Problem O. Isolated Building - Nonlinear Time History Analysis. Steel E =29000 ksi, Poissons Ratio = 0.3 Beams: W24X55; Columns: W14X90
|
|
|
- Christina Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
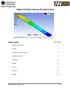
1 Problem O Isolated Building - Nonlinear Time History Analysis Steel E =29000 ksi, Poissons Ratio = 0.3 Beams: W24X55; Columns: W14X90 Rubber Isolator Properties Vertical (axial) stiffness = 10,000 k/in (linear) Initial shear stiffness in each direction = 10 k/in Shear yield force in each direction = 5 kips Ratio of post yield shear stiffness to initial shear stiffness = 0.2 Vertical Loading and Mass Roof: 75 psf DL Floor: 125 psf DL 20 psf LL 100 psf LL Time History Apply LP-TH0 in the X-direction and LP-TH90 in the Y-direction simultaneously. Each timehistory is given in units of g. There are 2000 timesteps, at an equal spacing of 0.02 sec, for a total of 40 sec. There are 5 accelerations points per line. To Do Plot time histories of Y-direction displacement at the 1st level and at the roof level. Plot a time history of the 1st level Y-direction displacement versus the Y-direction base shear. 6 thick concrete slab at roof Roof 2nd 1st thick concrete slab at 1st and 2nd floors Note: Provide diaphragm constraint at each level to make all diaphragms rigid. Note: Our intent is that you try this problem on your own first. After you have solved it on your own, you can step through our solution if desired. If you have problems trying to create the model, then follow the steps in our solution. 1
2 Problem O Solution 1. Click the drop down box in the status bar to change the units to kip-ft. 2. From the File menu select New Model From Template. This displays the Model Templates dialog box. 3. In this dialog box click on the Space Frame template button to display the Space Frame dialog box. 4. In this dialog box: Type 2 in the Number of Bays Along X edit box. Type 30 in the Bay Width Along X edit box. Type 30 in the Bay Width Along Y edit box. Uncheck the Restraints check box. Accept the rest of the default values. 5. Click in the window labeled X-Y Z=24 to make sure it is active. The window is active when its title is highlighted. 6. Click the Quick Draw Rectangular Shell Element button on the side toolbar. 7. Click once in each of the four quadrants in the plan view to input four shell elements. 8. Click the Down One Gridline button to move the plan display down to the X-Y Z= Click once in each of the four quadrants in the plan view to input four shell elements. 10. Click the Down One Gridline button to move the plan display down to the X-Y Z= From the Draw menu select Draw NLLink Element. 12. In the plan view of the X-Y Z=0 double click on each of the nine joints to draw nine NLLink elements. 13. Click the Pointer button to exit draw mode and enter select mode. 14. Click the drop down box in the status bar to change the units to kip-in. 2
3 15. From the Define menu select Materials... to display the Define Materials dialog box. Highlight the STEEL material and click the Modify/Show Material button to display the Material Property Data dialog box. 16. In this dialog box: Verify that the modulus of elasticity is and poisson s ratio is 0.3. Click the OK button twice to exit the dialog boxes. 17. From the Define menu select Frame Sections... to display the Define Frame Sections dialog box. 18. In the Click To area, click the drop-down box that says Import I/Wide Flange and then click on the Import I/Wide Flange item. 19. If the Section Property File dialog box appears then locate the Sections.pro file which should be located in the same directory as the SAP2000 program files. 20. A dialog box appears with a list of all wide flange sections in the database. In this dialog box: Scroll down and click on the W24X55 section. Scroll down to the W14X90 section, and click on it while holding down the Ctrl key on the keyboard. Click the OK button three times to exit all dialog boxes. 21. From the Define menu select Shell Sections... to display the Define Shell Sections dialog box. 22. In this dialog box: Click the Add New Section button to display the Shell Sections dialog box. À Type ROOF in the Section Name edit box. À Accept the default CONC material À Type 6 in the Membrane edit box. À Type 6 in the Bending edit box. À In the Type area verify that the Shell option is selected. À Click the OK button to return to the Define Shell Sections dialog box. 3
4 Click the Add New Section button to display the Shell Sections dialog box. À Type FLOOR in the Section Name edit box. À Accept the default CONC material À Type 10 in the Membrane edit box. À Type 10 in the Bending edit box. À In the Type area verify that the Shell option is selected. À Click the OK button twice to exit all dialog boxes. 23. From the Define menu select NLLink Properties... to display the Define NLLink Properties dialog box. 24. In this dialog box: Click the Modify/Show Property button to display the NLLink Property Data dialog box. À Select Isolator1 from the Type drop-down box. À Type.001 in the Mass edit box. À Check the U1 Direction check box. À Click the Modify/Show For U1 button to display the NLLink Directional Properties dialog box. ä Type in the Effective Stiffness edit box. ä Click the OK button to return to the NLLink Property Data dialog box. À Check the U2 Direction check box. À Check the U2 Nonlinear check box. À Click the Modify/Show For U2 button to display the NLLink Directional Properties dialog box. 4
5 ä In the Linear Properties area type 1.5 in the Effective Stiffness edit box. ä In the Nonlinear Properties area type 10 in the Stiffness edit box. ä Type 5 in the Yield Strength edit box. ä Type.2 in the Post Yield Stiffness Ratio edit box. ä Accept the rest of the default values. ä Click the OK button to return to the NLLink Property Data dialog box. À Check the U3 Direction check box. À Check the U3 Nonlinear check box. À Click the Modify/Show For U3 button to display the NLLink Directional Properties dialog box. ä In the Linear Properties area type 1.5 in the Effective Stiffness edit box. ä In the Nonlinear Properties area type 10 in the Stiffness edit box. ä Type 5 in the Yield Strength edit box. ä Type.2 in the Post Yield Stiffness Ratio edit box. ä Accept the rest of the default values. ä Click the OK button three times to exit all dialog boxes. 25. Click the drop down box in the status bar to change the units to kip-ft. 26. From the Define menu select Materials... to display the Define Materials dialog box. Highlight the CONC material and click the Modify/Show Section button to display the Material Property Data dialog box. 27. In this dialog box: Verify that the mass per unit volume is 4.657E-03 and that the weight per unit volume is Click the OK button twice to exit the dialog boxes. 28. Click in the window labeled X-Y Z=0 to make sure it is active. 29. Click the xz 2D View button on the main toolbar. 5
