Towards Real Time Simulation of Ship-Ship Interaction
|
|
|
- Lisa Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 12, 2018 Towards Real Time Simulation of Ship-Ship Interaction Lindberg, Ole; Bingham, Harry B.; Engsig-Karup, Allan Peter; Madsen, Per A. Published in: International Workshop on Water Waves and Floating Bodies Publication date: 2012 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Lindberg, O., Bingham, H. B., Engsig-Karup, A. P., & Madsen, P. A. (2012). Towards Real Time Simulation of Ship-Ship Interaction. In International Workshop on Water Waves and Floating Bodies General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the public portal for the purpose of private study or research. You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the public portal If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim.
2 The 27th International Workshop on Water Waves and Floating Bodies IWWWFB 2012 April 22-25, 2012, Copenhagen, Towards Real Time Simulation of Ship-Ship Interaction Ole Lindberg Allan P. Engsig-Karup DTU Informatics Harry B. Bingham Per A. Madsen We present recent and preliminary work directed towards the development of a simplified, physics-based model for improved simulation of ship-ship interaction that can be used for both analysis and real-time computing (i.e. with real-time constraints due to visualization). The goal is to implement the model into a large maritime simulator for training of naval officers, in particular tug boat helmsmen. Tug boat simulators are used for training of communication and situation awareness during manoeuvre involved with towing of large vessels. A main objective of the work is to improve and enable more accurate (realistic) and much faster ship-wave and shipship simulations than are currently possible. The coupling of simulation with visualization should improve the visual experience such that it can be perceived as more realistic in training. Today the state-of-art in real-time ship-ship interaction is for efficiency reasons and time-constraints in visualization based on model experiments in towing tanks and precomputed force tables. We anticipate that the fast, and highly parallel, algorithm described by Engsig-Karup et al. [2011] for execution on affordable modern high-throughput Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) can provide the basis for efficient simulations in combination with an accurate free-surface model for Ship- Ship simulation. Another area of application is the determination of wave disturbances from a ship in a coastal environment, channels and harbours. The model proposed in the following can in a simple and efficient way calculate the wave field from a ship sailing in a finite depth sea, even with variations in the height of sea bed. The generated wave field can be applied as an input to other models that simulate the marine environment on a larger scale. Ship-Wave Model In order to take full advantage of the accuracy and efficiency of the wave model discussed above, we will adopt a rough approximation of the ship geometry based on surface pressure distributions. This will of course limit the accuracy of the geometric description of the hull. The representation of sailing ships by a pressure distribution on the free surface is a classical We wish to thank Force Technology, and DTU Informatics for funding this project and the Danish Center for Scientific Computing for providing supercomputing resources.
3 idea that dates back at least to Thomson (Lord Kelvin) [1910]. Many applications of the idea exist in the literature, including e.g. recent work by Raven [2010], who used the idea for hull optimization based on wave-making resistance; and Li and Sclavounos [2002] who used surface pressures to study nonlinear solitary waves in shallow water as a model for a ship moving at sub-critical, critical and super-critical speed. To model a ship as a pressure distribution on the free surface, the hull must be approximated by a single-valued function of the horizontal coordinates: η ship = η ship (t,x,y). Ship appendices like bulbous bows or complex rudder tubes can not be represented and must be suitably smoothed out. The fluid pressure on the ship hull surface is the sum of the dynamic and the hydrostatic components. Clearly an approximation to the stationary ship is obtained by applying the hydrostatic component p ship = ρgη ship. As the ship begins to move, the flow induced dynamic components must be balanced by the applied surface pressure in order to maintain a constant hull form. The goal of this project is to find a robust means of predicting and applying this pressure in general, but we present here some preliminary work with constant applied pressures. The model is based on assuming inviscid, incompressible and irrotational potential flow. The free surface of the sea is described by the single-valued function η = η(t, x, y), where t is time and (x, y) the horizontal coordinates. Mass conservation is satisfied though the Laplace equation for the scalar velocity potential 2 φ = 0, z [ h,η], (1) where z is the vertical coordinate and h = h(x,y) is the distance from the mean sea level to the sea bed. The motion of the free surface is governed by the kinematic free surface boundary condition +u η = w, z = η, (2) t where u = φ R 2 is the horizontal velocity vector and w is the vertical free surface velocity. The forces on the free surface are governed by the dynamic free surface condition t u u+ p +gη = 0, z = η, (3) ρ where p is the pressure, ρ 1000kg/m 3 is the density and g = 9.81m/s 2 is the gravitational acceleration. The equations are solved in a moving reference frame attached to the ship and given by (τ,x m,y m ), where x m is forward and y m is the transverse direction relative to the ship. The ship is assumed not to move in the vertical direction and to be sailing in the the positive x direction. Based on these assumptions the coordinate transform from the fixed to the ship following frame of reference is τ = t, x m = x Vt, y m = y, z m = z, (4) where V = const. is the ship velocity in the x direction. The coordinate transform adds a convective term to the kinematic and dynamic free surface boundary conditions t τ V x m +u η = w, z = η, (5) V + 1 x m 2 u u+ p +gη = 0, z = η. (6) ρ The free surface boundary conditions are are solved in a ship following rectangular domain on the free surface and the Laplace equation is solved in a corresponding domain extending to the seabed, i.e. the solution domain is Ω = {[x m,y m,z m ] T R 3 : x m,min x m x m,max, y m,min y m y m,max, h z m η} (7)
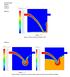
4 Figure 1: The Kelvin wave system generated by a moving pressure distribution with the parameters Fn(ship) = 0.30, Fn(depth) = 0.47, B/L = 0.2 and D/L = The semi analytical solution are below the center line and the numerical solutions are above the center line. The numerical solutions η h η and φ h φ are represented by local polynomials on a structured grid over the free surface boundary of Ω. The equations are transformed from the physical domain to a time independent computational domain, where the derivatives are approximated by higher-order finite differences. The temporal derivatives are approximated by the classical explicit fourth-order Runge-Kutta method. Details on the numerical approximations and solution methods are described by Engsig-Karup et al. [2009]. Applications In this preliminary work, the method has been tested on the double cosine "ship" geometry used in Li and Sclavounos [2002] where the pressure distribution is p(x m,y m ) = ρgdcos 2( πx ) m cos 2( πy ) m, L L B 2 x m L 2, B 2 y m B 2, (8) with D the draft, L the length and B the width of the "ship". The preliminary simulations have been promising and a snap shot illustrating a generated Kelvin Wave system is presented in Figure 1. The calculation are shown next to the far-field linear as expressed for example by Wehausen and Laitone [1960]. This semi-analytical solution has been used to find the theoretical wave system caused by the double cosine pressure distribution above and we present a qualitative comparison between this and out numerical solution to the linear problem in figure 1. The result is qualitatively in good agreement and we are now working on making a more quantitative comparison. The second application is a typical cargo ship. The ship geometry has been simplified such that the surface of the hull is described by a single valued function of the horizontal coordinates: The bulbous bow has been extended upwards through the free surface, the vertical sides of the hull have been mollified and sharp intersections between the still water level and the hull has been smoothed. The resultant wave system is seen in Figure 2. Conclusion The Kelvin wave system has been simulated around a ship propagating at subcritical fixed speed in still water using a potential flow model with linearized free surface boundary conditions.
5 Figure 2: The wave system generated by the hydro static pressure on a typical cargo ship sailing with at Froude numbers Fn(ship) = 0.20 and Fn(depth) = The geometric parameters of the ship are B/L = 0.13 and D/L = Preliminary results have been presented for a simple pressure patch which show good qualitative agreement with the semi-analytic solution. Future work will focus on including the nonlinear terms in the free-surface boundary conditions, and using the dynamic pressure on the ship hull to achieve a fixed geometry. The model will be implemented for parallel execution on modern high-throughput Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) and implemented in a real marine simulator to predict ship-ship interaction effects in real time. Acknowledgement We would like to thank Ingrid Marie Vincent Andersen for providing the ship hull sections. References A. P. Engsig-Karup, H. B. Bingham, and O. Lindberg. An efficient flexible-order model for 3d nonlinear water waves. Journal of Computational Physics, 228: , A. P Engsig-Karup, M. G. Madsen, and S. L. Glimberg. A massively parallel gpu-accelerated model for analysis of fully nonlinear free surface waves. Accepted for publication in Int. J. Num. Methods in Fluids, Y. Li and P. D. Sclavounos. Three-dimensional nonlinear solitary waves in shallow water genereated by an advancing disturbance. J. Fluid Mech., 470: , H. C. Raven. Validation of an approach to analyse and understand ship wave making. Journal of Maritime Science and Technology, 15: , William Thomson (Lord Kelvin). On ship waves. In Collected Works, pages Cambridge, J. V. Wehausen and E. V. Laitone. Surface waves. In Handbuch der Physik, pages Springer, 1960.
Towards real time simulation of ship-ship interaction - Part II: double body flow linearization and GPU implementation
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 21, 2018 Towards real time simulation of ship-ship interaction - Part II: double body flow linearization and GPU implementation Lindberg, Ole; Glimberg, Stefan Lemvig;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 21, 2018 Towards real time simulation of ship-ship interaction - Part II: double body flow linearization and GPU implementation Lindberg, Ole; Glimberg, Stefan Lemvig;
A GPU-based High-Performance Library with Application to Nonlinear Water Waves
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Glimberg, Stefan Lemvig; Engsig-Karup, Allan Peter Publication date: 2012 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Glimberg, Stefan Lemvig; Engsig-Karup, Allan Peter Publication date: 2012 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU
Very fast simulation of nonlinear water waves in very large numerical wave tanks on affordable graphics cards
 Very fast simulation of nonlinear water waves in very large numerical wave tanks on affordable graphics cards By Allan P. Engsig-Karup, Morten Gorm Madsen and Stefan L. Glimberg DTU Informatics Workshop
Very fast simulation of nonlinear water waves in very large numerical wave tanks on affordable graphics cards By Allan P. Engsig-Karup, Morten Gorm Madsen and Stefan L. Glimberg DTU Informatics Workshop
Performance auto-tuning of rectangular matrix-vector multiplication: how to outperform CUBLAS
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 23, 2018 Performance auto-tuning of rectangular matrix-vector multiplication: how to outperform CUBLAS Sørensen, Hans Henrik Brandenborg Publication date: 2010 Document
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 23, 2018 Performance auto-tuning of rectangular matrix-vector multiplication: how to outperform CUBLAS Sørensen, Hans Henrik Brandenborg Publication date: 2010 Document
Experimental Validation of the Computation Method for Strongly Nonlinear Wave-Body Interactions
 Experimental Validation of the Computation Method for Strongly Nonlinear Wave-Body Interactions by Changhong HU and Masashi KASHIWAGI Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University Kasuga
Experimental Validation of the Computation Method for Strongly Nonlinear Wave-Body Interactions by Changhong HU and Masashi KASHIWAGI Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University Kasuga
Aalborg Universitet. Numerical 3-D Modelling of Overflows Larsen, Torben; Nielsen, L.; Jensen, B.; Christensen, E. D.
 Aalborg Universitet Numerical 3-D Modelling of Overflows Larsen, Torben; Nielsen, L.; Jensen, B.; Christensen, E. D. Published in: Confernce Proceedings : 11th International Conference on Urban Drainage
Aalborg Universitet Numerical 3-D Modelling of Overflows Larsen, Torben; Nielsen, L.; Jensen, B.; Christensen, E. D. Published in: Confernce Proceedings : 11th International Conference on Urban Drainage
Determination of Angle of Attack (AOA) for Rotating Blades
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Determination of Angle of Attack (AOA) for Rotating Blades Shen, Wen Zhong; Hansen, Martin Otto Laver; Sørensen, Jens Nørkær Published in: Wind Energy Publication
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 1, 218 Determination of Angle of Attack (AOA) for Rotating Blades Shen, Wen Zhong; Hansen, Martin Otto Laver; Sørensen, Jens Nørkær Published in: Wind Energy Publication
Use of STAR-CCM+ in Marine and Off-Shore Engineering - Key Features and Future Developments - M. Perić, F. Schäfer, E. Schreck & J.
 Use of STAR-CCM+ in Marine and Off-Shore Engineering - Key Features and Future Developments - M. Perić, F. Schäfer, E. Schreck & J. Singh Contents Main features of STAR-CCM+ relevant for marine and offshore
Use of STAR-CCM+ in Marine and Off-Shore Engineering - Key Features and Future Developments - M. Perić, F. Schäfer, E. Schreck & J. Singh Contents Main features of STAR-CCM+ relevant for marine and offshore
A Review of the Implicit Motion Solver Algorithm in OpenFOAM to Simulate a Heaving Buoy
 A Review of the Implicit Motion Solver Algorithm in OpenFOAM to Simulate a Heaving Buoy Devolder, B., Schmitt, P., Rauwoens, P., Elsaesser, B., & Troch, P. (2015). A Review of the Implicit Motion Solver
A Review of the Implicit Motion Solver Algorithm in OpenFOAM to Simulate a Heaving Buoy Devolder, B., Schmitt, P., Rauwoens, P., Elsaesser, B., & Troch, P. (2015). A Review of the Implicit Motion Solver
The Study of Ship Motions in Regular Waves using a Mesh-Free Numerical Method
 The Study of Ship Motions in Regular Waves using a Mesh-Free Numerical Method by Bruce Kenneth Cartwright, B. Eng., M. Sc. Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Philosophy
The Study of Ship Motions in Regular Waves using a Mesh-Free Numerical Method by Bruce Kenneth Cartwright, B. Eng., M. Sc. Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Philosophy
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents Codes in the Frequency Domain... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. SCOPE... 2 2.1 Present Theoretical Limitations... 4 2.2 Numerical Aspects... 4 2.3 Software Engineering
Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents Codes in the Frequency Domain... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. SCOPE... 2 2.1 Present Theoretical Limitations... 4 2.2 Numerical Aspects... 4 2.3 Software Engineering
Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D
 Flow Science Report 08-15 Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D Gengsheng Wei Flow Science, Inc. October 2015 1. Introduction Mooring systems are common in offshore structures, ship
Flow Science Report 08-15 Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D Gengsheng Wei Flow Science, Inc. October 2015 1. Introduction Mooring systems are common in offshore structures, ship
Multibody Model for Planetary Gearbox of 500 kw Wind Turbine
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 19, 2018 Multibody Model for Planetary Gearbox of 500 kw Wind Turbine Jørgensen, Martin Felix Publication date: 2013 Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Jørgensen,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 19, 2018 Multibody Model for Planetary Gearbox of 500 kw Wind Turbine Jørgensen, Martin Felix Publication date: 2013 Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Jørgensen,
2-D Tank Sloshing Using the Coupled Eulerian- LaGrangian (CEL) Capability of Abaqus/Explicit
 2-D Tank Sloshing Using the Coupled Eulerian- LaGrangian (CEL) Capability of Abaqus/Explicit Jeff D. Tippmann, Sharat C. Prasad 2, and Parthiv N. Shah ATA Engineering, Inc. San Diego, CA 923 2 Dassault
2-D Tank Sloshing Using the Coupled Eulerian- LaGrangian (CEL) Capability of Abaqus/Explicit Jeff D. Tippmann, Sharat C. Prasad 2, and Parthiv N. Shah ATA Engineering, Inc. San Diego, CA 923 2 Dassault
Modelling of Wind Turbine Blades with ABAQUS
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 21, 2017 Modelling of Wind Turbine Blades with ABAQUS Bitsche, Robert Publication date: 2015 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link back to DTU Orbit Citation
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 21, 2017 Modelling of Wind Turbine Blades with ABAQUS Bitsche, Robert Publication date: 2015 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link back to DTU Orbit Citation
SPH: Towards the simulation of wave-body interactions in extreme seas
 SPH: Towards the simulation of wave-body interactions in extreme seas Guillaume Oger, Mathieu Doring, Bertrand Alessandrini, and Pierre Ferrant Fluid Mechanics Laboratory (CNRS UMR6598) Ecole Centrale
SPH: Towards the simulation of wave-body interactions in extreme seas Guillaume Oger, Mathieu Doring, Bertrand Alessandrini, and Pierre Ferrant Fluid Mechanics Laboratory (CNRS UMR6598) Ecole Centrale
Simulation of BSDF's generated with Window6 and TracePro prelimenary results
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 23, 2018 Simulation of BSDF's generated with Window6 and TracePro prelimenary results Iversen, Anne; Nilsson, Annica Publication date: 2011 Document Version Publisher's
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Aug 23, 2018 Simulation of BSDF's generated with Window6 and TracePro prelimenary results Iversen, Anne; Nilsson, Annica Publication date: 2011 Document Version Publisher's
Single Wake Meandering, Advection and Expansion - An analysis using an adapted Pulsed Lidar and CFD LES-ACL simulations
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jan 10, 2019 Single Wake Meandering, Advection and Expansion - An analysis using an adapted Pulsed Lidar and CFD LES-ACL simulations Machefaux, Ewan; Larsen, Gunner Chr.;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jan 10, 2019 Single Wake Meandering, Advection and Expansion - An analysis using an adapted Pulsed Lidar and CFD LES-ACL simulations Machefaux, Ewan; Larsen, Gunner Chr.;
Wave Uplift on Platforms or Docks in Variable Depth Jiin-Jen Lee and C.P. Lai"
 CHAPTER 149 ABSTRACT Wave Uplift on Platforms or Docks in Variable Depth Jiin-Jen Lee and C.P. Lai" Wave uplift forces on two dimensional platforms or docks in a variable depth medium has been studied
CHAPTER 149 ABSTRACT Wave Uplift on Platforms or Docks in Variable Depth Jiin-Jen Lee and C.P. Lai" Wave uplift forces on two dimensional platforms or docks in a variable depth medium has been studied
Nonlinear Potential Flow Solver Development in OpenFOAM
 Nonlinear Potential Flow Solver Development in OpenFOAM A. Mehmood Plymouth University, UK April 19,2016 A. Mehmood Table of Contents 1 Motivation 2 Solution Methodology Mathematical Formulation Sequence
Nonlinear Potential Flow Solver Development in OpenFOAM A. Mehmood Plymouth University, UK April 19,2016 A. Mehmood Table of Contents 1 Motivation 2 Solution Methodology Mathematical Formulation Sequence
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Proceedings of the 19th Nordic Seminar on Computational Mechanics. Publication date: 2006
 Aalborg Universitet Topology Optimization - Improved Checker-Board Filtering With Sharp Contours Pedersen, Christian Gejl; Lund, Jeppe Jessen; Damkilde, Lars; Kristensen, Anders Schmidt Published in: Proceedings
Aalborg Universitet Topology Optimization - Improved Checker-Board Filtering With Sharp Contours Pedersen, Christian Gejl; Lund, Jeppe Jessen; Damkilde, Lars; Kristensen, Anders Schmidt Published in: Proceedings
Transactions on Modelling and Simulation vol 10, 1995 WIT Press, ISSN X
 Hydrodynamic coefficients and motions due to a floating cylinder in waves D.D. Bhatta, M. Rahman Department of Applied Mathematics, Technical University of Nova Scotia, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3J
Hydrodynamic coefficients and motions due to a floating cylinder in waves D.D. Bhatta, M. Rahman Department of Applied Mathematics, Technical University of Nova Scotia, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3J
Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation
 Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Pop Worksheet! Teams of 2. Hand in to Jeramey after we discuss. Sketch the first few frames of a 2D explicit Euler mass-spring simulation for a 2x3 cloth network
Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Pop Worksheet! Teams of 2. Hand in to Jeramey after we discuss. Sketch the first few frames of a 2D explicit Euler mass-spring simulation for a 2x3 cloth network
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHALLOW WATERS EFFECTS ON SAILING SHIP "MIRCEA" HULL
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHALLOW WATERS EFFECTS ON SAILING SHIP "MIRCEA" HULL Petru Sergiu ȘERBAN 1 1 PhD Student, Department of Navigation and Naval Transport, Mircea cel Batran Naval Academy, Constanța,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHALLOW WATERS EFFECTS ON SAILING SHIP "MIRCEA" HULL Petru Sergiu ȘERBAN 1 1 PhD Student, Department of Navigation and Naval Transport, Mircea cel Batran Naval Academy, Constanța,
Robust and computationally efficient dynamic simulation of ORC systems: the thermocycle Modelica library
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 11, 2018 Robust and computationally efficient dynamic simulation of ORC systems: the thermocycle Modelica library Quoilin, S.; Desideri, A.; Bell, I.; Wronski, Jorrit;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 11, 2018 Robust and computationally efficient dynamic simulation of ORC systems: the thermocycle Modelica library Quoilin, S.; Desideri, A.; Bell, I.; Wronski, Jorrit;
Rotor Performance Enhancement Using Slats on the Inner Part of a 10MW Rotor
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 05, 2018 Rotor Performance Enhancement Using Slats on the Inner Part of a 10MW Rotor Gaunaa, Mac; Zahle, Frederik; Sørensen, Niels N.; Bak, Christian; Réthoré, Pierre-Elouan
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 05, 2018 Rotor Performance Enhancement Using Slats on the Inner Part of a 10MW Rotor Gaunaa, Mac; Zahle, Frederik; Sørensen, Niels N.; Bak, Christian; Réthoré, Pierre-Elouan
Numerical Estimation and Validation of Shallow Draft Effect on Roll Damping
 The 14 th International Ship Stability Workshop (ISSW), 29 th September- 1 st October 2014, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Numerical Estimation and Validation of Shallow Draft Effect on Roll Damping Toru Katayama
The 14 th International Ship Stability Workshop (ISSW), 29 th September- 1 st October 2014, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Numerical Estimation and Validation of Shallow Draft Effect on Roll Damping Toru Katayama
2D numerical simulation of ocean waves
 2D numerical simulation of ocean waves Qingjie. Du,*, Y.C. Dennis. Leung Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China * Corresponding author. Tel: +852 51743593,
2D numerical simulation of ocean waves Qingjie. Du,*, Y.C. Dennis. Leung Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China * Corresponding author. Tel: +852 51743593,
Accelerating Dense Linear Algebra on the GPU
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 2, 218 Sørensen, Hans Henrik Brandenborg Publication date: 211 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA):
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 2, 218 Sørensen, Hans Henrik Brandenborg Publication date: 211 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA):
Syddansk Universitet. Værktøj til videndeling og interaktion. Dai, Zheng. Published in: inform. Publication date: 2009
 Syddansk Universitet Værktøj til videndeling og interaktion Dai, Zheng Published in: inform Publication date: 2009 Document version Peer-review version Citation for pulished version (APA): Dai, Z. (2009).
Syddansk Universitet Værktøj til videndeling og interaktion Dai, Zheng Published in: inform Publication date: 2009 Document version Peer-review version Citation for pulished version (APA): Dai, Z. (2009).
Online Conformance Checking for Petri Nets and Event Streams
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 30, 2018 Online Conformance Checking for Petri Nets and Event Streams Burattin, Andrea Published in: Online Proceedings of the BPM Demo Track 2017 Publication date:
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Apr 30, 2018 Online Conformance Checking for Petri Nets and Event Streams Burattin, Andrea Published in: Online Proceedings of the BPM Demo Track 2017 Publication date:
Introduction. Chapter 1. Contents. 1.1 Background
 1 Introduction Chapter 1 Contents 1.1 Background 1.2 Two-Part Towing System 1.3 Overall objectives 1.4 Scope of the present study 1.5 Methodology 1.6 Organization of the Report 1.1 Background As an effective
1 Introduction Chapter 1 Contents 1.1 Background 1.2 Two-Part Towing System 1.3 Overall objectives 1.4 Scope of the present study 1.5 Methodology 1.6 Organization of the Report 1.1 Background As an effective
Numerical Wave Tank Modeling of Hydrodynamics of Permeable Barriers
 ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Numerical Wave Tank Modeling of Hydrodynamics of Permeable Barriers K. Rajendra & R. Balaji Indian
ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Numerical Wave Tank Modeling of Hydrodynamics of Permeable Barriers K. Rajendra & R. Balaji Indian
OMAE SLOSHING AND SWIRLING IN PARTIALLY LOADED PRISMATIC CHAMFERED TANKS
 Proceedings of the 36 th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore & Arctic Engineering June 25-30, 2017, Trondheim, Norway OMAE2017-61562 SLOSHING AND SWIRLING IN PARTIALLY LOADED PRISMATIC CHAMFERED
Proceedings of the 36 th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore & Arctic Engineering June 25-30, 2017, Trondheim, Norway OMAE2017-61562 SLOSHING AND SWIRLING IN PARTIALLY LOADED PRISMATIC CHAMFERED
Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM
 Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM p. 1/14 Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM Hrvoje Jasak and Henrik Rusche h.jasak@wikki.co.uk, h.rusche@wikki.co.uk Wikki, United Kingdom and Germany 4 December
Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM p. 1/14 Marine Hydrodynamics Solver in OpenFOAM Hrvoje Jasak and Henrik Rusche h.jasak@wikki.co.uk, h.rusche@wikki.co.uk Wikki, United Kingdom and Germany 4 December
Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement Lian Shen Department of Mechanical Engineering
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement Lian Shen Department of Mechanical Engineering
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Computer system for calculation of flow, resistance and propulsion of a ship at the design stage T. Bugalski, T. Koronowicz, J. Szantyr & G. Waberska Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery, Polish Academy of
Computer system for calculation of flow, resistance and propulsion of a ship at the design stage T. Bugalski, T. Koronowicz, J. Szantyr & G. Waberska Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery, Polish Academy of
Comparison of open-source code Nemoh with Wamit for cargo ship motions in shallow water
 Comparison of open-source code Nemoh with Wamit for cargo ship motions in shallow water G.Parisella 1 and T.P.Gourlay 2 Centre for Marine Science and Technology, Curtin University Research report 2016-23,
Comparison of open-source code Nemoh with Wamit for cargo ship motions in shallow water G.Parisella 1 and T.P.Gourlay 2 Centre for Marine Science and Technology, Curtin University Research report 2016-23,
Modeling Khowr-e Musa Multi-Branch Estuary Currents due to the Persian Gulf Tides Using NASIR Depth Average Flow Solver
 Journal of the Persian Gulf (Marine Science)/Vol.1/No.1/September 2010/6/45-50 Modeling Khowr-e Musa Multi-Branch Estuary Currents due to the Persian Gulf Tides Using NASIR Depth Average Flow Solver Sabbagh-Yazdi,
Journal of the Persian Gulf (Marine Science)/Vol.1/No.1/September 2010/6/45-50 Modeling Khowr-e Musa Multi-Branch Estuary Currents due to the Persian Gulf Tides Using NASIR Depth Average Flow Solver Sabbagh-Yazdi,
Simulation of Freak Wave Impact Using the Higher Order Spectrum
 Simulation of Freak Wave Impact Using the Higher Order Spectrum The Naval Hydro Pack Hrvoje Jasak and Vuko Vukčević Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, Uni Zagreb, Croatia Wikki Ltd.
Simulation of Freak Wave Impact Using the Higher Order Spectrum The Naval Hydro Pack Hrvoje Jasak and Vuko Vukčević Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, Uni Zagreb, Croatia Wikki Ltd.
Evaluation strategies in CT scanning
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Evaluation strategies in CT scanning Hiller, Jochen Publication date: 2012 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Evaluation strategies in CT scanning Hiller, Jochen Publication date: 2012 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link back to DTU
Coastal impact of a tsunami Review of numerical models
 Coastal impact of a tsunami Review of numerical models Richard Marcer 2 Content Physics to simulate Different approaches of modelling 2D depth average Full 3D Navier-Stokes 3D model Key point : free surface
Coastal impact of a tsunami Review of numerical models Richard Marcer 2 Content Physics to simulate Different approaches of modelling 2D depth average Full 3D Navier-Stokes 3D model Key point : free surface
Retrieval of 3D-position of a Passive Object Using Infrared LED s and Photodiodes Christensen, Henrik Vie
 Aalborg Universitet Retrieval of 3D-position of a Passive Object Using Infrared LED s and Photodiodes Christensen, Henrik Vie Publication date: 24 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version
Aalborg Universitet Retrieval of 3D-position of a Passive Object Using Infrared LED s and Photodiodes Christensen, Henrik Vie Publication date: 24 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version
Neural Network modeling of forward and inverse behavior of rotary MR damper
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jan 25, 2019 Neural Network modeling of forward and inverse behavior of rotary MR damper Bhowmik, Subrata; Høgsberg, Jan Becker; Weber, Felix Published in: Proceedings
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jan 25, 2019 Neural Network modeling of forward and inverse behavior of rotary MR damper Bhowmik, Subrata; Høgsberg, Jan Becker; Weber, Felix Published in: Proceedings
CFD FOR OFFSHORE APPLICATIONS USING REFRESCO. Arjen Koop - Senior Project Manager Offshore MARIN
 CFD FOR OFFSHORE APPLICATIONS USING REFRESCO Arjen Koop - Senior Project Manager Offshore MARIN COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) Advantages: Quantitative predictions Detailed insight in physical processes
CFD FOR OFFSHORE APPLICATIONS USING REFRESCO Arjen Koop - Senior Project Manager Offshore MARIN COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) Advantages: Quantitative predictions Detailed insight in physical processes
Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 8 Boston Computation of Velocity, Pressure and Temperature Distributions near a Stagnation Point in Planar Laminar Viscous Incompressible Flow E. Kaufman
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING
 CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
History Matching: Towards Geologically Reasonable Models
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 13, 018 History Matching: Towards Geologically Reasonable Models Melnikova, Yulia; Cordua, Knud Skou; Mosegaard, Klaus Publication date: 01 Document Version Publisher's
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 13, 018 History Matching: Towards Geologically Reasonable Models Melnikova, Yulia; Cordua, Knud Skou; Mosegaard, Klaus Publication date: 01 Document Version Publisher's
Driven Cavity Example
 BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
Aurélien Thinat Stéphane Cordier 1, François Cany
 SimHydro 2012:New trends in simulation - Hydroinformatics and 3D modeling, 12-14 September 2012, Nice Aurélien Thinat, Stéphane Cordier, François Cany Application of OpenFOAM to the study of wave loads
SimHydro 2012:New trends in simulation - Hydroinformatics and 3D modeling, 12-14 September 2012, Nice Aurélien Thinat, Stéphane Cordier, François Cany Application of OpenFOAM to the study of wave loads
ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Manoeuvrability Validation of Manoeuvring Simulation Models
 Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1 PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE 2 INTRODUCTION 3 PROCEDURE FOR VALIDATION OF A MANOEUVRING SIMULATION MODEL 3.1 The Report 3.2 Prediction of Forces 3.3 Modelling of Forces in the Mathematical
Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1 PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE 2 INTRODUCTION 3 PROCEDURE FOR VALIDATION OF A MANOEUVRING SIMULATION MODEL 3.1 The Report 3.2 Prediction of Forces 3.3 Modelling of Forces in the Mathematical
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS
 INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS HEC- RAS stands for Hydrologic Engineering Center s River Analysis System By U.S. Army Corps of Engineers One dimensional analysis of : 1. Steady flow 2. Unsteady flow 3. Sediment
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-RAS HEC- RAS stands for Hydrologic Engineering Center s River Analysis System By U.S. Army Corps of Engineers One dimensional analysis of : 1. Steady flow 2. Unsteady flow 3. Sediment
Experimental and numerical study of sloshing and swirling in partially filled membrane-type LNG tanks
 Maritime Transportation and Harvesting of Sea Resources Guedes Soares & Teixeira (Eds) 2018 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-8153-7993-5 Experimental and numerical study of sloshing and swirling
Maritime Transportation and Harvesting of Sea Resources Guedes Soares & Teixeira (Eds) 2018 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-8153-7993-5 Experimental and numerical study of sloshing and swirling
Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation
 Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Optional Reading for Last Time: Spring-Mass Systems Numerical Integration (Euler, Midpoint, Runge-Kutta) Modeling string, hair, & cloth HW2: Cloth & Fluid Simulation
Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Optional Reading for Last Time: Spring-Mass Systems Numerical Integration (Euler, Midpoint, Runge-Kutta) Modeling string, hair, & cloth HW2: Cloth & Fluid Simulation
Determining Ship Resistance Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
 Determining Ship Resistance Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Yasser M. Ahmed a, c, O. B. Yaakob a, b,*, M. F. A. Rashid a, A. H. Elbatran a, d JTSE a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
Determining Ship Resistance Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Yasser M. Ahmed a, c, O. B. Yaakob a, b,*, M. F. A. Rashid a, A. H. Elbatran a, d JTSE a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
FLUID MECHANICS TESTS
 FLUID MECHANICS TESTS Attention: there might be more correct answers to the questions. Chapter 1: Kinematics and the continuity equation T.2.1.1A flow is steady if a, the velocity direction of a fluid
FLUID MECHANICS TESTS Attention: there might be more correct answers to the questions. Chapter 1: Kinematics and the continuity equation T.2.1.1A flow is steady if a, the velocity direction of a fluid
Scientific Computations on GPUs First results from DTU Informatics
 Scientific Computations on GPUs First results from GPULab @ DTU Informatics Bernd Dammann Associate Professor Scientific Computing DTU Informatics Technical University of Denmark Technical University of
Scientific Computations on GPUs First results from GPULab @ DTU Informatics Bernd Dammann Associate Professor Scientific Computing DTU Informatics Technical University of Denmark Technical University of
Resistance and Propulsion
 MASTERS DEGREE IN NAVAL ARCHITECTURE AND PROPULSION Resistance and Propulsion Calculation of the Potential Flow around a Ship with a panel method Program DAWSON0 1 Resistance and Propulsion Calculation
MASTERS DEGREE IN NAVAL ARCHITECTURE AND PROPULSION Resistance and Propulsion Calculation of the Potential Flow around a Ship with a panel method Program DAWSON0 1 Resistance and Propulsion Calculation
A laboratory-dualsphysics modelling approach to support landslide-tsunami hazard assessment
 A laboratory-dualsphysics modelling approach to support landslide-tsunami hazard assessment Lake Lucerne case, Switzerland, 2007 Dr. Valentin Heller (www.drvalentinheller.com) Geohazards and Earth Processes
A laboratory-dualsphysics modelling approach to support landslide-tsunami hazard assessment Lake Lucerne case, Switzerland, 2007 Dr. Valentin Heller (www.drvalentinheller.com) Geohazards and Earth Processes
Wigley Hull. SeaFEM - Validation Case 2
 SeaFEM - Validation Case 2 Wigley Hull Compass Ingeniería y Sistemas, SA T. +34 93 218 19 89 F. +34 93 396 97 46 E. info@compassis.com c/ Tuset, 8 7-2 Barcelona 08006 C.I.F.: A 62485180 1 Validation Case
SeaFEM - Validation Case 2 Wigley Hull Compass Ingeniería y Sistemas, SA T. +34 93 218 19 89 F. +34 93 396 97 46 E. info@compassis.com c/ Tuset, 8 7-2 Barcelona 08006 C.I.F.: A 62485180 1 Validation Case
Realistic Animation of Fluids
 Realistic Animation of Fluids p. 1/2 Realistic Animation of Fluids Nick Foster and Dimitri Metaxas Realistic Animation of Fluids p. 2/2 Overview Problem Statement Previous Work Navier-Stokes Equations
Realistic Animation of Fluids p. 1/2 Realistic Animation of Fluids Nick Foster and Dimitri Metaxas Realistic Animation of Fluids p. 2/2 Overview Problem Statement Previous Work Navier-Stokes Equations
Mid-Year Report. Discontinuous Galerkin Euler Equation Solver. Friday, December 14, Andrey Andreyev. Advisor: Dr.
 Mid-Year Report Discontinuous Galerkin Euler Equation Solver Friday, December 14, 2012 Andrey Andreyev Advisor: Dr. James Baeder Abstract: The focus of this effort is to produce a two dimensional inviscid,
Mid-Year Report Discontinuous Galerkin Euler Equation Solver Friday, December 14, 2012 Andrey Andreyev Advisor: Dr. James Baeder Abstract: The focus of this effort is to produce a two dimensional inviscid,
Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Fluid Dynamics
 Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Fluid Dynamics 1 Introduction A thorough study of the laws of fluid mechanics is necessary to understand the fluid motion within the turbomachinery components. In this introductory
Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Fluid Dynamics 1 Introduction A thorough study of the laws of fluid mechanics is necessary to understand the fluid motion within the turbomachinery components. In this introductory
Eng Ship Structures 1 L E C T U R E 1 0 : F I N I T E E L E M E N T T E C H N I Q U E S I N S H I P S T R U C T U R A L D E S I G N
 Eng. 6002 Ship Structures 1 L E C T U R E 1 0 : F I N I T E E L E M E N T T E C H N I Q U E S I N S H I P S T R U C T U R A L D E S I G N Contents Introduction Linear Analysis Static Non-linear Analysis
Eng. 6002 Ship Structures 1 L E C T U R E 1 0 : F I N I T E E L E M E N T T E C H N I Q U E S I N S H I P S T R U C T U R A L D E S I G N Contents Introduction Linear Analysis Static Non-linear Analysis
A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean
 A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean Lian Shen Department of Civil Engineering Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21218 phone: (410) 516-5033 fax: (410) 516-7473 email: LianShen@jhu.edu
A Direct Simulation-Based Study of Radiance in a Dynamic Ocean Lian Shen Department of Civil Engineering Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21218 phone: (410) 516-5033 fax: (410) 516-7473 email: LianShen@jhu.edu
Free-surface flow under a sluice gate from deep water
 Free-surface flow under a sluice gate from deep water 1,2 L.H. Wiryanto, 1 J. Widjaja, 3 B. Supriyanto 1 Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, 3 Faculty of Art and Design, Bandung Institute of Technology
Free-surface flow under a sluice gate from deep water 1,2 L.H. Wiryanto, 1 J. Widjaja, 3 B. Supriyanto 1 Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, 3 Faculty of Art and Design, Bandung Institute of Technology
Simulation of a Free Surface Flow over a Container Vessel Using CFD
 Simulation of a Free Surface Flow over a Container Vessel Using CFD Krishna Atreyapurapu 1 Bhanuprakash Tallapragada 2 Kiran Voonna 3 M.E Student Professor Manager Dept. of Marine Engineering Dept. of
Simulation of a Free Surface Flow over a Container Vessel Using CFD Krishna Atreyapurapu 1 Bhanuprakash Tallapragada 2 Kiran Voonna 3 M.E Student Professor Manager Dept. of Marine Engineering Dept. of
LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA.
 12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
Tracking Human Mobility Using WiFi Signals
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 10, 2018 Tracking Human Mobility Using WiFi Signals Sapiezynski, Piotr; Stopczynski, Arkadiusz; Gatej, Radu ; Jørgensen, Sune Lehmann Published in: P L o S One Link
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 10, 2018 Tracking Human Mobility Using WiFi Signals Sapiezynski, Piotr; Stopczynski, Arkadiusz; Gatej, Radu ; Jørgensen, Sune Lehmann Published in: P L o S One Link
Design and Execution of Model Experiments to Validate Numerical Modelling of 2D Ship Operations in Pack Ice
 Design and Execution of Model Experiments to Validate Numerical Modelling of 2D Ship Operations in Pack Ice Roelof C. Dragt Offshore Engineering Faculty of Mechanical, Maritime and Material Engineering
Design and Execution of Model Experiments to Validate Numerical Modelling of 2D Ship Operations in Pack Ice Roelof C. Dragt Offshore Engineering Faculty of Mechanical, Maritime and Material Engineering
Continued Investigation of Small-Scale Air-Sea Coupled Dynamics Using CBLAST Data
 Continued Investigation of Small-Scale Air-Sea Coupled Dynamics Using CBLAST Data Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Continued Investigation of Small-Scale Air-Sea Coupled Dynamics Using CBLAST Data Dick K.P. Yue Center for Ocean Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
The Level Set Method. Lecture Notes, MIT J / 2.097J / 6.339J Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations
 The Level Set Method Lecture Notes, MIT 16.920J / 2.097J / 6.339J Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations Per-Olof Persson persson@mit.edu March 7, 2005 1 Evolving Curves and Surfaces Evolving
The Level Set Method Lecture Notes, MIT 16.920J / 2.097J / 6.339J Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations Per-Olof Persson persson@mit.edu March 7, 2005 1 Evolving Curves and Surfaces Evolving
Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right)
 Jared Bottlinger MAE598 Project 3 11/16/17 Task 1 a) Figure 1: Volume Fraction Of Water At 0.4s Task 1 b) Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right) Task
Jared Bottlinger MAE598 Project 3 11/16/17 Task 1 a) Figure 1: Volume Fraction Of Water At 0.4s Task 1 b) Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right) Task
Estimation of Hydrodynamic Forces and Motion Characteristics of a Trimaran Light Aboard Ship using Finite Element Method
 Estimation of Hydrodynamic Forces and Motion Characteristics of a Trimaran Light Aboard Ship using Finite Element Method A K D Velayudhan Department of Mechanical Engineering, Muthoot Institute of Technology
Estimation of Hydrodynamic Forces and Motion Characteristics of a Trimaran Light Aboard Ship using Finite Element Method A K D Velayudhan Department of Mechanical Engineering, Muthoot Institute of Technology
A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates
 A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates Peter Hjort Lauritzen Atmospheric Modeling & Predictability Section National Center for Atmospheric
A mass-conservative version of the semi- Lagrangian semi-implicit HIRLAM using Lagrangian vertical coordinates Peter Hjort Lauritzen Atmospheric Modeling & Predictability Section National Center for Atmospheric
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD
 18th Engineering Mechanics Division Conference (EMD007) NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD Abstract S. Fu University of Texas at Austin, Austin,
18th Engineering Mechanics Division Conference (EMD007) NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE SHALLOW WATER EQUATIONS USING A TIME-CENTERED SPLIT-IMPLICIT METHOD Abstract S. Fu University of Texas at Austin, Austin,
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW. An Introduction. -
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW An Introduction http://tsaad.utsi.edu - tsaad@utsi.edu OUTLINE General characteristics Surface Waves & Froude Number Effects Types of Channel flows The Hydraulic Jump Conclusion General
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW An Introduction http://tsaad.utsi.edu - tsaad@utsi.edu OUTLINE General characteristics Surface Waves & Froude Number Effects Types of Channel flows The Hydraulic Jump Conclusion General
Numerical study on a KVLCC2 model advancing in shallow water
 Yuan, Zhi-Ming and Kellett, Paula (2015) Numerical study on a KVLCC2 model advancing in shallow water. In: 9th International Workshop on Ship and Marine Hydrodynamics, 2015-08-25-2015-08-28, University
Yuan, Zhi-Ming and Kellett, Paula (2015) Numerical study on a KVLCC2 model advancing in shallow water. In: 9th International Workshop on Ship and Marine Hydrodynamics, 2015-08-25-2015-08-28, University
Numerical and experimental investigations into liquid sloshing in a rectangular tank
 The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Numerical and experimental investigations into liquid sloshing in a rectangular
The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Numerical and experimental investigations into liquid sloshing in a rectangular
Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models. C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak
 Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak Aerospace and Astronautics University of Washington, Seattle American Physical Society
Development of a Maxwell Equation Solver for Application to Two Fluid Plasma Models C. Aberle, A. Hakim, and U. Shumlak Aerospace and Astronautics University of Washington, Seattle American Physical Society
Skåne University Hospital Lund, Lund, Sweden 2 Deparment of Numerical Analysis, Centre for Mathematical Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
 Volume Tracking: A New Method for Visualization of Intracardiac Blood Flow from Three-Dimensional, Time-Resolved, Three-Component Magnetic Resonance Velocity Mapping Appendix: Theory and Numerical Implementation
Volume Tracking: A New Method for Visualization of Intracardiac Blood Flow from Three-Dimensional, Time-Resolved, Three-Component Magnetic Resonance Velocity Mapping Appendix: Theory and Numerical Implementation
Supercomputing of Tsunami Damage Mitigation Using Offshore Mega-Floating Structures
 International Innovation Workshop on Tsunami, Snow Avalanche and Flash Flood Energy Dissipation January 21-22, 2016, Maison Villemanzy in Lyon, France Supercomputing of Tsunami Damage Mitigation Using
International Innovation Workshop on Tsunami, Snow Avalanche and Flash Flood Energy Dissipation January 21-22, 2016, Maison Villemanzy in Lyon, France Supercomputing of Tsunami Damage Mitigation Using
Hydrodynamic modeling of flow around bridge piers
 Hydrodynamic modeling of flow around bridge piers E. D. Farsirotou*, J. V. Soulis^, V. D. Dermissis* *Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Civil Engineering Department, Division of Hydraulics and Environmental
Hydrodynamic modeling of flow around bridge piers E. D. Farsirotou*, J. V. Soulis^, V. D. Dermissis* *Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Civil Engineering Department, Division of Hydraulics and Environmental
Proposal for tutorial: Resilience in carrier Ethernet transport
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 16, 2018 Proposal for tutorial: Resilience in carrier Ethernet transport Berger, Michael Stübert; Wessing, Henrik; Ruepp, Sarah Renée Published in: 7th International
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 16, 2018 Proposal for tutorial: Resilience in carrier Ethernet transport Berger, Michael Stübert; Wessing, Henrik; Ruepp, Sarah Renée Published in: 7th International
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Efficiency and performances
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 2, No 3, 2012 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4399 Efficiency and performances
Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation
 Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Implicit Surfaces Marching Cubes/Tetras Collision Detection & Response Conservative Bounding Regions backtracking fixing Today Flow Simulations in Graphics Flow
Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Implicit Surfaces Marching Cubes/Tetras Collision Detection & Response Conservative Bounding Regions backtracking fixing Today Flow Simulations in Graphics Flow
Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement Lian Shen Department of Mechanical Engineering
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement Lian Shen Department of Mechanical Engineering
Application of Hydrodynamics and Dynamics Models for Efficient Operation of Modular Mini-AUVs in Shallow and Very-Shallow Waters
 Application of Hydrodynamics and Dynamics Models for Efficient Operation of Modular Mini-AUVs in Shallow and Very-Shallow Waters P. Ananthakrishnan Department of Ocean Engineering Florida Atlantic University
Application of Hydrodynamics and Dynamics Models for Efficient Operation of Modular Mini-AUVs in Shallow and Very-Shallow Waters P. Ananthakrishnan Department of Ocean Engineering Florida Atlantic University
MODELLING THE FLOW AROUND AN ISLAND AND A HEADLAND: APPLICATION OF A TWO MIXING LENGTH MODEL WITH TELEMAC3D. Nicolas Chini 1 and Peter K.
 MODELLING THE FLOW AROUND AN ISLAND AND A HEADLAND: APPLICATION OF A TWO MIXING LENGTH MODEL WITH TELEMAC3D Nicolas Chini 1 and Peter K. Stansby 2 Numerical modelling of the circulation around islands
MODELLING THE FLOW AROUND AN ISLAND AND A HEADLAND: APPLICATION OF A TWO MIXING LENGTH MODEL WITH TELEMAC3D Nicolas Chini 1 and Peter K. Stansby 2 Numerical modelling of the circulation around islands
DEVELOPMENT OF A CFD MODEL FOR SIMULATION OF SELF-PROPULSION TESTS
 DEVELOPMENT OF A CFD MODEL FOR SIMULATION OF SELF-PROPULSION TESTS Alexandre T. P. Alho Laboratório de Sistemas de Propulsão DENO/POLI, UFRJ INTRODUCTION Motivation Growing demand for high efficiency propulsion
DEVELOPMENT OF A CFD MODEL FOR SIMULATION OF SELF-PROPULSION TESTS Alexandre T. P. Alho Laboratório de Sistemas de Propulsão DENO/POLI, UFRJ INTRODUCTION Motivation Growing demand for high efficiency propulsion
Tilburg University. The use of canonical analysis Kuylen, A.A.A.; Verhallen, T.M.M. Published in: Journal of Economic Psychology
 Tilburg University The use of canonical analysis Kuylen, A.A.A.; Verhallen, T.M.M. Published in: Journal of Economic Psychology Publication date: 1981 Link to publication Citation for published version
Tilburg University The use of canonical analysis Kuylen, A.A.A.; Verhallen, T.M.M. Published in: Journal of Economic Psychology Publication date: 1981 Link to publication Citation for published version
Development of Compressible-Incompressible Link to Efficiently Model Bubble Dynamics near Floating Body Chao-Tsung Hsiao 1, Georges L.
 Development of Compressible-Incompressible Link to Efficiently Model Bubble Dynamics near Floating Body Chao-Tsung Hsiao 1, Georges L. Chahine 1 DYNAFLOW, INC. 1061-J Iron Bridge Road, Jessup, MD 0794,
Development of Compressible-Incompressible Link to Efficiently Model Bubble Dynamics near Floating Body Chao-Tsung Hsiao 1, Georges L. Chahine 1 DYNAFLOW, INC. 1061-J Iron Bridge Road, Jessup, MD 0794,
DNP Communication Function with RTDS GTNET-DNP& ASE Interface Test Results
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 17, 2018 DNP Communication Function with RTDS GTNET-DNP& ASE Interface Test Results Cha, Seung-Tae; Wu, Qiuwei; Saleem, Arshad; Østergaard, Jacob Publication date:
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 17, 2018 DNP Communication Function with RTDS GTNET-DNP& ASE Interface Test Results Cha, Seung-Tae; Wu, Qiuwei; Saleem, Arshad; Østergaard, Jacob Publication date:
Milovan Perić CD-adapco. Use of STAR-CCM+ in Marine and Offshore Engineering and Future Trends
 Milovan Perić CD-adapco Use of STAR-CCM+ in Marine and Offshore Engineering and Future Trends Introduction CD-adapco is developing simulation capabilities in STAR-CCM+ specifically for marine and offshore
Milovan Perić CD-adapco Use of STAR-CCM+ in Marine and Offshore Engineering and Future Trends Introduction CD-adapco is developing simulation capabilities in STAR-CCM+ specifically for marine and offshore
Training Convolutional Neural Networks for Translational Invariance on SAR ATR
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 28, 2019 Training Convolutional Neural Networks for Translational Invariance on SAR ATR Malmgren-Hansen, David; Engholm, Rasmus ; Østergaard Pedersen, Morten Published
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 28, 2019 Training Convolutional Neural Networks for Translational Invariance on SAR ATR Malmgren-Hansen, David; Engholm, Rasmus ; Østergaard Pedersen, Morten Published
A Multiscale Nested Modeling Framework to Simulate the Interaction of Surface Gravity Waves with Nonlinear Internal Gravity Waves
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Multiscale Nested Modeling Framework to Simulate the Interaction of Surface Gravity Waves with Nonlinear Internal Gravity
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. A Multiscale Nested Modeling Framework to Simulate the Interaction of Surface Gravity Waves with Nonlinear Internal Gravity
Solving the shallow-water equations by a pseudo-spectral method
 Solving the shallow-water equations by a pseudo-spectral method Simon Chabot June 9th, 2015 Abstract In this short tutorial, you will use python to solve a non-linear system of equations using a pseudo-spectral
Solving the shallow-water equations by a pseudo-spectral method Simon Chabot June 9th, 2015 Abstract In this short tutorial, you will use python to solve a non-linear system of equations using a pseudo-spectral
Realtime Water Simulation on GPU. Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research
 1 Realtime Water Simulation on GPU Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research 2 3 Overview Approaches to realtime water simulation Hybrid shallow water solver + particles Hybrid 3D tall cell water solver + particles
1 Realtime Water Simulation on GPU Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research 2 3 Overview Approaches to realtime water simulation Hybrid shallow water solver + particles Hybrid 3D tall cell water solver + particles
Citation for published version (APA): Kleefsman, K. M. T. (2005). Water impact loading on offshore structures. - A numerical study s.n.
 University of Groningen Water impact loading on offshore structures. - A numerical study Kleefsman, Kornelia Marchien Theresa IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Water impact loading on offshore structures. - A numerical study Kleefsman, Kornelia Marchien Theresa IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
NUMERICAL DIFFUSION AND DISSIPATION IN HYDROSTATIC MODELS OF INTERNAL WAVES
 NUMERICAL DIFFUSION AND DISSIPATION IN HYDROSTATIC MODELS OF INTERNAL WAVES Ben R. Hodges 1 (A.M., ASCE) and Sarah Kelly Delavan 2 ABSTRACT Analysis of numerical diffusion and dissipation rates in a hydrostatic
NUMERICAL DIFFUSION AND DISSIPATION IN HYDROSTATIC MODELS OF INTERNAL WAVES Ben R. Hodges 1 (A.M., ASCE) and Sarah Kelly Delavan 2 ABSTRACT Analysis of numerical diffusion and dissipation rates in a hydrostatic
