Managing Service Requests
|
|
|
- Loraine McKenzie
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes how to manage Prime Fulfillment service requests through the Service Request Manager window. It contains the following sections: Accessing the Service Request Manager Window, page 8-1 Viewing Service Request Details, page 8-3 Viewing the Status of Service Requests, page 8-8 Previewing Configlets, page 8-9 Editing Service Requests, page 8-10 Deploying Service Requests, page 8-10 Decommissioning Service Requests, page 8-12 Deleting Service Requests, page 8-13 Service Request States, page 8-13 Accessing the Service Request Manager Window To manage service requests, choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. Figure 8-1 shows the Service Request Manager window. 8-1
2 Accessing the Service Request Manager Window Chapter 8 Figure 8-1 Service Request Manager Window The Service Request Manager window shows the current list of service requests for this username. The window provides the following information about each service request: JobID The job number assigned to the service request by Prime Fulfillment. Data Files Shows if a data file is associated with the service request. A paper clip icon appears in the Data Files column if a service request has one or more templates associated with it. For more information about how templates and data files are used with service requests, see Chapter 9, Managing Templates and Data Files. State The transition state for the service request. See Service Request States, page 8-13 for more information. Type The type of service request. For example, MPLS VPN, L2VPN, VPLS, VRF, TE, or EVC. Operation Type The operation type for the service request. For example, ADD means that you are adding this service request, MODIFY that a service request has been changed from an earlier state, and DELETE that you are decommissioning this service request. Creator Username identity of person who created or last modified the service request. Customer Name Customer name for the service request. Policy Name Name of policy assigned to this service request. Last Modified Date and time the service request was created or last modified. Description Optional text description of the service request. You can use the buttons at the bottom of the Service Request Manager window to perform the following operations for service requests: Create Create a Prime Fulfillment service request. See other chapters in this guide for more information on creating services requests for particular services. Details View the service request history report, audit the service request, and view configlets. For more details, see Viewing Service Request Details, page 8-3. Status View links and access any available logs for a selected service request. For more details, see Viewing the Status of Service Requests, page 8-8. Configlet Preview Preview configlets that will be sent to a device for a specific service request. For more details, see Previewing Configlets, page
3 Chapter 8 Viewing Service Request Details Edit Edit a service request. For more details, see Editing Service Requests, page Deploy Deploy a service request. For more details, see Deploying Service Requests, page Decommission Decommission a service request. For more details, see Decommissioning Service Requests, page Delete Delete a service request. For more details, see Deleting Service Requests, page Viewing Service Request Details The service request details include the link endpoints for the service request, the history, and the configlet generated during the service request deployment operation. Use the service request details to troubleshoot a problem or error with the service request or to check the commands in the configlet. This section describes how to view the details of a service request, including the history, link details, and configlets. To view service request detail, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. Select the service request and click Details. The Service Request Details window appears. From the Service Request Details page, you can view more information about: Details > Links Service request links report. Details > History Service request history report. Details > Audit Not supported by Prime Fulfillment. Details > Configlets View the Prime Fulfillment generated configlet for the service request. The following sections describe the links, history, audit, and configlet details for a service request. Viewing Service Request Link Details The service request link details include the link endpoints, PE secured interface, VLAN ID, and whether a CE is present. To see this information, perform the following steps. Click Links on the Service Request Details window. The Service Request Link window appears. Choose a link and click Details. The Service Request Link Details window appears. Click OK to return to the Service Request Link window. Choose another link to view, or click OK to return to the Service Request Details window. 8-3
4 Viewing Service Request Details Chapter 8 Viewing Service Request History Information To view history information about the service request, perform the following steps. Click History on the Service Request Details window. The Service Request State Change Report window appears. The history report shows the following information about the service request: Element name The device, interface, and subinterfaces participating in this service request. State The transition states the element has gone through. Create Time The time the element was created for this service request. Report The action taken by Prime Fulfillment for the element in this service request. Click OK to return to the Service Request Details window. Viewing Audit Reports Service Requests This section describes how to view configuration and functional audit reports for Prime Fulfillment service requests. Viewing Configuration Audit Reports A configuration audit verifies if all the commands for a service (service intent) are present on the network elements that participate in the service. Each time a service request is deployed in Prime Fulfillment, a configuration audit occurs. When a configuration audit occurs, Prime Fulfillment verifies that all Cisco IOS commands are present and that they have the correct syntax. An audit also verifies that there were no errors during deployment. If the device configuration does not match what is defined in the service request, the audit flags a warning and sets the service request to a Failed Audit or Lost state. A configuration audit can fail if some of the commands are removed after provisioning from the network elements. This could happen if the commands are manually removed or they are removed as part of provisioning some other service. Another reason a configuration audit can fail is if Prime Fulfillment does not recognize commands in the configuration file. The default behavior in Prime Fulfillment is to skip unrecognized commands in the configuration file during the configuration audit. Such unrecognized commands might have be been present in an existing configuration or manually inserted in the configuration file. If an unrecognized command is at the start of a block of commands, Prime Fulfillment will skip the initial command and continue to parse the subcommands in the block. This might lead Prime Fulfillment to assume there is an error in the logic flow within the configuration file and cause the audit to fail. Configuration audits can be performed manually through the Prime Fulfillment Task Manager. For information on how to create a task to manually schedule a configuration audit, see Task Manager, page To display the Configuration Audit report for a service request, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. 8-4
5 Chapter 8 Viewing Service Request Details The Service Request Manager window appears. Choose a service request for the configuration audit. Click Details. The Service Request Details window appears. Click the Audit button and choose Config from the drop-down list. The Service Request Audit Report window appears. This window lists the device name and role, and a message regarding the status of your configuration audit. If the audit is unsuccessful, the message field lists details on the failed audit. The audit failure message indicates missing commands and configuration issues. Carefully review the information in the message field. If the audit fails, you must correct all errors and redeploy the service request. Click OK to return to the Service Request Details window. Viewing a Functional Audit Report A functional audit verifies that the links in a service request or VPN are working correctly. The audit checks the routes to remote CEs in the VRF route tables on the PE devices. Prime Fulfillment automatically provides a functional audit whenever a service request is deployed or force-redeployed. A functional audit could fail if BGP peering is incorrect, MPLS setup in the core is faulty, or remote links are down. Functional audits can be performed manually through the Prime Fulfillment Task Manager. For information on how to create a task to manually schedule a functional audit, see Task Manager, page To display the functional audit report for a service request, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. The Service Request Manager window appears. Choose a service request for the functional audit. Click Details. The Service Request Details window appears. Click the Audit button and choose Functional from the drop-down list. The Service Request Audit Report window appears. This window lists the device name and role, and a message regarding the status of your configuration audit. If the audit is unsuccessful, the message field lists details on the failed audit. The audit failure message indicates missing commands and configuration issues. Carefully review the information in the message field. If the audit fails, you must correct all errors and redeploy the service request. Click OK to return to the Service Request Details window. 8-5
