Workshop 1 on Minkowski Geometry using SketchPad
|
|
|
- Brian Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Workshop 1 on Minkowski Geometry using Sketchad reliminary remarks: To perform geometrical constructions in Minkowski geometry, you need some hyperbolic drawing requisites such as a hyperbolic compass for drawing rectangular hyperbolas and a hyperbolic perpendicular template for the construction of hyperbolic perpendiculars. hyperbolic compass is a compass which allows you to draw the rectangular hyperbola with the given centre and the given peripheral point. The axes as always in Minkowski Geometry are assumed to be horizontal and vertical. hyperbolic perpendicular template is an instrument used for drawing a hyperbolic perpendicular to a line from a point which may or not be on the line. In Minkowski Geometry we typically use an instrument based upon three points: The first two points are used to determine the direction of the straight object: a line, a ray or a segment. The last base point is the point through which the perpendicular must pass. It is convenient to use electronic devises to simulate the above-mentioned instruments. This can done using macros in Sketchpad. Such macros can either be opened during a particular session, or they can be registered as general purpose tools in Sketchad by collecting them in a special document Minkowski Tools stored in a special folder carrying the name Tool Folder. On the main screen in Sketchpad we are now offered a new icon on the toolbar. If we press down the mouse a list of general-purpose tools available is shown: 1
2 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part In this case we thus have the basic construction tools the hyperbolic compass and the hyperbolic perpendicular at our disposal. efore you start working on the exercises you may benefit from experimenting a little with these tools to get a feeling for how they work: The hyperbolic compass (using a centre point and a peripheral point): You must first select the centre. Subsequently the rectangular hyperbola pops up on the screen ready to be dropped at a given peripheral point. The hyperbolic perpendicular (using a prescribed point and a base line). To construct a hyperbolic perpendicular you must first select a base point through which the perpendicular must pass. Next you select two points on the base line (the straight object). When the first line point has been selected the perpendicular pops up on the screen ready to be dropped. To construct a hyperbolic bisector you must therefore first construct the midpoint of the segment, and then drop a hyperbolic perpendicular selecting the end points of the segment. Other hyperbolic tools Notice that you also have a hyperbola through three points at your disposal as a construction tool as well as a number of intersection tools involving hyperbolas since Sketchad does not support intersections with loci. Finally you have various measurement tools for measuring the distance between two points and the angle spanned by three points. They replace the corresponding Euclidean tools. Tools common with Euclidean Geometry What is the relevance of the other tools in Sketchad? Some become superfluous being limited strictly to This is the case e.g. for all tools dealing with circles or angles. Others are common for the Euclidean geometry and the Minkowski geometry. Especially noteworthy are the following construction tools: oint: oint on object, Midpoint, Intersection Line: Segment, Ray, arallel line olygon: Interior urve: Locus ertain transformation tools are also common: Translate Rotate but only with 180 i.e. a point symmetry! Dilate ut general rotations as well as reflections are restricted to the Euclidean Geometry since they involve Euclidean angles and must be constructed on the fly when needed in Minkowski Geometry! Finally certain measurements tools are also common: rea Ratio Slope The area is common because the symmetry transformations of the Minkowski Geometry all have determinants 1 and thus they all preserve Euclidean areas. It follows that the Minkowski area and the Euclidean area are the same (up to a common proportionality factor, which is conveniently taken to be 1. 2
3 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 1: The theorem of Thales G G F F F' F' onstruct a circle and a free point F on the periphery. Using a reflection in the centre we now obtain the opposite point F' on the periphery. onstruct a rectangular hyperbola and a free point F on the periphery. Using a reflection in the centre we now obtain the opposite point F' on the periphery. Remark: The reflection in the centre is technically implemented as a rotation by 180 around the centre. You might consider extending the radius F until it intersects the hyperbola in the opposite point. You must then use the intersection tool for straight objects and hyperbolas. t this point we have thus succeeded in constructing a circle with a diameter FF'. Select another free point G on the periphery. Verify that the angle FGF' is a right angle using slopes. t this point we have thus succeeded in constructing a rectangular hyperbola with a diameter FF'. Select another free point G on the periphery. Verify that the angle FGF' is a hyperbolic right angle using slopes. 3
4 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 2: The perpendicular bisector of a chord M M onstruct a circle with the centre and two free points and on the periphery. onstruct the chord, i.e. the segment joining and. onstruct the midpoint M for this chord. onstruct the associated radius M. Verify that the angle between the chord and the radius M is a right angle using slopes. onclusion: The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the centre of the circle. Remark: What happens with this theorem, when the two points and coincide? onstruct a rectangular hyperbola with the centre and two free points and on the periphery. onstruct the chord, i.e. the segment joining and. onstruct the midpoint M for this chord. onstruct the associated radius M. Verify that the angle between the chord and the radius M is a hyperbolic right angle using slopes. onclusion: The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the centre of the rectangular hyperbola. Remark: What happens with this theorem, when the two points and coincide? 4
