Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms
|
|
|
- Vivien Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Data Structure is a way of collecting and organising data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an effective way. Data Structures is about rendering data elements in terms of some relationship, for better organization and storage. For example, we have some data which has, player's name "Virat" and age 26. Here "Virat" is of String data type and 26 is of integer data type. We can organize this data as a record like Player record, which will have both player's name and age in it. Now we can collect and store player's records in a file or database as a data structure. For example: "Dhoni" 30, "Gambhir" 31, "Sehwag" 33 If you are aware of Object Oriented programming concepts, then a class also does the same thing, it collects different type of data under one single entity. The only difference being, data structures provides for techniques to access and manipulate data efficiently. In simple language, Data Structures are structures programmed to store ordered data, so that various operations can be performed on it easily. It represents the knowledge of data to be organized in memory. It should be designed and implemented in such a way that it reduces the complexity and increases the efficiency.
2 Basic types of Data Structures As we have discussed above, anything that can store data can be called as a data structure, hence Integer, Float, Boolean, Char etc, all are data structures. They are known as Primitive Data Structures. Then we also have some complex Data Structures, which are used to store large and connected data. Some example of Abstract Data Structure are : Linked List Tree Graph Stack, Queue etc. All these data structures allow us to perform different operations on data. We select these data structures based on which type of operation is required. We will look into these data structures in more details in our later lessons.
3 The data structures can also be classified on the basis of the following characteristics: Characterstic Description Linear In Linear data structures,the data items are arranged in a linear sequence. Example: Array Non-Linear In Non-Linear data structures,the data items are not in sequence. Example: Tree, Graph Homogeneous In homogeneous data structures,all the elements are of same type. Example: Array Non- Homogeneous In Non-Homogeneous data structure, the elements may or may not be of the same type. Example: Structures Static Static data structures are those whose sizes and structures associated memory locations are fixed, at compile time. Example: Array Dynamic Dynamic structures are those which expands or shrinks depending upon the program need and its execution. Also, their associated memory locations changes. Example: Linked List created using pointers What is an Algorithm?
4 An algorithm is a finite set of instructions or logic, written in order, to accomplish a certain predefined task. Algorithm is not the complete code or program, it is just the core logic(solution) of a problem, which can be expressed either as an informal high level description as pseudocode or using a flowchart. Every Algorithm must satisfy the following properties: 1. Input- There should be 0 or more inputs supplied externally to the algorithm. 2. Output- There should be atleast 1 output obtained. 3. Definiteness- Every step of the algorithm should be clear and well defined. 4. Finiteness- The algorithm should have finite number of steps. 1. Correctness- Every step of the algorithm must generate a correct output. An algorithm is said to be efficient and fast, if it takes less time to execute and consumes less memory space. The performance of an algorithm is measured on the basis of following properties : 1. Time Complexity 2. Space Complexity Space Complexity Its the amount of memory space required by the algorithm, during the course of its execution. Space complexity must be taken seriously for multiuser systems and in situations where limited memory is available.
5 An algorithm generally requires space for following components : Instruction Space: Its the space required to store the executable version of the program. This space is fixed, but varies depending upon the number of lines of code in the program. Data Space: Its the space required to store all the constants and variables(including temporary variables) value. Data Structures and Algorithms - Arrays Array is a container which can hold a fix number of items and these items should be of the same type. Most of the data structures make use of arrays to implement their algorithms. Following are the important terms to understand the concept of Array. Element Each item stored in an array is called an element. Index Each location of an element in an array has a numerical index, which is used to identify the element. Array Representation Arrays can be declared in various ways in different languages. For illustration, let's take C array declaration.
6 As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered. Index starts with 0. Array length is 10 which means it can store 10 elements. Each element can be accessed via its index. For example, we can fetch an element at index 6 as 9. Basic Operations Following are the basic operations supported by an array. Traverse print all the array elements one by one. Insertion Adds an element at the given index. Deletion Deletes an element at the given index. Search Searches an element using the given index or by the value. Update Updates an element at the given index. In C, when an array is initialized with size, then it assigns defaults values to its elements in following order. Data Type Default Value bool false char 0 int 0
7 float 0.0 double 0.0f void wchar_t 0 Insertion Operation Insert operation is to insert one or more data elements into an array. Based on the requirement, a new element can be added at the beginning, end, or any given index of array. Here, we see a practical implementation of insertion operation, where we add data at the end of the array Algorithm Let Array be a linear unordered array of MAX elements. Example Result Let LA be a Linear Array (unordered) with N elements and K is a positive integer such that K<=N. Following is the algorithm where ITEM is inserted into the K th position of LA 1. Start 2. Set J = N 3. Set N = N+1 4. Repeat steps 5 and 6 while J >= K 5. Set LA[J+1] = LA[J] 6. Set J = J-1
8 7. Set LA[K] = ITEM 8. Stop Example Following is the implementation of the above algorithm #include <stdio.h> main() { int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8}; int item = 10, k = 3, n = 5; int i = 0, j = n; printf("the original array elements are :\n"); for(i = 0; i<n; i++) { } printf("la[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]); n = n + 1; while( j >= k) { LA[j+1] = LA[j]; j = j - 1;
9 } LA[k] = item; printf("the array elements after insertion :\n"); for(i = 0; i<n; i++) { printf("la[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]); When we compile and execute the above program, it produces the following result Output The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8 The array elements after insertion : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 10 LA[4] = 7 LA[5] = 8 For other variations of array insertion operation click here
10 Deletion Operation Deletion refers to removing an existing element from the array and reorganizing all elements of an array. Algorithm Consider LA is a linear array with N elements and K is a positive integer such that K<=N. Following is the algorithm to delete an element available at the K th position of LA. 1. Start 2. Set J = K 3. Repeat steps 4 and 5 while J < N 4. Set LA[J] = LA[J + 1] 5. Set J = J+1 6. Set N = N-1 7. Stop Example Following is the implementation of the above algorithm #include <stdio.h> main() { int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8}; int k = 3, n = 5; int i, j; printf("the original array elements are :\n");
11 for(i = 0; i<n; i++) { } printf("la[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]); j = k; while( j < n) { LA[j-1] = LA[j]; j = j + 1; } n = n -1; printf("the array elements after deletion :\n"); for(i = 0; i<n; i++) { } printf("la[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]); } When we compile and execute the above program, it produces the following result Output
