CSE613: Parallel Programming, Spring 2012 Date: March 31. Homework #2. ( Due: April 14 )
|
|
|
- Jasmine Farmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE613: Parallel Programming, Spring 2012 Date: March 31 Homework #2 ( Due: April 14 ) Serial-BFS( G, s, d ) (Inputs are an unweighted directed graph G with vertex set G[V ], and a source vertex s G[V ]. For any vertex u G[V ], Γ(u) denotes the set of vertices adjacent to u. The output will be returned in d, where for each u G[V ], d[u] will be set to the sortest distance (i.e., number of edges on the sortest path) from s to u.) 1. for each u G[V ] do d[u] + initialize all distances to + } 2. d[s] 0 the source vertex is at distannce 0} 3. Q start with an empty FIFO queue Q} 4. Q.enque( s ) enqueue the source vertex} 5. while Q do iterate until the queue becomes empty} 6. u Q.deque( ) dequeue the first vertex u from the queue} 7. for each v Γ(u) do consider each vertex adjacent to u} 8. if d[v] = + then if that adjacent vertex v has not yet been visited} 9. d[v] d[u] + 1 distance to v is 1 more than that to u} 10. Q.enque( v ) enqueue v for future exploration} Figure 1: Serial breadth-first search (BFS) on a graph. Task 1. [ 135 Points ] Parallel BFS with Split Queues. (a) [ 10 Points ] Implement the serial BFS algorithm (Serial-BFS) given in Figure 1. (b) [ 25 Points ] Implement the parallel BFS algorithm (Parallel-BFS) given in Figure 2. Optimize your code as much as possible based on parts (d), (e) and (f). (c) [ 5 Points ] Explain how Parallel-BFS may give rise to race conditions. Also explain why the output will still be correct. (d) [ 15 Points ] The Q.nextSegment( ) function shown in Figure 3 locks a global data structure, and thus serializes all accesses to it. Explain how you will implement the function (particularly lines 4 and 6 7), and what value you will use for n seg so that in any given iteration of the while loop in Parallel-BFS the total time spent inside Q.nextSegment( ) by all threads is only O ( Q in p ). (e) [ 15 Points ] Show that in any given iteration of the while loop in Parallel-BFS, the same vertex may appear multiple times in Q in, but not more than once in any given queue of Q in. Modify the algorithm in Figure 2 so that exactly one of those multiple instances of the same vertex is expanded in lines 4 7 of Parallel-BFS-Thread. You are allowed to use only O (1) additional time per instance, and O (1) additional space per vertex for this 1
2 modification. Explain how and why your modification works as well as any (reasonable) support you need from the hardware for your approach to work. (f) [ 10 Points ] Optimize the space used by the queues in Q in and Q out. Initially in lines 4 and 5 of Parallel-BFS allocate a constant amount of space per queue (e.g., space for 256 vertices). Then during each enqueue operation check if there is space in the queue for adding the new vertex, and if not, double the size of the queue. Also just before returning from Parallel-BFS-Thread check if at least 25% of Q o is full, and if not, contract its size to two times the number of elements currently in it (but not below the initial size of the queue). When implementing these in cilk++ you need to use the Miser memory manager for thread safety and efficiency (chapter 10 of Intel Cilk++ SDK Programmer s Guide explains how to use Miser). (g) [ 10 Points ] Analyze the work and span of your implementation of Parallel-BFS in part (a) with all modifications outlined in parts (d), (e) and (f). (h) [ 20 Points ] Instead of using the centralized mechanism as shown in Q.nextSegment( ) (see Figure 3) for distributing work from Q in to all threads, implement the following distributed work-stealing mechanism. For 1 i p, thread i starts with queue Q in.q[i] as its input queue. However, whenever a thread becomes idle, it chooses a random thread, and steals half (2nd half) of the remaining vertices from that thread s queue. For efficiency you need to make sure that stealing does not involve explicit copying of the stolen vertices to a separate location. (i) [ 15 Points ] Create a table that compares the running times of your serial implementation in part (a), and the parallel implementations in parts (b) and (h) using all cores. For each input file (in Appendix 2) create a separate row in the table showing the running times of (a), (b) and (h) as well as the speedup factors of (b) and (h) w.r.t. (a). (j) [ 10 Points ] Identify the input file on which your serial implementation in part (a) takes the longest time not exceeding 10 minutes. Use that input file to generate a Cilkview scalability plot (see slides of lecture 3) for part (b) and one for part (h). Task 2. [ Optional, No Points ] Further Analysis of Parallel BFS with Split Queues. (a) [ No Points ] Analyze the number of attempted steals and the number of successful steals (both probabilistic and worst-case bounds) for the BFS implementation in part (h). 2
3 Parallel-BFS( G, s, d ) (Inputs are an unweighted directed graph G with vertex set G[V ], and a source vertex s G[V ]. For any vertex u G[V ], Γ(u) denotes the set of vertices adjacent to u. The output will be returned in d, where for each u G[V ], d[u] will be set to the sortest distance (i.e., number of edges on the sortest path) from s to u.) 1. for each u G[V ] do d[u] + initialize all distances to + } 2. d[s] 0 the source vertex is at distance 0} 3. p #processing cores 4. Q in collection of p empty FIFO queues Q in.q[1], Q in.q[2],..., Q in.q[p] Q in will hold vertices in the current BFS level} 5. Q out collection of p empty FIFO queues Q out.q[1], Q out.q[2],..., Q out.q[p] vertices in the next BFS level generated from Q in will be stored in Q out} 6. Q in.q[1].enque( s ) start with BFS level 0 by enqueueing the source vertex} 7. while Q in do iterate until Q in (i.e., the current BFS level) is empty } 8. n seg #segments to split Q in into (within Θ (1) factor) for concurrent processing 9. Q in.s seg Q in } n seg elements in Q in will be split into segments of size Q in.s seg 10. for i = 1 to p 1 do from vertices in Q in generate vertices 11. spawn Parallel-BFS-Thread( G, Q in, Q out.q[i], d ) in the next BFS level by launching p Parallel-BFS-Thread( G, Q in, Q out.q[p], d ) threads concurrent to the current thread} 13. sync wait until all vertices in Q in have been processed } 14. Q in Q out swap the roles of Q in and Q out} 15. Q out } empty the queues in Q out Parallel-BFS-Thread( G, Q i, Q o, d ) (Inputs are an unweighted directed graph G with vertex set G[V ], and a collection Q i of queues (shared by all threads) containing the input vertices for this level of BFS. All vertices in the next level of BFS discovered by the current thread will be put in the output queue Q o which is a single queue (as opposed to Q i ) used exclusively by the current thread. For each such vertex v the correct BFS level will be stored in d[v] by the current thread. For any vertex u G[V ], Γ(u) denotes the set of vertices adjacent to u.) 1. while ( S = Q i.nextsegment( ) ) do } extract a segment of vertices from Q i 2. while S do consider all vertices in this segment} 3. u S.extract( ) extract any vertex u from the seqment} 4. for each v Γ(u) do consider each vertex adjacent to u} 5. if d[v] = + then if that adjacent vertex v has not yet been visited} 6. d[v] d[u] + 1 distance to v is 1 more than that to u} 7. Q o.enque( v ) enqueue v in the output queue for future exploration} Figure 2: Parallel breadth-first search (BFS) on a graph. 3
4 Q.nextSegment( ) (Q is a collection of queues Q.q[1], Q.q[2],..., Q.q[t], for some t > 0. This function returns a segment of at most Q.s seg queued elements from one of Q s nonempty queues.) 1. Lock( ) 2. S 3. if Q > 0 then if at least one queue in Q is nonempty} 4. i smallest index such that Q.q[i] 5. k min ( Q.s seg, Q.q[i] ) 6. for j 1 to k do 7. S S Q.q[i].deque( ) 8. Unlock( ) 9. return S Figure 3: Get a segment of queued elements from a queue in the collection Q. APPENDIX 1: Input/Output Format for Task 1 Your code must read from standard input and write to standard output. Input Format: The first line of the input will contain three integers giving the number of vertices (n), number of edges (m), and the number of source vertices (r), respectively. Each of the next m lines will contain two integers u and v (1 u, v n) denoting a directed edge from vertex u to vertex v. The edges will be sorted in nondecreasing order of the first vertex. Each of the next r lines will contain one integer s (1 s n) giving the index of a source vertex. Output Format: The output will consist of r lines one for each source vertex. Line i (1 i r) will contain two indegers d i and c i, where d i is the maximum BFS level of a vertex from the i-th source vertex given in the input file, and c i is the checksum value as computed by the following function. // Computes a very simple checksum by adding all d values. // When some d[ i ] = infinity, replaces that infinity with nvertices // during checksum calculation, i.e., assumes that d[ i ] = nvertices. unsigned long long computechecksum( void ) cilk::reducer_opadd< unsigned long long > chksum; cilk_for ( int i = 0; i < nvertices; i++ ) chksum += d[ i ]; } return chksum.get_value( ); Sample Input/Output: Folder /work/01905/rezaul/cse613/hw2/samples on Lonestar. 4
5 APPENDIX 2: What to Turn in Please one compressed archive file (e.g., zip, tar.gz) containing the following items to cs.stonybrook.edu. Source code, makefiles and job scripts for Task 1. A PDF document containing all answers and plots. Output generated for the input files in /work/01905/rezaul/cse613/hw2/samples/turn-in/ on Lonestar. If the name of the input file is xxxxx-in.txt, please name the output files as xxxxx-1a-out.txt, xxxxx-1b-out.txt and xxxxx-1h-out.txt for tasks 1(a), 1(b) and 1(h), respectively. No need to generate an output if it takes more than an hour or overflows the RAM. In such cases simply state the cause of failure in the output file. Output files generated by Cilkview. APPENDIX 3: Things to Remember Please never run anything that takes more than a minute or uses multiple cores on TACC login nodes. TACC policy strictly prohibits such usage. They reserve the right to suspend your account if you do so. All runs must be submitted as jobs to compute nodes (even when you use Cilkview or PAPI). Please store all data in your work folder ($WORK), and not in your home folder ($HOME). When measuring running times please exclude the time needed for reading the input and writing the output. Measure only the time needed by the algorithm. Do the same thing when you run Cilkview. Please make sure that speedup values for trial runs (or measured speedups) are included in the Cilkview plots you generate. 5
CSE638: Advanced Algorithms, Spring 2013 Date: March 26. Homework #2. ( Due: April 16 )
 CSE638: Advanced Algorithms, Spring 2013 Date: March 26 Homework #2 ( Due: April 16 ) Task 1. [ 40 Points ] Parallel BFS with Cilk s Work Stealing. (a) [ 20 Points ] In homework 1 we analyzed and implemented
CSE638: Advanced Algorithms, Spring 2013 Date: March 26 Homework #2 ( Due: April 16 ) Task 1. [ 40 Points ] Parallel BFS with Cilk s Work Stealing. (a) [ 20 Points ] In homework 1 we analyzed and implemented
CSE 613: Parallel Programming
 CSE 613: Parallel Programming Lecture 3 ( The Cilk++ Concurrency Platform ) ( inspiration for many slides comes from talks given by Charles Leiserson and Matteo Frigo ) Rezaul A. Chowdhury Department of
CSE 613: Parallel Programming Lecture 3 ( The Cilk++ Concurrency Platform ) ( inspiration for many slides comes from talks given by Charles Leiserson and Matteo Frigo ) Rezaul A. Chowdhury Department of
Homework Assignment #3 Graph
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
Outlines: Graphs Part-2
 Elementary Graph Algorithms PART-2 1 Outlines: Graphs Part-2 Graph Search Methods Breadth-First Search (BFS): BFS Algorithm BFS Example BFS Time Complexity Output of BFS: Shortest Path Breath-First Tree
Elementary Graph Algorithms PART-2 1 Outlines: Graphs Part-2 Graph Search Methods Breadth-First Search (BFS): BFS Algorithm BFS Example BFS Time Complexity Output of BFS: Shortest Path Breath-First Tree
CSC263 Week 8. Larry Zhang.
 CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
The Cilk part is a small set of linguistic extensions to C/C++ to support fork-join parallelism. (The Plus part supports vector parallelism.
 Cilk Plus The Cilk part is a small set of linguistic extensions to C/C++ to support fork-join parallelism. (The Plus part supports vector parallelism.) Developed originally by Cilk Arts, an MIT spinoff,
Cilk Plus The Cilk part is a small set of linguistic extensions to C/C++ to support fork-join parallelism. (The Plus part supports vector parallelism.) Developed originally by Cilk Arts, an MIT spinoff,
Multicore programming in CilkPlus
 Multicore programming in CilkPlus Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, Canada CS3350 March 16, 2015 CilkPlus From Cilk to Cilk++ and Cilk Plus Cilk has been developed since 1994 at the MIT Laboratory
Multicore programming in CilkPlus Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, Canada CS3350 March 16, 2015 CilkPlus From Cilk to Cilk++ and Cilk Plus Cilk has been developed since 1994 at the MIT Laboratory
Announcements Problem Set 4 is out!
 CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
Operating Systems (234123) Spring (Homework 3 Wet) Homework 3 Wet
 Due date: Monday, 4/06/2012 12:30 noon Teaching assistants in charge: Operating Systems (234123) Spring-2012 Homework 3 Wet Anastasia Braginsky All emails regarding this assignment should be sent only
Due date: Monday, 4/06/2012 12:30 noon Teaching assistants in charge: Operating Systems (234123) Spring-2012 Homework 3 Wet Anastasia Braginsky All emails regarding this assignment should be sent only
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
Multithreaded Parallelism and Performance Measures
 Multithreaded Parallelism and Performance Measures Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) CS 3101 (Moreno Maza) Multithreaded Parallelism and Performance Measures CS 3101
Multithreaded Parallelism and Performance Measures Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) CS 3101 (Moreno Maza) Multithreaded Parallelism and Performance Measures CS 3101
Graphs. Graph G = (V, E) Types of graphs E = O( V 2 ) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V)
 Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Plan. 1 Parallelism Complexity Measures. 2 cilk for Loops. 3 Scheduling Theory and Implementation. 4 Measuring Parallelism in Practice
 lan Multithreaded arallelism and erformance Measures Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) CS 3101 1 2 cilk for Loops 3 4 Measuring arallelism in ractice 5 Announcements
lan Multithreaded arallelism and erformance Measures Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) CS 3101 1 2 cilk for Loops 3 4 Measuring arallelism in ractice 5 Announcements
CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal
 CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal Your Turn The array of vertices, which include dist, prev, and done fields (initialize dist to INFINITY and done to false ): V0: dist= prev= done= adj:
CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal Your Turn The array of vertices, which include dist, prev, and done fields (initialize dist to INFINITY and done to false ): V0: dist= prev= done= adj:
Elementary Graph Algorithms. Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph:
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Homework No. 4 Answers
 Homework No. 4 Answers CSCI 4470/6470 Algorithms, CS@UGA, Spring 2018 Due Thursday March 29, 2018 There are 100 points in total. 1. (20 points) Consider algorithm DFS (or algorithm To-Start-DFS in Lecture
Homework No. 4 Answers CSCI 4470/6470 Algorithms, CS@UGA, Spring 2018 Due Thursday March 29, 2018 There are 100 points in total. 1. (20 points) Consider algorithm DFS (or algorithm To-Start-DFS in Lecture
Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs» Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.)» Directed: (u, v)
Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs» Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.)» Directed: (u, v)
5.4 Shortest Paths. Jacobs University Visualization and Computer Graphics Lab. CH : Algorithms and Data Structures 456
 5.4 Shortest Paths CH08-320201: Algorithms and Data Structures 456 Definitions: Path Consider a directed graph G=(V,E), where each edge e є E is assigned a non-negative weight w: E -> R +. A path is a
5.4 Shortest Paths CH08-320201: Algorithms and Data Structures 456 Definitions: Path Consider a directed graph G=(V,E), where each edge e є E is assigned a non-negative weight w: E -> R +. A path is a
CSE 260 Lecture 19. Parallel Programming Languages
 CSE 260 Lecture 19 Parallel Programming Languages Announcements Thursday s office hours are cancelled Office hours on Weds 2p to 4pm Jing will hold OH, too, see Moodle Scott B. Baden /CSE 260/ Winter 2014
CSE 260 Lecture 19 Parallel Programming Languages Announcements Thursday s office hours are cancelled Office hours on Weds 2p to 4pm Jing will hold OH, too, see Moodle Scott B. Baden /CSE 260/ Winter 2014
Representations of Graphs
 ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
A Parallel Algorithm for the Single-Source Shortest Path Problem
 A Parallel Algorithm for the Single-Source Shortest Path Problem Kevin Kelley, Tao Schardl May 12, 2010 Outline The Problem Dijkstra s Algorithm Gabow s Scaling Algorithm Optimizing Gabow Parallelizing
A Parallel Algorithm for the Single-Source Shortest Path Problem Kevin Kelley, Tao Schardl May 12, 2010 Outline The Problem Dijkstra s Algorithm Gabow s Scaling Algorithm Optimizing Gabow Parallelizing