6 30. Click the Perspective Toggle button on the main toolbar. 31. Click the Set Intersecting Line select Mode button on the side toolbar and select all of the bottom level columns. Note: To use the Intersecting Line Selection option, click the Set Intersecting Line Select Mode button on the side tool bar. Then click the left mouse button to the left of the first level columns, and while holding down the left mouse button drag the mouse to the right of the first level columns. A rubberband line will appear and all elements that this rubberband line passes through will be selected. Release the left mouse button to make the selection. 32. Click the Set Intersecting Line select Mode button on the side toolbar and select all of the top level columns. 33. From the Assign menu select Frame and then Sections... from the submenu to display the Define Frame Sections dialog box. 34. In this dialog box: Click on W14X90 in the Frame Sections area to highlight it. 35. Click the Show Undeformed Shape button to remove the displayed frame element assignments. 36. Click the xy 2D View button on the main toolbar. The plan view of the X-Y Z=0 appears. 37. Click the Up One Gridline button to move the plan display up to the X-Y Z= Select all of the elements at this level by windowing. 39. Click the Up One Gridline button to move the plan display up to the X-Y Z= Select all of the elements at this level by windowing. 41. From the Assign menu select Frame and then Sections... from the submenu to display the Define Frame Sections dialog box. 42. In this dialog box: Click on W24X55 in the Frame Sections area to highlight it. 6
7 43. Click the Show Undeformed Shape button to remove the displayed frame element assignments. 44. Select all of the elements at the Z=24 level by windowing. 45. From the Assign menu select Shell and then Sections... from the submenu to display the Define Shell Sections dialog box. 46. In this dialog box: Click on ROOF in the Shell Sections area to highlight it. 47. Click the Down One Gridline button to move the plan display down to the X-Y Z= Select all of the elements at this level by windowing. 49. From the Assign menu select Shell and then Sections... from the submenu to display the Define Shell Sections dialog box. 50. In this dialog box: Click on FLOOR in the Shell Sections area to highlight it. 51. From the Define menu select Static Load Cases... to display the Define Static Load Case Names dialog box. 52. In this dialog box: Type DL in the Load edit box. Click the Change Load button. Type LL in the Load edit box. Select LIVE from the Type drop-down box. Type 0 in the Self Weight Multiplier edit box. Click the Add New Load button. 53. Click the drop down box in the status bar to change the units to lb-ft. 7
8 54. Select all of the elements at the Z=12 level by windowing. 55. From the Assign menu select Shell Static Loads and then Uniform... from the submenu to display the Shell Uniform Loads dialog box. 56. In this dialog box: Select LL from the Load Case Name drop-down box. Type -100 in the Load edit box. 57. Click the Up One Gridline button to move the plan display up to the X-Y Z= Select all of the elements at the Z=24 level by windowing. 59. From the Assign menu select Shell Static Loads and then Uniform... from the submenu to display the Shell Uniform Loads dialog box. 60. In this dialog box: Type -20 in the Load edit box. 61. Click the drop down box in the status bar to change the units to kip-ft. 62. Click the Show Undeformed Shape button to remove the displayed shell load assignments. 63. Click the Down One Gridline button to move the plan display down to the X-Y Z= Select all of the elements at the Z=12 level by windowing. 65. From the Edit menu select Replicate to display the Replicate dialog box. 66. In this dialog box: Select the Linear Tab. Type -12 in the Z Distance edit box. Type 1 in the Number edit box. 8
9 Note: Prior to defining time history functions, you should locate the time history files named Lp-th0 and Lp-th90 that are in the subdirectory named Examples beneath the directory where you installed SAP2000. Copy these files into the same directory as your SAP2000 input file. If the Examples subdirectory does not exist you may need to reinstall SAP2000, and select to install the examples. 67. From the Define menu select Time History Functions... to display the Define Time History Functions dialog box. 68. In this dialog box: Click the Add Function From File button to display the Time History Function Definition dialog box. À Type LPTH0 in the Function Name edit box. À Click the Open File button to display the Pick Function Data File dialog box. ä Locate and highlight the file named LP-TH0 ä Click the Open button to return to the Time History Function Definition dialog box. ä Type 5 in the Number Of Points Per Line edit box. ä Select the Function At Equal Time Step option. ä Type.02 in the Function At Equal Time Step edit box. ä Click the OK button to return to the Define Time History Functions dialog box. Click the Add Function From File button to display the Time History Function Definition dialog box. À Type LPTH90 in the Function Name edit box. À Click the Open File button to display the Pick Function Data File dialog box. ä Locate and highlight the file named LP-TH90. 9
10 ä Click the Open button to return to the Time History Function Definition dialog box. ä Type 5 in the Number Of Points Per Line edit box. ä Select the Function At Equal Time Step option. ä Type.02 in the Function At Equal Time Step edit box. ä Click the OK button twice to exit all dialog boxes. 69. From the Analyze menu select Set Options... to display the Analysis Options dialog box. Check the Dynamic Analysis check box, if it is not already checked. Click the Set Dynamic Parameters button to display the Dynamic Analysis Parameters dialog box. À Type 30 in the Number of Modes edit box. À In the Type Of Analysis area select the Ritz Vectors option. À Verify that ACCEL X, ACCEL Y and ACCEL Z are in the Ritz Load Vectors box in the Starting Ritz Vectors area. À Confirm that the Include NLLink Vectors box is checked. À Click the OK button twice to exit all dialog boxes. 70. From the Define menu select Time History Cases... to display the Define Time History Cases dialog box. 71. In this dialog box: Click the Add New History button to display the Time History Case Data dialog box. À Type GRAV in the History Case Name edit box. À Select Nonlinear from the Analysis Type drop-down box. À Click the Modify/Show button for modal damping to display the Modal Damping dialog box. 10
11 ä Type.05 in the Damping For All Modes edit box. ä Click the OK button. À Type 100 in the Number of Output Time Steps edit box. À Type.1 in the Output Time Step Size edit box. À Check the Envelopes check box. À In the Load drop-down box, select DL. À In the Function drop-down box, select RAMP. À Type 1 in the Scale Factor edit box. À Click the Add button. À Click the OK button to return to the Define Time History Cases dialog box. Click the Add New History button to display the Time History Case Data dialog box. À Type LP in the History Case Name edit box. À Select Nonlinear from the Analysis Type drop-down box. À Click the Modify/Show button for modal damping to display the Modal Damping dialog box. ä Type.05 in the Damping For All Modes edit box. ä In the Modal Damping Overrides area type Type 1 in the Mode box, type 0.02 in the Damping box and click the Add button. ä In the Modal Damping Overrides area type Type 2 in the Mode box and click the Add button. ä In the Modal Damping Overrides area type Type 3 in the Mode box and click the Add button. ä Click the OK button. À Type 2000 in the Number of Output Time Steps edit box. À Type.02 in the Output Time Step Size edit box. 11
