XML Information Set. Working Draft of May 17, 1999
|
|
|
- Avis Doyle
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 XML Information Set Working Draft of May 17, 1999 This version: Latest version: Editors: John Cowan David Megginson Copyright 1999 W3C (MIT, INRIA, Keio), All Rights Reserved. W3C liability, trademark, document use and software licensing rules apply. Abstract This specification describes an abstract data set containing the information available from an XML document. Status of this Document This is a W3C Working Draft for review by members of the W3C and other interested parties in the general public. Because it is the first public release, it contains many queries and open issues, all of which are clearly indicated in the document. While it is a Working Draft or a Proposed Recommendation it is subject to change. It may be updated, replaced or rendered obsolete by other W3C documents at any time. It is inappropriate to use W3C Working Drafts as reference material or to cite them as other than "work in progress." This work is part of the W3C XML Activity. Please review and send comments to www-xml-infoset-comments@w3.org, which is a publicly-archived mailing list.
2 Contents Introduction Information Items Namespace Processing Conformance Processor Limitations XML 1.0 Reporting Requirements What is not in the Information Set Other Open Issues References 1. Introduction This document specifies an abstract data set called the XML information set (Infoset), a description of the information available in a well-formed XML document [XML]. An XML document's information set consists of two or more information items (the information set for any well-formed XML document will contain at least the document information item and one element information item). An information item is an abstract representation of some component of an XML document: each information item has a set of associated properties, some of which are required to be available through the information set, and some of which are optionally available. The XML information set does not require or favor a specific interface or class of interfaces. This specification presents the information set as a tree for the sake of clarity and simplicity, but there is no requirement that the XML information set be made available through a tree structure; other types of interfaces, including (but not limited to) event-based and query-based interfaces are also capable of providing information conforming to the information set. As long as the information in the information set is made available to XML applications in one way or another, the requirements of this document are satisfied. Note: In this document, the words "must", "should", and "may" assume the meanings specified in RFC 2119 [RFC2119], except that the words do not appear in upper case. Note: To the best of the editors' knowledge and belief, the information set scheme described in this document satisfies the requirements of the XPointer-Information Set Liaison Statement [XPointer-Liason].
3 Note: To the best of the editors' knowledge and belief, the interface specified by the Document Object Model, level one core Recommendation [DOM] conforms to the XML Information Set as currently specified. 2. Information Items The XML information set can contain eleven different types of information items (in the following list, read "required" as "required if present in the original XML document"; see also Processor Limitations, below): 1. a document information item (required) 2. element information items (required) 3. attribute information items (required) 4. processing instruction information items (required) 5. character information items (required) 6. reference to unknown entity information items (required) 7. comment information items (optional) 8. a document type declaration information item (optional) 9. entity information items (required for unparsed entities, optional for others) 10. notation information items (required) 11. attribute declaration information items (optional) 2.1. The Document Information Item XML Definition: document (Section 2, Documents) XML Syntax: [1] Document (Section 2.1, Well-Formed XML Documents) There is always one document information item in the information set, and all other information items are related to the document information item, either directly or indirectly Document: Required Properties The document information item must have the following properties available in some form: 1. Query: Should comments and the document type declaration be required rather than optional? An ordered list of child information items, in the original document order. The list must contain exactly one element information item, together with one processing instruction information item for each processing instruction preceding the document element (either
4 2. 3. in the document entity or in a lower-level entity) or following the document entity; the list may optionally contain other information items as well (see below). An unordered set of notation information items, one for each notation declaration that the XML processor has read. An unordered set of entity information items, one for each unparsed entity (NDATA) declaration that the XML processor has read Document: Optional Properties The document information item may also have the following properties available in some form: 4. One comment information item for each comment outside the document element, added to the ordered list of child information items. The relative position of each comment information item in the list must reflect its position in the original document. Comments within the internal or external DTD subset are considered to follow the document type declaration information item and to precede the document element. 5. Exactly one document type declaration information item, added to the ordered list of child information items. The relative position of the document type declaration information item in the list must reflect its position in the original document. 6. One entity information item for each parsed entity declaration read by the processor, added to the unordered set of entities. There can also be an entity information item for the document entity and for the external DTD subset. 7. An unordered set of attribute declaration information items, one for each attribute declaration read by the processor Element Information Items XML Definition: element (Section 3, Logical Structures) XML Syntax: [39] Element (Section 3, Logical Structures) There is one element information item for each element appearing in the XML document. Exactly one of the element information items correspond to the document element (the root of the element tree), and all other element information items are contained within the document element, either directly or indirectly Elements: Required Properties An element information item must have the following properties available in some form: Query: Should comments be required rather than optional? Query: When Namespace processing is being performed, should the original prefix also be available?
5 Query: Should attribute starting with "xmlns" be included even when performing Namespace processing? The URI part, if any, of the element's name. If Namespace processing is not being performed, the URI part will always be null. The local part of the element's name. If Namespace processing is being performed, the prefix and colon (if any) will have been removed from the beginning of the name; if Namespace processing is not being performed, the local part will contain the entire name from the original document, including any colons. An ordered list of element, processing instruction, reference to unknown entity and character information items, one for each element, processing instruction, reference to an unknown entity, and character appearing immediately within the current element, in the original document order. If the element is empty, this list will have zero members. An unordered set of attribute information items, one for each of the attributes (specified or defaulted) for this element. If Namespace processing is being performed, attributes with names beginning with xmlns will be excluded from the set; if Namespace processing is not being performed, attribute with names beginning with xmlns are included in the set. If there are no non-#implied attributes specified or defaulted for the element, this set will be empty Elements: Optional Properties An element information item may also have the following properties available in some form: 5. One comment information item for each comment appearing immediately within the current element, added to the ordered list of elements, processing instructions, references to unknown entities, and characters appearing immediately within the current element. The relative position of each comment information item in the list must reflect its position in the original document. 6. A reference to the entity information item for the entity in which this element begins and ends Attribute Information Items XML Definition: attribute (Section 3.1, Start-Tags, End-Tags, and Empty-Element Tags) XML Syntax: [41] Attribute (Section 3.1, Start-Tags, End-Tags, and Empty-Element Tags) There is one attribute information item for each attribute (specified or defaulted) for each element in the document instance; when Namespace processing is being performed, attributes with names beginning with "xmlns" will not have corresponding information items.