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 18 Graph Algorithm Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Graphs Graph G = (V,
Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 18 Graph Algorithm Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Graphs Graph G = (V,
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Breadth First Search. Graph Traversal. CSE 2011 Winter Application examples. Two common graph traversal algorithms
 Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
CSE 431/531: Analysis of Algorithms. Greedy Algorithms. Lecturer: Shi Li. Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo
 CSE 431/531: Analysis of Algorithms Greedy Algorithms Lecturer: Shi Li Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo Main Goal of Algorithm Design Design fast algorithms to solve
CSE 431/531: Analysis of Algorithms Greedy Algorithms Lecturer: Shi Li Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo Main Goal of Algorithm Design Design fast algorithms to solve
CS61BL. Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting
 CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
Plan. 1 Parallelism Complexity Measures. 2 cilk for Loops. 3 Scheduling Theory and Implementation. 4 Measuring Parallelism in Practice
 lan Multithreaded arallelism and erformance Measures Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) CS 4435 - CS 9624 1 2 cilk for Loops 3 4 Measuring arallelism in ractice 5
lan Multithreaded arallelism and erformance Measures Marc Moreno Maza University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario (Canada) CS 4435 - CS 9624 1 2 cilk for Loops 3 4 Measuring arallelism in ractice 5
Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]
![Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch] Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]](/thumbs/81/84350835.jpg) Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
CSE 332: Data Abstractions Lecture 15: Topological Sort / Graph Traversals. Ruth Anderson Winter 2013
 CSE 332: Data Abstractions Lecture 15: Topological Sort / Graph Traversals Ruth Anderson Winter 2013 Announcements Homework 4 due Friday Feb 15 th at the BEGINNING of lecture Project 2 Phase B due Tues
CSE 332: Data Abstractions Lecture 15: Topological Sort / Graph Traversals Ruth Anderson Winter 2013 Announcements Homework 4 due Friday Feb 15 th at the BEGINNING of lecture Project 2 Phase B due Tues
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch DATA STRUCTURES ACS002 B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch DATA STRUCTURES ACS002 B. Tech
Theory of Computing. Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck
 Theory of Computing Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck How fast can we sort? There are deterministic algorithms that sort in worst case time O(n log n) Do better algorithms exist? Example [Andersson et
Theory of Computing Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck How fast can we sort? There are deterministic algorithms that sort in worst case time O(n log n) Do better algorithms exist? Example [Andersson et
CS6235. L15: Dynamic Scheduling
 L15: Dynamic Scheduling Administrative STRSM due March 23 (EXTENDED) Midterm coming - In class March 28, can bring one page of notes - Review notes, readings and review lecture - Prior exams are posted
L15: Dynamic Scheduling Administrative STRSM due March 23 (EXTENDED) Midterm coming - In class March 28, can bring one page of notes - Review notes, readings and review lecture - Prior exams are posted
Outline. Computer Science 331. Definitions: Paths and Their Costs. Computation of Minimum Cost Paths
 Outline Computer Science 33 Computation of Minimum-Cost Paths Dijkstra s Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture #34 Dijkstra s to Find Min-Cost Paths 3 Example 4 5 References
Outline Computer Science 33 Computation of Minimum-Cost Paths Dijkstra s Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture #34 Dijkstra s to Find Min-Cost Paths 3 Example 4 5 References
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up. Nicki Dell Spring 2014
 CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up Nicki Dell Spring 2014 Final Exam As also indicated on the web page: Next Tuesday, 2:30-4:20 in this room Cumulative but
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 28: Final review and class wrap-up Nicki Dell Spring 2014 Final Exam As also indicated on the web page: Next Tuesday, 2:30-4:20 in this room Cumulative but
CSE 431/531: Algorithm Analysis and Design (Spring 2018) Greedy Algorithms. Lecturer: Shi Li
 CSE 431/531: Algorithm Analysis and Design (Spring 2018) Greedy Algorithms Lecturer: Shi Li Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo Main Goal of Algorithm Design Design fast
CSE 431/531: Algorithm Analysis and Design (Spring 2018) Greedy Algorithms Lecturer: Shi Li Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo Main Goal of Algorithm Design Design fast
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms
 COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH
 CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH Announcements PA3 released Checkpoint due Tuesday, May 5 @10:00pm Final submission due Thursday, May 14 @10:00PM Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! I
CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH Announcements PA3 released Checkpoint due Tuesday, May 5 @10:00pm Final submission due Thursday, May 14 @10:00PM Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! I
Graph Theory. Many problems are mapped to graphs. Problems. traffic VLSI circuits social network communication networks web pages relationship
 Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Breadth First Search. cse2011 section 13.3 of textbook
 Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
You must include this cover sheet. Either type up the assignment using theory3.tex, or print out this PDF.
 15-122 Assignment 3 Page 1 of 12 15-122 : Principles of Imperative Computation Fall 2012 Assignment 3 (Theory Part) Due: Thursday, October 4 at the beginning of lecture. Name: Andrew ID: Recitation: The
15-122 Assignment 3 Page 1 of 12 15-122 : Principles of Imperative Computation Fall 2012 Assignment 3 (Theory Part) Due: Thursday, October 4 at the beginning of lecture. Name: Andrew ID: Recitation: The
Subject : Computer Science. Paper: Data Structures. Module: Priority Queue and Applications. Module No: CS/DS/14
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Data Structures Module: Priority Queue and Applications Module No: CS/DS/14 Quadrant 1- e-text Welcome to the e-pg Pathshala Lecture Series on Data Structures.
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Data Structures Module: Priority Queue and Applications Module No: CS/DS/14 Quadrant 1- e-text Welcome to the e-pg Pathshala Lecture Series on Data Structures.
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees
 Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
CSE 373: Practice Final
 CSE 373: Practice Final 1 Short Answer a) Provide two orderings [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7] that are worst-case for quick sort. Assume that you select the first element as the pivot. Explain why this is the worst-case.
CSE 373: Practice Final 1 Short Answer a) Provide two orderings [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7] that are worst-case for quick sort. Assume that you select the first element as the pivot. Explain why this is the worst-case.
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS Dijkstra s Algorithm: Questions Initialize the graph: Give all vertices a dist of INFINITY, set all done flags to false Start at s; give s dist = 0 and set prev field to -1 Enqueue
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS Dijkstra s Algorithm: Questions Initialize the graph: Give all vertices a dist of INFINITY, set all done flags to false Start at s; give s dist = 0 and set prev field to -1 Enqueue
Some Extra Information on Graph Search
 Some Extra Information on Graph Search David Kempe December 5, 203 We have given basic definitions of graphs earlier in class, and talked about how to implement them. We had also already mentioned paths,
Some Extra Information on Graph Search David Kempe December 5, 203 We have given basic definitions of graphs earlier in class, and talked about how to implement them. We had also already mentioned paths,
Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker
 Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker Graphs A graph is a set of vertices that are pairwise connected by edges. We distinguish between directed and undirected graphs. Why are we interested in graphs? Graphs
Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker Graphs A graph is a set of vertices that are pairwise connected by edges. We distinguish between directed and undirected graphs. Why are we interested in graphs? Graphs
Algorithm Design, Anal. & Imp., Homework 4 Solution
 Algorithm Design, Anal. & Imp., Homework 4 Solution Note: The solution is for your personal use for this course. You are not allowed to post the solution in public place. There could be mistakes in the
Algorithm Design, Anal. & Imp., Homework 4 Solution Note: The solution is for your personal use for this course. You are not allowed to post the solution in public place. There could be mistakes in the
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
( ) D. Θ ( ) ( ) Ο f ( n) ( ) Ω. C. T n C. Θ. B. n logn Ο
 CSE 0 Name Test Fall 0 Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The expected time for insertion sort for n keys is in which set? (All n! input permutations are equally
CSE 0 Name Test Fall 0 Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The expected time for insertion sort for n keys is in which set? (All n! input permutations are equally
Taking Stock. IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 20. Example. Shortest Paths Definitions
 Taking Stock IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 20 Jeff Linderoth Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lehigh University March 19, 2007 Last Time Minimum Spanning Trees Strongly
Taking Stock IE170: Algorithms in Systems Engineering: Lecture 20 Jeff Linderoth Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lehigh University March 19, 2007 Last Time Minimum Spanning Trees Strongly
ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring Lecture #3: Of Integers and Endians (pt. 2)
 ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2018 Lecture #3: Of Integers and Endians (pt. 2) Reading for Today: Davies Ch 2, MSP430 User's Guide Ch 6.1, 6.3 Reading for Next Class:
ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2018 Lecture #3: Of Integers and Endians (pt. 2) Reading for Today: Davies Ch 2, MSP430 User's Guide Ch 6.1, 6.3 Reading for Next Class:
Cilk. Cilk In 2008, ACM SIGPLAN awarded Best influential paper of Decade. Cilk : Biggest principle
 CS528 Slides are adopted from http://supertech.csail.mit.edu/cilk/ Charles E. Leiserson A Sahu Dept of CSE, IIT Guwahati HPC Flow Plan: Before MID Processor + Super scalar+ Vector Unit Serial C/C++ Coding
CS528 Slides are adopted from http://supertech.csail.mit.edu/cilk/ Charles E. Leiserson A Sahu Dept of CSE, IIT Guwahati HPC Flow Plan: Before MID Processor + Super scalar+ Vector Unit Serial C/C++ Coding
CMSC Introduction to Algorithms Spring 2012 Lecture 7
 CMSC 351 - Introduction to Algorithms Spring 2012 Lecture 7 Instructor: MohammadTaghi Hajiaghayi Scribe: Rajesh Chitnis 1 Introduction In this lecture we give an introduction to Data Structures like arrays,
CMSC 351 - Introduction to Algorithms Spring 2012 Lecture 7 Instructor: MohammadTaghi Hajiaghayi Scribe: Rajesh Chitnis 1 Introduction In this lecture we give an introduction to Data Structures like arrays,
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms March 5, 205 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/8.40J Profs. Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas, and Nancy Lynch Problem Set 4 Solutions Problem Set 4 Solutions This
Design and Analysis of Algorithms March 5, 205 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/8.40J Profs. Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas, and Nancy Lynch Problem Set 4 Solutions Problem Set 4 Solutions This
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 Spring 2010 s of s s are abstract data types that
s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 Spring 2010 s of s s are abstract data types that
Shortest path problems
 Next... Shortest path problems Single-source shortest paths in weighted graphs Shortest-Path Problems Properties of Shortest Paths, Relaxation Dijkstra s Algorithm Bellman-Ford Algorithm Shortest-Paths
Next... Shortest path problems Single-source shortest paths in weighted graphs Shortest-Path Problems Properties of Shortest Paths, Relaxation Dijkstra s Algorithm Bellman-Ford Algorithm Shortest-Paths
CMPSC 250 Analysis of Algorithms Spring 2018 Dr. Aravind Mohan Shortest Paths April 16, 2018
 1 CMPSC 250 Analysis of Algorithms Spring 2018 Dr. Aravind Mohan Shortest Paths April 16, 2018 Shortest Paths The discussion in these notes captures the essence of Dijkstra s algorithm discussed in textbook
1 CMPSC 250 Analysis of Algorithms Spring 2018 Dr. Aravind Mohan Shortest Paths April 16, 2018 Shortest Paths The discussion in these notes captures the essence of Dijkstra s algorithm discussed in textbook
CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory
 CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory Dustin Tseng Mike Li Wednesday January 16, 2006 Dustin Tseng Mike Li: CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science, Lecture
CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory Dustin Tseng Mike Li Wednesday January 16, 2006 Dustin Tseng Mike Li: CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science, Lecture
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
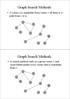 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Shared-memory Parallel Programming with Cilk Plus
 Shared-memory Parallel Programming with Cilk Plus John Mellor-Crummey Department of Computer Science Rice University johnmc@rice.edu COMP 422/534 Lecture 4 30 August 2018 Outline for Today Threaded programming
Shared-memory Parallel Programming with Cilk Plus John Mellor-Crummey Department of Computer Science Rice University johnmc@rice.edu COMP 422/534 Lecture 4 30 August 2018 Outline for Today Threaded programming
Department of Computer Science. COS 122 Operating Systems. Practical 3. Due: 22:00 PM
 Department of Computer Science COS 122 Operating Systems Practical 3 Due: 2018-09-13 @ 22:00 PM August 30, 2018 PLAGIARISM POLICY UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA The Department of Computer Science considers plagiarism
Department of Computer Science COS 122 Operating Systems Practical 3 Due: 2018-09-13 @ 22:00 PM August 30, 2018 PLAGIARISM POLICY UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA The Department of Computer Science considers plagiarism
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015
 CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #22, More Graph Searches, Some Sorting, and Efficient Sorting Algorithms John Ridgway April 21, 2015 1 Review of Uniform-cost Search Uniform-Cost
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #22, More Graph Searches, Some Sorting, and Efficient Sorting Algorithms John Ridgway April 21, 2015 1 Review of Uniform-cost Search Uniform-Cost
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms
 W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
CSE 100 Practice Final Exam
 CSE 100 Practice Final Exam Please note that this practice final only serves as a template and does not exhaustively cover all the topics that are on the actual final. The final exam will cover all the
CSE 100 Practice Final Exam Please note that this practice final only serves as a template and does not exhaustively cover all the topics that are on the actual final. The final exam will cover all the
University of Waterloo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 250 Algorithms and Data Structures
 University of Waterloo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 250 Algorithms and Data Structures Final Examination (17 pages) Instructor: Douglas Harder April 14, 2004 9:00-12:00 Name (last,
University of Waterloo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 250 Algorithms and Data Structures Final Examination (17 pages) Instructor: Douglas Harder April 14, 2004 9:00-12:00 Name (last,
Today: Amortized Analysis (examples) Multithreaded Algs.
 Today: Amortized Analysis (examples) Multithreaded Algs. COSC 581, Algorithms March 11, 2014 Many of these slides are adapted from several online sources Reading Assignments Today s class: Chapter 17 (Amortized
Today: Amortized Analysis (examples) Multithreaded Algs. COSC 581, Algorithms March 11, 2014 Many of these slides are adapted from several online sources Reading Assignments Today s class: Chapter 17 (Amortized
& ( D. " mnp ' ( ) n 3. n 2. ( ) C. " n
 CSE Name Test Summer Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to multiply two n " n matrices is: A. " n C. "% n B. " max( m,n, p). The
CSE Name Test Summer Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to multiply two n " n matrices is: A. " n C. "% n B. " max( m,n, p). The
Graph Algorithms: Chapters Part 1: Introductory graph concepts
 UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
Parallelism and Performance
 6.172 erformance Engineering of Software Systems LECTURE 13 arallelism and erformance Charles E. Leiserson October 26, 2010 2010 Charles E. Leiserson 1 Amdahl s Law If 50% of your application is parallel
6.172 erformance Engineering of Software Systems LECTURE 13 arallelism and erformance Charles E. Leiserson October 26, 2010 2010 Charles E. Leiserson 1 Amdahl s Law If 50% of your application is parallel
CSE 214 Computer Science II Heaps and Priority Queues
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Heaps and Priority Queues Spring 2018 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Introduction
CSE 214 Computer Science II Heaps and Priority Queues Spring 2018 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Introduction
Tutorial. Question There are no forward edges. 4. For each back edge u, v, we have 0 d[v] d[u].
![Tutorial. Question There are no forward edges. 4. For each back edge u, v, we have 0 d[v] d[u]. Tutorial. Question There are no forward edges. 4. For each back edge u, v, we have 0 d[v] d[u].](/thumbs/88/114871846.jpg) Tutorial Question 1 A depth-first forest classifies the edges of a graph into tree, back, forward, and cross edges. A breadth-first tree can also be used to classify the edges reachable from the source
Tutorial Question 1 A depth-first forest classifies the edges of a graph into tree, back, forward, and cross edges. A breadth-first tree can also be used to classify the edges reachable from the source
L16: Dynamic Task Queues and Synchronization
 L16: Dynamic Task Queues and Synchronization Administrative Midterm - In class, open notes - Currently scheduled for Wednesday, March 31 - Some students have requested we move it due to another exam in
L16: Dynamic Task Queues and Synchronization Administrative Midterm - In class, open notes - Currently scheduled for Wednesday, March 31 - Some students have requested we move it due to another exam in
Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations. CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5
 Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5 CSE 101: Design and analysis of algorithms Dijkstra s algorithm and priority queue implementations
Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5 CSE 101: Design and analysis of algorithms Dijkstra s algorithm and priority queue implementations
Sample Solutions to Homework #4
 National Taiwan University Handout #25 Department of Electrical Engineering January 02, 207 Algorithms, Fall 206 TA: Zhi-Wen Lin and Yen-Chun Liu Sample Solutions to Homework #4. (0) (a) Both of the answers
National Taiwan University Handout #25 Department of Electrical Engineering January 02, 207 Algorithms, Fall 206 TA: Zhi-Wen Lin and Yen-Chun Liu Sample Solutions to Homework #4. (0) (a) Both of the answers
Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms, 2 nd ed., Ch.
 Iterative Improvement Algorithm design technique for solving optimization problems Start with a feasible solution Repeat the following step until no improvement can be found: change the current feasible
Iterative Improvement Algorithm design technique for solving optimization problems Start with a feasible solution Repeat the following step until no improvement can be found: change the current feasible
Graph Algorithms. Definition
 Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graphs. Part II: SP and MST. Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College
 Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Topics Weighted graphs each edge (u, v) has a weight denoted w(u, v) or w uv stored in the adjacency list or adjacency matrix The weight of a path p =
Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Topics Weighted graphs each edge (u, v) has a weight denoted w(u, v) or w uv stored in the adjacency list or adjacency matrix The weight of a path p =
Lecture 3, Review of Algorithms. What is Algorithm?
 BINF 336, Introduction to Computational Biology Lecture 3, Review of Algorithms Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University What is Algorithm? Definition A process
BINF 336, Introduction to Computational Biology Lecture 3, Review of Algorithms Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University What is Algorithm? Definition A process
CSE 373 APRIL 17 TH TREE BALANCE AND AVL
 CSE 373 APRIL 17 TH TREE BALANCE AND AVL ASSORTED MINUTIAE HW3 due Wednesday Double check submissions Use binary search for SADict Midterm text Friday Review in Class on Wednesday Testing Advice Empty
CSE 373 APRIL 17 TH TREE BALANCE AND AVL ASSORTED MINUTIAE HW3 due Wednesday Double check submissions Use binary search for SADict Midterm text Friday Review in Class on Wednesday Testing Advice Empty
n 2 ( ) ( ) Ο f ( n) ( ) Ω B. n logn Ο
 CSE 220 Name Test Fall 20 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. 4 points each. The time to compute the sum of the n elements of an integer array is in:
CSE 220 Name Test Fall 20 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. 4 points each. The time to compute the sum of the n elements of an integer array is in:
CS 450 Exam 2 Mon. 4/11/2016
 CS 450 Exam 2 Mon. 4/11/2016 Name: Rules and Hints You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only additional resource you may consult during this exam. No calculators.
CS 450 Exam 2 Mon. 4/11/2016 Name: Rules and Hints You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only additional resource you may consult during this exam. No calculators.
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
AN 831: Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL
 AN 831: Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Host Pipelined Multithread Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Host Pipelined Multithread...3 1.1
AN 831: Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Host Pipelined Multithread Subscribe Send Feedback Latest document on the web: PDF HTML Contents Contents 1 Intel FPGA SDK for OpenCL Host Pipelined Multithread...3 1.1
Dijkstra s Shortest Path Algorithm
 Dijkstra s Shortest Path Algorithm DPV 4.4, CLRS 24.3 Revised, October 23, 2014 Outline of this Lecture Recalling the BFS solution of the shortest path problem for unweighted (di)graphs. The shortest path
Dijkstra s Shortest Path Algorithm DPV 4.4, CLRS 24.3 Revised, October 23, 2014 Outline of this Lecture Recalling the BFS solution of the shortest path problem for unweighted (di)graphs. The shortest path
Multithreaded Algorithms Part 1. Dept. of Computer Science & Eng University of Moratuwa
 CS4460 Advanced d Algorithms Batch 08, L4S2 Lecture 11 Multithreaded Algorithms Part 1 N. H. N. D. de Silva Dept. of Computer Science & Eng University of Moratuwa Announcements Last topic discussed is
CS4460 Advanced d Algorithms Batch 08, L4S2 Lecture 11 Multithreaded Algorithms Part 1 N. H. N. D. de Silva Dept. of Computer Science & Eng University of Moratuwa Announcements Last topic discussed is
2. True or false: even though BFS and DFS have the same space complexity, they do not always have the same worst case asymptotic time complexity.
 1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
( ) n 3. n 2 ( ) D. Ο
 CSE 0 Name Test Summer 0 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to multiply two n n matrices is: A. Θ( n) B. Θ( max( m,n, p) ) C.
CSE 0 Name Test Summer 0 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to multiply two n n matrices is: A. Θ( n) B. Θ( max( m,n, p) ) C.
HW4: Breadth-First Search
 HW4: Breadth-First Search Course: CMSC751/ENEE759K, Spring 2010 Title: Breadth-First Search Date Assigned: March 25th, 2010 Date Due: April 9th, 2010 11:59pm Contact: George Caragea - george@cs.umd.edu
HW4: Breadth-First Search Course: CMSC751/ENEE759K, Spring 2010 Title: Breadth-First Search Date Assigned: March 25th, 2010 Date Due: April 9th, 2010 11:59pm Contact: George Caragea - george@cs.umd.edu
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Chapter 6 Heapsort 1
 Chapter 6 Heapsort 1 Introduce Heap About this lecture Shape Property and Heap Property Heap Operations Heapsort: Use Heap to Sort Fixing heap property for all nodes Use Array to represent Heap Introduce
Chapter 6 Heapsort 1 Introduce Heap About this lecture Shape Property and Heap Property Heap Operations Heapsort: Use Heap to Sort Fixing heap property for all nodes Use Array to represent Heap Introduce
Outline. 1 Introduction. 2 Algorithm. 3 Example. 4 Analysis. 5 References. Idea
 Outline Computer Science 331 Graph Search: Breadth-First Search Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture #31 1 2 3 Example 4 5 References Mike Jacobson (University of
Outline Computer Science 331 Graph Search: Breadth-First Search Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lecture #31 1 2 3 Example 4 5 References Mike Jacobson (University of
Performance Optimization Part 1: Work Distribution and Scheduling
 Lecture 5: Performance Optimization Part 1: Work Distribution and Scheduling Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming CMU 15-418/15-618, Fall 2017 Programming for high performance Optimizing the
Lecture 5: Performance Optimization Part 1: Work Distribution and Scheduling Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming CMU 15-418/15-618, Fall 2017 Programming for high performance Optimizing the
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT
 CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
Homework #5 Algorithms I Spring 2017
 Homework #5 Algorithms I 600.463 Spring 2017 Due on: Saturday, March 18th, 11:59pm Late submissions: will NOT be accepted Format: Please start each problem on a new page. Where to submit: On Gradescope,
Homework #5 Algorithms I 600.463 Spring 2017 Due on: Saturday, March 18th, 11:59pm Late submissions: will NOT be accepted Format: Please start each problem on a new page. Where to submit: On Gradescope,
Flat Parallelization. V. Aksenov, ITMO University P. Kuznetsov, ParisTech. July 4, / 53
 Flat Parallelization V. Aksenov, ITMO University P. Kuznetsov, ParisTech July 4, 2017 1 / 53 Outline Flat-combining PRAM and Flat parallelization PRAM binary heap with Flat parallelization ExtractMin Insert
Flat Parallelization V. Aksenov, ITMO University P. Kuznetsov, ParisTech July 4, 2017 1 / 53 Outline Flat-combining PRAM and Flat parallelization PRAM binary heap with Flat parallelization ExtractMin Insert
Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS DASL Summer Program Path Planning References: http://robotics.mem.drexel.edu/mhsieh/courses/mem380i/index.html http://dasl.mem.drexel.edu/hing/bfsdfstutorial.htm
Lesson 1 Introduction to Path Planning Graph Searches: BFS and DFS DASL Summer Program Path Planning References: http://robotics.mem.drexel.edu/mhsieh/courses/mem380i/index.html http://dasl.mem.drexel.edu/hing/bfsdfstutorial.htm
Student Name: University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science CS 162 Spring 2011 I. Stoica FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION Wednesday, March 9, 2011 INSTRUCTIONS
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science CS 162 Spring 2011 I. Stoica FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION Wednesday, March 9, 2011 INSTRUCTIONS