5 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 3: ngle games onstruct a circle with the centre and two free points and on the periphery. Select a third free point on the periphery. Measure the peripheral angle. Move around. What do you observe? Does it make any difference if is inside or outside the arc? Measure the centre angle. What is the relation ship between the centre-angle and the peripheral angle? Remove the circle! onsider the segment and a free point outside. How would you construct the locus of points from which is seen under the same angle as from? onstruct a rectangular hyperbola with the centre and two free points and on the periphery. Select a third free point on the periphery. Measure the peripheral angle (using Minkowski tools!). Move around. What do you observe? Try also to measure the slopes and. What is the relations ship between the two slopes? Measure the centre angle. What is the relation ship between the centre-angle and the peripheral angle? Remove the hyperbola! onsider the segment and a free point outside. How would you construct the locus of points from which is seen under the same angle as from? 5
6 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 4: dding up angles O E O E onstruct a circle with the centre O and the unit point E on the periphery. onstruct two free points and on the periphery as well as the chord joining the two points. onstruct a parallel to the chord passing through the unit point E. The parallel intersects the circle in the third point. Measure the angles =EO, =EO and =EO. What is the relationship between, and? Measure the angle O. What do you observe? * The rest of the exercise is slightly more complicated! We now modify the construction. Let be the reflection of the unit point E in the radius segment O. onstruct as before. onstruct the parallels through and parallel with O. What do you observe? The parallel through intersects the circle in the D and the centre line OE in. Measure the angles DO as well as OD. What do you observe? Measure the distance D. What do you observe? onstruct a hyperbola with the centre O and the unit point E on the periphery. onstruct two free points and on the periphery as well as the chord joining the two points. onstruct a parallel to the chord passing through the unit point E. The parallel intersects the circle in the third point. Measure the Minkowski angles =EO, N=EO and =EO. What is the relationship between, and? Measure the angle O. What do you observe? * The rest of the exercise is slightly more complicated! We now modify the construction. Let be the hyperbolic reflection of the unit point E in the radius segment O. onstruct as before. onstruct the parallels through and parallel with O. What do you observe? The parallel through intersects the circle in the D and the centre line OE in. Measure the angles DO as well as OD. What do you observe? Measure the Minkowski distance D. What do you observe? 6
7 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 5: The perpendicular bisectors of a triangle onstruct a triangle. onstruct the midpoints for the three legs. onstruct the perpendicular bisectors for the three legs. What characteristic property of the perpendicular bisectors have you now successfully demonstrated? onstruct a circle passing through a vertex using the intersection point of the perpendicular bisectors as the centre. What is the characteristic property of the circle thus constructed? Remark: What happens when the intersection point of the perpendicular bisectors (the circum centre) falls on one of the legs of the triangle? What kind of triangle possesses this property? onstruct a triangle. onstruct the midpoints for the three legs. onstruct the hyperbolic perpendicular bisectors for the three legs. What characteristic property of the perpendicular bisectors have you now successfully demonstrated? onstruct a rectangular hyperbola passing through a vertex using the intersection point of the perpendicular bisectors as the centre. What is the characteristic property of the hyperbola thus constructed? Remark: What happens when the intersection point of the perpendicular bisectors (the circum centre) falls on one of the legs of the triangle? What kind of triangle possesses this property? 7
8 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 6: The altitudes of a triangle the Euler line onstruct a triangle. onstruct the three altitudes. What characteristic property of the altitudes have you now successfully demonstrated? onstruct the circumcentre O, i.e. the intersection point of the perpendicular bisectors as well. onstruct the centre of gravity G, i.e. the intersection point of medians as well. What can you say about the relationship between these three points: the orthocentre H (i.e. intersection point of the altitudes), the circumcentre O and the centre of gravity G? onstruct a triangle. onstruct the three hyperbolic altitudes. What characteristic property of the hyperbolic altitudes have you now successfully demonstrated? onstruct the hyperbolic circumcentre O, i.e. the intersection point of the hyperbolic perpendicular bisectors as well. onstruct the centre of gravity G, i.e. the intersection point of medians as well. What can you say about the relationship between these three points: the hyperbolic orthocentre H (i.e. intersection point of the altitudes), the hyperbolic circumcentre O and the centre of gravity G? 8
9 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 7: The nine-point circle M c M a M a M c M b M b onstruct a triangle. onstruct the midpoints of the three legs. onstruct the circle passing through these three midpoints. Remark: This circle is known as the midpoint circle or the Euler circle. It is also known as the nine-point circle and we will now try to justify this name. onstruct the altitudes of the triangle as well. What is the relationship between the base points of the altitudes and the midpoint circle? The midpoint circle intersects the three altitudes in three further points. What is special about these additional intersection points? Now you should be able to explain why it is being called a nine-point circle! onstruct a triangle. onstruct the midpoints of the three legs. onstruct the rectangular hyperbola passing through these three midpoints. Remark: This rectangular hyperbola is known as the midpoint hyperbola. It is also known as the nine-point hyperbola and we will now try to justify this name. onstruct the hyperbolic altitudes of the triangle as well. What is the relationship between the base points of the hyperbolic altitudes and the midpoint hyperbola? The midpoint hyperbola intersects the three altitudes in three further points. What is special about these additional intersection points? Now you should be able to explain why it is being called a nine-point hyperbola! 9
