|
|
|
- Edwin Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 CP5_6 The problems in this problem set cover lectures C5 and C6. 1. a. What are doubly linked lists? What is the record declaration for a node in a doubly linked list? head Figure 1. Sample Doubly Linked List Doubly linked lists have two pointers instead of the single pointer seen in singly linked lists. The pointers point to both the previous node in the list as well as the next node in the list. type Listnode is record Element : Elementtype; Next : Listptr; Prev : Listptr; -- this is the change made to singly linked lists end record; b. Write an algorithm to insert a node into a sorted doubly linked list. Use a diagram to show the sequence of operations that have to be performed to carry out the insertion step. Hint: Extend the approach used in class/ notes for singly linked lists. Preconditions: 1. User passes the list (called List) and the element to be inserted (called Element) to the insert procedure 2. List is already sorted Postconidtions: 1. Procedure returns the list with the element inserted in the correct position 2. List remains sorted Algorithm: Create three temporary Listptrs Current, Previous and NewNode Previous := null Current := List.Head; NewNode := new Listnode; NewNode.Element := Element
18 Loop exit when Current = Null exit when Current.Element > Element Previous := Current; Current := Current.Next; NewNode. Next := Current; NewNode.Prev:= Previous; If Previous = null L.Head := NewNode else Previous.Next := NewNode If Current /= null Current.Prev := NewNode; Return List Consider the doubly linked list shown in Figure 1. The insertion of a node with element 12 in the list, the insert operation is shown in Figures 2 and 3. head Initial State head Previous Current When loop is exited NewNode 12 Figure 2. Prior to Insertion
19 NewNode.Next := Current head Previous Current NewNode NewNode.Prev := Previous head Previous 12 Current Previous.Next := NewNode head Previous 12 NewNode Current NewNode
20 Current.Prev := NewNode head Previous Current Figure 3. After Insertion Operation c. Implement your algorithm as an Ada95 program. 12 NewNode Package Specification GNAT 3.15p ( ) Copyright Free Software Foundation, Inc. Checking: c:/docume~1/jayaka~1/mydocu~1/16070/code/doubly_linked_list.ads (source file time stamp: :46:40) Specification for doubly-linked lists Specified: Jayakanth Srinivasan Last Modified: February 11, package Doubly_Linked_List is subtype Elementtype is Integer; type Listnode; 12. type Listptr is access Listnode; 13. type Listnode is 14. record 15. Element : Elementtype; 16. Next : Listptr; 17. Prev : Listptr; -- this is the change made to singly linked lists 18. end record; type List is 21. record 22. Head : Listptr; 23. end record;
21 28. procedure Makeempty ( 29. L : in out List ); Pre: L is defined Post: L is empty function Isempty ( 34. L : in List ) 35. return Boolean; Pre: L is defined Post: returns True if L is empty, False otherwise procedure Display ( 40. L : in List ); Pre: L may be empty Post: displays the contents of L's Element fields, in the order in which they appear in L procedure Initialize ( 46. L : in out List ); Pre: L may be empty Post: Elements inserted into the list at correct position 50. procedure Insert_In_Order ( 51. L : in out List; 52. Element : in Elementtype ); end Doubly_Linked_List; 54 lines: No errors Package Implementation GNAT 3.15p ( ) Copyright Free Software Foundation, Inc. Compiling: c:/docume~1/jayaka~1/mydocu~1/16070/code/doubly_linked_list.adb (source file time stamp: :48:14) Implementation for doubly-linked lists Programmer: Jayakanth Srinivasan Last Modified: Feb 11, with Ada.Text_Io; 8. with Ada.Integer_Text_Io; 9. with Ada.Unchecked_Deallocation; use Ada.Text_Io; 12. use Ada.Integer_Text_Io; package body Doubly_Linked_List is create an instance of the free procedure 16. procedure Free is 17. new Ada.Unchecked_Deallocation(Listnode, Listptr); check if list is empty. List.Head will be null 19. function Isempty ( 20. L : in List ) 21. return Boolean is
22 22. begin 23. if L.Head = null then 24. return True; 25. else 26. return False; 27. end if; end Isempty; free all allocated memory at the end of the program 32. procedure Makeempty ( 33. L : in out List ) is 34. Temp : Listptr; begin 37. loop 38. exit when Isempty(L); 39. Temp := L.Head; 40. L.Head := Temp.Next; 41. Free(Temp); 42. end loop; 43. L.Head := null; 44. end Makeempty; initialize the list by setting the head pointed to null 47. procedure Initialize ( 48. L : in out List ) is 49. begin 50. L.Head := null; 51. end Initialize; displays the contents of the list 54. procedure Display ( 55. L : in List ) is 56. Temp : Listptr; 57. begin set the pointer to the head of the node 59. Temp:= L.Head; 60. while Temp /= null loop 61. Put(Temp.Element); 62. Put(", "); move pointer to the next node 64. Temp :=Temp.Next; 65. end loop; 66. New_Line; 67. end Display; insert elements in ascending order this procedure added :) 71. procedure Insert_In_Order ( 72. L : in out List; 73. Element : in Elementtype ) is 74. Current, 75. Previous, 76. Newnode : Listptr; 77. begin 78. Current := L.Head; 79. Previous := null;
23 create a node and set the data to element 81. Newnode := new Listnode; 82. Newnode.Element:= Element; check if the list is empty. 84. if Isempty(L)= False then 85. loop need two separate exits, otherwise there will be an execption at runtime 88. exit when Current = null; 89. exit when Current.Element >Element; 90. Previous := Current; 91. Current := Current.Next; 92. end loop; 93. end if; do insertion 95. Newnode.Prev:= Previous; 96. Newnode.Next := Current; 97. if Previous = null then list is empty 99. L.Head := Newnode; 100. else 101. Previous.Next := Newnode; 102. if Current /= null then 103. Current.Prev := Newnode; 104. end if; 105. end if; 106. end Insert_In_Order; end Doubly_Linked_List; 108 lines: No errors Test Program GNAT 3.15p ( ) Copyright Free Software Foundation, Inc. Compiling: c:/docume~1/jayaka~1/mydocu~1/16070/code/doubly_list_test.adb (source file time stamp: :49:02) Program to test the doubly linked list package Programmer: Jayakanth Srinivasan Date Last Modified : Feb 11, with Doubly_Linked_List; 8. use Doubly_Linked_List; procedure Doubly_List_Test is 11. My_List : List; begin initialize the list 15. Initialize(My_List); insert 1,3,2,4 into the list and display at each stage 18. Insert_In_Order(My_List, 1);
24 19. Display(My_List); 20. Insert_In_Order(My_List, 3); 21. Display(My_List); 22. Insert_In_Order(My_List, 2); 23. Display(My_List); 24. Insert_In_Order(My_List, 4); 25. Display(My_List); end Doubly_List_Test; 27 lines: No errors 2. What is the Shortest Path through the graph shown below using Dijkstra s algorithm. a b e 6 c 2 d Assume node A is the start node. Show all the steps in the computation of the shortest path. Initialize V = {a, b, c, d, e} E = {(a,b), (a,c), (b,e), (b,c), (c,b), (c,d), (c,e), (d,a), (d,e), (e.d)} S = { } Q = {a, b, c, d, e} D = [0,,,, ] Previous = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] Start at A Relax (a,b,10) Relax (a,c,5) S = {a} Q = {b, c, d, e} 7
25 D = [0, 10, 5,, ] Previous = [0,a, a, 0, 0] Move to C Relax(c,b,2) Relax (c,d,2) Relax(c,e,9) S = {a,c} Q = {b, d, e} D = [0, 7, 5, 7, 14] Previous = [0,c, a, c, c] Move to B (you can also move to D) Relax(b,e,1) Relax(b,c,3) S = {a, c, b} Q = { d, e} D = [0, 7, 5, 7, 8] Previous = [0, c, a, c, b] Move to D Relax(d,a,7) Relax(d,e,6) S = {a, c, b, d} Q = {e} D = [0, 7, 5, 7, 8] Previous = [0, c, a, c, b] Move to E Relax(e,d,4) S = {a, c, b, d, e} Q = {} D = [0, 7, 5, 7, 8] Previous = [0, c, a, c, b] 3. Define the following terms (as applied to graphs):
26 For a graph G = (V, E). where V is a finite nonempty set of vertices and E is the set of edges, a. Walk A walk is a sequence of vertices (v1, v2,, vk) in which each adjacent vertex pair is an edge b. Path A path is a walk with no repeated nodes c. Eulerian Path An Eulerian path in a graph is a path that uses each edge precisely once. d. Cycle A cycle is a path that begins and ends with the same vertex e. Degree of a vertex The degree of a vertex in an undirected graph is the number of edges incident with it, except that a loop at a vertex contributes twice to the degree of that vertex In a directed graph, the degree of the vertex is partitioned into indegree (number of edges entering a vertex) and outdegree (number of edges leaving a vertex). Note that a loop contributes to both the indegree and the outdegree.
A collision is said to occur when two or more keys hash to the same index location.
 Problem Set #8 Solutions Problem 1-9 points Given the tree below, traverse the tree a. Inorder : a/b c * d*e / f + g b. Preorder: * - / a b c / * d e + f g c. Postorder a b / c d e * f g + / * * - / /
Problem Set #8 Solutions Problem 1-9 points Given the tree below, traverse the tree a. Inorder : a/b c * d*e / f + g b. Preorder: * - / a b c / * d e + f g c. Postorder a b / c d e * f g + / * * - / /
03/31/03 Lab 7. Linked Lists
 03/31/03 Lab 7 Lists are a collection of items in which each item has a specific position. The specification for positioning the items provides some rules of order so this data structure is called an ordered
03/31/03 Lab 7 Lists are a collection of items in which each item has a specific position. The specification for positioning the items provides some rules of order so this data structure is called an ordered
Unified Engineering Spring 2005
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Cambridge, MA 02139 Unified Engineering Spring 2005 Problem Set #7 Solutions Problem C1. Understanding.ali files With the
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Cambridge, MA 02139 Unified Engineering Spring 2005 Problem Set #7 Solutions Problem C1. Understanding.ali files With the
Unified Engineering Spring 2005
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology epartment of eronautics and stronautics ambridge, M 09 Unified ngineering Spring 005 Problem Set #8 Solutions Problem 5. raphs, Shortest Path What is the Shortest
Massachusetts Institute of Technology epartment of eronautics and stronautics ambridge, M 09 Unified ngineering Spring 005 Problem Set #8 Solutions Problem 5. raphs, Shortest Path What is the Shortest
Problem Set 5 Solutions
 Problem Set 5 Solutions Problem 1 Part 1: Merge Sort is a sort algorithm that splits the items to be sorted into two groups, recursively sorts each group, and merges them into a final, sorted sequence.
Problem Set 5 Solutions Problem 1 Part 1: Merge Sort is a sort algorithm that splits the items to be sorted into two groups, recursively sorts each group, and merges them into a final, sorted sequence.
Advanced Linked Lists. Doubly Linked Lists Circular Linked Lists Multi- Linked Lists
 Advanced Linked Lists Doubly Linked Lists Circular Linked Lists Multi- Linked Lists Review The singly linked list: consists of nodes linked in a single direction. access and traversals begin with the first
Advanced Linked Lists Doubly Linked Lists Circular Linked Lists Multi- Linked Lists Review The singly linked list: consists of nodes linked in a single direction. access and traversals begin with the first
In the case above, only the x:= x+1 statement is executed and the result is 4;
 C-10 1. For X = 3 Case 1. IF x >= 0 THEN x:= x+1; ELSIF x >=1 THEN x := x + 2; END IF; In the case above, only the x:= x+1 statement is executed and the result is 4; Case 2. IF x >= 0 THEN x := x + 1;
C-10 1. For X = 3 Case 1. IF x >= 0 THEN x:= x+1; ELSIF x >=1 THEN x := x + 2; END IF; In the case above, only the x:= x+1 statement is executed and the result is 4; Case 2. IF x >= 0 THEN x := x + 1;
CS350: Data Structures. Doubly Linked Lists
 Doubly Linked Lists James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Doubly Linked Lists Adds an additional pointer to a the list nodes that points to the previous
Doubly Linked Lists James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Doubly Linked Lists Adds an additional pointer to a the list nodes that points to the previous
That means circular linked list is similar to the single linked list except that the last node points to the first node in the list.
 Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Circular Linked Lists and it operations Introduction: Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link
Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Circular Linked Lists and it operations Introduction: Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link
Note: The enumerations range from 0 to (number_of_elements_in_enumeration 1).
 C8-1 Algorithm 1. Use a subtype to represent the numbers for months 2. Use an enumeration to represent the named months 3. Use an enumeration to represent the roman months 4. Get the inputs from the user
C8-1 Algorithm 1. Use a subtype to represent the numbers for months 2. Use an enumeration to represent the named months 3. Use an enumeration to represent the roman months 4. Get the inputs from the user
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 LECTURE 4 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 3... Binary Heap Iterator Binary Heap Today Binary Heap 1 Binary Heap 2 Singly Heap - Add - example Binary
LECTURE 4 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 3... Binary Heap Iterator Binary Heap Today Binary Heap 1 Binary Heap 2 Singly Heap - Add - example Binary
GRAPH THEORY - FUNDAMENTALS
 GRAPH THEORY - FUNDAMENTALS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/graph_theory/graph_theory_fundamentals.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com A graph is a diagram of points and lines connected to the points. It has
GRAPH THEORY - FUNDAMENTALS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/graph_theory/graph_theory_fundamentals.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com A graph is a diagram of points and lines connected to the points. It has
LINKED LISTS cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015
 LINKED LISTS cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 5 due tonight at midnight -assignment 6 is out -YOU WILL BE SWITCHING PARTNERS! 3 assignment
LINKED LISTS cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 5 due tonight at midnight -assignment 6 is out -YOU WILL BE SWITCHING PARTNERS! 3 assignment
CS350: Data Structures Linked Lists
 Linked Lists James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Linked Lists Come in a variety of different forms - singly linked lists - doubly linked lists - circular
Linked Lists James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Linked Lists Come in a variety of different forms - singly linked lists - doubly linked lists - circular
Computer Science CS221 Test 4 Name
 Computer Science CS221 Test 4 Name 1. We looked at two different concrete classes that implemented the Queue interface, QueueAr which used an array as the underlying data structure, and QueueLi which used
Computer Science CS221 Test 4 Name 1. We looked at two different concrete classes that implemented the Queue interface, QueueAr which used an array as the underlying data structure, and QueueLi which used
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 LECTURE 5 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 4... Linked Lists Binary Heap Singly Linked List Insert at the beginning Insert after a node Today Linked
LECTURE 5 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 4... Linked Lists Binary Heap Singly Linked List Insert at the beginning Insert after a node Today Linked
Lecture C8: Trees part II 3 C 2 A 4 D. Response to 'Muddiest Part of the Lecture Cards' (16 respondents)
 Lecture C8: Trees part II Response to 'Muddiest Part of the Lecture Cards' (16 respondents) 1) Is the tree in the Depth first example actually a tree? (It has 6 vertices and 8 edges a tree has N verticed
Lecture C8: Trees part II Response to 'Muddiest Part of the Lecture Cards' (16 respondents) 1) Is the tree in the Depth first example actually a tree? (It has 6 vertices and 8 edges a tree has N verticed
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 07: Linked Lists MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2019 Linked Lists 2 Introduction Linked List Abstract Data Type SinglyLinkedList ArrayList Keep in Mind Introduction:
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 07: Linked Lists MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Spring 2019 Linked Lists 2 Introduction Linked List Abstract Data Type SinglyLinkedList ArrayList Keep in Mind Introduction:
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 8: Dynamically Allocated Linked Lists 2017-2018 Fall int x; x = 8; int A[4]; An array is stored as one contiguous block of memory. How can we add a fifth element to the
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 8: Dynamically Allocated Linked Lists 2017-2018 Fall int x; x = 8; int A[4]; An array is stored as one contiguous block of memory. How can we add a fifth element to the
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 07: Linked Lists and Iterators MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Linked Lists 2 Introduction Linked List Abstract Data Type General Implementation of the ListADT
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 07: Linked Lists and Iterators MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Linked Lists 2 Introduction Linked List Abstract Data Type General Implementation of the ListADT
CMPT 225. Lecture 6 linked list
 CMPT 225 Lecture 6 linked list 1 Last Lecture Class documentation Linked lists and its operations 2 Learning Outcomes At the end of this lecture, a student will be able to: define one of the concrete data
CMPT 225 Lecture 6 linked list 1 Last Lecture Class documentation Linked lists and its operations 2 Learning Outcomes At the end of this lecture, a student will be able to: define one of the concrete data
UNIT Name the different ways of representing a graph? a.adjacencymatrix b. Adjacency list
 UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
Agenda. Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList!
 Implementations I 1 Agenda Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList! Stack and queues Array-based implementations
Implementations I 1 Agenda Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList! Stack and queues Array-based implementations
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Lesson 1: Introduction to algorithms and basic data structures Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created
Lesson 1: Introduction to algorithms and basic data structures Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Lesson 1: Introduction to algorithms and basic data structures Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created by
Lesson 1: Introduction to algorithms and basic data structures Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created by
Sample Question Paper
 Scheme - I Sample Question Paper Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any FIVE of the following. 10 Marks a. Write any four applications of data structure. b. Sketch the diagram of circular queue. c. State
Scheme - I Sample Question Paper Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any FIVE of the following. 10 Marks a. Write any four applications of data structure. b. Sketch the diagram of circular queue. c. State
Agenda. Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList
 Implementations I 1 Agenda Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList Stack and queues Array-based implementations
Implementations I 1 Agenda Inner classes and implementation of ArrayList Nested classes and inner classes The AbstractCollection class Implementation of ArrayList Stack and queues Array-based implementations
CS32 Discussion Week 3
 CS32 Discussion Week 3 Muhao Chen muhaochen@ucla.edu http://yellowstone.cs.ucla.edu/~muhao/ 1 Outline Doubly Linked List Sorted Linked List Reverse a Linked List 2 Doubly Linked List A linked list where
CS32 Discussion Week 3 Muhao Chen muhaochen@ucla.edu http://yellowstone.cs.ucla.edu/~muhao/ 1 Outline Doubly Linked List Sorted Linked List Reverse a Linked List 2 Doubly Linked List A linked list where
Data Structures (CS301) LAB
 Data Structures (CS301) LAB Objectives The objectives of this LAB are, o Enabling students to implement Doubly Linked List practically using c++ and adding more functionality in it. Introduction to Singly
Data Structures (CS301) LAB Objectives The objectives of this LAB are, o Enabling students to implement Doubly Linked List practically using c++ and adding more functionality in it. Introduction to Singly
DATA STRUCTURE UNIT I
 DATA STRUCTURE UNIT I 1. What is Data Structure? A data structure is a mathematical or logical way of organizing data in the memory that consider not only the items stored but also the relationship to
DATA STRUCTURE UNIT I 1. What is Data Structure? A data structure is a mathematical or logical way of organizing data in the memory that consider not only the items stored but also the relationship to
Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers
 04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
Introduction to Computer Science II CS S-20 Linked Lists III
 Introduction to Computer Science II CS112-2012S-20 Linked Lists III David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 20-0: Linked List Previous Practical Example: removeat(int index)
Introduction to Computer Science II CS112-2012S-20 Linked Lists III David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 20-0: Linked List Previous Practical Example: removeat(int index)
Lecture No.04. Data Structures
 Lecture No.04 Data Structures Josephus Problem #include "CList.cpp" void main(int argc, char *argv[]) { CList list; int i, N=10, M=3; for(i=1; i
Lecture No.04 Data Structures Josephus Problem #include "CList.cpp" void main(int argc, char *argv[]) { CList list; int i, N=10, M=3; for(i=1; i
CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 3: ADT and Java interfaces Instructor: Olga Veksler 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia Outline Review Data Structures Abstract Data Types 2 Principles of OO Programming
CS2210 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 3: ADT and Java interfaces Instructor: Olga Veksler 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia Outline Review Data Structures Abstract Data Types 2 Principles of OO Programming
Implementation. Learn how to implement the List interface Understand the efficiency trade-offs between the ArrayList and LinkedList implementations
 Readings List Implementations Chapter 20.2 Objectives Learn how to implement the List interface Understand the efficiency trade-offs between the ArrayList and LinkedList implementations Additional references:
Readings List Implementations Chapter 20.2 Objectives Learn how to implement the List interface Understand the efficiency trade-offs between the ArrayList and LinkedList implementations Additional references:
Data structure is an organization of information, usually in memory, for better algorithm efficiency.
 Lecture 01 Introduction Wednesday, 29 July 2015 12:59 pm Data structure is an organization of information, usually in memory, for better algorithm efficiency. Abstract data types (ADTs) are a model for
Lecture 01 Introduction Wednesday, 29 July 2015 12:59 pm Data structure is an organization of information, usually in memory, for better algorithm efficiency. Abstract data types (ADTs) are a model for
Outline. Introduction. Representations of Graphs Graph Traversals. Applications. Definitions and Basic Terminologies
 Graph Chapter 9 Outline Introduction Definitions and Basic Terminologies Representations of Graphs Graph Traversals Breadth first traversal Depth first traversal Applications Single source shortest path
Graph Chapter 9 Outline Introduction Definitions and Basic Terminologies Representations of Graphs Graph Traversals Breadth first traversal Depth first traversal Applications Single source shortest path
Ashish Gupta, Data JUET, Guna
 Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
This is a set of practice questions for the final for CS16. The actual exam will consist of problems that are quite similar to those you have
 This is a set of practice questions for the final for CS16. The actual exam will consist of problems that are quite similar to those you have encountered on homeworks, the midterm, and on this practice
This is a set of practice questions for the final for CS16. The actual exam will consist of problems that are quite similar to those you have encountered on homeworks, the midterm, and on this practice
CS200: Graphs. Prichard Ch. 14 Rosen Ch. 10. CS200 - Graphs 1
 CS200: Graphs Prichard Ch. 14 Rosen Ch. 10 CS200 - Graphs 1 Graphs A collection of nodes and edges What can this represent? n A computer network n Abstraction of a map n Social network CS200 - Graphs 2
CS200: Graphs Prichard Ch. 14 Rosen Ch. 10 CS200 - Graphs 1 Graphs A collection of nodes and edges What can this represent? n A computer network n Abstraction of a map n Social network CS200 - Graphs 2
General Insert Operation
 General Insert Operation Inserting a new node before a node referenced by curr involves updating only adjacent links and does not affect the other elements in the sequence. General Insert Operation (continued)
General Insert Operation Inserting a new node before a node referenced by curr involves updating only adjacent links and does not affect the other elements in the sequence. General Insert Operation (continued)
Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis. Lecturer: Souad Alonazi
 Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis Lec(3) Stacks Lecturer: Souad Alonazi What is a stack? Stores a set of elements in a particular order Stack principle: LAST IN FIRST OUT = LIFO It means: the last element
Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis Lec(3) Stacks Lecturer: Souad Alonazi What is a stack? Stores a set of elements in a particular order Stack principle: LAST IN FIRST OUT = LIFO It means: the last element
CSE 101, Winter Discussion Section Week 1. January 8 - January 15
 CSE 101, Winter 2018 Discussion Section Week 1 January 8 - January 15 Important Annotations were added (post-lecture) to the tablet slides, to fill in a few gaps (Lecture 1) Look through Additional Resources
CSE 101, Winter 2018 Discussion Section Week 1 January 8 - January 15 Important Annotations were added (post-lecture) to the tablet slides, to fill in a few gaps (Lecture 1) Look through Additional Resources
CSED233: Data Structures (2018F) Lecture3: Arrays and Linked Lists
 (2018F) Lecture3: Arrays and Linked Lists Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Array Definition An array is a sequenced collection of variables all of the same type. Each variable, or cell, in an
(2018F) Lecture3: Arrays and Linked Lists Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Array Definition An array is a sequenced collection of variables all of the same type. Each variable, or cell, in an
Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms
 Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Data Structure is a way of collecting and organising data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an effective way. Data Structures
Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Data Structure is a way of collecting and organising data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an effective way. Data Structures
The combination of pointers, structs, and dynamic memory allocation allow for creation of data structures
 Data Structures in C C Programming and Software Tools N.C. State Department of Computer Science Data Structures in C The combination of pointers, structs, and dynamic memory allocation allow for creation
Data Structures in C C Programming and Software Tools N.C. State Department of Computer Science Data Structures in C The combination of pointers, structs, and dynamic memory allocation allow for creation
Directed Graph and Binary Trees
 and Dr. Nahid Sultana December 19, 2012 and Degrees Paths and Directed graphs are graphs in which the edges are one-way. This type of graphs are frequently more useful in various dynamic systems such as
and Dr. Nahid Sultana December 19, 2012 and Degrees Paths and Directed graphs are graphs in which the edges are one-way. This type of graphs are frequently more useful in various dynamic systems such as
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Abstract Data Types. Data Str. Client Prog. Add. Rem. Find. Show. 01/30/03 Lecture 7 1
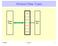 Abstract Data Types Add Client Prog Rem Find Data Str. Show 01/30/03 Lecture 7 1 Linear Lists It is an ordered collection of elements. Lists have items, size or length. Elements may have an index. Main
Abstract Data Types Add Client Prog Rem Find Data Str. Show 01/30/03 Lecture 7 1 Linear Lists It is an ordered collection of elements. Lists have items, size or length. Elements may have an index. Main
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II. Linked List. Li Xiong
 CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Linked List Li Xiong Roadmap Basic data structure Arrays Abstract data types Stacks Queues Implemented using resizing arrays Linked List Concept and implementations
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Linked List Li Xiong Roadmap Basic data structure Arrays Abstract data types Stacks Queues Implemented using resizing arrays Linked List Concept and implementations
Introduction to Stephe s Ada Library
 Introduction to Stephe s Ada Library Stephen Leake stephen_leake@acm.org Abstract Stephe s Ada Library (SAL) containers are designed to support the widest possible range of item and container types (limited/non-limited,
Introduction to Stephe s Ada Library Stephen Leake stephen_leake@acm.org Abstract Stephe s Ada Library (SAL) containers are designed to support the widest possible range of item and container types (limited/non-limited,
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Largest Online Community of VU Students
 WWW.VUPages.com http://forum.vupages.com WWW.VUTUBE.EDU.PK Largest Online Community of VU Students MIDTERM EXAMINATION SEMESTER FALL 2003 CS301-DATA STRUCTURE Total Marks:86 Duration: 60min Instructions
WWW.VUPages.com http://forum.vupages.com WWW.VUTUBE.EDU.PK Largest Online Community of VU Students MIDTERM EXAMINATION SEMESTER FALL 2003 CS301-DATA STRUCTURE Total Marks:86 Duration: 60min Instructions
UNIT III TREES. A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items.
 UNIT III TREES A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items. Tree: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that, there
UNIT III TREES A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items. Tree: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that, there
1. Stack Implementation Using 1D Array
 Lecture 5 Stacks 1 Lecture Content 1. Stack Implementation Using 1D Array 2. Stack Implementation Using Singly Linked List 3. Applications of Stack 3.1 Infix and Postfix Arithmetic Expressions 3.2 Evaluate
Lecture 5 Stacks 1 Lecture Content 1. Stack Implementation Using 1D Array 2. Stack Implementation Using Singly Linked List 3. Applications of Stack 3.1 Infix and Postfix Arithmetic Expressions 3.2 Evaluate
Count increments by 20 when I is even and decrements by 5 when I is odd.
 C11 Solutions 1. Count := 1; FOR I in 1.. 10 LOOP If I MOD 2 = 0 THEN FOR J in 1.. 10 LOOP Count:= Count + 2; END LOOP; ELSE FOR J in 1.. 5 LOOP Count := Count 1; END LOOP; END IF; END LOOP; Count = 76.
C11 Solutions 1. Count := 1; FOR I in 1.. 10 LOOP If I MOD 2 = 0 THEN FOR J in 1.. 10 LOOP Count:= Count + 2; END LOOP; ELSE FOR J in 1.. 5 LOOP Count := Count 1; END LOOP; END IF; END LOOP; Count = 76.
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS UNIT 1 - LINEAR DATASTRUCTURES 1. Write down the definition of data structures? A data structure is a mathematical or logical way of organizing data in the memory that consider
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS UNIT 1 - LINEAR DATASTRUCTURES 1. Write down the definition of data structures? A data structure is a mathematical or logical way of organizing data in the memory that consider
"apple" "grape" "grape" "grape" "apple"
 Test 1: CPS 100 Owen Astrachan and Dee Ramm February 21, 1997 Name: Honor code acknowledgment (signature) Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 TOTAL: value 10 pts. 9 pts. 21 pts.
Test 1: CPS 100 Owen Astrachan and Dee Ramm February 21, 1997 Name: Honor code acknowledgment (signature) Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 TOTAL: value 10 pts. 9 pts. 21 pts.
Linked Lists. Linked List vs Array vs Python List Singly Linked List Bag ADT Revisited Building Linked Lists
 Linked Lists Linked List vs Array vs Python List Singly Linked List Bag ADT Revisited Building Linked Lists Review Arrays Basic sequence container Provides easy and direct element access. Supported at
Linked Lists Linked List vs Array vs Python List Singly Linked List Bag ADT Revisited Building Linked Lists Review Arrays Basic sequence container Provides easy and direct element access. Supported at
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Tambaram, Chennai
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING III SEMESTER - R 2017 CS8381 DATA STRUCTURES LABORATORY LABORATORY MANUAL Name Register No Section
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Tambaram, Chennai 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING III SEMESTER - R 2017 CS8381 DATA STRUCTURES LABORATORY LABORATORY MANUAL Name Register No Section
S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis. Primitive Linear Non Linear
![S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis. Primitive Linear Non Linear S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis. Primitive Linear Non Linear](/thumbs/88/115506064.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) Explain different types of data structures with examples. [5] Ans.: Types of Data Structure : Data
S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) Explain different types of data structures with examples. [5] Ans.: Types of Data Structure : Data
CS S-20 Linked Lists III 1. We can then use the next pointer of the previous node to do removal (example on board)
 CS112-2012S-20 Linked Lists III 1 20-0: Linked List ious Practical Example: removeat(int index) remove( o) 20-1: removeat First need to get to node before the one we want to remove We can then use the
CS112-2012S-20 Linked Lists III 1 20-0: Linked List ious Practical Example: removeat(int index) remove( o) 20-1: removeat First need to get to node before the one we want to remove We can then use the
MATH 363 Final Wednesday, April 28. Final exam. You may use lemmas and theorems that were proven in class and on assignments unless stated otherwise.
 Final exam This is a closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Unless stated otherwise, justify all your steps. You may use lemmas and theorems that were proven in class and on assignments unless stated
Final exam This is a closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Unless stated otherwise, justify all your steps. You may use lemmas and theorems that were proven in class and on assignments unless stated
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture #9 Spring 2018
 CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture #9 Spring 2018 SINGLY LINKED LIST 3.1.3 Linked lists We will consider these for Singly linked lists Doubly linked lists Basic Singly Linked List class Node
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture #9 Spring 2018 SINGLY LINKED LIST 3.1.3 Linked lists We will consider these for Singly linked lists Doubly linked lists Basic Singly Linked List class Node
Objective Questions for Online Practical Exams under CBCS Scheme Subject: Data Structure-I (CS-113)
 Objective Questions for Online Practical Exams under CBCS Scheme Subject: Data Structure-I (CS-113) 1. The number of interchanges required to sort 5, 1, 6, 2 4 in ascending order using Bubble Sort (A)
Objective Questions for Online Practical Exams under CBCS Scheme Subject: Data Structure-I (CS-113) 1. The number of interchanges required to sort 5, 1, 6, 2 4 in ascending order using Bubble Sort (A)
Dynamic Data Structures
 Dynamic Data Structures We have seen that the STL containers vector, deque, list, set and map can grow and shrink dynamically. We now examine how some of these containers can be implemented in C++. To
Dynamic Data Structures We have seen that the STL containers vector, deque, list, set and map can grow and shrink dynamically. We now examine how some of these containers can be implemented in C++. To
The time and space are the two measure for efficiency of an algorithm.
 There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
CS 8391 DATA STRUCTURES
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK CS 8391 DATA STRUCTURES UNIT- I PART A 1. Define: data structure. A data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in the memory for
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK CS 8391 DATA STRUCTURES UNIT- I PART A 1. Define: data structure. A data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in the memory for
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013
 GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
Prelim 1. CS2110, October 2, 2014, 5:30 PM Extra Total Question TrueFalse Multiple Object Oriented
 Prelim 1 CS2110, October 2, 2014, 5:30 PM 1 2 3 4 5 Extra Total Question TrueFalse Multiple Object Oriented Recursion Lists Extra Credit Max 20 20 30 15 15 5 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and
Prelim 1 CS2110, October 2, 2014, 5:30 PM 1 2 3 4 5 Extra Total Question TrueFalse Multiple Object Oriented Recursion Lists Extra Credit Max 20 20 30 15 15 5 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and
Linked Lists and other Dynamic Data Structures
 Linked Lists and other Dynamic Data Structures Arrays Fixed in size Allocated in advance within a contiguous memory block Look-up is fast Resizing and Deleting is hard (reallocate and copy) Dynamic Data
Linked Lists and other Dynamic Data Structures Arrays Fixed in size Allocated in advance within a contiguous memory block Look-up is fast Resizing and Deleting is hard (reallocate and copy) Dynamic Data
CS 314 Midterm 2 Spring 2013
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 2 Spring 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Donghyuk Lixun Padmini Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. The
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 2 Spring 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Donghyuk Lixun Padmini Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. The
Fundamentals of Data Structure
 Fundamentals of Data Structure Set-1 1. Which if the following is/are the levels of implementation of data structure A) Abstract level B) Application level C) Implementation level D) All of the above 2.
Fundamentals of Data Structure Set-1 1. Which if the following is/are the levels of implementation of data structure A) Abstract level B) Application level C) Implementation level D) All of the above 2.
Linked Lists Structures
 Linked Lists Structures 1. Motivation... 2 2. Declaration of a node... 3 2.1. Operations on pointers:... 4 2.2. Disposition of a node... 5 2.3. Singly Linked Lists... 5 3. One-way linked lists... 6 3.1.
Linked Lists Structures 1. Motivation... 2 2. Declaration of a node... 3 2.1. Operations on pointers:... 4 2.2. Disposition of a node... 5 2.3. Singly Linked Lists... 5 3. One-way linked lists... 6 3.1.
1 Digraphs. Definition 1
 1 Digraphs Definition 1 Adigraphordirected graphgisatriplecomprisedofavertex set V(G), edge set E(G), and a function assigning each edge an ordered pair of vertices (tail, head); these vertices together
1 Digraphs Definition 1 Adigraphordirected graphgisatriplecomprisedofavertex set V(G), edge set E(G), and a function assigning each edge an ordered pair of vertices (tail, head); these vertices together
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2017
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
S.Y. B.Sc. (IT) : Sem. III. Data Structures
 S.Y. B.Sc. (IT) : Sem. III Data Structures Time : 2½ Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 75 Q.1Attempt the following (any THREE) [15] Q.1(a) What is an algorithm? Write down characteristics of
S.Y. B.Sc. (IT) : Sem. III Data Structures Time : 2½ Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 75 Q.1Attempt the following (any THREE) [15] Q.1(a) What is an algorithm? Write down characteristics of
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Graphs. The ultimate data structure. graphs 1
 Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
CSE 143 SAMPLE MIDTERM
 CSE 143 SAMPLE MIDTERM 1. (5 points) In some methods, you wrote code to check if a certain precondition was held. If the precondition did not hold, then you threw an exception. This leads to robust code
CSE 143 SAMPLE MIDTERM 1. (5 points) In some methods, you wrote code to check if a certain precondition was held. If the precondition did not hold, then you threw an exception. This leads to robust code
Chapter 6 Single-dimensional Arrays
 Chapter 6 Single-dimensional s 1. See the section "Declaring and Creating s." 2. You access an array using its index. 3. No memory is allocated when an array is declared. The memory is allocated when creating
Chapter 6 Single-dimensional s 1. See the section "Declaring and Creating s." 2. You access an array using its index. 3. No memory is allocated when an array is declared. The memory is allocated when creating
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 LECTURE 5 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 4... Linked Lists Singly Linked Lists Doubly Linked Lists Today Algorithmic problems using Linked Lists
LECTURE 5 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 4... Linked Lists Singly Linked Lists Doubly Linked Lists Today Algorithmic problems using Linked Lists
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure using C Model wer Subject Code: 22317 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given
WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure using C Model wer Subject Code: 22317 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given
FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE
 TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours (Maximum marks: 100)
TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours (Maximum marks: 100)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Abstract Data Types. Data Str. Client Prog. Add. Rem. Find. Show. 01/22/04 Lecture 4 1
 Abstract Data Types Add Client Prog Rem Find Data Str. Show 01/22/04 Lecture 4 1 Containers Powerful tool for programming data structures Provides a library of container classes to hold your objects 2
Abstract Data Types Add Client Prog Rem Find Data Str. Show 01/22/04 Lecture 4 1 Containers Powerful tool for programming data structures Provides a library of container classes to hold your objects 2
Spring 2008 Data Structures (CS301) LAB
 Spring 2008 Data Structures (CS301) LAB Objectives The objectives of this LAB are, o Enabling students to implement Singly Linked List practically using c++ and adding more functionality in it. o Enabling
Spring 2008 Data Structures (CS301) LAB Objectives The objectives of this LAB are, o Enabling students to implement Singly Linked List practically using c++ and adding more functionality in it. o Enabling
12 Abstract Data Types
 12 Abstract Data Types 12.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define the concept of an abstract data type (ADT). Define
12 Abstract Data Types 12.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define the concept of an abstract data type (ADT). Define
CS171 Midterm Exam. October 29, Name:
 CS171 Midterm Exam October 29, 2012 Name: You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed-book and closed-notes exam. You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. Read each problem carefully, and
CS171 Midterm Exam October 29, 2012 Name: You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed-book and closed-notes exam. You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. Read each problem carefully, and
DATA STRUCTURE : A MCQ QUESTION SET Code : RBMCQ0305
 Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
C++ - Lesson 2 This is a function prototype. a' is a function that takes an integer array argument and returns an integer pointer.
 C++ - Lesson 2 1. Explain the following declarations: a) int *a(int a[]); This is a function prototype. 'a' is a function that takes an integer array argument and returns an integer pointer. b) const char
C++ - Lesson 2 1. Explain the following declarations: a) int *a(int a[]); This is a function prototype. 'a' is a function that takes an integer array argument and returns an integer pointer. b) const char
LECTURE 03 LINKED LIST
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 03 LINKED LIST IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD LINKED LISTS DEFINITION A linked list is a data structure where each object is stored in
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 03 LINKED LIST IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD LINKED LISTS DEFINITION A linked list is a data structure where each object is stored in
CT11 (ALCCS) DATA STRUCTURE THROUGH C JUN 2015
 Solutions Q.1 a. What is a pointer? Explain how it is declared and initialized. (4) Different from other normal variables which can store values, pointers are special variables that can hold the address
Solutions Q.1 a. What is a pointer? Explain how it is declared and initialized. (4) Different from other normal variables which can store values, pointers are special variables that can hold the address
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
LINKED IMPLEMENTATION OF LIST
 LINKED IMPLEMENTATION OF LIST Mohd. Saeed 1, Mayank Gulati 2 1,2 Department of Information Technology, Shri Ramdeo Baba K.N. Engineering College, Nagpur (India) ABSTRACT This paper address about the link
LINKED IMPLEMENTATION OF LIST Mohd. Saeed 1, Mayank Gulati 2 1,2 Department of Information Technology, Shri Ramdeo Baba K.N. Engineering College, Nagpur (India) ABSTRACT This paper address about the link
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma studies Unit 4
 Pointer A pointer is a variable that contains address or location of another variable. Pointer is a derived data type in C. Pointers contain memory address as their values, so they can also be used to
Pointer A pointer is a variable that contains address or location of another variable. Pointer is a derived data type in C. Pointers contain memory address as their values, so they can also be used to
Information Science 2
 Information Science 2 - Applica(ons of Basic ata Structures- Week 03 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Agenda l Week 02 review l Introduction to Graph Theory - Basic
Information Science 2 - Applica(ons of Basic ata Structures- Week 03 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Agenda l Week 02 review l Introduction to Graph Theory - Basic
Priority Queues. 04/10/03 Lecture 22 1
 Priority Queues It is a variant of queues Each item has an associated priority value. When inserting an item in the queue, the priority value is also provided for it. The data structure provides a method
Priority Queues It is a variant of queues Each item has an associated priority value. When inserting an item in the queue, the priority value is also provided for it. The data structure provides a method
CMSC 341 Lecture 7 Lists
 CMSC 341 Lecture 7 Lists Today s Topics Linked Lists vs Arrays Nodes Using Linked Lists Supporting Actors (member variables) Overview Creation Traversal Deletion UMBC CMSC 341 Lists 2 Linked Lists vs Arrays
CMSC 341 Lecture 7 Lists Today s Topics Linked Lists vs Arrays Nodes Using Linked Lists Supporting Actors (member variables) Overview Creation Traversal Deletion UMBC CMSC 341 Lists 2 Linked Lists vs Arrays
Linear Structures. Linear Structure. Implementations. Array details. List details. Operations 4/18/2013
 Linear Structure Linear Structures Chapter 4 CPTR 318 Every non-empty linear structure has A unique element called first A unique element called last Every element except last has a unique successor Every
Linear Structure Linear Structures Chapter 4 CPTR 318 Every non-empty linear structure has A unique element called first A unique element called last Every element except last has a unique successor Every