12 À In the Start From Previous History drop-down box select GRAV. À Check the Envelopes check box. À In the Load drop-down box, select acc dir 1. À In the Function drop-down box, select LPTH0. À Type 32.2 in the Scale Factor edit box. À Click the Add button. À In the Load drop-down box, select acc dir 2. À In the Function drop-down box, select LPTH90. À Click the Add button. À Click the OK button twice to exit all dialog boxes. 72. Click in the window labeled X-Y Z=12 to make sure it is active. 73. Click the Up One Gridline button to move the plan display up to the X-Y Z= Select all elements at the Z=24 level by windowing. 75. From the Assign menu select Joint and then Constraints... from the submenu to display the Constraints dialog box. 76. In this dialog box: Click the drop-down box in the Click To area, and click Add Diaphragm to display the Diaphragm Constraint dialog box. À Type ROOF in the Constraint Name edit box. À Select the Z axis option in the Constraint Axis area if it is not already selected. À Click the OK button twice to assign the diaphragm constraint. 77. Click the Down One Gridline button to move the plan display down to the X-Y Z= Select all elements at the Z=12 level by windowing. 12
13 79. From the Assign menu select Joint and then Constraints... from the submenu to display the Constraints dialog box. 80. In this dialog box: Click the drop-down box in the Click To area, and click Add Diaphragm to display the Diaphragm Constraint dialog box. À Type 2ND in the Constraint Name edit box. À Select the Z axis option in the Constraint Axis area if it is not already selected. À Click the OK button twice to assign the diaphragm constraint. 81. Click the Down One Gridline button to move the plan display down to the X-Y Z= Select all elements at the Z=0 level by windowing. 83. From the Assign menu select Joint and then Constraints... from the submenu to display the Constraints dialog box. 84. In this dialog box: Click the drop-down box in the Click To area, and click Add Diaphragm to display the Diaphragm Constraint dialog box. À Type 1ST in the Constraint Name edit box. À Select the Z axis option in the Constraint Axis area if it is not already selected. À Click the OK button twice to assign the diaphragm constraint. 85. Click the Show Undeformed Shape button to remove the displayed diaphragm constraint assignments. 86. Click the Run Analysis button to run the analysis. Note: The analysis would run even quicker if we had not requested envelopes in the time history case data. 87. When the analysis is complete check the messages in the Analysis window (there should be no warnings or errors). Click the OK button to close the Analysis window. 88. Click in the window labeled X-Y Z=0 to make sure it is active. 13
14 89. Click the Set Elements button on the main toolbar (or select Set Elements from the View menu) to display the Set Elements Dialog box. 90. In this dialog box: Check the Labels box in the Joints area. 91. Click on the center joint, joint 13, in the plan at Z=0 to select it. 92. Click the Up One Gridline button twice to move the plan display up to the X-Y Z= Click on the center joint, joint 15, in the plan at Z=24 to select it. 94. Click the Set Elements button on the main toolbar (or select Set Elements from the View menu) to display the Set Elements Dialog box. 95. In this dialog box: Uncheck the Labels box in the Joints area. 96. From the Display menu select Show Time History Traces to display the Time History Display Definition dialog box. 97. In this dialog box: Click the Define Functions button to display the Time History Functions dialog box. À Highlight Joint 13. À Click the Modify/Show TH Function button to display the Time History Joint Function dialog box. ä Verify that the Displ option is selected in the Vector Type area. ä Select the UY option is selected in the Component area. ä Click the OK button to return to the Time History Functions dialog box. À Highlight Joint
15 À Click the Modify/Show TH Function button to display the Time History Joint Function dialog box. ä Verify that the Displ option is selected in the Vector Type area. ä Select the UY option is selected in the Component area. ä Click the OK button to return to the Time History Functions dialog box. À In the Click To area select Add Base Functions from the drop-down box to display the Base Functions dialog box. ä Check the Base Shear Y check box. ä Click the OK button twice to return to the Time History Display Definition dialog box. Select LP from The Time History Case drop-down box. Click on Joint 13 in the List of Functions to highlight (select) it. Hold down the Ctrl key on the keyboard and click on Joint 15 to add it to the selection. Click the Add button to move Joints 13 and 15 into the Plot Functions list. Click the Display button to display the displacement time histories. Note that there is very little difference between the 1st and roof level displacements. The structure is essentially moving as a rigid body on top of the isolators. Click the OK button to close the time history display and return to the Time History Display Definition dialog box. Click the F(t) vs F(t) tab. Select Joint 13 from the Horizontal drop-down box. Select Base Shear Y from the Vertical drop-down box. Click the Display button to display the force-displacement plot. Click the OK button to close the Time History Functions display and return to the Time History Display Definition dialog box. Click the Done button to close the Time History Display Definition dialog box. 15
TUTORIAL INCLUDING PUSHOVER ANALYSIS
 SAP2000 Integrated Finite Elements Analysis and Design of Structures DETAILED TUTORIAL INCLUDING PUSHOVER ANALYSIS Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 6.20 Beta June 1998 COPYRIGHT
SAP2000 Integrated Finite Elements Analysis and Design of Structures DETAILED TUTORIAL INCLUDING PUSHOVER ANALYSIS Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 6.20 Beta June 1998 COPYRIGHT
Important Note - Please Read:
 Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help
Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help
Important Note - Please Read:
 Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help
Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help
SAP 2000 Problem II Homework Problem P5.45. Recall from Lab #6 the Global and Local Reference Coordinate Systems for 2D Problems
 SAP 2000 Problem II Homework Problem P5.45 Recall from Lab #6 the Global and Local Reference Coordinate Systems for 2D Problems Z 2 Global (XYZ) Coordinate System Joint Displacements Applied Point Loads
SAP 2000 Problem II Homework Problem P5.45 Recall from Lab #6 the Global and Local Reference Coordinate Systems for 2D Problems Z 2 Global (XYZ) Coordinate System Joint Displacements Applied Point Loads
SAP2000 FEATURES & A TO Z PROBLEMS. Collected by: MSc. NGUYEN LAN BRIDGE AND TUNNEL DIVISION DA NANG UNIVERSITY
 SAP2000 FEATURES & A TO Z PROBLEMS Collected by: MSc. NGUYEN LAN BRIDGE AND TUNNEL DIVISION DA NANG UNIVERSITY INTERNAL CIRCULATION, 2007 SAP2000 FEATURES INTEGRATED SOFTWARE FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS &
SAP2000 FEATURES & A TO Z PROBLEMS Collected by: MSc. NGUYEN LAN BRIDGE AND TUNNEL DIVISION DA NANG UNIVERSITY INTERNAL CIRCULATION, 2007 SAP2000 FEATURES INTEGRATED SOFTWARE FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS &
1. Define the material properties. Activate the Data Entry menu if it s not already visible, and click on Materials.
 CE 533, Fall 2014 Guide for Using RISA3D 1 / 9 Example Structure. The procedure for calculating frequencies and modes shapes of a multidegree of freedom (MDOF) system will be demonstrated using the following
CE 533, Fall 2014 Guide for Using RISA3D 1 / 9 Example Structure. The procedure for calculating frequencies and modes shapes of a multidegree of freedom (MDOF) system will be demonstrated using the following
EXAMPLE 1. Static Analysis of Cantilever Column (Fixed-Base Column)
 EXAMPLE 1 Static Analysis of Cantilever Column (Fixed-Base Column) Calculate the top displacement, axial force, shear force and bending moment diagrams for the fixed base column described in the figure
EXAMPLE 1 Static Analysis of Cantilever Column (Fixed-Base Column) Calculate the top displacement, axial force, shear force and bending moment diagrams for the fixed base column described in the figure
Idealization of Design Strip in ADAPT RC
 ADAPT RC 2010 Tutorial Idealization of Design Strip in ADAPT RC Update: May 2010 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT RC 2010 Tutorial 1 Main Toolbar Menu Bar View Toolbar Structure View
ADAPT RC 2010 Tutorial Idealization of Design Strip in ADAPT RC Update: May 2010 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT RC 2010 Tutorial 1 Main Toolbar Menu Bar View Toolbar Structure View
ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode
 ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode Update: January 2014 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT-PT/RC 2014-Tutorial- 1 This ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial
ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode Update: January 2014 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT-PT/RC 2014-Tutorial- 1 This ADAPT-PT/RC 2014 Getting Started Tutorial
SAFI Sample Projects. Design of a Steel Structure. SAFI Quality Software Inc. 3393, chemin Sainte-Foy Ste-Foy, Quebec, G1X 1S7 Canada
 SAFI Sample Projects Design of a Steel Structure SAFI Quality Software Inc. 3393, chemin Sainte-Foy Ste-Foy, Quebec, G1X 1S7 Canada Contact: Rachik Elmaraghy, P.Eng., M.A.Sc. Tel.: 1-418-654-9454 1-800-810-9454
SAFI Sample Projects Design of a Steel Structure SAFI Quality Software Inc. 3393, chemin Sainte-Foy Ste-Foy, Quebec, G1X 1S7 Canada Contact: Rachik Elmaraghy, P.Eng., M.A.Sc. Tel.: 1-418-654-9454 1-800-810-9454
ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode
 ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode Update: September 2018 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT-PT/RC 2017-Tutorial- 1 This ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial
ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial ADAPT-RC mode Update: September 2018 Copyright ADAPT Corporation all rights reserved ADAPT-PT/RC 2017-Tutorial- 1 This ADAPT-PT/RC 2018 Getting Started Tutorial
Tekla Structures Analysis Guide. Product version 21.0 March Tekla Corporation
 Tekla Structures Analysis Guide Product version 21.0 March 2015 2015 Tekla Corporation Contents 1 Getting started with analysis... 7 1.1 What is an analysis model... 7 Analysis model objects...9 1.2 About
Tekla Structures Analysis Guide Product version 21.0 March 2015 2015 Tekla Corporation Contents 1 Getting started with analysis... 7 1.1 What is an analysis model... 7 Analysis model objects...9 1.2 About
Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis
 Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis 1. The software is available at the Open Access Labs (OAL) and the Virtual OAL at http://voal.tamu.edu in Programs under the Windows Start menu. The software can also
Frame Analysis Using Visual Analysis 1. The software is available at the Open Access Labs (OAL) and the Virtual OAL at http://voal.tamu.edu in Programs under the Windows Start menu. The software can also
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
USER INTERFACE MANUAL
 SAP2000 Integrated Finite Elements Analysis and Design of Structures GRAPHIC USER INTERFACE MANUAL Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 7.0 August 1998 COPYRIGHT The computer
SAP2000 Integrated Finite Elements Analysis and Design of Structures GRAPHIC USER INTERFACE MANUAL Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 7.0 August 1998 COPYRIGHT The computer
Advanced 3-D Tutorial
 Advanced 3-D Tutorial Introduction To demonstrate some of the features of VisualAnalysis we have put together this advanced tutorial for you to use. This tutorial assumes that you have a basic knowledge
Advanced 3-D Tutorial Introduction To demonstrate some of the features of VisualAnalysis we have put together this advanced tutorial for you to use. This tutorial assumes that you have a basic knowledge
SAFE DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE. Tutorial
 Tutorial SAFE DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE Tutorial ISO SAF112816M3 Rev. 0 Proudly developed in the United States of America November 2016 Copyright Copyright
Tutorial SAFE DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE Tutorial ISO SAF112816M3 Rev. 0 Proudly developed in the United States of America November 2016 Copyright Copyright
Solve the problem described in the figure below for the joint action of Ε y, E x
 EXAMPLE 4 Correcting mistakes in SAP 2000 Solve the problem described in the figure below for the joint action of Ε y, E x Input data - Column EZ (both in 1 st and 2 nd floor) has dimensions 50/30 (X/Y)
EXAMPLE 4 Correcting mistakes in SAP 2000 Solve the problem described in the figure below for the joint action of Ε y, E x Input data - Column EZ (both in 1 st and 2 nd floor) has dimensions 50/30 (X/Y)
Frame Analysis Using Multiframe4D
 Frame Analysis Using Multiframe4D 1. The software is on the computers in the college computing lab (http://thelab.tamu.edu) in Programs under the Windows Start menu. Multiframe4D is under the COSC menu.
