Lesson 5.2. The Traveling Salesperson Problem. Explore This
|
|
|
- Samuel Lucas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem In Lesson 4.5, you explored circuits that visited each vertex of your graph exactly once (Hamiltonian circuits). In this lesson, you will extend your thinking on this original problem and examine a type of problem known as a traveling salesperson problem (TP). These TPs involve finding a Hamiltonian circuit of minimum value such as time, distance, or cost. Optimization problems of this type are becoming increasingly important in the world of communications, warehousing, airlines networking, delivery truck routing, and building wiring. Explore This uppose you are a salesperson who lives in t. Louis. Once a week you have to travel to Minneapolis, hicago, and New Orleans and then return home to t. Louis. The graph in Figure 5.7 represents the trips that are available to you. The edges of the graph are labeled with the cost of each possible trip. For instance, the cost of making a trip from hicago to New Orleans is $910. When each edge of a graph is assigned a number (weight), the graph is called a weighted graph. The numbers associated with the edges often represent such things as distance, cost, or time. Minneapolis 400 hicago t. Louis 550 1, Figure 5.7. Graph of four cities with the costs of traveling between them. 910 New Orleans
2 242 hapter 5 More Graphs, ubgraphs, and Trees ince you own your own business, it is important that you minimize travel costs. To help save money, find the least expensive route that begins in t. Louis, visits each of the other cities exactly once, and returns to t. Louis. One way to solve the problem of finding the least expensive route in Figure 5.7 is to use the brute force method of listing every possible circuit, along with its cost. A tree diagram like the one in Figure 5.8 can help you list the possible routes. Inspection of the tree diagram shows that the optimal solution is the circuit, M,, N, or the circuit in reverse order, N,, M, , M N N M N 1, M ,260 1, N N M M ,5 2,990 2,600 2,990 2,600 2,5 Figure 5.8. Tree diagram of every possible circuit from t. Louis to each of the other cities and back to t. Louis. olving the TP for four vertices is not too difficult or time-consuming because only six possibilities need to be considered. But as the number of vertices increases, so does the number of possible circuits. Hence, checking all possibilities soon becomes impractical, if not impossible. Even with the help of a computer that can do computations at the rate of 1 billion per second, it would take more than 19 million years for the computer to find the weights of every circuit for a graph with 25 vertices!
3 Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem 243 More Efficient Algorithms Is it possible that a faster, more efficient algorithm exists? You might try, for example, to begin at a vertex, look for the vertex nearest to your starting vertex, move to it, and continue until you complete the circuit. To explore this method for the graph in Figure 5.7 on page 241, begin at t. Louis, move to the nearest neighboring vertex (hicago), then to the nearest vertex not yet visited, and return to t. Louis when you have visited all of the other cities ( , = 2,600). This procedure is known as the nearest-neighbor algorithm. Although the solution was reached quickly, notice that in this case, it is not the best possible one. A method such as this, which produces a quick and reasonably close-to-optimal solution, is known as a heuristic method. The choice of method now becomes a trade-off. The brute force method of inspecting every possible path guarantees the best route but is prohibitively slow. The nearest-neighbor method is quick but does not necessarily produce the optimal solution. There is no known computationally efficient method of solving all traveling salesperson problems. But with the discovery of more and more efficient algorithms, hope has increased that better solutions will be forthcoming. These solutions to TPs are of great interest because they translate into savings of millions of dollars for certain areas of the economy. Point of Interest The current record-setting solution for a TP was set in 2006 when an optimal 85,900-city tour was found. In this problem, the cities represented locations on a customized computer chip, and finding the shortest possible movement of the laser equated to minimizing the cost production cost of the chip. The table below shows several TP milestones. TP MILETONE Year Number of ities , , , , ,900 According to William J. ook, the ultimate travel challenge is currently a 1,904,771-city problem that consists of every town, city, and village in the world.
4 244 hapter 5 More Graphs, ubgraphs, and Trees Exercises In Exercises 1 through 4, a. onstruct a tree diagram showing all possible circuits that begin at, visit each vertex of the graph exactly once, and end at. b. Find the total weight of each route. c. Identify the shortest circuit. d. Use the nearest-neighbor algorithm to find the shortest circuit. e. Does the nearest-neighbor algorithm produce the optimal solution? D B 61 B D B 5 D B D 6 11 E 5. In a graph with 10 vertices, 9!, or , possible Hamiltonian circuits exist if the beginning vertex is known. a. Assume that a computer can perform calculations at the rate of 1 million per second. About how long will it take the computer to check 9! possibilities? What if the graph had 15 vertices (14! possible circuits)? b. According to a eptember 29, 2004 news report, the IBM BlueGene/L computer system can sustain speeds of 36 teraflops 36 trillion computations per second! How long will it take this new system to check a graph with 9! possible circuits? With 14! possible circuits? With 20! possible circuits?
