Objectives. In this session, you will learn to:
|
|
|
- Aileen Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TRS
2 Objectives n this session, you will learn to: Store data in a tree istinguish types of inary tree Traverse a inary Tree norder PreOrder PostOrder onstruct a inary Tree onstruct an expression inary tree
3 Storing ata in a Tree onsider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. folder may further contain any number of sub folders and files. n such a case, it is not possible to represent the structure linearly because all the items have a hierarchical relationship among themselves. n such a case, it would be good if you have a data structure that enables you to store your data in a nonlinear fashion. irectory structure:
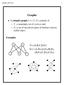
4 efining Trees tree is a nonlinear data structure that represent a hierarchical relationship among the various data elements. Trees are used in applications in which the relation between data elements needs to be represented in a hierarchy. K J L M
5 efining Trees (ontd.) ach element in a tree is referred to as a node. The topmost node in a tree is called root. root K J L M node
6 efining Trees (ontd.) ach node in a tree can further have subtrees below its hierarchy. root K J L M node
7 Tree Terminology Let us discuss various terms that are most frequently used with trees. Leaf node: t refers to a node with no children. Nodes,,,,, J, L, and M are leaf nodes. K J L M
8 Tree Terminology (ontd.) Subtree: portion of a tree, which can be viewed as a separate tree in itself is called a subtree. subtree can also contain just one node called the root node. hildren of a node: The roots of the subtrees of a node are called the children of the node. Tree with root, containing nodes,,, and is a subtree of node.,,, and are children of node. is the parent of these nodes. K J L M
9 Tree Terminology (ontd.) dge: link from the parent to a child node is referred to as an edge. egree of a node: t refers to the number of subtrees of a node in a tree. egree of node is 1 egree of node is 2 egree of node is 3 egree of node is 4 dge K J L M
10 Tree Terminology (ontd.) Siblings/rothers: t refers to the children of the same node. Nodes,, and are siblings of each other. Nodes,,, and are siblings of each other. K J L M
11 Tree Terminology (ontd.) nternal node: t refers to any node between the root and a leaf node. Level of a node: t refers to the distance (in number of nodes) of a node from the root. Root always lies at level 0. s you move down the tree, the level increases by one. Level 0 Nodes,,, and K are internal nodes. Level 1 K J L Level 2 M Level 3
12 Tree Terminology (ontd.) epth of a tree: Refers to the total number of levels in the tree. The depth of the following tree is 4. Level 0 Level 1 K J L Level 2 M Level 3
13 Just a minute onsider the following tree and answer the questions that follow: a. What is the depth of the tree? b. Which nodes are children of node? c. Which node is the parent of node? d. What is the level of node? e. Which nodes are the siblings of node? f. Which nodes are the siblings of node? g. Which nodes are leaf nodes? root nswer: a. 4 b. and c. d. 2 e. does not have any siblings f. The only sibling of is g.,,, and
14 efining inary Trees inary tree is a specific type of tree in which each node can have at most two children namely left child and right child. There are various types of binary trees: Strictly binary tree ull binary tree omplete binary tree Strictly binary tree: binary tree in which every node, except for the leaf nodes, has non-empty left and right children.
15 efining inary Trees (ontd.) ull binary tree: binary tree of depth d that contains exactly 2d 1 nodes. epth = 3 Total number of nodes = 23 1 = 7
16 efining inary Trees (ontd.) omplete binary tree: binary tree with n nodes and depth d whose nodes correspond to the nodes numbered from 0 to n 1 in the full binary tree of depth k ull inary Tree omplete inary Tree ncomplete inary Tree
17 Representing a inary Tree rray representation of binary trees: ll the nodes are represented as the elements of an array inary Tree [0] [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] f there are n nodes in a binary tree, then for any node with index i, where 0 < i < n 1: Parent of i is at (i 1)/2. Left child of i is at 2i + 1: f 2i + 1 > n 1, then the node does not have a left child. Right child of i is at 2i + 2: rray Representation f 2i + 2 > n 1, then the node does have a right child.
18 Representing a inary Tree (ontd.) Linked representation of a binary tree: t uses a linked list to implement a binary tree. ach node in the linked representation holds the following information: ata Reference to the left child Reference to the right child f a node does not have a left child or a right child or both, the respective left or right child fields of that node point to NULL. ata Node
19 Representing a inary Tree (ontd.) root root inary Tree Linked Representation 80
20 inary Tree Node Struct node { nt info; Struct node *left,*right; }
21 OPRTONS ON TRS Traversing a inary Tree 1)TRVRSN You can implement various operations on a binary tree. common operation on a binary tree is traversal. Traversal refers to the process of visiting all the nodes of a binary tree once. There are three ways for traversing a binary tree: norder traversal Preorder traversal Postorder traversal
22 NORR TRVRSL Steps for traversing a tree in inorder sequence are as follows: 1. Traverse the left subtree 2. Visit root 3. Traverse the right subtree Let us consider an example.
23 norder Traversal (ontd.) is is not not NULL. NULL. The left subtree of node to traverse the left Therefore, move to node. subtree of. root
24 norder Traversal (ontd.) The left subtree of node is NULL. Therefore, visit node. root
25 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is not NULL Therefore, move to the right subtree of node root
26 norder Traversal (ontd.) Left subtree of is empty. Therefore, visit node. root
27 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is empty. Therefore, move to node. root
28 norder Traversal (ontd.) The left subtree of has been visited. Therefore, visit node. root
29 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is not empty. Therefore, move to the right subtree of. root
30 norder Traversal (ontd.) Left subtree of is empty. Therefore, visit node. root
31 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is empty. Therefore, move to node. root
32 norder Traversal (ontd.) Left subtree of has been visited. Therefore, visit node. root
33 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is not empty. Therefore, move to the right subtree of. root
34 norder Traversal (ontd.) Left subtree of is not empty. Therefore, move to the left subtree of. root
35 norder Traversal (ontd.) Left subtree of is empty. Therefore, visit node. root
36 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is empty. Therefore, move to node. root
37 norder Traversal (ontd.) The left subtree of node has been visited. Therefore, visit node. root
38 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is not empty. Therefore, move to the right subtree of node. root
39 norder Traversal (ontd.) Left subtree of is not empty. Therefore, move to the left subtree of node. root
40 norder Traversal (ontd.) Left subtree of is empty. Therefore, visit. root
41 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is empty. Therefore, move to node. root
42 norder Traversal (ontd.) Visit node. root
43 norder Traversal (ontd.) Right subtree of is empty. root Traversal complete
44 LORTM LORTM NORRTRVRS() { 1. set top=0, stack[top]=null, ptr = root 2. Repeat while ptr!=null 2.1 set top=top set stack[top]=ptr 2.3 set ptr=ptr->left 3. Set ptr=stack[top], top=top-1 4. Repeat while ptr!=null 4.1 print ptr->info 4.2 if ptr->right!=null then 4.2.1set ptr=ptr->right goto step Set ptr=stack[top], top=top-1 }
45 PRORR TRVRSL Steps for traversing a tree in preorder sequence are as follows: 1. Visit root 2. Traverse the left subtree 3. Traverse the right subtree
46 Preorder Traversal (ontd.) Perform the preorder traversal of the following tree. Preorder Traversal:
47 LORTM LORTM PRORRTRVRS() { 1. set top=0, stack[top]=null, ptr = root 2. Repeat while ptr!=null 2.1 print ptr -> info 2.2 if (ptr -> right!= NULL) top = top set stack [ top] = ptr -> right 2.3 if ( ptr -> left!= NULL) ptr=ptr -> left else ptr=stack[top], top=top-1 }
48 Postorder Traversal Steps for traversing a tree in postorder sequence are as follows: 1. Traverse the left subtree 2. Traverse the right subtree 3. Visit the root
49 Postorder Traversal (ontd.) Perform the postorder traversal of the following tree. Postorder Traversal:
50 LORTM LORTM POSTORRTRVRS() { 1. set top = 0, stack [top] = NULL, ptr = root 2. Repeat while ptr!=null 2.1 top = top +1, stack [ top ] = ptr 2.2 if (ptr -> right!= NULL) top = top set stack [ top] = - ( ptr -> right ) 2.3 ptr = ptr -> left 3. ptr = stack [top], top = top-1 4. Repeat while ( ptr > 0 ) 4.1 print ptr -> info 4.2 ptr = stack [top], top = top-1 5. if (ptr < 0) 5.1 set ptr = - ptr 5.2 o to step 2 }
51 Recursive Traversal mplementation
52 Just a minute n traversal method, root is processed before traversing the left and right subtrees. nswer: Preorder
53 xpression inary Tree Traversal f an expression is represented as a binary tree, the inorder traversal of the tree gives us an infix expression, whereas the postorder traversal gives us a postfix expression as shown in igure.
54 onstruction of inary Tree iven an order of traversal of a tree, it is possible to construct a tree; for example, consider the folowing order: norder = We can construct the binary trees shown in igure by using this order of traversal
55 onstruction of inary Tree Therefore, we conclude that given only one order of traversal of a tree, it is possible to construct a number of binary trees; a unique binary tree cannot be constructed with only one order of traversal. or construction of a unique binary tree, we require two orders, in which one has to be inorder; the other can be preorder or postorder. or example, consider the following orders: norder = Postorder =
56 onstruction of inary Tree norder = Postorder = We can construct the unique binary tree shown in igure by using these orders of traversal: unique binary tree constructed using its inorder and postorder.
57 Just a minute onstruct the binary tree with the following: norder:- Postorder:-
58 Postorder Traversal (ontd.)
59 Summary n this session, you learned that: tree is a nonlinear data structure that represents a hierarchical relationship among the various data elements. binary tree is a specific type of tree in which each node can have a maximum of two children. inary trees can be implemented by using arrays as well as linked lists, depending upon requirement. Traversal of a tree is the process of visiting all the nodes of the tree once. There are three types of traversals, namely inorder, preorder, and postorder traversal.
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
Trees and Tree Traversals. Binary Trees. COMP 210: Object-Oriented Programming Lecture Notes 8. Based on notes by Logan Mayfield
 OMP 210: Object-Oriented Programming Lecture Notes 8 Trees and Tree Traversals ased on notes by Logan Mayfield In these notes we look at inary Trees and how to traverse them. inary Trees Imagine a list.
OMP 210: Object-Oriented Programming Lecture Notes 8 Trees and Tree Traversals ased on notes by Logan Mayfield In these notes we look at inary Trees and how to traverse them. inary Trees Imagine a list.
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
Data Structures - Binary Trees and Operations on Binary Trees
 ata Structures - inary Trees and Operations on inary Trees MS 275 anko drovic (UI) MS 275 October 15, 2018 1 / 25 inary Trees binary tree is a finite set of elements. It can be empty partitioned into three
ata Structures - inary Trees and Operations on inary Trees MS 275 anko drovic (UI) MS 275 October 15, 2018 1 / 25 inary Trees binary tree is a finite set of elements. It can be empty partitioned into three
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
Tree Structures. A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node
 Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Each element of a binary tree is called a node of the tree. The following figure shows a binary tree with 9 nodes where A is the root.
 212 lgorithms & ata Structures Spring 05/06 Lecture Notes # 14 Outline ntroduction to Trees inary Trees: asic efinitions Traversing inary Trees Node Representation of inary Trees Primitive unctions in
212 lgorithms & ata Structures Spring 05/06 Lecture Notes # 14 Outline ntroduction to Trees inary Trees: asic efinitions Traversing inary Trees Node Representation of inary Trees Primitive unctions in
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Section 5.5. Left subtree The left subtree of a vertex V on a binary tree is the graph formed by the left child L of V, the descendents
 Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Trees! Ellen Walker! CPSC 201 Data Structures! Hiram College!
 Trees! Ellen Walker! CPSC 201 Data Structures! Hiram College! ADTʼs Weʼve Studied! Position-oriented ADT! List! Stack! Queue! Value-oriented ADT! Sorted list! All of these are linear! One previous item;
Trees! Ellen Walker! CPSC 201 Data Structures! Hiram College! ADTʼs Weʼve Studied! Position-oriented ADT! List! Stack! Queue! Value-oriented ADT! Sorted list! All of these are linear! One previous item;
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Binary Trees. Height 1
 Binary Trees Definitions A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes that shows parent-child relationship such that There is a special node called root Remaining nodes are portioned into subsets T1,T2,T3.
Binary Trees Definitions A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes that shows parent-child relationship such that There is a special node called root Remaining nodes are portioned into subsets T1,T2,T3.
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree
 CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu Introduction to Tree Tree is a non-linear data structure
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu Introduction to Tree Tree is a non-linear data structure
BST Implementation. Data Structures. Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr University of Ain Shams
 Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Lecture 4 Binary search trees (BST) Dr. Mahmoud Attia Sakr mahmoud.sakr@cis.asu.edu.eg Cairo, Egypt, October 2012 Binary Search Trees (BST) 1. Hierarchical data structure with a single reference to root
Binary Trees. Reading: Lewis & Chase 12.1, 12.3 Eck Programming Course CL I
 inary Trees Reading: Lewis & hase 12.1, 12.3 Eck 9.4.1 Objectives Tree basics Learn the terminology used when talking about trees iscuss methods for traversing trees iscuss a possible implementation of
inary Trees Reading: Lewis & hase 12.1, 12.3 Eck 9.4.1 Objectives Tree basics Learn the terminology used when talking about trees iscuss methods for traversing trees iscuss a possible implementation of
Trees. CSE 373 Data Structures
 Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
Unit III - Tree TREES
 TREES Unit III - Tree Consider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. A folder may
TREES Unit III - Tree Consider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. A folder may
CSC148 Week 6. Larry Zhang
 CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
Why Do We Need Trees?
 CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
Data Structures. Binary Trees. Root Level = 0. number of leaves:?? leaves Depth (Maximum level of the tree) leaves or nodes. Level=1.
 Data Structures inary Trees number of leaves:?? height leaves Depth (Maximum level of the tree) leaves or nodes Root Level = 0 Level=1 57 feet root 2 Level=2 Number of nodes: 2 (2+1) - 1 = 7 2 inary Trees
Data Structures inary Trees number of leaves:?? height leaves Depth (Maximum level of the tree) leaves or nodes Root Level = 0 Level=1 57 feet root 2 Level=2 Number of nodes: 2 (2+1) - 1 = 7 2 inary Trees
CSCI-401 Examlet #5. Name: Class: Date: True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false.
 Name: Class: Date: CSCI-401 Examlet #5 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The root node of the standard binary tree can be drawn anywhere in the tree diagram. 2.
Name: Class: Date: CSCI-401 Examlet #5 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The root node of the standard binary tree can be drawn anywhere in the tree diagram. 2.
Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed
 Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Computer Science Department 2015 2016 Department of Computer Science _ UHD 1 What this Lecture
Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Computer Science Department 2015 2016 Department of Computer Science _ UHD 1 What this Lecture
Trees. Tree Structure Binary Tree Tree Traversals
 Trees Tree Structure Binary Tree Tree Traversals The Tree Structure Consists of nodes and edges that organize data in a hierarchical fashion. nodes store the data elements. edges connect the nodes. The
Trees Tree Structure Binary Tree Tree Traversals The Tree Structure Consists of nodes and edges that organize data in a hierarchical fashion. nodes store the data elements. edges connect the nodes. The
Lec 17 April 8. Topics: binary Trees expression trees. (Chapter 5 of text)
 Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Graphs V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
 Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Topic 14. The BinaryTree ADT
 Topic 14 The BinaryTree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree
Topic 14 The BinaryTree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree
Trees. Trees. CSE 2011 Winter 2007
 Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 19, 2016 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 7: Trees Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees Uses Of Trees Chapter 7: Trees
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 19, 2016 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 7: Trees Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees Uses Of Trees Chapter 7: Trees
[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree
![[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree [ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree](/thumbs/80/82537139.jpg) [ DATA STRUCTURES ] Chapter - 07 : Trees A Tree is a non-linear data structure in which items are arranged in a sorted sequence. It is used to represent hierarchical relationship existing amongst several
[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Chapter - 07 : Trees A Tree is a non-linear data structure in which items are arranged in a sorted sequence. It is used to represent hierarchical relationship existing amongst several
BBM 201 Data structures
 BBM 201 Data structures Lecture 11: Trees 2018-2019 Fall Content Terminology The Binary Tree The Binary Search Tree Data Structures and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, Carrano and Henry, 2013
BBM 201 Data structures Lecture 11: Trees 2018-2019 Fall Content Terminology The Binary Tree The Binary Search Tree Data Structures and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, Carrano and Henry, 2013
6-TREE. Tree: Directed Tree: A directed tree is an acyclic digraph which has one node called the root node
 6-TREE Data Structure Management (330701) Tree: A tree is defined as a finite set of one or more nodes such that There is a special node called the root node R. The remaining nodes are divided into n 0
6-TREE Data Structure Management (330701) Tree: A tree is defined as a finite set of one or more nodes such that There is a special node called the root node R. The remaining nodes are divided into n 0
7.1 Introduction. A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w
 Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers
 04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
Introduction to Binary Trees
 Introduction to inary Trees 1 ackground ll data structures examined so far are linear data structures. Each element in a linear data structure has a clear predecessor and a clear successor. Precessors
Introduction to inary Trees 1 ackground ll data structures examined so far are linear data structures. Each element in a linear data structure has a clear predecessor and a clear successor. Precessors
Chapter 4 Trees. Theorem A graph G has a spanning tree if and only if G is connected.
 Chapter 4 Trees 4-1 Trees and Spanning Trees Trees, T: A simple, cycle-free, loop-free graph satisfies: If v and w are vertices in T, there is a unique simple path from v to w. Eg. Trees. Spanning trees:
Chapter 4 Trees 4-1 Trees and Spanning Trees Trees, T: A simple, cycle-free, loop-free graph satisfies: If v and w are vertices in T, there is a unique simple path from v to w. Eg. Trees. Spanning trees:
Trees. Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT
 Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Binary Trees Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Binary Trees 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Trees Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 Binary Trees A binary tree is either empty or it contains a root node and left- and right-subtrees that are also
Binary Trees 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Trees Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 Binary Trees A binary tree is either empty or it contains a root node and left- and right-subtrees that are also
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Sidra Malik sidra.malik@ciitlahore.edu.pk Tree? In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes
Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Sidra Malik sidra.malik@ciitlahore.edu.pk Tree? In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes
ITEC2620 Introduction to Data Structures
 T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture 4a inary Trees Review of Linked Lists Linked-Lists dynamic length arbitrary memory locations access by following links an only traverse link in forward direction
T2620 ntroduction to ata Structures Lecture 4a inary Trees Review of Linked Lists Linked-Lists dynamic length arbitrary memory locations access by following links an only traverse link in forward direction
Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 -
 Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 - Hanyang University Jong-Il Park Basic Tree Concepts Logical structures Chap. 2~4 Chap. 5 Chap. 6 Linear list Tree Graph Linear structures Non-linear structures Linear Lists
Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 - Hanyang University Jong-Il Park Basic Tree Concepts Logical structures Chap. 2~4 Chap. 5 Chap. 6 Linear list Tree Graph Linear structures Non-linear structures Linear Lists
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson
 Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading: Carrano, Chapter 15 Introduction to trees The data structures we have seen so far to implement
Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading: Carrano, Chapter 15 Introduction to trees The data structures we have seen so far to implement
COSC 2011 Section N. Trees: Terminology and Basic Properties
 COSC 2011 Tuesday, March 27 2001 Overview Trees and Binary Trees Quick review of definitions and examples Tree Algorithms Depth, Height Tree and Binary Tree Traversals Preorder, postorder, inorder Binary
COSC 2011 Tuesday, March 27 2001 Overview Trees and Binary Trees Quick review of definitions and examples Tree Algorithms Depth, Height Tree and Binary Tree Traversals Preorder, postorder, inorder Binary
CISC 235 Topic 3. General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 CISC 235 Topic 3 General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Outline General Trees Terminology, Representation, Properties Binary Trees Representations, Properties, Traversals Recursive Algorithms
CISC 235 Topic 3 General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Outline General Trees Terminology, Representation, Properties Binary Trees Representations, Properties, Traversals Recursive Algorithms
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Data Structures. Trees. By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini. M.A. Eljinini, PhD
 Data Structures Trees By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini Trees Are collections of items arranged in a tree like data structure (none linear). Items are stored inside units called nodes. However: We can use
Data Structures Trees By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini Trees Are collections of items arranged in a tree like data structure (none linear). Items are stored inside units called nodes. However: We can use
CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Tree Tree is a non-linear
CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Tree Tree is a non-linear
A Hierarchical Structure. Lecture11: Tree I. Tree Data Structures. Unix/Linux file systems. Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH
 Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2015F) Lecture11: Tree I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2015F) Lecture11: Tree I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees
 COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Bioinformatics Programming. EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang)
 Bioinformatics Programming EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang) 1 Tree 2 A Tree Structure A tree structure means that the data are organized so that items of information are related by branches 3 Definition
Bioinformatics Programming EE, NCKU Tien-Hao Chang (Darby Chang) 1 Tree 2 A Tree Structure A tree structure means that the data are organized so that items of information are related by branches 3 Definition
tree nonlinear Examples
 The Tree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree example 10-2
The Tree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree example 10-2
Tree. A path is a connected sequence of edges. A tree topology is acyclic there is no loop.
 Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Lesson 3: trees and visits Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created by Dr. Gabriele D Angelo) International
Lesson 3: trees and visits Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created by Dr. Gabriele D Angelo) International
Successor/Predecessor Rules in Binary Trees
 Successor/Predecessor Rules in inary Trees Thomas. nastasio July 7, 2003 Introduction inary tree traversals are commonly made in one of three patterns, inorder, preorder, and postorder. These traversals
Successor/Predecessor Rules in inary Trees Thomas. nastasio July 7, 2003 Introduction inary tree traversals are commonly made in one of three patterns, inorder, preorder, and postorder. These traversals
Garbage Collection: recycling unused memory
 Outline backtracking garbage collection trees binary search trees tree traversal binary search tree algorithms: add, remove, traverse binary node class 1 Backtracking finding a path through a maze is an
Outline backtracking garbage collection trees binary search trees tree traversal binary search tree algorithms: add, remove, traverse binary node class 1 Backtracking finding a path through a maze is an
Principles of Computer Science
 Principles of Computer Science Binary Trees 08/11/2013 CSCI 2010 - Binary Trees - F.Z. Qureshi 1 Today s Topics Extending LinkedList with Fast Search Sorted Binary Trees Tree Concepts Traversals of a Binary
Principles of Computer Science Binary Trees 08/11/2013 CSCI 2010 - Binary Trees - F.Z. Qureshi 1 Today s Topics Extending LinkedList with Fast Search Sorted Binary Trees Tree Concepts Traversals of a Binary
CSC148H Week 8. Sadia Sharmin. July 12, /29
 CSC148H Week 8 Sadia Sharmin July 12, 2017 1/29 Motivating Trees I A data structure is a way of organizing data I Stacks, queues, and lists are all linear structures I They are linear in the sense that
CSC148H Week 8 Sadia Sharmin July 12, 2017 1/29 Motivating Trees I A data structure is a way of organizing data I Stacks, queues, and lists are all linear structures I They are linear in the sense that
Introduction to Computers and Programming. Concept Question
 Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Cpt S 122 Data Structures. Data Structures Trees
 Cpt S 122 Data Structures Data Structures Trees Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Motivation Trees are one of the most important and extensively
Cpt S 122 Data Structures Data Structures Trees Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Motivation Trees are one of the most important and extensively
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk I. Yu, D. Karabeg INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Function growth & estimation of running time, trees Issued: 24. 08. 2016 Exercise
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk I. Yu, D. Karabeg INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Function growth & estimation of running time, trees Issued: 24. 08. 2016 Exercise
Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science. Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department
 Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department HL Topics 1-7, D1-4 1: System design 2: Computer Organisation 3: Networks 4: Computational
Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department HL Topics 1-7, D1-4 1: System design 2: Computer Organisation 3: Networks 4: Computational
a graph is a data structure made up of nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges
 1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
Trees 11/15/16. Chapter 11. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Chapter 11 Trees Definition of a general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: A single node r, the root Sets that are general trees, called
Chapter 11 Trees Definition of a general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: A single node r, the root Sets that are general trees, called
Data Structures And Algorithms
 Data Structures And Algorithms Binary Trees Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester 2017-2018 Definitions Linked lists, arrays, queues, stacks are linear structures not suitable to represent hierarchical data,
Data Structures And Algorithms Binary Trees Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester 2017-2018 Definitions Linked lists, arrays, queues, stacks are linear structures not suitable to represent hierarchical data,
Binary Tree. Binary tree terminology. Binary tree terminology Definition and Applications of Binary Trees
 Binary Tree (Chapter 0. Starting Out with C++: From Control structures through Objects, Tony Gaddis) Le Thanh Huong School of Information and Communication Technology Hanoi University of Technology 11.1
Binary Tree (Chapter 0. Starting Out with C++: From Control structures through Objects, Tony Gaddis) Le Thanh Huong School of Information and Communication Technology Hanoi University of Technology 11.1
Tree. Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11. Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni. Sep 3,2010
 SE-286: Data Structures t and Programming Tree Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11 Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni 1 Trees Nature Lover sviewofatree leaves branches root 3 Computer
SE-286: Data Structures t and Programming Tree Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11 Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni 1 Trees Nature Lover sviewofatree leaves branches root 3 Computer
Tree: non-recursive definition. Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps. Tree: recursive definition. Tree: example.
 Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Binary Trees. Examples:
 Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Binary Trees A tree is a data structure that is made of nodes and pointers, much like a linked list. The difference between them lies in how they are organized: In a linked list each node is connected
Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University
 Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture The concept of binary tree, its terms, and its operations Full binary tree theorem Idea
Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture The concept of binary tree, its terms, and its operations Full binary tree theorem Idea
Why Use Binary Trees? Data Structures - Binary Trees 1. Trees (Contd.) Trees
 Why Use Binary Trees? - Binary Trees 1 Dr. TGI Fernando 1 2 February 24, 2012 Fundamental data structure Combines the advantages of an ordered array and a linked list. You can search an ordered array quickly
Why Use Binary Trees? - Binary Trees 1 Dr. TGI Fernando 1 2 February 24, 2012 Fundamental data structure Combines the advantages of an ordered array and a linked list. You can search an ordered array quickly
Section Summary. Introduction to Trees Rooted Trees Trees as Models Properties of Trees
 Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Trees. Introduction & Terminology. February 05, 2018 Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1
 Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
Trees Introduction & Terminology Cinda Heeren / Geoffrey Tien 1 Review: linked lists Linked lists are constructed out of nodes, consisting of a data element a pointer to another node Lists are constructed
Trees 3/19/14. Mammal. Dog Pig Cat
 Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Data Structures - Binary Trees 1
 Data Structures - Binary Trees 1 Dr. TGI Fernando 1 2 February 24, 2012 1 Email: gishantha@dscs.sjp.ac.lk 2 URL: http://tgifernando.wordpress.com/ Dr. TGI Fernando () Data Structures - Binary Trees 1 February
Data Structures - Binary Trees 1 Dr. TGI Fernando 1 2 February 24, 2012 1 Email: gishantha@dscs.sjp.ac.lk 2 URL: http://tgifernando.wordpress.com/ Dr. TGI Fernando () Data Structures - Binary Trees 1 February
A Hierarchical Structure. Lecture11: Trees I. Tree Data Structures. Unix/Linux file systems. Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH
 Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2013F) Lecture11: Trees I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2013F) Lecture11: Trees I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
There are many other applications like constructing the expression tree from the postorder expression. I leave you with an idea as how to do it.
 Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms Prof. Hema Murthy Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 49 Module 09 Other applications: expression tree
Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms Prof. Hema Murthy Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 49 Module 09 Other applications: expression tree
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Trees
 Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Trees We ve spent a lot of time looking at a variety of structures where there is a natural linear ordering of the elements in arrays,
Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Trees We ve spent a lot of time looking at a variety of structures where there is a natural linear ordering of the elements in arrays,
Trees. T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
 Trees Terminology. Rooted Trees. Traversals. Labeled Trees and Expression Trees. Tree ADT. Tree Implementations. Binary Search Trees. Optimal Search Trees T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
Trees Terminology. Rooted Trees. Traversals. Labeled Trees and Expression Trees. Tree ADT. Tree Implementations. Binary Search Trees. Optimal Search Trees T.U. Cluj-Napoca -DSA Lecture 2 - M. Joldos 1
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) Linear search can be used for lists stored in an array as well as for linked lists. (It's the method used in the find
 IX. Binary Trees IX-1 IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following:
IX. Binary Trees IX-1 IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following:
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections
 Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
Programming III Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Nathan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Copyright 2002- by
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10)
 IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI KUALA LUMPUR
 STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Determine if a given tree is an instance of a particular type (e.g. binary, and later heap, etc.) Describe
Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Determine if a given tree is an instance of a particular type (e.g. binary, and later heap, etc.) Describe
CS61B Lecture #20: Trees. Last modified: Mon Oct 8 21:21: CS61B: Lecture #20 1
 CS61B Lecture #20: Trees Last modified: Mon Oct 8 21:21:22 2018 CS61B: Lecture #20 1 A Recursive Structure Trees naturally represent recursively defined, hierarchical objects with more than one recursive
CS61B Lecture #20: Trees Last modified: Mon Oct 8 21:21:22 2018 CS61B: Lecture #20 1 A Recursive Structure Trees naturally represent recursively defined, hierarchical objects with more than one recursive
Also, recursive methods are usually declared private, and require a public non-recursive method to initiate them.
 Laboratory 11: Expression Trees and Binary Search Trees Introduction Trees are nonlinear objects that link nodes together in a hierarchical fashion. Each node contains a reference to the data object, a
Laboratory 11: Expression Trees and Binary Search Trees Introduction Trees are nonlinear objects that link nodes together in a hierarchical fashion. Each node contains a reference to the data object, a
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 10 / 10 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? A few comments about Doubly Linked Lists w/ dummy head/tail Trees Binary trees
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 10 / 10 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? A few comments about Doubly Linked Lists w/ dummy head/tail Trees Binary trees
Chapter Summary. Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees
 Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
Chapter Contents. Trees. Tree Concepts. Hierarchical Organization. Hierarchical Organization. Hierarchical Organization.
 Chapter Contents Chapter 18 Tree Concepts Hierarchical Organizations Tree Terminology Traversals of a Tree Traversals of a Binary Tree Traversals of a General Tree Java Interfaces for Interfaces for All
Chapter Contents Chapter 18 Tree Concepts Hierarchical Organizations Tree Terminology Traversals of a Tree Traversals of a Binary Tree Traversals of a General Tree Java Interfaces for Interfaces for All
Trees. Estruturas de Dados / Programação 2 Árvores. Márcio Ribeiro twitter.com/marciomribeiro. Introduc)on. Hierarchical structure
 Introduc)on Linear structures Removing this idea, treasure of applicaons Estruturas de Dados / Programação 2 Árvores Márcio Ribeiro marcio@ic.ufal.br twitter.com/marciomribeiro Hierarchical structure Companies
Introduc)on Linear structures Removing this idea, treasure of applicaons Estruturas de Dados / Programação 2 Árvores Márcio Ribeiro marcio@ic.ufal.br twitter.com/marciomribeiro Hierarchical structure Companies
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections. 2501ICT Logan
 Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Logan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Queues and Stacks Queues and Stacks
Stacks, Queues and Hierarchical Collections 2501ICT Logan Contents Linked Data Structures Revisited Stacks Queues Trees Binary Trees Generic Trees Implementations 2 Queues and Stacks Queues and Stacks
