EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DETERMINING DAMPING RATIO OF STEEL BRIDGES
|
|
|
- Fay Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DETERMINING DAMPING RATIO OF STEEL BRIDGES Muharrem AKTAS 1, Serdar KUYUK 2, Cemal YILMAZ 3, Elif AGCAKOCA 4, Erkan ÇELEBİ 5 ABSTRACT Damping property of a light-weight structure is especially required in design stage when dynamic response is considered. Since damping ratio cannot be directly derived from other structural properties; an experimental study is essential on completed structures of similar characteristics. Damping ratio calculated from existing structure is not sufficient for direct use in new design but it is the only way so far. This study aims to identify the damping ratio of a scaled steel pedestrian bridge. Main goal is to prove amplitude dependency of damping ratio for such structures. Tested bridge span is in 6.84 m length and 0.90 m wide. All the members are connected with bolts and the bridge is pin supported. Bridge was initially imposed with an initial deflection at mid span and released to make damped free vibration. Acceleration records were taken for the case of eight different initial displacement applied prior to free vibration. The damping ratio calculated after applying each initial amplitude value provides information about the sensitivity level of the structure s damping ratio. Damping ratio is calculated with log decrement equations by using both displacement and acceleration records. However, displacement records are not direct records obtained instrumentally but they are calculated by numerical integration of recorded acceleration data. Moreover; exponential curve fitting is employed to each test records to determine the damping ratio of the structure. Results prove that damping ratio of the structure is correlated with initial displacement applied to the structure. Moreover; using acceleration data recorded with instrumentation rather than displacement data calculated with numerical integration is more accurate. 1 Assist. Prof. Dr., Sakarya University, Sakarya, muharrema@sakarya.edu.tr 2 Assist. Prof. Dr., Sakarya University, Sakarya, serdarkuyuk@gmail.com 3 Research Assist. MSc., Sakarya University, Sakarya, f.cemalyilmaz@gmail.com 4 Assist. Prof. Dr., Sakarya University, Sakarya, elifd@sakarya.edu.tr 5 Prof. Dr., Sakarya University, Sakarya, ecelebi@sakarya.edu.tr 1
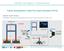
2 INTRODUCTION Damping property, a measure of energy dissipation in a vibrating system, is especially required in design stage of structures when dynamic response is considered. Since damping ratio cannot be directly derived from other structural properties; an experimental study is essential on completed structures of similar characteristics. Damping ratio calculated from other similar structure is not sufficient for direct use in new design but it is the only way so far. There are basically three different test types that can be used to determine damping coefficient. One is ambient excitation in which the source of the vibration is wind, traffic or other environmental effects. Implementing the test results to determine the targeted value is some time out of control because of the uncontrolled timing and direction of the ambient effects. Since the amplitude of the sources is small, only linear behaviour of structures can be tested with ambient vibration. The smaller equipment needed to conduct the test makes this approach encouraging. However; a high density of measuring points is needed in ambient vibration test for more realistic models (Ivanovic et al., 2000). A forced vibration test approach generally achieved by contra-rotating eccentric masses gives accurate results. This mechanical exciter creates a sinusoidal force in horizontal direction (Littler, 1995). It is possible to observe higher modes, with artificially created large amplitude by dynamic shaker which generally mounted on the top of the structure (Luco et al., 1988). But performing this test is more difficult than the well-known snap-back method. In snap-back method, first an amount of initial displacement is imposed to the structure prior to vibration. Then, the structure is suddenly released from this initial displacement causing vibration. Once the structure released from its initial condition it is left to vibrate freely until the structure brought to rest by the effects of damping. This paper presents