5 Lesson 5.2 The Traveling alesperson Problem Give two examples of a situation in which a solution to the traveling salesperson problem would be beneficial. 7. The following figure shows a circuit board and the distances in millimeters between holes that must be drilled by a drilling machine. ince it is advantageous in terms of time to minimize the distance traveled, find the shortest possible circuit for the machine to travel and the total distance for that circuit. (Assume the machine has to begin and end at point.) B 8.0 A Point of Interest Mathematicians in IBM s Tokyo Research Laboratory have developed a drill route optimization system that has a TP approximation algorithm as its core. The new system reduces the drill route length on a circuit board by an average of 80% and the operation time by 15% on the average. 8. A delivery person must visit each of his warehouses daily. His delivery route begins and ends at his garage (G). The table below shows the approximate travel time (in minutes) between stops. G A B D G A B D a. Draw a weighted complete graph with 5 vertices to represent the information in the table. b. Use the nearest-neighbor algorithm to find the quickest route starting at G, visiting each of the vertices of the graph exactly once, and ending at G. c. What is the travel time of the route in part b?
6 246 hapter 5 More Graphs, ubgraphs, and Trees Projects 9. An algorithm, known by such names as the sorted-edges algorithm and the cheapest-link algorithm, provides another quick and simple way to find an approximate solution to the TP. Investigate this algorithm. Write a brief report on the algorithm and give an example to show how it works. 10. reate a TP poster that illustrates the use of the nearest-neighbor algorithm. At a minimum, your poster should include the following elements. A map of your neighborhood, town, or state with five or six selected locations highlighted. A table that shows the distances between each pair of selected locations. A weighted graph that models the situation. An explanation of how the algorithm is used to find the minimum distance from one selected starting location to each of the others and to return to the original starting point. 11. elect five colleges or universities that you might be interested in attending. After researching the schools of choice, write a paper that incorporates the following. A short paragraph on each school explaining your interest. A weighted, complete graph that shows the five schools and your home. An optimal route based on the shortest path that starts at your home, visits each of the five schools, and returns to your home.
Unit 7 Day 6. Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route
 Unit 7 Day 6 Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route 1 Warm Up Day 7: 1. Draw a planar graph with 6 vertices. 2. Is a K 9,3 graph planar? Explain your reasoning.
Unit 7 Day 6 Section 5.2 Traveling Salesman Problem & Section 5.3 Finding the Shortest Route 1 Warm Up Day 7: 1. Draw a planar graph with 6 vertices. 2. Is a K 9,3 graph planar? Explain your reasoning.
Mathematical Thinking
 Mathematical Thinking Chapter 2 Hamiltonian Circuits and Spanning Trees It often happens in mathematics that what appears to be a minor detail in the statement of a problem can have a profound effect on
Mathematical Thinking Chapter 2 Hamiltonian Circuits and Spanning Trees It often happens in mathematics that what appears to be a minor detail in the statement of a problem can have a profound effect on
Warm -Up. 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices?
 Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
Warm -Up 1. Draw a connected graph with 4 vertices and 7 edges. What is the sum of the degrees of all the vertices? 1. Is this graph a. traceable? b. Eulerian? 3. Eulerize this graph. Warm-Up Eulerize
6.2 Initial Problem. Section 6.2 Network Problems. 6.2 Initial Problem, cont d. Weighted Graphs. Weighted Graphs, cont d. Weighted Graphs, cont d
 Section 6.2 Network Problems Goals Study weighted graphs Study spanning trees Study minimal spanning trees Use Kruskal s algorithm 6.2 Initial Problem Walkways need to be built between the buildings on
Section 6.2 Network Problems Goals Study weighted graphs Study spanning trees Study minimal spanning trees Use Kruskal s algorithm 6.2 Initial Problem Walkways need to be built between the buildings on
1. trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) How many different spanning. trees does the network shown in figure (b) have?
 2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
2/28/18, 8:24 M 1. (a) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (a) have? (b) ow many different spanning trees does the network shown in figure (b) have? L K M P N O L K M P N
IE 102 Spring Routing Through Networks - 1
 IE 102 Spring 2017 Routing Through Networks - 1 The Bridges of Koenigsberg: Euler 1735 Graph Theory began in 1735 Leonard Eüler Visited Koenigsberg People wondered whether it is possible to take a walk,
IE 102 Spring 2017 Routing Through Networks - 1 The Bridges of Koenigsberg: Euler 1735 Graph Theory began in 1735 Leonard Eüler Visited Koenigsberg People wondered whether it is possible to take a walk,
Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1
 Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1 Name Period: 6. Construct a graph with three critical paths. 7. Determine the minimum project time and the critical path for the following
Honors ICM- Graph Theory Unit 7 Homework Packet Homework Day 1 Name Period: 6. Construct a graph with three critical paths. 7. Determine the minimum project time and the critical path for the following
Study Guide Mods: Date:
 Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
Graph Theory Name: Study Guide Mods: Date: Define each of the following. It may be helpful to draw examples that illustrate the vocab word and/or counterexamples to define the word. 1. Graph ~ 2. Vertex
1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions.
 SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
SSII 2014 1 Instructor: Benjamin Wilson Name: 1. Read each problem carefully and follow the instructions. 2. No credit will be given for correct answers without supporting work and/ or explanation. 3.
Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring
 Traveling Salesman Problems Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring 6.1 What Is a Traveling Salesman Problem? The traveling salesman is a convenient metaphor for many different real-life applications. The
Traveling Salesman Problems Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring 6.1 What Is a Traveling Salesman Problem? The traveling salesman is a convenient metaphor for many different real-life applications. The
A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit.
 Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
Math 167 Review of Chapter 2 1 (c) Janice Epstein CHAPTER 2 BUSINESS EFFICENCY A path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. A circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian
MATH 103: Contemporary Mathematics Study Guide for Chapter 6: Hamilton Circuits and the TSP
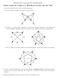 MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
The Travelling Salesman Problem
 The Travelling Salesman Problem The travelling salesman problem cannot be solved directly without vast amounts of processing power, since every possible Hamiltonian cycle would need to be measured. For
The Travelling Salesman Problem The travelling salesman problem cannot be solved directly without vast amounts of processing power, since every possible Hamiltonian cycle would need to be measured. For
Finite Math A Chapter 6 Notes Hamilton Circuits
 Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
Chapter 6: The Mathematics of Touring (Hamilton Circuits) and Hamilton Paths 6.1 Traveling Salesman Problems/ 6.2 Hamilton Paths and Circuits A traveling salesman has clients in 5 different cities. He
Section Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.3 Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits What You Will Learn Hamilton Paths Hamilton Circuits Complete Graphs Traveling Salesman Problems 14.3-2 Hamilton Paths A Hamilton path is a path that
Section 14.3 Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits What You Will Learn Hamilton Paths Hamilton Circuits Complete Graphs Traveling Salesman Problems 14.3-2 Hamilton Paths A Hamilton path is a path that
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem. Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths.
 Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths. Recall: an Euler path is a path that travels through every edge of a graph once and only once; an Euler circuit
Chapter 6. The Traveling-Salesman Problem Section 1. Hamilton circuits and Hamilton paths. Recall: an Euler path is a path that travels through every edge of a graph once and only once; an Euler circuit
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 6 Test Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The number of edges in K12 is 1) 2) The number of Hamilton
Chapter 6 Test Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The number of edges in K12 is 1) 2) The number of Hamilton
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is where a least cost Hamiltonian circuit is found. CHAPTER 1 URBAN SERVICES
 Math 167 eview 1 (c) Janice Epstein HPE 1 UN SEVIES path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit. Math 167 eview
Math 167 eview 1 (c) Janice Epstein HPE 1 UN SEVIES path that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian path. circuit that visits every vertex exactly once is a Hamiltonian circuit. Math 167 eview
OPTIMIZATION 6 NETWORK. Optimization is the. Lessons. 1 Optimum Spanning Networks. 2 Scheduling Projects Using Critical Paths
 UNIT 6 NETWORK Optimization is the process of finding the best. This process is important throughout mathematics and in everyday life. Everywhere you look, you ll see people trying to get the best, whether
UNIT 6 NETWORK Optimization is the process of finding the best. This process is important throughout mathematics and in everyday life. Everywhere you look, you ll see people trying to get the best, whether
What Time Where Muddy City 10 min MSTLessonPlan.docx MSTWorksheets.pptx Discussion 5 min MSTLessonPlan.docx
 MST Lesson Plan Overview Minimal Spanning Trees Summary Many networks link our society: telephone networks, utility supply networks, computer networks, and road networks. For a particular network there
MST Lesson Plan Overview Minimal Spanning Trees Summary Many networks link our society: telephone networks, utility supply networks, computer networks, and road networks. For a particular network there
The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method Lecture 30 Sections 6.1, 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman Problem
The Traveling Salesman Problem Brute Force Method Lecture 30 Sections 6.1, 6.3 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Nov 3, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman Problem
Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1
 AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
Topics Covered. Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm
 Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Graph Theory Topics Covered Introduction to Graphs Euler s Theorem Hamiltonian Circuits The Traveling Salesman Problem Trees and Kruskal s Algorithm What is a graph? A collection of points, called vertices
Midterm 1 : Correction. Friday, Feb. 23.
