SPH3U1 Lesson 05 Kinematics
|
|
|
- Reginald Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VECTORS IN TWO-DIMENSIONS LEARNING GOALS Students will Draw vector scale diagrams to visualize and analyze the nature of motion in a plane. Analyze motion by using scale diagrams to add vectors. Solve two-dimensional vector problems using scale diagrams and trigonometry. WEBSITE AND TEXTBOOK RESOURCES Reading Video Nelson Physics 11 Section 2.1 Pg Physics Classroom Vectors Khan Academy (Visualizing 2D Vectors) Earl Haig (Putting Bearings on Vectors and Adding Vectors) Interactive Figures Adding and Subtracting Vectors (Visual Demonstrations) DISPLACEMENT VECTORS Balls, rockets, bullets, cars, boats, planes, and sparks all have 2D motion. We can quantify their motion using horizontal and vertical vectors. We have seen both horizontal and vertical vectors of objects in motion. A. Draw a displacement vector that represents an object moving in the East direction and a separate vector representing an object moving in the North direction. Indicate the initial and final positions of the object in both cases. The displacement, Δ of an object is a vector that points from an initial position, to its final position,. The vector s magnitude is equal to the straight-line distance between the two positions. STEPS TO DRAWING VECTORS 1. Draw an x,y axis. 2. Measure the angle starting from the x-axis or based on the letter direction provided. A direction like [N15 0 E] is read north, fifteen degrees east. This direction is found by starting at the north line and measuring 15 0 towards the east. 3. Draw the vector based on a length scale you specify. W N S 15 0 [N15 0 E] E MAGNITUDE AND DIRECTION The following diagram depicts the motion of a typical student. Based on the displacement vectors shown in the diagram, what is the magnitude and direction of the student s displacement? (Hint: Start with a protractor located at the student s home to help you find the direction.) 1
2 From Home to School From Home to the Diner From Home to the Sports Complex VECTORS IN A PLANE Imagine describing the motion of an expert water-skier to someone who had not watched the skier demonstrate his technique. You would probably do a lot of pointing in different directions. In a sense, you would be using vectors to describe the skier s motion. You will represent vector quantities with arrows that point in the direction of the quantity. The length of the arrow is proportional to the magnitude of the quantity you are representing, so you need an appropriate scale to represent the magnitude. Vector quantities have direction, so you need a frame of reference or coordinate system to represent a direction. The map to the right is an excellent example of using vectors to locate the displacement between two objects. Each displacement vector has an appropriate length that follows the scale at the bottom and the angle drawn correctly. ADDING VECTORS GRAPHICALLY Addition of vectors starts with some basic rules of arithmetic and then includes a few more rules. You have known for a long time that you cannot add apples and oranges or centimetres and metres. Similarly, you can only add vectors that represent the same quantity and are drawn to the same scale. Read the steps on the next page to find out how to add vectors graphically. Then use the method described to do EXAMPLE 1 below. 2
3 EXAMPLE 1: ADDING GRAPHICALLY A dog chases a cat 400 m [W] and turns to travel another 600 m [N50 o E]. Find the total displacement of the dog by drawing a scale vector diagram. Check your answer using sine/cosine laws on the triangle you drew. is the displacement Δ! 3
4 PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1. An airplane flies 100 km north in 20 min, then 150 km west in 40 min and finally 500 km south in 52 min. a. What is the total distance and total displacement of the plane? b. What are the average velocity and average speed for the trip? 2. A pleasure boat heads out from the marina and travels 2.7 km [S] to a small island. It then travels 3.4 km [S26 0 E] to another island. What is the boats displacement for the entire journey? Solve using a scale diagram and then solve again using the sine and cosine law. 3. A plane is flying at a constant velocity through the air at 120 km/h [S]. The wind is blowing at a velocity of 50 km/h [W]. These two velocities can be added to determine the plane s total velocity with respect to the ground. a. Find the total velocity (add the velocity vectors ie. tip-to-tail). b. If the plane is flying between two cities that are 500 km apart, how long does the trip take? 4. A jogger runs at a velocity of 2.8 m/s [W] for 50 minutes and then at a velocity of 3.2 m/s [N30 0 W] for 30 minutes. Calculate the total displacement of the jogger. 5. A hiker heads [N40 0 W] for 4.0 km, then [E10 0 N] for 3.0 km and finally she walks 2.5 km [S40 0 W]. (Hint: this one has to be done in 2 steps if you use sine and cosine law, but can be done in one step using a scale diagram.) a. What was her total displacement? b. In what direction should she walk to get back to her starting point in the shortest possible distance? c. If her average speed is 4.0 km/h for the entire trip, what was her average velocity? Answers: 1. a) 750 km and 427 km [S21 0 W] b) 229 km/h [S21 0 W] km [S15 0 E] 3. a) 130 km/h [S23 0 W] b) 3.8 h x 10 4 m [W24 0 N] 5. a) 2.1 km [N36 0 W] b) [S36 0 E] c) 0.87 km/h [N36 0 W] 4
5 VECTORS IN TWO-DIMENSIONS VECTOR COMPONENTS LEARNING GOALS Students will use components to add vectors by: Splitting vectors into simpler horizontal and vertical parts; Adding the vertical parts to each other, then adding the horizontal parts to each other; Finally adding the horizontal and vertical parts to each other. WEBSITE AND TEXTBOOK RESOURCES Reading Nelson Physics 11 Section 2.2 Pg Physics Classroom Vector Components and Addition Interactive Figure Vector Addition of Components ADDING SCALARS SIMPLY Say you want to add in your head. You might first split them up: 67 = Then you might add = 140 Then you might add = 12 Finally you add = = You often use this method in your head because it is easier to do each simpler operation than to do the entire addition at once. The component method for adding vectors works the same way. Each vector is split into simpler parts we call components that are easier to add. VECTOR COMPONENTS Vectors in 2-D have their direction often in between two simple, cardinal directions; for example 34 m [N32 0 E] is between north and east. This has a north part and an east part (see diagram) 45 m [W15 0 S] is between west and south. This has a west part and a south part (see diagram) N x 32 = 34 = = = 34 = 3432 = 28.8 y 34 m 32 0 W y x 45 m 15 0 E 15 = 45 = = = S Study the calculations in the diagram. Each of the two vectors has been split up using simple trigonometry into two other vectors (dashed lines, placed tip-to-tail) that add up to the original vector. These new vectors are called components. They are all parallel to the axes. 5
6 Instead of adding the two original vectors, we now add up the four components instead: 18.0 m [E] m [N] m [W] m [S] First, add the N-S (or y) vectors: 28.8 m [N] m [S] = 17.2 m [N] Then, add the E-W (or x) vectors: 18.0 m [E] m [W] = 25.5 m [W] You now have the components of the answer. Add them using a scale diagram or using the Pythagorean theorem and the tangent of an angle: N = = m R!" = " = 34 W 25.5 m θ E The sum of the two vectors is therefore 30.8 m [W34 0 N]. S This method takes about as much math as using the sine and cosine laws to add the vectors; however, in this case, all the trigonometry you need to know is SOH CAH TOA. If you have to add three or more vectors, this method is MUCH FASTER than using the sine and cosine laws. Any number of vectors can be added together at once. PRACTICE PROBLEMS Pg 69 Q1,2 Pg 71 Q1,2Pg. 75 Q1-6 6
7
8
SPH3U1 Lesson 09 Kinematics
 VECTORS IN TWO-DIMENSIONS LEARNING GOALS Students will Draw vector scale diagrams to visualize and analyze the nature of motion in a plane. Analyze motion by using scale diagrams to add vectors. Solve
VECTORS IN TWO-DIMENSIONS LEARNING GOALS Students will Draw vector scale diagrams to visualize and analyze the nature of motion in a plane. Analyze motion by using scale diagrams to add vectors. Solve
Preview. Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1 Preview Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Section 1 Preview Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors
 Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors Motion in two dimensions must use vectors and vector diagrams. Vector Representation: tail head magnitude (size): given by the length
Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors Motion in two dimensions must use vectors and vector diagrams. Vector Representation: tail head magnitude (size): given by the length
Math 4: Advanced Algebra Ms. Sheppard-Brick B Quiz Review Sections and
 3B Quiz Review Sections 2.8 2.10 and 3.1 3.6 Key Facts To add vectors, place the tail of one vector (the side without the arrow) at the head of the other vector (the side with the arrow). Draw the vector
3B Quiz Review Sections 2.8 2.10 and 3.1 3.6 Key Facts To add vectors, place the tail of one vector (the side without the arrow) at the head of the other vector (the side with the arrow). Draw the vector
GPS SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects.
 GPS SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects. b. Compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. SCALARS AND VECTORS Scalars only have magnitude
GPS SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects. b. Compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. SCALARS AND VECTORS Scalars only have magnitude
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods
 Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
DATE: NAME: CLASS: BLM 5-1 SKILL BUILDER
 DAT: AM: CLASS: SKILL BUILDR Interpreting Vectors Goal nhance your understanding of vectors. What to Do Read about each vector operation, and study the steps. Then solve the Practice Problems that follow.
DAT: AM: CLASS: SKILL BUILDR Interpreting Vectors Goal nhance your understanding of vectors. What to Do Read about each vector operation, and study the steps. Then solve the Practice Problems that follow.
2.1 Motion in Two Dimensions A Scale Diagram Approach
 Figure The motion of these cyclists is two-dimensional in the plane of the road. carr LInK aval offi cers use gyroscopic compasses and satellite navigation to navigate Canada s naval fl eet. However, every
Figure The motion of these cyclists is two-dimensional in the plane of the road. carr LInK aval offi cers use gyroscopic compasses and satellite navigation to navigate Canada s naval fl eet. However, every
Chapter 3: Vectors & 2D Motion. Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University
 Chapter 3: Vectors & 2D Motion Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Vectors What is a vector? Examples? Notation:! a or! a or a 2 Vector Addition Graphical Methods Triangle, parallelogram, polygon
Chapter 3: Vectors & 2D Motion Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Vectors What is a vector? Examples? Notation:! a or! a or a 2 Vector Addition Graphical Methods Triangle, parallelogram, polygon
Adding vectors. Let s consider some vectors to be added.
 Vectors Some physical quantities have both size and direction. These physical quantities are represented with vectors. A common example of a physical quantity that is represented with a vector is a force.
Vectors Some physical quantities have both size and direction. These physical quantities are represented with vectors. A common example of a physical quantity that is represented with a vector is a force.
7.4. The Sine and Cosine Ratios. Investigate. Tools
 7.4 The Sine and osine Ratios We depend on ships and aircraft to transport goods and people all over the world. If you were the captain of a ship or the pilot of an airplane, how could you make sure that
7.4 The Sine and osine Ratios We depend on ships and aircraft to transport goods and people all over the world. If you were the captain of a ship or the pilot of an airplane, how could you make sure that
Name: Block: What I can do for this unit:
 Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
Chapter 2 Trigonometry
 Foundations of Math 11 Chapter 2 Note Package Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Review (No Practice Questions for this Lesson) Page 1 The Beauty of Triangles (No Notes for this Page) Page 2 Pythagoras Review (No Notes
Foundations of Math 11 Chapter 2 Note Package Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Review (No Practice Questions for this Lesson) Page 1 The Beauty of Triangles (No Notes for this Page) Page 2 Pythagoras Review (No Notes
Name Period. (b) Now measure the distances from each student to the starting point. Write those 3 distances here. (diagonal part) R measured =
 Lesson 5: Vectors and Projectile Motion Name Period 5.1 Introduction: Vectors vs. Scalars (a) Read page 69 of the supplemental Conceptual Physics text. Name at least 3 vector quantities and at least 3
Lesson 5: Vectors and Projectile Motion Name Period 5.1 Introduction: Vectors vs. Scalars (a) Read page 69 of the supplemental Conceptual Physics text. Name at least 3 vector quantities and at least 3
Honors Pre-Calculus. 6.1: Vector Word Problems
 Honors Pre-Calculus 6.1: Vector Word Problems 1. A sled on an inclined plane weighs 00 lb, and the plane makes an angle of 0 degrees with the horizontal. What force, perpendicular to the plane, is exerted
Honors Pre-Calculus 6.1: Vector Word Problems 1. A sled on an inclined plane weighs 00 lb, and the plane makes an angle of 0 degrees with the horizontal. What force, perpendicular to the plane, is exerted
Precalculus eday #3 Assignment
 Name Date Score Precalculus eday #3 Assignment 1. If X = 35, Y = 84, and Z = 91, what is the cosine of B? 2. If X = 60, Y = 25, and Z = 65, what is the sine of B? 3. In the triangle shown above m A = 43,
Name Date Score Precalculus eday #3 Assignment 1. If X = 35, Y = 84, and Z = 91, what is the cosine of B? 2. If X = 60, Y = 25, and Z = 65, what is the sine of B? 3. In the triangle shown above m A = 43,
Week 8 Problems. #2 Points possible: 1. Total attempts: 2 Enter your answer rounded to two decimal places.
 Week 8 Problems Name: Neal Nelson Show Scored View # Points possible:. Total attempts: A pilot is flying over a straight highway. He determines the angles of depression to two mileposts,.6 mi apart, to
Week 8 Problems Name: Neal Nelson Show Scored View # Points possible:. Total attempts: A pilot is flying over a straight highway. He determines the angles of depression to two mileposts,.6 mi apart, to
Review Journal 7 Page 57
 Student Checklist Unit 1 - Trigonometry 1 1A Prerequisites: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve a missing side of a right triangle. Note p. 2 1B Prerequisites: I can convert within the imperial
Student Checklist Unit 1 - Trigonometry 1 1A Prerequisites: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve a missing side of a right triangle. Note p. 2 1B Prerequisites: I can convert within the imperial
Non Right Triangle Vector Addition. Sections 1.7 and 1.8
 Non Right Triangle Vector Addition Sections 1.7 and 1.8 Question: Why in the name of all that is good would someone want to do something like THAT? Answer: Because there is no law that states vectors must
Non Right Triangle Vector Addition Sections 1.7 and 1.8 Question: Why in the name of all that is good would someone want to do something like THAT? Answer: Because there is no law that states vectors must
Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8-2 Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio
 Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8- Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio 8-1: The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Focused Learning Target:
Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8- Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio 8-1: The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Focused Learning Target:
Displacement-time and Velocity-time Graphs
 PhysicsFactsheet April Number Displacement- and Velocity- Graphs This Factsheet explains how motion can be described using graphs, in particular how - graphs and - graphs can be used. Displacement- graphs
PhysicsFactsheet April Number Displacement- and Velocity- Graphs This Factsheet explains how motion can be described using graphs, in particular how - graphs and - graphs can be used. Displacement- graphs
Geo, Chap 8 Practice Test, EV Ver 1
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geo, Chap 8 Practice Test, EV Ver 1 Short Answer Find the length of the missing side. Leave your answer in simplest radical form. 1. (8-1) 2. (8-1) A grid shows the positions of
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geo, Chap 8 Practice Test, EV Ver 1 Short Answer Find the length of the missing side. Leave your answer in simplest radical form. 1. (8-1) 2. (8-1) A grid shows the positions of
Part Five: Trigonometry Review. Trigonometry Review
 T.5 Trigonometry Review Many of the basic applications of physics, both to mechanical systems and to the properties of the human body, require a thorough knowledge of the basic properties of right triangles,
T.5 Trigonometry Review Many of the basic applications of physics, both to mechanical systems and to the properties of the human body, require a thorough knowledge of the basic properties of right triangles,
Unit 1 Trigonometry. Topics and Assignments. General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes:
 1 Unit 1 Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes: 1.1 Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems
1 Unit 1 Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes: 1.1 Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems
Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry
 10C Name: Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry 3.1 The Tangent Ratio Outcome : Develop and apply the tangent ratio to solve problems that involve right triangles. Definitions: Adjacent side: the side
10C Name: Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry 3.1 The Tangent Ratio Outcome : Develop and apply the tangent ratio to solve problems that involve right triangles. Definitions: Adjacent side: the side
MBF 3C. Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School. Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons
 MBF 3C Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons Allow no more than 15 class days for this unit This includes time for review
MBF 3C Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons Allow no more than 15 class days for this unit This includes time for review
9.1 Use Trigonometry with Right Triangles
 9.1 Use Trigonometry with Right Triangles Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing lengths in right triangles. Find trigonometric ratios using right triangles. Use trigonometric ratios to find angle
9.1 Use Trigonometry with Right Triangles Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing lengths in right triangles. Find trigonometric ratios using right triangles. Use trigonometric ratios to find angle
Grade Common Core Math
 th 5 Grade Common Core Math Printable Review Problems Standards Included:.-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the
th 5 Grade Common Core Math Printable Review Problems Standards Included:.-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the
Math 4: Advanced Algebra Ms. Sheppard-Brick A Quiz Review LT ,
 4A Quiz Review LT 3.4 3.10, 4.1 4.3 Key Facts Know how to use the formulas for projectile motion. The formulas will be given to you on the quiz, but you ll need to know what the variables stand for Horizontal:
4A Quiz Review LT 3.4 3.10, 4.1 4.3 Key Facts Know how to use the formulas for projectile motion. The formulas will be given to you on the quiz, but you ll need to know what the variables stand for Horizontal:
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the.
 2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
We ve defined vectors as quantities that have a magnitude and a direction Displacement, velocity, and acceleration Represent by an arrow whose length
 We ve defined vectors as quantities that have a magnitude and a direction Displacement, velocity, and acceleration Represent by an arrow whose length represents magnitude and head represents direction
We ve defined vectors as quantities that have a magnitude and a direction Displacement, velocity, and acceleration Represent by an arrow whose length represents magnitude and head represents direction
Year 10 Term 2 Homework
 Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 2 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 9 Year 10 Term 2 Week 9 Homework 1 9.1 Trigonometry with right Triangles........................... 1 9.1.1
Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 2 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 9 Year 10 Term 2 Week 9 Homework 1 9.1 Trigonometry with right Triangles........................... 1 9.1.1
Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes
 First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. Trigonometry Notes.0 PRE-REQUISITES: SOLVING RIGHT TRIANGLES.1 ANGLES IN STANDARD POSITION 6 Ch..1 HW: p. 83 #1,, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 8. - TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF AN ANGLE
First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. Trigonometry Notes.0 PRE-REQUISITES: SOLVING RIGHT TRIANGLES.1 ANGLES IN STANDARD POSITION 6 Ch..1 HW: p. 83 #1,, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 8. - TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF AN ANGLE
Local Linearity (Tangent Plane) Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3
 Local Linearity and the Tangent Plane - 1 Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of
Local Linearity and the Tangent Plane - 1 Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the value of tan 59, to four decimal places. a.
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the value of tan 59, to four decimal places. a.
Youngstown State University Trigonometry Final Exam Review (Math 1511)
 Youngstown State University Trigonometry Final Exam Review (Math 1511) 1. Convert each angle measure to decimal degree form. (Round your answers to thousandths place). a) 75 54 30" b) 145 18". Convert
Youngstown State University Trigonometry Final Exam Review (Math 1511) 1. Convert each angle measure to decimal degree form. (Round your answers to thousandths place). a) 75 54 30" b) 145 18". Convert
T.5 The Law of Sines and Cosines and Its Applications
 1 T.5 The Law of Sines and Cosines and Its Applications The concepts of solving triangles developed in section T4 can be extended to all triangles. A triangle that is not right-angled is called an oblique
1 T.5 The Law of Sines and Cosines and Its Applications The concepts of solving triangles developed in section T4 can be extended to all triangles. A triangle that is not right-angled is called an oblique
MATH 229 TRIGONOMETRY. COURSE PACK (Fall 2018) Mark Turner Mathematics Division Cuesta College
 MATH 9 TRIGONOMETRY COURSE PACK (Fall 08) Mark Turner Mathematics Division Cuesta College Angles and Triangles. Find the complement and supplement of 60. Complement = Supplement =. Use the Pythagorean
MATH 9 TRIGONOMETRY COURSE PACK (Fall 08) Mark Turner Mathematics Division Cuesta College Angles and Triangles. Find the complement and supplement of 60. Complement = Supplement =. Use the Pythagorean
Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3
 Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of more than two variables and their level surfaces.
Unit #19 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of more than two variables and their level surfaces.
FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE
 1 of 6 FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE Now we come to the part where you need to just bear down and memorize. To make the process a bit simpler, I am providing all of the key info that they re going
1 of 6 FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE Now we come to the part where you need to just bear down and memorize. To make the process a bit simpler, I am providing all of the key info that they re going
Chapter 8 Diagnostic Test
 Chapter 8 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 422 455 1. Determine the measures of the indicated angles in each diagram. b) 2. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio to four decimal places. sin
Chapter 8 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 422 455 1. Determine the measures of the indicated angles in each diagram. b) 2. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio to four decimal places. sin
CURRICULUM CATALOG. GSE Geometry ( ) GA
 2018-19 CURRICULUM CATALOG Table of Contents COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: TRANSFORMATIONS IN THE COORDINATE PLANE... 2 UNIT 2: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS PART 1... 2 UNIT 3: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE,
2018-19 CURRICULUM CATALOG Table of Contents COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: TRANSFORMATIONS IN THE COORDINATE PLANE... 2 UNIT 2: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS PART 1... 2 UNIT 3: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE,
Higher tier unit 6a check in test. Calculator
 Higher tier unit 6a check in test Calculator Q1. The point A has coordinates (2, 3). The point B has coordinates (6, 8). M is the midpoint of the line AB. Find the coordinates of M. Q2. The points A, B
Higher tier unit 6a check in test Calculator Q1. The point A has coordinates (2, 3). The point B has coordinates (6, 8). M is the midpoint of the line AB. Find the coordinates of M. Q2. The points A, B
The Crooked Foundation The Bird House. 100ft. Inter-Island Journey. East Fence. 150ft. South Fence
 13.1 - Opening Per Date It is another beautiful day on the Big Island, and Grandma is out and about planning her net set of projects. First she wants to build a bird house for her new team of homing pigeons.