6 Viewing Service Request Details Chapter 8 Viewing Service Request Configlets After you deploy the service request, Prime Fulfillment generates Cisco IOS or IOS XR commands to turn on appropriate services on all the network devices that participate in the service request. Note For IOS devices, the configlets will appear as CLI commands. For IOS XR devices, the configlets can be viewed in XML or CLI format. For information about viewing configlets for IOS XR devices, see Viewing Configlets on IOS XR Devices, page 8-6. To view the configlets that are generated, perform the following steps. Step 6 Step 7 Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager to view the available service requests. Check the appropriate check box to select the service request for which you want to view the associated configlets. Click the Details button. The Service Request Details window appears. Click the Configlets button. The Service Request Configlets window appears. This window displays a list of devices for which configlets have been generated. To view configlets that were generated for a device, select a device and click the View Configlet button. The Service Request Configlet window updates showing the configlet. By default, the latest generated configlet is displayed. If applicable, you can display configlets for a device based on the time of creation. Choose the desired time of creation in the Create Time list to display a specific configlet based on the time the configlet was generated for the service request. Click OK when you are finished viewing the configlet. Viewing Configlets on IOS XR Devices By default, service requests for IOS XR devices log the configuration sent to the device in XML format. Therefore, when configlets are viewed for IOS XR devices, they are displayed in raw XML format. Prime Fulfillment also allows the configlet to be viewed in CLI format. This feature is enabled by setting the DCPL property DCS/getCommitCLIConfigAfterDownload to true (the default setting). Note The DCPL property DCS/getCommitCLIConfigAfterDownload must be set to true to display the configlet(s) in CLI format. On setting the DCPL property to true, CLI configlets will only be available for subsequent service request deployments. They will not be available for configlets that were deployed before the DCPL property was set to true. To view the configlets for IOS XR devices in XML or CLI formats, or both, perform the following steps. 8-6
7 Chapter 8 Viewing Service Request Details Step 6 Step 7 Step 8 Step 9 Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager to view the available service requests. Check the appropriate check box to select the service request for which you want to view the associated configlets. Click the Details button. The Service Request Details window appears. Click the Configlets button. The Service Request Configlets window appears. This window displays a list of devices for which configlets have been generated. To view configlets that were generated for an IOS XR device, select an IOS XR device and click the View Configlet button. The Service Request Configlet window appears showing the configlet in CLI format. By default, the latest generated configlet is displayed. If applicable, you can display configlets for a device based on the time of creation. Choose the desired time of creation in the Create Time list to display a specific configlet based on the time the configlet was generated for the service request. To view the configlet in XML format, click the XML Configlet radio button. The window refreshes and displays the configlet in XML format. To toggle among different formats, use the following radio buttons: XML Configlet Displays the configlet in XML format. CLI Configlet Displays the configlet in CLI format. This the default selection. Both Displays the configlet side by side in both XML and CLI formats. Click OK when you are finished viewing the configlet. Editing Configuration Files To view or edit an existing router configuration file, perform the following steps. Note Exercise caution when editing a configuration file, particularly if you then choose to make the edited file the running configuration file. Click the Inventory > Physical Inventory > Devices. The Devices Inventory window appears. Check the check box next to the device name to choose the configuration file versions you want to view. Click Config. The Device Configurations window appears. The Device Configurations window displays the list of the current versions of the configuration files for the selected device. The configurations are listed by date and time. The configuration file listed first is the latest version. Choose the version of the configuration file you want to view, then click Edit. 8-7
8 Viewing the Status of Service Requests Chapter 8 Step 6 The contents of the selected configuration file are displayed. You can view or edit the displayed device configuration file. If necessary, edit the configuration file. When finished editing the file, click Save. Viewing the Status of Service Requests From the Service Request Manager window, you can obtain status information on a service request as detailed in the following sections. Viewing Links To view information about links associated with a service request, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager to view the available service requests. Check the appropriate check box to select the service request for which you want to view the associated links. Click the Status button and choose Links. The SR Link window appears. This window displays a list of links associated with this service request. When you are finished reviewing the information, click the Return to SRs button. Viewing Logs To view logs associated with a service request, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager to view the available service requests. Check the appropriate check box to select the service request for which you want to view the associated links. Click the Status button and choose Logs. The Task Logs window appears. This window displays the task by Runtime Task Name, and the Action, Start Time, End Time, and the Status of the task. You can use this window to view or delete the logs. To view the log, check the check box for the row that represents the task and click the View Log button. The Task Log page appears. 8-8
9 Chapter 8 Previewing Configlets Step 6 It is possible to set the types of log level you want to view. Specify the Log Level and click Filter button to view that information you want to view. Click Return to Logs to specify another log to view. When you are finished reviewing the log information, click the Close button. Previewing Configlets The preview configlet operation allows you to preview the configlet(s) that will be sent to a device (or devices) for a selected service request before the device is actually provisioned. This allows you to check that the service request is generating the expected configlet(s), including any templates that may be applied. Note the following caveats: The preview configlet preview feature is available to service requests in all states except In Progress and Closed. The preview configlet feature is not supported for TEM service requests. To preview configlets for a service request, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. In the Service Request Manager window, select a service request and click Configlet Preview. Choose one of the following from the drop-down list: For Deploy Generates the configlet(s) that would be generated by a Deploy operation. For Force Deploy Generates the configlet(s) that would be generated by a Force Deploy operation. These choices mimic the two different deployment options available, as the type of deployment may affect the configlet generated. The Configlet Preview window appears. This window contains the generated configlets for each device in the service request. Note This operation may take some time, as the configlet(s) must be uploaded from the device. After you review the configlets, click OK to return to the Service Request Manager window. This feature is also available through the Deploy Service Request window, when a task is created to deploy the selected service request(s). Navigate to the Deploy Service Request window by choosing one or more service requests in the Service Request Manager window. Then choose Deploy > Deploy or Deploy > Force Deploy. The Deploy Service Request window that appears contains a table representing the selected service requests. Click on the Configlet Preview link in this table to show preview configlets. 8-9
10 Editing Service Requests Chapter 8 Editing Service Requests To edit a service request, perform the following steps. Choose Service Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. Select the service request you want to modify and click Edit. The Service Request Editor window appears. Note The exact name and contents of this window will vary based on the type of service request being edited. Make the desired changes in the editor and click Save. The Service Requests window reappears with the corresponding state of the service request set to In Progress and the Operation Type changed to Modify. In order for the changes to be provisioned on the network, you must deploy the service request. For information about how to deploy a service request, see Deploying Service Requests, page After deployment, look for the service request state to go to Deployed to indicate a successful deployment. Deploying Service Requests To apply policies to network devices, you must deploy the service request. When you deploy a service request, Prime Fulfillment compares the device information in the Repository (the Prime Fulfillment database) with the current device configuration and generates a configlet. To apply device changes to network devices, you must deploy the service request. When you deploy a service request, Prime Fulfillment compares the device information in the Repository (the Prime Fulfillment database) with the current device configuration and generates a configlet. Service Deployment To deploy the service requests immediately or schedule their deployment, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. The Service Requests Manager window appears. Check the check box next to the Job ID for the service request you want to deploy. Click the Deploy drop-down list. You have two deployment options: Deploy: Use Deploy when the service request state is Requested or Invalid. Force Deploy: Use Force Deploy when the service request state is Deployed or Failed Audit. Choose Deploy. The Deploy Service Request dialog box appears, which allows you to schedule when you want to deploy the selected service request. 8-10
11 Chapter 8 Deploying Service Requests Step 6 Step 7 Complete the fields in this dialog box to schedule the service requested as needed. When satisfied with the schedule settings, click Save. You return to the Service Request Manager window. Check the Status display in the pop-up window at the lower corner of the window. If the service request has been deployed successfully, the Status display appears and shows a check in the Succeeded check box. To update the State from Requested to Deployed, check the Auto Refresh check box. Note You can view logs to check on the task status and whether or not it completed successfully. For information on viewing logs, see Viewing Logs, page 8-8. Monitoring Service Requests To monitor a service request that is being deployed, you must use the task logs to help you troubleshoot why a service request has failed or to find more details about a service request. To monitor a service request, perform the following steps. Step 6 Step 7 Choose Operate > Tasks > Task Manager. The Task Logs window appears. Click Find to refresh the window. The task that is executing will be the first in the list of tasks that are being performed in Prime Fulfillment. Choose the task you want to monitor and click Logs. Choose the run-time task that you want to monitor and click View Log. Choose the log level from the Log Level drop-down list and click Filter. The log levels are All, Severe, Warning, Info, Config, Fine, Finer, and Finest. Click Return to Logs. Click Close in the Task Logs window. Simulated Deployment of Service Requests Simulate deploy is an additional option when deploying a service request. To use this feature, you must first set the DCPL property Services\Common\allowSimulateDeploy to true. When enabled, any service request that you can deploy by a standard deploy operation (for example, moving a service request from the Requested to Deployed state) can also be deployed in simulation mode. In a simulated deployment the provisioning flow proceeds as normal up to the point at which the configlet is to be downloaded to the device. For example, a live configuration will still be uploaded from the device. However, when downloading a configlet, Prime Fulfillment will act as if in echo mode (that is, the 8-11
12 Decommissioning Service Requests Chapter 8 configuration will not be downloaded to the actual device). In effect, this is echo mode on a per service request basis. Multiple deployment operations, both standard and simulated, can run concurrently using a mixture of echo-based transport and live device interactions. To simulate deploy a service request, perform the following steps. Step 6 Step 7 Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. The Service Requests Manager window appears. Check the check box next to the Job ID for the service request you want to deploy. Click the Deploy drop-down list. Assuming the DCPL property Services\Common\allowSimulateDeploy has been set to true, you have three deployment options: Deploy Force Deploy Simulate Deploy Choose Simulate Deploy. The Deploy Service Request dialog box appears, which allows you to schedule when you want to simulate deploy the selected service request. Complete the fields in this dialog box to schedule the service requested as needed. When satisfied with the schedule settings, click Save. You return to the Service Request Manager window. Check the Status display in the pop-up window at the lower corner of the window. If the service request has been deployed successfully, the Status display appears and shows a check in the Succeeded check box. To update the State from Requested to Deployed, check the Auto Refresh check box. Note You can view logs to check on the task status and whether or not it completed successfully. For information on viewing logs, see Viewing Logs, page 8-8. Decommissioning Service Requests To decommission a service request, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. In the Service Request Manager window, select the service request you want to decommission and click Decommission. The Confirm Decommission Service Request(s) window appears. Click OK to confirm the decommissioning of the service request. The Service Request Manager window reappears with the corresponding Operation Type changed to Delete. 8-12
13 Chapter 8 Deleting Service Requests Step 6 Deploy the service request by selecting it and clicking Deploy > Deploy. This is necessary for the changes to be provisioned to the network. In the Deploy Service Request window, select the time at which the deployment should take place (default is immediately), and click Save. After deployment, look for the service request state to go to Closed to indicate that the service request has been decommissioned successfully. Deleting Service Requests The Delete operation is designed to remove a service request from the repository without affecting the network. To delete a service request, perform the following steps. Choose Operate > Service Requests > Service Request Manager. In the Service Request Manager window, select the service request you want to decommission and click Delete. From the drop-down list choose one of the following: Delete The regular delete can only be used on the service request in Closed state. Note The regular delete cannot be used on TE Resource, TE Tunnel, or TE Protection service requests because these cannot be decommissioned. These three types of service requests can only be force deleted. Force Delete During force delete, the repository checks the necessary dependency on the service request before it can be deleted, so if a service request cannot be deleted, there will be an error message. The Delete Service Request(s) window appears. Click OK to confirm the delete or force delete operation. Service Request States A service request transition state describes the different stages a service request enters during the provisioning process. For example, when you deploy a service request, Prime Fulfillment compares the device information in the Repository (the Prime Fulfillment database) with the current device configuration and generates a configlet. When the configlet is generated and downloaded to the device, the service request enters the Pending state. When the device is audited, the service request enters the Deployed state. Prime Fulfillment service requests are processed in parallel, except when multiple service requests attempt to configure the same device. In this case, the service requests are processed sequentially (that is, only one write to the device can happen at a time). 8-13
14 Service Request States Chapter 8 Figure 8-2, Service Requests States Transition Diagram, shows a high-level diagram of the relationships and movement among Prime Fulfillment service request states. Figure 8-2 Service Requests States Transition Diagram REQUESTED IN PROGRESS Table 8-1, Summary of Prime Fulfillment Service Request States, describes the functions of each Prime Fulfillment service request state. They are listed in alphabetical order. Table 8-1 Summary of Prime Fulfillment Service Request States Service Request Type Broken (valid only for MPLS services) Closed Deployed Description The router is correctly configured but the service is unavailable (due to a broken cable or Layer 2 problem, for example). An MPLS service request moves to Broken if the auditor finds the routing and forwarding tables for this service, but they do not match the service intent. A service request moves to Closed if the service request should no longer be used during the provisioning or auditing process. A service request moves to the Closed state only upon successful audit of a decommission service request. Prime Fulfillment does not remove a service request from the database to allow for extended auditing. Only a specific administrator purge action results in service requests being removed. A service request moves to Deployed if the intention of the service request is found in the router configuration file. Deployed indicates that the configuration file has been downloaded to the router, and the intent of the request has been verified at the configuration level. That is, Prime Fulfillment downloaded the configlets to the routers and the service request passed the audit process. 8-14
15 Chapter 8 Service Request States Table 8-1 Summary of Prime Fulfillment Service Request States (continued) Service Request Type Failed Audit Failed Deploy Functional (valid only for MPLS services) Invalid Lost Pending Requested Description This state indicates that Prime Fulfillment downloaded the configlet to the router successfully, but the service request did not pass the audit. Therefore, the service did not move to the Deployed state. The Failed Audit state is initiated from the Pending state. After a service request is deployed successfully, it cannot re-enter the Failed Audit state (except if the service request is redeployed). The cause for a Failed Deploy status is that DCS reports that either the upload of the initial configuration file from the routers failed or the download of the configuration update to the routers failed (due to lost connection, faulty password, and so on). An MPLS service request moves to Functional when the auditor finds the VPN routing and forwarding tables (VRF) for this service and they match with the service intent. This state requires that both the configuration file audit and the routing audit are successful. Invalid indicates that the service request information is incorrect in some way. A service request moves to Invalid if the request was either internally inconsistent or not consistent with the rest of the existing network/router configurations (for example, no more interfaces were available on the router). The Provisioning Driver cannot generate configuration updates to service this request. A service request moves to Lost when the Auditor cannot find a configuration-level verification of intent in the router configuration files. The service request was in the Deployed state, but now some or all router configuration information is missing. A service request can move to the Lost state only when the service request had been Deployed. A service request moves to Pending when the Provisioning Driver determines that the request looks consistent and was able to generate the required configuration updates for this request. Pending indicates that the service request has generated the configuration updates and the configuration updates are successfully downloaded to the routers. The Auditor regards pending service requests as new requests and begins the audit. If the service has been freshly provisioned and not yet audited, it is not an error (pending audit). However, if an audit is performed and the service is still pending, it is in an error state. If the service is newly entered and not yet deployed, it is not an error. However, if a Deploy is done and it remains Requested, the service is in an error state. 8-15