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Spring 00 Math Group F Midterm : Correction. Friday, Feb... (a) Draw a graph with vertices A, B, C and D in which the valence of vertices A and D is and the valence
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Spring 00 Math Group F Midterm : Correction. Friday, Feb... (a) Draw a graph with vertices A, B, C and D in which the valence of vertices A and D is and the valence
Real-World Applications of Graph Theory
 Real-World Applications of Graph Theory St. John School, 8 th Grade Math Class February 23, 2018 Dr. Dave Gibson, Professor Department of Computer Science Valdosta State University 1 What is a Graph? A
Real-World Applications of Graph Theory St. John School, 8 th Grade Math Class February 23, 2018 Dr. Dave Gibson, Professor Department of Computer Science Valdosta State University 1 What is a Graph? A
1. The Highway Inspector s Problem
 MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
MATH 100 Survey of Mathematics Fall 2009 1. The Highway Inspector s Problem The Königsberg Bridges over the river Pregel C c d e A g D a B b Figure 1. Bridges f Is there a path that crosses every bridge
 Graph Applications, Class Notes, CS 3137 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Web References: http://www.tsp.gatech.edu/index.html http://www-e.uni-magdeburg.de/mertens/tsp/tsp.html TSP applets A Hamiltonian
Graph Applications, Class Notes, CS 3137 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Web References: http://www.tsp.gatech.edu/index.html http://www-e.uni-magdeburg.de/mertens/tsp/tsp.html TSP applets A Hamiltonian
Notes for Recitation 9
 6.042/18.062J Mathematics for Computer Science October 8, 2010 Tom Leighton and Marten van Dijk Notes for Recitation 9 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Now we re going to talk about a famous optimization
6.042/18.062J Mathematics for Computer Science October 8, 2010 Tom Leighton and Marten van Dijk Notes for Recitation 9 1 Traveling Salesperson Problem Now we re going to talk about a famous optimization
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering. Qian Zhu 2/23/2011
 Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Precept 4: Traveling Salesman Problem, Hierarchical Clustering Qian Zhu 2/23/2011 Agenda Assignment: Traveling salesman problem Hierarchical clustering Example Comparisons with K-means TSP TSP: Given the
Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]
![Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks] Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]](/thumbs/89/97991710.jpg) Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
14 Graph Theory. Exercise Set 14-1
 14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
14 Graph Theory Exercise Set 14-1 1. A graph in this chapter consists of vertices and edges. In previous chapters the term was used as a visual picture of a set of ordered pairs defined by a relation or
11-5 Networks. Königsberg Bridge Problem
 Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Section 11-5 Networks 1 11-5 Networks In the 1700s, the people of Königsberg, Germany (now Kaliningrad in Russia), used to enjoy walking over the bridges of the Pregel River. There were three landmasses
Undirected Network Summary
 Undirected Network Summary Notice that the network above has multiple edges joining nodes a to d and the network has a loop at node d. Also c is called an isolated node as it is not connected to any other
Undirected Network Summary Notice that the network above has multiple edges joining nodes a to d and the network has a loop at node d. Also c is called an isolated node as it is not connected to any other
Section Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 14.3 Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # September 11, 2013 Section 14.3 Examples/Handout 18 September 11, 2013 Section 14.3 Notes 19 2.3-2 What You Will
Section 14.3 Hamilton Paths, and Hamilton Circuits INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # September 11, 2013 Section 14.3 Examples/Handout 18 September 11, 2013 Section 14.3 Notes 19 2.3-2 What You Will
Circuits and Paths. April 13, 2014
 Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
Optimal tour along pubs in the UK
 1 From Facebook Optimal tour along 24727 pubs in the UK Road distance (by google maps) see also http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/pubs/index.html (part of TSP homepage http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/
1 From Facebook Optimal tour along 24727 pubs in the UK Road distance (by google maps) see also http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/pubs/index.html (part of TSP homepage http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/
Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms
 Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring 2019 Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms Our first category of algorithms are called brute-force algorithms. Levitin defines
Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring 2019 Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms Our first category of algorithms are called brute-force algorithms. Levitin defines
Introduction to Networks
 LESSON 1 Introduction to Networks Exploratory Challenge 1 One classic math puzzle is the Seven Bridges of Königsberg problem which laid the foundation for networks and graph theory. In the 18th century
LESSON 1 Introduction to Networks Exploratory Challenge 1 One classic math puzzle is the Seven Bridges of Königsberg problem which laid the foundation for networks and graph theory. In the 18th century
A region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that is divided up by the network.
 Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
MEI Further Mathematics Support Programme
 Further Mathematics Support Programme the Further Mathematics Support Programme www.furthermaths.org.uk Modelling and problem solving with Networks Sharon Tripconey Let Maths take you Further Nov 2009
Further Mathematics Support Programme the Further Mathematics Support Programme www.furthermaths.org.uk Modelling and problem solving with Networks Sharon Tripconey Let Maths take you Further Nov 2009
Chapter 5 Review. 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.
 DM_Final.qxp:DM.qxp // 8: AM Page 89 Chapter Review. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. Is the following graph planar or nonplanar? If it is planar, redraw it
DM_Final.qxp:DM.qxp // 8: AM Page 89 Chapter Review. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. Is the following graph planar or nonplanar? If it is planar, redraw it
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION
 SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory 14.1 Graphs, Paths and Circuits Definitions A graph is a finite set of points called vertices (singular form is vertex) connected
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
Graphs. Reading Assignment. Mandatory: Chapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2. Peeking into Computer Science. Jalal Kawash 2010
 Graphs Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1.efine directed and undirected graphs 2.Use graphs to model
Graphs Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1.efine directed and undirected graphs 2.Use graphs to model
GRAPH THEORY AND LOGISTICS
 GRAPH THEORY AND LOGISTICS Maja Fošner and Tomaž Kramberger University of Maribor Faculty of Logistics Mariborska cesta 2 3000 Celje Slovenia maja.fosner@uni-mb.si tomaz.kramberger@uni-mb.si Abstract This
GRAPH THEORY AND LOGISTICS Maja Fošner and Tomaž Kramberger University of Maribor Faculty of Logistics Mariborska cesta 2 3000 Celje Slovenia maja.fosner@uni-mb.si tomaz.kramberger@uni-mb.si Abstract This
Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around
 1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
1 Finite Math A Chapter 5: Euler Paths and Circuits The Mathematics of Getting Around Academic Standards Covered in this Chapter: *************************************************************************************
Crossing bridges. Crossing bridges Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science. Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics. Königsberg (Prussia)
 15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
Mathematics (JAN13MD0101) General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January Unit Decision TOTAL
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Decision 1 Friday 25 January 2013 General Certificate of Education Advanced
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Mathematics Unit Decision 1 Friday 25 January 2013 General Certificate of Education Advanced
UTILIZATION OF GIS AND GRAPH THEORY FOR DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL MAILING ROUTE *
 UTILIZATION OF GIS AND GRAPH THEORY FOR DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL MAILING ROUTE * Dr. Mufid Abudiab, Michael Starek, Rene Lumampao, and An Nguyen Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi 1500 Ocean Drive Corpus
UTILIZATION OF GIS AND GRAPH THEORY FOR DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL MAILING ROUTE * Dr. Mufid Abudiab, Michael Starek, Rene Lumampao, and An Nguyen Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi 1500 Ocean Drive Corpus
10/30/2013. Chapter 7: The Mathematics of Networks. Network. Network. Network. Network. Optimal Network. 7.1 Networks and Trees
 Network Chapter 7: The Mathematics of Networks Our definition of a network is going to be really simple essentially, a network is a graph that is connected. In this context the term is most commonly used
Network Chapter 7: The Mathematics of Networks Our definition of a network is going to be really simple essentially, a network is a graph that is connected. In this context the term is most commonly used
Traveling Salesman Problem. Algorithms and Networks 2014/2015 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij
 Traveling Salesman Problem Algorithms and Networks 2014/2015 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij 1 Contents TSP and its applications Heuristics and approximation algorithms Construction heuristics,
Traveling Salesman Problem Algorithms and Networks 2014/2015 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij 1 Contents TSP and its applications Heuristics and approximation algorithms Construction heuristics,
56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997
 56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997 Answer #1 and any five of the remaining six problems! possible score 1. Multiple Choice 25 2. Traveling Salesman Problem 15 3.
56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997 Answer #1 and any five of the remaining six problems! possible score 1. Multiple Choice 25 2. Traveling Salesman Problem 15 3.
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes
 Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 13 Notes Graph Theory David J. Gisch Networks and Euler Circuits Network Representation Network: A collection of points or objects that are interconnected in some
Exercise 1. D-ary Tree
 CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Winter 2018 Homework 1 Solutions Due: 01/19/2018, 11.59 PM Exercise 1. D-ary Tree A d-ary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has at most d children. Show
CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Winter 2018 Homework 1 Solutions Due: 01/19/2018, 11.59 PM Exercise 1. D-ary Tree A d-ary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has at most d children. Show
MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak
 MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a 50-50 chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following:
MTH-129 Review for Test 4 Luczak 1. On each of three consecutive days the National Weather Service announces that there is a 50-50 chance of rain. Assuming that they are correct, answer the following:
Lecture 1: An Introduction to Graph Theory
 Introduction to Graph Theory Instructor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 1: An Introduction to Graph Theory Week 1 Mathcamp 2011 Mathematicians like to use graphs to describe lots of different things. Groups,
Introduction to Graph Theory Instructor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 1: An Introduction to Graph Theory Week 1 Mathcamp 2011 Mathematicians like to use graphs to describe lots of different things. Groups,
CPSC W2: Quiz 2 Sample Solutions
 CPSC 320 2017W2: Quiz 2 Sample Solutions January 27, 2018 1 Wall-E Loman If you nd a path with no obstacles, it probably doesn't lead anywhere. Frank A. Clark We dene TSP just as before: The Traveling
CPSC 320 2017W2: Quiz 2 Sample Solutions January 27, 2018 1 Wall-E Loman If you nd a path with no obstacles, it probably doesn't lead anywhere. Frank A. Clark We dene TSP just as before: The Traveling
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs
 Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Innovative Systems Design and Engineering ISSN (Paper) ISSN (Online) Vol.5, No.1, 2014
 Abstract Tool Path Optimization of Drilling Sequence in CNC Machine Using Genetic Algorithm Prof. Dr. Nabeel Kadim Abid Al-Sahib 1, Hasan Fahad Abdulrazzaq 2* 1. Thi-Qar University, Al-Jadriya, Baghdad,
Abstract Tool Path Optimization of Drilling Sequence in CNC Machine Using Genetic Algorithm Prof. Dr. Nabeel Kadim Abid Al-Sahib 1, Hasan Fahad Abdulrazzaq 2* 1. Thi-Qar University, Al-Jadriya, Baghdad,
Travelling Salesman Problem. Algorithms and Networks 2015/2016 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij
 Travelling Salesman Problem Algorithms and Networks 2015/2016 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij 1 Contents TSP and its applications Heuristics and approximation algorithms Construction heuristics,
Travelling Salesman Problem Algorithms and Networks 2015/2016 Hans L. Bodlaender Johan M. M. van Rooij 1 Contents TSP and its applications Heuristics and approximation algorithms Construction heuristics,
Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet
 Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet Combinatorial Optimization is the way in which combinatorial thought is applied to real world optimization problems. Optimization entails achieving the sufficient
Math 3012 Combinatorial Optimization Worksheet Combinatorial Optimization is the way in which combinatorial thought is applied to real world optimization problems. Optimization entails achieving the sufficient
Unit graph theory UNIT 4
 Unit graph theory UNIT 4 Concept Characteristics What is a Graph Really? Get in groups of three and discuss what you think a graph really is. Come up with three statements that describe the characteristics
Unit graph theory UNIT 4 Concept Characteristics What is a Graph Really? Get in groups of three and discuss what you think a graph really is. Come up with three statements that describe the characteristics
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms. Genetic Algorithms
 Introduction to Genetic Algorithms Genetic Algorithms We ve covered enough material that we can write programs that use genetic algorithms! More advanced example of using arrays Could be better written
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms Genetic Algorithms We ve covered enough material that we can write programs that use genetic algorithms! More advanced example of using arrays Could be better written
Graphs And Algorithms
 Graphs nd lgorithms Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 1 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1. efine directed and undirected graphs 2. Use
Graphs nd lgorithms Mandatory: hapter 3 Sections 3.1 & 3.2 Reading ssignment 2 1 Graphs bstraction of ata 3 t the end of this section, you will be able to: 1. efine directed and undirected graphs 2. Use
Week 12: Running Time and Performance
 Week 12: Running Time and Performance 1 Most of the problems you have written in this class run in a few seconds or less Some kinds of programs can take much longer: Chess algorithms (Deep Blue) Routing
Week 12: Running Time and Performance 1 Most of the problems you have written in this class run in a few seconds or less Some kinds of programs can take much longer: Chess algorithms (Deep Blue) Routing
Spanning Tree. Lecture19: Graph III. Minimum Spanning Tree (MSP)
 Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
Lesson 4.2. Critical Paths
 Lesson. ritical Paths It is relatively easy to find the shortest time needed to complete a project if the project consists of only a few activities. ut as the tasks increase in number, the problem becomes
Lesson. ritical Paths It is relatively easy to find the shortest time needed to complete a project if the project consists of only a few activities. ut as the tasks increase in number, the problem becomes
1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map
![1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map 1 Euler Circuits. Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map](/thumbs/83/88762945.jpg) 1 Euler Circuits Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map Suppose you needed to vist a number of locations in the
1 Euler Circuits Many of the things we do in daily life involve networks, like the one shown below [Houston Street Map]. Figure 1: Houston City Map Suppose you needed to vist a number of locations in the
Questions... How does one show the first problem is NP-complete? What goes on in a reduction? How hard are NP-complete problems?
