Unit 5, Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs
|
|
|
- Russell Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 5, Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs 1. Given the rule: Complete the table for the function rule for the following input values: input output 2. Here is an input-output rule: Complete the table for the input-output rule: input output 3. Andre s school orders some new supplies for the chemistry lab. The online store shows a pack of 10 test tubes costs $4 less than a set of nested beakers. In order to fully equip the lab, the school orders 12 sets of beakers and 8 packs of test tubes. a. Write an equation that shows the cost of a pack of test tubes,, in terms of the cost of a set of beakers,. b. The school office receives a bill for the supplies in the amount of $348. Write an equation with and that describes this situation. c. Since is in terms of from the first equation, this expression can be substituted into the second Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs 1
2 equation where appears. Write an equation that shows this substitution. d. Solve the equation for. e. How much did the school pay for a set of beakers? For a pack of test tubes? (from Unit 4, Lesson 15) 4. Solve: (from Unit 4, Lesson 14) 5. For what value of do the expressions and have the same value? (from Unit 4, Lesson 9) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs 2
3 Unit 5, Lesson 2: Introduction to Functions 1. Here are several function rules. Calculate the output for each rule when you use -6 as the input. 2. A group of students is timed while sprinting 100 meters. Each student s speed can be found by dividing 100 m by their time. Is each statement true or false? Explain your reasoning. a. Speed is a function of time. b. Time is a function of distance. c. Speed is a function of number of students racing. d. Time is a function of speed. 3. Diego s history teacher writes a test for the class with 26 questions. The test is worth 123 points and has two types of questions: multiple choice worth 3 points each, and essays worth 8 points each. How many essay questions are on the test? Explain or show your reasoning. (from Unit 4, Lesson 15) 4. These tables correspond to inputs and outputs. Which of these input and output tables could represent a function rule, and which ones could not? Explain or show your reasoning. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 2: Introduction to Functions 1
4 Table A: Table B: input output input output Table C: Table D: input output input output Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 2: Introduction to Functions 2
5 Unit 5, Lesson 3: Equations for Functions 1. Here is an equation that represents a function:. Select all the different equations that describe the same function: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. 2. a. Graph a system of linear equations with no solutions. b. Write an equation for each line you graph. (from Unit 4, Lesson 13) 3. Brown rice costs $2 per pound, and beans cost $1.60 per pound. Lin has $10 to spend on these items Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 3: Equations for Functions 1
6 to make a large meal of beans and rice for a potluck dinner. Let be the number of pounds of beans Lin buys and be the number of pounds of rice she buys when she spends all her money on this meal. a. Write an equation relating the two variables. b. Rearrange the equation so is the independent variable. c. Rearrange the equation so is the independent variable. 4. Solve each equation and check your answer. a. b. c. (from Unit 4, Lesson 6) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 3: Equations for Functions 2
7 Unit 5, Lesson 4: Tables, Equations, and Graphs of Functions 1. The graph and the table show the high temperatures in a city over a 10-day period. day temperature (degrees F) a. What was the high temperature on Day 7? b. On which days was the high temperature 61 degrees? c. Is the high temperature a function of the day? Explain how you know. d. Is the day a function of the high temperature? Explain how you know. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Functions Lesson 4: Tables, Equations, and Graphs of 1
8 2. The amount Lin s sister earns at her part-time job is proportional to the number of hours she works. She earns $9.60 per hour. a. Write an equation in the form to describe this situation, where represents the hours she works and represents the dollars she earns. b. Is a function of? Explain how you know. c. Write an equation describing as a function of. 3. Use the equation to complete the table, then graph the line using as the dependent variable Solve the system of equations: (from Unit 4, Lesson 13) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Functions Lesson 4: Tables, Equations, and Graphs of 2
9 Unit 5, Lesson 5: More Graphs of Functions 1. Match each diagram to the function described, then label the axes appropriately 1. The function inputs the age of an oak tree and outputs a prediction of the height of the tree. 2. The function inputs the edge length of a cube and outputs the volume. 3. The function inputs the distance traveled and predicts the amount of fuel left in the tank. 4. The function inputs the height of a triangle with base 12 and outputs the area. 5. The function inputs the time of day and predicts the temperature. 6. The function inputs the time of day and predicts the number of cars washed at a student car wash. 2. The solution to a system of equations is. Choose two equations that might make up the system. A. B. C. D. E. (from Unit 4, Lesson 13) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 5: More Graphs of Functions 1
10 3. A car is traveling on a small highway and is either going 55 miles per hour or 35 miles per hour, depending on the speed limits, until it reaches its destination 200 miles away. Letting represent the amount of time in hours that the car is going 55 miles per hour, and being the time in hours that the car is going 35 miles per hour, an equation describing the relationship is: a. If the car spends 2.5 hours going 35 miles per hour on the trip, how long does it spend going 55 miles per hour? b. If the car spends 3 hours going 55 miles per hour on the trip, how long does it spend going 35 miles per hour? c. If the car spends no time going 35 miles per hour, how long would the trip take? Explain your reasoning. (from Unit 5, Lesson 3) 4. The graph represents an object that is shot upwards from a tower and then falls to the ground. The independent variable is time in seconds and the dependent variable is the object s height above the ground in meters. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 5: More Graphs of Functions 2
11 a. How tall is the tower from which the object was shot? b. When did the object hit the ground? c. Estimate the greatest height the object reached and the time it took to reach that height. Indicate this situation on the graph. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 5: More Graphs of Functions 3
12 Unit 5, Lesson 6: Even More Graphs of Functions 1. Match the graph to the following situations (you can use a graph multiple times). For each match, name possible independent and dependent variables and how you would label the axes. a. Tyler pours the same amount of milk from a bottle every morning. b. A plant grows the same amount every week. c. The day started very warm but then it got colder. d. A carnival has an entry fee of $5 and tickets for rides cost $1 each. 2. Jada fills her aquarium with water. The graph shows the height of the water, in cm, in the aquarium as a function of time in minutes. Invent a story of how Jada fills the aquarium that fits the graph. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 6: Even More Graphs of Functions 1
13 3. Recall the formula for area of a circle. a. Write an equation relating a circle s radius,, and area,. b. Is area a function of the radius? Is radius a function of the area? c. Fill in the missing parts of the table. 3 (from Unit 5, Lesson 4) 4. The points with coordinates,, and all lie on the line. a. Create a graph, plot the points, and sketch the line. b. What is the slope of the line you graphed? c. What does this slope tell you about the relationship between lengths and widths of rectangles with perimeter 24? Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 6: Even More Graphs of Functions 2
14 (from Unit 3, Lesson 11) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 6: Even More Graphs of Functions 3
15 Unit 5, Lesson 7: Connecting Representations of Functions 1. The equation and the tables represent two different functions. Use the equation and the table to answer the questions. This table represents as a function of a. When is -3, is or greater? b. When is 21, what is the value of? What is the value of that goes with this value of? c. When is 6, is or greater? d. For what values of do we know that is greater than? 2. Match each function rule with the value that could not be a possible input for that function. A. 3 divided by the input 1. 3 B. Add 4 to the input, then divide this value into 3 C. Subtract 3 from the input, then divide this value into (from Unit 5, Lesson 2) 3. Elena and Lin are training for a race. Elena runs her mile a constant speed of 7.5 miles per hour. Lin s times are recorded every minute: Unit 5: Functions and Volume Functions Lesson 7: Connecting Representations of 1
16 time (minutes) distance (miles) a. Who finished their mile first? b. This is a graph of Lin s progress. Draw a graph to represent Elena s mile on the same axes. c. For these models, is distance a function of time? Is time a function of distance? Explain how you know. 4. Find a value of that makes the equation true: Explain your reasoning, and check that your answer is correct. (from Unit 4, Lesson 4) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Functions Lesson 7: Connecting Representations of 2
17 Unit 5, Lesson 8: Linear Functions 1. Two cars drive on the same highway in the same direction. The graphs show the distance,, of each one as a function of time,. Which car drives faster? Explain how you know. 2. Two car services offer to pick you up and take you to your destination. Service A charges 40 cents to pick you up and 30 cents for each mile of your trip. Service B charges $1.10 to pick you up and charges cents for each mile of your trip. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 8: Linear Functions 1
18 a. Match the services to the Lines and. b. For Service B, is the additional charge per mile greater or less than 30 cents per mile of the trip? Explain your reasoning. 3. Kiran and Clare like to race each other home from school. They run at the same speed, but Kiran's house is slightly closer to school than Clare's house. On a graph, their distance from their homes in meters is a function of the time from when they begin the race in seconds. a. As you read the graphs left to right, would the lines go up or down? b. What is different about the lines representing Kiran's run and Clare's run? c. What is the same about the lines representing Kiran's run and Clare's run? 4. Write an equation for each line. (from Unit 3, Lesson 11) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 8: Linear Functions 2