Frame Analysis Using Multiframe4D 1. The software is on the computers in the college computing lab (http://thelab.tamu.edu) in Programs under the Windows Start menu. Multiframe4D is under the COSC menu.
SAFIR training session level 1 Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. Example: 3D structural model of a beam. 3D steel beam with thermal insulation
 SAFIR training session level 1 Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore Example: 3D structural model of a beam 3D steel beam with thermal insulation T. Gernay & J.M. Franssen 3D Beam 1 1. General description
SAFIR training session level 1 Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore Example: 3D structural model of a beam 3D steel beam with thermal insulation T. Gernay & J.M. Franssen 3D Beam 1 1. General description
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis
 Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Truss Bridge Analysis Using SAP2000
 Truss Bridge Analysis Using SAP2000 SAP2000 is a structural analysis and design program that allows users to create and test a computer animated model of their figure. The program calculates dead loads,
Truss Bridge Analysis Using SAP2000 SAP2000 is a structural analysis and design program that allows users to create and test a computer animated model of their figure. The program calculates dead loads,
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Yavuz YARDIM. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Yavuz YARDIM
 Then click OK three times to close windows Now we define the Layout Next step will defining deck section Go to bridge Deck section Add new deck section Choose steel and concrete deck section ( Steel girder)
Then click OK three times to close windows Now we define the Layout Next step will defining deck section Go to bridge Deck section Add new deck section Choose steel and concrete deck section ( Steel girder)
The Generate toolbar has convenient tools to create typical structural shapes.
 Frame Analysis Using Multiframe 1. The software is on the computers in the College of Architecture in Programs under the Windows Start menu (see https://wikis.arch.tamu.edu/display/helpdesk/computer+accounts
Frame Analysis Using Multiframe 1. The software is on the computers in the College of Architecture in Programs under the Windows Start menu (see https://wikis.arch.tamu.edu/display/helpdesk/computer+accounts
create 2 new grid lines
 STEP 1: open your class-01 Project file _ go to Level 1 _ select grid line 1 _ type CO (copy) _ repeat for grid line 3 as shown in image 1 Architectural Column STEP 2: from the Ribbon under the Home tab
STEP 1: open your class-01 Project file _ go to Level 1 _ select grid line 1 _ type CO (copy) _ repeat for grid line 3 as shown in image 1 Architectural Column STEP 2: from the Ribbon under the Home tab
Version October 2015 RFEM 5. Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method. Introductory Example
 Version October 2015 Program RFEM 5 Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method Introductory Example All rights, including those of translations, are reserved. No portion of this book may be
Version October 2015 Program RFEM 5 Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method Introductory Example All rights, including those of translations, are reserved. No portion of this book may be
Basic Modeling 1 Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006
 Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents 3 1 5 1.1 Start Tekla Structures 6 1.2 Create a New Model BasicModel1 7 1.3 Create Grids 10 1.4
Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents 3 1 5 1.1 Start Tekla Structures 6 1.2 Create a New Model BasicModel1 7 1.3 Create Grids 10 1.4
17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES
 17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES The Current Building Codes Use the Terminology: Principal Direction without a Unique Definition 17.1 INTRODUCTION { XE "Building Codes" }Currently
17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES The Current Building Codes Use the Terminology: Principal Direction without a Unique Definition 17.1 INTRODUCTION { XE "Building Codes" }Currently
RSPile. Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis. Pile Analysis Software. Grouped Pile Analysis
 RSPile Pile Analysis Software Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis Grouped Pile Analysis Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate how to model grouped piles under a cap. The finished product of this tutorial
RSPile Pile Analysis Software Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis Grouped Pile Analysis Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate how to model grouped piles under a cap. The finished product of this tutorial
2D Tutorial. Project Description: Running VisualAnalysis: Setting Up the Project:
 2D Tutorial Project Description: This project has been set-up to demonstrate the basic features of VisualAnalysis. You will model and analyze the following two-dimensional frame with a curved glue-laminated
2D Tutorial Project Description: This project has been set-up to demonstrate the basic features of VisualAnalysis. You will model and analyze the following two-dimensional frame with a curved glue-laminated
MANUAL COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES INC.
 SAP2000 Integrated Finite Element Analysis and Design of Structures VERIFICATION MANUAL COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES INC. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 6.1 Revised July 1997
SAP2000 Integrated Finite Element Analysis and Design of Structures VERIFICATION MANUAL COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES INC. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 6.1 Revised July 1997
CME-TRUSS (Version 2.1) User's Manual
 CME-TRUSS (Version 2.1) User's Manual INTRODUCTION CME-TRUSS is an interactive program for structural analysis of two-dimensional trusses. The software is written in the Microsoft Visual Basic for Windows
CME-TRUSS (Version 2.1) User's Manual INTRODUCTION CME-TRUSS is an interactive program for structural analysis of two-dimensional trusses. The software is written in the Microsoft Visual Basic for Windows
FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING
 FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Purpose of FB-MultiPier Validation testing Performing validation of structural analysis software delineates the capabilities and limitations
FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Purpose of FB-MultiPier Validation testing Performing validation of structural analysis software delineates the capabilities and limitations
Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D
 Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D Buoy Chain Sea Bed Suction Pile Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering 00 Overview
Lateral Loading of Suction Pile in 3D Buoy Chain Sea Bed Suction Pile Integrated Solver Optimized for the next generation 64-bit platform Finite Element Solutions for Geotechnical Engineering 00 Overview
STRUCTURAL CONCRETE SOFTWARE ADAPT-ABI 2009 GETTING STARTED GUIDE. Copyright 2009
 STRUCTURAL CONCRETE SOFTWARE ADAPT-ABI 2009 GETTING STARTED GUIDE Copyright 2009 Copyright ADAPT Corporation 2009 all rights reserved support@adaptsoft.com www.adaptsoft.com ADAPT Corporation, Redwood
STRUCTURAL CONCRETE SOFTWARE ADAPT-ABI 2009 GETTING STARTED GUIDE Copyright 2009 Copyright ADAPT Corporation 2009 all rights reserved support@adaptsoft.com www.adaptsoft.com ADAPT Corporation, Redwood
Multiframe Oct 2008
 Multiframe 11.01 3 Oct 2008 Windows Release Note This release note describes the Windows version 11.01 of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008.
Multiframe 11.01 3 Oct 2008 Windows Release Note This release note describes the Windows version 11.01 of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008.
WoodWorks Design Office User Guide U.S. Sizer Tutorial Instructions
 WoodWorks Design Office Sizer Shearwalls Connections Database Editor 2017 User Guide U.S. Sizer Tutorial Instructions For U.S. Design Office 11 Canadian Wood Council American Wood Council Developed by
WoodWorks Design Office Sizer Shearwalls Connections Database Editor 2017 User Guide U.S. Sizer Tutorial Instructions For U.S. Design Office 11 Canadian Wood Council American Wood Council Developed by
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007
 CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
Advance Design. Tutorial
 TUTORIAL 2018 Advance Design Tutorial Table of Contents About this tutorial... 1 How to use this guide... 3 Lesson 1: Preparing and organizing your model... 4 Step 1: Start Advance Design... 5 Step 2:
TUTORIAL 2018 Advance Design Tutorial Table of Contents About this tutorial... 1 How to use this guide... 3 Lesson 1: Preparing and organizing your model... 4 Step 1: Start Advance Design... 5 Step 2:
Steel Structures Tutorial
 AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Steel Structures Tutorial STL8 Pin and Hanger Rolled Beam Example Topics Covered Steel rolled beam with cover plates input as girder system. Schedule based input. Pin and hanger
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Steel Structures Tutorial STL8 Pin and Hanger Rolled Beam Example Topics Covered Steel rolled beam with cover plates input as girder system. Schedule based input. Pin and hanger
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Step by Step. Tutorial for AxisVM X4. Edited by: Inter-CAD Kft.
 Step by Step Tutorial for AxisVM X4 Edited by: Inter-CAD Kft. 2018 Inter-CAD Kft. All rights reserved All brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks. Intentionally blank page Step
Step by Step Tutorial for AxisVM X4 Edited by: Inter-CAD Kft. 2018 Inter-CAD Kft. All rights reserved All brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks. Intentionally blank page Step
CE Advanced Structural Analysis. Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 SAP2000 Plane Elasticity February 27 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza 1. Rectangular
Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu.
 1. BEAM MODEL Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a new model with the New Icon. In the dialogue
1. BEAM MODEL Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a new model with the New Icon. In the dialogue
Multiframe Windows Version 16. User Manual
 Multiframe Windows Version 16 User Manual Bentley Systems, Incorporated 2013 License & Copyright Multiframe Program & User Manual 2013 Bentley Systems, Incorporated iii Table of Contents License & Copyright...
Multiframe Windows Version 16 User Manual Bentley Systems, Incorporated 2013 License & Copyright Multiframe Program & User Manual 2013 Bentley Systems, Incorporated iii Table of Contents License & Copyright...
SAP2000. Linear and Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis and Design of Three-Dimensional Structures BASIC ANALYSIS REFERENCE
 SAP2000 Linear and Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis and Design of Three-Dimensional Structures BASIC ANALYSIS REFERENCE COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES INC. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California,
SAP2000 Linear and Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis and Design of Three-Dimensional Structures BASIC ANALYSIS REFERENCE COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES INC. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California,
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Analysis Steps 1. Start Abaqus and choose to create a new model database
 Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
GBTUL 1.0. Buckling and Vibration Analysis of Thin-Walled Members USER MANUAL. Rui Bebiano Nuno Silvestre Dinar Camotim
 GBTUL 1.0 Buckling and Vibration Analysis of Thin-Walled Members USER MANUAL Rui Bebiano Nuno Silvestre Dinar Camotim Department of Civil Engineering and Architecture, DECivil/IST Technical University
GBTUL 1.0 Buckling and Vibration Analysis of Thin-Walled Members USER MANUAL Rui Bebiano Nuno Silvestre Dinar Camotim Department of Civil Engineering and Architecture, DECivil/IST Technical University
Floor System Tutorial
 AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Floor System Tutorial FS3 - Floorbeam Stringer Floor System Example Topics Covered Superstructure composed of floorbeams and stringers System Superstructure Definition Rolled beam
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Floor System Tutorial FS3 - Floorbeam Stringer Floor System Example Topics Covered Superstructure composed of floorbeams and stringers System Superstructure Definition Rolled beam
Steel Structure Tutorial
 AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Steel Structure Tutorial STL5 - Two Span Rolled Beam Example BrD and BrR Training STL5 - Two Span Rolled Beam Example Topics Covered Steel rolled beam with cover plates input as
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Steel Structure Tutorial STL5 - Two Span Rolled Beam Example BrD and BrR Training STL5 - Two Span Rolled Beam Example Topics Covered Steel rolled beam with cover plates input as
Bridge Design using the STAAD.Pro/Beava AASHTO Code
 Bridge Design using the STAAD.Pro/Beava AASHTO Code By IEG Group, Bentley Systems Bentley Systems Inc. March 12, 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction.1 2.0 Creating the Bridge Geometry/Structural Analysis
Bridge Design using the STAAD.Pro/Beava AASHTO Code By IEG Group, Bentley Systems Bentley Systems Inc. March 12, 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction.1 2.0 Creating the Bridge Geometry/Structural Analysis
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC6 Two Span Reinforced Concrete Slab System Example
 AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC6 Two Span Reinforced Concrete Slab System Example AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training 6" A A 30'-0" 30'-0" B #11's #11's 1'-6"
AASHTOWare BrD/BrR 6.8 Reinforced Concrete Structure Tutorial RC6 Two Span Reinforced Concrete Slab System Example AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training 6" A A 30'-0" 30'-0" B #11's #11's 1'-6"
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Tutorial for MASTAN2 version 3.0
 Tutorial for version 3.0 Developed by: Ronald D. Ziemian Professor of Civil Engineering Bucknell University William McGuire Professor of Civil Engineering, Emeritus Cornell University JOHN WILEY & SONS,
Tutorial for version 3.0 Developed by: Ronald D. Ziemian Professor of Civil Engineering Bucknell University William McGuire Professor of Civil Engineering, Emeritus Cornell University JOHN WILEY & SONS,
Background CE 342. Why RISA-2D? Availability
 Background CE 342 RISA-2D RISA-2D is a structural analysis program, which can model: Beams, frames, trusses and plates. Any linear elastic structural material. Typical supports, such as pins, rollers and
Background CE 342 RISA-2D RISA-2D is a structural analysis program, which can model: Beams, frames, trusses and plates. Any linear elastic structural material. Typical supports, such as pins, rollers and
Pre-Lab Excel Problem
 Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
RISA 3D. Verification Problems. Rapid Interactive Structural Analysis 3 Dimensional
 RISA 3D Rapid Interactive Structural Analysis 3 Dimensional Verification Problems 26632 Towne Centre Drive, Suite 210 Foothill Ranch, California 92610 (949) 951 5815 (949) 951 5848 (FAX) www.risatech.com
RISA 3D Rapid Interactive Structural Analysis 3 Dimensional Verification Problems 26632 Towne Centre Drive, Suite 210 Foothill Ranch, California 92610 (949) 951 5815 (949) 951 5848 (FAX) www.risatech.com
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
PLAXIS 2D - SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION 3 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most
Custom Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006
 Custom Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents...i 4...3 4.1 Define Custom Part of Fastener Plate...3
Custom Components for Precast Concrete Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents...i 4...3 4.1 Define Custom Part of Fastener Plate...3
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Large Deformation Analysis of Beam-Plate in Bending
 H. Kim 2004 1 ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Large Deformation Analysis of Beam-Plate in Bending Hyonny Kim September 28, 2004 In this tutorial, you ll learn how to: Create a 3D model using shell elements. Conduct
H. Kim 2004 1 ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Large Deformation Analysis of Beam-Plate in Bending Hyonny Kim September 28, 2004 In this tutorial, you ll learn how to: Create a 3D model using shell elements. Conduct
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran
 Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4. ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I. Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC
 Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
CE Advanced Structural Analysis. Lab 1 Introduction to SAP2000
 Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 1 Introduction to SAP2000 January 09 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza Objectives:
Department of Civil & Geological Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CE 463.3 Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 1 Introduction to SAP2000 January 09 th, 2013 T.A: Ouafi Saha Professor: M. Boulfiza Objectives:
3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss
 TF 3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 40 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type:
TF 3. Check by Eurocode 3 a Steel Truss Applicable CivilFEM Product: All CivilFEM Products Level of Difficulty: Moderate Interactive Time Required: 40 minutes Discipline: Structural Steel Analysis Type:
Run multiple analyses which vary soil spring constants and damping ratio to account for uncertainties of soil data.
 Heavier equipment with faster machine speeds coupled with higher costs have made rule-of-thumb approaches and "rigid structure" assumptions either unsafe or too conservative for the design of many structures
Heavier equipment with faster machine speeds coupled with higher costs have made rule-of-thumb approaches and "rigid structure" assumptions either unsafe or too conservative for the design of many structures
CHECK STRESS ON DECK BASED ON SDI REQUIREMENTS
 ANALYSIS OF NON-COMPOSITE CONCRETE SLAB ON METAL DECK Lab #7 Question #2 A 6" total depth lightweight concrete slab with compressive strength of 3000psi is placed simply supported on a galvanized steel
ANALYSIS OF NON-COMPOSITE CONCRETE SLAB ON METAL DECK Lab #7 Question #2 A 6" total depth lightweight concrete slab with compressive strength of 3000psi is placed simply supported on a galvanized steel
Multiframe May 2010 Release Note
 Multiframe 12.02 18 May 2010 Release Note This release note describes the version 12.02 release of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/7. Contents
Multiframe 12.02 18 May 2010 Release Note This release note describes the version 12.02 release of Multiframe, Steel Designer and Section Maker. This release will run on Windows XP/2003/Vista/7. Contents
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
TABLE OF CONTENTS WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN? INSTALLING ADVANCE DESIGN... 8 System requirements... 8 Advance Design installation...
 Starting Guide 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Welcome to Advance Design... 5 About this guide... 6 Where to find information?... 6 Contacting technical support... 6 WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN?...
Starting Guide 2019 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Welcome to Advance Design... 5 About this guide... 6 Where to find information?... 6 Contacting technical support... 6 WHAT IS ADVANCE DESIGN?...
Three- Span Continuous Horizontally Curved. Composite Steel TUB Girder Bridge
 Three- Span Continuous Horizontally Curved Composite Steel TUB Girder Bridge WIZARD, ANALYSIS AND DESIGN TUB Girder Curved Contents Bridge Information Material and Section Properties Wizard Modelling Tweaks
Three- Span Continuous Horizontally Curved Composite Steel TUB Girder Bridge WIZARD, ANALYSIS AND DESIGN TUB Girder Curved Contents Bridge Information Material and Section Properties Wizard Modelling Tweaks
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description
 Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Creating a Text Frame. Create a Table and Type Text. Pointer Tool Text Tool Table Tool Word Art Tool
 Pointer Tool Text Tool Table Tool Word Art Tool Picture Tool Clipart Tool Creating a Text Frame Select the Text Tool with the Pointer Tool. Position the mouse pointer where you want one corner of the text
Pointer Tool Text Tool Table Tool Word Art Tool Picture Tool Clipart Tool Creating a Text Frame Select the Text Tool with the Pointer Tool. Position the mouse pointer where you want one corner of the text
It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius This end fixed Shell-shell intersection dimensions and loading
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius Material properties: 0.08 E = 2.07 1011 N/m2 = 0.29 All dimensions in meters Line load of 1000 N/m 0.0075 radius
Problem description It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius Material properties: 0.08 E = 2.07 1011 N/m2 = 0.29 All dimensions in meters Line load of 1000 N/m 0.0075 radius
1st Point. 2nd Point. hold shift & drag along Y. Splines
 Splines STEP 1: open 3DS Max _ from the Command Panel under the Create tab click on Shapes (note: shapes are really Splines) _ under Object Type click on Ellipse STEP 2: Expand the Keyboard Entry tab type
Splines STEP 1: open 3DS Max _ from the Command Panel under the Create tab click on Shapes (note: shapes are really Splines) _ under Object Type click on Ellipse STEP 2: Expand the Keyboard Entry tab type
Advanced Application 1. Steel Structure
 Advanced Application 1 Steel Structure Steel Structure Summary Figure 1.1 Steel Building 1 Structural Plans & Section 1 2 3 4 36000 12000 12000 12000 E C4 SG1 SG1 SG1 C2 C2 C4 SG1A D C B A 38400 10800
Advanced Application 1 Steel Structure Steel Structure Summary Figure 1.1 Steel Building 1 Structural Plans & Section 1 2 3 4 36000 12000 12000 12000 E C4 SG1 SG1 SG1 C2 C2 C4 SG1A D C B A 38400 10800
General Information Project management Introduction... 4 Getting Started Input geometry... 7
 Tutorial Shell Tutorial Shell All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database or retrieval system or published,
Tutorial Shell Tutorial Shell All information in this document is subject to modification without prior notice. No part or this manual may be reproduced, stored in a database or retrieval system or published,
GETTING STARTED COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES INC.