10 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 8: Kissing circles Q Q R R onstruct a circle and select three points, Q and R on the circle. onstruct the radii and the tangents associated with the three points, Q and R. The three tangents span a triangle with the vertices, and being the intersection points, such that falls on the side, Q on the side and R on the side. What is the relationship between the circle and the triangle? onstruct the three circles having the vertices, and as centre and passing respectively through the three points, Q and R. Hide the original circle as well as the three radii. The three remaining circles are known as kissing circles of the triple points, and. How can you construct kissing circles if the original given data is the triple? Will all triples of points have kissing circles? onstruct a rectangular hyperbola and select three points, Q and R on the hyperbola. onstruct the radii and the tangents associated with the three points, Q and R. The three tangents span a triangle with the vertices, and being the intersection points, such that falls on the side, Q on the side and R on the side. What is the relationship between the hyperbola and the triangle? onstruct the three rectangular hyperbolas having the vertices, and as centre and passing respectively through the three points, Q and R. Hide the original hyperbola as well as the three radii. The three remaining hyperbolas are known as kissing hyperbolas of the triple, and. How can you construct kissing hyperbolas if the original given data is the triple? Will all triples of points have kissing hyperbolas? 10
11 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part note on Minkowski reflections efore we continue with the next exercise it will be useful to consider transformations in Minkowski geometry in some detail. If we want to reflect a point in the line l generated by the point, we must first construct the hyperbolic perpendicular to the mirror axis l through : 0 ' l The hyperbolic perpendicular intersects the mirror axis l in the foot point 0. We then know that the reflection is the point on the perpendicular lying symmetrical around 0. ut point symmetry is common to Minkowski and Euclidean Geometry. So now we can simply rotate around 0 with 180 and the resulting point ' is the hyperbolic reflection. Once you can reflect points, you can reflect other objects as well. Straight lines are reflected using two points, one conveniently being the fix point i.e. the intersection with the mirror axis. Other objects like hyperbolas are most easily reflected as loci. So you select a free point F on the hyperbola and reflect in the mirror axis l. Selecting the free point F as well as the reflection point F' you can now construct the Locus of F' driven by F. nd that precisely is the reflected image of the original hyperbola: 0 ' l Of course the image is just another rectangular hyperbola with horizontal and vertical asymptotes. In fact the new centre is just the reflection of the old centre, so in this case it would in fact be very easy to construct the mirror image using just two points. Remark: In fact you may even reflect a Euclidean circle in this way. Euclidean circle in Minkowski geometry is of course just a special conic with eccentricity 2. So the resulting image is just another special conic with the same eccentricity, i.e. the image is another circle! 11
12 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Exercise 9: Reflection games O ' ' O onstruct a triangle and the circumscribed circle together with its centre the circum-centre O. Reflect the circumscribed circle in the three sides of the triangle a, b and c. What do you observe? What is the special significance of the point associated with these three reflected circles? Reflect the circum-centre O in the three sides of the triangle thus creating the centre of the reflected circles: ', ' and '. What is the relationship between the triangle and the dual triangle '''? Repeat the construction with the dual triangle '''. What is the result? onstruct the midpoints of the original triangle as well as the midpoints of the dual triangle. What do you observe? onstruct the midpoint circle of the original triangle as well as for the dual triangle '''. What do you observe? onstruct a triangle and the circumscribed hyperbola together with its centre the circum-centre O. Reflect the circumscribed hyperbola in the three sides of the triangle a, b and c (using hyperbolic reflections!). What do you observe? What is the special significance of the point associated with the reflected hyperbolas? Reflect the circum-centre O in the three sides of the triangle thus creating the centre of the reflected hyperbolas: ', ' and '. What is the relationship between the triangle and the dual triangle '''? Repeat the construction with the dual triangle '''. What is the result? onstruct the midpoints of the original triangle as well as the midpoints of the dual triangle. What do you observe? onstruct the midpoint hyperbola of the original triangle as well as for the dual triangle '''. What do you observe? 12
Workshop 2 in Minkowski Geometry: Conic sections Shadowing Euclidean and Minkowski Geometry
 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 econd part Workshop 2 in Minkowski Geometry: onic sections hadowing Euclidean and Minkowski Geometry In the second part of the workshop we will investigate conic sections in
Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 econd part Workshop 2 in Minkowski Geometry: onic sections hadowing Euclidean and Minkowski Geometry In the second part of the workshop we will investigate conic sections in
