Abstract Class (2) Abstract Classes and Interfaces. Abstract Class (1) Abstract Class (3) EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017
|
|
|
- Jason Eaton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Abstract Class (2) Abstract Classes and Interfaces EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG public abstract class Polygon { double[] sides; Polygon(double[] sides) { this.sides = sides; void grow() { for(int i = 0; i < sides.length; i ++) { sides[i] ++; double getperimeter() { double perimeter = 0; for(int i = 0; i < sides.length; i ++) { perimeter += sides[i]; return perimeter; abstract double getarea(); Method getarea not implemented and shown signature only. Polygon cannot be used as a dynamic type Writing new Polygon(...) is forbidden! 3 of 20 Abstract Class (1) Problem: A polygon may be either a triangle or a rectangle. Given a polygon, we may either Grow its shape by incrementing the size of each of its sides; Compute and return its perimeter; or Compute and return its area. For a rectangle with length and width, its area is length width. For a triangle with sides a, b, and c, its area, according to Heron s formula, is s(s a)(s b)(s c) where s = a + b + c 2 How would you solve this problem in Java, while minimizing code duplicates? 2 of 20 Abstract Class (3) public class Rectangle extends Polygon { Rectangle(double length, double width) { super(new double[4]); sides[0] = length; sides[1] = width; sides[2] = length; sides[3] = width; double getarea() { return sides[0] * sides[1]; Method getperimeter is inherited from the super-class Polygon. Method getarea is implemented in the sub-class Rectangle. Rectangle can be used as a dynamic type Writing Polygon p = new Rectangle(3, 4) allowed! 4 of 20
2 Abstract Class (4) public class Triangle extends Polygon { Triangle(double side1, double side2, double side3) { super(new double[3]); sides[0] = side1; sides[1] = side2; sides[2] = side3; double getarea() { /* Heron s formula */ double s = getperimeter() * 0.5; double area = Math.sqrt( s * (s - sides[0]) * (s - sides[1]) * (s - sides[2])); return area; Method getperimeter is inherited from Polygon. Method getarea is implemented in the sub-class Triangle. Triangle can be used as a dynamic type Writing Polygon p = new Triangle(3, 4, 5) allowed! 5 of 20 Abstract Class (6) 1 public class PolygonConstructor { 2 Polygon getpolygon(double[] sides) { 3 Polygon p = null; 4 if(sides.length == 3) { 5 p = new Triangle(sides[0], sides[1], sides[2]); 6 7 else if(sides.length == 4) { 8 p = new Rectangle(sides[0], sides[1]); 9 10 return p; void grow(polygon p) { p.grow(); 13 Polymorphism: Line 2 may accept as return value any object whose static type is Polygon or any of its sub-classes. Line 5 returns an object whose dynamic type is Triangle; Line 7 of 20 8 returns an object whose dynamic type is Rectangle. Abstract Class (5) 1 public class PolygonCollector { 2 Polygon[] polygons; 3 int numberofpolygons; 4 PolygonCollector() { polygons = new Polygon[10]; 5 void addpolygon(polygon p) { 6 polygons[numberofpolygons] = p; numberofpolygons ++; 7 8 void growall() { 9 for(int i = 0; i < numberofpolygons; i ++) { 10 polygons[i].grow(); Polymorphism: Line 5 may accept as argument any object whose static type is Polygon or any of its sub-classes. Dynamic Binding: Line 10 calls the version of grow inherited to the dynamic type of polygons[i]. 6 of 20 Abstract Class (7.1) 1 public class PolygonTester { 2 public static void main(string[] args) { 3 Polygon p; 4 p = new Rectangle(3, 4); /* polymorphism */ 5 System.out.println(p.getPerimeter()); /* 14.0 */ 6 System.out.println(p.getArea()); /* 12.0 */ 7 p = new Triangle(3, 4, 5); /* polymorphism */ 8 System.out.println(p.getPerimeter()); /* 12.0 */ 9 System.out.println(p.getArea()); /* 6.0 */ PolygonCollector col = new PolygonCollector(); 12 col.addpolygon(new Rectangle(3, 4)); /* polymorphism */ 13 col.addpolygon(new Triangle(3, 4, 5)); /* polymorphism */ 14 System.out.println(col.polygons[0]. getperimeter ()); /* 14.0 */ 15 System.out.println(col.polygons[1]. getperimeter ()); /* 12.0 */ 16 col.growall(); 17 System.out.println(col.polygons[0]. getperimeter ()); /* 18.0 */ 18 System.out.println(col.polygons[1]. getperimeter ()); /* 15.0 */ 8 of 20
3 Abstract Class (7.2) 1 PolygonConstructor con = new PolygonConstructor(); 2 double[] recsides = {3, 4, 3, 4; p = con. getpolygon (recsides); 3 System.out.println(p instanceof Polygon); 4 System.out.println(p instanceof Rectangle); 5 System.out.println(p instanceof Triangle); 6 System.out.println(p.getPerimeter()); /* 14.0 */ 7 System.out.println(p.getArea()); /* 12.0 */ 8 con.grow( p ); 9 System.out.println(p.getPerimeter()); /* 18.0 */ 10 System.out.println(p.getArea()); /* 20.0 */ 11 double[] trisides = {3, 4, 5; p = con. getpolygon (trisides); 12 System.out.println(p instanceof Polygon); 13 System.out.println(p instanceof Rectangle); 14 System.out.println(p instanceof Triangle); 15 System.out.println(p.getPerimeter()); /* 12.0 */ 16 System.out.println(p.getArea()); /* 6.0 */ 17 con.grow( p ); 18 System.out.println(p.getPerimeter()); /* 15.0 */ 19 System.out.println(p.getArea()); /* */ 20 9 of 20 Interface (1.1) We may implement Point using two representation systems: The Cartesian system stores the absolute positions of x and y. The Polar system stores the relative position: the angle (in radian) phi and distance r from the origin (0.0). As far as users of a Point object p is concerned, being able to call p.getx() and gety() is what matters. How p.getx() and p.gety() are internally computed, depending on the dynamic type of p, do not matter to users. 11 of 20 Abstract Class (8) An abstract class : Typically has at least one method with no implementation body May define common implementations inherited to sub-classes. Recommended to use an abstract class as the static type of: A variable e.g., Polygon p A method parameter e.g., void grow(polygon p) A method return value e.g., Polygon getpolygon(double[] sides) It is forbidden to use an abstract class as a dynamic type e.g., Polygon p = new Polygon(...) is not allowed! Instead, create objects whose dynamic types are descendant classes of the abstract class Exploit dynamic binding! e.g., Polygon p = con.getpolygon(recsides) This is is as if we did Polygon p = new Rectangle(...) 10 of 20 Interface (1.2) As an example, we consider the point which is represented as: r = 2a, = 30 [ polar system ] x = 2a cos30 = a 3, y = 2a sin30 = a [ cartesian system ] 12 of 20
4 Interface (2) interface Point { double getx(); double gety(); An interface Point defines how users may access a point: either get its x coordinate or its y coordinate. Methods getx and gety similar to getarea in Polygon, have no implementations, but signatures only. Point cannot be used as a dynamic type Writing new Point(...) is forbidden! 13 of 20 Interface (4) public class PolarPoint implements Point { double phi; double r; public PolarPoint(double r, double phi) { this.r = r; this.phi = phi; public double getx() { return Math.cos(phi) * r; public double gety() { return Math.sin(phi) * r; PolarPoint is a possible implementation of Point. Attributes phi and r declared according to the Polar system All method from the interface Point are implemented in the sub-class PolarPoint. PolarPoint can be used as a dynamic type Point p = new PolarPoint(3, 6 ) allowed! [360 = 2 ] 15 of 20 Interface (3) public class CartesianPoint implements Point { double x; double y; CartesianPoint(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; public double getx() { return x; public double gety() { return y; CartesianPoint is a possible implementation of Point. Attributes x and y declared according to the Cartesian system All method from the interface Point are implemented in the sub-class CartesianPoint. CartesianPoint can be used as a dynamic type Point p = new CartesianPoint(3, 4) allowed! 14 of 20 Interface (5) 1 public class PointTester { 2 public static void main(string[] args) { 3 double A = 5; 4 double X = A * Math.sqrt(3); 5 double Y = A; 6 Point p; 7 p = new CartisianPoint(X, Y); /* polymorphism */ 8 print("(" + p. getx() + ", " + p. gety() + ")"); /* dyn. bin. */ 9 p = new PolarPoint(2 * A, Math.toRadians(30)); /* polymorphism */ 10 print("(" + p. getx() + ", " + p. gety() + ")"); /* dyn. bin. */ Lines 4 and 7 illustrate polymorphism, how? Lines 6 and 9 illustrate dynamic binding, how? 16 of 20
5 Interface (6) An interface : Has all its methods with no implementation bodies. Leaves complete freedom to its implementors. Recommended to use an interface as the static type of: A variable e.g., Point p A method parameter e.g., void moveup(point p) A method return value e.g., Point getpoint(double v1, double v2, boolean iscartesian) It is forbidden to use an interface as a dynamic type e.g., Point p = new Point(...) is not allowed! Instead, create objects whose dynamic types are descendant classes of the interface Exploit dynamic binding! 17 of 20 Index (1) Abstract Class (1) Abstract Class (2) Abstract Class (3) Abstract Class (4) Abstract Class (5) Abstract Class (6) Abstract Class (7.1) Abstract Class (7.2) Abstract Class (8) Interface (1.1) Interface (1.2) Interface (2) Interface (3) Interface (4) 19 of 20 Abstract Classes vs. Interfaces: When to Use Which? Use interfaces when: There is a common set of functionalities that can be implemented via a variety of strategies. e.g., Interface Point declares signatures of getx() and gety(). Each descendant class represents a different implementation strategy for the same set of functionalities. CartesianPoint and PolarPoinnt represent different strategies for supporting getx() and gety(). Use abstract classes when: Some (not all) implementations can be shared by descendants, and some (not all) implementations cannot be shared. e.g., Abstract class Polygon: Defines implementation of getperimeter, to be shared by Rectangle and Triangle. Declares signature of getarea, to be implemented by Rectangle and Triangle. 18 of 20 Index (2) Interface (5) Interface (6) Abstract Classes vs. Interfaces: When to Use Which? 20 of 20
Abstract Classes and Interfaces
 Abstract Classes and Interfaces EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Abstract Class (1) Problem: A polygon may be either a triangle or a rectangle. Given a polygon, we
Abstract Classes and Interfaces EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Abstract Class (1) Problem: A polygon may be either a triangle or a rectangle. Given a polygon, we
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 20, 2014 Abstract
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 20, 2014 Abstract
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance Introduction Generalization/specialization Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract
CSE 8B Programming Assignments Spring Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3:
 PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENT 3: Read Savitch: Chapter 7 Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3: ShapeP3.java PointP3.java CircleP3.java RectangleP3.java TriangleP3.java
PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENT 3: Read Savitch: Chapter 7 Programming: You will have 5 files all should be located in a dir. named PA3: ShapeP3.java PointP3.java CircleP3.java RectangleP3.java TriangleP3.java
More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario
 More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario The Story So Far... Classes as collections of fields and methods. Methods can access fields, and
More About Classes CS 1025 Computer Science Fundamentals I Stephen M. Watt University of Western Ontario The Story So Far... Classes as collections of fields and methods. Methods can access fields, and
Abstract Classes Interfaces CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development
 Abstract Classes Interfaces CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development Jeffrey Miller, Ph.D. jeffrey.miller@usc.edu Abstract Classes Outline USC CSCI 201L Abstract Classes An abstract class is a way for
Abstract Classes Interfaces CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development Jeffrey Miller, Ph.D. jeffrey.miller@usc.edu Abstract Classes Outline USC CSCI 201L Abstract Classes An abstract class is a way for
Abstract Classes Interfaces CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development
 Abstract Classes Interfaces CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development Jeffrey Miller, Ph.D. jeffrey.miller@usc.edu Abstract Classes Outline USC CSCI 201L Abstract Classes An abstract class is a way for
Abstract Classes Interfaces CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development Jeffrey Miller, Ph.D. jeffrey.miller@usc.edu Abstract Classes Outline USC CSCI 201L Abstract Classes An abstract class is a way for
COMP 401 PATTERNS, INTERFACES AND OBJECTEDITOR. Instructor: Prasun Dewan
 COMP 401 PATTERNS, INTERFACES AND OBJECTEDITOR Instructor: Prasun Dewan A TALE OF TWO PIAZZA THREADS In part 1 of Assignment 5, we are required to create a line class that implements the line pattern for
COMP 401 PATTERNS, INTERFACES AND OBJECTEDITOR Instructor: Prasun Dewan A TALE OF TWO PIAZZA THREADS In part 1 of Assignment 5, we are required to create a line class that implements the line pattern for
Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the
Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the
Classes. Classes. Classes. Class Circle with methods. Class Circle with fields. Classes and Objects in Java. Introduce to classes and objects in Java.
 Classes Introduce to classes and objects in Java. Classes and Objects in Java Understand how some of the OO concepts learnt so far are supported in Java. Understand important features in Java classes.
Classes Introduce to classes and objects in Java. Classes and Objects in Java Understand how some of the OO concepts learnt so far are supported in Java. Understand important features in Java classes.
Programming 2. Inheritance & Polymorphism
 Programming 2 Inheritance & Polymorphism Motivation Lame Shape Application public class LameShapeApplication { Rectangle[] therects=new Rectangle[100]; Circle[] thecircles=new Circle[100]; Triangle[] thetriangles=new
Programming 2 Inheritance & Polymorphism Motivation Lame Shape Application public class LameShapeApplication { Rectangle[] therects=new Rectangle[100]; Circle[] thecircles=new Circle[100]; Triangle[] thetriangles=new
Outline. Inheritance. Abstract Classes Interfaces. Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism.
 Outline Inheritance Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism Abstract Classes Interfaces 1 OOP Principles Encapsulation Methods and data are combined in classes Not
Outline Inheritance Class Extension Overriding Methods Inheritance and Constructors Polymorphism Abstract Classes Interfaces 1 OOP Principles Encapsulation Methods and data are combined in classes Not
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 26 March 23, 2016 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch Chapter 24 Inheritance Example public class { private int x; public () { x = 0; } public void incby(int
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 26 March 23, 2016 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch Chapter 24 Inheritance Example public class { private int x; public () { x = 0; } public void incby(int
Object Oriented Programming. Week 1 Part 3 Writing Java with Eclipse and JUnit
 Object Oriented Programming Part 3 Writing Java with Eclipse and JUnit Today's Lecture Test Driven Development Review (TDD) Building up a class using TDD Adding a Class using Test Driven Development in
Object Oriented Programming Part 3 Writing Java with Eclipse and JUnit Today's Lecture Test Driven Development Review (TDD) Building up a class using TDD Adding a Class using Test Driven Development in
CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
 CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) OBJECT-ORIENTED
CH. 2 OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016) OBJECT-ORIENTED
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance (part II) Polymorphism Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance (part II) Polymorphism Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes
CS170 Introduction to Computer Science Midterm 2
 CS170 Introduction to Computer Science Midterm 2 03/25/2009 Name: Solution You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed book and closednotes exam, and you are not to use any other resource than
CS170 Introduction to Computer Science Midterm 2 03/25/2009 Name: Solution You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed book and closednotes exam, and you are not to use any other resource than
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance (part II) Polymorphism Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Inheritance (part II) Polymorphism Version of January 21, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes
CSCE145 Test 2-Review 03/29/2015 Hongkai Yu
 CSCE145 Test 2-Review 03/29/2015 Hongkai Yu 1. What results are printed when the main method in TestBase is executed? public class Base private int value; public Base(int x) value = x; System.out.println(
CSCE145 Test 2-Review 03/29/2015 Hongkai Yu 1. What results are printed when the main method in TestBase is executed? public class Base private int value; public Base(int x) value = x; System.out.println(
Inheritance Systems. Merchandise. Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress 9.1.1
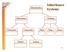 Merchandise Inheritance Systems Electronics Clothing Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress Digital Analog 9.1.1 Another AcademicDisciplines Hierarchy Mathematics Engineering Algebra Probability Geometry
Merchandise Inheritance Systems Electronics Clothing Television Camcorder Shirt Shoe Dress Digital Analog 9.1.1 Another AcademicDisciplines Hierarchy Mathematics Engineering Algebra Probability Geometry
Java Programming. U Hou Lok. Java Aug., Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Taiwan University
 Java Programming U Hou Lok Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Taiwan University Java 272 8 19 Aug., 2016 U Hou Lok Java Programming 1 / 51 A Math Toolbox: Math Class The
Java Programming U Hou Lok Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Taiwan University Java 272 8 19 Aug., 2016 U Hou Lok Java Programming 1 / 51 A Math Toolbox: Math Class The
CSCI-142 Exam 1 Review September 25, 2016 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community
 CSCI-12 Exam 1 Review September 25, 2016 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community http://csc.cs.rit.edu 1. Provide a detailed explanation of what the following code does: 1 public boolean checkstring
CSCI-12 Exam 1 Review September 25, 2016 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community http://csc.cs.rit.edu 1. Provide a detailed explanation of what the following code does: 1 public boolean checkstring
Reusing Classes. Hendrik Speleers
 Hendrik Speleers Overview Composition Inheritance Polymorphism Method overloading vs. overriding Visibility of variables and methods Specification of a contract Abstract classes, interfaces Software development
Hendrik Speleers Overview Composition Inheritance Polymorphism Method overloading vs. overriding Visibility of variables and methods Specification of a contract Abstract classes, interfaces Software development
Object Oriented Programming. Java-Lecture 11 Polymorphism
 Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 11 Polymorphism Abstract Classes and Methods There will be a situation where you want to develop a design of a class which is common to many classes. Abstract class
Object Oriented Programming Java-Lecture 11 Polymorphism Abstract Classes and Methods There will be a situation where you want to develop a design of a class which is common to many classes. Abstract class
Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap. Inheritance & Polymorphism 1
 Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap Inheritance & Polymorphism 1 Introduction! Besides composition, another form of reuse is inheritance.! With inheritance, an object can inherit behavior from another object,
Inheritance & Polymorphism Recap Inheritance & Polymorphism 1 Introduction! Besides composition, another form of reuse is inheritance.! With inheritance, an object can inherit behavior from another object,
Interfaces. Relatedness of types. Interface as a contract. The area and perimeter of shapes 7/15/15. Savitch ch. 8.4
 Relatedness of types Interfaces Savitch ch. 8.4 Consider the task of writing classes to represent 2D shapes such as Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle. There are certain attributes or operations that are
Relatedness of types Interfaces Savitch ch. 8.4 Consider the task of writing classes to represent 2D shapes such as Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle. There are certain attributes or operations that are
1.00/ Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving. Quiz 2 / November 5, 2004
 1.00/1.001 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Quiz 2 / November 5, 2004 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do
1.00/1.001 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Quiz 2 / November 5, 2004 Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have 90 minutes to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do
Java Object Oriented Design. CSC207 Fall 2014
 Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
index.pdf January 21,
 index.pdf January 21, 2013 1 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Circle Let s complete the implementation of the class Circle. Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Version
index.pdf January 21, 2013 1 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Circle Let s complete the implementation of the class Circle. Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Version
중간고사 학과학번이름. 1. Point 클래스이다. 다음물음에답하라. (40 점 ) 단국대학교응용컴퓨터공학 JAVA 프로그래밍 I 중간고사 (2016 년가을학기 ) 2016 년 10 월 27 일 담당교수 : 단국대학교응용컴퓨터공학박경신
 중간고사 담당교수 : 단국대학교응용컴퓨터공학박경신 답은반드시답안지에기술할것. 공간이부족할경우반드시답안지몇쪽의뒤에있다고명기한후기술할것. 그외의경우의답안지뒤쪽이나연습지에기술한내용은답안으로인정안함. 답에는반드시네모를쳐서확실히표시할것. 답안지에학과, 학번, 이름외에본인의암호 (4자리숫자 ) 를기입하면성적공고시학번대신암호를사용할것임. 1. Point 클래스이다. 다음물음에답하라.
중간고사 담당교수 : 단국대학교응용컴퓨터공학박경신 답은반드시답안지에기술할것. 공간이부족할경우반드시답안지몇쪽의뒤에있다고명기한후기술할것. 그외의경우의답안지뒤쪽이나연습지에기술한내용은답안으로인정안함. 답에는반드시네모를쳐서확실히표시할것. 답안지에학과, 학번, 이름외에본인의암호 (4자리숫자 ) 를기입하면성적공고시학번대신암호를사용할것임. 1. Point 클래스이다. 다음물음에답하라.
Advanced Placement Computer Science. Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Advanced Placement Computer Science Inheritance and Polymorphism What s past is prologue. Don t write it twice write it once and reuse it. Mike Scott The University of Texas at Austin Inheritance, Polymorphism,
Advanced Placement Computer Science Inheritance and Polymorphism What s past is prologue. Don t write it twice write it once and reuse it. Mike Scott The University of Texas at Austin Inheritance, Polymorphism,
In this lab, you will be given the implementation of the classes GeometricObject, Circle, and Rectangle, as shown in the following UML class diagram.
 Jordan University Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Computer Engineering Object-Oriented Problem Solving: CPE 342 Lab-8 Eng. Asma Abdel Karim In this lab, you will be given the implementation
Jordan University Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Computer Engineering Object-Oriented Problem Solving: CPE 342 Lab-8 Eng. Asma Abdel Karim In this lab, you will be given the implementation
Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and IT (North Jeddah Branch) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@kau.edu.sa www.sanlp.org/malik/cpit305/ap.html
Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and IT (North Jeddah Branch) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@kau.edu.sa www.sanlp.org/malik/cpit305/ap.html
Inheritance. EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Inheritance EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Why Inheritance: A Motivating Example Problem: A student management system stores data about students. There are two
Inheritance EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Why Inheritance: A Motivating Example Problem: A student management system stores data about students. There are two
COMP200 INHERITANCE. OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed
 1 1 COMP200 INHERITANCE OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed 2 Inheritance Derive new classes (subclass) from existing ones (superclass). Only the Object class (java.lang) has no superclass Every
1 1 COMP200 INHERITANCE OOP using Java, from slides by Shayan Javed 2 Inheritance Derive new classes (subclass) from existing ones (superclass). Only the Object class (java.lang) has no superclass Every
Chapter 14 Abstract Classes and Interfaces
 Chapter 14 Abstract Classes and Interfaces 1 What is abstract class? Abstract class is just like other class, but it marks with abstract keyword. In abstract class, methods that we want to be overridden
Chapter 14 Abstract Classes and Interfaces 1 What is abstract class? Abstract class is just like other class, but it marks with abstract keyword. In abstract class, methods that we want to be overridden
Inheritance, and Polymorphism.
 Inheritance and Polymorphism by Yukong Zhang Object-oriented programming languages are the most widely used modern programming languages. They model programming based on objects which are very close to
Inheritance and Polymorphism by Yukong Zhang Object-oriented programming languages are the most widely used modern programming languages. They model programming based on objects which are very close to
Generics in Java. EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Generics in Java EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Motivating Example: A Book of Objects 1 class Book { 2 String[] names; 3 Object[] records; 4 /* add a name-record
Generics in Java EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Motivating Example: A Book of Objects 1 class Book { 2 String[] names; 3 Object[] records; 4 /* add a name-record
Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2)
 Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2) Table of Contents 1 Reusing Classes... 2 1.1 Composition... 2 1.2 Inheritance... 4 1.2.1 Extending Classes... 5 1.2.2 Method Overriding... 7 1.2.3
Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2) Table of Contents 1 Reusing Classes... 2 1.1 Composition... 2 1.2 Inheritance... 4 1.2.1 Extending Classes... 5 1.2.2 Method Overriding... 7 1.2.3
Motivating Example: Observations (1) Generics in Java. Motivating Example: A Book of Objects. Motivating Example: Observations (2)
 Motivating Example: Observations (1) Generics in Java EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG In the Book class: By declaring the attribute Object[] records We meant that
Motivating Example: Observations (1) Generics in Java EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG In the Book class: By declaring the attribute Object[] records We meant that
Topic 5 Polymorphism. " Inheritance is new code that reuses old code. Polymorphism is old code that reuses new code.
 Topic 5 Polymorphism " Inheritance is new code that reuses old code. Polymorphism is old code that reuses new code. 1 Polymorphism Another feature of OOP literally having many forms object variables in
Topic 5 Polymorphism " Inheritance is new code that reuses old code. Polymorphism is old code that reuses new code. 1 Polymorphism Another feature of OOP literally having many forms object variables in
Lecture 12: Classes II
 Lecture 12: Classes II Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Encapsulation Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding
Lecture 12: Classes II Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Encapsulation Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding
No Inheritance: ResidentStudent Class. Inheritance. Why Inheritance: A Motivating Example. No Inheritance: NonResidentStudent Class
 No Inheritance: ResidentStudent Class Inheritance EECS23 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 218 CHEN-WEI WANG class ResidentStudent { String ; Course[] ; int ; double premiumrate; /* there s
No Inheritance: ResidentStudent Class Inheritance EECS23 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 218 CHEN-WEI WANG class ResidentStudent { String ; Course[] ; int ; double premiumrate; /* there s
Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Inheritance and Polymorphism Recitation 10/(16,17)/2008 CS 180 Department of Computer Science, Purdue University Project 5 Due Wed, Oct. 22 at 10 pm. All questions on the class newsgroup. Make use of lab
Inheritance and Polymorphism Recitation 10/(16,17)/2008 CS 180 Department of Computer Science, Purdue University Project 5 Due Wed, Oct. 22 at 10 pm. All questions on the class newsgroup. Make use of lab
Method Overriding in Java
 Method Overriding in Java Whenever same method name is existing in both base class and derived class with same types of parameters or same order of parameters is known as method Overriding. Method must
Method Overriding in Java Whenever same method name is existing in both base class and derived class with same types of parameters or same order of parameters is known as method Overriding. Method must
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 26 March 26, 2015 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch Chapter 24 public interface Displaceable { public int getx(); public int gety(); public void move
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 26 March 26, 2015 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch Chapter 24 public interface Displaceable { public int getx(); public int gety(); public void move
Inheritance. EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Inheritance EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Why Inheritance: A Motivating Example Problem: A student management system stores data about students. There are two kinds
Inheritance EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Why Inheritance: A Motivating Example Problem: A student management system stores data about students. There are two kinds
Lecture Notes Chapter #9_b Inheritance & Polymorphism
 Lecture Notes Chapter #9_b Inheritance & Polymorphism Inheritance results from deriving new classes from existing classes Root Class all java classes are derived from the java.lang.object class GeometricObject1
Lecture Notes Chapter #9_b Inheritance & Polymorphism Inheritance results from deriving new classes from existing classes Root Class all java classes are derived from the java.lang.object class GeometricObject1
Interfaces Java. Overview. n Java interfaces. q Introduction. q Sintaxe. q UML notation. q Multi-inheritance of interfaces
 Interfaces Java jvo@ualg.pt José Valente de Oliveira 11-1 Overview n Java interfaces q Introduction q Sintaxe q UML notation q Multi-inheritance of interfaces q (Some) Java pre-defined interfaces q Design
Interfaces Java jvo@ualg.pt José Valente de Oliveira 11-1 Overview n Java interfaces q Introduction q Sintaxe q UML notation q Multi-inheritance of interfaces q (Some) Java pre-defined interfaces q Design
CISC 3115 Modern Programming Techniques Spring 2018 Section TY3 Exam 2 Solutions
 Name CISC 3115 Modern Programming Techniques Spring 2018 Section TY3 Exam 2 Solutions 1. a. (25 points) A rational number is a number that can be represented by a pair of integers a numerator and a denominator.
Name CISC 3115 Modern Programming Techniques Spring 2018 Section TY3 Exam 2 Solutions 1. a. (25 points) A rational number is a number that can be represented by a pair of integers a numerator and a denominator.
Polymorphism CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development
 Polymorphism CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development Jeffrey Miller, Ph.D. jeffrey.miller@usc.edu Program Outline USC CSCI 201L Polymorphism Based on the inheritance hierarchy, an object with a compile-time
Polymorphism CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development Jeffrey Miller, Ph.D. jeffrey.miller@usc.edu Program Outline USC CSCI 201L Polymorphism Based on the inheritance hierarchy, an object with a compile-time
Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism. Motivations. Suppose you will define classes to model circles,
 Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the best way to design
Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the best way to design
COMP 250. inheritance (cont.) interfaces abstract classes
 COMP 250 Lecture 31 inheritance (cont.) interfaces abstract classes Nov. 20, 2017 1 https//goo.gl/forms/ymqdaeilt7vxpnzs2 2 class Object boolean equals( Object ) int hashcode( ) String tostring( ) Object
COMP 250 Lecture 31 inheritance (cont.) interfaces abstract classes Nov. 20, 2017 1 https//goo.gl/forms/ymqdaeilt7vxpnzs2 2 class Object boolean equals( Object ) int hashcode( ) String tostring( ) Object
CS-140 Fall 2017 Test 1 Version Practice Practice for Nov. 20, Name:
 CS-140 Fall 2017 Test 1 Version Practice Practice for Nov. 20, 2017 Name: 1. (10 points) For the following, Check T if the statement is true, the F if the statement is false. (a) T F : If a child overrides
CS-140 Fall 2017 Test 1 Version Practice Practice for Nov. 20, 2017 Name: 1. (10 points) For the following, Check T if the statement is true, the F if the statement is false. (a) T F : If a child overrides
Chapter 21- Using Generics Case Study: Geometric Bunch. Class: Driver. package csu.matos; import java.util.arraylist; public class Driver {
 Chapter 21- Using Generics Case Study: Geometric Bunch In this example a class called GeometricBunch is made to wrap around a list of GeometricObjects. Circle and Rectangle are subclasses of GeometricObject.
Chapter 21- Using Generics Case Study: Geometric Bunch In this example a class called GeometricBunch is made to wrap around a list of GeometricObjects. Circle and Rectangle are subclasses of GeometricObject.
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 25 November 1, 2017 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch (Chapter 24) Announcements HW7: Chat Client Available Soon Due: Tuesday, November 14 th at 11:59pm
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 25 November 1, 2017 Inheritance and Dynamic Dispatch (Chapter 24) Announcements HW7: Chat Client Available Soon Due: Tuesday, November 14 th at 11:59pm
COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism
 COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism Ibrahim Albluwi Composition A GuitarString has a RingBuffer. A MarkovModel has a Symbol Table. A Symbol Table has a Binary
COS226 - Spring 2018 Class Meeting # 13 March 26, 2018 Inheritance & Polymorphism Ibrahim Albluwi Composition A GuitarString has a RingBuffer. A MarkovModel has a Symbol Table. A Symbol Table has a Binary
25. Generic Programming
 25. Generic Programming Java Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Generic Programming Outline Polymorphism and Generic Programming Casting Objects and the instanceof Operator The protected Data and
25. Generic Programming Java Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Generic Programming Outline Polymorphism and Generic Programming Casting Objects and the instanceof Operator The protected Data and
About This Lecture. Data Abstraction - Interfaces and Implementations. Outline. Object Concepts. Object Class, Protocol and State.
 Revised 01/09/05 About This Lecture Slide # 2 Data Abstraction - Interfaces and Implementations In this lecture we will learn how Java objects and classes can be used to build abstract data types. CMPUT
Revised 01/09/05 About This Lecture Slide # 2 Data Abstraction - Interfaces and Implementations In this lecture we will learn how Java objects and classes can be used to build abstract data types. CMPUT
CSEN 202: Introduction to Computer Programming
 June 23, 2012 : Final exam Model Solutions Instructions. Please read carefully before proceeding. (a) The duration of this exam is 180 minutes. (b) Non-programmable calculators are allowed. (c) No books
June 23, 2012 : Final exam Model Solutions Instructions. Please read carefully before proceeding. (a) The duration of this exam is 180 minutes. (b) Non-programmable calculators are allowed. (c) No books
Constants are named in ALL_CAPS, using upper case letters and underscores in their names.
 Naming conventions in Java The method signature Invoking methods All class names are capitalized Variable names and method names start with a lower case letter, but every word in the name after the first
Naming conventions in Java The method signature Invoking methods All class names are capitalized Variable names and method names start with a lower case letter, but every word in the name after the first
CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Java
CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Java
Derived and abstract data types. TDT4205 Lecture 15
 1 Derived and abstract data types TDT4205 Lecture 15 2 Where we were We ve looked at static semantics for primitive types and how it relates to type checking We ve hinted at derived types using a multidimensional
1 Derived and abstract data types TDT4205 Lecture 15 2 Where we were We ve looked at static semantics for primitive types and how it relates to type checking We ve hinted at derived types using a multidimensional
Documenting, Using, and Testing Utility Classes
 Documenting, Using, and Testing Utility Classes Readings: Chapter 2 of the Course Notes EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Structure of Project: Packages and Classes
Documenting, Using, and Testing Utility Classes Readings: Chapter 2 of the Course Notes EECS2030: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Structure of Project: Packages and Classes
Inheritance (Extends) Overriding methods IS-A Vs. HAS-A Polymorphism. superclass. is-a. subclass
 Inheritance and Polymorphism Inheritance (Extends) Overriding methods IS-A Vs. HAS-A Polymorphism Inheritance (semantics) We now have two classes that do essentially the same thing The fields are exactly
Inheritance and Polymorphism Inheritance (Extends) Overriding methods IS-A Vs. HAS-A Polymorphism Inheritance (semantics) We now have two classes that do essentially the same thing The fields are exactly
Java Programming. Abstract classes and Interfaces
 Java Programming Abstract classes and Interfaces Classes A class is composed of data methods public class Rectangle { private double width, height; public Rectangle(double width, double height) { this.width=
Java Programming Abstract classes and Interfaces Classes A class is composed of data methods public class Rectangle { private double width, height; public Rectangle(double width, double height) { this.width=
An introduction to Java II
 An introduction to Java II Bruce Eckel, Thinking in Java, 4th edition, PrenticeHall, New Jersey, cf. http://mindview.net/books/tij4 jvo@ualg.pt José Valente de Oliveira 4-1 Java: Generalities A little
An introduction to Java II Bruce Eckel, Thinking in Java, 4th edition, PrenticeHall, New Jersey, cf. http://mindview.net/books/tij4 jvo@ualg.pt José Valente de Oliveira 4-1 Java: Generalities A little
Polymorphism and Interfaces. CGS 3416 Spring 2018
 Polymorphism and Interfaces CGS 3416 Spring 2018 Polymorphism and Dynamic Binding If a piece of code is designed to work with an object of type X, it will also work with an object of a class type that
Polymorphism and Interfaces CGS 3416 Spring 2018 Polymorphism and Dynamic Binding If a piece of code is designed to work with an object of type X, it will also work with an object of a class type that
Lesson11-Inheritance-Abstract-Classes. The GeometricObject case
 Lesson11-Inheritance-Abstract-Classes The GeometricObject case GeometricObject class public abstract class GeometricObject private string color = "White"; private DateTime datecreated = new DateTime(2017,
Lesson11-Inheritance-Abstract-Classes The GeometricObject case GeometricObject class public abstract class GeometricObject private string color = "White"; private DateTime datecreated = new DateTime(2017,
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 24 March 24, 2014 Java ASM Interfaces and Subtyping Announcements HW 07 due tomorrow at midnight Exam 2, in class, a week from Friday (April 4th) The
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 24 March 24, 2014 Java ASM Interfaces and Subtyping Announcements HW 07 due tomorrow at midnight Exam 2, in class, a week from Friday (April 4th) The
Abstract Data Types (ADTs), Classes, and Objects
 Abstract Data Types (ADTs), Classes, and Objects Readings: OOSC2 Chapters 6, 7, 8 EECS3311: Software Design Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Abstract Data Type (ADT) abstract implementation details are not specified!
Abstract Data Types (ADTs), Classes, and Objects Readings: OOSC2 Chapters 6, 7, 8 EECS3311: Software Design Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Abstract Data Type (ADT) abstract implementation details are not specified!
More Java Basics. class Vector { Object[] myarray;... //insert x in the array void insert(object x) {...} Then we can use Vector to hold any objects.
![More Java Basics. class Vector { Object[] myarray;... //insert x in the array void insert(object x) {...} Then we can use Vector to hold any objects. More Java Basics. class Vector { Object[] myarray;... //insert x in the array void insert(object x) {...} Then we can use Vector to hold any objects.](/thumbs/77/74905841.jpg) More Java Basics 1. INHERITANCE AND DYNAMIC TYPE-CASTING Java performs automatic type conversion from a sub-type to a super-type. That is, if a method requires a parameter of type A, we can call the method
More Java Basics 1. INHERITANCE AND DYNAMIC TYPE-CASTING Java performs automatic type conversion from a sub-type to a super-type. That is, if a method requires a parameter of type A, we can call the method
Abstract Classes and Polymorphism CSC 123 Fall 2018 Howard Rosenthal
 Abstract Classes and Polymorphism CSC 123 Fall 2018 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Define and discuss abstract classes Define and discuss abstract methods Introduce polymorphism Much of the information
Abstract Classes and Polymorphism CSC 123 Fall 2018 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Define and discuss abstract classes Define and discuss abstract methods Introduce polymorphism Much of the information
Introduction to OOP with Java. Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017
 Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 11: Inheritance and Polymorphism Part 1 Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad
Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 11: Inheritance and Polymorphism Part 1 Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad
INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Inheritance Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket Extremely common in modern OOP languages Managing
INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Inheritance Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket Extremely common in modern OOP languages Managing
Page 1 of 16. Proctors are unable to respond to queries about the interpretation of exam questions. Do your best to answer exam questions as written.
 Page 1 of 16 HAND IN Answers Are Recorded on Question Paper QUEEN'S UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF COMPUTING CISC212, FALL TERM, 2005 FINAL EXAMINATION 9am to 12noon, 19 DECEMBER 2005 Instructor: Alan McLeod If
Page 1 of 16 HAND IN Answers Are Recorded on Question Paper QUEEN'S UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF COMPUTING CISC212, FALL TERM, 2005 FINAL EXAMINATION 9am to 12noon, 19 DECEMBER 2005 Instructor: Alan McLeod If
- Aggregation - UML diagram - Self-Referential Classes - Generisity
 - Aggregation - UML diagram - Self-Referential Classes - Generisity 1 Class Circle public class Circle private double xcenter; // x center coordinate private double ycenter; // y center coordinate private
- Aggregation - UML diagram - Self-Referential Classes - Generisity 1 Class Circle public class Circle private double xcenter; // x center coordinate private double ycenter; // y center coordinate private
CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2018
 Logistics CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2018 Best and worst programming practices September 11, 2018 Reminder Recap: software architecture vs. design Class website: https://people.cs.umass.edu/~brun/class/2018fall/cs520/
Logistics CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2018 Best and worst programming practices September 11, 2018 Reminder Recap: software architecture vs. design Class website: https://people.cs.umass.edu/~brun/class/2018fall/cs520/
CS18000: Programming I
 CS18000: Programming I Data Abstraction January 25, 2010 Prof. Chris Clifton Announcements Book is available (Draft 2.0) Syllabus updated with readings corresponding to new edition Lab consulting hours
CS18000: Programming I Data Abstraction January 25, 2010 Prof. Chris Clifton Announcements Book is available (Draft 2.0) Syllabus updated with readings corresponding to new edition Lab consulting hours
Announcement. Agenda 7/31/2008. Polymorphism, Dynamic Binding and Interface. The class will continue on Tuesday, 12 th August
 Polymorphism, Dynamic Binding and Interface 2 4 pm Thursday 7/31/2008 @JD2211 1 Announcement Next week is off The class will continue on Tuesday, 12 th August 2 Agenda Review Inheritance Abstract Array
Polymorphism, Dynamic Binding and Interface 2 4 pm Thursday 7/31/2008 @JD2211 1 Announcement Next week is off The class will continue on Tuesday, 12 th August 2 Agenda Review Inheritance Abstract Array
Inheritance and Polymorphism. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Inheritance and Polymorphism CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Model classes with similar properties and methods: Circles, rectangles
Inheritance and Polymorphism CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Model classes with similar properties and methods: Circles, rectangles
Java and OOP. Part 3 Extending classes. OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1
 Java and OOP Part 3 Extending classes OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1 Inheritance Suppose we want a version of an existing class, which is slightly different from it. We want to avoid starting again
Java and OOP Part 3 Extending classes OOP in Java : W. Milner 2005 : Slide 1 Inheritance Suppose we want a version of an existing class, which is slightly different from it. We want to avoid starting again
Java: Classes. An instance of a class is an object based on the class. Creation of an instance from a class is called instantiation.
 Java: Classes Introduction A class defines the abstract characteristics of a thing (object), including its attributes and what it can do. Every Java program is composed of at least one class. From a programming
Java: Classes Introduction A class defines the abstract characteristics of a thing (object), including its attributes and what it can do. Every Java program is composed of at least one class. From a programming
CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2017
 Logistics CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2017 Best and worst programming practices September 12, 2017 Recap: software architecture vs. design Recap: software architecture examples
Logistics CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2017 Best and worst programming practices September 12, 2017 Recap: software architecture vs. design Recap: software architecture examples
On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle
 Berner Fachhochschule Engineering and Information Technology On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle Prof. Dr. Eric Dubuis Berner Fachhochschule, Engineering and Information Technology @ Biel Course
Berner Fachhochschule Engineering and Information Technology On Polymorphism and the Open-Closed Principle Prof. Dr. Eric Dubuis Berner Fachhochschule, Engineering and Information Technology @ Biel Course
Class, Variable, Constructor, Object, Method Questions
 Class, Variable, Constructor, Object, Method Questions http://www.wideskills.com/java-interview-questions/java-classes-andobjects-interview-questions https://www.careerride.com/java-objects-classes-methods.aspx
Class, Variable, Constructor, Object, Method Questions http://www.wideskills.com/java-interview-questions/java-classes-andobjects-interview-questions https://www.careerride.com/java-objects-classes-methods.aspx
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn how to describe objects and classes and how to define classes and create objects
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn how to describe objects and classes and how to define
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn how to describe objects and classes and how to define
Inheritance and objects
 Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket
Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket
CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2017
 CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2017 Best and worst programming practices September 12, 2017 Logistics Recap: software architecture vs. design Specification Architecture Development
CS 520 Theory and Practice of Software Engineering Fall 2017 Best and worst programming practices September 12, 2017 Logistics Recap: software architecture vs. design Specification Architecture Development
We are on the GUI fast track path
 We are on the GUI fast track path Chapter 13: Exception Handling Skip for now Chapter 14: Abstract Classes and Interfaces Sections 1 9: ActionListener interface Chapter 15: Graphics Skip for now Chapter
We are on the GUI fast track path Chapter 13: Exception Handling Skip for now Chapter 14: Abstract Classes and Interfaces Sections 1 9: ActionListener interface Chapter 15: Graphics Skip for now Chapter
Polymorphism: Interfaces and Iteration. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Polymorphism: Interfaces and Iteration Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline A shape object hierarchy Classes that extend Versus classes that implements Java interfaces How Java handles multiple-inheritance
Polymorphism: Interfaces and Iteration Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline A shape object hierarchy Classes that extend Versus classes that implements Java interfaces How Java handles multiple-inheritance
AP CS Unit 6: Inheritance Programs
 AP CS Unit 6: Inheritance Programs Program 1. Complete the Rectangle class. The Rectangle public class Rectangle{ class represents private int x1, y1, x2, y2; a rectangle in a standard coordinate plane
AP CS Unit 6: Inheritance Programs Program 1. Complete the Rectangle class. The Rectangle public class Rectangle{ class represents private int x1, y1, x2, y2; a rectangle in a standard coordinate plane
Multiple Inheritance, Abstract Classes, Interfaces
 Multiple Inheritance, Abstract Classes, Interfaces Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 8 of The Object-Oriented Thought Process by Matt Weisfeld, and other sources. Frameworks
Multiple Inheritance, Abstract Classes, Interfaces Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 8 of The Object-Oriented Thought Process by Matt Weisfeld, and other sources. Frameworks
CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1
 Name: CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1 Directions: Test is closed book, closed notes. Answer every question; write solutions in spaces provided. Use backs of pages for scratch work. Good
Name: CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1 Directions: Test is closed book, closed notes. Answer every question; write solutions in spaces provided. Use backs of pages for scratch work. Good
Classes and Objects. EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Classes and Objects EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Separation of Concerns: App/Tester vs. Model In EECS1022: Model Component: One or More Java Classes e.g., Person
Classes and Objects EECS2030 B: Advanced Object Oriented Programming Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Separation of Concerns: App/Tester vs. Model In EECS1022: Model Component: One or More Java Classes e.g., Person
CS180. Exam 1 Review
 CS180 Exam 1 Review What is the output to the following code? System.out.println("2 + 2 = " + (2 + 2)); System.out.println("2 + 2 = " + 2 + 2); What is the output to the following code? System.out.println(String.valueOf(15+20));
CS180 Exam 1 Review What is the output to the following code? System.out.println("2 + 2 = " + (2 + 2)); System.out.println("2 + 2 = " + 2 + 2); What is the output to the following code? System.out.println(String.valueOf(15+20));
HAS-A Relationship. Association is a relationship where all objects have their own lifecycle and there is no owner.
 HAS-A Relationship Association is a relationship where all objects have their own lifecycle and there is no owner. For example, teacher student Aggregation is a specialized form of association where all
HAS-A Relationship Association is a relationship where all objects have their own lifecycle and there is no owner. For example, teacher student Aggregation is a specialized form of association where all
Object Oriented Programming 2015/16. Final Exam June 28, 2016
 Object Oriented Programming 2015/16 Final Exam June 28, 2016 Directions (read carefully): CLEARLY print your name and ID on every page. The exam contains 8 pages divided into 4 parts. Make sure you have
Object Oriented Programming 2015/16 Final Exam June 28, 2016 Directions (read carefully): CLEARLY print your name and ID on every page. The exam contains 8 pages divided into 4 parts. Make sure you have
Some client code. output. subtype polymorphism As dynamic binding occurs the behavior (i.e., methods) follow the objects. Squarer
 public class Base { protected int theint = 100; System.out.println( theint ); public class Doubler extends Base { System.out.println( theint*2 ); public class Tripler extends Base { System.out.println(
public class Base { protected int theint = 100; System.out.println( theint ); public class Doubler extends Base { System.out.println( theint*2 ); public class Tripler extends Base { System.out.println(
ESc101 : Fundamental of Computing. Object Oriented programming
 ESc101 : Fundamental of Computing I Semester 2008-09 Lecture 22 Object Oriented programming Method Overloading in Java. Constructor Building complex classes using Point class Circle, Triangle,... 1 Method
ESc101 : Fundamental of Computing I Semester 2008-09 Lecture 22 Object Oriented programming Method Overloading in Java. Constructor Building complex classes using Point class Circle, Triangle,... 1 Method