6 Query: Should xml:lang and xml:space also be excluded and modeled as character properties instead? Attributes declared in the DTD with a default value of #IMPLIED and not specified in the element's start tag are not represented by attribute information items Attributes: Required Properties An attribute information item must have the following properties available in some form: Query: When Namespace processing is being performed, should the original prefix also be available? The URI part, if any, of the attribute's name. If Namespace processing is not being performed, the URI part will always be null. The local part of the attribute's name. If Namespace processing is being performed, the prefix and colon (if any) will have been removed from the beginning of the name; if Namespace processing is not being performed, the local part will contain the entire name including any colons. An ordered list of character information items, one for each character appearing in the normalized attribute value Attributes: Optional Properties In addition, for each attribute information item, the following property may optionally be available in some form: 4. A reference to the attribute declaration information item corresponding to this attribute Processing Instruction Information Items XML Definition: processing instruction (Section 2.6, Processing Instructions) XML Syntax: [16] PI (Section 2.6, Processing Instructions) There is one processing instruction information item for every processing instruction in the document. The XML declaration and text declarations for external parsed entities are not considered processing instructions Processing Instructions: Required Properties A processing instruction information item must have the following properties available in some form: 1. The target part of the processing instruction's content (an XML name). 2. The content of the processing instruction, excluding the target and any whitespace immediately following it. The content may be the empty string.
7 Processing Instructions: Optional Properties A processing instruction information item may also have the following properties available in some form: 3. A reference to the entity information item for the entity in which this processing instruction appears Reference to Unknown Entity Information Items XML Definition: Section 4.4.3, Included If Validating There is one reference to unknown entity information item for each reference to an entity not included by a non-validating XML processor, either because the processor has not read the declaration or because the processor does not include external parsed entities. A validating XML processor will never generate reference to unknown entity information items for a valid XML document Reference to Unknown Entity: Required Properties A reference to unknown entity information item must have the following information available in some form: 1. The name of the entity referenced Reference to Unknown Entity: Optional Properties A reference to unknown entity information item may also have the following properties available in some form: 2. A reference to the entity information item for an external parsed entity, if the processor has read the declaration. 3. A reference to the entity information item for the entity in which this reference appears Character Information Items XML Definition: characters (Section 2.2, Characters) XML Syntax: [2] Char (Section 2.2, Characters) There is one character information item for each non-markup character that appears within the document element, either literally, as a character reference, or within a CDATA section. There is also one character information item for each character that appears in a normalized attribute value.
8 Note, however, that a CR (#xd) character that is followed by a LF (#xa) character is not represented by any information item. Furthermore, a CR character that is not followed by a LF character is treated as a LF character. This rule does not apply to CR characters created by character references such as or. Each character is a logically-separate information item, but processing software is free to chunk characters into larger groups as necessary Characters: Required Properties A character information item must have the following properties available in some form: 1. The ISO character code (in the range 0 to hex 0010FFFF) of the character. 2. A flag indicating whether the character is whitespace appearing within element content (see [XML], 2.10 "White Space Handling"). Validating processors are required by XML 1.0 to provide this information; non-validating processors may always set this flag to false Characters: Optional Properties A character information item may also have the following properties available in some form: Query: Should the inherited values of xml:lang and xml:space also be modeled as optional character properties? An indication of whether the character was included literally, as a character reference, as part of a CDATA section, or through one of the predefined XML entities. A reference to the entity information item for the entity in which this character appears Comment Information Items XML Definition: comment (Section 2.5, Comments) XML Syntax: [15] Comment (Section 2.5, Comments) Query: Should comment information items be required? The optional comment information item corresponds to a single XML comment in the original document Comments: Required Properties Query: Should the contents of the comment be optional, so that only its position may be reported? If a comment information item is included, the following properties must be available: 1. The content of the comment.
9 Comments: Optional Properties A comment information item may also have the following properties available in some form: 1. A reference to the entity information item for the entity in which this comment appears The Document Type Declaration Information Item XML Definition: document type declaration (section 2.8, Prolog and Document Type Declaration) XML Syntax: [28] doctypedecl (section 2.8, Prolog and Document Type Declaration) If the XML document has a document type declaration, then the information set may optionally contain a single document type declaration information item Document Type Declaration: Optional Properties A document type declaration information item may have the following properties available in some form: 1. A reference to the entity information item for the external DTD subset. The public and system identifiers for the external DTD subset are available through this information item Entity Information Items XML Definition: entity (section 4, Physical Structures) XML Syntax: [70] EntityDecl (section 4.2, Entity Declarations) Entity information items are optional, except for information items representing unparsed external (NDATA) entities, which are required to appear in the information set. There is at most one entity information item for each entity, internal or external, declared in the DTD: when the same entity is declared more than once, only the first declaration is used. There is also at most one entity information item for the document instance, and at most one for the DTD external subset (if there is one). Query: Is it confusing to represent the external DTD subset with an entity information item? (The XML Recommendation treats the external subset essentially as an external parameter entity, except that it does not have an entity name.) Entities: Required Properties
10 The entity information item, if included, must have the following information available in some form: 1. An indication of the type of the entity (internal parameter entity, external parameter entity, internal general entity, external general entity, unparsed entity, document entity, or external DTD subset). 2. The name of the entity. If the information item represents the document entity or the external DTD subset, the name is null. 3. The system identifier of the entity. If the information item represents an internal entity, the system identifier is always null, and if it represents the document entity, the value may be null; otherwise, it must have a non-null value. 4. The public identifier of the entity, if one is available. For internal entities, the value is always null. 5. A reference to the notation information item associated with the entity, if the entity is an unparsed (NDATA) entity. For entities other than unparsed entities, the value is always null Entities: Optional Properties An entity information item may also have the following information available in some form: Query: Should the information from the XML declaration or text declaration also be optionally available? The text of the entity, if it is an internal entity. A reference to the entity information item for the entity in which the entity was declared Notation Information Items XML Definition: notation (section 4.7, Notation Declarations) XML Syntax: [82] NotationDecl (section 4.7, Notation Declarations) There is one notation information item for each notation declared in the DTD Notations: Required Properties A notation information item must have the following properties available: 1. The name of the notation. 2. The system identifier of the notation, if one was specified. 3. The public identifier of the notation, if one was specified Notations: Optional Properties