damping ratio on the basis of analysis of test results obtained by applying snap-back approach. Amount of initial displacement is varied to discuss whether there is a correlation between damping coefficient and imposed initial displacement. Acceleration records were taken with a high quality accelerometer. Displacement of the bridge is not recorded directly but calculated by numerical integration. Both records are used to determine the damping coefficient to see the effect of using directly measured data and calculated data. Figure 1. a) Experimental setup of scaled steel frame bridge b) Numerical model c) placement of accelerometer d) illustration of fixed support 2
3 M. Aktas, S. Kuyuk, C. Yılmaz, E.Dogan and E. Celebi 3 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY AND METHODS Experiments are conducted on a scaled pedestrian bridge whose span and width is 6.84 m and 0.90 m, respectively (Figure 1-a-b). All the members are connected with bolts and the bridge is supported to soil with the boundary conditions shown in Figure 1d. Oscillations are recorded with high quality Capacitive Force Micromachined accelerometer, which has 32-bit high resolution and has 120 db dynamic range, located at mid-span of the bridge (Figure 1-c). The transverse acceleration waveform with 100 sample per seconds extracted from sensor is converted to velocity, displacement and frequency spectrums after applying standard signal-processing techniques such as base line corrections and Butterworth band pass filtering. Frequency content of signals are derived by applying Fast Fourier Transform. Free vibration decay is calculated for the test specimen excited with eight different initial displacement; cm, cm, cm, cm, cm, cm, cm, cm applied at the mid-span. Application of initial displacement is done by controlled human power. It is not given as impact force but rather, applied pulling and releasing the middle of bridge. Figure 2. Unfiltered (Row) and Filtered data recorded for the test case with an initial displacement of 1 mm Figure 3. Unfiltered (Row) and Filtered data recorded for the test case with an initial displacement of 12 mm Row data are first filtered to avoid noises by using our written Matlab code (Matlab, 2013). Unfiltered data and filtered data are plotted for two extreme cases, with minimum (Figure 2) and maximum (Figure 2) initial displacement. Noises are more evident at the beginning of the free vibration as expected. Also, Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT) is applied to see the frequency content of the structure. Fundemantal frequency of record show the natural frequency of the structure. It is 3
4 easy to obtain this dynamic characteristic from the case with minimum initial displacement rather than the case with maximum initial displacement. For instance, natural frequency of 4 Hz is easily obtained by displacement and acceleration record when initial deflection of 1 mm is applied (Figure 2). However, when an initial deflection of 12 mm is applied two fundamental frequencies obtained. Authors think that the first one is resulted from the impact effect of the larger initial deflection applied prior to free vibration. As its effect decays the natural frequency of 4 Hz is also obtainable from FFT. Calculating Damping ratios of Bridge: The equivalent damping ratio is calculated by using two different approaches to the well-known logdecrement equations. First approach uses the direct calculation with log-decrement equation and second method uses curve fitting to exponential envelope curve. Using Directly Log-Decrement Equations: The equivalent viscous damping ratio, of the structure is calculated from the filtered damped free vibration record by using log-decrement equation given below (Chopra, 2012); x = 1 2p ln u i u i+1 (1) where, u i and u i+1 denotes two successive peak deflections. However, in most dynamic analysis experiments, deflections are not directly recorded, but they are obtained by calculating the numerical integrations of recorded accelerations. Thus, damping ratio can also be calculated by using two successive peak accelerations, ü i and ü i 1 ; x = 1 2p ln ü i ü i+1 (2) Instead of using two successive amplitudes, using two amplitudes several cycles apart is easy and suitable when decay of motion is slow. In that case, the log-decrement equations over j cycles can be expressed as; x = 1 2p j ln u i u i+ j or x = 1 2p j ln ü i ü i+ j (3) Amplitudes of filtered damped free vibration record are determined for both acceleration and deflection record. Using Equation 1-2, damping ratio at each data point is calculated with these successive amplitudes and plotted next to each data record. Mean and median value of calculated damping ratio as well as result from Equation 3 is also included in the plot (Figure 3-4). Detailed result is given for two extreme case of initial condition of 1 mm and 12 mm in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively. 4