 Even More NP Questions... How does one show the first problem is NP-complete? What goes on in a reduction? How hard are NP-complete problems? Reduction We say that problem A reduces to problem B, if there
Even More NP Questions... How does one show the first problem is NP-complete? What goes on in a reduction? How hard are NP-complete problems? Reduction We say that problem A reduces to problem B, if there
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms. Brute-Force Approach
 CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
New Versions of Adjacency The Traveling Salesman Problem Example V (5 Cities) Brute Force Algorithm & Permutations 48 State Capital Example Random
 Intro Math Problem Solving December 7 New Versions of Adjacency The Traveling Salesman Problem Example V (5 Cities) Brute Force Algorithm & Permutations 48 State Capital Example Random Sampling Algorithm
Intro Math Problem Solving December 7 New Versions of Adjacency The Traveling Salesman Problem Example V (5 Cities) Brute Force Algorithm & Permutations 48 State Capital Example Random Sampling Algorithm
Lesson 18: There is Only One Line Passing Through a Given Point with a Given
 Lesson 18: There is Only One Line Passing Through a Given Point with a Given Student Outcomes Students graph equations in the form of using information about slope and intercept. Students know that if
Lesson 18: There is Only One Line Passing Through a Given Point with a Given Student Outcomes Students graph equations in the form of using information about slope and intercept. Students know that if
When the boundaries or names of countries
 CHAPTER Graphs as Models 4 When the boundaries or names of countries change, cartographers have to be prepared to provide the public with new maps. For years, mapmakers and mathematicians alike have wondered
CHAPTER Graphs as Models 4 When the boundaries or names of countries change, cartographers have to be prepared to provide the public with new maps. For years, mapmakers and mathematicians alike have wondered
val(y, I) α (9.0.2) α (9.0.3)
 CS787: Advanced Algorithms Lecture 9: Approximation Algorithms In this lecture we will discuss some NP-complete optimization problems and give algorithms for solving them that produce a nearly optimal,
CS787: Advanced Algorithms Lecture 9: Approximation Algorithms In this lecture we will discuss some NP-complete optimization problems and give algorithms for solving them that produce a nearly optimal,
The Traveling Salesman Problem Outline/learning Objectives The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
Chapter 6 Hamilton Joins the Circuit Outline/learning Objectives To identify and model Hamilton circuit and Hamilton path problems. To recognize complete graphs and state the number of Hamilton circuits
The Traveling Salesman Problem
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
The Traveling Salesman Problem Hamilton path A path that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once. Hamilton circuit A circuit that visits each vertex of the graph once and only once (at the end,
Electronically Filed - City of St. Louis - May 27, :02 PM
 Electronically Filed - City of St. Louis - May 27, 2014-03:02 PM Electronically Filed - City of St. Louis - May 27, 2014-03:02 PM Electronically Filed - City of St. Louis - May 27, 2014-03:02 PM Electronically
Electronically Filed - City of St. Louis - May 27, 2014-03:02 PM Electronically Filed - City of St. Louis - May 27, 2014-03:02 PM Electronically Filed - City of St. Louis - May 27, 2014-03:02 PM Electronically
TSP! Find a tour (hamiltonian circuit) that visits! every city exactly once and is of minimal cost.!
 TSP! Find a tour (hamiltonian circuit) that visits! every city exactly once and is of minimal cost.! Local Search! TSP! 1 3 5 6 4 What should be the neighborhood?! 2-opt: Find two edges in the current
TSP! Find a tour (hamiltonian circuit) that visits! every city exactly once and is of minimal cost.! Local Search! TSP! 1 3 5 6 4 What should be the neighborhood?! 2-opt: Find two edges in the current
PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL
 GRAPH TRAVERSAL PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL Path finding refers to determining the shortest path between two vertices in a graph. We discussed the Floyd Warshall algorithm previously, but you may
GRAPH TRAVERSAL PATH FINDING AND GRAPH TRAVERSAL Path finding refers to determining the shortest path between two vertices in a graph. We discussed the Floyd Warshall algorithm previously, but you may
Street-Routing Problems
 Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Street-Routing Problems Lecture 26 Sections 5.1-5.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 25, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Street-Routing Problems Wed, Oct 25, 2017 1 / 21 1
Chapter 1. Urban Services. Chapter Outline. Chapter Summary
 Chapter 1 Urban Services Chapter Outline Introduction Section 1.1 Euler Circuits Section 1.2 Finding Euler Circuits Section 1.3 Beyond Euler Circuits Section 1.4 Urban Graph Traversal Problems Chapter
Chapter 1 Urban Services Chapter Outline Introduction Section 1.1 Euler Circuits Section 1.2 Finding Euler Circuits Section 1.3 Beyond Euler Circuits Section 1.4 Urban Graph Traversal Problems Chapter
CAP 4630 Artificial Intelligence
 CAP 4630 Artificial Intelligence Instructor: Sam Ganzfried sganzfri@cis.fiu.edu 1 http://www.ultimateaiclass.com/ https://moodle.cis.fiu.edu/ 2 Solving problems by search 3 8-puzzle 4 8-queens 5 Search
CAP 4630 Artificial Intelligence Instructor: Sam Ganzfried sganzfri@cis.fiu.edu 1 http://www.ultimateaiclass.com/ https://moodle.cis.fiu.edu/ 2 Solving problems by search 3 8-puzzle 4 8-queens 5 Search
Section 3.4 Basic Results of Graph Theory
 1 Basic Results of Graph Theory Section 3.4 Basic Results of Graph Theory Purpose of Section: To formally introduce the symmetric relation of a (undirected) graph. We introduce such topics as Euler Tours,
1 Basic Results of Graph Theory Section 3.4 Basic Results of Graph Theory Purpose of Section: To formally introduce the symmetric relation of a (undirected) graph. We introduce such topics as Euler Tours,
Approximation Algorithms
 15-251: Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Spring 2019, Lecture 14 March 5, 2019 Approximation Algorithms 1 2 SAT 3SAT Clique Hamiltonian- Cycle given a Boolean formula F, is it satisfiable? same,
15-251: Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Spring 2019, Lecture 14 March 5, 2019 Approximation Algorithms 1 2 SAT 3SAT Clique Hamiltonian- Cycle given a Boolean formula F, is it satisfiable? same,
Chapter 4 Review. 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter. 2. Draw a graph for the following task table.
 hapter Review 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. raw a graph for the following task table. Task Time Prerequisites Start 0 None 1 5,, I, inish. a. List the
hapter Review 1. Write a summary of what you think are the important points of this chapter.. raw a graph for the following task table. Task Time Prerequisites Start 0 None 1 5,, I, inish. a. List the
MAS 341: GRAPH THEORY 2016 EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MS 41: PH THEOY 2016 EXM SOLUTIONS 1. Question 1 1.1. Explain why any alkane C n H 2n+2 is a tree. How many isomers does C 6 H 14 have? Draw the structure of the carbon atoms in each isomer. marks; marks
MS 41: PH THEOY 2016 EXM SOLUTIONS 1. Question 1 1.1. Explain why any alkane C n H 2n+2 is a tree. How many isomers does C 6 H 14 have? Draw the structure of the carbon atoms in each isomer. marks; marks
Undirected graphs and networks
 Gen. Maths h. 1(1) Page 1 Thursday, ecember 0, 1999 1:10 PM Undirected graphs and networks 1 V co covverage rea of study Units 1 & Geometry In this chapter 1 Vertices and edges 1 Planar graphs 1 ulerian
Gen. Maths h. 1(1) Page 1 Thursday, ecember 0, 1999 1:10 PM Undirected graphs and networks 1 V co covverage rea of study Units 1 & Geometry In this chapter 1 Vertices and edges 1 Planar graphs 1 ulerian
Introduction to Computer Science
 Introduction to Computer Science CSCI 09 Readings St. Amant, Ch. China nhe- Andrew Goodney Fall 08 An algorithm (pronounced AL-go-rithum) is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. The word derives
Introduction to Computer Science CSCI 09 Readings St. Amant, Ch. China nhe- Andrew Goodney Fall 08 An algorithm (pronounced AL-go-rithum) is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. The word derives
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE 101, Winter 018 D/Q Greed SP s DP LP, Flow B&B, Backtrack Metaheuristics P, NP Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 8: Greed Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Optimization
CSE 101, Winter 018 D/Q Greed SP s DP LP, Flow B&B, Backtrack Metaheuristics P, NP Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 8: Greed Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Optimization
CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound
 CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound Reminders > HW8 due today > HW9 will be posted tomorrow start early program will be slow, so debugging will be slow... Review of previous lectures > Complexity
CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound Reminders > HW8 due today > HW9 will be posted tomorrow start early program will be slow, so debugging will be slow... Review of previous lectures > Complexity
Mathematics 504 CST. Mid-Year Examination January Question/Answer Booklet. Student's Name FOR TEACHER USE ONLY. Part A /24.
 563-504 Mathematics 504 CST Mid-Year Examination January 2011 Question/Answer Booklet Student's Name Group Date FOR TEACHER USE ONLY Part A /24 Part B /16 Part C /60 Total /100 Question/Answer Booklet
563-504 Mathematics 504 CST Mid-Year Examination January 2011 Question/Answer Booklet Student's Name Group Date FOR TEACHER USE ONLY Part A /24 Part B /16 Part C /60 Total /100 Question/Answer Booklet
CS 440 Theory of Algorithms /
 CS 440 Theory of Algorithms / CS 468 Algorithms in Bioinformaticsi Brute Force. Design and Analysis of Algorithms - Chapter 3 3-0 Brute Force A straightforward approach usually based on problem statement
CS 440 Theory of Algorithms / CS 468 Algorithms in Bioinformaticsi Brute Force. Design and Analysis of Algorithms - Chapter 3 3-0 Brute Force A straightforward approach usually based on problem statement
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics
 Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu P, NP-Problems Class
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu P, NP-Problems Class
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Integer Programming. Xi Chen. Department of Management Science and Engineering International Business School Beijing Foreign Studies University
 Integer Programming Xi Chen Department of Management Science and Engineering International Business School Beijing Foreign Studies University Xi Chen (chenxi0109@bfsu.edu.cn) Integer Programming 1 / 42
Integer Programming Xi Chen Department of Management Science and Engineering International Business School Beijing Foreign Studies University Xi Chen (chenxi0109@bfsu.edu.cn) Integer Programming 1 / 42
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES. Alessandro Artale UniBZ - artale/z
 CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
Condensed. Mathematics MD01. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Unit Decision 1.
 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2015 Mathematics MD01 Unit Decision 1 Tuesday 16 June 2015 1.30 pm to 3.00 pm For this paper you must have: the blue AQA booklet of
General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2015 Mathematics MD01 Unit Decision 1 Tuesday 16 June 2015 1.30 pm to 3.00 pm For this paper you must have: the blue AQA booklet of