 SAP2000 Linear and Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis and Design of Three-Dimensional Structures GETTING STARTED COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES INC. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA
SAP2000 Linear and Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis and Design of Three-Dimensional Structures GETTING STARTED COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES INC. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA
SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION
 2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
2 SUBMERGED CONSTRUCTION OF AN EXCAVATION This tutorial illustrates the use of PLAXIS for the analysis of submerged construction of an excavation. Most of the program features that were used in Tutorial
USER S MANUAL OF FORMWORKS PLUS FOR
 USER S MANUAL OF FORMWORKS PLUS FOR VECTOR5 by Kyle Blosser Serhan Guner Frank J. Vecchio May 2016 Copyright by K. Blosser, S. Guner, F. J. Vecchio (2016) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 4 2. Create
USER S MANUAL OF FORMWORKS PLUS FOR VECTOR5 by Kyle Blosser Serhan Guner Frank J. Vecchio May 2016 Copyright by K. Blosser, S. Guner, F. J. Vecchio (2016) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 4 2. Create
System Components for Steel Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 21, 2006
 System Components for Steel Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 21, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents 2...3 2.1 About System Components...3 2.2 Column Base Plates...5 2.3 Beam
System Components for Steel Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 21, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents 2...3 2.1 About System Components...3 2.2 Column Base Plates...5 2.3 Beam
SAP2000 Version Release Notes
 SAP2000 Version 17.3.0 Release Notes Copyright Computers and Structures, Inc., 2015 Notice Date: 2015-07-02 This file lists all changes made to SAP2000 since the previous version. Most changes do not affect
SAP2000 Version 17.3.0 Release Notes Copyright Computers and Structures, Inc., 2015 Notice Date: 2015-07-02 This file lists all changes made to SAP2000 since the previous version. Most changes do not affect
ROSE-HULMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 Introduction to Working Model Welcome to Working Model! What is Working Model? It's an advanced 2-dimensional motion simulation package with sophisticated editing capabilities. It allows you to build and
Introduction to Working Model Welcome to Working Model! What is Working Model? It's an advanced 2-dimensional motion simulation package with sophisticated editing capabilities. It allows you to build and
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial Problem Description A table made of steel tubing with a solid steel top and shelf is loaded with an oblique impulse load. Determine the transient response of the
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial Problem Description A table made of steel tubing with a solid steel top and shelf is loaded with an oblique impulse load. Determine the transient response of the
Tutorial 4 Arch Bridge
 Tutorial 4 Arch Bridge Civil TUTORIAL 4. ARCH BRIDGE Summary 1 Analysis Model and Load Cases / 2 File Opening and Preferences Setting 5 Enter Material and Section Properties 6 Structural Modeling Using
Tutorial 4 Arch Bridge Civil TUTORIAL 4. ARCH BRIDGE Summary 1 Analysis Model and Load Cases / 2 File Opening and Preferences Setting 5 Enter Material and Section Properties 6 Structural Modeling Using
Installation Guide. Beginners guide to structural analysis
 Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Module 3: Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam
 Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016)
 Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016) Problem Description A round bar with tapered diameter has a total load of 1000 N applied to its top face. The bottom of the bar is completely fixed. Determine
Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016) Problem Description A round bar with tapered diameter has a total load of 1000 N applied to its top face. The bottom of the bar is completely fixed. Determine
Revised Iain A MacLeod
 LUSAS User Guidelines Revised 20.06.14 Iain A MacLeod Contents 1 Geometrical features and meshes... 1 2 Toolbars... 1 3 Inserting points... 1 4 Inserting a line between two points... 1 5 Creating a dataset...
LUSAS User Guidelines Revised 20.06.14 Iain A MacLeod Contents 1 Geometrical features and meshes... 1 2 Toolbars... 1 3 Inserting points... 1 4 Inserting a line between two points... 1 5 Creating a dataset...
Tutorial. Spring Foundation
 Page i Preface This tutorial provides an example on how to model a spring foundation using BRIGADE/Plus. Page ii Contents 1 OVERVIEW... 1 2 GEOMETRY... 1 3 MATERIAL AND SECTION PROPERTIES... 2 4 STEP DEFINITION...
Page i Preface This tutorial provides an example on how to model a spring foundation using BRIGADE/Plus. Page ii Contents 1 OVERVIEW... 1 2 GEOMETRY... 1 3 MATERIAL AND SECTION PROPERTIES... 2 4 STEP DEFINITION...
Figure E3-1 A plane struss structure under applied loading. Start MARC Designer. From the main menu, select STATIC STRESS ANALYSIS.
 Example 3 Static Stress Analysis on a Plane Truss Structure Problem Statement: In this exercise, you will use MARC Designer software to carry out a static stress analysis on a simple plane truss structure,
Example 3 Static Stress Analysis on a Plane Truss Structure Problem Statement: In this exercise, you will use MARC Designer software to carry out a static stress analysis on a simple plane truss structure,
AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015
 AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015 M N D O T B R I D G E S T A T E A I D Page 1 PS1 - Simple Span Prestressed I Beam Example (BrR 6.7.1) 1. From the Bridge Explorer create
AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015 M N D O T B R I D G E S T A T E A I D Page 1 PS1 - Simple Span Prestressed I Beam Example (BrR 6.7.1) 1. From the Bridge Explorer create
Practical modeling of diaphragm walls and foundation rafts with piles part I
 Practical modeling of diaphragm walls and foundation rafts with piles part I FE mesh This example concerns modeling of a deep excavation protected by concrete wall an then by a construction of foundation
Practical modeling of diaphragm walls and foundation rafts with piles part I FE mesh This example concerns modeling of a deep excavation protected by concrete wall an then by a construction of foundation
Importing a PATRAN 2.5 Model into P3
 LESSON 1 Importing a PATRAN 2.5 Model into P3 Objectives: Read a PATRAN 2.5 neutral file into P3. Import PATRAN 2.5 result files into your P3 database. Work with multiple load cases. PATRAN 303 Exercise
LESSON 1 Importing a PATRAN 2.5 Model into P3 Objectives: Read a PATRAN 2.5 neutral file into P3. Import PATRAN 2.5 result files into your P3 database. Work with multiple load cases. PATRAN 303 Exercise