5 M. Aktas, S. Kuyuk, C. Yılmaz, E.Dogan and E. Celebi 5 Figure 3. Determining using equation 1, 2 and 3 for Experiment 1 (initial condition of 1 mm) Figure 4. Determining using equation 1, 2 and3 for Experiment 8 (initial condition of 12 mm) Using Exponential Envelope Curves: Displacement of a structure under ideally viscous damped condition, decay within an exponential envelope defined by Equation 4 (Chopra, 2012). u nt ( t) e (4) where is amplitude n is angular frequency and t is time. Ideally it is assumed that the peak displacement values are on points of this exponential curve. However, positions of peak displacements are near to these points on the exponential curve. But for most cases the divergence is negligible. Peak values of the data set are fitted with an exponential curve 5
6 of the form p n. u pt ( t) ae in which n p. Since is known from FFT, ζ can be calculated from n RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Log-decrement equations are used with filtered damped free vibration records, which are obtained from eight vibration tests. Mean and median values of damping ratio calculated by employing equation 1 and 2 using each two successive amplitude pair are presented in Figure 5. Damping ratio calculated by using two amplitudes, which are several cycles apart, is also included in Figure 5 for comparison purpose using Equation 3. Figure 5. Damping ratio calculated with a) using displacement record, Equation 1 and 3 b) using acceleration record, Equation 2 and 3 Figure 5 clearly prove the correlation between the value of damping ratio and initial displacement applied prior to the free damped vibration. As the initial deflection increases the damping ratio is also increase. However, the tendency in the increase of the line is not as steep as the start point. In other words, the line tends to go to horizontal asymptotes. This more clear in Figure 5b, which is obtained from displacement record. One important finding is that using displacement record rather than acceleration changes damping ratio value. For instance damping ratio calculated by using displacement records is higher than that is found by using acceleration record. This difference is more evident for the test case with higher initial displacement. Damping ratio calculated by equating ζω n to the amplitude of fitted curve of exponential form is presented in detail in Figure 6. Damping ratio value calculated with curve fitting method is tabulated with those obtained from Equation 1-3 in Table 1. For comparison purpose average of results obtained from Equation 1-3, and Equation 2-3 are plotted in Figure 7 with the results obtained from curve fitting method. 6
7 M. Aktas, S. Kuyuk, C. Yılmaz, E.Dogan and E. Celebi 7 Figure 6 Fitting exponential curves to the displacement amplitudes in the decay range Table 1. Damping values calculated for each test by employing Equation 1-3 and curve fitting method. Exp. # Initial Disp. (mm) Using Deflection Record Using Acceleration Record Using Equation 1 Using Exp. Using Equation 2 Using Exp. mean median Equation 3 Curve mean median Equation 3 Curve Results indicate that there is a divergence between results obtained for initial displacement less than 6 mm. After this point, damping ratio calculated from both curve fitting and log-decrement equation agrees well. They both go to asymptote as expected. However, this is not the case when displacement 7
8 records are used to determine the damping ratio. Differences between the damping ratio values with respect to reference values are tabulated in Table 2. Figure 7. Comparison of results obtained from all approaches Table 2. Damping values calculated for each test by employing Equation 1-3 and curve fitting method Exp. # Initial Disp. (mm) Displacement Record % difference between reference Curve Fitting For Displacement Record Curve Fitting For Acceleration Record
9 M. Aktas, S. Kuyuk, C. Yılmaz, E.Dogan and E. Celebi 9 CONCLUSIONS Damping ratio of a steel pedestrian bridge model is determined using free vibration decay tests with different excitation amplitudes created by introducing different amount of initial displacement. Logdecrement equations and exponential curve fitting methods are employed both on acceleration and displacement record obtained during the test. Results indicate that using acceleration records are more reliable since displacements are not directly recorded but numerically calculated from acceleration records. Also, different excitation amplitudes need to be introduced in free vibration decay test. In this study damping ratio of 1-7 % is calculated by using different initial excitation such as from 2 mm to 12 mm. Different amount of initial excitation must be introduced into the structure until asymptotic change in damping ratio is achieved. REFERENCES Chopra AK (2012) Dynamics of Structures, 4 th Ed., Prentice Hall Book Company, California Ivanovic SS, Trifunac MD, Todorovska MI (2000) Ambient vibration tests of structures-a review, ISET Journal of Earthquake Technology, 407(37): Littler JD (1995) An assessment of some of the different methods for estimating damping from full-scale testing, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 57(2-3): Luco JE (1995) Isolation of soil-structure interaction effects by full-scale forced vibration tests, Earthquake Engineerimg and Structural Dynamics, 16(1): 1 21 Matlab (2013a) The MathWorks, Inc. Natick, Massachusetts, United States 9
CHAPTER 5 RANDOM VIBRATION TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY
 117 CHAPTER 5 RANDOM VIBRATION TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 5.1 INTRODUCTION Random vibration tests are usually specified as acceptance, screening and qualification tests by commercial, industrial, and military
117 CHAPTER 5 RANDOM VIBRATION TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 5.1 INTRODUCTION Random vibration tests are usually specified as acceptance, screening and qualification tests by commercial, industrial, and military
ME scope Application Note 42 Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) FRFs
 ME scope Application Note 42 Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) FRFs NOTE: This Application Note uses commands in the VES-3600 Advanced Signal Processing Check Help About to verify authorization of these
ME scope Application Note 42 Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) FRFs NOTE: This Application Note uses commands in the VES-3600 Advanced Signal Processing Check Help About to verify authorization of these
Help Page for the Java-Powered Simulation for Experimental Structural Dynamics
 Help Page for the Java-Powered Simulation for Experimental Structural Dynamics Table of Contents Introduction How to Use the Virtual Laboratory o Control Panel o Animation Panel o Response Plot Panel o
Help Page for the Java-Powered Simulation for Experimental Structural Dynamics Table of Contents Introduction How to Use the Virtual Laboratory o Control Panel o Animation Panel o Response Plot Panel o
Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems
 Chapter 26 Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems (1989-2-24-25-28-29-21-211-217-) (In collaboration with Dr. Nima Tafazzoli, Dr. Federico Pisanò, Mr. Kohei Watanabe and Mr.
Chapter 26 Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems (1989-2-24-25-28-29-21-211-217-) (In collaboration with Dr. Nima Tafazzoli, Dr. Federico Pisanò, Mr. Kohei Watanabe and Mr.
Using Impulse Response Functions to Evaluate Baseball Bats
 Using Impulse Response Functions to Evaluate aseball ats David L. Formenti David Ottman Mark H. Richardson lackhawk Technology, Inc. Hillerich & radsby o. Vibrant Technology, Inc Santa ruz, A Loomis, A
Using Impulse Response Functions to Evaluate aseball ats David L. Formenti David Ottman Mark H. Richardson lackhawk Technology, Inc. Hillerich & radsby o. Vibrant Technology, Inc Santa ruz, A Loomis, A
Accurately measuring 2D position using a composed moiré grid pattern and DTFT
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Accurately measuring 2D position using a composed moiré grid pattern and DTFT S. Van
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Accurately measuring 2D position using a composed moiré grid pattern and DTFT S. Van
Dynamic - Time-History