11 4. A reference to the entity information item for the entity in which the notation was declared Attribute Declaration Information Items XML Definition: attribute declaration (section 3.3, Attribute-List Declarations) XML Syntax: [53] AttDef (section 3.3, Attribute-List Declarations) Attribute declaration information items are an optional part of the information set. There is at most one attribute declaration information item for each attribute declared in an ATTLIST declaration within the DTD: if an attribute is declared more than once for the same element, only the first declaration is used Attribute Declarations: Required Properties An attribute declaration information item, if present, must have the following properties available in some form: 1. The name of the attribute as declared, including any Namespace prefix. 2. The name of the element type for which the attribute was declared. 3. The default value of the attribute. If the attribute was declared with the default value #IMPLIED or #REQUIRED, this value will be null Attribute Declarations: Optional Properties If an attribute declaration information item is provided for an XML document, the following properties may be available in some form: Query: Should any of this information be required? The XML type of the attribute (ID, IDREF, IDREFS, NMTOKEN, NMTOKENS, ENTITY, ENTITIES, NOTATION, or ENUMERATION). A list of allowed values for the attribute, if it has the type NOTATION or ENUMERATION. The default declaration type of the attribute (REQUIRED, IMPLIED, FIXED, or DEFAULTED). A reference to the entity information item for the entity in which the attribute was declared. 3. Namespace Processing Namespace processing [Namespaces] represents a virtual transformation of an XML document, where elements and attributes acquire new, two-part names based on declarations made with
12 specially-named attributes. As a result, for any single XML document there are two possible instantiations of the XML Information Set: one without Namespace processing, and one with. Query: Is it best for the Information Set to explicitly allow for a document without Namespace processing? The XML Information Set provides a single model that is capable of describing a document either without or with Namespace processing, at user option: element and attribute names have both URI parts and local parts, and the URI parts will simply be null when Namespace processing is not in force. Consider the following example: <?xml version="1.0"?> <msg:message dc:date=" " xmlns:dc=" xmlns:msg=" >Phone home!</msg:message> Without Namespace processing, the Information Set for this document will contain the following items in some form (for simplicity's sake, some properties have been omitted): A Document information item. An Element information item with the URI part null and the local part "msg:message". An Attribute information item with the URI part null and the local part "dc:date". An Attribute information item with the URI part null and the local part "xmlns:dc". An Attribute information item with the URI part null and the local part "xmlns:msg". Eleven Character information items for the character data, and an additional 68 Character information items for the attribute values. With Namespace processing, the Information Set for the same XML document will contain the following items in some form: A Document information item. An Element information item with the URI part " and the local part "message". An Attribute information item with the URI part " and the local part "date". Eleven Character information items for the character data, and an additional 8 Character information items for the attribute value. If an XML document contains no names that include colons and no attribute names that begin with the letters "xmlns", then the XML Information Set will be instantiated identically with or
13 without Namespace processing. 4. Conformance An XML processor conforms to the XML Information Set if it provides all the required information items and all required associated information. For instance, attributes are required information items, and an XML processor that does not report the existence of attributes, as well as their names (and URI parts if Namespace processing is being performed) and values, does not conform to the XML Information Set. Some information items are optional, and some required information items have optional information associated with them. If a processor is required to or chooses to report an information item, then it is required to supply at least what the XML Information Set defines for that item in order to conform. For instance, if a processor chooses to supply entity information items, which are optional, then it is required to supply names for the entities, since the XML Information Set specifies that entity information items are required to make knowledge available about entity names. However, since entity information items are optional, a processor which does not supply them at all also conforms to the XML Information Set. XML Processors may optionally provide additional information not found in the XML Information Set; for instance, the XML Information Set excludes whitespace that occurs between attributes from the information set, but an XML Processor that provides this information conforms as long as it provides the information that is required by the XML Information Set. 5. Processor Limitations The information set for an XML document can contain only information that a processor has actually read. The XML 1.0 Recommendation [XML] explicitly allows non-validating XML processors to omit parsing the external DTD subset and external entities (both parsed general entities and parameter entities). As a result, it is possible that a non-validating processor will omit reading attribute and entity declarations or actual markup that will affect the quantity and quality of information included in the information set. Wherever this specification designates information as required, it is important to note that the information is required only if the processor actually reads the part of the XML document in which the information appears. Validating processors must report all required information; non-validating processors may omit information that appears outside of the top-level document entity (either in the external DTD subset or in an external text entity) if they do not read the other entities.
14 6. XML 1.0 Reporting Requirements Although the XML 1.0 Recommendation [XML] is primarily concerned with XML syntax, it also includes some specific reporting requirements for processors. The reporting requirements include errors, which are outside the scope of this specification, and document information; all of the XML 1.0 requirements for document information reporting have been integrated into the XML information set specification (numbers in parentheses refer to sections of the Recommendation): 1. An XML processor must always provide all characters in a document that are not part of markup to the application (2.10). We have interpreted this requirement to refer only to characters within the document element. 2. A validating XML processor must inform the application which of the character data in a document is whitespace appearing within element content (2.10). 3. An XML processor must pass a single LF character in place of CR or CR-LF characters appearing in its input. 4. An XML processor must normalize the value of attributes according to the rules in clause 3.3 before passing them to the application. This implies that the value of attributes after normalization are passed to the application (3.3). 5. An XML processor must pass the names and external identifiers (system identifiers, public identifiers or both) of declared notations to the application (4.7). 6. When the name of an unparsed entity appears as the explicit or default value of an ENTITY or ENTITIES attribute, an XML processor must provide the names, system identifiers, and (if present) public identifiers of both the entity and its notation to the application (4.6, 4.7). 7. An XML processor must pass processing instructions to the application. (2.6) 8. An XML processor (necessarily a non-validating one) that does not include the replacement text of an external parsed entity in place of an entity reference must notify the application that it recognized but did not read the entity (4.4.3). 9. A validating XML processor must include the replacement text of an entity in place of an entity reference. (5.2) 10. A validating XML processor must supply the default value of attributes declared in the DTD for a given element type but not appearing in the element's start tag (5.2). 7. What is not in the Information Set The following information is not represented in the current version of the XML Information Set: Query: Should any of this information be included?
15 The information in the XML declaration and text declarations. Element content models from ELEMENT declarations. The grouping and ordering of attribute declarations in ATTLIST declarations. Whitespace outside the document element. Whitespace within start-tags (other than significant whitespace in attribute values) and end-tags. The difference between CR, CR-LF, and LF line termination. The unnormalized form of attribute values (see Attribute-Value Normalization [XML]). The order of attributes within a start-tag. The order of declarations within the DTD. The boundaries of conditional sections. Any ignored declarations, including those within an IGNORE conditional section, as well as entity and attribute declarations ignored because previous entity declarations overrode them. Furthermore, the XML Infoset does not provide any method of assigning a single series of numbers to all child nodes of an element or of the document that is guaranteed to be reliable regardless of the underlying XML processor. Although such a method would be desirable, it is considered unachievable, due to the difficulties produced by references to unknown entities and optional information items. In other words, there is no reliable way to specify something like "the second child of this element" without restricting both the type of processor and the types of children being counted. For more information, see the section on processor limitations. 8. Other Open Issues [3a, 3c] Links are not currently represented in the information set. Should they be? In particular, should ID-IDREF connections be represented? [3b] Should there be a specification of partial information sets? [7] How do we interoperate with DOM? [22] Should the Infoset model different degrees of ordering for different application domains? [18] Are there remaining problems with hierarchically-scoped information? Should this document specify what information (if any) a validating processor must make available for a well-formed but invalid document?
16 9. References DOM Document Object Model (DOM) Level 1 Specification, eds. Vidur Apparao, Steve Byrne, Mike Champion, et alii. 1 October Available at Namespaces Namespaces in XML, eds. Tim Bray, Dave Hollander, and Andrew Layman. 14 January Available at RFC2119 Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels, ed. S. Bradner. March Available at XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0, eds. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, and Michael Sperberg-McQueen. 10 February Available at XPointer-Liason XPointer-Information Set Liason Statement, ed. Steven J. DeRose. 24 February Available at
XML: Introduction. !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... Directive... 9:11
 !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
!important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
Chapter 1: Getting Started. You will learn:
 Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
2009 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. XML Syntax
 Data-centric XML XML Syntax 2 What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language Derived from SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) Two goals: large-scale electronic publishing exchange of wide variety of data
Data-centric XML XML Syntax 2 What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language Derived from SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) Two goals: large-scale electronic publishing exchange of wide variety of data
Chapter 7: XML Namespaces
 7. XML Namespaces 7-1 Chapter 7: XML Namespaces References: Tim Bray, Dave Hollander, Andrew Layman: Namespaces in XML. W3C Recommendation, World Wide Web Consortium, Jan 14, 1999. [http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/rec-xml-names-19990114],
7. XML Namespaces 7-1 Chapter 7: XML Namespaces References: Tim Bray, Dave Hollander, Andrew Layman: Namespaces in XML. W3C Recommendation, World Wide Web Consortium, Jan 14, 1999. [http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/rec-xml-names-19990114],
[MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document
![[MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document [MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document](/thumbs/76/73543375.jpg) [MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft
[MS-XML]: Microsoft Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Fourth Edition Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft
Tutorial 2: Validating Documents with DTDs
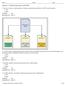 1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
Network Working Group Internet-Draft August 2005 Expires: February 2, Atom Link No Follow draft-snell-atompub-feed-nofollow-03.
 Network Working Group J. Snell Internet-Draft August 2005 Expires: February 2, 2006 Status of this Memo Atom Link No Follow draft-snell-atompub-feed-nofollow-03.txt By submitting this Internet-Draft, each
Network Working Group J. Snell Internet-Draft August 2005 Expires: February 2, 2006 Status of this Memo Atom Link No Follow draft-snell-atompub-feed-nofollow-03.txt By submitting this Internet-Draft, each
Network Working Group Internet-Draft October 27, 2007 Intended status: Experimental Expires: April 29, 2008
 Network Working Group J. Snell Internet-Draft October 27, 2007 Intended status: Experimental Expires: April 29, 2008 Status of this Memo Atom Publishing Protocol Feature Discovery draft-snell-atompub-feature-12.txt
Network Working Group J. Snell Internet-Draft October 27, 2007 Intended status: Experimental Expires: April 29, 2008 Status of this Memo Atom Publishing Protocol Feature Discovery draft-snell-atompub-feature-12.txt
Request for Comments: 2803 Category: Informational IBM April Digest Values for DOM (DOMHASH) Status of this Memo
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 2803 Category: Informational H. Maruyama K. Tamura N. Uramoto IBM April 2000 Digest Values for DOM (DOMHASH) Status of this Memo This memo provides information
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 2803 Category: Informational H. Maruyama K. Tamura N. Uramoto IBM April 2000 Digest Values for DOM (DOMHASH) Status of this Memo This memo provides information
Microsoft XML Namespaces Standards Support Document
 [MS-XMLNS]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
[MS-XMLNS]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
Microsoft XML Namespaces Standards Support Document
 [MS-XMLNS]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
[MS-XMLNS]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
XML Security Derived Keys
 http://www.w3.org/tr/2009/wd-xmlsec-deriv... 1 3/28/2009 11:33 AM XML Security Derived Keys W3C Working Draft 26 February 2009 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2009/wd-xmlsec-derivedkeys-20090226/ Latest
http://www.w3.org/tr/2009/wd-xmlsec-deriv... 1 3/28/2009 11:33 AM XML Security Derived Keys W3C Working Draft 26 February 2009 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2009/wd-xmlsec-derivedkeys-20090226/ Latest
Network Working Group Internet-Draft August 2005 Expires: February 2, Atom Link No Follow draft-snell-atompub-feed-nofollow-00.
 Network Working Group J. Snell Internet-Draft August 2005 Expires: February 2, 2006 Status of this Memo Atom Link No Follow draft-snell-atompub-feed-nofollow-00.txt By submitting this Internet-Draft, each
Network Working Group J. Snell Internet-Draft August 2005 Expires: February 2, 2006 Status of this Memo Atom Link No Follow draft-snell-atompub-feed-nofollow-00.txt By submitting this Internet-Draft, each
XML ELECTRONIC SIGNATURES
 XML ELECTRONIC SIGNATURES Application according to the international standard XML Signature Syntax and Processing DI Gregor Karlinger Graz University of Technology Institute for Applied Information Processing
XML ELECTRONIC SIGNATURES Application according to the international standard XML Signature Syntax and Processing DI Gregor Karlinger Graz University of Technology Institute for Applied Information Processing
Network Working Group Internet-Draft January 25, 2006 Expires: July 29, Feed Rank draft-snell-atompub-feed-index-05.txt. Status of this Memo
 Network Working Group J. Snell Internet-Draft January 25, 2006 Expires: July 29, 2006 Status of this Memo Feed Rank draft-snell-atompub-feed-index-05.txt By submitting this Internet-Draft, each author
Network Working Group J. Snell Internet-Draft January 25, 2006 Expires: July 29, 2006 Status of this Memo Feed Rank draft-snell-atompub-feed-index-05.txt By submitting this Internet-Draft, each author
ISO/IEC INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 29500-3 Fourth edition 2015-07-01 Information technology Document description and processing languages Office Open XML File Formats Part 3: Markup Compatibility and Extensibility
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 29500-3 Fourth edition 2015-07-01 Information technology Document description and processing languages Office Open XML File Formats Part 3: Markup Compatibility and Extensibility
CSC Web Technologies, Spring Web Data Exchange Formats
 CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 4913 Category: Experimental July 2007
 Network Working Group S. Legg Request for Comments: 4913 eb2bcom Category: Experimental July 2007 Status of This Memo Abstract Syntax Notation X (ASN.X) Representation of Encoding Instructions for the
Network Working Group S. Legg Request for Comments: 4913 eb2bcom Category: Experimental July 2007 Status of This Memo Abstract Syntax Notation X (ASN.X) Representation of Encoding Instructions for the
[MS-XHTML]: Internet Explorer Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) Standards Support Document
![[MS-XHTML]: Internet Explorer Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) Standards Support Document [MS-XHTML]: Internet Explorer Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) Standards Support Document](/thumbs/74/71246538.jpg) [MS-XHTML]: Internet Explorer Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation.
[MS-XHTML]: Internet Explorer Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation.
Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2
 Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2 Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2 W3C Working Draft 24 January 2003 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2003/wd-wsdl12-20030124 Latest
Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2 Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2 W3C Working Draft 24 January 2003 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2003/wd-wsdl12-20030124 Latest
Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 (Second Edition) W3C Recommendation 6 October Abstract. Status of this Document
 Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 (Second Edition) W3C Recommendation 6 October 2000 This version: (XHTML, XML, PDF, XHTML review version with color-coded revision indicators) Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/rec-xml
Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 (Second Edition) W3C Recommendation 6 October 2000 This version: (XHTML, XML, PDF, XHTML review version with color-coded revision indicators) Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/rec-xml
2006 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. Document Types
 Data-centric XML Document Types Purpose 2006 Martin v. Löwis Document Type Definitions define a vocabulary set of allowed element names set of attributes per element name data type given for each attribute
Data-centric XML Document Types Purpose 2006 Martin v. Löwis Document Type Definitions define a vocabulary set of allowed element names set of attributes per element name data type given for each attribute
XML Query Requirements
 XML Query Requirements Page 1 of 10 XML Query Requirements W3C Working Draft 15 February 2001 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2001/wd-xmlquery-req-20010215 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xmlquery-req
XML Query Requirements Page 1 of 10 XML Query Requirements W3C Working Draft 15 February 2001 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2001/wd-xmlquery-req-20010215 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xmlquery-req
An updated events syntax for XML-based markup languages
 XHTML Events Module XHTML Events Module An updated events syntax for XML-based markup languages W3C Working Draft 21 December 1999 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/wd-xhtml-events-19991221 (Postscript
XHTML Events Module XHTML Events Module An updated events syntax for XML-based markup languages W3C Working Draft 21 December 1999 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/wd-xhtml-events-19991221 (Postscript
SDPL : XML Basics 2. SDPL : XML Basics 1. SDPL : XML Basics 4. SDPL : XML Basics 3. SDPL : XML Basics 5
 2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
XPath Expression Syntax
 XPath Expression Syntax SAXON home page Contents Introduction Constants Variable References Parentheses and operator precedence String Expressions Boolean Expressions Numeric Expressions NodeSet expressions
XPath Expression Syntax SAXON home page Contents Introduction Constants Variable References Parentheses and operator precedence String Expressions Boolean Expressions Numeric Expressions NodeSet expressions
Overview. Introduction. Introduction XML XML. Lecture 16 Introduction to XML. Boriana Koleva Room: C54
 Overview Lecture 16 Introduction to XML Boriana Koleva Room: C54 Email: bnk@cs.nott.ac.uk Introduction The Syntax of XML XML Document Structure Document Type Definitions Introduction Introduction SGML
Overview Lecture 16 Introduction to XML Boriana Koleva Room: C54 Email: bnk@cs.nott.ac.uk Introduction The Syntax of XML XML Document Structure Document Type Definitions Introduction Introduction SGML
from XMLAttributes Author: Jan-Eike Michels Source: U.S.A. Status: SQL:2003 TC and SQL:200x WD change proposal Date: March 8, 2004
 Title: Removing Attribute Value Normalization from Author: Jan-Eike Michels Source: U.S.A. Status: SQL:2003 TC and SQL:200x WD change proposal Date: March 8, 2004 Abstract This paper points out an inconsistency
Title: Removing Attribute Value Normalization from Author: Jan-Eike Michels Source: U.S.A. Status: SQL:2003 TC and SQL:200x WD change proposal Date: March 8, 2004 Abstract This paper points out an inconsistency
[MS-XMLSS]: Microsoft XML Schema (Part 1: Structures) Standards Support Document
![[MS-XMLSS]: Microsoft XML Schema (Part 1: Structures) Standards Support Document [MS-XMLSS]: Microsoft XML Schema (Part 1: Structures) Standards Support Document](/thumbs/75/72488038.jpg) [MS-XMLSS]: Microsoft XML Schema (Part 1: Structures) Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open
[MS-XMLSS]: Microsoft XML Schema (Part 1: Structures) Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open
The concept of DTD. DTD(Document Type Definition) Why we need DTD
 Contents Topics The concept of DTD Why we need DTD The basic grammar of DTD The practice which apply DTD in XML document How to write DTD for valid XML document The concept of DTD DTD(Document Type Definition)
Contents Topics The concept of DTD Why we need DTD The basic grammar of DTD The practice which apply DTD in XML document How to write DTD for valid XML document The concept of DTD DTD(Document Type Definition)
Copyright 2007 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe. Slide 27-1
 Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Network Working Group. Category: Informational Betrusted, Inc. J. Reagle W3C December 2003
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 3653 Category: Informational J. Boyer PureEdge Solutions M. Hughes Betrusted, Inc. J. Reagle W3C December 2003 XML-Signature XPath Filter 2.0 Status of this
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 3653 Category: Informational J. Boyer PureEdge Solutions M. Hughes Betrusted, Inc. J. Reagle W3C December 2003 XML-Signature XPath Filter 2.0 Status of this
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 ISO/IEC 29341-18-12 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD Edition 1.0 2011-08 colour inside Information technology UPnP device architecture Part 18-12: Remote Access Device Control Protocol Remote Access Discovery Agent
ISO/IEC 29341-18-12 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD Edition 1.0 2011-08 colour inside Information technology UPnP device architecture Part 18-12: Remote Access Device Control Protocol Remote Access Discovery Agent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Representing Web Data: XML
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
Introduction to XML. XML: basic elements
 Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES. XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
ISO/IEC TR TECHNICAL REPORT
 TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/IEC TR 22250-1 First edition 2002-02-15 Information technology Document description and processing languages Regular Language Description for XML (RELAX) Part 1: RELAX Core Technologies
TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/IEC TR 22250-1 First edition 2002-02-15 Information technology Document description and processing languages Regular Language Description for XML (RELAX) Part 1: RELAX Core Technologies
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML. Objectives. Duration. Audience. Pre-Requisites
 XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda
 NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2
 Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2 Part 3: Bindings Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2 Part 3: Bindings W3C Working Draft 11 June 2003 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2003/wd-wsdl12-bindings-20030611
Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2 Part 3: Bindings Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 1.2 Part 3: Bindings W3C Working Draft 11 June 2003 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2003/wd-wsdl12-bindings-20030611
Chapter 1: XML Syntax
 1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
[MS-TTML]: Internet Explorer Timed Text Markup Language (TTML) 1.0 Standards Support Documentation
![[MS-TTML]: Internet Explorer Timed Text Markup Language (TTML) 1.0 Standards Support Documentation [MS-TTML]: Internet Explorer Timed Text Markup Language (TTML) 1.0 Standards Support Documentation](/thumbs/74/71246483.jpg) [MS-TTML]: Internet Explorer Timed Text Markup Language (TTML) 1.0 Standards Support Documentation Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft
[MS-TTML]: Internet Explorer Timed Text Markup Language (TTML) 1.0 Standards Support Documentation Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft
JSON-LD 1.0 Processing Algorithms and API
 This document was produced by a group operating under the 5 February 2004 W3C Patent Policy. W3C maintains a public list of any patent disclosures made in connection with the deliverables of the group;
This document was produced by a group operating under the 5 February 2004 W3C Patent Policy. W3C maintains a public list of any patent disclosures made in connection with the deliverables of the group;
Foreword... v Introduction... vi. 1 Scope Normative references Terms and definitions Extensible Datatypes schema overview...
 Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 Extensible Datatypes schema overview... 2 5 Common constructs... 3 5.1 Common types...
Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 Extensible Datatypes schema overview... 2 5 Common constructs... 3 5.1 Common types...
Chapter 1: XML Syntax
 1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
Cache Operation. Version 31-Jul Wireless Application Protocol WAP-175-CacheOp a
 Cache Operation Version 31-Jul-2001 Wireless Application Protocol WAP-175-CacheOp-20010731-a A list of errata and updates to this document is available from the WAP Forum Web site, http://www.wapforum.org/,
Cache Operation Version 31-Jul-2001 Wireless Application Protocol WAP-175-CacheOp-20010731-a A list of errata and updates to this document is available from the WAP Forum Web site, http://www.wapforum.org/,
Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML
 Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML Abstract John W. Shipman 2013-08-24 12:16 Describes the Document Type Definition notation for describing the schema of an SGML or XML document type.
Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML Abstract John W. Shipman 2013-08-24 12:16 Describes the Document Type Definition notation for describing the schema of an SGML or XML document type.
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013
 Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
[MS-PICSL]: Internet Explorer PICS Label Distribution and Syntax Standards Support Document
![[MS-PICSL]: Internet Explorer PICS Label Distribution and Syntax Standards Support Document [MS-PICSL]: Internet Explorer PICS Label Distribution and Syntax Standards Support Document](/thumbs/96/129029370.jpg) [MS-PICSL]: Internet Explorer PICS Label Distribution and Syntax Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft
[MS-PICSL]: Internet Explorer PICS Label Distribution and Syntax Standards Support Document Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft
XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps
 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps Erik Wilde 16.7.2001 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps 1 Outline what is XML? a syntax (not a data model!) what is the data model behind XML? XML Information Set
XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps Erik Wilde 16.7.2001 XML Metadata Standards and Topic Maps 1 Outline what is XML? a syntax (not a data model!) what is the data model behind XML? XML Information Set
Filter Query Language
 1 2 3 4 Document Number: DSP0212 Date: 2012-12-13 Version: 1.0.0 5 6 7 8 Document Type: Specification Document Status: DMTF Standard Document Language: en-us 9 DSP0212 10 11 Copyright notice Copyright
1 2 3 4 Document Number: DSP0212 Date: 2012-12-13 Version: 1.0.0 5 6 7 8 Document Type: Specification Document Status: DMTF Standard Document Language: en-us 9 DSP0212 10 11 Copyright notice Copyright
WAP Binary XML Content Format Document id WAP-192-WBXML Version 1.3 Approved Version 15 th May 2000
 WAP Binary XML Content Format Document id WAP-192-WBXML-20000515 Version 1.3 Approved Version 15 th May 2000 This Document Document Identifier 192 Date 15 th May 2000 Subject: Version 1.3 WBXML Wireless
WAP Binary XML Content Format Document id WAP-192-WBXML-20000515 Version 1.3 Approved Version 15 th May 2000 This Document Document Identifier 192 Date 15 th May 2000 Subject: Version 1.3 WBXML Wireless
extensible Markup Language
 extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
XML Query (XQuery) Requirements
 Página 1 de 15 XML Query (XQuery) Requirements W3C Working Draft 12 November 2003 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2003/wd-xquery-requirements-20031112 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xquery-requirements
Página 1 de 15 XML Query (XQuery) Requirements W3C Working Draft 12 November 2003 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2003/wd-xquery-requirements-20031112 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xquery-requirements
Introduction to XML. Chapter 133
 Chapter 133 Introduction to XML A. Multiple choice questions: 1. Attributes in XML should be enclosed within. a. single quotes b. double quotes c. both a and b d. none of these c. both a and b 2. Which
Chapter 133 Introduction to XML A. Multiple choice questions: 1. Attributes in XML should be enclosed within. a. single quotes b. double quotes c. both a and b d. none of these c. both a and b 2. Which
Table of Checkpoints for User Agent Accessibility Guidelines 1.0
 Table of Checkpoints for User Agent Accessibility Guidelines 1.0 3 October 2002 This version: http://www.w3.org/wai/ua/wd-uaag10-20021003/uaag10-chktable This document is an appendix to: http://www.w3.org/wai/ua/wd-uaag10-20021003/
Table of Checkpoints for User Agent Accessibility Guidelines 1.0 3 October 2002 This version: http://www.w3.org/wai/ua/wd-uaag10-20021003/uaag10-chktable This document is an appendix to: http://www.w3.org/wai/ua/wd-uaag10-20021003/
No Trade Secrets. Microsoft does not claim any trade secret rights in this documentation.
 [MS-WSSTS]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
[MS-WSSTS]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation for protocols, file formats, languages,
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
Outline. XML vs. HTML and Well Formed vs. Valid. XML Overview. CSC309 Tutorial --XML 4. Edward Xia
 CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
WAP Binary XML Content Format Proposed Version 15-Aug-1999
 WAP Binary XML Content Format Proposed Version 15-Aug-1999 Wireless Application Protocol Binary XML Content Format Specification Version 1.2 Disclaimer: This document is subject to change without notice.
WAP Binary XML Content Format Proposed Version 15-Aug-1999 Wireless Application Protocol Binary XML Content Format Specification Version 1.2 Disclaimer: This document is subject to change without notice.
Using UML To Define XML Document Types
 Using UML To Define XML Document Types W. Eliot Kimber ISOGEN International, A DataChannel Company Created On: 10 Dec 1999 Last Revised: 14 Jan 2000 Defines a convention for the use of UML to define XML
Using UML To Define XML Document Types W. Eliot Kimber ISOGEN International, A DataChannel Company Created On: 10 Dec 1999 Last Revised: 14 Jan 2000 Defines a convention for the use of UML to define XML
XML: Extensible Markup Language
 XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
Information Technology Document Schema Definition Languages (DSDL) Part 1: Overview
 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 34 Date: 2008-09-17 ISO/IEC FCD 19757-1 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 34/WG 1 Secretariat: Japanese Industrial Standards Committee Information Technology Document Schema Definition Languages (DSDL)
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 34 Date: 2008-09-17 ISO/IEC FCD 19757-1 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 34/WG 1 Secretariat: Japanese Industrial Standards Committee Information Technology Document Schema Definition Languages (DSDL)
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML and DTD. Mario Alviano A.Y. 2017/2018. University of Calabria, Italy 1 / 28
 1 / 28 XML and DTD Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 XML syntax 3 Namespace 4 Document Type Definition (DTD) 5 Exercises Outline 3 / 28 1 Introduction
1 / 28 XML and DTD Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 XML syntax 3 Namespace 4 Document Type Definition (DTD) 5 Exercises Outline 3 / 28 1 Introduction
IBM. XML and Related Technologies Dumps Braindumps Real Questions Practice Test dumps free
 000-141 Dumps 000-141 Braindumps 000-141 Real Questions 000-141 Practice Test 000-141 dumps free IBM 000-141 XML and Related Technologies http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/000-141 collections
000-141 Dumps 000-141 Braindumps 000-141 Real Questions 000-141 Practice Test 000-141 dumps free IBM 000-141 XML and Related Technologies http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/000-141 collections
Question Bank XML (Solved/Unsolved) Q.1 Fill in the Blanks: (1 Mark each)
 Q.1 Fill in the Blanks: (1 Mark each) 1. With XML, you can create your own elements, also called tags. 2. The beginning or first element in XML is called the root (document) element. 3. Jon Bosak is known
Q.1 Fill in the Blanks: (1 Mark each) 1. With XML, you can create your own elements, also called tags. 2. The beginning or first element in XML is called the root (document) element. 3. Jon Bosak is known
Foreword... v Introduction... vi. 1 Scope Normative references Terms and definitions DTLL schema overview...
 Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 DTLL schema overview... 2 5 Common constructs... 3 5.1 Common types... 3 5.1.1 XPath
Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 DTLL schema overview... 2 5 Common constructs... 3 5.1 Common types... 3 5.1.1 XPath
ISO/IEC INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Information technology Document Schema Definition Languages (DSDL) Part 11: Schema association
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 19757-11 First edition 2011-11-01 Information technology Document Schema Definition Languages (DSDL) Part 11: Schema association Technologies de l'information Langages de
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 19757-11 First edition 2011-11-01 Information technology Document Schema Definition Languages (DSDL) Part 11: Schema association Technologies de l'information Langages de
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Markup Languages: XHTML 1.0
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Markup Languages: XHTML 1.0 HTML Hello World! Document Type Declaration Document Instance Guy-Vincent Jourdan :: CSI 3140 :: based on Jeffrey C. Jackson
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Markup Languages: XHTML 1.0 HTML Hello World! Document Type Declaration Document Instance Guy-Vincent Jourdan :: CSI 3140 :: based on Jeffrey C. Jackson
ST.96 - ANNEX VI TRANSFORMATION RULES AND GUIDELINES. Version 3.0
 page: 3.96.vi.1 ST.96 - ANNEX VI TRANSFORMATION RULES AND GUIDELINES Version 3.0 Revision approved by the XML4IP Task Force of the Committee of WIPO Standards (CWS) on February 26, 2018 Table of Contents
page: 3.96.vi.1 ST.96 - ANNEX VI TRANSFORMATION RULES AND GUIDELINES Version 3.0 Revision approved by the XML4IP Task Force of the Committee of WIPO Standards (CWS) on February 26, 2018 Table of Contents
CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0
 WEB TECHNOLOGIES A COMPUTER SCIENCE PERSPECTIVE CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0 Modified by Ahmed Sallam Based on original slides by Jeffrey C. Jackson reserved. 0-13-185603-0 HTML HELLO WORLD! Document
WEB TECHNOLOGIES A COMPUTER SCIENCE PERSPECTIVE CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0 Modified by Ahmed Sallam Based on original slides by Jeffrey C. Jackson reserved. 0-13-185603-0 HTML HELLO WORLD! Document
IEEE LANGUAGE REFERENCE MANUAL Std P1076a /D3
 LANGUAGE REFERENCE MANUAL Std P1076a-1999 2000/D3 Clause 10 Scope and visibility The rules defining the scope of declarations and the rules defining which identifiers are visible at various points in the
LANGUAGE REFERENCE MANUAL Std P1076a-1999 2000/D3 Clause 10 Scope and visibility The rules defining the scope of declarations and the rules defining which identifiers are visible at various points in the
7.1 Introduction. extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML
 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2
 Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
XML Schema Part 1: Structures Second Edition
 Page 1 of 210 XML Schema Part 1: Structures Second Edition W3C Recommendation 28 October 2004 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2004/rec-xmlschema-1-20041028/ Latest version: Previous version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2004/per-xmlschema-1-20040318/
Page 1 of 210 XML Schema Part 1: Structures Second Edition W3C Recommendation 28 October 2004 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2004/rec-xmlschema-1-20041028/ Latest version: Previous version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2004/per-xmlschema-1-20040318/
XACML Profile for Requests for Multiple Resources
 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 XACML Profile for Requests for Multiple Resources Working Draft 03, 3 August 2004 Document identifier: oasis-xacml-profile-multiple-resources-wd-03
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 XACML Profile for Requests for Multiple Resources Working Draft 03, 3 August 2004 Document identifier: oasis-xacml-profile-multiple-resources-wd-03
Semistructured Data and XML
 Semistructured Data and XML Computer Science E-66 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Structured Data The logical models we've covered thus far all use some type of schema to define the structure
Semistructured Data and XML Computer Science E-66 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Structured Data The logical models we've covered thus far all use some type of schema to define the structure
Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa
 NPFL092 Technology for Natural Language Processing Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa November 28, 2018 Charles Univeristy in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Institute of Formal
NPFL092 Technology for Natural Language Processing Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa November 28, 2018 Charles Univeristy in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Institute of Formal
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 7 XML
 Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Semistructured Data Store Mapping with XML and Its Reconstruction
 Semistructured Data Store Mapping with XML and Its Reconstruction Enhong CHEN 1 Gongqing WU 1 Gabriela Lindemann 2 Mirjam Minor 2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Science and Technology of
Semistructured Data Store Mapping with XML and Its Reconstruction Enhong CHEN 1 Gongqing WU 1 Gabriela Lindemann 2 Mirjam Minor 2 1 Department of Computer Science University of Science and Technology of
Contents ISO/IEC FDIS Page
 Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 Notation... 3 4.1 XPath... 3 4.2 Predicate Logic... 3 5 Syntax... 4 5.1 Well-formedness...
Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 Notation... 3 4.1 XPath... 3 4.2 Predicate Logic... 3 5 Syntax... 4 5.1 Well-formedness...
Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors
 Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors Topologi Technical Note. August 13, 2002 Rick Jelliffe SGML and XML Editing Concrete Syntax (ECS) This draft paper formalizes the lexical
Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors Topologi Technical Note. August 13, 2002 Rick Jelliffe SGML and XML Editing Concrete Syntax (ECS) This draft paper formalizes the lexical
ISO. International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32 Data Management and Interchange WG4 SQL/MM. Secretariat: USA (ANSI)
 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32 N 0736 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32/WG 4 SQL/MM:VIE-006 January, 2002 ISO International Organization for Standardization ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32 Data Management and Interchange WG4 SQL/MM Secretariat:
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32 N 0736 ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32/WG 4 SQL/MM:VIE-006 January, 2002 ISO International Organization for Standardization ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32 Data Management and Interchange WG4 SQL/MM Secretariat:
Obsoletes: 2070, 1980, 1942, 1867, 1866 Category: Informational June 2000
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 2854 Obsoletes: 2070, 1980, 1942, 1867, 1866 Category: Informational D. Connolly World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) L. Masinter AT&T June 2000 The text/html Media
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 2854 Obsoletes: 2070, 1980, 1942, 1867, 1866 Category: Informational D. Connolly World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) L. Masinter AT&T June 2000 The text/html Media
Data Exchange. Hyper-Text Markup Language. Contents: HTML Sample. HTML Motivation. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Problems w/html
 Data Exchange Contents: Mariano Cilia / cilia@informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Origins (HTML) Schema DOM, SAX Semantic Data Exchange Integration Problems MIX Model 1 Hyper-Text Markup Language HTML Hypertext:
Data Exchange Contents: Mariano Cilia / cilia@informatik.tu-darmstadt.de Origins (HTML) Schema DOM, SAX Semantic Data Exchange Integration Problems MIX Model 1 Hyper-Text Markup Language HTML Hypertext:
XML SCHEMA INFERENCE WITH XSLT
 XML SCHEMA INFERENCE WITH XSLT By SCOTT MCCOLLUM BUNTIN A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
XML SCHEMA INFERENCE WITH XSLT By SCOTT MCCOLLUM BUNTIN A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
Intro to XML. Borrowed, with author s permission, from:
 Intro to XML Borrowed, with author s permission, from: http://business.unr.edu/faculty/ekedahl/is389/topic3a ndroidintroduction/is389androidbasics.aspx Part 1: XML Basics Why XML Here? You need to understand
Intro to XML Borrowed, with author s permission, from: http://business.unr.edu/faculty/ekedahl/is389/topic3a ndroidintroduction/is389androidbasics.aspx Part 1: XML Basics Why XML Here? You need to understand
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2017 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid= 2465 1
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2017 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid= 2465 1
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML. Overview. How the Web is Today. Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington
 Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
XML: Managing with the Java Platform
 In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
D. Crocker, Ed. Updates: RFC4871 June 10, 2009 (if approved) Intended status: Standards Track Expires: December 12, 2009
 DKIM D. Crocker, Ed. Internet-Draft Brandenburg InternetWorking Updates: RFC4871 June 10, 2009 (if approved) Intended status: Standards Track Expires: December 12, 2009 RFC 4871 DomainKeys Identified Mail
DKIM D. Crocker, Ed. Internet-Draft Brandenburg InternetWorking Updates: RFC4871 June 10, 2009 (if approved) Intended status: Standards Track Expires: December 12, 2009 RFC 4871 DomainKeys Identified Mail
M359 Block5 - Lecture12 Eng/ Waleed Omar
 Documents and markup languages The term XML stands for extensible Markup Language. Used to label the different parts of documents. Labeling helps in: Displaying the documents in a formatted way Querying
Documents and markup languages The term XML stands for extensible Markup Language. Used to label the different parts of documents. Labeling helps in: Displaying the documents in a formatted way Querying
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 16684-1 First edition 2012-02-15 Graphic technology Extensible metadata platform (XMP) specification Part 1: Data model, serialization and core properties Technologie graphique
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 16684-1 First edition 2012-02-15 Graphic technology Extensible metadata platform (XMP) specification Part 1: Data model, serialization and core properties Technologie graphique
XDS An Extensible Structure for Trustworthy Document Content Verification Simon Wiseman CTO Deep- Secure 3 rd June 2013
 Assured and security Deep-Secure XDS An Extensible Structure for Trustworthy Document Content Verification Simon Wiseman CTO Deep- Secure 3 rd June 2013 This technical note describes the extensible Data
Assured and security Deep-Secure XDS An Extensible Structure for Trustworthy Document Content Verification Simon Wiseman CTO Deep- Secure 3 rd June 2013 This technical note describes the extensible Data
PART. Oracle and the XML Standards
 PART I Oracle and the XML Standards CHAPTER 1 Introducing XML 4 Oracle Database 10g XML & SQL E xtensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-markup language, meaning that the language, as specified by the
PART I Oracle and the XML Standards CHAPTER 1 Introducing XML 4 Oracle Database 10g XML & SQL E xtensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-markup language, meaning that the language, as specified by the
Appendix H XML Quick Reference
 HTML Appendix H XML Quick Reference What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). XML allows developers to create their own document elements
HTML Appendix H XML Quick Reference What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a subset of the Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). XML allows developers to create their own document elements
Network Working Group. September 24, XML Media Types draft-murata-xml-00.txt. Status of this Memo
 Network Working Group Internet-Draft Expires: March 24, 2000 M. Murata Fuji Xerox Information Systems S. St.Laurent September 24, 1999 XML Media Types draft-murata-xml-00.txt Status of this Memo This document
Network Working Group Internet-Draft Expires: March 24, 2000 M. Murata Fuji Xerox Information Systems S. St.Laurent September 24, 1999 XML Media Types draft-murata-xml-00.txt Status of this Memo This document
Information Systems. DTD and XML Schema. Nikolaj Popov
 Information Systems DTD and XML Schema Nikolaj Popov Research Institute for Symbolic Computation Johannes Kepler University of Linz, Austria popov@risc.uni-linz.ac.at Outline DTDs Document Type Declarations
Information Systems DTD and XML Schema Nikolaj Popov Research Institute for Symbolic Computation Johannes Kepler University of Linz, Austria popov@risc.uni-linz.ac.at Outline DTDs Document Type Declarations