13.1 - Opening Per Date It is another beautiful day on the Big Island, and Grandma is out and about planning her net set of projects. First she wants to build a bird house for her new team of homing pigeons.
Projectile Motion SECTION 3. Two-Dimensional Motion. Objectives. Use of components avoids vector multiplication.
 Projectile Motion Key Term projectile motion Two-Dimensional Motion Previously, we showed how quantities such as displacement and velocity were vectors that could be resolved into components. In this section,
Projectile Motion Key Term projectile motion Two-Dimensional Motion Previously, we showed how quantities such as displacement and velocity were vectors that could be resolved into components. In this section,
1. Determine the remaining sides and angles of the triangle ABC. Show all work and / or support your answer.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Review: Chapters 7, 8 Chapter 7: Applications of Trigonometry and Vectors 1. Determine the remaining sides and angles of the triangle ABC. 2. Determine the remaining sides and angles
Trigonometry Final Exam Review: Chapters 7, 8 Chapter 7: Applications of Trigonometry and Vectors 1. Determine the remaining sides and angles of the triangle ABC. 2. Determine the remaining sides and angles
Angles of a Triangle. Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to Finding the third angle of a triangle
 Angles of a Triangle Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to 180 0 Finding the third angle of a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Is defined as the square of the length of the
Angles of a Triangle Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to 180 0 Finding the third angle of a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Is defined as the square of the length of the
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES
 AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
AP Physics 1 and 2 Summer Assignment
 AP Physics 1 and 2 Summer Assignment Due: First Day of Class Welcome to AP Physics! You are responsible for the material covered in the first three chapters of your textbook. The questions that follow
AP Physics 1 and 2 Summer Assignment Due: First Day of Class Welcome to AP Physics! You are responsible for the material covered in the first three chapters of your textbook. The questions that follow
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS This tutorial is essential pre-requisite material for anyone studying mechanical engineering. This tutorial uses the principle of learning by example.
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TUTORIAL 5 COORDINATE SYSTEMS This tutorial is essential pre-requisite material for anyone studying mechanical engineering. This tutorial uses the principle of learning by example.
Patterning Math Lab 4a
 Patterning Math Lab 4a This lab is an exploration of transformations of functions, a topic covered in your Precalculus textbook in Section 1.5. As you do the exercises in this lab you will be closely reading
Patterning Math Lab 4a This lab is an exploration of transformations of functions, a topic covered in your Precalculus textbook in Section 1.5. As you do the exercises in this lab you will be closely reading
Algebra II. Chapter 13 Notes Sections 13.1 & 13.2
 Algebra II Chapter 13 Notes Sections 13.1 & 13.2 Name Algebra II 13.1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Day One Today I am using SOHCAHTOA and special right triangle to solve trig problems. I am successful
Algebra II Chapter 13 Notes Sections 13.1 & 13.2 Name Algebra II 13.1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Day One Today I am using SOHCAHTOA and special right triangle to solve trig problems. I am successful
Non-right Triangles: Law of Cosines *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49405 1 Non-right Triangles: Law of Cosines * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will:
OpenStax-CNX module: m49405 1 Non-right Triangles: Law of Cosines * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will:
Vector Addition. Qty Item Part Number 1 Force Table ME-9447B 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME Carpenter s level 1 String
 rev 05/2018 Vector Addition Equipment List Qty Item Part Number 1 Force Table ME-9447B 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME-8979 1 Carpenter s level 1 String Purpose The purpose of this lab is for the student to gain
rev 05/2018 Vector Addition Equipment List Qty Item Part Number 1 Force Table ME-9447B 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME-8979 1 Carpenter s level 1 String Purpose The purpose of this lab is for the student to gain
Trigonometry * Scott Starks. 1 Trigonometry
 OpenStax-CNX module: m38633 1 Trigonometry * Scott Starks This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 Trigonometry 1.1 Introduction Trigonometry
OpenStax-CNX module: m38633 1 Trigonometry * Scott Starks This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 Trigonometry 1.1 Introduction Trigonometry
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 8-1 Similarity in Right Triangles
 8 Find this vocabular word in Lesson 8-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Finding Geometric Means The geometric mean of two positive numbers is the positive square root of their. Find the geometric mean of
8 Find this vocabular word in Lesson 8-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Finding Geometric Means The geometric mean of two positive numbers is the positive square root of their. Find the geometric mean of
The cosine ratio is a ratio involving the hypotenuse and one leg (adjacent to angle) of the right triangle Find the cosine ratio for. below.
 The Cosine Ratio The cosine ratio is a ratio involving the hypotenuse and one leg (adjacent to angle) of the right triangle. From the diagram to the right we see that cos C = This means the ratio of the
The Cosine Ratio The cosine ratio is a ratio involving the hypotenuse and one leg (adjacent to angle) of the right triangle. From the diagram to the right we see that cos C = This means the ratio of the
Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics. Geometrical Reasoning. Mr Black's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9. Shape
 Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics Geometrical Reasoning Mr Black's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9 Shape Geometrical Reasoning Contents Differentiated Independent Learning Worksheets Drawing and Measuring
Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics Geometrical Reasoning Mr Black's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9 Shape Geometrical Reasoning Contents Differentiated Independent Learning Worksheets Drawing and Measuring
Unit 6: Triangle Geometry
 Unit 6: Triangle Geometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 9 Principles Name: lock: What I can do for this unit: fter Practice fter Review How I id 6-1 I can recognize similar triangles using the ngle Test,
Unit 6: Triangle Geometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 9 Principles Name: lock: What I can do for this unit: fter Practice fter Review How I id 6-1 I can recognize similar triangles using the ngle Test,
Algebra II Trigonometric Functions
 Slide 1 / 162 Slide 2 / 162 Algebra II Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 162 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Slide 1 / 162 Slide 2 / 162 Algebra II Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 162 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Two-Dimensional Waves
 Two-Dimensional Waves In our previous lessons, we discussed one-dimensional waves waves that can only travel in straight lines, such as along the length of a spring. In this next part of the unit, we will
Two-Dimensional Waves In our previous lessons, we discussed one-dimensional waves waves that can only travel in straight lines, such as along the length of a spring. In this next part of the unit, we will
Angle, symmetry and transformation
 Terms Illustrations Definition Acute angle An angle greater than 0 and less than 90. Alternate angles Where two straight lines are cut by a third, as in the diagrams, the angles d and f (also c and e)
Terms Illustrations Definition Acute angle An angle greater than 0 and less than 90. Alternate angles Where two straight lines are cut by a third, as in the diagrams, the angles d and f (also c and e)
Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry
 Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry Review of Triangles Recall that the sum of all angles in any triangle is 180. Let s look at what this means for a right triangle: A right angle is an angle which
Section 4.1: Introduction to Trigonometry Review of Triangles Recall that the sum of all angles in any triangle is 180. Let s look at what this means for a right triangle: A right angle is an angle which
ACTIVITY TWO CONSTANT VELOCITY IN TWO DIRECTIONS
 1 ACTIVITY TWO CONSTANT VELOCITY IN TWO DIRECTIONS Purpose The overall goal of this activity is for students to analyze the motion of an object moving with constant velocity along a diagonal line. In this
1 ACTIVITY TWO CONSTANT VELOCITY IN TWO DIRECTIONS Purpose The overall goal of this activity is for students to analyze the motion of an object moving with constant velocity along a diagonal line. In this
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14
 Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
Unit #20 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3
 Unit #20 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of more than two variables and their level surfaces.
Unit #20 : Functions of Many Variables, and Vectors in R 2 and R 3 Goals: To introduce tangent planes for functions of two variables. To consider functions of more than two variables and their level surfaces.
Graphing Trigonometric Functions: Day 1
 Graphing Trigonometric Functions: Day 1 Pre-Calculus 1. Graph the six parent trigonometric functions.. Apply scale changes to the six parent trigonometric functions. Complete the worksheet Exploration:
Graphing Trigonometric Functions: Day 1 Pre-Calculus 1. Graph the six parent trigonometric functions.. Apply scale changes to the six parent trigonometric functions. Complete the worksheet Exploration:
DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK
 DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK Sine Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine Adjacent Hypotenuse sin θ = opp. hyp. cos θ = adj. hyp. tan θ = opp. adj. Tangent Opposite Adjacent a 2 + b 2 = c 2 csc θ = hyp. opp. sec θ =
DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK Sine Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine Adjacent Hypotenuse sin θ = opp. hyp. cos θ = adj. hyp. tan θ = opp. adj. Tangent Opposite Adjacent a 2 + b 2 = c 2 csc θ = hyp. opp. sec θ =
UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry
 Year 12 Further Mathematics UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry CHAPTER 8 - TRIGONOMETRY This module covers the application of geometric and trigonometric knowledge and techniques to various two-
Year 12 Further Mathematics UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry CHAPTER 8 - TRIGONOMETRY This module covers the application of geometric and trigonometric knowledge and techniques to various two-
A lg e b ra II. Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio
 1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc Length & Area of a Sector
1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc Length & Area of a Sector
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 162. Slide 2 / 162. Slide 3 / 162. Trigonometric Functions. Trig Functions
 Slide 1 / 162 Algebra II Slide 2 / 162 Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 162 Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Slide 1 / 162 Algebra II Slide 2 / 162 Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 162 Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Math 144 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle
 1 p 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Math 1 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle We use right triangles to study trigonometry. In right triangles, we have found many relationships between the
1 p 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Math 1 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle We use right triangles to study trigonometry. In right triangles, we have found many relationships between the
Chapter 6 Review. Extending Skills with Trigonometry. Check Your Understanding
 hapter 6 Review Extending Skills with Trigonometry heck Your Understanding. Explain why the sine law holds true for obtuse angle triangles as well as acute angle triangles. 2. What dimensions of a triangle
hapter 6 Review Extending Skills with Trigonometry heck Your Understanding. Explain why the sine law holds true for obtuse angle triangles as well as acute angle triangles. 2. What dimensions of a triangle
Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1
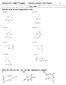 Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1 Day 1 HW Find the value of each trigonometric ratio. Write the ratios for sinp, cosp, and tanp. Remember to simplify! 9. 10. 11. Packet Unit 5
Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1 Day 1 HW Find the value of each trigonometric ratio. Write the ratios for sinp, cosp, and tanp. Remember to simplify! 9. 10. 11. Packet Unit 5
: Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for θ. Special Right Triangles:
 ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER 13 NOTES Section 13-1 Right Triangle Trig Understand and use trigonometric relationships of acute angles in triangles. 12.F.TF.3 CC.9- Determine side lengths of right triangles by using
ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER 13 NOTES Section 13-1 Right Triangle Trig Understand and use trigonometric relationships of acute angles in triangles. 12.F.TF.3 CC.9- Determine side lengths of right triangles by using
Lesson Title 2: Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios
 Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231
 1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
30 o. 60 o 1. INSTRUCTIONAL PLAN Day 3
 INSTRUCTIONAL PLAN Day 3 Subject: Trigonometry Topic: Special Right Triangles, Problem Solving and Applications of Right Triangles Target Learners: College Students Objectives: At the end of the lesson,
INSTRUCTIONAL PLAN Day 3 Subject: Trigonometry Topic: Special Right Triangles, Problem Solving and Applications of Right Triangles Target Learners: College Students Objectives: At the end of the lesson,
Trigonometry. This booklet belongs to: Period. HW Mark: RE-Submit. Questions that I find difficult LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES
 HW Mark: 10 9 8 7 6 RE-Submit Trigonometry This booklet belongs to: Period LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES Questions that I find difficult Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. REVIEW TEST Your teacher
HW Mark: 10 9 8 7 6 RE-Submit Trigonometry This booklet belongs to: Period LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES Questions that I find difficult Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. REVIEW TEST Your teacher
MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY
 MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY SECTION PAGE NUMBERS HOMEWORK Prerequisite p. 0 - # 3 Skills 4. p. 8-9 #4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,, 4. p. 37 39 #bde, acd, 3, 4acde, 5, 6ace, 7, 8, 9, 0,, 4.3 p. 46-47 #aef,, 3, 4, 5defgh,
MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY SECTION PAGE NUMBERS HOMEWORK Prerequisite p. 0 - # 3 Skills 4. p. 8-9 #4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,, 4. p. 37 39 #bde, acd, 3, 4acde, 5, 6ace, 7, 8, 9, 0,, 4.3 p. 46-47 #aef,, 3, 4, 5defgh,
Important. Compact Trigonometry CSO Prioritized Curriculum. Essential. Page 1 of 6
 Essential Important Compact Trigonometry CSO Prioritized Curriculum M.O.T.3.1 apply the right triangle definition of the six trigonometric functions of an angle to determine the values of the function
Essential Important Compact Trigonometry CSO Prioritized Curriculum M.O.T.3.1 apply the right triangle definition of the six trigonometric functions of an angle to determine the values of the function
Middle School Mathematics Trimester 2 Subject Overview
 1 Class 7 Linear Graphs Sequences Data Handling Perimeter and Area Read and plot coordinates of points determined by geometric information in all four quadrants Generate coordinate pairs that satisfy a
1 Class 7 Linear Graphs Sequences Data Handling Perimeter and Area Read and plot coordinates of points determined by geometric information in all four quadrants Generate coordinate pairs that satisfy a
2.3 Projectile Motion
 Figure 1 An Olympic ski jumper uses his own body as a projectile. projectile an object that moves along a two-dimensional curved trajectory in response to gravity projectile motion the motion of a projectile
Figure 1 An Olympic ski jumper uses his own body as a projectile. projectile an object that moves along a two-dimensional curved trajectory in response to gravity projectile motion the motion of a projectile
Math 1201 Chapter 2 Review
 ath 1201 hapter 2 Review ultiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. etermine tan and tan. 8 10 a. tan = 1.25; tan = 0.8 c. tan = 0.8; tan = 1.25 b.
ath 1201 hapter 2 Review ultiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. etermine tan and tan. 8 10 a. tan = 1.25; tan = 0.8 c. tan = 0.8; tan = 1.25 b.
The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared.
 Math 1 TOOLKITS TOOLKIT: Pythagorean Theorem & Its Converse The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared. a 2 +
Math 1 TOOLKITS TOOLKIT: Pythagorean Theorem & Its Converse The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared. a 2 +
Math Analysis Final Exam Review. Chapter 1 Standards
 Math Analysis Final Exam Review Chapter 1 Standards 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f 1g Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing sides in a right triangle Use the sine, cosine, and tangent functions to find missing
Math Analysis Final Exam Review Chapter 1 Standards 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f 1g Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing sides in a right triangle Use the sine, cosine, and tangent functions to find missing
 Algebra Lab Investigating Trigonometri Ratios You an use paper triangles to investigate the ratios of the lengths of sides of right triangles. Virginia SOL Preparation for G.8 The student will solve realworld
Algebra Lab Investigating Trigonometri Ratios You an use paper triangles to investigate the ratios of the lengths of sides of right triangles. Virginia SOL Preparation for G.8 The student will solve realworld
CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and graphs
 Ch 5. Trigonometry 6. Angles 6. Right triangles 6. Trig funs for general angles 5.: Trigonometric functions and graphs 5.5 Inverse functions CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and
Ch 5. Trigonometry 6. Angles 6. Right triangles 6. Trig funs for general angles 5.: Trigonometric functions and graphs 5.5 Inverse functions CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and
Curriculum Catalog
 2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents GEOMETRY COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION... 1 UNIT 2: LOGIC... 2 UNIT 3: ANGLES AND PARALLELS... 2 UNIT 4: CONGRUENT TRIANGLES
2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents GEOMETRY COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION... 1 UNIT 2: LOGIC... 2 UNIT 3: ANGLES AND PARALLELS... 2 UNIT 4: CONGRUENT TRIANGLES
Notes: Topics in these sets: Vectors, vector translations, congruence (SSS, SAS), CPCTC, slope and distance applications
 Notes: Topics in these sets: Vectors, vector translations, congruence (SSS, SAS), CPCTC, slope and distance applications HW Set 6 can be assigned once the first problem in Problem Set 10 has been completed.
Notes: Topics in these sets: Vectors, vector translations, congruence (SSS, SAS), CPCTC, slope and distance applications HW Set 6 can be assigned once the first problem in Problem Set 10 has been completed.
ME 201 Engineering Mechanics: Statics. Unit 1.2 Scalars and Vectors Vector Operations Vector Addition of Forces
 ME 201 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Unit 1.2 Scalars and Vectors Vector Operations Vector ddition of Forces dditional ssistance Tutoring Center Mck 272 Engineering Mechanics Help Lab us 9 Scalar Scalars
ME 201 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Unit 1.2 Scalars and Vectors Vector Operations Vector ddition of Forces dditional ssistance Tutoring Center Mck 272 Engineering Mechanics Help Lab us 9 Scalar Scalars
Blue Pelican Pre-Calculus First Semester
 Blue Pelican Pre-Calculus First Semester Absent-student Version 1.01 Copyright 2010-2012 by Charles E. Cook; Refugio, Tx (All rights reserved) Pre Calculus Syllabus (First Semester) Unit 1: Algebra review
Blue Pelican Pre-Calculus First Semester Absent-student Version 1.01 Copyright 2010-2012 by Charles E. Cook; Refugio, Tx (All rights reserved) Pre Calculus Syllabus (First Semester) Unit 1: Algebra review
1 Trigonometry -Ideas and Applications
 1 Trigonometry -Ideas and Applications 1.1 A second look at graphs The sine and cosine are basic entities of trigonometry, for the other four functions can be defined in terms of them. The graphs can be
1 Trigonometry -Ideas and Applications 1.1 A second look at graphs The sine and cosine are basic entities of trigonometry, for the other four functions can be defined in terms of them. The graphs can be
MPM2D. Key Questions & Concepts. Grade 10Math. peace. love. pi.
 MPM2D Key Questions & Concepts Grade 10Math peace. love. pi. Unit I: Linear Systems Important Stuff Equations of Lines Slope à Tells us about what the line actually looks like; represented by m; equation
MPM2D Key Questions & Concepts Grade 10Math peace. love. pi. Unit I: Linear Systems Important Stuff Equations of Lines Slope à Tells us about what the line actually looks like; represented by m; equation
2009 GCSE Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved
 2 This book is under copyright to GCSE Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents angles 3 bearings 8 triangle similarity 9 triangle congruency 11 Pythagoras
2 This book is under copyright to GCSE Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents angles 3 bearings 8 triangle similarity 9 triangle congruency 11 Pythagoras
SECONDARY MATH Area of a Triangle and Law of Sines
 SECONDARY MATH 3 7-1 Area of a Triangle and Law of Sines Goal: Be the first team to find (r j h g f)(x). WARM UP COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS Person #1 f(x) = x 2 7x + 6 Person #2 g(x) = 2 +10 4 Person #3
SECONDARY MATH 3 7-1 Area of a Triangle and Law of Sines Goal: Be the first team to find (r j h g f)(x). WARM UP COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS Person #1 f(x) = x 2 7x + 6 Person #2 g(x) = 2 +10 4 Person #3
ACT Math test Trigonometry Review
 Many students are a little scared of trig, but the ACT seems to overcompensate for that fact by testing trig in an extremely straightforward way. ACT trig is basically all about right triangles. When it
Many students are a little scared of trig, but the ACT seems to overcompensate for that fact by testing trig in an extremely straightforward way. ACT trig is basically all about right triangles. When it
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
PARRENTHORN HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department. YEAR 11 GCSE PREPARATION Revision Booklet
 PARRENTHORN HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department YEAR GCSE PREPARATION Revision Booklet Name: _ Class: Teacher: GEOMETRY & MEASURES Area, Perimeter, Volume & Circles AREA FORMULAS Area is the space a 2D
PARRENTHORN HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department YEAR GCSE PREPARATION Revision Booklet Name: _ Class: Teacher: GEOMETRY & MEASURES Area, Perimeter, Volume & Circles AREA FORMULAS Area is the space a 2D
This simple one is based on looking at various sized right angled triangles with angles 37 (36á9 ), 53 (53á1 ) and 90.
 TRIGONOMETRY IN A RIGHT ANGLED TRIANGLE There are various ways of introducing Trigonometry, including the use of computers, videos and graphics calculators. This simple one is based on looking at various
TRIGONOMETRY IN A RIGHT ANGLED TRIANGLE There are various ways of introducing Trigonometry, including the use of computers, videos and graphics calculators. This simple one is based on looking at various