 1 Dynamic - Time-History This module calculates the transient (history) response of a model subject to dynamic loads in which viscous damping is present. It enables the dynamic analysis of models subject
1 Dynamic - Time-History This module calculates the transient (history) response of a model subject to dynamic loads in which viscous damping is present. It enables the dynamic analysis of models subject
Design procedures of seismic-isolated container crane at port
 Design procedures of seismic-isolated container crane at port T.Sugano 1, M.Takenobu 1, T.Suzuki 1, and Y.Shiozaki 2 1 Port and Airport Research Institute,Yokosuka, Japan 2 JFE R&D Corporation,Kawasaki,Japan
Design procedures of seismic-isolated container crane at port T.Sugano 1, M.Takenobu 1, T.Suzuki 1, and Y.Shiozaki 2 1 Port and Airport Research Institute,Yokosuka, Japan 2 JFE R&D Corporation,Kawasaki,Japan
Graphical Interface Toolbox for Modal Analysis
 Proceedings of the Ninth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Society 14-16 April, 2011, Auckland, New Zealand S. Beskhyroun Graphical Interface Toolbox for Modal
Proceedings of the Ninth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Society 14-16 April, 2011, Auckland, New Zealand S. Beskhyroun Graphical Interface Toolbox for Modal
ODS & Modal Testing Using a Transmissibility Chain
 ODS & Modal Testing Using a Transmissibility Chain Brian Schwarz, Patrick McHargue, Mark Richardson Vibrant Technology, Inc. Centennial, CO Click here for the presentation ABSTRACT In this paper, we show
ODS & Modal Testing Using a Transmissibility Chain Brian Schwarz, Patrick McHargue, Mark Richardson Vibrant Technology, Inc. Centennial, CO Click here for the presentation ABSTRACT In this paper, we show
Vibration Transducer Calibration System
 0 1 Overview is designed for calibrating sensitivity, frequency response characteristic and amplitude linearity of acceleration transducer. There are three basic operation modes for the calibration system:
0 1 Overview is designed for calibrating sensitivity, frequency response characteristic and amplitude linearity of acceleration transducer. There are three basic operation modes for the calibration system:
Modal Analysis of Intermediate Shaft Used in Automobile Gear Box
 Modal Analysis of Intermediate Shaft Used in Automobile Gear Box Mr. Shekhar Dive PG Student, Mechanical Engineering Department, Siddhant College of Engineering, University of Pune, Pune, Maharashtra,
Modal Analysis of Intermediate Shaft Used in Automobile Gear Box Mr. Shekhar Dive PG Student, Mechanical Engineering Department, Siddhant College of Engineering, University of Pune, Pune, Maharashtra,
Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 121 Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation Tohru Jomen
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 121 Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation Tohru Jomen
17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES
 17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES The Current Building Codes Use the Terminology: Principal Direction without a Unique Definition 17.1 INTRODUCTION { XE "Building Codes" }Currently
17. SEISMIC ANALYSIS MODELING TO SATISFY BUILDING CODES The Current Building Codes Use the Terminology: Principal Direction without a Unique Definition 17.1 INTRODUCTION { XE "Building Codes" }Currently
DESCRIPTION OF THE LABORATORY RESEARCH FACILITY:
 DESCRIPTION OF THE LAORATORY RESEARCH FACILITY: Introduction Drexel researchers have designed and built a laboratory (Figure 1) in order to support several ongoing field research projects and to facilitate
DESCRIPTION OF THE LAORATORY RESEARCH FACILITY: Introduction Drexel researchers have designed and built a laboratory (Figure 1) in order to support several ongoing field research projects and to facilitate
Support Systems for Developing System Models
 Support Systems for Developing System Models Hasan G. Pasha, Karan Kohli, Randall J. Allemang, David L. Brown and Allyn W. Phillips University of Cincinnati Structural Dynamics Research Lab (UC-SDRL),
Support Systems for Developing System Models Hasan G. Pasha, Karan Kohli, Randall J. Allemang, David L. Brown and Allyn W. Phillips University of Cincinnati Structural Dynamics Research Lab (UC-SDRL),
Static, modal and dynamic behaviour of a stress ribbon footbridge: Experimental and computational results
 Static, modal and dynamic behaviour of a stress ribbon footbridge: Experimental and computational results Castaño, Javier 1 ; Cosido, Óscar 2 ; Pereda, José 3 ; Cacho-Pérez, Mariano 3 ; Lorenzana, Antolín
Static, modal and dynamic behaviour of a stress ribbon footbridge: Experimental and computational results Castaño, Javier 1 ; Cosido, Óscar 2 ; Pereda, José 3 ; Cacho-Pérez, Mariano 3 ; Lorenzana, Antolín
Reduction of squeal on laminated brake disc fastened with distributed contact pressure
 Recent Researches in Engineering Mechanics, Urban & Naval Transportation and Tourism Reduction of squeal on laminated brake disc fastened with distributed contact pressure Y.KUBOTA, K.OKUBO, T.FUJII Mechanical
Recent Researches in Engineering Mechanics, Urban & Naval Transportation and Tourism Reduction of squeal on laminated brake disc fastened with distributed contact pressure Y.KUBOTA, K.OKUBO, T.FUJII Mechanical
Interaction between a tethered sphere and a free surface flow
 Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems 205 Interaction between a tethered sphere and a free surface flow M. Greco 1, S. Malavasi 2 & D. Mirauda 1 1 Department I.F.A., Basilicata University,
Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems 205 Interaction between a tethered sphere and a free surface flow M. Greco 1, S. Malavasi 2 & D. Mirauda 1 1 Department I.F.A., Basilicata University,
1.12 Optimal Filters (Wiener Filters)
 Random Data 75 1.12 Optimal Filters (Wiener Filters) In calculating turbulent spectra we frequently encounter a noise tail just as the spectrum roles down the inertial subrange (-5/3 slope region) toward
Random Data 75 1.12 Optimal Filters (Wiener Filters) In calculating turbulent spectra we frequently encounter a noise tail just as the spectrum roles down the inertial subrange (-5/3 slope region) toward
Yaw-Roll Coupled Oscillations of a Slender Delta Wing
 Yaw-Roll Coupled Oscillations of a Slender Delta Wing John C. Worley * Auburn University Aerospace Engineering, Auburn, Alabama, 3683 Reported are the results of experiments conducted on a slender delta
Yaw-Roll Coupled Oscillations of a Slender Delta Wing John C. Worley * Auburn University Aerospace Engineering, Auburn, Alabama, 3683 Reported are the results of experiments conducted on a slender delta
DEVELOPMENT OF SUBSTRUCTURED SHAKING TABLE TEST METHOD
 DEVELOPMENT OF SUBSTRUCTURED SHAKING TABLE TEST METHOD Akira IGARASHI 1, Hirokazu IEMURA 2 And Takanori SUWA 3 SUMMARY Since various kinds of issues arise in the practical application of structural response
DEVELOPMENT OF SUBSTRUCTURED SHAKING TABLE TEST METHOD Akira IGARASHI 1, Hirokazu IEMURA 2 And Takanori SUWA 3 SUMMARY Since various kinds of issues arise in the practical application of structural response
STUDY ON MODEL REDUCTION OF LARGE STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS FOR ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL
 4"' Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics Institute of Materials Engineering Australasia Ltd 2005 STUDY ON MODEL REDUCTION OF LARGE STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS FOR ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL J. Boffa, N. Zhang
4"' Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics Institute of Materials Engineering Australasia Ltd 2005 STUDY ON MODEL REDUCTION OF LARGE STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS FOR ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL J. Boffa, N. Zhang
Defining the Global Error of a Multi-Axis Vibration Test: An Application of MIL-STD-810G Method 527 Annex C
 Defining the Global Error of a Multi-Axis Vibration Test: An Application of MIL-STD-810G Method 527 Annex C Joel Hoksbergen Team Corporation joel.hoksbergen@teamcorporation.com ESTECH 2014 MIMO Concepts
Defining the Global Error of a Multi-Axis Vibration Test: An Application of MIL-STD-810G Method 527 Annex C Joel Hoksbergen Team Corporation joel.hoksbergen@teamcorporation.com ESTECH 2014 MIMO Concepts
DS-0322 Tracking Analysis Software Operation manual Basic Operation procedure for Constant-ratio Tracking Analysis
 DS-0322 Tracking Analysis Software Operation manual Basic Operation procedure for Constant-ratio Tracking Analysis ONO SOKKI CO., LTD. There are two types of tracking analysis, i.e., one is "constant ratio
DS-0322 Tracking Analysis Software Operation manual Basic Operation procedure for Constant-ratio Tracking Analysis ONO SOKKI CO., LTD. There are two types of tracking analysis, i.e., one is "constant ratio
Optimization to Reduce Automobile Cabin Noise
 EngOpt 2008 - International Conference on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 June 2008. Optimization to Reduce Automobile Cabin Noise Harold Thomas, Dilip Mandal, and Narayanan Pagaldipti
EngOpt 2008 - International Conference on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 June 2008. Optimization to Reduce Automobile Cabin Noise Harold Thomas, Dilip Mandal, and Narayanan Pagaldipti
ME scope Application Note 18 Simulated Multiple Shaker Burst Random Modal Test
 ME scope Application Note 18 Simulated Multiple Shaker Burst Random Modal Test The steps in this Application Note can be duplicated using any Package that includes the VES-4600 Advanced Signal Processing
ME scope Application Note 18 Simulated Multiple Shaker Burst Random Modal Test The steps in this Application Note can be duplicated using any Package that includes the VES-4600 Advanced Signal Processing
VIBbox 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution
 VIBbox 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution VIBbox is a high-accuracy, high channel count, dynamic signal analyzer system for sound and vibration applications. VIBbox packages four DT9857E modules in
VIBbox 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution VIBbox is a high-accuracy, high channel count, dynamic signal analyzer system for sound and vibration applications. VIBbox packages four DT9857E modules in
Designing flapping wings as oscillating structures
 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization May 9-4,, Orlando, Florida, USA Designing flapping wings as oscillating structures Zhiyuan Zhang, Ashok V. Kumar, Raphael T. Haftka University
th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization May 9-4,, Orlando, Florida, USA Designing flapping wings as oscillating structures Zhiyuan Zhang, Ashok V. Kumar, Raphael T. Haftka University
istrdyn - integrated Stress, Thermal, and Rotor Dynamics
 istrdyn - integrated Stress, Thermal, and Rotor Dynamics Jeffcott Rotor Analysis Example istrdyn Modeling, Solutions, and Result Processing July 2007 This presentation shows an analysis sequence using
istrdyn - integrated Stress, Thermal, and Rotor Dynamics Jeffcott Rotor Analysis Example istrdyn Modeling, Solutions, and Result Processing July 2007 This presentation shows an analysis sequence using
Methodology for Prediction of Sliding and Rocking of Rigid Bodies Using Fast Non-Linear Analysis (FNA) Formulation
 Methodology for Prediction of Sliding and Rocking of Rigid Bodies Using Fast Non-Linear Analysis (FNA) Formulation Sohrab Esfandiari - ENOVA Engineering Services Robert P. Kennedy- RPK Structural Consulting
Methodology for Prediction of Sliding and Rocking of Rigid Bodies Using Fast Non-Linear Analysis (FNA) Formulation Sohrab Esfandiari - ENOVA Engineering Services Robert P. Kennedy- RPK Structural Consulting
Verifying finite element model of fixed roof cylindrical liquid container from full scale vibration test results
 Verifying finite element model of fixed roof cylindrical liquid container from full scale vibration test results Moslem Amiri, Saeed Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi Civil Engineering Department, K.N. Toosi University
Verifying finite element model of fixed roof cylindrical liquid container from full scale vibration test results Moslem Amiri, Saeed Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi Civil Engineering Department, K.N. Toosi University
VR9500. Advantages Ease of Use. Features
 Ease of Use system and confi gured a test within minutes of unpacking the box. Additionally, our customer support PC & Windows Integration The integrates seamlessly with your PC and Windows operating system,
Ease of Use system and confi gured a test within minutes of unpacking the box. Additionally, our customer support PC & Windows Integration The integrates seamlessly with your PC and Windows operating system,
KINETICS Vibration Isolation Manual
 The Pitfalls of Combining Internal & External Equipment Isolation Introduction: Almost all Make-up Air Units (MAU), Air Handling Units (AHU), and Rooftop Units (RTU) have internal spring-type isolation
The Pitfalls of Combining Internal & External Equipment Isolation Introduction: Almost all Make-up Air Units (MAU), Air Handling Units (AHU), and Rooftop Units (RTU) have internal spring-type isolation
Dynamic soil-tunnel interaction in layered half-space for incident P- and SV-waves
 Earthq Sci (2015) 28(4):275 284 DOI 10.1007/s11589-015-0130-3 RESEARCH PAPER Dynamic soil-tunnel interaction in layered half-space for incident P- and SV-waves Jia Fu. Jianwen Liang. Lin Qin Received:
Earthq Sci (2015) 28(4):275 284 DOI 10.1007/s11589-015-0130-3 RESEARCH PAPER Dynamic soil-tunnel interaction in layered half-space for incident P- and SV-waves Jia Fu. Jianwen Liang. Lin Qin Received:
A building structural-performance monitoring system using RFID tag with sensors
 icccbe 21 Nottingham University Press Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) A building structural-performance monitoring system using
icccbe 21 Nottingham University Press Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) A building structural-performance monitoring system using
WinIGS. Windows Based Integrated Grounding System Design Program. Structural Dynamic Analysis Training Guide. Last Revision: February 2017
 WinIGS Windows Based Integrated Grounding System Design Program Structural Dynamic Analysis Training Guide Last Revision: February 2017 Copyright A. P. Sakis Meliopoulos 2009-2017 NOTICES Copyright Notice
WinIGS Windows Based Integrated Grounding System Design Program Structural Dynamic Analysis Training Guide Last Revision: February 2017 Copyright A. P. Sakis Meliopoulos 2009-2017 NOTICES Copyright Notice
Hands-on Lab. LabVIEW Simulation Tool Kit
 Hands-on Lab LabVIEW Simulation Tool Kit The LabVIEW Simulation Tool Kit features a comprehensive suite of tools to test designs. This lab provides a primer to implementing a simulation. This will be useful
Hands-on Lab LabVIEW Simulation Tool Kit The LabVIEW Simulation Tool Kit features a comprehensive suite of tools to test designs. This lab provides a primer to implementing a simulation. This will be useful
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley
 OpenFresco Framework for Hybrid Simulation: OpenSSL Example Andreas Schellenberg, Hong K. Kim, Yoshikazu Takahashi, Gregory L. Fenves, and Stephen A. Mahin Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
OpenFresco Framework for Hybrid Simulation: OpenSSL Example Andreas Schellenberg, Hong K. Kim, Yoshikazu Takahashi, Gregory L. Fenves, and Stephen A. Mahin Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
WP1 NUMERICAL BENCHMARK INVESTIGATION
 WP1 NUMERICAL BENCHMARK INVESTIGATION 1 Table of contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 1 st example: beam under pure bending... 3 2.1 Definition of load application and boundary conditions... 4 2.2 Definition
WP1 NUMERICAL BENCHMARK INVESTIGATION 1 Table of contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 1 st example: beam under pure bending... 3 2.1 Definition of load application and boundary conditions... 4 2.2 Definition
OpenFresco Framework for Hybrid Simulation: UI-SimCor v2.6 Example
 OpenFresco Framework for Hybrid Simulation: UI-SimCor v2.6 Example Andreas Schellenberg, Hong K. Kim, Yoshikazu Takahashi, Gregory L. Fenves, and Stephen A. Mahin Department of Civil and Environmental
OpenFresco Framework for Hybrid Simulation: UI-SimCor v2.6 Example Andreas Schellenberg, Hong K. Kim, Yoshikazu Takahashi, Gregory L. Fenves, and Stephen A. Mahin Department of Civil and Environmental
K-Beam Accelerometer. Acceleration. Capacitive MEMS, Triaxial Accelerometer. Type 8395A...
 Acceleration K-Beam Accelerometer Type 8395A... Capacitive MEMS, Triaxial Accelerometer Type 8395A is a high-sensitivity, low noise triaxial accelerometer which simultaneously measures acceleration and/or
Acceleration K-Beam Accelerometer Type 8395A... Capacitive MEMS, Triaxial Accelerometer Type 8395A is a high-sensitivity, low noise triaxial accelerometer which simultaneously measures acceleration and/or
EXPLICIT DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME UP TO COLLAPSE
 EXPLICIT DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME UP TO COLLAPSE ABSTRACT: K. Kocamaz 1, K. Tuncay 2 and B. Binici 3 1 Res. Assist., Civil Eng. Department, Middle East Technical University, Ankara
EXPLICIT DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME UP TO COLLAPSE ABSTRACT: K. Kocamaz 1, K. Tuncay 2 and B. Binici 3 1 Res. Assist., Civil Eng. Department, Middle East Technical University, Ankara
KINETIC FRICTION TROUGH SURFACE MICRO ANALYSIS
 International Journal of Metallurgical & Materials Science and Engineering (IJMMSE) ISSN 2278-2516 Vol. 3, