Arc Consistency and Domain Splitting in CSPs
|
|
|
- Piers Welch
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Arc Consistency and Domain Splitting in CSPs CPSC 322 CSP 3 Textbook Poole and Mackworth: 4.5 and 4.6 Lecturer: Alan Mackworth October 3, 2012
2 Lecture Overview Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) - Recap: Generate & Test - Recap: Graph search Arc consistency - GAC algorithm - Complexity analysis - Domain splitting 2
3 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs): Definition Definition: A constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) consists of: a set of variables V a domain dom(v) for each variable V V a set of constraints C Definition: A possible world of a CSP is an assignment of values to all of its variables. Definition: A model of a CSP is a possible world that satisfies all constraints. An example CSP: V = {V 1,V 2 } dom(v 1 ) = {1,2,3} dom(v 2 ) = {1,2} C = {C 1,C 2,C 3 } C 1 : V 2 2 C 2 : V 1 + V 2 < 5 C 3 : V 1 > V 2 Possible worlds for this CSP: {V 1 =1, V 2 =1} {V 1 =1, V 2 =2} {V 1 =2, V 2 =1} (one model) {V 1 =2, V 2 =2} {V 1 =3, V 2 =1} (another model) {V 1 =3, V 2 =2} 3
4 Generate and Test (G&T) Algorithms Generate and Test: - Generate possible worlds one at a time. - Test constraints for each one. Example: 3 variables A,B,C For a in dom(a) For b in dom(b) For c in dom(c) if {A=a, B=b, C=c} satisfies all constraints return {A=a, B=b, C=c} fail Simple, but slow: - k variables, each domain size d, c constraints: O(cd k ) 4
5 Lecture Overview Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) - Recap: Generate & Test - Recap: Graph search Arc consistency - GAC algorithm - Complexity analysis - Domain splitting 5
6 Backtracking algorithms Explore search space via DFS but evaluate each constraint as soon as all its variables are bound. Any partial assignment that doesn t satisfy the constraint can be pruned. Example: - 3 variables A, B,C, each with domain {1,2,3,4} - {A = 1, B = 1} is inconsistent with constraint A B regardless of the value of the other variables Fail. Prune! 6
7 CSP as Graph Searching Check unary constraints on V 1 If not satisfied PRUNE V 1 = v 1 {} V 1 = v k Check constraints on V 1 and V 2 If not satisfied PRUNE V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v 1 V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v 2 V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v k V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v 1 V 3 = v 1 V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v 1 V 3 = v 2
8 Standard Search vs. Specific R&R systems Constraint Satisfaction (Problems): State: assignments of values to a subset of the variables Successor function: assign values to a free variable Goal test: all variables assigned a value and all constraints satisfied? Solution: possible world that satisfies the constraints Heuristic function: none (all solutions at the same distance from start) Planning : State Successor function Goal test Solution Heuristic function Inference State Successor function Goal test Solution Heuristic function 8
9 CSP as Graph Searching Check unary constraints on V 1 If not satisfied PRUNE V 1 = v 1 {} V 1 = v k Check constraints on V 1 and V 2 If not satisfied PRUNE V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v 1 V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v 2 V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v k V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v 1 V 3 = v 1 V 1 = v 1 V 2 = v 1 V 3 = v 2 Problem? Performance heavily depends on the order in which variables are considered. E.g. only 2 constraints: V n =V n-1 and V n V n-1
10 CSP as a Search Problem: another formulation States: partial assignment of values to variables Start state: empty assignment Successor function: states with the next variable assigned Assign any previously unassigned variable A state assigns values to some subset of variables: E.g. {V 7 = v 1, V 2 = v 1, V 15 = v 1 } Neighbors of node {V 7 = v 1, V 2 = v 1, V 15 = v 1 }: nodes {V 7 = v 1, V 2 = v 1, V 15 = v 1, V x = y} for some variable V x V \ {V 7, V 2, V 15 } and all values y dom(v x ) Goal state: complete assignments of values to variables that satisfy all constraints That is, models Solution: assignment (the path doesn t matter) 10
11 CSP as Graph Searching 3 Variables: A,B,C. All with domains = {1,2,3,4} Constraints: A<B, B<C
12 Selecting variables in a smart way Backtracking relies on one or more heuristics to select which variables to consider next. - E.g. variable involved in the largest number of constraints: If you are going to fail on this branch, fail early! - Can also be smart about which values to consider first This is a different use of the word heuristic! - Still true in this context Can be computed cheaply during the search Provides guidance to the search algorithm - But not true anymore in this context Estimate of the distance to the goal Both meanings are used frequently in the AI literature. heuristic means serves to discover : goal-oriented. Does not mean unreliable! 12
13 Learning Goals for solving CSPs so far Verify whether a possible world satisfies a set of constraints i.e. whether it is a model - a solution. Implement the Generate-and-Test Algorithm. Explain its disadvantages. Solve a CSP by search (specify neighbors, states, start state, goal state). Compare strategies for CSP search. Implement pruning for DFS search in a CSP. 13
14 Lecture Overview Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) - Recap: Generate & Test - Recap: Graph search Arc consistency - GAC algorithm - Complexity analysis - Domain splitting 14
15 Can we do better than Search? Key idea prune the domains as much as possible before searching for a solution. Def.: A variable is domain consistent if no value of its domain is ruled impossible by any unary constraints. Example: dom(v 2 ) = {1, 2, 3, 4}. V 2 2 Variable V 2 is not domain consistent. - It is domain consistent once we remove 2 from its domain. Trivial for unary constraints. Trickier for k-ary ones. 15
16 Graph Searching Repeats Work 3 Variables: A,B,C. All with domains = {1,2,3,4} Constraints: A<B, B<C A 4 is rediscovered 3 times. So is C 1 - Solution: remove values from A s domain and C s, once and for all
17 Constraint network: definition Def. A constraint network is defined by a graph, with - one node for every variable (drawn as circle) - one node for every constraint (drawn as rectangle) - undirected edges running between variable nodes and constraint nodes whenever a given variable is involved in a given constraint. Example: - Two variables X and Y - One constraint: X<Y X X< Y Y 17
18 Constraint network: definition Def. A constraint network is defined by a graph, with - one node for every variable (drawn as circle) - one node for every constraint (drawn as rectangle) - Edges/arcs running between variable nodes and constraint nodes whenever a given variable is involved in a given constraint. Whiteboard example: 3 Variables A,B,C 3 Constraints: A<B, B<C, A+3=C 6 edges/arcs in the constraint network: A,A<B, B,A<B B,B<C, C,B<C A, A+3=C, C,A+3=C 18
19 A more complicated example How many variables are there in this constraint network? Variables are drawn as circles How many constraints are there? Constraints are drawn as rectangles 19
20 Arc Consistency Definition: An arc <x, r(x,y)> is arc consistent if for each value x in dom(x) there is some value y in dom(y) such that r(x,y) is satisfied. A network is arc consistent if all its arcs are arc consistent. A 1,2,3 A< B 2,3 B Is this arc consistent? A Not arc consistent: No value in domain of B that satisfies A<B if A=3 T F T F Arc consistent: Both B=2 and B=3 have ok values for A (e.g. A=1) 2,5,7 A< B/2 2,3,13 B 20
21 How can we enforce Arc Consistency? If an arc <X, r(x,y)> is not arc consistent - Delete all values x in dom(x) for which there is no corresponding value in dom(y) - This deletion makes the arc <X, r(x,y)> arc consistent. - This removal can never rule out any models/solutions Why? X 2,3,4 X< Y 1,2,3 Y Run this example: in ( (Save to a local file and open file.) 21
22 Lecture Overview Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) - Recap: Generate & Test - Recap: Graph search Arc consistency - GAC algorithm - Complexity analysis - Domain splitting 22
23 Arc Consistency Algorithm: high level strategy Consider the arcs in turn, making each arc consistent Reconsider arcs that could be made inconsistent again by this pruning of the domains Eventually reach a fixed point : all arcs consistent Run simple problem 1 in AIspace for an example: 23
24 Which arcs need to be reconsidered? When we reduce the domain of a variable X to make an arc X,c arc consistent, which arcs do we need to reconsider? Z 1 T c 1 H Z 2 E S c 2 Z 3 E c 3 X every arc Z,c' where c c involves Z and X: c Y c 4 A You do not need to reconsider other arcs - If arc Y,c was arc consistent before, it will still be arc consistent - If an arc X,c' was arc consistent before, it will still be arc consistent - Nothing changes for arcs of constraints not involving X 24
25 Which arcs need to be reconsidered? Consider the arcs in turn, making each arc consistent Reconsider arcs that could be made inconsistent again by this pruning DO trace on simple problem 1 and on scheduling problem 1, trying to predict - which arcs are not consistent and - which arcs need to be reconsidered after each removal in 25
26 TDA: ToDoArcs, blue arcs in AIspace Arc consistency algorithm (for binary constraints) Procedure GAC(V,dom,C) Inputs V: a set of variables dom: a function such that dom(x) is the domain of variable X C: set of constraints to be satisfied Output arc-consistent domains for each variable Local D X is a set of values for each variable X TDA is a set of arcs 1: for each variable X do 2: D X dom(x) 3: TDA { X,c X V, c C and X scope(c)} 4: while (TDA {}) 5: select X,c TDA 6: TDA TDA \ { X,c } ND X : values x for X for which there a value for y supporting x Scope of constraint c is the set of variables involved in that constraint X s domain changed: arcs (Z,c ) for variables Z sharing a constraint c with X could become inconsistent 7: ND X {x x D X and y D Y s.t. (x, y) satisfies c} 8: if (ND X D X ) then 9: TDA TDA { Z,c' X scope(c'), c' c, Z scope(c') \ {X} } 10: D X ND X 11: return {D X X is a variable} 26
27 Arc Consistency Algorithm: Interpreting Outcomes Three possible outcomes (when all arcs are arc consistent): Each domain has a single value, e.g. (Download the file and load it as a local file in AIspace) We have a (unique) solution. At least one domain is empty, e.g. No solution! All values are ruled out for this variable. Some domains have more than one value, e.g. built-in example simple problem 2 There may be a solution, multiple ones, or none Need to solve this new CSP (usually simpler) problem: same constraints, domains have been reduced
28 Lecture Overview Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) - Recap: Generate & Test - Recap: Graph search Arc consistency - GAC algorithm - Complexity analysis - Domain splitting 28
29 Arc Consistency Algorithm: Complexity Worst-case complexity of arc consistency procedure on a problem with N variables let d be the max size of a variable domain let c be the number of constraints How often will we prune the domain of variable V? O(d) times How many arcs will be put on the ToDoArc list when pruning domain of variable V? - O(degree of variable V) - In total, across all variables: sum of degrees of all variables = 2*number of constraints, i.e. 2*c Together: we will only put O(dc) arcs on the ToDoArc list Checking consistency is O(d 2 ) for each of them Overall complexity: O(cd 3 ) Compare to O(d N ) of DFS!! Arc consistency is MUCH faster
30 Lecture Overview Solving Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) - Recap: Generate & Test - Recap: Graph search Arc consistency - GAC algorithm - Complexity analysis - Domain splitting 30
31 Can we have an arc consistent network with non-empty domains that has no solution? YES NO Example: vars A, B, C with domain {1, 2} and constraints A B, B C, A C Or see AIspace CSP applet Simple Problem 2
32 Domain splitting (or case analysis) Arc consistency ends: Some domains have more than one value may or may not have a solution A. Apply Depth-First Search with Pruning or B. Split the problem in a number of disjoint cases: CSP with dom(x) = {x 1, x 2, x 3, x 4 } becomes CSP 1 with dom(x) = {x 1, x 2 } and CSP 2 with dom(x) = {x 3, x 4 } Solution to CSP is the union of solutions to CSP i 32
33 Domain splitting Each smaller CSP is easier to solve Arc consistency might already solve it For each subcsp, which arcs have to be on the ToDoArcs list when we get the subcsp by splitting the domain of X? arcs <Z, r(z,x)> arcs <Z, r(z,x)> and <X, r(z,x)> All arcs A 1 T c 1 H A 2 E S c 2 A 3 E c 3 X c T H I S Y c 4 A
34 Domain splitting in action Trace it on simple problem 2
35 Searching by domain splitting CSP, apply AC If domains with multiple values Split on one CSP 1, apply AC If domains with multiple values Split on one CSP 2, apply AC If domains with multiple values..split on one How many CSPs do we need to keep around at a time? With depth m and 2 children at each split: O(2m). It s a DFS. 35
36 Learning Goals for today s class Define/read/write/trace/debug the arc consistency algorithm. Compute its complexity and assess its possible outcomes Define/read/write/trace/debug domain splitting and its integration with arc consistency Coming up: local search, Section 4.8
Lecture 9 Arc Consistency
 Computer Science CPSC 322 Lecture 9 Arc Consistency (4.5, 4.6) Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap of Lecture 8 Arc Consistency for CSP Domain Splitting 2 Problem Type Static Sequential Constraint Satisfaction
Computer Science CPSC 322 Lecture 9 Arc Consistency (4.5, 4.6) Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap of Lecture 8 Arc Consistency for CSP Domain Splitting 2 Problem Type Static Sequential Constraint Satisfaction
Domain Splitting CPSC 322 CSP 4. Textbook 4.6. February 4, 2011
 Domain Splitting CPSC 322 CSP 4 Textbook 4.6 February 4, 2011 Pace Discussion of feedback 2 fine, 1 could go faster 2: recap too long, 3: sometimes rushed later (as a consequence) Coloured card questions
Domain Splitting CPSC 322 CSP 4 Textbook 4.6 February 4, 2011 Pace Discussion of feedback 2 fine, 1 could go faster 2: recap too long, 3: sometimes rushed later (as a consequence) Coloured card questions
CSPs: Arc Consistency & Domain Splitting
 CSPs: Arc Consistency & Domain Splitting Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 13 (Textbook Chpt 4.5,4.6) February, 01, 2010 CPSC 322, Lecture 13 Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap (CSP as search & Constraint
CSPs: Arc Consistency & Domain Splitting Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 13 (Textbook Chpt 4.5,4.6) February, 01, 2010 CPSC 322, Lecture 13 Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap (CSP as search & Constraint
Local Search for CSPs
 Local Search for CSPs Alan Mackworth UBC CS CSP February, 0 Textbook. Lecture Overview Domain splitting: recap, more details & pseudocode Local Search Time-permitting: Stochastic Local Search (start) Searching
Local Search for CSPs Alan Mackworth UBC CS CSP February, 0 Textbook. Lecture Overview Domain splitting: recap, more details & pseudocode Local Search Time-permitting: Stochastic Local Search (start) Searching
CSPs: Search and Arc Consistency
 CSPs: Search and Arc Consistency CPSC 322 CSPs 2 Textbook 4.3 4.5 CSPs: Search and Arc Consistency CPSC 322 CSPs 2, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 Search 3 Consistency 4 Arc Consistency CSPs: Search
CSPs: Search and Arc Consistency CPSC 322 CSPs 2 Textbook 4.3 4.5 CSPs: Search and Arc Consistency CPSC 322 CSPs 2, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 Search 3 Consistency 4 Arc Consistency CSPs: Search
Planning: Wrap up CSP Planning Logic: Intro
 Planning: Wrap up CSP Planning Logic: Intro Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 Planning 3 ebruary 25, 2013 Textbook 8.4, 5.1 GAC vs. AC GAC = Generalized Arc Consistency (for k-ary constraints) AC = Arc Consistency
Planning: Wrap up CSP Planning Logic: Intro Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 Planning 3 ebruary 25, 2013 Textbook 8.4, 5.1 GAC vs. AC GAC = Generalized Arc Consistency (for k-ary constraints) AC = Arc Consistency
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2 Deepak Kumar October 2017 CSP Formulation (as a special case of search) State is defined by n variables x 1, x 2,, x n Variables can take on values from a domain
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Part 2 Deepak Kumar October 2017 CSP Formulation (as a special case of search) State is defined by n variables x 1, x 2,, x n Variables can take on values from a domain
Search with Costs and Heuristic Search
 Search with Costs and Heuristic Search Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 Search 3 January 14, 2013 Textbook 3.5.3, 3.6, 3.6.1 1 Today s Lecture Recap from last lecture, combined with AIspace demo Search with costs:
Search with Costs and Heuristic Search Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 Search 3 January 14, 2013 Textbook 3.5.3, 3.6, 3.6.1 1 Today s Lecture Recap from last lecture, combined with AIspace demo Search with costs:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Chapter 6
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A constraint satisfaction problem consists of three components, X, D, and C: X is a set of variables, {X 1,..., X n }. D is a
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems A constraint satisfaction problem consists of three components, X, D, and C: X is a set of variables, {X 1,..., X n }. D is a
Lecture 18. Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1
 Lecture 18 Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1 Outline Chapter 6 - Constraint Satisfaction Problems Path Consistency & Global Constraints Sudoku Example Backtracking
Lecture 18 Questions? Monday, February 20 CS 430 Artificial Intelligence - Lecture 18 1 Outline Chapter 6 - Constraint Satisfaction Problems Path Consistency & Global Constraints Sudoku Example Backtracking
Branch & Bound (B&B) and Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 Branch & Bound (B&B) and Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 CSP 1 January 25, 2013 P&M textbook 3.7.4 & 4.0-4.2 Lecture Overview Recap Branch & Bound Wrap up of search module
Branch & Bound (B&B) and Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 CSP 1 January 25, 2013 P&M textbook 3.7.4 & 4.0-4.2 Lecture Overview Recap Branch & Bound Wrap up of search module
Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS 580 (001) - Spring 2018 Amarda Shehu Department of Computer Science George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA February 28, 2018 Amarda Shehu (580)
Lecture 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS 580 (001) - Spring 2018 Amarda Shehu Department of Computer Science George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA February 28, 2018 Amarda Shehu (580)
Search. (Textbook Chpt ) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 2. May, 10, CPSC 322, Lecture 2 Slide 1
 Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 2 (Textbook Chpt 3.0-3.4) May, 10, 2012 CPSC 322, Lecture 2 Slide 1 Colored Cards You need to have 4 colored index cards Come and get them from me if you still
Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 2 (Textbook Chpt 3.0-3.4) May, 10, 2012 CPSC 322, Lecture 2 Slide 1 Colored Cards You need to have 4 colored index cards Come and get them from me if you still
Uninformed Search Strategies
 Uninformed Search Strategies Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 Search 2 January 11, 2013 Textbook 3.5 1 Today s Lecture Lecture 4 (2-Search1) Recap Uninformed search + criteria to compare search algorithms - Depth
Uninformed Search Strategies Alan Mackworth UBC CS 322 Search 2 January 11, 2013 Textbook 3.5 1 Today s Lecture Lecture 4 (2-Search1) Recap Uninformed search + criteria to compare search algorithms - Depth
Uniformed Search (cont.)
 Uniformed Search (cont.) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 6 (Textbook finish 3.5) Sept, 16, 2013 CPSC 322, Lecture 6 Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap DFS vs BFS Uninformed Iterative Deepening (IDS) Search
Uniformed Search (cont.) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 6 (Textbook finish 3.5) Sept, 16, 2013 CPSC 322, Lecture 6 Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap DFS vs BFS Uninformed Iterative Deepening (IDS) Search
Uninformed Search. (Textbook Chpt 3.5) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 5. May 18, CPSC 322, Lecture 5 Slide 1
 Uninformed Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 5 (Textbook Chpt 3.5) May 18, 2017 CPSC 322, Lecture 5 Slide 1 Recap Search is a key computational mechanism in many AI agents We will study the basic
Uninformed Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 5 (Textbook Chpt 3.5) May 18, 2017 CPSC 322, Lecture 5 Slide 1 Recap Search is a key computational mechanism in many AI agents We will study the basic
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CPSC 322 CSP 1 Poole & Mackworth textbook: Sections 4.0-4.2 Lecturer: Alan Mackworth September 28, 2012 Problem Type Static Sequential Constraint Satisfaction Logic
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CPSC 322 CSP 1 Poole & Mackworth textbook: Sections 4.0-4.2 Lecturer: Alan Mackworth September 28, 2012 Problem Type Static Sequential Constraint Satisfaction Logic
Recap Arc Consistency Example Local Search Hill Climbing. Local Search. CPSC 322 CSPs 4. Textbook 4.8. Local Search CPSC 322 CSPs 4, Slide 1
 Local Search CPSC 322 CSPs 4 Textbook 4.8 Local Search CPSC 322 CSPs 4, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 Arc Consistency Example 3 Local Search 4 Hill Climbing Local Search CPSC 322 CSPs 4, Slide 2 Arc
Local Search CPSC 322 CSPs 4 Textbook 4.8 Local Search CPSC 322 CSPs 4, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 Arc Consistency Example 3 Local Search 4 Hill Climbing Local Search CPSC 322 CSPs 4, Slide 2 Arc
General Methods and Search Algorithms
 DM811 HEURISTICS AND LOCAL SEARCH ALGORITHMS FOR COMBINATORIAL OPTIMZATION Lecture 3 General Methods and Search Algorithms Marco Chiarandini 2 Methods and Algorithms A Method is a general framework for
DM811 HEURISTICS AND LOCAL SEARCH ALGORITHMS FOR COMBINATORIAL OPTIMZATION Lecture 3 General Methods and Search Algorithms Marco Chiarandini 2 Methods and Algorithms A Method is a general framework for
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Inference The core topic of the following lectures
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Inference The core topic of the following lectures
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (Backtracking Search)
 CSC8:"Introducon"to"Arficial"Intelligence" Constraint Satisfaction Problems (Backtracking Search) Chapter 6 6.: Formalism 6.: Constraint Propagation 6.: Backtracking Search for CSP 6. is about local search
CSC8:"Introducon"to"Arficial"Intelligence" Constraint Satisfaction Problems (Backtracking Search) Chapter 6 6.: Formalism 6.: Constraint Propagation 6.: Backtracking Search for CSP 6. is about local search
Outline. Best-first search
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Constraint Satisfaction. AI Slides (5e) c Lin
 Constraint Satisfaction 4 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 4 1 4 Constraint Satisfaction 4.1 Constraint satisfaction problems 4.2 Backtracking search 4.3 Constraint propagation 4.4 Local search
Constraint Satisfaction 4 AI Slides (5e) c Lin Zuoquan@PKU 2003-2018 4 1 4 Constraint Satisfaction 4.1 Constraint satisfaction problems 4.2 Backtracking search 4.3 Constraint propagation 4.4 Local search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe Standard search problems: State is a black box : arbitrary data structure Goal test
Constraint Satisfaction Problems slides from: Padhraic Smyth, Bryan Low, S. Russell and P. Norvig, Jean-Claude Latombe Standard search problems: State is a black box : arbitrary data structure Goal test
10/11/2017. Constraint Satisfaction Problems II. Review: CSP Representations. Heuristic 1: Most constrained variable
 //7 Review: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems II AIMA: Chapter 6 A CSP consists of: Finite set of X, X,, X n Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable D, D, D
//7 Review: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems II AIMA: Chapter 6 A CSP consists of: Finite set of X, X,, X n Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable D, D, D
CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION
 9// CONSRAI ISFACION oday Reading AIMA Chapter 6 Goals Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference Search + Inference 9// 8-queens problem How would you go about deciding where to put
9// CONSRAI ISFACION oday Reading AIMA Chapter 6 Goals Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference Search + Inference 9// 8-queens problem How would you go about deciding where to put
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence. Peter Ljunglöf. 30 January, 2018
 DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 7: Constraint satisfaction problems CHAPTER 7: CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 30 January, 2018 1 TABLE
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 7: Constraint satisfaction problems CHAPTER 7: CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 30 January, 2018 1 TABLE
CMU-Q Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro
 CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro AI PLANNING APPROACHES SO FAR Goal: Find the (best) sequence of actions that take
CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 7: Searching in solution space Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro AI PLANNING APPROACHES SO FAR Goal: Find the (best) sequence of actions that take
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Course material: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3 rd Edition,
Constraint Satisfaction Problems CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Course material: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3 rd Edition,
6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions
 6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions Open Book, Open Notes 1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical
6.034 Quiz 1, Spring 2004 Solutions Open Book, Open Notes 1 Tree Search (12 points) Consider the tree shown below. The numbers on the arcs are the arc lengths. Assume that the nodes are expanded in alphabetical
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems In which we see how treating states as more than just little black boxes leads to the invention of a range of powerful new search methods and a deeper understanding of
Constraint Satisfaction Problems In which we see how treating states as more than just little black boxes leads to the invention of a range of powerful new search methods and a deeper understanding of
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D)
 Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-6) CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS Outline What is a CSP CSP applications Backtracking search
Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-6) CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS Outline What is a CSP CSP applications Backtracking search
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction Problem
 CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problem Constraint Satisfaction Problems So far we have seen a problem can be solved by searching in space of states These states can be evaluated
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problem Constraint Satisfaction Problems So far we have seen a problem can be solved by searching in space of states These states can be evaluated
CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION
 CONSRAI ISFACION oday Reading AIMA Read Chapter 6.1-6.3, Skim 6.4-6.5 Goals Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference (Search + Inference) 1 8-queens problem How would you go about
CONSRAI ISFACION oday Reading AIMA Read Chapter 6.1-6.3, Skim 6.4-6.5 Goals Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference (Search + Inference) 1 8-queens problem How would you go about
Local Search. (Textbook Chpt 4.8) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 14. May, 30, CPSC 322, Lecture 14 Slide 1
 Local Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 14 (Textbook Chpt 4.8) May, 30, 2017 CPSC 322, Lecture 14 Slide 1 Announcements Assignment1 due now! Assignment2 out today CPSC 322, Lecture 10 Slide 2 Lecture
Local Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 14 (Textbook Chpt 4.8) May, 30, 2017 CPSC 322, Lecture 14 Slide 1 Announcements Assignment1 due now! Assignment2 out today CPSC 322, Lecture 10 Slide 2 Lecture
Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming
 Outline DM87 SCHEDULING, TIMETABLING AND ROUTING Lecture 3 Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming 1. Special Purpose Algorithms 2. Constraint Programming Marco Chiarandini DM87 Scheduling,
Outline DM87 SCHEDULING, TIMETABLING AND ROUTING Lecture 3 Mathematical Programming Formulations, Constraint Programming 1. Special Purpose Algorithms 2. Constraint Programming Marco Chiarandini DM87 Scheduling,
Constraint Satisfaction
 Constraint Satisfaction Philipp Koehn 1 October 2015 Outline 1 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for
Constraint Satisfaction Philipp Koehn 1 October 2015 Outline 1 Constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for
Today. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence COMP 3501 / COMP Lecture 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) CSP Definition
 Today COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 5 Finish up 2-player games Discuss homework Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. JGH 318 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) CSP s are our first work on factored
Today COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 5 Finish up 2-player games Discuss homework Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. JGH 318 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) CSP s are our first work on factored
Example: Map coloring
 Today s s lecture Local Search Lecture 7: Search - 6 Heuristic Repair CSP and 3-SAT Solving CSPs using Systematic Search. Victor Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 The relationship between problem structure and
Today s s lecture Local Search Lecture 7: Search - 6 Heuristic Repair CSP and 3-SAT Solving CSPs using Systematic Search. Victor Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 The relationship between problem structure and
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Revised by Hankui Zhuo, March 14, 2018 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search
Revised by Hankui Zhuo, March 14, 2018 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search
Announcements. Solution to Assignment 1 is posted Assignment 2 is available Video automatically uploaded (see web page)
 Announcements Solution to Assignment 1 is posted Assignment 2 is available Video automatically uploaded (see web page) c D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2017 CPSC 322 Lecture 4 1 / 27 Review: Searching A frontier
Announcements Solution to Assignment 1 is posted Assignment 2 is available Video automatically uploaded (see web page) c D. Poole and A. Mackworth 2017 CPSC 322 Lecture 4 1 / 27 Review: Searching A frontier
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Announcements. Reminder: CSPs. Today. Example: N-Queens. Example: Map-Coloring. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Announcements Assignment due on Monday 11.59pm Email search.py and searchagent.py to me Next
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 22.0472-001 Fall 2009 Lecture 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems II Announcements Assignment due on Monday 11.59pm Email search.py and searchagent.py to me Next
Lars Schmidt-Thieme, Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL), University of Hildesheim, Germany, Course on Artificial Intelligence,
 Course on Artificial Intelligence, winter term 2012/2013 0/35 Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence 3. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning
Course on Artificial Intelligence, winter term 2012/2013 0/35 Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence 3. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Berlin Chen Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan Normal University References: 1. S. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Berlin Chen Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan Normal University References: 1. S. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence:
Solving Problems by Searching: Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Course 16 :198 :520 : Introduction To Artificial Intelligence Lecture 6 Solving Problems by Searching: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Abdeslam Boularias Wednesday, October 19, 2016 1 / 1 Outline We consider
Course 16 :198 :520 : Introduction To Artificial Intelligence Lecture 6 Solving Problems by Searching: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Abdeslam Boularias Wednesday, October 19, 2016 1 / 1 Outline We consider
What is Search For? CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is Search For? Assumptions about the world: a single agent, deterministic actions, fully observed state, discrete state space Planning:
Artificial Intelligence
 Contents Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller What
Contents Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller What
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller SA-1 Contents
Artificial Intelligence 5. Constraint Satisfaction Problems CSPs as Search Problems, Solving CSPs, Problem Structure Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller SA-1 Contents
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Last update: February 25, 2010 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CMSC 421, Chapter 5 CMSC 421, Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local
Last update: February 25, 2010 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CMSC 421, Chapter 5 CMSC 421, Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local
A fuzzy constraint assigns every possible tuple in a relation a membership degree. The function
 Scribe Notes: 2/13/2013 Presenter: Tony Schnider Scribe: Nate Stender Topic: Soft Constraints (Ch. 9 of CP handbook) Soft Constraints Motivation Soft constraints are used: 1. When we seek to find the best
Scribe Notes: 2/13/2013 Presenter: Tony Schnider Scribe: Nate Stender Topic: Soft Constraints (Ch. 9 of CP handbook) Soft Constraints Motivation Soft constraints are used: 1. When we seek to find the best
Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Thursday: Chapter 8
 Constraint t Satisfaction Problems Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Tuesday: Chapter 7 Thursday: Chapter 8 Outline What is a CSP Backtracking for CSP Local search for
Constraint t Satisfaction Problems Reading: Chapter 6 (3 rd ed.); Chapter 5 (2 nd ed.) For next week: Tuesday: Chapter 7 Thursday: Chapter 8 Outline What is a CSP Backtracking for CSP Local search for
Outline. Best-first search
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/8/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 Today Efficient Solution
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 5: CSPs II 9/8/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 Today Efficient Solution
Logic: TD as search, Datalog (variables)
 Logic: TD as search, Datalog (variables) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 23 (Textbook Chpt 5.2 & some basic concepts from Chpt 12) June, 8, 2017 CPSC 322, Lecture 23 Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap Top
Logic: TD as search, Datalog (variables) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 23 (Textbook Chpt 5.2 & some basic concepts from Chpt 12) June, 8, 2017 CPSC 322, Lecture 23 Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap Top
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Chapter 6 Constraint Satisfaction Problems CS5811 - Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University Outline CSP problem definition Backtracking search
Australia Western Australia Western Territory Northern Territory Northern Australia South Australia South Tasmania Queensland Tasmania Victoria
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Example: Map-Coloring Western Northern Territory South Queensland New South Wales Tasmania Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints:
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Example: Map-Coloring Western Northern Territory South Queensland New South Wales Tasmania Variables WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints:
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Recall Search problems: Find the sequence of actions that leads to the goal. Sequence of actions means a path in the search space. Paths come with
Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Recall Search problems: Find the sequence of actions that leads to the goal. Sequence of actions means a path in the search space. Paths come with
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Comments about assign 1. Quick search recap. Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Search uninformed BFS, DFS, IDS. Adversarial search
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS5 David Kauchak Fall 00 http://www.xkcd.com/78/ Some material borrowed from: Sara Owsley Sood and others Comments about assign Grading actually out of 60 check
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) CS5 David Kauchak Fall 00 http://www.xkcd.com/78/ Some material borrowed from: Sara Owsley Sood and others Comments about assign Grading actually out of 60 check
CS188 Spring 2010 Section 2: CSP s
 CS188 Spring 2010 Section 2: CSP s 1 Campus Layout ( ) You are asked to determine the layout of a new, small college. The campus will have three structures: an administration building (A), a bus stop (B),
CS188 Spring 2010 Section 2: CSP s 1 Campus Layout ( ) You are asked to determine the layout of a new, small college. The campus will have three structures: an administration building (A), a bus stop (B),
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 Outline CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs Chapter 5 2 Constraint satisfaction
Constraint satisfaction problems. CS171, Winter 2018 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Richard Lathrop
 Constraint satisfaction problems CS171, Winter 2018 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Richard Lathrop Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables, X 1, X 2,, X n
Constraint satisfaction problems CS171, Winter 2018 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Richard Lathrop Constraint Satisfaction Problems What is a CSP? Finite set of variables, X 1, X 2,, X n
AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems. Maria Simi
 AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems Maria Simi Constraints satisfaction LESSON 3 SEARCHING FOR SOLUTIONS Searching for solutions Most problems cannot be solved by constraint propagation
AI Fundamentals: Constraints Satisfaction Problems Maria Simi Constraints satisfaction LESSON 3 SEARCHING FOR SOLUTIONS Searching for solutions Most problems cannot be solved by constraint propagation
Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.3)
 Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.) Some slides adapted from Richard Lathrop, USC/ISI, CS 7 Review: The Minimax Rule Idea: Make the best move for MAX assuming that MIN always replies
Games and Adversarial Search II Alpha-Beta Pruning (AIMA 5.) Some slides adapted from Richard Lathrop, USC/ISI, CS 7 Review: The Minimax Rule Idea: Make the best move for MAX assuming that MIN always replies
Constraint (Logic) Programming
 Constraint (Logic) Programming Roman Barták Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic bartak@ktiml.mff.cuni.cz Sudoku Combinatorial puzzle, whose goal is to enter
Constraint (Logic) Programming Roman Barták Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic bartak@ktiml.mff.cuni.cz Sudoku Combinatorial puzzle, whose goal is to enter
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Search and Lookahead Bernhard Nebel, Julien Hué, and Stefan Wölfl Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg June 4/6, 2012 Nebel, Hué and Wölfl (Universität Freiburg) Constraint
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Search and Lookahead Bernhard Nebel, Julien Hué, and Stefan Wölfl Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg June 4/6, 2012 Nebel, Hué and Wölfl (Universität Freiburg) Constraint
CS 4100 // artificial intelligence
 CS 4100 // artificial intelligence instructor: byron wallace Constraint Satisfaction Problems Attribution: many of these slides are modified versions of those distributed with the UC Berkeley CS188 materials
CS 4100 // artificial intelligence instructor: byron wallace Constraint Satisfaction Problems Attribution: many of these slides are modified versions of those distributed with the UC Berkeley CS188 materials
Admin. Quick search recap. Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)! Intro Example: 8-Queens. Where should I put the queens in columns 3 and 4?
 Admin Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)! CS David Kauchak Spring 0 Final project comments: Use preexisting code Get your data now! Use preexisting data sets Finding good references Google scholar
Admin Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)! CS David Kauchak Spring 0 Final project comments: Use preexisting code Get your data now! Use preexisting data sets Finding good references Google scholar
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Robert Platt Northeastern University Some images and slides are used from: 1. AIMA What is a CSP? The space of all search problems states and actions are atomic goals are
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Robert Platt Northeastern University Some images and slides are used from: 1. AIMA What is a CSP? The space of all search problems states and actions are atomic goals are
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
 1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 7 Feb 2012 Many
1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 7 Feb 2012 Many
Example: Map-Coloring. Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Australia. Example: Map-Coloring contd. Outline. Constraint graph
 Example: Map-Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Northern erritory ueensland Chapter 5 South New South Wales asmania Variables, N,,, V, SA, Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent
Example: Map-Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problems Western Northern erritory ueensland Chapter 5 South New South Wales asmania Variables, N,,, V, SA, Domains D i = {red,green,blue} Constraints: adjacent
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
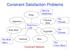 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior
 PART III: Search Outline Depth-first Search Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior Best-First Search
PART III: Search Outline Depth-first Search Chronological Backtracking Conflict Directed Backjumping Dynamic Backtracking Branching Strategies Branching Heuristics Heavy Tail Behavior Best-First Search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Introduction and Backtracking Search
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Introduction and Backtracking Search This lecture topic (two lectures) Chapter 6.1 6.4, except 6.3.3 Next lecture topic (two lectures) Chapter 7.1 7.5 (Please read
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Introduction and Backtracking Search This lecture topic (two lectures) Chapter 6.1 6.4, except 6.3.3 Next lecture topic (two lectures) Chapter 7.1 7.5 (Please read
Constraint satisfaction search. Combinatorial optimization search.
 CS 1571 Introduction to AI Lecture 8 Constraint satisfaction search. Combinatorial optimization search. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) Objective:
CS 1571 Introduction to AI Lecture 8 Constraint satisfaction search. Combinatorial optimization search. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) Objective:
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Luke Zettlemoyer Multiple slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Luke Zettlemoyer Multiple slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore What is Search For? Models of the world: single agent, deterministic
4 Search Problem formulation (23 points)
 4 Search Problem formulation (23 points) Consider a Mars rover that has to drive around the surface, collect rock samples, and return to the lander. We want to construct a plan for its exploration. It
4 Search Problem formulation (23 points) Consider a Mars rover that has to drive around the surface, collect rock samples, and return to the lander. We want to construct a plan for its exploration. It
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Chapter 6
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Office hours Office hours for Assignment 1 (ASB9810 in CSIL): Sep 29th(Fri) 12:00 to 13:30 Oct 3rd(Tue) 11:30 to 13:00 Late homework policy You get four late
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 6 Office hours Office hours for Assignment 1 (ASB9810 in CSIL): Sep 29th(Fri) 12:00 to 13:30 Oct 3rd(Tue) 11:30 to 13:00 Late homework policy You get four late
CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION
 CONSRAI ISFACION oday Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference Search 1 8-queens problem Exploit the constraints Constraint Satisfaction Problems Advantages of CSPs Use general-purpose
CONSRAI ISFACION oday Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ypes of CSPs Inference Search 1 8-queens problem Exploit the constraints Constraint Satisfaction Problems Advantages of CSPs Use general-purpose
CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence
 CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence Fall 2013 Chapter 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Jonathan Voris (based on slides by Sal Stolfo) Assignment 3 Go Encircling Game Ancient Chinese game Dates back At
CS W4701 Artificial Intelligence Fall 2013 Chapter 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problems Jonathan Voris (based on slides by Sal Stolfo) Assignment 3 Go Encircling Game Ancient Chinese game Dates back At
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Announcements Grading questions:
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore 1 1 Announcements Grading questions:
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Large Scale: Problems with A* What is Search For? Example: N-Queens
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Announcements Grading questions: don t panic, talk to us Newsgroup: check it out Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Announcements Grading questions: don t panic, talk to us Newsgroup: check it out Lecture 4: CSPs 9/9/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] What is Search
Constraint Satisfaction Problems [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] What is Search
Backtracking Search (CSPs)
 CSC384: Intro to Artificial Intelligence Backtracking Search (CSPs STATE REPRESENTATION: Factored representation of state ALGORITHMS: general purpose for particular types of constraints (versus problem
CSC384: Intro to Artificial Intelligence Backtracking Search (CSPs STATE REPRESENTATION: Factored representation of state ALGORITHMS: general purpose for particular types of constraints (versus problem
SYNERGY INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY,DHENKANAL LECTURE NOTES ON DIGITAL ELECTRONICS CIRCUIT(SUBJECT CODE:PCEC4202)
 Lecture No:5 Boolean Expressions and Definitions Boolean Algebra Boolean Algebra is used to analyze and simplify the digital (logic) circuits. It uses only the binary numbers i.e. 0 and 1. It is also called
Lecture No:5 Boolean Expressions and Definitions Boolean Algebra Boolean Algebra is used to analyze and simplify the digital (logic) circuits. It uses only the binary numbers i.e. 0 and 1. It is also called
Lec-5-HW-1, TM basics
 Lec-5-HW-1, TM basics (Problem 0)-------------------- Design a Turing Machine (TM), T_sub, that does unary decrement by one. Assume a legal, initial tape consists of a contiguous set of cells, each containing
Lec-5-HW-1, TM basics (Problem 0)-------------------- Design a Turing Machine (TM), T_sub, that does unary decrement by one. Assume a legal, initial tape consists of a contiguous set of cells, each containing
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Today. Example: Map-Coloring. Example: Cryptarithmetic.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 5: CSPs II 2/2/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 1 due Thursday Lecture videos reminder: don t count on
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture 5: CSPs II 2/2/2010 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Announcements Project 1 due Thursday Lecture videos reminder: don t count on
Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 COMP3411/ 9414/ 9814: Artificial Intelligence Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems [Russell & Norvig: 6.1,6.2,6.3,6.4,4.1] COMP3411/9414/9814 18s1 Constraint Satisfaction Problems 1 Outline Constraint
COMP3411/ 9414/ 9814: Artificial Intelligence Week 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems [Russell & Norvig: 6.1,6.2,6.3,6.4,4.1] COMP3411/9414/9814 18s1 Constraint Satisfaction Problems 1 Outline Constraint
Heuristic Search: A* CPSC 322 Search 4 January 19, Textbook 3.6 Taught by: Vasanth
 Heuristic Search: A* CPSC 322 Search 4 January 19, 2011 Textbook 3.6 Taught by: Vasanth 1 Lecture Overview Recap Search heuristics: admissibility and examples Recap of BestFS Heuristic search: A* 2 Example
Heuristic Search: A* CPSC 322 Search 4 January 19, 2011 Textbook 3.6 Taught by: Vasanth 1 Lecture Overview Recap Search heuristics: admissibility and examples Recap of BestFS Heuristic search: A* 2 Example
Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
 Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz 2. Termin: Constraint Satisfaction Dr. Stefan Kopp Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology AG A Recall: Best-first search Best-first search =
Spezielle Themen der Künstlichen Intelligenz 2. Termin: Constraint Satisfaction Dr. Stefan Kopp Center of Excellence Cognitive Interaction Technology AG A Recall: Best-first search Best-first search =
Lecture 6 Analysis of A*, B&B Search Refinements
 Computer Science CPSC 322 Lecture 6 Analysis of A*, B&B Search Refinements (Ch 3.7.1-3.7.4) Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap of previous lecture Analysis of A* Branch-and-Bound Cycle checking, multiple path
Computer Science CPSC 322 Lecture 6 Analysis of A*, B&B Search Refinements (Ch 3.7.1-3.7.4) Slide 1 Lecture Overview Recap of previous lecture Analysis of A* Branch-and-Bound Cycle checking, multiple path
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Section 1 3 Constraint Satisfaction 1 Outline Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) Backtracking search for CSPs Local search for CSPs Constraint Satisfaction
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Chapter 5 Section 1 3 Constraint Satisfaction 1 Outline Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) Backtracking search for CSPs Local search for CSPs Constraint Satisfaction
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Recap: Search
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4 and 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Recap: Search Search problem: States (configurations of the
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4 and 5: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides from Dan Klein Recap: Search Search problem: States (configurations of the
Local Search. (Textbook Chpt 4.8) Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 14. Oct, 7, CPSC 322, Lecture 14 Slide 1
 Local Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 14 (Textbook Chpt 4.8) Oct, 7, 2013 CPSC 322, Lecture 14 Slide 1 Department of Computer Science Undergraduate Events More details @ https://www.cs.ubc.ca/students/undergrad/life/upcoming-events
Local Search Computer Science cpsc322, Lecture 14 (Textbook Chpt 4.8) Oct, 7, 2013 CPSC 322, Lecture 14 Slide 1 Department of Computer Science Undergraduate Events More details @ https://www.cs.ubc.ca/students/undergrad/life/upcoming-events
Space of Search Strategies. CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence. Constraint Satisfaction. Recap: Search Problem. Example: Map-Coloring 11/30/2012
 /0/0 CSE 57: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Space of Search Strategies Blind Search DFS, BFS,
/0/0 CSE 57: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Daniel Weld Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Space of Search Strategies Blind Search DFS, BFS,
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Optimization Bernhard Nebel, Julien Hué, and Stefan Wölfl Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg July 17, 2012 Nebel, Hué and Wölfl (Universität Freiburg) Constraint
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Optimization Bernhard Nebel, Julien Hué, and Stefan Wölfl Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg July 17, 2012 Nebel, Hué and Wölfl (Universität Freiburg) Constraint
