Midterm 1 : Correction. Friday, Feb. 23.
|
|
|
- August Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Spring 00 Math Group F Midterm : Correction. Friday, Feb... (a) Draw a graph with vertices A, B, C and D in which the valence of vertices A and D is and the valence of vertices B and C is. A B C D (b) Is it possible to draw a graph on the same vertices in which A, B and C have valence and D has valence? (explain). Answer. It is impossible, because the number of odd-valent vertices is always even.. For each of the graphs below, determine the minimal number of edges that need to be removed to disconnect it. One must remove edges to disconnect this graph Removing three edges is needed in order to disconnect this graph.
2 . For each of the graphs below, say whether it admits an Euler circuit or not. If it does, draw an Euler circuit on the graph ; if it doesn't, nd an ecient Eulerization of the graph and use it to obtain a circuit that reuses a minimum number of edges. his graph admits an Euler circuit, as verified by the one that is represented above. 0 0 his graph doesn t have any Euler circuit; on the left you see an Eulerization with three added vertices (which is optimal since there are six odd valent vertices in the graph) and an Euler circuit in the Eulerized graph; on the right you see a circuit that covers all edges while reusing a minimal number of them, obtained by "squeezing" the Euler circuit from the Eulerized graph.. B A C E 0 D a) For the graph above, nd the hamiltonian circuit obtained by applying the nearest neighbor algorithm, starting at A. What is the cost of that circuit? Answer. One obtains the circuit ABCEDA, the cost of which is = 0. b) Same question, replacing the nearest-neighbor algorithm by the sorted-edges algorithm. Answer. his time one obtains the circuit AEBCDA, the cost of which is =. c) How many hamiltonian circuits would one have to consider in order to apply the brute force method here? Since there are vertices, the number of hamiltonian circuits in this graph (the complete graph with vertices) is ( )!/ =!/ =.
3 .a) In some states, license plates use a mixture of letters and numerals. How many possible plates could be constructed using three letters followed by two numerals? Answer. here are 0 0 dierent possibilities. b) You own a chain of nine appartment complexes (including the one you live in), and you plan to visit each of your properties. If it takes / minute to compute the total length of a tour, how long will it take (in minutes) to apply the brute force algorithm to nd the optimal tour? Answer. he total number of tours is (!)/ =!/. Since each tour requires a half-minute of computation time, applying the brute force algorithm in this situation will take (/) (!/) minutes, or 000 minutes.. Apply Kruskal's algorithm to the graph below.
4 . Consider the order-requirement digraph below. 0 (a) What is (are) the critical path(s)? Answer here are two critical paths here : qnd. (b) Give an estimate of the minimal amount of time needed to nish the job in the following situations : (i) You don't know the number of processors. Answer. If we don't know the number of processors, the best estimate we can give is that the job will require at least 0 minutes (length of the critical path). (ii) here is one processor. Answer. With one processor, the minimal amount of time is equal to the total task time, which is minutes here. (iii) here are two processors Answer. otal task time divided by is / =. minutes, so the minimal amount of time needed is at least 0 minutes. (iv) here are three processors. For three processors, we get / =.... ; since this is lower than the length of a critical path, we again can only say in this case that the job will require at least 0 minutes.. For the order-requirement digraph below, nd the schedules (on two processors) obtained by applying the critical-path scheduling method and the decreasing-time list scheduling method. 0 0 Schedule obtained with the critical path scheduling method. Schedule obtained with the decreasing time list method. Answer. he priority list obtained by the critical-path analysis is, while the priority list from the decreasing-time list is. hese lists yield the schedules represented above.
5 . You must pack the following weights into bins that can hold no more than lbs : lbs, lbs, lb,lbs, lbs, lbs, lb, lb, lbs, lbs, lb, lbs, lbs. (a) Use the next-t algorithm to pack the weights ; represent your solution below (b) Same question, using this time the rst-t decreasing algorithm Answer. he list of weights in nonincreasing order is :,,,,,,,,,,,,. Applying the rst-t algorithm to it gives the following packing : (c) Again the same question, using the worst-t decreasing algorithm. Answer. We use the list from question (b), and obtain : 0. rue or false? (a) A heuristic algorithm does not necessarily produce optimal results. RUE (b) he path produced by the sorted-edges algorithm when solving the traveling salesman problem may be dependent on the starting city. FALSE (c) A spanning tree of a graph must contain every edge of a graph. FALSE (d) When scheduling tasks using the list-processing algorithm, decreasing the time required by each task may increase the completion time. RUE ; see textbook page. (e) he worst-t algorithm never uses more boxes than the rst-t algorithm. FALSE
7 Next choice is 4, not 3...
 Math 0 opics for rst exam Chapter 1: Street Networks Operations research Goal: determine how to carry out a sequence of tasks most eciently Ecient: least cost, least time, least distance,... Example: reading
Math 0 opics for rst exam Chapter 1: Street Networks Operations research Goal: determine how to carry out a sequence of tasks most eciently Ecient: least cost, least time, least distance,... Example: reading
Study Guide Mods: Date:
 Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions.
 SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit.
 Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1
 AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is where a least cost Hamiltonian circuit is found. CHAPTER 1 URBAN SERVICES
 Math 167 eview 1 (c) Janice Epstein HPE 1 UN SEVIES path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit. Math 167 eview
Math 167 eview 1 (c) Janice Epstein HPE 1 UN SEVIES path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit. Math 167 eview
The Traveling Salesman Problem
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION
 SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
The Travelling Salesman Problem
 The Travelling Salesman Problem The travelling salesman problem cannot be solved directly without vast amounts of processing power, since every possible Hamiltonian cycle would need to be measured. For
The Travelling Salesman Problem The travelling salesman problem cannot be solved directly without vast amounts of processing power, since every possible Hamiltonian cycle would need to be measured. For
Mathematical Thinking
 Mathematical Thinking Chapter 2 Hamiltonian Circuits and Spanning Trees It often happens in mathematics that what appears to be a minor detail in the statement of a problem can have a profound effect on
Mathematical Thinking Chapter 2 Hamiltonian Circuits and Spanning Trees It often happens in mathematics that what appears to be a minor detail in the statement of a problem can have a profound effect on
Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet
 Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet Combinatorial Optimization is the way in which combinatorial thought is applied to real world optimization problems. Optimization entails achieving the sufficient
Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet Combinatorial Optimization is the way in which combinatorial thought is applied to real world optimization problems. Optimization entails achieving the sufficient
Finite Math A Chapter 6 Notes Hamilton Circuits
 Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
a) Graph 2 and Graph 3 b) Graph 2 and Graph 4 c) Graph 1 and Graph 4 d) Graph 1 and Graph 3 e) Graph 3 and Graph 4 f) None of the above
 Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
Mathematics 105: Math as a Liberal Art. Final Exam. Name Instructor: Ramin Naimi Spring 2008 Close book. Closed notes. No Calculators. NO CELL PHONES! Please turn off your cell phones and put them away.
Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A tree is A) any graph that is connected and every
Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A tree is A) any graph that is connected and every
Note that there are questions printed on both sides of each page!
 Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
Math 1001 Name: Fall 2007 Test 1 Student ID: 10/5/07 Time allowed: 50 minutes Section: 10:10 11:15 12:20 This exam includes 7 pages, including this one and a sheet for scratch work. There are a total of
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes
 Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
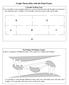
Math 100 Homework 4 B A C E
 Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem. Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths.
 Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths. Recall: an Euler path is a path that travels through every edge of a graph once and only once; an Euler circuit
Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths. Recall: an Euler path is a path that travels through every edge of a graph once and only once; an Euler circuit
Topics Covered. Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm
 Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Coping with the Limitations of Algorithm Power Exact Solution Strategies Backtracking Backtracking : A Scenario
 Coping with the Limitations of Algorithm Power Tackling Difficult Combinatorial Problems There are two principal approaches to tackling difficult combinatorial problems (NP-hard problems): Use a strategy
Coping with the Limitations of Algorithm Power Tackling Difficult Combinatorial Problems There are two principal approaches to tackling difficult combinatorial problems (NP-hard problems): Use a strategy
CPSC W1: Midterm 1 Sample Solution
 CPSC 320 2017W1: Midterm 1 Sample Solution January 26, 2018 Problem reminders: EMERGENCY DISTRIBUTION PROBLEM (EDP) EDP's input is an undirected, unweighted graph G = (V, E) plus a set of distribution
CPSC 320 2017W1: Midterm 1 Sample Solution January 26, 2018 Problem reminders: EMERGENCY DISTRIBUTION PROBLEM (EDP) EDP's input is an undirected, unweighted graph G = (V, E) plus a set of distribution
CPSC W2: Quiz 2 Sample Solutions
 CPSC 320 2017W2: Quiz 2 Sample Solutions January 27, 2018 1 Wall-E Loman If you nd a path with no obstacles, it probably doesn't lead anywhere. Frank A. Clark We dene TSP just as before: The Traveling
CPSC 320 2017W2: Quiz 2 Sample Solutions January 27, 2018 1 Wall-E Loman If you nd a path with no obstacles, it probably doesn't lead anywhere. Frank A. Clark We dene TSP just as before: The Traveling
IE 102 Spring Routing Through Networks - 1
 IE 102 Spring 2017 Routing Through Networks - 1 The Bridges of Koenigsberg: Euler 1735 Graph Theory began in 1735 Leonard Eüler Visited Koenigsberg People wondered whether it is possible to take a walk,
IE 102 Spring 2017 Routing Through Networks - 1 The Bridges of Koenigsberg: Euler 1735 Graph Theory began in 1735 Leonard Eüler Visited Koenigsberg People wondered whether it is possible to take a walk,
The Bridges of Konigsberg Problem Can you walk around the town crossing each bridge only once?
 The Bridges of Konigsberg Problem Can you walk around the town crossing each bridge only once? Many people had tried the walk and felt that it was impossible, but no one knew for sure. In 1736, Leonard
The Bridges of Konigsberg Problem Can you walk around the town crossing each bridge only once? Many people had tried the walk and felt that it was impossible, but no one knew for sure. In 1736, Leonard
(Refer Slide Time: 01:00)
 Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture minus 26 Heuristics for TSP In this lecture, we continue our discussion
Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture minus 26 Heuristics for TSP In this lecture, we continue our discussion
1. The Highway Inspector s Problem
 MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost
 Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost Figure 8-24 Two possible maximum flows for the same network Data Structures and Algorithms in Java 1 Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost (continued) Figure 8-25 Finding a maximum
Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost Figure 8-24 Two possible maximum flows for the same network Data Structures and Algorithms in Java 1 Maximum Flows of Minimum Cost (continued) Figure 8-25 Finding a maximum
Lesson 5.2. The Traveling Salesperson Problem. Explore This
 Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem In Lesson 4.5, you explored circuits that visited each vertex of your graph exactly once (Hamiltonian circuits). In this lesson, you will extend your thinking
Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem In Lesson 4.5, you explored circuits that visited each vertex of your graph exactly once (Hamiltonian circuits). In this lesson, you will extend your thinking
MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak
 MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a 50-50 chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following:
MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a 50-50 chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following:
Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]
![Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks] Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]](/thumbs/89/97991710.jpg) Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
A region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that is divided up by the network.
 Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering. Qian Zhu 2/23/2011
 Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
1. trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) How many different spanning. trees does the network shown in figure (b) have?
 2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Questions? You are given the complete graph of Facebook. What questions would you ask? (What questions could we hope to answer?)
 P vs. NP What now? Attribution These slides were prepared for the New Jersey Governor s School course The Math Behind the Machine taught in the summer of 2011 by Grant Schoenebeck Large parts of these
P vs. NP What now? Attribution These slides were prepared for the New Jersey Governor s School course The Math Behind the Machine taught in the summer of 2011 by Grant Schoenebeck Large parts of these
Theorem 2.9: nearest addition algorithm
 There are severe limits on our ability to compute near-optimal tours It is NP-complete to decide whether a given undirected =(,)has a Hamiltonian cycle An approximation algorithm for the TSP can be used
There are severe limits on our ability to compute near-optimal tours It is NP-complete to decide whether a given undirected =(,)has a Hamiltonian cycle An approximation algorithm for the TSP can be used
Simple Graph. General Graph
 Graph Theory A graph is a collection of points (also called vertices) and lines (also called edges), with each edge ending at a vertex In general, it is allowed for more than one edge to have the same
Graph Theory A graph is a collection of points (also called vertices) and lines (also called edges), with each edge ending at a vertex In general, it is allowed for more than one edge to have the same
Mathematics (JAN13MD0101) General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January Unit Decision TOTAL
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Decision 1 Friday 25 January 2013 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Decision 1 Friday 25 January 2013 General Certificate of Education Advanced
CSCE 350: Chin-Tser Huang. University of South Carolina
 CSCE 350: Data Structures and Algorithms Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Announcement Homework 2 will be returned on Thursday; solution will be available on class website
CSCE 350: Data Structures and Algorithms Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Announcement Homework 2 will be returned on Thursday; solution will be available on class website
Math 15 - Spring Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so:
 Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam, Math 170, Section 002 Spring 2012
 Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam, Math 170, Section 002 Spring 2012 Multiple choice questions. Question 1. Suppose we have a rectangle with one side of length 5 and a diagonal of length 13. What is
Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam, Math 170, Section 002 Spring 2012 Multiple choice questions. Question 1. Suppose we have a rectangle with one side of length 5 and a diagonal of length 13. What is
Graphs and Puzzles. Eulerian and Hamiltonian Tours.
 Graphs and Puzzles. Eulerian and Hamiltonian Tours. CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 11 (B00), Day 7 (A00) February 3, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Exam Announcements Seating Chart on Website Good
Graphs and Puzzles. Eulerian and Hamiltonian Tours. CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 11 (B00), Day 7 (A00) February 3, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Exam Announcements Seating Chart on Website Good
Chinese Postman Problem
 Special Topics Chinese Postman Problem In real life, not all problems will be perfect Euler Circuits. If no Euler Circuit exists (there are odd valences present), you want to minimize the length of the
Special Topics Chinese Postman Problem In real life, not all problems will be perfect Euler Circuits. If no Euler Circuit exists (there are odd valences present), you want to minimize the length of the
EECS 203 Lecture 20. More Graphs
 EECS 203 Lecture 20 More Graphs Admin stuffs Last homework due today Office hour changes starting Friday (also in Piazza) Friday 6/17: 2-5 Mark in his office. Sunday 6/19: 2-5 Jasmine in the UGLI. Monday
EECS 203 Lecture 20 More Graphs Admin stuffs Last homework due today Office hour changes starting Friday (also in Piazza) Friday 6/17: 2-5 Mark in his office. Sunday 6/19: 2-5 Jasmine in the UGLI. Monday
Sarah Will Math 490 December 2, 2009
 Sarah Will Math 490 December 2, 2009 Euler Circuits INTRODUCTION Euler wrote the first paper on graph theory. It was a study and proof that it was impossible to cross the seven bridges of Königsberg once
Sarah Will Math 490 December 2, 2009 Euler Circuits INTRODUCTION Euler wrote the first paper on graph theory. It was a study and proof that it was impossible to cross the seven bridges of Königsberg once
Student Name and ID Number. MATH 3012 Final Exam, December 11, 2014, WTT
 MATH 3012 Final Exam, December 11, 2014, WTT Student Name and ID Number 1. Consider the 11-element set X consisting of the three capital letters {A, B, C} and the eight digits {0, 1, 2,..., 7}. a. How
MATH 3012 Final Exam, December 11, 2014, WTT Student Name and ID Number 1. Consider the 11-element set X consisting of the three capital letters {A, B, C} and the eight digits {0, 1, 2,..., 7}. a. How
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE 101, Winter 018 D/Q Greed SP s DP LP, Flow B&B, Backtrack Metaheuristics P, NP Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 8: Greed Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Optimization
CSE 101, Winter 018 D/Q Greed SP s DP LP, Flow B&B, Backtrack Metaheuristics P, NP Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 8: Greed Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Optimization
Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm
 Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 12 (B00), Day 8 (A00) February 8, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Vocabulary Path (or walk): describes a route from one vertex
Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 12 (B00), Day 8 (A00) February 8, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Vocabulary Path (or walk): describes a route from one vertex
Graph Theory(Due with the Final Exam)
 Graph Theory(ue with the Final Exam) Possible Walking Tour.. Is it possible to start someplace(either in a room or outside) and walk through every doorway once and only once? Explain. If it is possible,
Graph Theory(ue with the Final Exam) Possible Walking Tour.. Is it possible to start someplace(either in a room or outside) and walk through every doorway once and only once? Explain. If it is possible,
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
2 Approximation Algorithms for Metric TSP
 Comp260: Advanced Algorithms Tufts University, Spring 2002 Professor Lenore Cowen Scribe: Stephanie Tauber Lecture 3: The Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) 1 Introduction A salesman wishes to visit every
Comp260: Advanced Algorithms Tufts University, Spring 2002 Professor Lenore Cowen Scribe: Stephanie Tauber Lecture 3: The Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) 1 Introduction A salesman wishes to visit every
Circuits and Paths. April 13, 2014
 Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
Eulerian tours. Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck. April 20, 2016
 Eulerian tours Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ April 20, 2016 Seven Bridges of Konigsberg Is there a path that crosses each
Eulerian tours Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ April 20, 2016 Seven Bridges of Konigsberg Is there a path that crosses each
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
11.4 Bipartite Multigraphs
 11.4 Bipartite Multigraphs Introduction Definition A graph G is bipartite if we can partition the vertices into two disjoint subsets U and V such that every edge of G has one incident vertex in U and the
11.4 Bipartite Multigraphs Introduction Definition A graph G is bipartite if we can partition the vertices into two disjoint subsets U and V such that every edge of G has one incident vertex in U and the
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory. Applied Discrete Mathematics
 Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory Applied Discrete Mathematics Table of Contents Counting Pages 1-8 Graph Theory Pages 9-16 Exam Study Sheet Page 17 Counting Information I. Product Rule: A B C = A * B
Packet #6: Counting & Graph Theory Applied Discrete Mathematics Table of Contents Counting Pages 1-8 Graph Theory Pages 9-16 Exam Study Sheet Page 17 Counting Information I. Product Rule: A B C = A * B
MATH 103: Contemporary Mathematics Study Guide for Chapter 6: Hamilton Circuits and the TSP
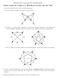 MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics
 Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu P, NP-Problems Class
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu P, NP-Problems Class
PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL
 GRAPH TRAVERSAL PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL Path finding refers to determining the shortest path between two vertices in a graph. We discussed the Floyd Warshall algorithm previously, but you may
GRAPH TRAVERSAL PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL Path finding refers to determining the shortest path between two vertices in a graph. We discussed the Floyd Warshall algorithm previously, but you may
14 Graph Theory. Exercise Set 14-1
 14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
Unit 7 Day 6. Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route
 Unit 7 Day 6 Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route 1 Warm Up Day 7: 1. Draw a planar graph with 6 vertices. 2. Is a K 9,3 graph planar? Explain your reasoning.
Unit 7 Day 6 Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route 1 Warm Up Day 7: 1. Draw a planar graph with 6 vertices. 2. Is a K 9,3 graph planar? Explain your reasoning.
The Algorithm Design Manual
 Steven S. Skiena The Algorithm Design Manual With 72 Figures Includes CD-ROM THE ELECTRONIC LIBRARY OF SCIENCE Contents Preface vii I TECHNIQUES 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 2 2.1 2.2 2.3
Steven S. Skiena The Algorithm Design Manual With 72 Figures Includes CD-ROM THE ELECTRONIC LIBRARY OF SCIENCE Contents Preface vii I TECHNIQUES 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 2 2.1 2.2 2.3
How can we lay cable at minimum cost to make every telephone reachable from every other? What is the fastest route between two given cities?
 1 Introduction Graph theory is one of the most in-demand (i.e. profitable) and heavily-studied areas of applied mathematics and theoretical computer science. May graph theory questions are applied in this
1 Introduction Graph theory is one of the most in-demand (i.e. profitable) and heavily-studied areas of applied mathematics and theoretical computer science. May graph theory questions are applied in this
Number Theory and Graph Theory
 1 Number Theory and Graph Theory Chapter 7 Graph properties By A. Satyanarayana Reddy Department of Mathematics Shiv Nadar University Uttar Pradesh, India E-mail: satya8118@gmail.com 2 Module-2: Eulerian
1 Number Theory and Graph Theory Chapter 7 Graph properties By A. Satyanarayana Reddy Department of Mathematics Shiv Nadar University Uttar Pradesh, India E-mail: satya8118@gmail.com 2 Module-2: Eulerian
Math 130 Final Exam Study Guide. 1. Voting
 1 Math 130 Final Exam Study Guide 1. Voting (a) Be able to interpret a top choice ballot, preference ballot and preference schedule (b) Given a preference schedule, be able to: i. find the winner of an
1 Math 130 Final Exam Study Guide 1. Voting (a) Be able to interpret a top choice ballot, preference ballot and preference schedule (b) Given a preference schedule, be able to: i. find the winner of an
ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 71 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS 1. If F : X X is a function, define f (x) to be (f f)(x), and inductively define f k (x) (f f k 1 )(x) for each integer k. (So f (x) (f f )(x) f(f(f(x))) for instance.) We
MATH 71 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS 1. If F : X X is a function, define f (x) to be (f f)(x), and inductively define f k (x) (f f k 1 )(x) for each integer k. (So f (x) (f f )(x) f(f(f(x))) for instance.) We
Math 170, Section 002 Spring 2012 Practice Exam 2 with Solutions
 Math 170, Section 002 Spring 2012 Practice Exam 2 with Solutions Contents 1 Problems 2 2 Solution key 10 3 Solutions 11 1 1 Problems Question 1: A right triangle has hypothenuse of length 25 in and an
Math 170, Section 002 Spring 2012 Practice Exam 2 with Solutions Contents 1 Problems 2 2 Solution key 10 3 Solutions 11 1 1 Problems Question 1: A right triangle has hypothenuse of length 25 in and an
CS 440 Theory of Algorithms /
 CS 440 Theory of Algorithms / CS 468 Algorithms in Bioinformaticsi Brute Force. Design and Analysis of Algorithms - Chapter 3 3-0 Brute Force A straightforward approach usually based on problem statement
CS 440 Theory of Algorithms / CS 468 Algorithms in Bioinformaticsi Brute Force. Design and Analysis of Algorithms - Chapter 3 3-0 Brute Force A straightforward approach usually based on problem statement
Traveling Salesman Problem. Algorithms and Networks 2014/2015 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij
 Traveling Salesman Problem Algorithms and Networks 2014/2015 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij 1 Contents TSP and its applications Heuristics and approximation algorithms Construction heuristics,
Traveling Salesman Problem Algorithms and Networks 2014/2015 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij 1 Contents TSP and its applications Heuristics and approximation algorithms Construction heuristics,
Module 6 P, NP, NP-Complete Problems and Approximation Algorithms
 Module 6 P, NP, NP-Complete Problems and Approximation Algorithms Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu
Module 6 P, NP, NP-Complete Problems and Approximation Algorithms Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu
Optimal tour along pubs in the UK
 1 From Facebook Optimal tour along 24727 pubs in the UK Road distance (by google maps) see also http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/pubs/index.html (part of TSP homepage http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/
1 From Facebook Optimal tour along 24727 pubs in the UK Road distance (by google maps) see also http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/pubs/index.html (part of TSP homepage http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/
15CS43: DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
 15CS43: DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS QUESTION BANK MODULE1 1. What is an algorithm? Write step by step procedure to write an algorithm. 2. What are the properties of an algorithm? Explain with an
15CS43: DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS QUESTION BANK MODULE1 1. What is an algorithm? Write step by step procedure to write an algorithm. 2. What are the properties of an algorithm? Explain with an
GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS
 GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS DR. ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models (1) A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes)
GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS DR. ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models (1) A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes)
Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees. March 23, 2008
 Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees March 23, 2008 Outline 1 11.1 Graphs: An Introduction 2 11.2 Paths and Circuits 3 11.3 Matrix Representations of Graphs 4 11.5 Trees Graphs: Basic Definitions Informally, a
Chapter 11: Graphs and Trees March 23, 2008 Outline 1 11.1 Graphs: An Introduction 2 11.2 Paths and Circuits 3 11.3 Matrix Representations of Graphs 4 11.5 Trees Graphs: Basic Definitions Informally, a
Fundamentals of Computer Science II
 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Museum 102 kvertanen@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Textbook Resources
Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Museum 102 kvertanen@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Textbook Resources
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 2: Transportation problems
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 2: Transportation problems David Glickenstein September 15, 2014 1 Readings This is based on Chartrand Chapter 3 and Bondy-Murty 18.1, 18.3 (part on Closure of a Graph).
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 2: Transportation problems David Glickenstein September 15, 2014 1 Readings This is based on Chartrand Chapter 3 and Bondy-Murty 18.1, 18.3 (part on Closure of a Graph).
1. a graph G = (V (G), E(G)) consists of a set V (G) of vertices, and a set E(G) of edges (edges are pairs of elements of V (G))
 10 Graphs 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models 1. a graph G = (V (G), E(G)) consists of a set V (G) of vertices, and a set E(G) of edges (edges are pairs of elements of V (G)) 2. an edge is present, say e = {u,
10 Graphs 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models 1. a graph G = (V (G), E(G)) consists of a set V (G) of vertices, and a set E(G) of edges (edges are pairs of elements of V (G)) 2. an edge is present, say e = {u,
CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II. Keith Vertanen Museum
 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Museum 102 496-4385 kvertanen@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen
CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Museum 102 496-4385 kvertanen@mtech.edu http://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen
 Graph Applications, Class Notes, CS 3137 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Web References: http://www.tsp.gatech.edu/index.html http://www-e.uni-magdeburg.de/mertens/tsp/tsp.html TSP applets A Hamiltonian
Graph Applications, Class Notes, CS 3137 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Web References: http://www.tsp.gatech.edu/index.html http://www-e.uni-magdeburg.de/mertens/tsp/tsp.html TSP applets A Hamiltonian
MEI Further Mathematics Support Programme
 Further Mathematics Support Programme the Further Mathematics Support Programme www.furthermaths.org.uk Modelling and problem solving with Networks Sharon Tripconey Let Maths take you Further Nov 2009
Further Mathematics Support Programme the Further Mathematics Support Programme www.furthermaths.org.uk Modelling and problem solving with Networks Sharon Tripconey Let Maths take you Further Nov 2009
MAS 341: GRAPH THEORY 2016 EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MS 41: PH THEOY 2016 EXM SOLUTIONS 1. Question 1 1.1. Explain why any alkane C n H 2n+2 is a tree. How many isomers does C 6 H 14 have? Draw the structure of the carbon atoms in each isomer. marks; marks
MS 41: PH THEOY 2016 EXM SOLUTIONS 1. Question 1 1.1. Explain why any alkane C n H 2n+2 is a tree. How many isomers does C 6 H 14 have? Draw the structure of the carbon atoms in each isomer. marks; marks
Travelling Salesman Problem. Algorithms and Networks 2015/2016 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij
 Travelling Salesman Problem Algorithms and Networks 2015/2016 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij 1 Contents TSP and its applications Heuristics and approximation algorithms Construction heuristics,
Travelling Salesman Problem Algorithms and Networks 2015/2016 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij 1 Contents TSP and its applications Heuristics and approximation algorithms Construction heuristics,
Math 101 Final Exam Study Notes:
 Math 101 Final Exam Study Notes: *Please remember there is a large set of final exam review problems in Doc Sharing (under Course Tools in MLP). Highlighted are what might be considered formulas* I. Graph
Math 101 Final Exam Study Notes: *Please remember there is a large set of final exam review problems in Doc Sharing (under Course Tools in MLP). Highlighted are what might be considered formulas* I. Graph
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Lecture 10 Graph Algorithms
 Lecture 10 Graph Algorithms Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) 1 Graph Theory Study of the properties of graph structures It provides us with a language with which to talk about graphs Keys to solving problems
Lecture 10 Graph Algorithms Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) 1 Graph Theory Study of the properties of graph structures It provides us with a language with which to talk about graphs Keys to solving problems
1 The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Comp 260: Advanced Algorithms Tufts University, Spring 2018 Prof. Lenore Cowen Scribe: Duc Nguyen Lecture 3a: The Traveling Salesman Problem 1 The Traveling Salesman Problem The Traveling Salesman Problem
Comp 260: Advanced Algorithms Tufts University, Spring 2018 Prof. Lenore Cowen Scribe: Duc Nguyen Lecture 3a: The Traveling Salesman Problem 1 The Traveling Salesman Problem The Traveling Salesman Problem
CS170 First Midterm Answers 17 Feb { What are the strongly connected components of the directed graph shown below?
 S70 First Midterm Answers 7 Feb 998 Answer to Version of Question. (3 points) { What are the strongly connected components of the directed graph shown below? A 000000 0000 00000 0 E H 0 0 00 0000 0 00
S70 First Midterm Answers 7 Feb 998 Answer to Version of Question. (3 points) { What are the strongly connected components of the directed graph shown below? A 000000 0000 00000 0 E H 0 0 00 0000 0 00
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1
 Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Finite Math A, Chapter 8: Scheduling 1 Finite Math A Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Scheduling Chapter 8: The Mathematics of Scheduling Pd 2 & 6 Pd 4 & 7 Lesson Homework Tues Wed 8.1, 8.2 The Basic Elements
Algorithm Design Techniques. Hwansoo Han
 Algorithm Design Techniques Hwansoo Han Algorithm Design General techniques to yield effective algorithms Divide-and-Conquer Dynamic programming Greedy techniques Backtracking Local search 2 Divide-and-Conquer
Algorithm Design Techniques Hwansoo Han Algorithm Design General techniques to yield effective algorithms Divide-and-Conquer Dynamic programming Greedy techniques Backtracking Local search 2 Divide-and-Conquer
Undirected Network Summary
 Undirected Network Summary Notice that the network above has multiple edges joining nodes a to d and the network has a loop at node d. Also c is called an isolated node as it is not connected to any other
Undirected Network Summary Notice that the network above has multiple edges joining nodes a to d and the network has a loop at node d. Also c is called an isolated node as it is not connected to any other
Warm -Up. 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices?
 Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms
 Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring 2019 Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms Our first category of algorithms are called brute-force algorithms. Levitin defines
Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring 2019 Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms Our first category of algorithms are called brute-force algorithms. Levitin defines
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms
 CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 21: Finish Sorting, P vs NP Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 2017 Today Announcements Finish up sorting Radix Sort Final comments on sorting Complexity
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 21: Finish Sorting, P vs NP Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 2017 Today Announcements Finish up sorting Radix Sort Final comments on sorting Complexity
Mathematics MD01. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination. Unit Decision 1
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Decision 1 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Decision 1 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
MITOCW watch?v=zm5mw5nkzjg
 MITOCW watch?v=zm5mw5nkzjg The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=zm5mw5nkzjg The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Chapter 3. Planning and Scheduling. Chapter Objectives. Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them.
 Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. State the assumptions for the scheduling model. Compute the lower bound on the completion time for a list of independent
Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. State the assumptions for the scheduling model. Compute the lower bound on the completion time for a list of independent
What Is An Algorithm? Algorithms are the ideas behind computer programs. An algorithm is the thing which stays the same whether
 What Is An Algorithm? Algorithms are the ideas behind computer programs An algorithm is the thing which stays the same whether the program is in Pascal running on a Cray innew York or is in BASIC running
What Is An Algorithm? Algorithms are the ideas behind computer programs An algorithm is the thing which stays the same whether the program is in Pascal running on a Cray innew York or is in BASIC running
CS 245 Midterm Exam Solution Winter 2015
 CS 245 Midterm Exam Solution Winter 2015 This exam is open book and notes. You can use a calculator and your laptop to access course notes and videos (but not to communicate with other people). You have
CS 245 Midterm Exam Solution Winter 2015 This exam is open book and notes. You can use a calculator and your laptop to access course notes and videos (but not to communicate with other people). You have