12 The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8 The array elements after deletion : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 7 LA[3] = 8 Search Operation You can perform a search for an array element based on its value or its index. Algorithm Consider LA is a linear array with N elements and K is a positive integer such that K<=N. Following is the algorithm to find an element with a value of ITEM using sequential search. 1. Start 2. Set J = 0 3. Repeat steps 4 and 5 while J < N 4. IF LA[J] is equal ITEM THEN GOTO STEP 6 5. Set J = J PRINT J, ITEM 7. Stop Example Following is the implementation of the above algorithm #include <stdio.h>
13 main() { int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8}; int item = 5, n = 5; int i = 0, j = 0; printf("the original array elements are :\n"); for(i = 0; i<n; i++) { } printf("la[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]); while( j < n){ if( LA[j] == item ) { break; } } j = j + 1; } printf("found element %d at position %d\n", item, j+1);
14 When we compile and execute the above program, it produces the following result Output The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8 Found element 5 at position 3 Data Structure and Algorithms - Linked List A linked list is a sequence of data structures, which are connected together via links. Linked List is a sequence of links which contains items. Each link contains a connection to another link. Linked list is the second mostused data structure after array. Following are the important terms to understand the concept of Linked List. Link Each link of a linked list can store a data called an element. Next Each link of a linked list contains a link to the next link called Next. LinkedList A Linked List contains the connection link to the first link called First. Linked List Representation
15 Linked list can be visualized as a chain of nodes, where every node points to the next node. As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered. Linked List contains a link element called first. Each link carries a data field(s) and a link field called next. Each link is linked with its next link using its next link. Last link carries a link as null to mark the end of the list. Types of Linked List Following are the various types of linked list. Simple Linked List Item navigation is forward only. Doubly Linked List Items can be navigated forward and backward. Circular Linked List Last item contains link of the first element as next and the first element has a link to the last element as previous. Basic Operations Following are the basic operations supported by a list. Insertion Adds an element at the beginning of the list. Deletion Deletes an element at the beginning of the list.
16 Display Displays the complete list. Search Searches an element using the given key. Delete Deletes an element using the given key. Insertion Operation Adding a new node in linked list is a more than one step activity. We shall learn this with diagrams here. First, create a node using the same structure and find the location where it has to be inserted. Imagine that we are inserting a node B (NewNode), between A (LeftNode) and C (RightNode). Then point B.next to C NewNode.next > RightNode; It should look like this Now, the next node at the left should point to the new node. LeftNode.next > NewNode;
17 This will put the new node in the middle of the two. The new list should look like this Similar steps should be taken if the node is being inserted at the beginning of the list. While inserting it at the end, the second last node of the list should point to the new node and the new node will point to NULL. Deletion Operation Deletion is also a more than one step process. We shall learn with pictorial representation. First, locate the target node to be removed, by using searching algorithms. The left (previous) node of the target node now should point to the next node of the target node LeftNode.next > TargetNode.next;
18 This will remove the link that was pointing to the target node. Now, using the following code, we will remove what the target node is pointing at. TargetNode.next > NULL; We need to use the deleted node. We can keep that in memory otherwise we can simply deallocate memory and wipe off the target node completely. Reverse Operation This operation is a thorough one. We need to make the last node to be pointed by the head node and reverse the whole linked list.
19 First, we traverse to the end of the list. It should be pointing to NULL. Now, we shall make it point to its previous node We have to make sure that the last node is not the lost node. So we'll have some temp node, which looks like the head node pointing to the last node. Now, we shall make all left side nodes point to their previous nodes one by one. Except the node (first node) pointed by the head node, all nodes should point to their predecessor, making them their new successor. The first node will point to NULL. We'll make the head node point to the new first node by using the temp node. The linked list is now reversed. To see linked list implementation in C programming language, please click here.
20 Data Structure and Algorithms - Queue Queue is an abstract data structure, somewhat similar to Stacks. Unlike stacks, a queue is open at both its ends. One end is always used to insert data (enqueue) and the other is used to remove data (dequeue). Queue follows First-In-First-Out methodology, i.e., the data item stored first will be accessed first. A real-world example of queue can be a single-lane one-way road, where the vehicle enters first, exits first. More real-world examples can be seen as queues at the ticket windows and bus-stops. Queue Representation As we now understand that in queue, we access both ends for different reasons. The following diagram given below tries to explain queue representation as data structure
21 As in stacks, a queue can also be implemented using Arrays, Linkedlists, Pointers and Structures. For the sake of simplicity, we shall implement queues using one-dimensional array. Basic Operations Queue operations may involve initializing or defining the queue, utilizing it, and then completely erasing it from the memory. Here we shall try to understand the basic operations associated with queues enqueue() add (store) an item to the queue. dequeue() remove (access) an item from the queue. Few more functions are required to make the above-mentioned queue operation efficient. These are peek() Gets the element at the front of the queue without removing it. isfull() Checks if the queue is full. isempty() Checks if the queue is empty. In queue, we always dequeue (or access) data, pointed by front pointer and while enqueing (or storing) data in the queue we take help of rear pointer. Let's first learn about supportive functions of a queue peek() This function helps to see the data at the front of the queue. The algorithm of peek() function is as follows Algorithm begin procedure peek
22 return queue[front] end procedure Implementation of peek() function in C programming language Example int peek() { return queue[front]; } isfull() As we are using single dimension array to implement queue, we just check for the rear pointer to reach at MAXSIZE to determine that the queue is full. In case we maintain the queue in a circular linked-list, the algorithm will differ. Algorithm of isfull() function Algorithm begin procedure isfull if rear equals to MAXSIZE return true else return false endif
23 end procedure Implementation of isfull() function in C programming language Example bool isfull() { if(rear == MAXSIZE - 1) return true; else return false; } isempty() Algorithm of isempty() function Algorithm begin procedure isempty if front is less than MIN OR front is greater than rear return true else return false endif end procedure
24 If the value of front is less than MIN or 0, it tells that the queue is not yet initialized, hence empty. Here's the C programming code Example bool isempty() { if(front < 0 front > rear) return true; else return false; } Enqueue Operation Queues maintain two data pointers, front and rear. Therefore, its operations are comparatively difficult to implement than that of stacks. The following steps should be taken to enqueue (insert) data into a queue Step 1 Check if the queue is full. Step 2 If the queue is full, produce overflow error and exit. Step 3 If the queue is not full, increment rear pointer to point the next empty space. Step 4 Add data element to the queue location, where the rear is pointing. Step 5 return success.
25 Sometimes, we also check to see if a queue is initialized or not, to handle any unforeseen situations. Algorithm for enqueue operation procedure enqueue(data) if queue is full return overflow endif rear rear + 1 queue[rear] data return true
26 end procedure Implementation of enqueue() in C programming language Example int enqueue(int data) if(isfull()) return 0; rear = rear + 1; queue[rear] = data; return 1; end procedure Dequeue Operation Accessing data from the queue is a process of two tasks access the data where front is pointing and remove the data after access. The following steps are taken to perform dequeue operation Step 1 Check if the queue is empty. Step 2 If the queue is empty, produce underflow error and exit. Step 3 If the queue is not empty, access the data where front is pointing.
27 Step 4 Increment front pointer to point to the next available data element. Step 5 Return success. Algorithm for dequeue operation procedure dequeue if queue is empty return underflow end if data = queue[front] front front + 1 return true
28 end procedure Implementation of dequeue() in C programming language Example int dequeue() { if(isempty()) return 0; int data = queue[front]; front = front + 1; } return data; For a complete Queue program in C programming language, please click here. Previous Page Print Next Page Advertisements
Queue: Queue Representation: Basic Operations:
 Queue: Queue is an abstract data structure, somewhat similar to Stacks. Unlike stacks, a queue is open at both its ends. One end is always used to insert data (enqueue) and the other is used to remove
Queue: Queue is an abstract data structure, somewhat similar to Stacks. Unlike stacks, a queue is open at both its ends. One end is always used to insert data (enqueue) and the other is used to remove
Lecture Data Structure Stack
 Lecture Data Structure Stack 1.A stack :-is an abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
Lecture Data Structure Stack 1.A stack :-is an abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
UNIT-2 Stack & Queue
 UNIT-2 Stack & Queue 59 13. Stack A stack is an Abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
UNIT-2 Stack & Queue 59 13. Stack A stack is an Abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
Data Structures & Algorithms Quick Guide. Data Structures & Algorithms Overview
 Data Structures & Algorithms Quick Guide https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/dsa_quick_guide.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Data Structures & Algorithms Overview Data Structure
Data Structures & Algorithms Quick Guide https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/dsa_quick_guide.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Data Structures & Algorithms Overview Data Structure
UNIT-1. Chapter 1(Introduction and overview) 1. Asymptotic Notations 2. One Dimensional array 3. Multi Dimensional array 4. Pointer arrays.
 UNIT-1 Chapter 1(Introduction and overview) 1. Asymptotic Notations 2. One Dimensional array 3. Multi Dimensional array 4. Pointer arrays. Chapter 2 (Linked lists) 1. Definition 2. Single linked list 3.
UNIT-1 Chapter 1(Introduction and overview) 1. Asymptotic Notations 2. One Dimensional array 3. Multi Dimensional array 4. Pointer arrays. Chapter 2 (Linked lists) 1. Definition 2. Single linked list 3.
DATA STRUCTURES USING C
 DATA STRUCTURES USING C DATA STRUCTURES USING C LECTURE NOTES Prepared by Dr. Subasish Mohapatra Department of Computer Science and Application College of Engineering and Technology, Bhubaneswar Biju Patnaik
DATA STRUCTURES USING C DATA STRUCTURES USING C LECTURE NOTES Prepared by Dr. Subasish Mohapatra Department of Computer Science and Application College of Engineering and Technology, Bhubaneswar Biju Patnaik
Linked List Tree Graph. Stack, Queue etc.
 Introduction to Data Structures Data Structure is a way of collecting and organising data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an effective way. Data Structures is about rendering
Introduction to Data Structures Data Structure is a way of collecting and organising data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an effective way. Data Structures is about rendering
A. Year / Module Semester Subject Topic 2016 / V 2 PCD Pointers, Preprocessors, DS
 Syllabus: Pointers and Preprocessors: Pointers and address, pointers and functions (call by reference) arguments, pointers and arrays, address arithmetic, character pointer and functions, pointers to pointer,initialization
Syllabus: Pointers and Preprocessors: Pointers and address, pointers and functions (call by reference) arguments, pointers and arrays, address arithmetic, character pointer and functions, pointers to pointer,initialization
Linked List. April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1
 Linked List April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Introduction head A linked list is a data structure which can change during execution. Successive elements are connected by pointers. Last element
Linked List April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Introduction head A linked list is a data structure which can change during execution. Successive elements are connected by pointers. Last element
After completing this tutorial you will be at intermediate level of expertise from where you can take yourself to higher level of expertise.
 About the Tutorial Data Structures are the programmatic way of storing data so that data can be used efficiently. Almost every enterprise application uses various types of data structures in one or the
About the Tutorial Data Structures are the programmatic way of storing data so that data can be used efficiently. Almost every enterprise application uses various types of data structures in one or the
 CS6202 - PROGRAMMING & DATA STRUCTURES I Unit IV Part - A 1. Define Stack. A stack is an ordered list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top. It is an abstract data type
CS6202 - PROGRAMMING & DATA STRUCTURES I Unit IV Part - A 1. Define Stack. A stack is an ordered list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top. It is an abstract data type
Abstract Data Type: Stack
 Abstract Data Type: Stack Stack operations may involve initializing the stack, using it and then de-initializing it. Apart from these basic stuffs, a stack is used for the following two primary operations
Abstract Data Type: Stack Stack operations may involve initializing the stack, using it and then de-initializing it. Apart from these basic stuffs, a stack is used for the following two primary operations
DEEPIKA KAMBOJ UNIT 2. What is Stack?
 What is Stack? UNIT 2 Stack is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner. You must have seen a pile of plates where one plate is placed on top of another. Now, when you
What is Stack? UNIT 2 Stack is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner. You must have seen a pile of plates where one plate is placed on top of another. Now, when you
LIFO : Last In First Out
 Introduction Stack is an ordered list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top. Stack is a data structure that is particularly useful in applications involving reversing.
Introduction Stack is an ordered list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top. Stack is a data structure that is particularly useful in applications involving reversing.
CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Linked Queues
 CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Linked Queues Professor Henry Carter Spring 2018 Recap A queue simulates a waiting line, where objects are removed in the same order they are added The primary
CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Linked Queues Professor Henry Carter Spring 2018 Recap A queue simulates a waiting line, where objects are removed in the same order they are added The primary
1 P age DS & OOPS / UNIT II
 UNIT II Stacks: Definition operations - applications of stack. Queues: Definition - operations Priority queues - De que Applications of queue. Linked List: Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Circular
UNIT II Stacks: Definition operations - applications of stack. Queues: Definition - operations Priority queues - De que Applications of queue. Linked List: Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Circular
The time and space are the two measure for efficiency of an algorithm.
 There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Queues ArrayQueue Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Version of March 10, 2014 Abstract These lecture notes are meant to be looked
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Queues ArrayQueue Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Version of March 10, 2014 Abstract These lecture notes are meant to be looked
DATA STRUCUTRES. A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.
 DATA STRUCUTRES A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. An algorithm, which is a finite sequence of instructions, each of which
DATA STRUCUTRES A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. An algorithm, which is a finite sequence of instructions, each of which
COMP 213 Advanced Object-oriented Programming Lecture 8 The Queue ADT (cont.)
 COMP 213 Advanced Object-oriented Programming Lecture 8 The Queue ADT (cont.) Recall: The Queue ADT A data structure in which elements enter at one end and are removed from the opposite end is called a
COMP 213 Advanced Object-oriented Programming Lecture 8 The Queue ADT (cont.) Recall: The Queue ADT A data structure in which elements enter at one end and are removed from the opposite end is called a
Stack and Queue. Stack:
 Stack and Queue Stack: Abstract Data Type A stack is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in first-out (LIFO) principle. In the pushdown stacks only two operations
Stack and Queue Stack: Abstract Data Type A stack is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in first-out (LIFO) principle. In the pushdown stacks only two operations
FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE
 TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours (Maximum marks: 100)
TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours (Maximum marks: 100)
1. Introduction. Lecture Content
 Lecture 6 Queues 1 Lecture Content 1. Introduction 2. Queue Implementation Using Array 3. Queue Implementation Using Singly Linked List 4. Priority Queue 5. Applications of Queue 2 1. Introduction A queue
Lecture 6 Queues 1 Lecture Content 1. Introduction 2. Queue Implementation Using Array 3. Queue Implementation Using Singly Linked List 4. Priority Queue 5. Applications of Queue 2 1. Introduction A queue
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Model wer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in
WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Model wer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in
MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI KUALA LUMPUR
 STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
CMSC 341 Lecture 6 Templates, Stacks & Queues. Based on slides by Shawn Lupoli & Katherine Gibson at UMBC
 CMSC 341 Lecture 6 Templates, Stacks & Queues Based on slides by Shawn Lupoli & Katherine Gibson at UMBC Today s Topics Data types in C++ Overloading functions Templates How to implement them Possible
CMSC 341 Lecture 6 Templates, Stacks & Queues Based on slides by Shawn Lupoli & Katherine Gibson at UMBC Today s Topics Data types in C++ Overloading functions Templates How to implement them Possible
Data Structure Series
 Data Structure Series This series is actually something I started back when I was part of the Sweet.Oblivion staff, but then some things happened and I was no longer able to complete it. So now, after
Data Structure Series This series is actually something I started back when I was part of the Sweet.Oblivion staff, but then some things happened and I was no longer able to complete it. So now, after
That means circular linked list is similar to the single linked list except that the last node points to the first node in the list.
 Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Circular Linked Lists and it operations Introduction: Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link
Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Circular Linked Lists and it operations Introduction: Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link
ADVANCED DATA STRUCTURES USING C++ ( MT-CSE-110 )
 ADVANCED DATA STRUCTURES USING C++ ( MT-CSE-110 ) Unit - 2 By: Gurpreet Singh Dean Academics & H.O.D. (C.S.E. / I.T.) Yamuna Institute of Engineering & Technology, Gadholi What is a Stack? A stack is a
ADVANCED DATA STRUCTURES USING C++ ( MT-CSE-110 ) Unit - 2 By: Gurpreet Singh Dean Academics & H.O.D. (C.S.E. / I.T.) Yamuna Institute of Engineering & Technology, Gadholi What is a Stack? A stack is a
CSEN 301 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CSEN 301 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 5: Queues: Implementation and usage Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher slim.abdennadher@guc.edu.eg German University Cairo, Department of Media Engineering and Technology
CSEN 301 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 5: Queues: Implementation and usage Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher slim.abdennadher@guc.edu.eg German University Cairo, Department of Media Engineering and Technology
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma studies Unit 4
 Pointer A pointer is a variable that contains address or location of another variable. Pointer is a derived data type in C. Pointers contain memory address as their values, so they can also be used to
Pointer A pointer is a variable that contains address or location of another variable. Pointer is a derived data type in C. Pointers contain memory address as their values, so they can also be used to
Solution: The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix to postfix conversion.
 1. What is the full form of LIFO? The full form of LIFO is Last In First Out. 2. Give some examples for stack application. The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix
1. What is the full form of LIFO? The full form of LIFO is Last In First Out. 2. Give some examples for stack application. The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix
Queues. CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms. Topic 5
 CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 5 Queues Implementations of the Queue ADT Queue specification Queue interface Block (array) representations of queues Recursive (linked) representations of
CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 5 Queues Implementations of the Queue ADT Queue specification Queue interface Block (array) representations of queues Recursive (linked) representations of
Queues. October 20, 2017 Hassan Khosravi / Geoffrey Tien 1
 Queues October 20, 2017 Hassan Khosravi / Geoffrey Tien 1 Queue ADT Queue ADT should support at least the first two operations: enqueue insert an item to the back of the queue dequeue remove an item from
Queues October 20, 2017 Hassan Khosravi / Geoffrey Tien 1 Queue ADT Queue ADT should support at least the first two operations: enqueue insert an item to the back of the queue dequeue remove an item from
Programming. Lists, Stacks, Queues
 Programming Lists, Stacks, Queues Summary Linked lists Create and insert elements Iterate over all elements of the list Remove elements Doubly Linked Lists Circular Linked Lists Stacks Operations and implementation
Programming Lists, Stacks, Queues Summary Linked lists Create and insert elements Iterate over all elements of the list Remove elements Doubly Linked Lists Circular Linked Lists Stacks Operations and implementation
Insert. SEMCOM Page 1 of 11
 CHARUTAR VIDYA MANDAL S SEMCOM Vallabh Vidyanagar Faculty Name: Ami D. Trivedi Class: FYBCA Subject: US02CBCA01 (Advanced C Programming and Introduction to Data Structures) *UNIT 4 (Some More Data structures
CHARUTAR VIDYA MANDAL S SEMCOM Vallabh Vidyanagar Faculty Name: Ami D. Trivedi Class: FYBCA Subject: US02CBCA01 (Advanced C Programming and Introduction to Data Structures) *UNIT 4 (Some More Data structures
Ashish Gupta, Data JUET, Guna
 Introduction In general, Queue is line of person waiting for their turn at some service counter like ticket window at cinema hall, at bus stand or at railway station etc. The person who come first, he/she
Introduction In general, Queue is line of person waiting for their turn at some service counter like ticket window at cinema hall, at bus stand or at railway station etc. The person who come first, he/she
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today Introduction to Linked Lists Stacks and Queues using Linked Lists Next Time Iterative Algorithms on Linked Lists Reading:
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today Introduction to Linked Lists Stacks and Queues using Linked Lists Next Time Iterative Algorithms on Linked Lists Reading:
Queues. Lesson 4. CS 32: Data Structures Dept. of Computer Science
 Queues Lesson 4 Outline What is a queue? Straight queue Circular Queue Sequential Implementation Linked Implementation Application: Topological sort Deques Final Notes Outline What is a queue? Straight
Queues Lesson 4 Outline What is a queue? Straight queue Circular Queue Sequential Implementation Linked Implementation Application: Topological sort Deques Final Notes Outline What is a queue? Straight
Linked List in Data Structure. By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra
 Linked List in Data Structure By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra Linked List Like arrays, Linked List is a linear data
Linked List in Data Structure By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra Linked List Like arrays, Linked List is a linear data
MODULE 5: Pointers, Preprocessor Directives and Data Structures
 MODULE 5: Pointers, Preprocessor Directives and Data Structures 1. What is pointer? Explain with an example program. Solution: Pointer is a variable which contains the address of another variable. Two
MODULE 5: Pointers, Preprocessor Directives and Data Structures 1. What is pointer? Explain with an example program. Solution: Pointer is a variable which contains the address of another variable. Two
Graphs: Graph Data Structure:
 Graphs: A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the links
Graphs: A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the links
CMSC 341 Lecture 6 STL, Stacks, & Queues. Based on slides by Lupoli, Dixon & Gibson at UMBC
 CMSC 341 Lecture 6 STL, Stacks, & Queues Based on slides by Lupoli, Dixon & Gibson at UMBC Templates 2 Common Uses for Templates Some common algorithms that easily lend themselves to templates: Swap what
CMSC 341 Lecture 6 STL, Stacks, & Queues Based on slides by Lupoli, Dixon & Gibson at UMBC Templates 2 Common Uses for Templates Some common algorithms that easily lend themselves to templates: Swap what
CHARUTAR VIDYA MANDAL S SEMCOM Vallabh Vidyanagar
 CHARUTAR VIDYA MANDAL S SEMCOM Vallabh Vidyanagar Faculty Name: Ami D. Trivedi Class: FYBCA Subject: US02CBCA01 (Advanced C Programming and Introduction to Data Structures) *UNIT 3 (Introduction to Data
CHARUTAR VIDYA MANDAL S SEMCOM Vallabh Vidyanagar Faculty Name: Ami D. Trivedi Class: FYBCA Subject: US02CBCA01 (Advanced C Programming and Introduction to Data Structures) *UNIT 3 (Introduction to Data
Cpt S 122 Data Structures. Data Structures
 Cpt S 122 Data Structures Data Structures Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Topics Introduction Self Referential Structures Dynamic Memory Allocation
Cpt S 122 Data Structures Data Structures Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Topics Introduction Self Referential Structures Dynamic Memory Allocation
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Using C Model Answer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Using C Model Answer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 10: Implementation of Linked Lists (Linked stacks and queues, Circular linked lists) 2015-2016 Fall Linked list implementation of stacks The cost of insert and delete at
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 10: Implementation of Linked Lists (Linked stacks and queues, Circular linked lists) 2015-2016 Fall Linked list implementation of stacks The cost of insert and delete at
Data Structures and Algorithms. Chapter 5. Dynamic Data Structures and Abstract Data Types
 1 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 5 and Abstract Data Types Werner Nutt 2 Acknowledgments The course follows the book Introduction to Algorithms, by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest and Stein, MIT Press
1 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 5 and Abstract Data Types Werner Nutt 2 Acknowledgments The course follows the book Introduction to Algorithms, by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest and Stein, MIT Press
MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct.
 MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the elements may locate at far positions
MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the elements may locate at far positions
An Introduction to Queues With Examples in C++
 An Introduction to Queues With Examples in C++ Prof. David Bernstein James Madison University Computer Science Department bernstdh@jmu.edu Motivation Queues are very straightforward but are slightly more
An Introduction to Queues With Examples in C++ Prof. David Bernstein James Madison University Computer Science Department bernstdh@jmu.edu Motivation Queues are very straightforward but are slightly more
Final Exam Data Structure course. No. of Branches (5)
 Page ١of 5 College Of Science and Technology Khan younis - Palestine Computer Science & Inf. Tech. Information Technology Data Structure (Theoretical Part) Time: 2 Hours Name: ID: Mark: Teacher 50 Mahmoud
Page ١of 5 College Of Science and Technology Khan younis - Palestine Computer Science & Inf. Tech. Information Technology Data Structure (Theoretical Part) Time: 2 Hours Name: ID: Mark: Teacher 50 Mahmoud
Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues
 Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues 18.1 Introduction to the Stack ADT Introduction to the Stack ADT Stack: a LIFO (last in, first out) data structure Examples: plates in a cafeteria return addresses for function
Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues 18.1 Introduction to the Stack ADT Introduction to the Stack ADT Stack: a LIFO (last in, first out) data structure Examples: plates in a cafeteria return addresses for function
Objective Questions for Online Practical Exams under CBCS Scheme Subject: Data Structure-I (CS-113)
 Objective Questions for Online Practical Exams under CBCS Scheme Subject: Data Structure-I (CS-113) 1. The number of interchanges required to sort 5, 1, 6, 2 4 in ascending order using Bubble Sort (A)
Objective Questions for Online Practical Exams under CBCS Scheme Subject: Data Structure-I (CS-113) 1. The number of interchanges required to sort 5, 1, 6, 2 4 in ascending order using Bubble Sort (A)
Answers. 1. (A) Attempt any five : 20 Marks
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
CS11001/CS11002 Programming and Data Structures (PDS) (Theory: 3-0-0)
 CS11001/CS11002 Programming and Data Structures (PDS) (Theory: 3-0-0) Class Teacher: Pralay Mitra Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Conceptual Idea
CS11001/CS11002 Programming and Data Structures (PDS) (Theory: 3-0-0) Class Teacher: Pralay Mitra Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Conceptual Idea
Linked Lists. Linked list: a collection of items (nodes) containing two components: Data Address (link) of the next node in the list
 Linked Lists Introduction : Data can be organized and processed sequentially using an array, called a sequential list Problems with an array Array size is fixed Unsorted array: searching for an item is
Linked Lists Introduction : Data can be organized and processed sequentially using an array, called a sequential list Problems with an array Array size is fixed Unsorted array: searching for an item is
DOWNLOAD PDF LINKED LIST PROGRAMS IN DATA STRUCTURE
 Chapter 1 : What is an application of linear linked list data structures? - Quora A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements
Chapter 1 : What is an application of linear linked list data structures? - Quora A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements
+ Abstract Data Types
 Linked Lists Abstract Data Types An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is: a set of values a set of operations Sounds familiar, right? I gave a similar definition for a data structure. Abstract Data Types Abstract
Linked Lists Abstract Data Types An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is: a set of values a set of operations Sounds familiar, right? I gave a similar definition for a data structure. Abstract Data Types Abstract
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 CS301- Data Structures Question No: 1 Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the
Definition of Stack. 5 Linked Structures. Stack ADT Operations. ADT Stack Operations. A stack is a LIFO last in, first out structure.
 5 Linked Structures Definition of Stack Logical (or ADT) level: A stack is an ordered group of homogeneous items (elements), in which the removal and addition of stack items can take place only at the
5 Linked Structures Definition of Stack Logical (or ADT) level: A stack is an ordered group of homogeneous items (elements), in which the removal and addition of stack items can take place only at the
Linked Lists. Linked list: a collection of items (nodes) containing two components: Data Address (link) of the next node in the list
 Linked Lists Introduction : Data can be organized and processed sequentially using an array, called a sequential list Problems with an array Array size is fixed Unsorted array: searching for an item is
Linked Lists Introduction : Data can be organized and processed sequentially using an array, called a sequential list Problems with an array Array size is fixed Unsorted array: searching for an item is
Lists (Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues
 (Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues By: Pramod Parajuli, Department of Computer Science, St. Xavier
(Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues By: Pramod Parajuli, Department of Computer Science, St. Xavier
CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures Lecture #1: Stacks and Queues
 CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures Lecture #1: Stacks and Queues Alan J. Hu (Slides borrowed from Steve Wolfman) Be sure to check course webpage! http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs221 1 Lab 1 is available.
CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures Lecture #1: Stacks and Queues Alan J. Hu (Slides borrowed from Steve Wolfman) Be sure to check course webpage! http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs221 1 Lab 1 is available.
Lesson 3: Understanding General Software Development
 Lesson 3: Understanding General Software Development 1. Arrange the various activities of an application lifecycle in the order in which they are likely to occur. a) Requirements analysis, design, coding,
Lesson 3: Understanding General Software Development 1. Arrange the various activities of an application lifecycle in the order in which they are likely to occur. a) Requirements analysis, design, coding,
Summer Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009
 15-111 Summer 2 2009 Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009 Exam Notes The exam is from 10:30 to 1:30 PM in Wean Hall 5419A. The exam will be primarily conceptual. The major emphasis is on understanding
15-111 Summer 2 2009 Final Exam Review Session August 5, 2009 Exam Notes The exam is from 10:30 to 1:30 PM in Wean Hall 5419A. The exam will be primarily conceptual. The major emphasis is on understanding
EC8393FUNDAMENTALS OF DATA STRUCTURES IN C Unit 3
 UNIT 3 LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 1. Define Data Structures Data Structures is defined as the way of organizing all data items that consider not only the elements stored but also stores the relationship between
UNIT 3 LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 1. Define Data Structures Data Structures is defined as the way of organizing all data items that consider not only the elements stored but also stores the relationship between
Data Structures. Lecture 5 : The Queues
 0 Data Structures Lecture 5 : Dr. Essam Halim Houssein Lecturer, Faculty of Computers and Informatics, Benha University http://bu.edu.eg/staff/esamhalim14 2 A queue is logically a first in first out (FIFO
0 Data Structures Lecture 5 : Dr. Essam Halim Houssein Lecturer, Faculty of Computers and Informatics, Benha University http://bu.edu.eg/staff/esamhalim14 2 A queue is logically a first in first out (FIFO
Lecture 4 Stack and Queue
 Lecture 4 Stack and Queue Bo Tang @ SUSTech, Spring 2018 Our Roadmap Stack Queue Stack vs. Queue 2 Stack A stack is a sequence in which: Items can be added and removed only at one end (the top) You can
Lecture 4 Stack and Queue Bo Tang @ SUSTech, Spring 2018 Our Roadmap Stack Queue Stack vs. Queue 2 Stack A stack is a sequence in which: Items can be added and removed only at one end (the top) You can
DS Assignment II. Full Sized Image
 DS Assignment II 1. A) For the Towers of Hanoi problem, show the call tree during the recursive call Towers(3, A, C, B). In the tree, label the root node as Towers (3, A, C, B) while marking all the intermediate
DS Assignment II 1. A) For the Towers of Hanoi problem, show the call tree during the recursive call Towers(3, A, C, B). In the tree, label the root node as Towers (3, A, C, B) while marking all the intermediate
CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures ADTs, Stacks, and Queues
 CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures ADTs, Stacks, and Queues Alan J. Hu (Slides borrowed from Steve Wolfman) Be sure to check course webpage! http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs221 1 Lab 1 available very
CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures ADTs, Stacks, and Queues Alan J. Hu (Slides borrowed from Steve Wolfman) Be sure to check course webpage! http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs221 1 Lab 1 available very
Ashish Gupta, Data JUET, Guna
 Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
Abstract Data Types. Definitions, Implementations, and Uses
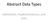 Abstract Data Types Definitions, Implementations, and Uses ADT An abstract data representation without reference to a specific implementation TABLE QUEUE STACK The primitive operations on the ADT elements
Abstract Data Types Definitions, Implementations, and Uses ADT An abstract data representation without reference to a specific implementation TABLE QUEUE STACK The primitive operations on the ADT elements
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT III LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES PART A 1. What is meant by data
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT III LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES PART A 1. What is meant by data
Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues. Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright Publishing as Pearson 2009 Addison-Wesley Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley 18.1 Introduction to
Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright Publishing as Pearson 2009 Addison-Wesley Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley 18.1 Introduction to
DATA STRUCTURES USING C
 DATA STRUCTURES USING C Revision 1.1 1 December, 2016 Er. Gaurav Khandelwal Professor Department of Computer Science KCRI COLLEGE ALWAR 301001 RAJASTHAN 2016-2017 KCRI COLLEGE Page 1 CONTENTS UNIT-1 3-7
DATA STRUCTURES USING C Revision 1.1 1 December, 2016 Er. Gaurav Khandelwal Professor Department of Computer Science KCRI COLLEGE ALWAR 301001 RAJASTHAN 2016-2017 KCRI COLLEGE Page 1 CONTENTS UNIT-1 3-7
l Determine if a number is odd or even l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between a and z (inclusive)
 Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to: l Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to: l Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
CS200: Queues. Prichard Ch. 8. CS200 - Queues 1
 CS200: Queues Prichard Ch. 8 CS200 - Queues 1 Queues First In First Out (FIFO) structure Imagine a checkout line So removing and adding are done from opposite ends of structure. 1 2 3 4 5 add to tail (back),
CS200: Queues Prichard Ch. 8 CS200 - Queues 1 Queues First In First Out (FIFO) structure Imagine a checkout line So removing and adding are done from opposite ends of structure. 1 2 3 4 5 add to tail (back),
Lists, Stacks and Queues in C. CHAN Hou Pong, Ken CSCI2100A Data Structures Tutorial 4
 Lists, Stacks and Queues in C CHAN Hou Pong, Ken CSCI2100A Data Structures Tutorial 4 Outline Structure Linked List Overview Implementation Stack Overview Implementation Queue Overview Implementation 2
Lists, Stacks and Queues in C CHAN Hou Pong, Ken CSCI2100A Data Structures Tutorial 4 Outline Structure Linked List Overview Implementation Stack Overview Implementation Queue Overview Implementation 2
CS 302 ALGORITHMS AND DATA STRUCTURES
 CS 302 ALGORITHMS AND DATA STRUCTURES A famous quote: Program = Algorithm + Data Structure General Problem You have some data to be manipulated by an algorithm E.g., list of students in a school Each student
CS 302 ALGORITHMS AND DATA STRUCTURES A famous quote: Program = Algorithm + Data Structure General Problem You have some data to be manipulated by an algorithm E.g., list of students in a school Each student
ESc101: (Linear, Circular, Doubly) Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Trees. Introduction to Linked Lists
 ESc101: (Linear, Circular, Doubly) Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Trees Instructor: Krithika Venkataramani Semester 2, 2011-2012 1 Introduction to Linked Lists Each bead connected to the next through a
ESc101: (Linear, Circular, Doubly) Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Trees Instructor: Krithika Venkataramani Semester 2, 2011-2012 1 Introduction to Linked Lists Each bead connected to the next through a
! A data type for which: ! An ADT may be implemented using various. ! Examples:
 Stacks and Queues Unit 6 Chapter 19.1-2,4-5 CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman 1 Abstract Data Type A data type for which: - only the properties of the data and the operations to be performed on the data are
Stacks and Queues Unit 6 Chapter 19.1-2,4-5 CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman 1 Abstract Data Type A data type for which: - only the properties of the data and the operations to be performed on the data are
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
12 Abstract Data Types
 12 Abstract Data Types 12.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define the concept of an abstract data type (ADT). Define
12 Abstract Data Types 12.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Define the concept of an abstract data type (ADT). Define
Insertions and removals follow the Fist-In First-Out rule: Insertions: at the rear of the queue Removals: at the front of the queue
 Queues CSE 2011 Fall 2009 9/28/2009 7:56 AM 1 Queues: FIFO Insertions and removals follow the Fist-In First-Out rule: Insertions: at the rear of the queue Removals: at the front of the queue Applications,
Queues CSE 2011 Fall 2009 9/28/2009 7:56 AM 1 Queues: FIFO Insertions and removals follow the Fist-In First-Out rule: Insertions: at the rear of the queue Removals: at the front of the queue Applications,
Stacks and Queues. Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms
 Stacks and Queues Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms Two New ADTs Define two new abstract data types Both are restricted lists Can be implemented using arrays
Stacks and Queues Chris Kiekintveld CS 2401 (Fall 2010) Elementary Data Structures and Algorithms Two New ADTs Define two new abstract data types Both are restricted lists Can be implemented using arrays
Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues
 Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues 18.1 Introduction to the Stack ADT Introduction to the Stack ADT Stack a LIFO (last in, first out) data structure Examples plates in a cafeteria return addresses for function
Chapter 18: Stacks And Queues 18.1 Introduction to the Stack ADT Introduction to the Stack ADT Stack a LIFO (last in, first out) data structure Examples plates in a cafeteria return addresses for function
How can we improve this? Queues 6. Topological ordering: given a sequence of. should occur prior to b, provide a schedule. Queues 5.
 Queues 1 Queues A Queue is a sequential organization of items in which the first element entered is the first removed. They are often referred to as FIFO, which stands for first in first out. Examples:
Queues 1 Queues A Queue is a sequential organization of items in which the first element entered is the first removed. They are often referred to as FIFO, which stands for first in first out. Examples:
Actually, C provides another type of variable which allows us to do just that. These are called dynamic variables.
 When a program is run, memory space is immediately reserved for the variables defined in the program. This memory space is kept by the variables until the program terminates. These variables are called
When a program is run, memory space is immediately reserved for the variables defined in the program. This memory space is kept by the variables until the program terminates. These variables are called
Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed
 Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Computer Science Department 2015 2016 1 What this Lecture is about: Stack Structure Stack
Associate Professor Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Computer Science Department 2015 2016 1 What this Lecture is about: Stack Structure Stack
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 CS 11 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today Object-Oriented Programming Concluded Stacks, Queues, and Priority Queues as Abstract Data Types Reference types: Basic
CS 11 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today Object-Oriented Programming Concluded Stacks, Queues, and Priority Queues as Abstract Data Types Reference types: Basic
Circular Queue can be created in three ways they are: Using single linked list Using double linked list Using arrays
 Circular Queue: Implementation and Applications In linear queue, when we delete any element, only front increment by one but position is not used later. So, when we perform more add and delete operations,
Circular Queue: Implementation and Applications In linear queue, when we delete any element, only front increment by one but position is not used later. So, when we perform more add and delete operations,
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Algorithms and Data Structures PD Dr. rer. nat. habil. Ralf Peter Mundani Computation in Engineering / BGU Scientific Computing in Computer Science / INF Summer Term 2018 Part 2: Data Structures PD Dr.
Algorithms and Data Structures PD Dr. rer. nat. habil. Ralf Peter Mundani Computation in Engineering / BGU Scientific Computing in Computer Science / INF Summer Term 2018 Part 2: Data Structures PD Dr.
Fun facts about recursion
 Outline examples of recursion principles of recursion review: recursive linked list methods binary search more examples of recursion problem solving using recursion 1 Fun facts about recursion every loop
Outline examples of recursion principles of recursion review: recursive linked list methods binary search more examples of recursion problem solving using recursion 1 Fun facts about recursion every loop
CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Queues
 CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Queues Professor Henry Carter Spring 2018 Recap Recursion solves problems by solving smaller version of the same problem Three components Applicable in a range
CSC 1052 Algorithms & Data Structures II: Queues Professor Henry Carter Spring 2018 Recap Recursion solves problems by solving smaller version of the same problem Three components Applicable in a range
2. List Implementations (a) Class Templates (b) Contiguous (c) Simply Linked (d) Simply Linked with Position Pointer (e) Doubly Linked
 Chapter 6 LISTS AND STRINGS 1. List Specifications 2. List Implementations (a) Class Templates (b) Contiguous (c) Simply Linked (d) Simply Linked with Position Pointer (e) Doubly Linked 3. Strings 4. Application:
Chapter 6 LISTS AND STRINGS 1. List Specifications 2. List Implementations (a) Class Templates (b) Contiguous (c) Simply Linked (d) Simply Linked with Position Pointer (e) Doubly Linked 3. Strings 4. Application:
 Class / Sem: I CSE / II Semester Subject Code: CS 6202 Subject: Programming and Data Structures I Prepared by T. Vithya Unit IV - LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES STACKS AND QUEUES Stack ADT Evaluating arithmetic
Class / Sem: I CSE / II Semester Subject Code: CS 6202 Subject: Programming and Data Structures I Prepared by T. Vithya Unit IV - LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES STACKS AND QUEUES Stack ADT Evaluating arithmetic
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science. First Examination
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science First Examination CS 225 Data Structures and Software Principles Spring 2007 7p-9p, Thursday, March 1 Name: NetID: Lab Section
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science First Examination CS 225 Data Structures and Software Principles Spring 2007 7p-9p, Thursday, March 1 Name: NetID: Lab Section
DC54 DATA STRUCTURES DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. Write a function that computes x^y using Recursion. The property that x^y is simply a product of x and x^(y-1 ). For example, 5^4= 5 * 5^3. The recursive definition of x^y can be represented as
Q.2 a. Write a function that computes x^y using Recursion. The property that x^y is simply a product of x and x^(y-1 ). For example, 5^4= 5 * 5^3. The recursive definition of x^y can be represented as
Where does the insert method place the new entry in the array? Assume array indexing starts from 0(zero).
 Suppose we have a circular array implementation of the queue,with ten items in the queue stored at data[2] through data[11]. The current capacity of an array is 12. Where does the insert method place the
Suppose we have a circular array implementation of the queue,with ten items in the queue stored at data[2] through data[11]. The current capacity of an array is 12. Where does the insert method place the
Queues. Gaddis 18.4, Molly A. O'Neil CS 2308 :: Spring 2016
 Queues Gaddis 18.4, 18.6 Molly A. O'Neil CS 2308 :: Spring 2016 The Queue ADT A queue is an abstract data type that stores a collection of elements of the same type The elements of a queue are accessed
Queues Gaddis 18.4, 18.6 Molly A. O'Neil CS 2308 :: Spring 2016 The Queue ADT A queue is an abstract data type that stores a collection of elements of the same type The elements of a queue are accessed