16 Service Request States Chapter 8 Table 8-1 Summary of Prime Fulfillment Service Request States (continued) Service Request Type In Progress Wait Deploy Description Whenever a service request is requested for deployment, irrespective of its current state, it displays the In Progress state. The In Progress state is an intermediate state between Requested and Deployed. Whenever multiple service requests are concurrently requested for deployment, they all display the state of In Progress. This service request state pertains only when downloading configlets using Cisco Configuration Engine. Wait Deploy indicates that the configlet has been generated, but it has not been downloaded because the device is not currently online. The configlet is staged in the repository until such time as the Cisco Configuration Engine notifies Prime Fulfillment that the device is up. Configlets in the Wait Deploy state are then downloaded to the device. Table 8-2, User Operations on Prime Fulfillment Service Requests, describes user operations and their impact on Prime Fulfillment service requests. Table 8-2 User Operations on Prime Fulfillment Service Requests User Operations Decommission Force Deploy Force Delete Delete Description This user operation removes the service from all devices in the service request. This user operation allows you to Deploy a service request from any state except Closed. This is equivalent to restarting the state diagram. The service request can move from its current state to any other possible state. However, it does not move to the Requested state. This user operation removes a service request from the database irrespective of its state. If you Force Delete a service request from the Prime Fulfillment repository before first decommissioning the service request, the service remains running on the network (specifically, the configuration remains on the devices on which the service was provisioned), but all record of the service request that created the service is removed from Prime Fulfillment. When a service request is deleted, it is removed from the Prime Fulfillment database. 8-16
Setting Up Logical Inventory
 CHAPTER 3 VRFs There are two VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) models. In the traditional VRF model, the operator first creates a VPN object and then associates it to an MPLS VPN link. The necessary VRF
CHAPTER 3 VRFs There are two VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) models. In the traditional VRF model, the operator first creates a VPN object and then associates it to an MPLS VPN link. The necessary VRF
Defining VPNs and Provisioning Service Requests
 CHAPTER 5 Defining VPNs and Provisioning Service Requests The focus of the VPN Solutions Center: IPsec Solution product is the service provided for a customer on the link between the customer s edge device
CHAPTER 5 Defining VPNs and Provisioning Service Requests The focus of the VPN Solutions Center: IPsec Solution product is the service provided for a customer on the link between the customer s edge device
Managing Templates and Data Files
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter explains the use of templates and data files in Prime Provisioning. It contains the following sections: Overview, page 10-1 Basic Template and Data File Tasks, page 10-5 Using Templates
CHAPTER 10 This chapter explains the use of templates and data files in Prime Provisioning. It contains the following sections: Overview, page 10-1 Basic Template and Data File Tasks, page 10-5 Using Templates
Managing MPLS VPN Services
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes the tasks required to get started using Cisco Prime Fulfillment 6.2, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) virtual private network (VPN). The information in the section
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes the tasks required to get started using Cisco Prime Fulfillment 6.2, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) virtual private network (VPN). The information in the section
Using Inventory Manager
 14 CHAPTER This chapter explains how Inventory Manager provides a method of managing mass changes to inventory and service model data in the Prime Provisioning provisioning process. In this process, Inventory
14 CHAPTER This chapter explains how Inventory Manager provides a method of managing mass changes to inventory and service model data in the Prime Provisioning provisioning process. In this process, Inventory
Monitoring. Ping CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter explains the monitoring activity. It contains the following sections: Ping, page 10-1 SLA, page 10-3 Task Manager, page 10-23 Reports, page 10-27 Ping Ping is the way Prime Provisioning
CHAPTER 10 This chapter explains the monitoring activity. It contains the following sections: Ping, page 10-1 SLA, page 10-3 Task Manager, page 10-23 Reports, page 10-27 Ping Ping is the way Prime Provisioning
Prime Fulfillment Process Diagram - TE Traffic Admission. Preconfiguration (incl. Discovery) Check Link Perf. Resource Management
 CHAPTER 41 is the first step towards enabling services on TE tunnels. There are a number of mechanisms that can be used for forwarding traffic into a tunnel to provide basic IP connectivity. The current
CHAPTER 41 is the first step towards enabling services on TE tunnels. There are a number of mechanisms that can be used for forwarding traffic into a tunnel to provide basic IP connectivity. The current
Inventory - Discovery
 APPENDIXE This appendix describes how to use the Discovery feature to discover devices, connections, and services for the Prime Provisioning provisioning process. It contains the following sections: Overview
APPENDIXE This appendix describes how to use the Discovery feature to discover devices, connections, and services for the Prime Provisioning provisioning process. It contains the following sections: Overview
Smart Install in LMS CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 6 Smart Install (SI) is a plug-and-play configuration and image management feature that provides zero-touch deployment for new switches. You can configure SI on a switch which will then be the
CHAPTER 6 Smart Install (SI) is a plug-and-play configuration and image management feature that provides zero-touch deployment for new switches. You can configure SI on a switch which will then be the
Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
 CHAPTER 27 This chapter describes how to configure MPLS VPN PE-CE links in the Prime Fulfillment provisioning process. MPLS VPN PE-CE Link Overview To provision an MPLS VPN service in Prime Fulfillment,
CHAPTER 27 This chapter describes how to configure MPLS VPN PE-CE links in the Prime Fulfillment provisioning process. MPLS VPN PE-CE Link Overview To provision an MPLS VPN service in Prime Fulfillment,
Managing MPLS Traffic Engineering Services
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter contains a detailed description of the Cisco Prime Fulfillment Traffic Engineering Management (TEM) product, including the various features, the GUI, and the step-by-step processes
CHAPTER 7 This chapter contains a detailed description of the Cisco Prime Fulfillment Traffic Engineering Management (TEM) product, including the various features, the GUI, and the step-by-step processes
Prime Fulfillment Process Diagram - Protection Management. Preconfiguration (incl. Discovery) Check Link Perf. Protection Management
 CHAPTER 40 This chapter describes the process of creating and managing the protection of network elements using automated protection tools. See Chapter 38, Basic Tunnel Management for a description of
CHAPTER 40 This chapter describes the process of creating and managing the protection of network elements using automated protection tools. See Chapter 38, Basic Tunnel Management for a description of
Adding Additional Information to Services
 APPENDIXF This appendix describes how the additional information feature is supported in Prime Provisioning. It contains the following sections: Overview, page F-1 Prerequisites and Limitations, page F-1
APPENDIXF This appendix describes how the additional information feature is supported in Prime Provisioning. It contains the following sections: Overview, page F-1 Prerequisites and Limitations, page F-1
Managing RAN Backhaul Services
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to use Prime Fulfillment to manage radio access network (RAN) backhaul services in Prime Fulfillment. It contains the following sections: Overview of RAN Backhaul Services,
CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to use Prime Fulfillment to manage radio access network (RAN) backhaul services in Prime Fulfillment. It contains the following sections: Overview of RAN Backhaul Services,
Managing Deployment. Understanding Deployment CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 8 The settings and policies you define in Security Manager must be deployed to your devices so that you can implement them in your network. The steps you take to deploy configurations to devices
CHAPTER 8 The settings and policies you define in Security Manager must be deployed to your devices so that you can implement them in your network. The steps you take to deploy configurations to devices
Using NetShow Commands
 CHAPTER 10 Network show (NetShow) commands represent a set of read-only commands. These are primarily, show commands that you can run on devices that are managed in LMS. You can specify the commands that
CHAPTER 10 Network show (NetShow) commands represent a set of read-only commands. These are primarily, show commands that you can run on devices that are managed in LMS. You can specify the commands that
Using the Topology Tool
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter explains about how topology tool provides a graphical view of networks set up through the Prime Provisioning web client. It gives a graphical representation of the various physical
CHAPTER 12 This chapter explains about how topology tool provides a graphical view of networks set up through the Prime Provisioning web client. It gives a graphical representation of the various physical
A P P E N D I X Scripts Cisco Prime Provisioning 6.5 API Programmer Guide OL C-1
 APPENDIXC These UNIX shell scripts automate the input of XML requests to, and process the resulting output from, the Northbound Interface (NBI) Application Programmers Interface (API) of the Cisco Prime
APPENDIXC These UNIX shell scripts automate the input of XML requests to, and process the resulting output from, the Northbound Interface (NBI) Application Programmers Interface (API) of the Cisco Prime
Working with Reports. User Roles Required to Manage Reports CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 Cisco Prime Network (Prime Network) provides a Report Manager that enables you to schedule, generate, view, and export reports of the information managed by Prime Network. You can save the generated
CHAPTER 10 Cisco Prime Network (Prime Network) provides a Report Manager that enables you to schedule, generate, view, and export reports of the information managed by Prime Network. You can save the generated
Managing Site-to-Site VPNs
 CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
Managing Load Plans in OTBI Enterprise for HCM Cloud Service
 Managing Load Plans in OTBI Enterprise for HCM Cloud Service Copyright 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 1 Objective After completing this lesson, you should be able to use Configuration
Managing Load Plans in OTBI Enterprise for HCM Cloud Service Copyright 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 1 Objective After completing this lesson, you should be able to use Configuration
VPN Console: Monitoring Menu
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter provides an explanation of collection tasks and reports categorized under the Monitoring menu option, as follows: Collect Router Configuration Files, page 8-2 Collect VPN Accounting
CHAPTER 8 This chapter provides an explanation of collection tasks and reports categorized under the Monitoring menu option, as follows: Collect Router Configuration Files, page 8-2 Collect VPN Accounting
Open SDN Controller Applications
 The following topics describe the five applications that Open SDN Controller provides to facilitate the day-to-day administration of your network: BGPLS Manager, page 1 Inventory Manager, page 3 Model
The following topics describe the five applications that Open SDN Controller provides to facilitate the day-to-day administration of your network: BGPLS Manager, page 1 Inventory Manager, page 3 Model
Ethernet Local Management Interface
 This chapter provides conceptual and configuration information of the protocol., on page 1 E-LMI Communication, on page 1 E-LMI Operation, on page 2 Supported Functions, on page 3 Limitations, on page
This chapter provides conceptual and configuration information of the protocol., on page 1 E-LMI Communication, on page 1 E-LMI Operation, on page 2 Supported Functions, on page 3 Limitations, on page
Cisco. Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM)
 Cisco 642-780 Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM) Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/642-780 QUESTION: 56 Which command should be used to verify
Cisco 642-780 Maintaining Cisco Service Provider VPNs and MPLS Networks (MSPVM) Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/642-780 QUESTION: 56 Which command should be used to verify
Getting Started. Installation Notes. Checking the API Status. Checking from the API CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to begin service provisioning with the Cisco Prime Fulfillment application program interface (API) and includes API-related installation notes, verifying the status
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to begin service provisioning with the Cisco Prime Fulfillment application program interface (API) and includes API-related installation notes, verifying the status
Managing Site-to-Site VPNs: The Basics
 CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
Icon and State Reference
 and State Reference Device Reachability and Admin States, page 1 Port and Interface States, page 3 Circuit/VC States, page 4 Link Serviceability States, page 7 Link Characteristics, page 7 Equipment Operational
and State Reference Device Reachability and Admin States, page 1 Port and Interface States, page 3 Circuit/VC States, page 4 Link Serviceability States, page 7 Link Characteristics, page 7 Equipment Operational
Overview of Inventory Management
 CHAPTER 1 Inventory Management in Cisco Prime LAN Management 4.1 groups the various activities in LMS involved in managing your inventory: your network devices. You can access these features from the Inventory
CHAPTER 1 Inventory Management in Cisco Prime LAN Management 4.1 groups the various activities in LMS involved in managing your inventory: your network devices. You can access these features from the Inventory
Setting Up Physical Inventory
 CHAPTER 4 Devices Every network element that Cisco Prime Fulfillment manages must be defined as a device in the system. An element is any device from which Prime Fulfillment can collect information. In
CHAPTER 4 Devices Every network element that Cisco Prime Fulfillment manages must be defined as a device in the system. An element is any device from which Prime Fulfillment can collect information. In
Impact Analysis in MPLS Networks
 CHAPTER 7 The following topics provide an overview of the Cisco MPLS Assurance Manager 1.0 (Cisco MPLS-AM) service impact analysis (IA) solution and supported scenarios, which are used in VPN networks
CHAPTER 7 The following topics provide an overview of the Cisco MPLS Assurance Manager 1.0 (Cisco MPLS-AM) service impact analysis (IA) solution and supported scenarios, which are used in VPN networks
Setting Up the Server
 Managing Licenses, page 1 Cross-launch from Prime Collaboration Provisioning, page 5 Integrating Prime Collaboration Servers, page 6 Single Sign-On for Prime Collaboration, page 7 Changing the SSL Port,
Managing Licenses, page 1 Cross-launch from Prime Collaboration Provisioning, page 5 Integrating Prime Collaboration Servers, page 6 Single Sign-On for Prime Collaboration, page 7 Changing the SSL Port,
Performing Diagnostics
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes the Diagnostics application in Cisco Prime Provisioning 6.3. Introduction This section provides an overview of the Cisco Prime Provisioning Diagnostics application. The
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes the Diagnostics application in Cisco Prime Provisioning 6.3. Introduction This section provides an overview of the Cisco Prime Provisioning Diagnostics application. The
Managing Site-to-Site VPNs: The Basics
 CHAPTER 23 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
CHAPTER 23 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
CLIQ Web Manager. User Manual. The global leader in door opening solutions V 6.1
 CLIQ Web Manager User Manual V 6.1 The global leader in door opening solutions Program version: 6.1 Document number: ST-003478 Date published: 2016-03-31 Language: en-gb Table of contents 1 Overview...9
CLIQ Web Manager User Manual V 6.1 The global leader in door opening solutions Program version: 6.1 Document number: ST-003478 Date published: 2016-03-31 Language: en-gb Table of contents 1 Overview...9
Traffic Engineering Management Provisioning
 1 CHAPTER This chapter describes the provisioning support for Traffic Engineering Management (TEM) provided in Cisco Prime Provisioning. The TEM API solution provides bulk provisioning, updating, and deletion
1 CHAPTER This chapter describes the provisioning support for Traffic Engineering Management (TEM) provided in Cisco Prime Provisioning. The TEM API solution provides bulk provisioning, updating, and deletion
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
 Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Defining IPsec Networks and Customers
 CHAPTER 4 Defining the IPsec Network Elements In this product, a VPN network is a unique group of targets; a target can be a member of only one network. Thus, a VPN network allows a provider to partition
CHAPTER 4 Defining the IPsec Network Elements In this product, a VPN network is a unique group of targets; a target can be a member of only one network. Thus, a VPN network allows a provider to partition
Repository Views. Creating Repository Views. Creating Views Sybase Repository. New and Upgrade Installation APPENDIXD
 APPENDIXD A view is a stored query accessible as a virtual table composed of the result set of a query. Unlike ordinary tables (base tables) in a relational database, a view does not form part of the physical
APPENDIXD A view is a stored query accessible as a virtual table composed of the result set of a query. Unlike ordinary tables (base tables) in a relational database, a view does not form part of the physical
Working with Tickets in Cisco Prime Network Vision
 CHAPTER 10 Working with Tickets in Cisco Prime Network Vision These topics describe how to work with tickets in Prime Network Vision: What are Tickets?, page 10-1 User Roles Required to Work with Tickets
CHAPTER 10 Working with Tickets in Cisco Prime Network Vision These topics describe how to work with tickets in Prime Network Vision: What are Tickets?, page 10-1 User Roles Required to Work with Tickets
Managing Auto Smartports in LMS
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter tells you how to configure, apply and manage Auto Smartports macros on the ASP-capable devices using LMS. This chapter contains: What are Auto Smartports? Auto Smartports Supported
CHAPTER 4 This chapter tells you how to configure, apply and manage Auto Smartports macros on the ASP-capable devices using LMS. This chapter contains: What are Auto Smartports? Auto Smartports Supported
Managing CX Devices in Multiple Device Mode
 Tip Device inventory management applies to PRSM in Multiple Device mode only. If you are configuring a CX device through a direct connection to the device, you do not need to add the device to the inventory
Tip Device inventory management applies to PRSM in Multiple Device mode only. If you are configuring a CX device through a direct connection to the device, you do not need to add the device to the inventory
Deploying Devices. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 3.1. Job Aid
 Deploying Devices Cisco Prime Infrastructure 3.1 Job Aid Copyright Page THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION,
Deploying Devices Cisco Prime Infrastructure 3.1 Job Aid Copyright Page THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION,
ForeScout Extended Module for Tenable Vulnerability Management
 ForeScout Extended Module for Tenable Vulnerability Management Version 2.7.1 Table of Contents About Tenable Vulnerability Management Module... 4 Compatible Tenable Vulnerability Products... 4 About Support
ForeScout Extended Module for Tenable Vulnerability Management Version 2.7.1 Table of Contents About Tenable Vulnerability Management Module... 4 Compatible Tenable Vulnerability Products... 4 About Support
The safer, easier way to help you pass any IT exams. Exam : 4A Alcatel-Lucent Virtual Private Routed Networks.
 http://www.51- pass.com Exam : 4A0-106 Title : Alcatel-Lucent Virtual Private Routed Networks Version : Demo 1 / 10 1.Click the exhibit. What is wrong with the VPRN configuration applied on this Alcatel-Lucent
http://www.51- pass.com Exam : 4A0-106 Title : Alcatel-Lucent Virtual Private Routed Networks Version : Demo 1 / 10 1.Click the exhibit. What is wrong with the VPRN configuration applied on this Alcatel-Lucent
SAML-Based SSO Configuration
 Prerequisites, page 1 SAML SSO Configuration Task Flow, page 5 Reconfigure OpenAM SSO to SAML SSO Following an Upgrade, page 9 SAML SSO Deployment Interactions and Restrictions, page 9 Prerequisites NTP
Prerequisites, page 1 SAML SSO Configuration Task Flow, page 5 Reconfigure OpenAM SSO to SAML SSO Following an Upgrade, page 9 SAML SSO Deployment Interactions and Restrictions, page 9 Prerequisites NTP
Create Templates To Automate Device Configuration Changes
 Create Templates To Automate Device Configuration Changes See Configure Devices for information on how to configure your devices using out-of-the-box configuration templates that are supplied with Cisco
Create Templates To Automate Device Configuration Changes See Configure Devices for information on how to configure your devices using out-of-the-box configuration templates that are supplied with Cisco
NSX-T Data Center Migration Coordinator Guide. 5 APR 2019 VMware NSX-T Data Center 2.4
 NSX-T Data Center Migration Coordinator Guide 5 APR 2019 VMware NSX-T Data Center 2.4 You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware website at: https://docs.vmware.com/ If you
NSX-T Data Center Migration Coordinator Guide 5 APR 2019 VMware NSX-T Data Center 2.4 You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware website at: https://docs.vmware.com/ If you
Roxen Content Provider
 Roxen Content Provider Generation 3 Templates Purpose This workbook is designed to provide a training and reference tool for placing University of Alaska information on the World Wide Web (WWW) using the
Roxen Content Provider Generation 3 Templates Purpose This workbook is designed to provide a training and reference tool for placing University of Alaska information on the World Wide Web (WWW) using the
Manage Device Software Images
 Set Up Software Image Management, page 1 Copy Software Images from Devices to the Image Repository (Create a Baseline), page 5 How Do I Find Out Which Images Are Used by Network Devices?, page 6 How Do
Set Up Software Image Management, page 1 Copy Software Images from Devices to the Image Repository (Create a Baseline), page 5 How Do I Find Out Which Images Are Used by Network Devices?, page 6 How Do
Performing Administrative Tasks
 CHAPTER 6 This section provides information about administrative tasks. It includes these topics: Stopping and Restarting the Cisco License Manager Server, page 6-1 How to Manage Users, page 6-2 Working
CHAPTER 6 This section provides information about administrative tasks. It includes these topics: Stopping and Restarting the Cisco License Manager Server, page 6-1 How to Manage Users, page 6-2 Working
Getting Started Using Cisco License Manager
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter provides information about the initial setup of Cisco License Manager and an overview of recommended steps to quickly add users and devices and obtain and deploy licenses. This chapter
CHAPTER 5 This chapter provides information about the initial setup of Cisco License Manager and an overview of recommended steps to quickly add users and devices and obtain and deploy licenses. This chapter
MPLS over GRE. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for MPLS VPN L3VPN over GRE
 The feature provides a mechanism for tunneling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets over a non-mpls network. This feature utilizes MPLS over generic routing encapsulation (MPLSoGRE) to encapsulate
The feature provides a mechanism for tunneling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets over a non-mpls network. This feature utilizes MPLS over generic routing encapsulation (MPLSoGRE) to encapsulate
Setting up Cisco Configuration Engine with Prime Fulfillment
 APPENDIXB Setting up Cisco Configuration Engine with Prime Fulfillment Overview This appendix gives information about downloading to a server using Cisco Configuration Engine with Prime Fulfillment. For
APPENDIXB Setting up Cisco Configuration Engine with Prime Fulfillment Overview This appendix gives information about downloading to a server using Cisco Configuration Engine with Prime Fulfillment. For
Inventory Reports. Detailed Device Report CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 2 include the following device reports. Detailed Device Report Device Attributes Reports Generating a 24-Hour Inventory Change Report Hardware Reports Management Status Reports Software Reports
CHAPTER 2 include the following device reports. Detailed Device Report Device Attributes Reports Generating a 24-Hour Inventory Change Report Hardware Reports Management Status Reports Software Reports
Backup and Restore Operations
 Backup Data Type, page 1 Backup and Restore Repositories, page 2 On-Demand and Scheduled Backups, page 3 Cisco ISE Restore Operation, page 8 Export Authentication and Authorization Policy Configuration,
Backup Data Type, page 1 Backup and Restore Repositories, page 2 On-Demand and Scheduled Backups, page 3 Cisco ISE Restore Operation, page 8 Export Authentication and Authorization Policy Configuration,
Managing Configurations
 CHAPTER 3 The Configurations page is your starting point for managing device configurations for network elements managed by Cisco Prime Network by using the CM tools. The following table lists the main
CHAPTER 3 The Configurations page is your starting point for managing device configurations for network elements managed by Cisco Prime Network by using the CM tools. The following table lists the main
Using Baseline Templates to Check Configuration Compliance
 CHAPTER 6 Using Baseline Templates to Check Configuration Compliance This chapter contains the following: What is a Baseline Template? Features of Baseline Templates Baseline Template Management Window
CHAPTER 6 Using Baseline Templates to Check Configuration Compliance This chapter contains the following: What is a Baseline Template? Features of Baseline Templates Baseline Template Management Window
MPLS VPN over mgre. Finding Feature Information. Last Updated: November 1, 2012
 MPLS VPN over mgre Last Updated: November 1, 2012 The MPLS VPN over mgre feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity
MPLS VPN over mgre Last Updated: November 1, 2012 The MPLS VPN over mgre feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity
L2VPN Provisioning. L2VPN Service Definitions CHAPTER
 1 CHAPTER To provision L2VPN using the Cisco Prime Provisioning API, you need an L2VPN service policy of a specific subtype and an L2VPN service request. The service policy (defined in a service definition)
1 CHAPTER To provision L2VPN using the Cisco Prime Provisioning API, you need an L2VPN service policy of a specific subtype and an L2VPN service request. The service policy (defined in a service definition)
Domain Setup Guide. NetBrain Integrated Edition 7.1. All-in-One Appliance
 NetBrain Integrated Edition 7.1 Domain Setup Guide All-in-One Appliance Version 7.1a Last Updated 2018-09-27 Copyright 2004-2018 NetBrain Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Contents 1. Setting Up
NetBrain Integrated Edition 7.1 Domain Setup Guide All-in-One Appliance Version 7.1a Last Updated 2018-09-27 Copyright 2004-2018 NetBrain Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Contents 1. Setting Up
This section contains context-sensitive Online Help content for the Web Client > Monitor tab.
 This section contains context-sensitive Online Help content for the Web Client > tab. Viewing Switch CPU Information, page 2 Viewing Switch Memory Information, page 2 Viewing Switch Traffic and Errors
This section contains context-sensitive Online Help content for the Web Client > tab. Viewing Switch CPU Information, page 2 Viewing Switch Memory Information, page 2 Viewing Switch Traffic and Errors
Configuring IP SLAs LSP Health Monitor Operations
 Configuring IP SLAs LSP Health Monitor Operations This module describes how to configure an IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) label switched path (LSP) Health Monitor. LSP health monitors enable you to
Configuring IP SLAs LSP Health Monitor Operations This module describes how to configure an IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) label switched path (LSP) Health Monitor. LSP health monitors enable you to
Provisioning Overlay Networks
 This chapter has the following sections: Using Cisco Virtual Topology System, page 1 Creating Overlays, page 2 Creating Network using VMware, page 4 Creating Subnetwork using VMware, page 4 Creating Routers
This chapter has the following sections: Using Cisco Virtual Topology System, page 1 Creating Overlays, page 2 Creating Network using VMware, page 4 Creating Subnetwork using VMware, page 4 Creating Routers
Provisioning an OCH Network Connection
 Provisioning an OCH Network Connection Cisco EPN Manager 2.0 Job Aid Copyright Page THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
Provisioning an OCH Network Connection Cisco EPN Manager 2.0 Job Aid Copyright Page THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
Backup and Restore Operations
 Backup Data Type Backup Data Type, on page 1 Backup and Restore Repositories, on page 1 On-Demand and Scheduled Backups, on page 3 Cisco ISE Restore Operation, on page 8 Export Authentication and Authorization
Backup Data Type Backup Data Type, on page 1 Backup and Restore Repositories, on page 1 On-Demand and Scheduled Backups, on page 3 Cisco ISE Restore Operation, on page 8 Export Authentication and Authorization
TE Resource Management
 CHAPTER 37 TE resource management is defined as the tuning of certain properties on the TE interfaces to optimize the tunnel placement. The highlighted box in Figure 37-1 shows where in Prime Fulfillment
CHAPTER 37 TE resource management is defined as the tuning of certain properties on the TE interfaces to optimize the tunnel placement. The highlighted box in Figure 37-1 shows where in Prime Fulfillment
Monitoring MPLS Services
 CHAPTER 17 The following topics describe how to view and manage aspects of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) services using Cisco Prime Network Vision (Prime Network Vision), including the MPLS service
CHAPTER 17 The following topics describe how to view and manage aspects of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) services using Cisco Prime Network Vision (Prime Network Vision), including the MPLS service
Managing Modular Infrastructure by using OpenManage Essentials (OME)
 Managing Modular Infrastructure by using OpenManage Essentials (OME) This technical white paper describes how to manage the modular infrastructure by using Dell EMC OME. Dell Engineering June 2017 A Dell
Managing Modular Infrastructure by using OpenManage Essentials (OME) This technical white paper describes how to manage the modular infrastructure by using Dell EMC OME. Dell Engineering June 2017 A Dell
Dell EMC OpenManage Mobile. Version User s Guide (Android)
 Dell EMC OpenManage Mobile Version 2.0.20 User s Guide (Android) Notes, cautions, and warnings NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product. CAUTION: A CAUTION
Dell EMC OpenManage Mobile Version 2.0.20 User s Guide (Android) Notes, cautions, and warnings NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product. CAUTION: A CAUTION
Storage Profiles. Storage Profiles. Storage Profiles, page 12
 , page 1 Disk Groups and Disk Group Configuration Policies, page 2 RAID Levels, page 6 Automatic Disk Selection, page 7 Supported LUN Modifications, page 8 Unsupported LUN Modifications, page 8 Disk Insertion
, page 1 Disk Groups and Disk Group Configuration Policies, page 2 RAID Levels, page 6 Automatic Disk Selection, page 7 Supported LUN Modifications, page 8 Unsupported LUN Modifications, page 8 Disk Insertion
Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase. Red Hat Developers Documentation Team :15:48 UTC
 Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase Red Hat Developers Documentation Team 2018-12-20 14:15:48 UTC Table of Contents Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase...............................................
Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase Red Hat Developers Documentation Team 2018-12-20 14:15:48 UTC Table of Contents Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase...............................................
Managing Workflows. Starting Prime Network Administration CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 Prime Network Administration can be used to manage deployed workflow templates. Topics include: Starting Prime Network Administration, page 10-1 Viewing the List of Templates and Template Properties,
CHAPTER 10 Prime Network Administration can be used to manage deployed workflow templates. Topics include: Starting Prime Network Administration, page 10-1 Viewing the List of Templates and Template Properties,
Access Network Workflow
 Overview, page 1 Prerequisites for Using Cisco, page 2 Supported Devices, page 2 Using, page 3 Overview The Access Network workflow in Cisco Prime Infrastructure automates the access switch deployment
Overview, page 1 Prerequisites for Using Cisco, page 2 Supported Devices, page 2 Using, page 3 Overview The Access Network workflow in Cisco Prime Infrastructure automates the access switch deployment
Cisco Prime Network Client Overview
 CHAPTER 1 Cisco Prime Network (Prime Network) provides a suite of GUI tools that offer an intuitive interface for managing the network and services, and for performing required system administration activities.
CHAPTER 1 Cisco Prime Network (Prime Network) provides a suite of GUI tools that offer an intuitive interface for managing the network and services, and for performing required system administration activities.
Demo KACE K1000 System Management Appliance
 Demo KACE K1000 System Management Appliance Quick Start Guide Product Domain: Cloud Client Computing Author: Dan Coleman Version: 1.01 Table of Contents 1 Product Overview... 3 1.1 Lab Preparation Considerations
Demo KACE K1000 System Management Appliance Quick Start Guide Product Domain: Cloud Client Computing Author: Dan Coleman Version: 1.01 Table of Contents 1 Product Overview... 3 1.1 Lab Preparation Considerations
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
 The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (L3VPN) services, over an IP core network, using L2TPv3 multipoint tunneling instead of MPLS. This allows L2TPv3 tunnels
The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (L3VPN) services, over an IP core network, using L2TPv3 multipoint tunneling instead of MPLS. This allows L2TPv3 tunnels
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Survey Creation Workflow These are the high level steps that are followed to successfully create and deploy a new survey:
 Overview of Survey Administration The first thing you see when you open up your browser to the Ultimate Survey Software is the Login Page. You will find that you see three icons at the top of the page,
Overview of Survey Administration The first thing you see when you open up your browser to the Ultimate Survey Software is the Login Page. You will find that you see three icons at the top of the page,
Spirent TestCenter Segment Routing AppNote
 Spirent TestCenter Segment Routing AppNote Table of contents Executive Summary....................................................................2 Overview of Segment Routing..............................................................2
Spirent TestCenter Segment Routing AppNote Table of contents Executive Summary....................................................................2 Overview of Segment Routing..............................................................2
Use Plug and Play to Deploy New Devices
 About Plug and Play, page 1 Prerequisites for Using Plug and Play, page 2 Plug and Play Workflow, page 2 Use the Plug and Play Dashboard to Monitor New Device Deployments, page 4 Create Plug and Play Profiles
About Plug and Play, page 1 Prerequisites for Using Plug and Play, page 2 Plug and Play Workflow, page 2 Use the Plug and Play Dashboard to Monitor New Device Deployments, page 4 Create Plug and Play Profiles
Manage Administrators and Admin Access Policies
 Manage Administrators and Admin Access Policies Role-Based Access Control, on page 1 Cisco ISE Administrators, on page 1 Cisco ISE Administrator Groups, on page 3 Administrative Access to Cisco ISE, on
Manage Administrators and Admin Access Policies Role-Based Access Control, on page 1 Cisco ISE Administrators, on page 1 Cisco ISE Administrator Groups, on page 3 Administrative Access to Cisco ISE, on
Labeling NEs Using Business Tags
 CHAPTER 7 A business tag is a string that is meaningful to the business, and which can be used to label a component of a network element for use in Prime Network screens and reports. Business tags are
CHAPTER 7 A business tag is a string that is meaningful to the business, and which can be used to label a component of a network element for use in Prime Network screens and reports. Business tags are
BGP Event-Based VPN Import
 The feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is driven by events; when a BGP path changes, all of its imported copies
The feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is driven by events; when a BGP path changes, all of its imported copies
Multi-VRF Support. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Multi-VRF Support
 The feature allows you to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge (CE) device. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for,
The feature allows you to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge (CE) device. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for,
AuditConfigurationArchiveandSoftwareManagementChanges (Network Audit)
 This section contains the following topics: Audit Configuration Archive and Software Management Changes (Network Audit), on page 1 Audit Changes Made By Users (Change Audit), on page 1 Audit Actions Executed
This section contains the following topics: Audit Configuration Archive and Software Management Changes (Network Audit), on page 1 Audit Changes Made By Users (Change Audit), on page 1 Audit Actions Executed
VMware Mirage Getting Started Guide
 Mirage 5.8 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced by a new edition. To check for more recent editions of this document,
Mirage 5.8 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced by a new edition. To check for more recent editions of this document,
ISE Deployment Assistant. Administration & User Guide
 ISE Deployment Assistant Administration & User Guide SecurView Inc. 05-24-2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Audience...7 1.2 IDA Benefits...7 1.2.1 Readiness Assessment... 7 1.2.2 Generating Configuration
ISE Deployment Assistant Administration & User Guide SecurView Inc. 05-24-2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Audience...7 1.2 IDA Benefits...7 1.2.1 Readiness Assessment... 7 1.2.2 Generating Configuration
Audit Reports. Change Audit Reports CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter explains: Change Viewing System Audit Log Report Performance Generating a Inventory and Config Audit Trail Report Device Administration Reports and IPSLA Audit Report You can perform
CHAPTER 9 This chapter explains: Change Viewing System Audit Log Report Performance Generating a Inventory and Config Audit Trail Report Device Administration Reports and IPSLA Audit Report You can perform
Deploying IWAN Routers
 Deploying IWAN Routers Cisco Prime Infrastructure 3.1 Job Aid Copyright Page THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
Deploying IWAN Routers Cisco Prime Infrastructure 3.1 Job Aid Copyright Page THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
Junos Space Connectivity Services Director Release 3.0R1 Release Notes
 Junos Space Connectivity Services Director Release 3.0R1 Release Notes 27 June, 2018 Contents Introduction........................................................ 2 Release Notes for Connectivity Services
Junos Space Connectivity Services Director Release 3.0R1 Release Notes 27 June, 2018 Contents Introduction........................................................ 2 Release Notes for Connectivity Services
Modern Requirements4TFS 2018 Update 1 Release Notes
 Modern Requirements4TFS 2018 Update 1 Release Notes Modern Requirements 6/22/2018 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 3 3. APPLICATION SETUP... 3 GENERAL... 4 1. FEATURES...
Modern Requirements4TFS 2018 Update 1 Release Notes Modern Requirements 6/22/2018 Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 3 3. APPLICATION SETUP... 3 GENERAL... 4 1. FEATURES...
Network Model Configuration Expert Mode
 This section contains the following topics: Expert Mode Overview Expert Mode Overview, on page 1 Navigation and Commit, on page 2 Configuring a Network Model Using the Expert Mode, on page 3 The Expert
This section contains the following topics: Expert Mode Overview Expert Mode Overview, on page 1 Navigation and Commit, on page 2 Configuring a Network Model Using the Expert Mode, on page 3 The Expert
Welch Allyn RetinaVue Network
 Welch Allyn RetinaVue Network EMR Deployment Portal Guide Software version 1.X 2018 Welch Allyn. All rights are reserved. To support the intended use of the product described in this publication, the purchaser
Welch Allyn RetinaVue Network EMR Deployment Portal Guide Software version 1.X 2018 Welch Allyn. All rights are reserved. To support the intended use of the product described in this publication, the purchaser
Understanding the Cisco Prime LMS Interface
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides a brief description of the elements in the Cisco Prime LMS user interface. It explains: Understanding the Interface Elements Understanding the Sitemap Navigating Menus Adding
CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides a brief description of the elements in the Cisco Prime LMS user interface. It explains: Understanding the Interface Elements Understanding the Sitemap Navigating Menus Adding
The BLR Employee Handbook Builder allows you to create your own customized employee handbook. Benefits include:
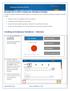 Introduction to BLR s Employee Handbook Builder The BLR Employee Handbook Builder allows you to create your own customized employee handbook. Benefits include: Ability to work on a handbook from any computer
Introduction to BLR s Employee Handbook Builder The BLR Employee Handbook Builder allows you to create your own customized employee handbook. Benefits include: Ability to work on a handbook from any computer
System Performance Measures:
 February 2019 System Performance Measures: HDX 1.0 Data Submission Guidance CONTENTS 1. Purpose of this Guidance... 3 2. The HUD Homelessness Data Exchange (HDX)... 5 Create an HDX Account... 5 Update
February 2019 System Performance Measures: HDX 1.0 Data Submission Guidance CONTENTS 1. Purpose of this Guidance... 3 2. The HUD Homelessness Data Exchange (HDX)... 5 Create an HDX Account... 5 Update
Create Templates to Automate Device Configuration Changes
 Create Templates to Automate Device Configuration Changes About Template Editor, on page 1 Create Projects, on page 1 Create Templates, on page 2 Template Form Editor, on page 7 Create and Associate Templates
Create Templates to Automate Device Configuration Changes About Template Editor, on page 1 Create Projects, on page 1 Create Templates, on page 2 Template Form Editor, on page 7 Create and Associate Templates
Onboard Devices with Network Plug and Play
 About Network Plug and Play, on page 1 Network Plug and Play Use Cases, on page 3 Manage Plug and Play Devices, on page 4 Manage Plug and Play Workflows, on page 11 Manage Plug and Play Settings, on page
About Network Plug and Play, on page 1 Network Plug and Play Use Cases, on page 3 Manage Plug and Play Devices, on page 4 Manage Plug and Play Workflows, on page 11 Manage Plug and Play Settings, on page
Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase. Red Hat Developers Documentation Team :54:11 UTC
 Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase Red Hat Developers Documentation Team 2019-02-15 17:54:11 UTC Table of Contents Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase...............................................
Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase Red Hat Developers Documentation Team 2019-02-15 17:54:11 UTC Table of Contents Using Eclipse Che IDE to develop your codebase...............................................