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric Activities
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Constructions Quiz Review November 29, 2017
 Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5
 UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5 Geometry Unit 5 Overview: Circles With and Without Coordinates In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention
UNIT 5 GEOMETRY TEMPLATE CREATED BY REGION 1 ESA UNIT 5 Geometry Unit 5 Overview: Circles With and Without Coordinates In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention
Appendix. Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 Appendix Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics The correlation shows how the activities in Exploring Geometry with The Geometer s Sketchpad
Appendix Correlation to the High School Geometry Standards of the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics The correlation shows how the activities in Exploring Geometry with The Geometer s Sketchpad
Exterior Region Interior Region
 Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
CONSTRUCTIONS Introduction Division of a Line Segment
 216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
PASS. 5.2.b Use transformations (reflection, rotation, translation) on geometric figures to solve problems within coordinate geometry.
 Geometry Name Oklahoma cademic tandards for Oklahoma P PRCC odel Content Frameworks Current ajor Curriculum Topics G.CO.01 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle,
Geometry Name Oklahoma cademic tandards for Oklahoma P PRCC odel Content Frameworks Current ajor Curriculum Topics G.CO.01 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle,
3 Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, flat ) or three-dimensional ( solid ).
 Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
An Introduction to GeoGebra
 An Introduction to GeoGebra Downloading and Installing Acquiring GeoGebra GeoGebra is an application for exploring and demonstrating Geometry and Algebra. It is an open source application and is freely
An Introduction to GeoGebra Downloading and Installing Acquiring GeoGebra GeoGebra is an application for exploring and demonstrating Geometry and Algebra. It is an open source application and is freely
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended. Mathematics. Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c
 Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Common Core Specifications for Geometry
 1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry: Traditional Pathway
 GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
Geometry. Geometry. Domain Cluster Standard. Congruence (G CO)
 Domain Cluster Standard 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Domain Cluster Standard 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE
 MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE 2018-2019 Standards (ACT included) ALCOS#1 Know the precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined
MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE 2018-2019 Standards (ACT included) ALCOS#1 Know the precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined
G12 Centers of Triangles
 Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 45 6. Turn this page over and complete the activity with a different original shape. Scale actor 1 6 0.5 3 3.1 Perimeter of Original shape Measuring Perimeter Perimeter of
Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 45 6. Turn this page over and complete the activity with a different original shape. Scale actor 1 6 0.5 3 3.1 Perimeter of Original shape Measuring Perimeter Perimeter of
Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop
 Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Outline 1. asic Construction, Measurement and Transformation
Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Don Spickler Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Salisbury University Geometer's Sketchpad Workshop Outline 1. asic Construction, Measurement and Transformation
Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015 to the Common Core State Standards for Bid Category 13-040-10 A Correlation of Pearson, Common Core Pearson Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Common Core 2015 to the Common Core State Standards for Bid Category 13-040-10 A Correlation of Pearson, Common Core Pearson Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment
K-12 Geometry Standards
 Geometry K.G Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1. Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes, and describe
Geometry K.G Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1. Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes, and describe
Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide,
 Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 Domain Abbreviation Congruence G-CO Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry G-SRT Modeling with Geometry *G-MG Geometric Measurement
Madison County Schools Suggested Geometry Pacing Guide, 2016 2017 Domain Abbreviation Congruence G-CO Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry G-SRT Modeling with Geometry *G-MG Geometric Measurement
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Elementary Planar Geometry
 Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Construction Instructions. Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment.
 Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
PROPORTION PLANAR GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONES AND GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIP
 PROPORTION PLANAR GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONES AND GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIP The relationship regarding dimensions between two or more figures, or between two parts or a part and the whole is called PROPORTION.
PROPORTION PLANAR GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONES AND GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIP The relationship regarding dimensions between two or more figures, or between two parts or a part and the whole is called PROPORTION.
Geometry/Pre AP Geometry Common Core Standards
 1st Nine Weeks Transformations Transformations *Rotations *Dilation (of figures and lines) *Translation *Flip G.CO.1 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle,
1st Nine Weeks Transformations Transformations *Rotations *Dilation (of figures and lines) *Translation *Flip G.CO.1 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle, circle,
Geometry Common Core State Standard (CCSS) Math
 = ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
= ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
YEC Geometry Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide
 YEC Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide Quarter 1st 2nd 3rd 4th Units 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 G.CO.1 G.CO.2 G.CO.6 G.CO.9 G.CO.3 G.CO.7 G.CO.10 G.CO.4 G.CO.8 G.CO.11 Congruence G.CO.5 G.CO.12 G.CO.13 Similarity, Right
YEC Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide Quarter 1st 2nd 3rd 4th Units 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 G.CO.1 G.CO.2 G.CO.6 G.CO.9 G.CO.3 G.CO.7 G.CO.10 G.CO.4 G.CO.8 G.CO.11 Congruence G.CO.5 G.CO.12 G.CO.13 Similarity, Right
VOCABULARY. Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8. WORD IMAGE DEFINITION An angle with measure between 0 and A triangle with three acute angles.
 Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Course: Geometry PAP Prosper ISD Course Map Grade Level: Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block Days. Unit Title
 Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Geometry GEOMETRY. Congruence
 Geometry Geometry builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday life.
Geometry Geometry builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday life.
Mid-point & Perpendicular Bisector of a line segment AB
 Mid-point & Perpendicular isector of a line segment Starting point: Line Segment Midpoint of 1. Open compasses so the points are approximately ¾ of the length of apart point 3. y eye - estimate the midpoint
Mid-point & Perpendicular isector of a line segment Starting point: Line Segment Midpoint of 1. Open compasses so the points are approximately ¾ of the length of apart point 3. y eye - estimate the midpoint
Geometry. (F) analyze mathematical relationships to connect and communicate mathematical ideas; and
 (1) Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is (A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life,
(1) Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is (A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life,
Common Core Cluster. Experiment with transformations in the plane. Unpacking What does this standard mean that a student will know and be able to do?
 Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Honors Geometry Pacing Guide Honors Geometry Pacing First Nine Weeks
 Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Mathematics High School Geometry
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry
 Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry Geometry is a course required for graduation and course is aligned with the College and Career Ready Standards for Mathematics in High School. Throughout
Mathematics Standards for High School Geometry Geometry is a course required for graduation and course is aligned with the College and Career Ready Standards for Mathematics in High School. Throughout
, Geometry, Quarter 1
 2017.18, Geometry, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1.
2017.18, Geometry, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1.
Mathematics Pacing Guide Alignment with Common Core Standards. Essential Questions What is congruence?
 Time Frame: 6 Weeks September/October Unit 1: Congruence Mathematics Pacing Guide Alignment with Standards Experiment with Transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle,
Time Frame: 6 Weeks September/October Unit 1: Congruence Mathematics Pacing Guide Alignment with Standards Experiment with Transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle,
Curriki Geometry Glossary
 Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
2003/2010 ACOS MATHEMATICS CONTENT CORRELATION GEOMETRY 2003 ACOS 2010 ACOS
 CURRENT ALABAMA CONTENT PLACEMENT G.1 Determine the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a second line through a given point. G.2 Justify theorems related to pairs of angles, including angles
CURRENT ALABAMA CONTENT PLACEMENT G.1 Determine the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a second line through a given point. G.2 Justify theorems related to pairs of angles, including angles
Geometry Syllabus Holt McDougal Geometry (Aligned with SCCCR Standards) Ridgeland Hardeeville High School
 Geometry Syllabus 2016-2017 Holt McDougal Geometry (Aligned with SCCCR Standards) Ridgeland Hardeeville High School TOPIC SCCCR STANDARD DAYS REQUIRED BASICS OF GEOMETRY: About points, lines, planes angles
Geometry Syllabus 2016-2017 Holt McDougal Geometry (Aligned with SCCCR Standards) Ridgeland Hardeeville High School TOPIC SCCCR STANDARD DAYS REQUIRED BASICS OF GEOMETRY: About points, lines, planes angles
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
104, 107, 108, 109, 114, 119, , 129, 139, 141, , , , , 180, , , 128 Ch Ch1-36
 111.41. Geometry, Adopted 2012 (One Credit). (c) Knowledge and skills. Student Text Practice Book Teacher Resource: Activities and Projects (1) Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical
111.41. Geometry, Adopted 2012 (One Credit). (c) Knowledge and skills. Student Text Practice Book Teacher Resource: Activities and Projects (1) Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical
Standards to Topics. Common Core State Standards 2010 Geometry
 Standards to Topics G-CO.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Standards to Topics G-CO.01 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Geometry Indiana Standards Worktext Correlations
 Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry
 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Geometry 2015 correlated to the New York Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Geometry Standards for Mathematical Practice SMP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere
Test #1: Chapters 1, 2, 3 Test #2: Chapters 4, 7, 9 Test #3: Chapters 5, 6, 8 Test #4: Chapters 10, 11, 12
 Progress Assessments When the standards in each grouping are taught completely the students should take the assessment. Each assessment should be given within 3 days of completing the assigned chapters.
Progress Assessments When the standards in each grouping are taught completely the students should take the assessment. Each assessment should be given within 3 days of completing the assigned chapters.
Curriculum Scope & Sequence
 BOE APPROVED 3/27/12 REVISED 9/25/12 Curriculum Scope & Sequence Subject/Grade Level: MATHEMATICS/HIGH SCHOOL Course: GEOMETRY CP/HONORS *The goals and standards addressed are the same for both levels
BOE APPROVED 3/27/12 REVISED 9/25/12 Curriculum Scope & Sequence Subject/Grade Level: MATHEMATICS/HIGH SCHOOL Course: GEOMETRY CP/HONORS *The goals and standards addressed are the same for both levels
Compass and Straight Edge. Compass/Straight Edge. Constructions with some proofs.
 Compass and Straight Edge Compass/Straight Edge Constructions with some proofs. To Construct the Perpendicular isector of a line. 1. Place compass at, set over halfway and draw 2 arcs. 2. Place compass
Compass and Straight Edge Compass/Straight Edge Constructions with some proofs. To Construct the Perpendicular isector of a line. 1. Place compass at, set over halfway and draw 2 arcs. 2. Place compass
Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Summer March 31, 2018 Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/61/
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Summer March 31, 2018 Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/61/
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards. Geometry. Table of Contents. Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8
 Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Geometry Table of Contents Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8 Geometry Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Geometry Table of Contents Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8 Geometry Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions
Common Core State Standards High School Geometry Constructions
 ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry
 Mathematics Scope & Sequence 2016-17 Geometry Revised: June 21, 2016 First Grading Period (24 ) Readiness Standard(s) G.5A investigate patterns to make conjectures about geometric relationships, including
Mathematics Scope & Sequence 2016-17 Geometry Revised: June 21, 2016 First Grading Period (24 ) Readiness Standard(s) G.5A investigate patterns to make conjectures about geometric relationships, including
Ohio s Learning Standards Mathematics Scope and Sequence YEC Geometry
 Youngstown City School District English Language Arts Scope and Sequence Grade K Ohio s Learning Standards Mathematics Scope and Sequence YEC Geometry Mathematics Standards Scope and Sequence, YEC Geometry
Youngstown City School District English Language Arts Scope and Sequence Grade K Ohio s Learning Standards Mathematics Scope and Sequence YEC Geometry Mathematics Standards Scope and Sequence, YEC Geometry
Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards
 Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards Module 1: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Module 2: Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Module 3: Extending to Three Dimensions Module 4: Connecting
Sequence of Geometry Modules Aligned with the Standards Module 1: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Module 2: Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Module 3: Extending to Three Dimensions Module 4: Connecting
Geometry Critical Areas of Focus
 Ohio s Learning Standards for Mathematics include descriptions of the Conceptual Categories. These descriptions have been used to develop critical areas for each of the courses in both the Traditional
Ohio s Learning Standards for Mathematics include descriptions of the Conceptual Categories. These descriptions have been used to develop critical areas for each of the courses in both the Traditional
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses. Geometry. Course Outline
 The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
Ohio Tutorials are designed specifically for the Ohio Learning Standards to prepare students for the Ohio State Tests and end-ofcourse
 Tutorial Outline Ohio Tutorials are designed specifically for the Ohio Learning Standards to prepare students for the Ohio State Tests and end-ofcourse exams. Math Tutorials offer targeted instruction,
Tutorial Outline Ohio Tutorials are designed specifically for the Ohio Learning Standards to prepare students for the Ohio State Tests and end-ofcourse exams. Math Tutorials offer targeted instruction,
DISCOVERING CONICS WITH. Dr Toh Pee Choon NIE 2 June 2016
 DISCOVERING CONICS WITH Dr Toh Pee Choon MTC @ NIE 2 June 2016 Introduction GeoGebra is a dynamic mathematics software that integrates both geometry and algebra Open source and free to download www.geogebra.org
DISCOVERING CONICS WITH Dr Toh Pee Choon MTC @ NIE 2 June 2016 Introduction GeoGebra is a dynamic mathematics software that integrates both geometry and algebra Open source and free to download www.geogebra.org
Pearson Mathematics Geometry
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
Russell County Pacing Guide
 August Experiment with transformations in the plane. 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance
August Experiment with transformations in the plane. 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance
GEOMETRY Graded Course of Study
 GEOMETRY Graded Course of Study Conceptual Category: Domain: Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane. Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions. Prove geometric theorems both formally
GEOMETRY Graded Course of Study Conceptual Category: Domain: Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane. Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions. Prove geometric theorems both formally
Pearson Geometry Common Core 2015
 A Correlation of Geometry Common Core to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics High School , Introduction This document demonstrates how meets the Mathematics High School, PARRC Model Content
A Correlation of Geometry Common Core to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics High School , Introduction This document demonstrates how meets the Mathematics High School, PARRC Model Content
Geometry. Instructional Activities:
 GEOMETRY Instructional Activities: Geometry Assessment: A. Direct Instruction A. Quizzes B. Cooperative Learning B. Skill Reviews C. Technology Integration C. Test Prep Questions D. Study Guides D. Chapter
GEOMETRY Instructional Activities: Geometry Assessment: A. Direct Instruction A. Quizzes B. Cooperative Learning B. Skill Reviews C. Technology Integration C. Test Prep Questions D. Study Guides D. Chapter
The School District of Palm Beach County GEOMETRY HONORS Unit A: Essentials of Geometry
 MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 MAFS.912.G-CO.4.12 MAFS.912.G-GPE.2.7 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 Unit A: Essentials of Mathematics Florida Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line
MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 MAFS.912.G-CO.4.12 MAFS.912.G-GPE.2.7 MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 Unit A: Essentials of Mathematics Florida Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
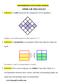 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
Grade 8 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map
 Grade 8 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessment Common Core State Standards Standards
Grade 8 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessment Common Core State Standards Standards
GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview
 GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview Semester 1 Semester 2 Unit 1 ( 5 1/2 Weeks) Unit 2 Unit 3 (2 Weeks) Unit 4 (1 1/2 Weeks) Unit 5 (Semester Break Divides Unit) Unit 6 ( 2 Weeks) Unit 7 (7 Weeks) Lines and Angles,
GEOMETRY Curriculum Overview Semester 1 Semester 2 Unit 1 ( 5 1/2 Weeks) Unit 2 Unit 3 (2 Weeks) Unit 4 (1 1/2 Weeks) Unit 5 (Semester Break Divides Unit) Unit 6 ( 2 Weeks) Unit 7 (7 Weeks) Lines and Angles,
5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited
 230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
ME 111: Engineering Drawing. Geometric Constructions
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking Deeply About Simple Things
 The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking eeply bout Simple Things University of Utah Teacher s Math ircle Monday, February 4 th, 2008 y Troy Jones Waterford School Important Terms (the word line may be
The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking eeply bout Simple Things University of Utah Teacher s Math ircle Monday, February 4 th, 2008 y Troy Jones Waterford School Important Terms (the word line may be
Other Materials/Projects
 GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE: 1st Nine Weeks UNIT 1: Transformations and Congruence Week Module Standards Learning Target WEEK ONE Goals Expectations Pre-Assessment Proportional Relationships Other Materials/Projects
GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE: 1st Nine Weeks UNIT 1: Transformations and Congruence Week Module Standards Learning Target WEEK ONE Goals Expectations Pre-Assessment Proportional Relationships Other Materials/Projects
Test Blueprint Dysart Math Geometry #2 Comp. AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE. 27.9% on Test. # on AP. # on Test. % on Test
 Blueprint AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE Page 1 27.9 AZ-HS.G-CO.A.1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Blueprint AZ-HS.G-CO CONGRUENCE Page 1 27.9 AZ-HS.G-CO.A.1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Course Number: Course Title: Geometry
 Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Conic Sections and Locii
 Lesson Summary: Students will investigate the ellipse and the hyperbola as a locus of points. Activity One addresses the ellipse and the hyperbola is covered in lesson two. Key Words: Locus, ellipse, hyperbola
Lesson Summary: Students will investigate the ellipse and the hyperbola as a locus of points. Activity One addresses the ellipse and the hyperbola is covered in lesson two. Key Words: Locus, ellipse, hyperbola
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry
 Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry Readiness Standard(s) First Six Weeks (29 ) Coordinate Geometry G.7.B use slopes and equations of lines to investigate geometric relationships, including parallel
Mathematics Scope & Sequence Geometry Readiness Standard(s) First Six Weeks (29 ) Coordinate Geometry G.7.B use slopes and equations of lines to investigate geometric relationships, including parallel
Use throughout the course: for example, Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Proving Lines Parallel. Polygons and Parallelograms Parallelograms
 Geometry Correlated to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills TEKS Units Lessons G.1 Mathematical Process Standards The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
Geometry Correlated to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills TEKS Units Lessons G.1 Mathematical Process Standards The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
The School District of Palm Beach County GEOMETRY HONORS Unit A: Essentials of Geometry
 Unit A: Essentials of G CO Congruence G GPE Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations G MG Modeling G GMD Measurement & Dimension MAFS.912.G CO.1.1 MAFS.912.G CO.4.12 MAFS.912.G GPE.2.7 MAFS.912.G
Unit A: Essentials of G CO Congruence G GPE Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations G MG Modeling G GMD Measurement & Dimension MAFS.912.G CO.1.1 MAFS.912.G CO.4.12 MAFS.912.G GPE.2.7 MAFS.912.G
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
DO NOT LOSE THIS REVIEW! You will not be given another copy.
 Geometry Fall Semester Review 2011 Name: O NOT LOS THIS RVIW! You will not be given another copy. The answers will be posted on your teacher s website and on the classroom walls. lso, review the vocabulary
Geometry Fall Semester Review 2011 Name: O NOT LOS THIS RVIW! You will not be given another copy. The answers will be posted on your teacher s website and on the classroom walls. lso, review the vocabulary
GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP
 2017-2018 MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP Department of Curriculum and Instruction RCCSD Congruence Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions Prove geometric theorems Common Core Major Emphasis
2017-2018 MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY CURRICULUM MAP Department of Curriculum and Instruction RCCSD Congruence Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions Prove geometric theorems Common Core Major Emphasis
Lesson 3: Rectangles Inscribed in Circles
 Classwork Opening Exercise Using only a compass and straightedge, find the location of the center of the circle below. Follow the steps provided. Draw chord. AAAA Construct a chord perpendicular to AAAA
Classwork Opening Exercise Using only a compass and straightedge, find the location of the center of the circle below. Follow the steps provided. Draw chord. AAAA Construct a chord perpendicular to AAAA
GEOMETRY. PARALLEL LINES Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal.
 GOMTRY RLLL LINS Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal. Theorem 2: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then the alternate
GOMTRY RLLL LINS Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal. Theorem 2: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then the alternate
Unit 1: Tools of Geometry
 Unit 1: Tools of Geometry Geometry CP Pacing Guide First Nine Weeks Tennessee State Math Standards Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel G.CO.A.1 line, and line segment,
Unit 1: Tools of Geometry Geometry CP Pacing Guide First Nine Weeks Tennessee State Math Standards Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel G.CO.A.1 line, and line segment,
GEOMETRY. Changes to the original 2010 COS is in red. If it is red and crossed out, it has been moved to another course.
 The Geometry course builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday
The Geometry course builds on Algebra I concepts and increases students knowledge of shapes and their properties through geometry-based applications, many of which are observable in aspects of everyday
Florida Association of Mu Alpha Theta January 2017 Geometry Team Solutions
 Geometry Team Solutions Florida ssociation of Mu lpha Theta January 017 Regional Team nswer Key Florida ssociation of Mu lpha Theta January 017 Geometry Team Solutions Question arts () () () () Question
Geometry Team Solutions Florida ssociation of Mu lpha Theta January 017 Regional Team nswer Key Florida ssociation of Mu lpha Theta January 017 Geometry Team Solutions Question arts () () () () Question
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ACCELERATED GEOMETRY (June 2014)
 UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
Correlation of Discovering Geometry 5th Edition to Florida State Standards
 Correlation of 5th Edition to Florida State s MAFS content is listed under three headings: Introduced (I), Developed (D), and Applied (A). Developed standards are the focus of the lesson, and are being
Correlation of 5th Edition to Florida State s MAFS content is listed under three headings: Introduced (I), Developed (D), and Applied (A). Developed standards are the focus of the lesson, and are being
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry
 NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
Chapter 7. Some triangle centers. 7.1 The Euler line Inferior and superior triangles
 hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
Geometric Constructions
 Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Make geometric constructions. (Formalize and explain processes)
 Standard 5: Geometry Pre-Algebra Plus Algebra Geometry Algebra II Fourth Course Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Part 3 Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships
Standard 5: Geometry Pre-Algebra Plus Algebra Geometry Algebra II Fourth Course Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Benchmark 1 - Part 3 Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships
