS6501 Internet Programming Unit IV Part - A 1. What is PHP? PHP - Hypertext Preprocessor -one of the most popular server-side scripting languages for creating dynamic Web pages. - an open-source technology
Web Design and Application Development
 Yarmouk University Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees (PFISR) Web Design and Application Development Dr. Abdel-Karim Al-Tamimi altamimi@yu.edu.jo Lecture 01 A. Al-Tamimi 1 Lecture Overview
Yarmouk University Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees (PFISR) Web Design and Application Development Dr. Abdel-Karim Al-Tamimi altamimi@yu.edu.jo Lecture 01 A. Al-Tamimi 1 Lecture Overview
Web Technologies Present and Future of XML
 Web Technologies Present and Future of XML Faculty of Computer Science A.I.Cuza University of Iasi, Romania busaco@infoiasi.ro http://www.infoiasi.ro/~busaco Ph.D. Student: Multimedia Object Manipulation
Web Technologies Present and Future of XML Faculty of Computer Science A.I.Cuza University of Iasi, Romania busaco@infoiasi.ro http://www.infoiasi.ro/~busaco Ph.D. Student: Multimedia Object Manipulation
M359 Block5 - Lecture12 Eng/ Waleed Omar
 Documents and markup languages The term XML stands for extensible Markup Language. Used to label the different parts of documents. Labeling helps in: Displaying the documents in a formatted way Querying
Documents and markup languages The term XML stands for extensible Markup Language. Used to label the different parts of documents. Labeling helps in: Displaying the documents in a formatted way Querying
CSC Web Technologies, Spring Web Data Exchange Formats
 CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
Web Programming Paper Solution (Chapter wise)
 What is valid XML document? Design an XML document for address book If in XML document All tags are properly closed All tags are properly nested They have a single root element XML document forms XML tree
What is valid XML document? Design an XML document for address book If in XML document All tags are properly closed All tags are properly nested They have a single root element XML document forms XML tree
 XML Introduction 1. XML Stands for EXtensible Mark-up Language (XML). 2. SGML Electronic Publishing challenges -1986 3. HTML Web Presentation challenges -1991 4. XML Data Representation challenges -1996
XML Introduction 1. XML Stands for EXtensible Mark-up Language (XML). 2. SGML Electronic Publishing challenges -1986 3. HTML Web Presentation challenges -1991 4. XML Data Representation challenges -1996
Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5. HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION
 Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5 HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION Objectives Explore the history of the Internet, the Web, and HTML Compare the different versions of HTML Study the syntax
Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5 HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION Objectives Explore the history of the Internet, the Web, and HTML Compare the different versions of HTML Study the syntax
Some more XML applications and XML-related standards (XLink, XPointer, XForms)
 Some more XML applications and XML-related standards (XLink, XPointer, XForms) Patryk Czarnik XML and Applications 2014/2015 Lecture 12 19.01.2015 Standards for inter-document relations XPointer addressing
Some more XML applications and XML-related standards (XLink, XPointer, XForms) Patryk Czarnik XML and Applications 2014/2015 Lecture 12 19.01.2015 Standards for inter-document relations XPointer addressing
extensible Markup Language
 extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards
 Disclaimer: All words, pictures are adopted from Learning Web Design (3 rd eds.) by Jennifer Niederst Robbins, published by O Reilly 2007. Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards CSc2320 In this chapter
Disclaimer: All words, pictures are adopted from Learning Web Design (3 rd eds.) by Jennifer Niederst Robbins, published by O Reilly 2007. Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards CSc2320 In this chapter
02 Structured Web. Semantic Web. Documents in XML
 Semantic Web 02 Structured Web Documents in XML Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science Air University, Islamabad, Pakistan www.imranihsan.com Role of XML in the Semantic Web Most
Semantic Web 02 Structured Web Documents in XML Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science Air University, Islamabad, Pakistan www.imranihsan.com Role of XML in the Semantic Web Most
Tutorial 2: Validating Documents with DTDs
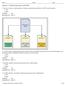 1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
What is XML? XML is designed to transport and store data.
 What is XML? XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML is designed to transport and store data. HTML was designed to display data. XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry
What is XML? XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML is designed to transport and store data. HTML was designed to display data. XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry
EXtensible Markup Language XML
 EXtensible Markup Language XML 1 What is XML? XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry data, not to display data XML tags are not predefined.
EXtensible Markup Language XML 1 What is XML? XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry data, not to display data XML tags are not predefined.
5/19/2015. Objectives. JavaScript, Sixth Edition. Introduction to the World Wide Web (cont d.) Introduction to the World Wide Web
 Objectives JavaScript, Sixth Edition Chapter 1 Introduction to JavaScript When you complete this chapter, you will be able to: Explain the history of the World Wide Web Describe the difference between
Objectives JavaScript, Sixth Edition Chapter 1 Introduction to JavaScript When you complete this chapter, you will be able to: Explain the history of the World Wide Web Describe the difference between
Understanding Page Template Components. Brandon Scheirman Instructional Designer, OmniUpdate
 Understanding Page Template Components Brandon Scheirman Instructional Designer, OmniUpdate Where do PCFs come from??.pcf .PCF Agenda Implementation Process Terminology used in Template Development Hands-on
Understanding Page Template Components Brandon Scheirman Instructional Designer, OmniUpdate Where do PCFs come from??.pcf .PCF Agenda Implementation Process Terminology used in Template Development Hands-on
XML Motivations. Semi-structured data. Principles of Information and Database Management 198:336 Week 8 Mar 28 Matthew Stone.
 XML Motivations Principles of Information and Database Management 198:336 Week 8 Mar 28 Matthew Stone Semi-structured data Relaxing traditional schema Storing more complex objects Standardized data Using
XML Motivations Principles of Information and Database Management 198:336 Week 8 Mar 28 Matthew Stone Semi-structured data Relaxing traditional schema Storing more complex objects Standardized data Using
More XML Schemas, XSLT, Intro to PHP. CS174 Chris Pollett Oct 15, 2007.
 More XML Schemas, XSLT, Intro to PHP CS174 Chris Pollett Oct 15, 2007. Outline XML Schemas XSLT PHP Overview of data types There are two categories of data types in XML Schemas: simple types -- which are
More XML Schemas, XSLT, Intro to PHP CS174 Chris Pollett Oct 15, 2007. Outline XML Schemas XSLT PHP Overview of data types There are two categories of data types in XML Schemas: simple types -- which are
XML: Managing with the Java Platform
 In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
Layered approach. Data
 Layered approach (by T. Berners-Lee) The Semantic Web principles are implemented in the layers of Web technologies and standards semantics relational data Selfdescr. doc. Data Data Rules Ontology vocabulary
Layered approach (by T. Berners-Lee) The Semantic Web principles are implemented in the layers of Web technologies and standards semantics relational data Selfdescr. doc. Data Data Rules Ontology vocabulary
XML. extensible Markup Language. ... and its usefulness for linguists
 XML extensible Markup Language... and its usefulness for linguists Thomas Mayer thomas.mayer@uni-konstanz.de Fachbereich Sprachwissenschaft, Universität Konstanz Seminar Computerlinguistik II (Miriam Butt)
XML extensible Markup Language... and its usefulness for linguists Thomas Mayer thomas.mayer@uni-konstanz.de Fachbereich Sprachwissenschaft, Universität Konstanz Seminar Computerlinguistik II (Miriam Butt)
Semantic Web. XML and XML Schema. Morteza Amini. Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95
 ه عا ی Semantic Web XML and XML Schema Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95 Outline Markup Languages XML Building Blocks XML Applications Namespaces XML Schema 2 Outline Markup Languages
ه عا ی Semantic Web XML and XML Schema Morteza Amini Sharif University of Technology Fall 94-95 Outline Markup Languages XML Building Blocks XML Applications Namespaces XML Schema 2 Outline Markup Languages
Birkbeck (University of London)
 Birkbeck (University of London) MSc Examination Department of Computer Science and Information Systems Internet and Web Technologies (COIY063H7) 15 Credits Date of Examination: 3 June 2016 Duration of
Birkbeck (University of London) MSc Examination Department of Computer Science and Information Systems Internet and Web Technologies (COIY063H7) 15 Credits Date of Examination: 3 June 2016 Duration of
11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML)
 11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) Introduction Extensible Markup Language is a Meta language that describes the contents of the document. So these tags can be called as self-describing data tags. XML
11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) Introduction Extensible Markup Language is a Meta language that describes the contents of the document. So these tags can be called as self-describing data tags. XML
Introduction to XML. University of California, Santa Cruz Extension Computer and Information Technology
 Introduction to XML University of California, Santa Cruz Extension Computer and Information Technology Presented by: Bennett Smith bennettsmith@idevelopsoftware.com Introduction Answer the question What
Introduction to XML University of California, Santa Cruz Extension Computer and Information Technology Presented by: Bennett Smith bennettsmith@idevelopsoftware.com Introduction Answer the question What
XML for Java Developers G Session 2 - Sub-Topic 1 Beginning XML. Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti
 XML for Java Developers G22.3033-002 Session 2 - Sub-Topic 1 Beginning XML Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Objectives
XML for Java Developers G22.3033-002 Session 2 - Sub-Topic 1 Beginning XML Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Objectives
Understanding this structure is pretty straightforward, but nonetheless crucial to working with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
 Extra notes - Markup Languages Dr Nick Hayward HTML - DOM Intro A brief introduction to HTML's document object model, or DOM. Contents Intro What is DOM? Some useful elements DOM basics - an example References
Extra notes - Markup Languages Dr Nick Hayward HTML - DOM Intro A brief introduction to HTML's document object model, or DOM. Contents Intro What is DOM? Some useful elements DOM basics - an example References
Chapter 13: Introduction to XML. Informatics Practices Class XII. By- Deepak Bhinde
 Chapter 13: Introduction to XML Informatics Practices Class XII By- Deepak Bhinde PGT (Comp.Sc.) What is XML? extensible Markup Language (XML) is a text-based mark-up language which allows to create application
Chapter 13: Introduction to XML Informatics Practices Class XII By- Deepak Bhinde PGT (Comp.Sc.) What is XML? extensible Markup Language (XML) is a text-based mark-up language which allows to create application
Databases and Internet Applications
 Databases and Internet Applications Part 1 Chapter 7.1-7.5 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2016 1 Uniform Resource Identifiers Uniform naming schema to identify resources on the Internet A resource can
Databases and Internet Applications Part 1 Chapter 7.1-7.5 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2016 1 Uniform Resource Identifiers Uniform naming schema to identify resources on the Internet A resource can
General introduction to the TEI, markup, and XML
 General introduction to the TEI, markup, and XML TEI@Oxford July 2009 In which we are introduced Aims of Course 1. Examine the concept of markup and XML encoding 2. Provide hands-on experience in using
General introduction to the TEI, markup, and XML TEI@Oxford July 2009 In which we are introduced Aims of Course 1. Examine the concept of markup and XML encoding 2. Provide hands-on experience in using
> Semantic Web Use Cases and Case Studies
 > Semantic Web Use Cases and Case Studies Case Study: Improving Web Search using Metadata Peter Mika, Yahoo! Research, Spain November 2008 Presenting compelling search results depends critically on understanding
> Semantic Web Use Cases and Case Studies Case Study: Improving Web Search using Metadata Peter Mika, Yahoo! Research, Spain November 2008 Presenting compelling search results depends critically on understanding
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY- VIRUDHUNAGAR
 UNIT IV Part A 1. WHAT IS THE USE OF XML NAMESPACE? XML allows document authors to create custom elements. This extensibility can result in naming collisions (i.e. different elements that have the same
UNIT IV Part A 1. WHAT IS THE USE OF XML NAMESPACE? XML allows document authors to create custom elements. This extensibility can result in naming collisions (i.e. different elements that have the same
XML Applications. Prof. Andrea Omicini DEIS, Ingegneria Due Alma Mater Studiorum, Università di Bologna a Cesena
 XML Applications Prof. Andrea Omicini DEIS, Ingegneria Due Alma Mater Studiorum, Università di Bologna a Cesena Outline XHTML XML Schema XSL & XSLT Other XML Applications 2 XHTML HTML vs. XML HTML Presentation
XML Applications Prof. Andrea Omicini DEIS, Ingegneria Due Alma Mater Studiorum, Università di Bologna a Cesena Outline XHTML XML Schema XSL & XSLT Other XML Applications 2 XHTML HTML vs. XML HTML Presentation
- What we actually mean by documents (the FRBR hierarchy) - What are the components of documents
 Purpose of these slides Introduction to XML for parliamentary documents (and all other kinds of documents, actually) Prof. Fabio Vitali University of Bologna Part 1 Introduce the principal aspects of electronic
Purpose of these slides Introduction to XML for parliamentary documents (and all other kinds of documents, actually) Prof. Fabio Vitali University of Bologna Part 1 Introduce the principal aspects of electronic
XML. XML Syntax. An example of XML:
 XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. Defined in the XML 1.0 Specification
XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. Defined in the XML 1.0 Specification
7.1 Introduction. 7.1 Introduction (continued) - Problem with using SGML: - SGML is a meta-markup language
 7.1 Introduction - SGML is a meta-markup language - Developed in the early 1980s; ISO std. In 1986 - HTML was developed using SGML in the early 1990s - specifically for Web documents - Two problems with
7.1 Introduction - SGML is a meta-markup language - Developed in the early 1980s; ISO std. In 1986 - HTML was developed using SGML in the early 1990s - specifically for Web documents - Two problems with
User Interaction: XML and JSON
 User Interaction: XML and JSON Asst. Professor Donald J. Patterson INF 133 Fall 2011 1 What might a design notebook be like? Cooler What does a design notebook entry look like? HTML and XML 1989: Tim Berners-Lee
User Interaction: XML and JSON Asst. Professor Donald J. Patterson INF 133 Fall 2011 1 What might a design notebook be like? Cooler What does a design notebook entry look like? HTML and XML 1989: Tim Berners-Lee
Outline. XML vs. HTML and Well Formed vs. Valid. XML Overview. CSC309 Tutorial --XML 4. Edward Xia
 CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
CSS - Cascading Style Sheets
 CSS - Cascading Style Sheets As a W3C standard, CSS provides a powerful mechanism for defining the presentation of elements in web pages. With CSS style rules, you can instruct the web browser to render
CSS - Cascading Style Sheets As a W3C standard, CSS provides a powerful mechanism for defining the presentation of elements in web pages. With CSS style rules, you can instruct the web browser to render
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction to XML
 Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a language defined by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C, http://www.w3c.org), the body that sets the standards for the Web. You can use XML to create
Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a language defined by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C, http://www.w3c.org), the body that sets the standards for the Web. You can use XML to create
1.264 Lecture 13 XML
 1.264 Lecture 13 XML What is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is: a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) proposed recommendation for a file format to easily and cheaply distribute electronic documents
1.264 Lecture 13 XML What is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is: a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) proposed recommendation for a file format to easily and cheaply distribute electronic documents
XML (Extensible Markup Language
 XML (Extensible Markup Language XML is a markup language. XML stands for extensible Markup Language. The XML standard was created by W3C to provide an easy to use and standardized way to store self describing
XML (Extensible Markup Language XML is a markup language. XML stands for extensible Markup Language. The XML standard was created by W3C to provide an easy to use and standardized way to store self describing
Introduction Syntax and Usage XML Databases Java Tutorial XML. November 5, 2008 XML
 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial November 5, 2008 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial Outline 1 Introduction 2 Syntax and Usage Syntax Well Formed and Valid Displaying
Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial November 5, 2008 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial Outline 1 Introduction 2 Syntax and Usage Syntax Well Formed and Valid Displaying
- XML. - DTDs - XML Schema - XSLT. Web Services. - Well-formedness is a REQUIRED check on XML documents
 Purpose of this day Introduction to XML for parliamentary documents (and all other kinds of documents, actually) Prof. Fabio Vitali University of Bologna Introduce the principal aspects of electronic management
Purpose of this day Introduction to XML for parliamentary documents (and all other kinds of documents, actually) Prof. Fabio Vitali University of Bologna Introduce the principal aspects of electronic management
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES. XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
Agenda. XML Generics. XML for Java Developers G Session 1 - Main Theme Markup Language Technologies (Part I)
 XML for Java Developers G22.3033-002 Session 1 - Main Theme Markup Language Technologies (Part I) Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical
XML for Java Developers G22.3033-002 Session 1 - Main Theme Markup Language Technologies (Part I) Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical
XML Namespaces. What does it EXACTLY mean? Why Do We Need Namespaces?
 XML Namespaces What does it EXACTLY mean? Why Do We Need Namespaces? 1. To distinguish between elements and attributes from different vocabularies with different meanings. 2. To group all related elements
XML Namespaces What does it EXACTLY mean? Why Do We Need Namespaces? 1. To distinguish between elements and attributes from different vocabularies with different meanings. 2. To group all related elements
XML is a popular multi-language system, and XHTML depends on it. XML details languages
 1 XML XML is a popular multi-language system, and XHTML depends on it XML details languages XML 2 Many of the newer standards, including XHTML, are based on XML = Extensible Markup Language, so we will
1 XML XML is a popular multi-language system, and XHTML depends on it XML details languages XML 2 Many of the newer standards, including XHTML, are based on XML = Extensible Markup Language, so we will
Enabling Grids for E-sciencE ISSGC 05. XML documents. Richard Hopkins, National e-science Centre, Edinburgh June
 ISSGC 05 XML documents Richard Hopkins, National e-science Centre, Edinburgh June 2005 www.eu-egee.org Overview Goals General appreciation of XML Sufficient detail to understand WSDLs Structure Philosophy
ISSGC 05 XML documents Richard Hopkins, National e-science Centre, Edinburgh June 2005 www.eu-egee.org Overview Goals General appreciation of XML Sufficient detail to understand WSDLs Structure Philosophy
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institue of Technology
 Branch: - 6th Sem IT Year/Sem : - 3rd /2014 Subject & Subject Code : Faculty Name : - Nitin Padariya Pre Upload Date: 31/12/2013 Submission Date: 9/1/2014 [1] Explain the need of web server and web browser
Branch: - 6th Sem IT Year/Sem : - 3rd /2014 Subject & Subject Code : Faculty Name : - Nitin Padariya Pre Upload Date: 31/12/2013 Submission Date: 9/1/2014 [1] Explain the need of web server and web browser
Chapter 7: XML Namespaces
 7. XML Namespaces 7-1 Chapter 7: XML Namespaces References: Tim Bray, Dave Hollander, Andrew Layman: Namespaces in XML. W3C Recommendation, World Wide Web Consortium, Jan 14, 1999. [http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/rec-xml-names-19990114],
7. XML Namespaces 7-1 Chapter 7: XML Namespaces References: Tim Bray, Dave Hollander, Andrew Layman: Namespaces in XML. W3C Recommendation, World Wide Web Consortium, Jan 14, 1999. [http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/rec-xml-names-19990114],
XML Overview, part 1
 XML Overview, part 1 Norman Gray Revision 1.4, 2002/10/30 XML Overview, part 1 p.1/28 Contents The who, what and why XML Syntax Programming with XML Other topics The future http://www.astro.gla.ac.uk/users/norman/docs/
XML Overview, part 1 Norman Gray Revision 1.4, 2002/10/30 XML Overview, part 1 p.1/28 Contents The who, what and why XML Syntax Programming with XML Other topics The future http://www.astro.gla.ac.uk/users/norman/docs/
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 12 (Wrap-up) http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 12 (Wrap-up) http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 9. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 9 Dr Nick Hayward DEV Week assessment Course total = 25% project outline and introduction developed using a chosen markup language consider and
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 9 Dr Nick Hayward DEV Week assessment Course total = 25% project outline and introduction developed using a chosen markup language consider and