19 Unit 5, Lesson 9: Linear Models 1. On the first day after the new moon, 2% of the moon's surface is illuminated. On the second day, 6% is illuminated. a. Based on this information, predict the day on which the moon's surface is 50% illuminated and 100% illuminated. b. The moon's surface is 100% illuminated on day 14. Does this agree with the prediction you made? c. Is the percentage illumination of the moon's surface a linear function of the day? 2. In science class, Jada uses a graduated cylinder with water in it to measure the volume of some marbles. After dropping in 4 marbles so they are all under water, the water in the cylinder is at a height of 10 milliliters. After dropping in 6 marbles so they are all under water, the water in the cylinder is at a height of 11 milliliters. a. What is the volume of 1 marble? b. How much water was in the cylinder before any marbles were dropped in? c. What should be the height of the water after 13 marbles are dropped in? d. Is the volume of water a linear relationship with the number of marbles dropped in the graduated cylinder? If so, what does the slope of the line mean? If not, explain your reasoning. 3. Solve each of these equations. Explain or show your reasoning. (from Unit 4, Lesson 5) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 9: Linear Models 1
20 4. For a certain city, the high temperatures (in degrees Celsius) are plotted against the number of days after the new year. Based on this information, is the high temperature in this city a linear function of the number of days after the new year? 5. The school designed their vegetable garden to have a perimeter of 32 feet with the length measuring two feet more than twice the width. a. Using to represent the length of the garden and to represent its width, write and solve a system of equations that describes this situation. b. What are the dimensions of the garden? Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 9: Linear Models 2
21 (from Unit 4, Lesson 15) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 9: Linear Models 3
22 Unit 5, Lesson 10: Piecewise Linear Functions 1. The graph shows the distance of a car from home as a function of time. Describe what a person watching the car may be seeing. 2. The equation and the graph represent two functions. Use the equation and the graph to answer the questions. a. When is 4, is the output of the equation or the graph greater? b. What value for produces the same output in both the graph and the equation? (from Unit 5, Lesson 7) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 10: Piecewise Linear Functions 1
23 3. This graph shows a trip on a bike trail. The trail has markers every 0.5 km showing the distance from the beginning of the trail. a. When was the bike rider going the fastest? b. When was the bike rider going the slowest? c. During what times was the rider going away from the beginning of the trail? d. During what times was the rider going back towards the beginning of the trail? e. During what times did the rider stop? 4. The expression represents the volume of liquid of a container after seconds. The expression represents the volume of liquid of another container after seconds. What does the equation mean in this situation? (from Unit 4, Lesson 9) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 10: Piecewise Linear Functions 2
24 Unit 5, Lesson 11: Filling containers 1. Cylinder A, B, and C have the same radius but different heights. Put the cylinders in order of their volume from least to greatest. 2. Two cylinders, and, each started with different amounts of water. The graph shows how the height of the water changed as the volume of water increased in each cylinder. Match the graphs of and to Cylinders P and Q. Explain your reasoning. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 11: Filling containers 1
25 3. Which of the following graphs could represent the volume of water in a cylinder as a function of its height? Explain your reasoning. 4. Together, the areas of the rectangles sum to 30 square centimeters. a. Write an equation showing the relationship between and. b. Fill in the table with the missing values (from Unit 5, Lesson 3) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 11: Filling containers 2
26 Unit 5, Lesson 12: How Much Will Fit? 1. a. Sketch a cube and label its side length as 4 cm (this will be Cube A). b. Sketch a cube with sides that are twice as long as Cube A and label its side length (this will be Cube B). c. Find the volumes of Cube A and Cube B. 2. Several glass aquariums of various sizes are for sale at a pet shop. They are all shaped like rectangular prisms. A 15-gallon tank is 24 inches long, 12 inches wide, and 12 inches tall. Match the dimensions of the other tanks with the volume of water they can each hold. A. Tank 1: 36 inches long, 18 inches wide, and 12 inches tall B. Tank 2: 16 inches long, 8 inches wide, and 10 inches tall 1. 5 gallons gallons gallons C. Tank 3: 30 inches long, 12 inches wide, and 12 inches tall gallons D. Tank 4: 20 inches long, 10 inches wide, and 12 inches tall 3. Two paper drink cups are shaped like cones. The small cone can hold 6 oz of water. The large cone is the height and the diameter of the small cone. Which of these could be the amount of water the large cone holds? A. 8 cm B. 14 oz C. 4.5 oz D. 14 cm 4. The graph represents the volume of a cylinder with a height equal to its radius. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 12: How Much Will Fit? 1
27 a. When the diameter is 2, what is the radius of the cylinder? b. Express the volume of a cube of side length as an equation. c. Make a table for volume of the cube at,,, and. d. Which volume is greater: the volume of the cube when, or the volume of the cylinder when its diameter is 3? (from Unit 5, Lesson 7) 5. Select all the points that are on a line with slope 2 that also contains the point. A. B. C. D. E. (from Unit 3, Lesson 10) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 12: How Much Will Fit? 2
28 6. Solve: (from Unit 4, Lesson 14) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 12: How Much Will Fit? 3
29 Unit 5, Lesson 13: The Volume of a Cylinder 1. Match each set of information about a circle with the area of that circle. A. Circle A has a radius of 4 units. 1. square units B. Circle B has a radius of 10 units. 2. approximately 314 square units C. Circle C has a diameter of 16 units. 3. square units D. Circle D has a circumference of units. 4. square units 2. a. Sketch a cylinder. b. Label its radius 3 and its height 10. c. Shade in one of its bases. 3. At a farm, animals are fed bales of hay and buckets of grain. Each bale of hay is in the shape a rectangular prism. The base has side lengths 2 feet and 3 feet, and the height is 5 feet. Each bucket of grain is a cylinder with a diameter of 3 feet. The height of the bucket is 5 feet, the same as the height of the bale. a. Which is larger in area, the rectangular base of the bale or the circular base of the bucket? Explain how you know. b. Which is larger in volume, the bale or the bucket? Explain how you know. 4. Three cylinders have a height of 8 cm. Cylinder 1 has a radius of 1 cm. Cylinder 2 has a radius of 2 cm. Cylinder 3 has a radius of 3 cm. Find the volume of each cylinder. 5. A one-quart container of tomato soup is shaped like a rectangular prism. A soup bowl shaped like a Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 13: The Volume of a Cylinder 1
30 hemisphere can hold 8 oz of liquid. How many bowls will the soup container fill? Recall that 1 quart is equivalent to 32 fluid ounces (oz). (from Unit 5, Lesson 12) 6. Two students join a puzzle solving club and get faster at finishing the puzzles as they get more practice. Student A improves their times faster than Student B. a. Match the students to the Lines and. b. Which student was faster at puzzle solving before practice? (from Unit 5, Lesson 8) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 13: The Volume of a Cylinder 2
31 Unit 5, Lesson 14: Finding Cylinder Dimensions 1. Complete the table with all of the missing information about three different cylinders. diameter of base area of base (square height volume (cubic (units) units) (units) units) A cylinder has volume and radius 3. What is its height? 3. Three cylinders have a volume of 2826 cm 3. Cylinder A has a height of 900 cm. Cylinder B has a height of 225 cm. Cylinder C has a height of 100 cm. Find the radius of each cylinder. Use 3.14 as an approximation for. 4. A gas company s delivery truck has a cylindrical tank that is 14 feet in diameter and 40 feet long. a. Sketch the tank, and mark the radius and the height. b. How much gas can fit in the tank? (from Unit 5, Lesson 13) 5. Here is a graph that shows the water height of the ocean between September 22 and September 24, 2016 in Bodega Bay, CA. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 14: Finding Cylinder Dimensions 1
32 a. Estimate the water height at 12 p.m. on September 22. b. How many times was the water height 5 feet? Find two times when this happens. c. What was the lowest the water got during this time period? When does this occur? d. Does the water ever reach a height of 6 feet? (from Unit 5, Lesson 5) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 14: Finding Cylinder Dimensions 2
33 Unit 5, Lesson 15: The Volume of a Cone 1. A cylinder and cone have the same height and radius. The height of each is 5 cm, and the radius is 2 cm. Calculate the volume of the cylinder and the cone. 2. The volume of this cone is cubic units. What is the volume of a cylinder that has the same base area and the same height? 3. A cylinder has a diameter of 6 cm and a volume of cm 3. a. Sketch the cylinder. b. Find its height and radius in centimeters. c. Label your sketch with the cylinder s height and radius. (from Unit 5, Lesson 14) 4. Lin wants to get some custom T-shirts printed for her basketball team. Shirts cost $10 each if you order 10 or fewer shirts and $9 each if you order 11 or more shirts. a. Make a graph that shows the total cost of buying shirts, for 0 through 15 shirts. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 15: The Volume of a Cone 1
34 b. There are 10 people on the team. Do they save money if they buy an extra shirt? Explain your reasoning. c. What is the slope of the graph between 0 and 10? What does it mean in the story? d. What is the slope of the graph between 11 and 15? What does it mean in the story? (from Unit 5, Lesson 10) 5. In the following graphs, the horizontal axis represents time and the vertical axis represents distance from school. Write a possible story for each graph. (from Unit 5, Lesson 6) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 15: The Volume of a Cone 2
35 Unit 5, Lesson 16: Finding Cone Dimensions 1. The volume of this cylinder is cubic units. What is the volume of a cone that has the same base area and the same height? (from Unit 5, Lesson 15) 2. A cone has volume cubic inches. Its height is 4 inches. What is its radius? 3. A cone has volume. a. If the cone s radius is 1, what is its height? b. If the cone s radius is 2, what is its height? c. If the cone s radius is 5, what is its height? d. If the cone s radius is, what is its height? e. If the cone's radius in, then what is the height? 4. Three people are playing near the water. Person A stands on the dock. Person B starts at the top of a pole and ziplines into the water. Person C climbs out of the water and up the zipline pole. Match the people to the graphs where the horizontal axis represents time in seconds and the vertical axis represents height above the water level in feet. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 16: Finding Cone Dimensions 1
36 (from Unit 5, Lesson 6) 5. A room is 15 feet tall. An architect wants to include a window that is 6 feet tall. The distance between the floor and the bottom of the window is feet. The distance between the ceiling and the top of the window is feet. This relationship can be described by the equation a. Which variable is independent based on the equation given? b. If the architect wants to be 3, what does this mean? What value of would work with the given value for? c. The customer wants the window to have 5 feet of space above it. Is the customer describing or? What is the value of the other variable? (from Unit 5, Lesson 3) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 16: Finding Cone Dimensions 2
37 Unit 5, Lesson 17: Scaling One Dimension 1. A cylinder has a volume of cm 3 and height. Complete this table for volume of cylinders with the same radius but different heights. height (cm) volume (cm 3 ) 2. A cylinder has a radius of 3 cm and a height of 5 cm. a. What is the volume of the cylinder? b. What is the volume of the cylinder when its height is tripled? c. What is the volume of the cylinder when its height is halved? 3. A graduated cylinder that is 24 cm tall can hold 1 L of water. What is the radius of the cylinder? What is the height of the 500 ml mark? The 250 ml mark? Recall that 1 liter (L) is equal to 1000 milliliters (ml). 4. An ice cream shop offers two ice cream cones. The waffle cone holds 12 ounces and is 5 inches tall. The sugar cone also holds 12 ounces and is 8 inches tall. Which cone has a larger radius? (from Unit 5, Lesson 16) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 17: Scaling One Dimension 1
38 5. A 6 oz paper cup is shaped like a cone with a diameter of 4 inches. How many ounces of water will a plastic cylindrical cup with a diameter of 4 inches hold if it is the same height as the paper cup? (from Unit 5, Lesson 15) 6. Lin s smart phone was fully charged when she started school at 8:00 a.m. At 9:20 a.m., it was 90% charged, and at noon, it was 72% charged. a. When do you think her battery will die? b. Is battery life a function of time? If yes, is it a linear function? Explain your reasoning. (from Unit 5, Lesson 9) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 17: Scaling One Dimension 2
39 Unit 5, Lesson 18: Scaling Two Dimensions 1. There are many cylinders with a height of 18 meters. Let represent the radius in meters and represent the volume in cubic meters. a. Write an equation that represents the volume as a function of the radius. b. Complete this table, giving three possible examples. 1 c. If the radius of a cylinder is doubled, does the volume double? Explain how you know. d. Is the graph of this function a line? Explain how you know. 2. As part of a competition, Diego must spin around in a circle 6 times and then run to a tree. The time he spends on each spin is represented by and the time he spends running is. He gets to the tree 21 seconds after he starts spinning. a. Write an equation showing the relationship between and. b. Rearrange the equation so that it shows as a function of. c. If it takes Diego 1.2 seconds to spin around each time, how many seconds did he spend running? (from Unit 5, Lesson 3) 3. The table and graph represent two functions. Use the table and graph to answer the questions. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 18: Scaling Two Dimensions 1
40 a. For which values of is the output from the table less than the output from the graph? b. In the graphed function, which values of give an output of 0? (from Unit 5, Lesson 7) 4. A cone has a radius of 3 units and a height of 4 units. a. What is this volume of this cone? b. Another cone has quadruple the radius, and the same height. How many times larger is the new cone s volume? Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 18: Scaling Two Dimensions 2
41 Unit 5, Lesson 19: Estimating a Hemisphere 1. A baseball fits snugly inside a transparent display cube. The length of an edge of the cube is 2.9 inches. Is the baseball s volume greater than, less than, or equal to cubic inches? Explain how you know. 2. There are many possible cones with a height of 18 meters. Let represent the radius in meters and represent the volume in cubic meters. a. Write an equation that represents the volume as a function of the radius. b. Complete this table for the function, giving three possible examples. 2 c. If you double the radius of a cone, does the volume double? Explain how you know. d. Is the graph of this function a line? Explain how you know. (from Unit 5, Lesson 18) 3. A hemisphere fits snugly inside a cylinder with a radius of 6 cm. A cone fits snugly inside the same hemisphere. a. What is the volume of the cylinder? b. What is the volume of the cone? c. Estimate the volume of the hemisphere by calculating the average of the volumes of the cylinder and cone. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 19: Estimating a Hemisphere 1
42 4. a. Find the hemisphere s diameter if its radius is 6 cm. b. Find the hemisphere s diameter if its radius is m. c. Find the hemisphere s diameter if its radius is ft. d. Find the hemisphere s radius if its diameter is 6 cm. e. Find the hemisphere s radius if its diameter is m. f. Find the hemisphere s radius if its diameter is ft. 5. After almost running out of space on her phone, Elena checks with a couple of friends who have the same phone to see how many pictures they have on their phones and how much memory they take up. The results are shown in the table. number of photos 2,523 3,148 1,875 memory used in MB 8,072 10,106 6,037 a. Could this information be reasonably modeled with a linear function? Explain your reasoning. b. Elena needs to delete photos to create 1,200 MB of space. Estimate the number of photos should she delete. (from Unit 5, Lesson 9) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 19: Estimating a Hemisphere 2
43 Unit 5, Lesson 20: The Volume of a Sphere 1. Match the description of each sphere to its correct volume. A. Sphere A: radius of 4 cm 1. cm 3 B. Sphere B: diameter of 6 cm 2. cm 3 C. Sphere C: radius of 8 cm D. Sphere D: radius of 6 cm 3. cm 3 4. cm 3 2. a. A cube s volume is 512 cubic units. What is the length of its edge? b. If a sphere fits snugly inside this cube, what is its volume? c. What fraction of the cube is taken up by the sphere? What percentage is this? Explain or show your reasoning. 3. Sphere A has radius 2 cm. Sphere B has radius 4 cm. a. Calculate the volume of each sphere. b. The radius of Sphere B is double that of Sphere A. How many times greater is the volume of B? 4. Three cones have a volume of cm 3. Cone A has a radius of 2 cm. Cone B has a radius of 3 cm. Cone C has a radius of 4 cm. Find the height of each cone. (from Unit 5, Lesson 16) 5. The graph represents the average price of regular gasoline in the United States in dollars as a function of the number of months after January Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 20: The Volume of a Sphere 1
44 a. How many months after January 2014 was the price of gas the greatest? b. Did the average price of gas ever get below $2? c. Describe what happened to the average price of gas in (from Unit 5, Lesson 5) 6. While conducting an inventory in their bicycle shop, the owner noticed the number of bicycles is 2 fewer than 10 times the number of tricycles. They also know there are 410 wheels on all the bicycles and tricycles in the store. Write and solve a system of equations to find the number of bicycles in the store. (from Unit 4, Lesson 15) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 20: The Volume of a Sphere 2
45 Unit 5, Lesson 21: Cylinders, Cones, and Spheres 1. A scoop of ice cream has a 3 inch radius. How tall should the ice cream cone of the same radius be in order to contain all of the ice cream inside the cone? 2. Calculate the volume of the following shapes with the given information. For the first three questions, give each answer both in terms of and by using to approximate. Make sure to include units. a. Sphere with a diameter of 6 inches b. Cylinder with a height of 6 inches and a diameter of 6 inches c. Cone with a height of 6 inches and a radius of 3 inches d. How are these three volumes related? 3. A coin-operated bouncy ball dispenser has a large glass sphere that holds many spherical balls. The large glass sphere has a radius of 9 inches. Each bouncy ball has radius of 1 inch and sits inside the dispenser. Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 21: Cylinders, Cones, and Spheres 1
46 If there are 243 bouncy balls in the large glass sphere, what proportion of the large glass sphere s volume is taken up by bouncy balls? Explain how you know. 4. A farmer has a water tank for cows in the shape of a cylinder with radius of 7 ft and a height of 3 ft. The tank comes equipped with a sensor to alert the farmer to fill it up when the water falls to 20% capacity. What is the volume of the tank be when the sensor turns on? (from Unit 5, Lesson 13) Unit 5: Functions and Volume Lesson 21: Cylinders, Cones, and Spheres 2
Unit 5, Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs
 Unit 5, Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs Let s make some rules. 1.1: Dividing by 0 Study the statements carefully. because because What value can be used in place of to create true statements? Explain your
Unit 5, Lesson 1: Inputs and Outputs Let s make some rules. 1.1: Dividing by 0 Study the statements carefully. because because What value can be used in place of to create true statements? Explain your
Unit 7, Lesson 1: Relationships of Angles
 Unit 7, Lesson 1: Relationships of Angles 1. Here are questions about two types of angles. Draw a right angle. How do you know it s a right angle? What is its measure in degrees? Draw a straight angle.
Unit 7, Lesson 1: Relationships of Angles 1. Here are questions about two types of angles. Draw a right angle. How do you know it s a right angle? What is its measure in degrees? Draw a straight angle.
Test Booklet. Subject: MA, Grade: 10 TAKS Grade 10 Math Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: MA, Grade: 10 TAKS Grade 10 Math 2009 Student name: Author: Texas District: Texas Released Tests Printed: Saturday July 14, 2012 1 The grid below shows the top view of a 3-dimensional
Test Booklet Subject: MA, Grade: 10 TAKS Grade 10 Math 2009 Student name: Author: Texas District: Texas Released Tests Printed: Saturday July 14, 2012 1 The grid below shows the top view of a 3-dimensional
For Exercises 3 6, find the volume of the following spheres. In some spheres, the diameter is given. In others, the radius is given.
 Applications. A playground ball has a diameter of 8 cm. a. Sketch a cylinder that fits the playground ball, and label its height and base. b. What is the volume of the cylinder? c. What is the volume of
Applications. A playground ball has a diameter of 8 cm. a. Sketch a cylinder that fits the playground ball, and label its height and base. b. What is the volume of the cylinder? c. What is the volume of
Monday 3/26 Problems due on Tues 4/3
 8th Grade Spring Break Homework Name: Per: Monday 3/26 Problems due on Tues 4/3. Solve the system of equations: y = 4x - 3 y = -2x + 9 2. Use a graph to find x and y values that make both y = -⅔x + 3 and
8th Grade Spring Break Homework Name: Per: Monday 3/26 Problems due on Tues 4/3. Solve the system of equations: y = 4x - 3 y = -2x + 9 2. Use a graph to find x and y values that make both y = -⅔x + 3 and
422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES. The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power.
 UNIT 12 Solid Figures The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power. 422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES Gas-powered engines are driven by little explosions that move pistons up and down in cylinders. When
UNIT 12 Solid Figures The volume of an engine s cylinders affects its power. 422 UNIT 12 SOLID FIGURES Gas-powered engines are driven by little explosions that move pistons up and down in cylinders. When
Name Class Date. Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities
 4-1 Reteaching Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities An important life skill is to be able to a read graph. When looking at a graph, you should check the title, the labels on the axes, and the general
4-1 Reteaching Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities An important life skill is to be able to a read graph. When looking at a graph, you should check the title, the labels on the axes, and the general
Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional
 Unit 3, Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional Relationships Let s study some graphs. 1.1: Notice and Wonder: Two Graphs What do you notice? What do you wonder? Unit 3: Linear Relationships Relationships
Unit 3, Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional Relationships Let s study some graphs. 1.1: Notice and Wonder: Two Graphs What do you notice? What do you wonder? Unit 3: Linear Relationships Relationships
Unit 7: Area and Volume
 Unit 7: Area and Volume Name Math 8, Period Rectangular Prism Triangular Prism Cylinder Cone Sphere Concepts and Skills to be mastered: By the end of this section students should be able to: 1. Find the
Unit 7: Area and Volume Name Math 8, Period Rectangular Prism Triangular Prism Cylinder Cone Sphere Concepts and Skills to be mastered: By the end of this section students should be able to: 1. Find the
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 11 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED:
 ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED: Naming 3D shapes Nets Volume of Prisms Volume of Pyramids Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Pyramids Surface Area using Nets Accelerated
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY TOPICS COVERED: Naming 3D shapes Nets Volume of Prisms Volume of Pyramids Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Pyramids Surface Area using Nets Accelerated
10-1. Enrichment. You Can Count On It!
 10-1 You Can Count On It! How many triangles are there in the figure at the right? How many parallelograms? When counting shapes in a figure like this, you usually have to think of different sizes. There
10-1 You Can Count On It! How many triangles are there in the figure at the right? How many parallelograms? When counting shapes in a figure like this, you usually have to think of different sizes. There
Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3)
 Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3) (136) 11.1 Space Figures and Cross Sections Page 692-693 #7-23 odd, 35 (137) 11.2/11.4 Surface Areas and Volumes of Prisms Page 703-705 #1, 2, 7-9, 11-13, 25,
Assignment Guide: Chapter 11 Geometry (L3) (136) 11.1 Space Figures and Cross Sections Page 692-693 #7-23 odd, 35 (137) 11.2/11.4 Surface Areas and Volumes of Prisms Page 703-705 #1, 2, 7-9, 11-13, 25,
1: #1 4, ACE 2: #4, 22. ACER 3: #4 6, 13, 19. ACE 4: #15, 25, 32. ACE 5: #5 7, 10. ACE
 Homework Answers from ACE: Filling and Wrapping ACE Investigation 1: #1 4, 10 13. ACE Investigation : #4,. ACER Investigation 3: #4 6, 13, 19. ACE Investigation 4: #15, 5, 3. ACE Investigation 5: #5 7,
Homework Answers from ACE: Filling and Wrapping ACE Investigation 1: #1 4, 10 13. ACE Investigation : #4,. ACER Investigation 3: #4 6, 13, 19. ACE Investigation 4: #15, 5, 3. ACE Investigation 5: #5 7,
Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes
 26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
26 Geometry Solids Identify Three-Dimensional Figures Notes A three dimensional figure has THREE dimensions length, width, and height (or depth). Intersecting planes can form three dimensional figures
1. Expand and simplify: 9. Determine the area of the triangle. a. 5 b. 2. Simplify: a. ( 3) c. ( 2) d. 4 ( 2) 3. e ( 3) ( 5)
 Math 08 Final Exam Review. Expand and simplify: (Section.6). Simplify: ( ) ( ) 00 d. ( ) (Section.,.6,.) (Section.,.,.) 6 ( ) ( ) e. 6 6 8 (Section.,.6,.) (Section.,.) ( 6 ) (Section.,.,.). Translate into
Math 08 Final Exam Review. Expand and simplify: (Section.6). Simplify: ( ) ( ) 00 d. ( ) (Section.,.6,.) (Section.,.,.) 6 ( ) ( ) e. 6 6 8 (Section.,.6,.) (Section.,.) ( 6 ) (Section.,.,.). Translate into
Name Date Class. 1. What is the volume of a cube whose side length measures 21 cm? Show your thinking.
 Name Date Class 1. What is the volume of a cube whose side length measures 21 cm? Show your thinking. 2. The volume of a cube is 13,824 mm 3. What is the side length of the cube? Show your thinking. 3.
Name Date Class 1. What is the volume of a cube whose side length measures 21 cm? Show your thinking. 2. The volume of a cube is 13,824 mm 3. What is the side length of the cube? Show your thinking. 3.
Additional Practice. Name Date Class
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Volume. 4. A box in the shape of a cube has a volume of 64 cubic inches. What is the length of a side of the box? A in B. 16 in. C. 8 in D.
 Name: ate: 1. In the accompanying diagram, a rectangular container with the dimensions 10 inches by 15 inches by 20 inches is to be filled with water, using a cylindrical cup whose radius is 2 inches and
Name: ate: 1. In the accompanying diagram, a rectangular container with the dimensions 10 inches by 15 inches by 20 inches is to be filled with water, using a cylindrical cup whose radius is 2 inches and
25 Questions EOG Review #1 EOG REVIEW
 Questions EOG Review # EOG REVIEW Solve each: Give the BEST Answer. Name Period 9. Represent as a percent: 8% b. 80% c..4% d..8%. A rectangle is 4 meters long. It has a diagonal that is meters. How wide
Questions EOG Review # EOG REVIEW Solve each: Give the BEST Answer. Name Period 9. Represent as a percent: 8% b. 80% c..4% d..8%. A rectangle is 4 meters long. It has a diagonal that is meters. How wide
5th Grade. Slide 1 / 115. Slide 2 / 115. Slide 3 / 115. Measurement & Data. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 115 Metric Measurement
Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 115 Metric Measurement
5th Grade. Standard Measurement Conversions. Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115. Slide 4 / 115. Slide 3 / 115. Slide 5 / 115.
 Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes Volume of a
Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes Volume of a
5th Grade. Measurement & Data.
 1 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015 11 23 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes Volume of
1 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015 11 23 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes Volume of
Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional
 Unit 3, Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional Relationships Let s study some graphs. 1.1: Notice and Wonder: Two Graphs What do you notice? What do you wonder? Unit 3: Linear Relationships Relationships
Unit 3, Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional Relationships Let s study some graphs. 1.1: Notice and Wonder: Two Graphs What do you notice? What do you wonder? Unit 3: Linear Relationships Relationships
8 th Grade Math STAAR Review
 8 th Grade Math STAAR Review 1. Five students are each trying to raise the same amount of money for a fundraiser. The table below shows how much of each student s goal has been met. Write the numbers in
8 th Grade Math STAAR Review 1. Five students are each trying to raise the same amount of money for a fundraiser. The table below shows how much of each student s goal has been met. Write the numbers in
SPHERES WHAT YOU LL LEARN. Ø Finding the surface area of a sphere Ø Finding the volume of a sphere
 SPHERES A sphere is the locus of points in space that are a given distance from a point. The point is called the center of the sphere. A radius of a sphere is a segment from the center to a point on the
SPHERES A sphere is the locus of points in space that are a given distance from a point. The point is called the center of the sphere. A radius of a sphere is a segment from the center to a point on the
Problem Solving: Volume
 28 LESSON Problem Solving: Volume READ Soup Can To the right is a diagram of a soup can. To the nearest tenth of a centimeter, what is the volume of the can? 8 cm The can looks like a, so use that volume
28 LESSON Problem Solving: Volume READ Soup Can To the right is a diagram of a soup can. To the nearest tenth of a centimeter, what is the volume of the can? 8 cm The can looks like a, so use that volume
MATH-G P- Geometry Formulas Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MATH-G P- Geometry Formulas Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2M8EKV 1 A soda can has a diameter of 6 centimeters and a height of 13 centimeters. Which is closest to the surface area
MATH-G P- Geometry Formulas Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2M8EKV 1 A soda can has a diameter of 6 centimeters and a height of 13 centimeters. Which is closest to the surface area
FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet. Modeling and Geometry
 FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet Modeling and Geometry Table of Contents MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.2 EOC Practice... 6 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.3 EOC Practice... 8 Modeling with
FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet Modeling and Geometry Table of Contents MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.2 EOC Practice... 6 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.3 EOC Practice... 8 Modeling with
GRADE 5. Mathematics. Administered April 2018 RELEASED
 STAAR State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness GRADE 5 Administered April 2018 RELEASED Copyright 2018, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work
STAAR State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness GRADE 5 Administered April 2018 RELEASED Copyright 2018, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work
5th Grade Measurement & Data
 Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement
Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement
5th Grade. Standard Measurement Conversions. Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115. Slide 4 / 115. Slide 3 / 115. Slide 5 / 115.
 Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes click on the
Slide 1 / 115 Slide 2 / 115 5th Grade Measurement & Data 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 115 Table of Contents Standard Measurement Conversions Metric Measurement Conversions Unit Cubes click on the
Revision Booklet. Grade 6
 Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
STAAR Mixed Practice HW
 Show all work and label units of measurement. 1. The equation y = x + 7 represents a linear relationship that is non-proportional. What change could you make to the equation to make it proportional? Name:
Show all work and label units of measurement. 1. The equation y = x + 7 represents a linear relationship that is non-proportional. What change could you make to the equation to make it proportional? Name:
8th Pre Algebra End of Year Review
 8th Pre Algebra End of Year Review 1. 2. 8p (t + 5m) 3. Name the property shown by the statement. 8. z 8 9. x y z 10. Simplify 9j(5)(3k) 7 3 4 = 3 4 7 4. Make a scatter plot of the data. Does there appear
8th Pre Algebra End of Year Review 1. 2. 8p (t + 5m) 3. Name the property shown by the statement. 8. z 8 9. x y z 10. Simplify 9j(5)(3k) 7 3 4 = 3 4 7 4. Make a scatter plot of the data. Does there appear
Name: Period: 2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review
 2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the number of lunch combinations that can be created if you order a soup, sandwich, drink and dessert. There are 4 soup choices, 5 sandwich choices, 3 drink
2018 Geometry Spring Final Exam Review 1. Find the number of lunch combinations that can be created if you order a soup, sandwich, drink and dessert. There are 4 soup choices, 5 sandwich choices, 3 drink
Name Date PD. Volume
 Name Date PD Volume Volume the number of cubic units needed to fill a solid. To find the volume of a prism or cylinder, multiply the base area (B) by the height h. Rectangular prisms Formula: V Bh (what
Name Date PD Volume Volume the number of cubic units needed to fill a solid. To find the volume of a prism or cylinder, multiply the base area (B) by the height h. Rectangular prisms Formula: V Bh (what
Applications. 38 Filling and Wrapping
 Applications 1. Cut a sheet of paper in half so you have two identical half-sheets of paper. Tape the long sides of one sheet together to form a cylinder. Tape the short sides from the second sheet together
Applications 1. Cut a sheet of paper in half so you have two identical half-sheets of paper. Tape the long sides of one sheet together to form a cylinder. Tape the short sides from the second sheet together
3 Dimensional Solids. Table of Contents. 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres
 Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
Practice A Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Parallelograms
 8-1 Practice A Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Parallelograms Find the perimeter of each figure. 1. 5 ft 2. 3. 13 cm 4 ft 6 cm 3x in. 10x in. 18 ft 38 cm 26x in. Graph and find the area of each figure
8-1 Practice A Perimeter and Area of Rectangles and Parallelograms Find the perimeter of each figure. 1. 5 ft 2. 3. 13 cm 4 ft 6 cm 3x in. 10x in. 18 ft 38 cm 26x in. Graph and find the area of each figure
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula
 Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Lesson 1 - Area Review Shape Words Formula Rectangle The area A of a rectangle is the product of the length and the width w. A = w Parallelogram The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any base
Course 2 Unit 4 Practice
 Course 2 Unit 4 Practice Lesson 13-1 1. Model with mathematics. Two angles are supplementary. One measures (3x)8 and the other measures 518. a. Draw a pair of adjacent, supplementary angles and label them
Course 2 Unit 4 Practice Lesson 13-1 1. Model with mathematics. Two angles are supplementary. One measures (3x)8 and the other measures 518. a. Draw a pair of adjacent, supplementary angles and label them
Math 7 Accelerated Summer Review
 No calculator #1-41 Math 7 Accelerated Review Solve. 1) 5 9 w = 10 2) 4y 5y + 6 = 7y + 3 3)!! x 2 = 8 4)!! 9 w = 10 Solve for the indicated variable. 5) C = 2πr; r 6) S = B +! Pl; l! 7) Rewrite 3x + 4y
No calculator #1-41 Math 7 Accelerated Review Solve. 1) 5 9 w = 10 2) 4y 5y + 6 = 7y + 3 3)!! x 2 = 8 4)!! 9 w = 10 Solve for the indicated variable. 5) C = 2πr; r 6) S = B +! Pl; l! 7) Rewrite 3x + 4y
Geometric Probabiltiy
 Geometric Probabiltiy Reteaching 101 Math Course 3, Lesson 101 Geometric Probability: The probability based on the area of the regions Probability = Formula: area of included region area of known region
Geometric Probabiltiy Reteaching 101 Math Course 3, Lesson 101 Geometric Probability: The probability based on the area of the regions Probability = Formula: area of included region area of known region
Name: Period 3/23/12 4/12/12 Pre-AP
 Name: Period 3/23/12 4/12/12 Pre-AP UNIT 14: SOLIDS I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Face Edge Vertex Cross section Prism Height Surface area Lateral surface area Net Volume Scale
Name: Period 3/23/12 4/12/12 Pre-AP UNIT 14: SOLIDS I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Face Edge Vertex Cross section Prism Height Surface area Lateral surface area Net Volume Scale
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
Lesson 10T ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name Period Date Use the table of names at the right to name each solid. 1. 2. Names of Solids 3. 4. 4 cm 4 cm Cone Cylinder Hexagonal prism Pentagonal pyramid Rectangular
MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2YBSPT 1 What is the volume of a cube with a length of 8 inches? A 96 in 3 B 256 in 3 C 512 in 3 D 384 in
MATH-8 Review Volume of 3D shapes 2018 N Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2YBSPT 1 What is the volume of a cube with a length of 8 inches? A 96 in 3 B 256 in 3 C 512 in 3 D 384 in
Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry
 Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Day Classwork Day Homework Monday 2/12 Tuesday 2/13 Wednesday 2/14 Areas of Regular Polygons 1 HW 11.1 Volume of Prisms & Cylinders 2 HW 11.4 Volume of Pyramids and Cones
Unit 11 Three Dimensional Geometry Day Classwork Day Homework Monday 2/12 Tuesday 2/13 Wednesday 2/14 Areas of Regular Polygons 1 HW 11.1 Volume of Prisms & Cylinders 2 HW 11.4 Volume of Pyramids and Cones
3 Dimensional Geometry Chapter Questions. 1. What are the differences between prisms and pyramids? Cylinders and cones?
 3 Dimensional Geometry Chapter Questions 1. What are the differences between prisms and pyramids? Cylinders and cones? 2. What is volume and how is it found? 3. How are the volumes of cylinders, cones
3 Dimensional Geometry Chapter Questions 1. What are the differences between prisms and pyramids? Cylinders and cones? 2. What is volume and how is it found? 3. How are the volumes of cylinders, cones
8-3. A butterfly house at a local zoo is a rectangular prism with dimensions 20' 15' 10' and contains 625 butterflies.
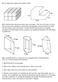 8-1. Compute the volume of the figures below. 8-2. Carefully draw the prisms below onto your paper. One way to do this is to draw the two bases first and then to connect the corresponding vertices of the
8-1. Compute the volume of the figures below. 8-2. Carefully draw the prisms below onto your paper. One way to do this is to draw the two bases first and then to connect the corresponding vertices of the
Problem Sets. GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area
 GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area Problem Sets Video tutorials: http://bit.ly/eurekapusd Info for parents: http://bit.ly/pusdmath 5 GRADE Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 5
GRADE 5 MODULE 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area Problem Sets Video tutorials: http://bit.ly/eurekapusd Info for parents: http://bit.ly/pusdmath 5 GRADE Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 5
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
The Geometry of Solids
 CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures
 Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name a solid that fits each description. 1. a can of beans 2. a shoe box 3. a pyramid with five lateral faces 4. a solid with six vertices 5. a prism with bases shaped
Lesson 10 ~ Three-Dimensional Figures Name a solid that fits each description. 1. a can of beans 2. a shoe box 3. a pyramid with five lateral faces 4. a solid with six vertices 5. a prism with bases shaped
12-4 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders. Find the volume of each prism.
 Find the volume of each prism. 3. the oblique rectangular prism shown at the right 1. The volume V of a prism is V = Bh, where B is the area of a base and h is the height of the prism. If two solids have
Find the volume of each prism. 3. the oblique rectangular prism shown at the right 1. The volume V of a prism is V = Bh, where B is the area of a base and h is the height of the prism. If two solids have
2. 4 m. 6 in. 4 m 4 m. 5. the amount of topsoil needed to put a 2 in. thick layer on the top of a square garden
 6 Find the surface area and volume.. in.. 4 m. 5 in. 6 in. 4 m 4 m 0 yd 6 yd 6 yd SA = SA = SA = Choose the most appropriate measure. Write perimeter, surface area, or volume. 4. the distance around the
6 Find the surface area and volume.. in.. 4 m. 5 in. 6 in. 4 m 4 m 0 yd 6 yd 6 yd SA = SA = SA = Choose the most appropriate measure. Write perimeter, surface area, or volume. 4. the distance around the
3. Draw the orthographic projection (front, right, and top) for the following solid. Also, state how many cubic units the volume is.
 PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
Grade 8 Final Exam Review APPLICATIONS AND PROBLEM SOLVING
 Grade 8 Final Exam Review APPLICATIONS AND PROBLEM SOLVING UNIT 1: Square Roots and The Pythagorean Theorem 1. A pizza box has a square top. The area of the top is 1501 cm 2. Calculate the length of the
Grade 8 Final Exam Review APPLICATIONS AND PROBLEM SOLVING UNIT 1: Square Roots and The Pythagorean Theorem 1. A pizza box has a square top. The area of the top is 1501 cm 2. Calculate the length of the
9.55 in. containers have the same surface area as the ball? If not, which container has a surface area that is closer to that of the ball?
 11.8 Start Thinking You buy a friend a basketball as a gift. You want to construct a container to put the ball in to disguise it when it is wrapped. You construct the two containers shown in the diagram.
11.8 Start Thinking You buy a friend a basketball as a gift. You want to construct a container to put the ball in to disguise it when it is wrapped. You construct the two containers shown in the diagram.
Math Mealy Mountain Collegiate. Sample Midterm Exam. Name:
 Math 2202 Mealy Mountain Collegiate Sample Midterm Exam Name: Formulas Square Rectangle A = s 2 A = l x w P 2l 2 w Triangle C 2 r A b h 2 Circle A r 2 C d or Cube Rectangle Prism SA = 6s 2 SA =2(l x w)+2(lxh)+2(wxh)
Math 2202 Mealy Mountain Collegiate Sample Midterm Exam Name: Formulas Square Rectangle A = s 2 A = l x w P 2l 2 w Triangle C 2 r A b h 2 Circle A r 2 C d or Cube Rectangle Prism SA = 6s 2 SA =2(l x w)+2(lxh)+2(wxh)
5th Grade Mathematics Essential Standards
 Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Revision Booklet. Grade 6
 Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Private Educational Directorate Ahlia school MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT 2017-2018 Revision Booklet For the 2 nd semester Final Exam Grade 6 NAME : DATE : Prepared by
MATHEMATICS Grade 2 Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations. Organizing Topic Benchmark Indicator Number and Number Systems
 Standard: Number, Number Sense and A. Use place value concepts to represent whole numbers using numerals, words and physical models. 1. Use place value concepts to represent, compare and order whole numbers
Standard: Number, Number Sense and A. Use place value concepts to represent whole numbers using numerals, words and physical models. 1. Use place value concepts to represent, compare and order whole numbers
Eureka Math. Grade 5, Module 5. Student File_B. Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Units Eureka Math Grade 5, Module 5 Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 205 Great Minds. No part
A Story of Units Eureka Math Grade 5, Module 5 Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 205 Great Minds. No part
m5) volume What would the volume be of this cube, if each segment was 1 cm? m5) volume
 The amount of space occupied by a 3D object, expressed in cubic units. What would the volume be of this cube, if each segment was 1 cm? All volume is the area of the base times the height. V= v= Cube Rectangular/
The amount of space occupied by a 3D object, expressed in cubic units. What would the volume be of this cube, if each segment was 1 cm? All volume is the area of the base times the height. V= v= Cube Rectangular/
Groveport Madison Local School District Second Grade Math Content Standards Planning Sheets
 Standard: Measurement A. Explain the need for standard units of measure. B. Select appropriate units for length, weight, volume (capacity) and time, using: objects; i.e., non-standard units Second Grade
Standard: Measurement A. Explain the need for standard units of measure. B. Select appropriate units for length, weight, volume (capacity) and time, using: objects; i.e., non-standard units Second Grade
Common Core. Mathematics Instruction
 0 Common Core Mathematics Instruction 8 Table of Contents Unit : Expressions and Equations (Exponents) and the Number System.............................. Lesson Properties of Integer Exponents....................
0 Common Core Mathematics Instruction 8 Table of Contents Unit : Expressions and Equations (Exponents) and the Number System.............................. Lesson Properties of Integer Exponents....................
2. a. approximately cm 3 or 9p cm b. 20 layers c. approximately cm 3 or 180p cm Answers will vary.
 Answers Investigation ACE Assignment Choices Problem. Core Other Connections Problem. Core,, Other Applications 7, ; Connections 7 0; unassigned choices from previous problems Problem. Core 7 Other Connections,
Answers Investigation ACE Assignment Choices Problem. Core Other Connections Problem. Core,, Other Applications 7, ; Connections 7 0; unassigned choices from previous problems Problem. Core 7 Other Connections,
Homework Assignment. U8 Intro Area of Circles Review p. 3 / Volume of Cones 8.1 Volume of Cylinders Practice p. 6-7 / 10
 Math 8 Name Unit 8 - Volume LEARNING TARGETS I CAN solve problems involving the volume of cylinders. I CAN solve problems involving the volume of cones. I CAN solve problems involving the volume of spheres.
Math 8 Name Unit 8 - Volume LEARNING TARGETS I CAN solve problems involving the volume of cylinders. I CAN solve problems involving the volume of cones. I CAN solve problems involving the volume of spheres.
Volume of Spheres. A geometric plane passing through the center of a sphere divides it into. into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere.
 9.6 Surface Area and Volume of Spheres Goal Find surface areas and volumes of spheres. Key Words sphere hemisphere A globe is an example of a sphere. A sphere is the set of all points in space that are
9.6 Surface Area and Volume of Spheres Goal Find surface areas and volumes of spheres. Key Words sphere hemisphere A globe is an example of a sphere. A sphere is the set of all points in space that are
Complete the following to the best of your ability. DO NOT use a calculator. Show all work.
 Name: Summer Work Algebra 1 2016 Complete the following to the best of your ability. DO NOT use a calculator. Show all work. 1. You have a 35 degree angle. Determine the complementary angle AND the supplementary
Name: Summer Work Algebra 1 2016 Complete the following to the best of your ability. DO NOT use a calculator. Show all work. 1. You have a 35 degree angle. Determine the complementary angle AND the supplementary
Identify the following 3-D Geometric Shapes
 5.1 Intro January 3, 2011 4:55 PM Identify the following 3-D Geometric Shapes Important Terms Chapter 5 Page 1 - - - - - Face: Any flat area on a prism Curved Area: The curved part of a cylinder or cone
5.1 Intro January 3, 2011 4:55 PM Identify the following 3-D Geometric Shapes Important Terms Chapter 5 Page 1 - - - - - Face: Any flat area on a prism Curved Area: The curved part of a cylinder or cone
Adding Rational Numbers
 -3 Adding Rational Numbers This balance scale weighs positive and negative numbers. Negative numbers go on the left of the balance. Positive numbers go on the right. The scale will tip to the left side
-3 Adding Rational Numbers This balance scale weighs positive and negative numbers. Negative numbers go on the left of the balance. Positive numbers go on the right. The scale will tip to the left side
Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE. CCM Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date:
 Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE CCM6+ 2015-16 Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Coordinate Plane Introduction graph and 3-6 label Reflect
Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE CCM6+ 2015-16 Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Coordinate Plane Introduction graph and 3-6 label Reflect
CHAPTER 12. Extending Surface Area and Volume
 CHAPTER 12 Extending Surface Area and Volume 0 Learning Targets Students will be able to draw isometric views of three-dimensional figures. Students will be able to investigate cross-sections of three-dimensional
CHAPTER 12 Extending Surface Area and Volume 0 Learning Targets Students will be able to draw isometric views of three-dimensional figures. Students will be able to investigate cross-sections of three-dimensional
4) Simplify 5( 6) Simplify. 8) Solve 1 x 2 4
 Algebra Summer Assignment 1) Simplify x 4y 10 x ) Simplify 4y 6x 3( x y) 3) Simplify 1 3 ( x 3) 4) Simplify 5( x 9x) (3x 4) 7 5) Simplify ( x 3)( x ) 6) Simplify ( x 4) 3 7) Simplify ( 5x 8)(4x 1) 8) Solve
Algebra Summer Assignment 1) Simplify x 4y 10 x ) Simplify 4y 6x 3( x y) 3) Simplify 1 3 ( x 3) 4) Simplify 5( x 9x) (3x 4) 7 5) Simplify ( x 3)( x ) 6) Simplify ( x 4) 3 7) Simplify ( 5x 8)(4x 1) 8) Solve
Ratio of Marbles Red:Green Blue:Total 3.
 MAFS.6.RP.1.1 1. Jordan has 3 blue marbles and 8 red marbles. What is the ratio of blue marbles to red marbles? A. 3:3 B. 3:5 C. 3:8 D. 3:11 2. A jar of marbles is shown. MAFS.6.RP.1.3 6. Tom knows that
MAFS.6.RP.1.1 1. Jordan has 3 blue marbles and 8 red marbles. What is the ratio of blue marbles to red marbles? A. 3:3 B. 3:5 C. 3:8 D. 3:11 2. A jar of marbles is shown. MAFS.6.RP.1.3 6. Tom knows that
Understanding Addition and Subtraction Strategies Unit
 Understanding Addition and Subtraction Strategies Unit PA EC: M3.D.1.1.1 E: Extend or find a missing element in a pattern of numbers. *Pattern must show 3 repetitions *When multiples are used limit to
Understanding Addition and Subtraction Strategies Unit PA EC: M3.D.1.1.1 E: Extend or find a missing element in a pattern of numbers. *Pattern must show 3 repetitions *When multiples are used limit to
PAF Chapter Prep Section Mathematics Class 6 Worksheets for Intervention Classes
 The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Mathematics Class 6 Worksheets for Intervention Classes Topic: Percentage Q1. Convert it into fractions and its lowest term: a) 25% b) 75% c) 37% Q2. Convert the
The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Mathematics Class 6 Worksheets for Intervention Classes Topic: Percentage Q1. Convert it into fractions and its lowest term: a) 25% b) 75% c) 37% Q2. Convert the
Milestones Review 2016 Math
 Milestones Review 2016 Math CCGPS Day 1 Write an expression that shows subtract 5 from 9 and then multiply the result by 6. Write an expression that shows the quotient of 72 and 9 multiplied by 3 Interpret
Milestones Review 2016 Math CCGPS Day 1 Write an expression that shows subtract 5 from 9 and then multiply the result by 6. Write an expression that shows the quotient of 72 and 9 multiplied by 3 Interpret
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 15 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY II TOPICS COVERED:
 ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 15 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY II TOPICS COVERED: Volume of Cylinders Volume of Cones Volume of Spheres Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Cylinders Accelerated Mathematics
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 15 DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY II TOPICS COVERED: Volume of Cylinders Volume of Cones Volume of Spheres Surface Area of Prisms Surface Area of Cylinders Accelerated Mathematics
Number Sense. I CAN DO THIS! Third Grade Mathematics Name. Problems or Examples. 1.1 I can count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000.
 Number Sense 1.1 I can count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. 1.2 I can compare and order numbers to 10,000. What is the smallest whole number you can make using the digits 4, 3, 9, and 1? Use
Number Sense 1.1 I can count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. 1.2 I can compare and order numbers to 10,000. What is the smallest whole number you can make using the digits 4, 3, 9, and 1? Use
REVIEW FOR BASIC MATH SKILLS FINAL EXAM (December 2008) (Basic 4-Function, 10-Key Calculator Allowed No Scientific or Graphing Calculators)
 REVIEW FOR BASIC MATH SKILLS FINAL EXAM (December 008) (Basic 4-Function, 0-Key Calculator Allowed No Scientific or Graphing Calculators) In order to be prepared for the final exam, students should be
REVIEW FOR BASIC MATH SKILLS FINAL EXAM (December 008) (Basic 4-Function, 0-Key Calculator Allowed No Scientific or Graphing Calculators) In order to be prepared for the final exam, students should be
Pre-Algebra HS Semester 2 Practice Exam B
 1. A right triangle is shown below. 5 What is the value of x? 1 17 4 169 12 x Figure is not drawn to scale. 4. Which of the following measurements represent a right triangle? I., 4, 5 II. 5, 12, 1 III.
1. A right triangle is shown below. 5 What is the value of x? 1 17 4 169 12 x Figure is not drawn to scale. 4. Which of the following measurements represent a right triangle? I., 4, 5 II. 5, 12, 1 III.
Summer Math Exercises. For students who are entering. Geometry
 Summer Math Exercises For students who are entering Geometry It has been discovered that idle students lose learning over the summer months. To help you succeed next fall and perhaps to help you learn
Summer Math Exercises For students who are entering Geometry It has been discovered that idle students lose learning over the summer months. To help you succeed next fall and perhaps to help you learn
5.2C Lesson: Proportions from Tables and Graphs*
 5.2C Lesson: Proportions from Tables and Graphs* Name: Period: 1. The following table shows the relationship between the amount of cherries (in pounds) and the cost. Cost ($) 1.50 3.00 4.50 6.00 7.50 Amount
5.2C Lesson: Proportions from Tables and Graphs* Name: Period: 1. The following table shows the relationship between the amount of cherries (in pounds) and the cost. Cost ($) 1.50 3.00 4.50 6.00 7.50 Amount
Name ANSWER KEY Date Period Score. Place your answers in the answer column. Show work clearly and neatly. FOCUS ON WHAT IS NECESSARY FOR SUCCESS!
 OAKS Test Review PRACTICE Name ANSWER KEY Date Period Score Place your answers in the answer column. Show work clearly and neatly. FOCUS ON WHAT IS NECESSARY FOR SUCCESS! Solve:. n = 5. 4(4x ) = (x + 4)
OAKS Test Review PRACTICE Name ANSWER KEY Date Period Score Place your answers in the answer column. Show work clearly and neatly. FOCUS ON WHAT IS NECESSARY FOR SUCCESS! Solve:. n = 5. 4(4x ) = (x + 4)
7th Grade Advanced Pre-Algebra Math Summer Assignment
 7th Grade Advanced Pre-Algebra Math Summer Assignment The purpose of this summer assignment is to review and strengthen mathematical skills essential for success in Pre-Algebra. The assignment consists
7th Grade Advanced Pre-Algebra Math Summer Assignment The purpose of this summer assignment is to review and strengthen mathematical skills essential for success in Pre-Algebra. The assignment consists
3.1 Start Thinking. 3.1 Warm Up. 3.1 Cumulative Review Warm Up. Consider the equation y x.
 3.1 Start Thinking Consider the equation y x. Are there any values of x that you cannot substitute into the equation? If so, what are they? Are there any values of y that you cannot obtain as an answer?
3.1 Start Thinking Consider the equation y x. Are there any values of x that you cannot substitute into the equation? If so, what are they? Are there any values of y that you cannot obtain as an answer?
Eighth Grade Mathematics 2017 Released Items Analysis
 Step Up to the by GF Educators, Inc. Eighth Grade Mathematics 2017 Released s Teacher: Copyright 2017 Edition I www.stepup.com 8th Grade Mathematics Released s Name: Teacher: Date: Step Up to the by GF
Step Up to the by GF Educators, Inc. Eighth Grade Mathematics 2017 Released s Teacher: Copyright 2017 Edition I www.stepup.com 8th Grade Mathematics Released s Name: Teacher: Date: Step Up to the by GF
Chapter 3: Functions
 Chapter 3: Functions Index: A: Introduction to Functions 1 Page 2 B: Introduction to Functions 2 (U3 L1) Page 8 C: Function Notation (U3 L2) Page 13 D: Graphs of Functions (U3 L3) Page 18 E: Graphical
Chapter 3: Functions Index: A: Introduction to Functions 1 Page 2 B: Introduction to Functions 2 (U3 L1) Page 8 C: Function Notation (U3 L2) Page 13 D: Graphs of Functions (U3 L3) Page 18 E: Graphical
CHAPTER 12. Extending Surface Area and Volume
 CHAPTER 12 Extending Surface Area and Volume 0 1 Learning Targets Students will be able to draw isometric views of three-dimensional figures. Students will be able to investigate cross-sections of three-dimensional
CHAPTER 12 Extending Surface Area and Volume 0 1 Learning Targets Students will be able to draw isometric views of three-dimensional figures. Students will be able to investigate cross-sections of three-dimensional
Name: DUE: HOUR: 2015/2016 Geometry Final Exam Review
 Name: DUE: HOUR: 2015/2016 Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Find x. 2. Find y. x = 3. A right triangle is shown below. Find the lengths x, y, and z. y = 4. Find x. x = y = z = x = 5. Find x. x = 6. ABC ~
Name: DUE: HOUR: 2015/2016 Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Find x. 2. Find y. x = 3. A right triangle is shown below. Find the lengths x, y, and z. y = 4. Find x. x = y = z = x = 5. Find x. x = 6. ABC ~
16.3 Volume of Cones
 Name Class Date 16. Volume of Cones Essential Question: How do you calculate the volumes of composite figures that include cones? Explore G.11.D Apply the formulas for the volume of three-dimensional figures,
Name Class Date 16. Volume of Cones Essential Question: How do you calculate the volumes of composite figures that include cones? Explore G.11.D Apply the formulas for the volume of three-dimensional figures,
12-6 Surface Area and Volumes of Spheres. Find the surface area of each sphere or hemisphere. Round to the nearest tenth. SOLUTION: ANSWER: 1017.
 Find the surface area of each sphere or hemisphere. Round to the nearest tenth. 3. sphere: area of great circle = 36π yd 2 We know that the area of a great circle is r.. Find 1. Now find the surface area.
Find the surface area of each sphere or hemisphere. Round to the nearest tenth. 3. sphere: area of great circle = 36π yd 2 We know that the area of a great circle is r.. Find 1. Now find the surface area.
8 th Grade - SBAC Review #1 Name:
 8 th Grade - SBAC Review #1 Name: 1. Each day, Maria walks from home to school and then from school to home. The graphs below show the distance that Maria is from home at different times during her walk.
8 th Grade - SBAC Review #1 Name: 1. Each day, Maria walks from home to school and then from school to home. The graphs below show the distance that Maria is from home at different times during her walk.
UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
 UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use the idea of measuring volume that we studied to find the volume of various 3 dimensional figures. We will also learn about
UNIT 11 VOLUME AND THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will use the idea of measuring volume that we studied to find the volume of various 3 dimensional figures. We will also learn about
Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem
 MPM 1D Unit 6: Measurement Lesson 1 Date: Learning goal: how to use Pythagorean Theorem to find unknown side length in a right angle triangle. Investigate: 1. What type of triangle is in the centre of
MPM 1D Unit 6: Measurement Lesson 1 Date: Learning goal: how to use Pythagorean Theorem to find unknown side length in a right angle triangle. Investigate: 1. What type of triangle is in the centre of
Integrated Algebra Regents Exam 0109 Page 1
 Integrated Algebra Regents Exam 0109 Page 1 1. 010901ia, P.I. A.M. On a certain day in Toronto, Canada, the temperature was 15 Celsius (C). Using the 9 formula F C3, Peter converts this 5 temperature to
Integrated Algebra Regents Exam 0109 Page 1 1. 010901ia, P.I. A.M. On a certain day in Toronto, Canada, the temperature was 15 Celsius (C). Using the 9 formula F C3, Peter converts this 5 temperature to
CHAPTER. Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC. Three-Dimensional Figures 217
 CHAPTER 9 Three-Dimensional Figures Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC Three-Dimensional Figures 7 9. Three-Dimensional Figures Objective: to classify three-dimensional figures A solid is a three-dimensional
CHAPTER 9 Three-Dimensional Figures Daniel Nickerson Salisbury, NC Three-Dimensional Figures 7 9. Three-Dimensional Figures Objective: to classify three-dimensional figures A solid is a three-dimensional
MATH 099 HOMEWORK TWO
 MATH 099 HOMEWORK TWO STUDENT S NAME 1) Matthew needs to rent a car for 1 day. He will be charged a daily fee of $30.00 in addition to 5 cents for every mile he drives. Assign the variable by letting x
MATH 099 HOMEWORK TWO STUDENT S NAME 1) Matthew needs to rent a car for 1 day. He will be charged a daily fee of $30.00 in addition to 5 cents for every mile he drives. Assign the variable by letting x
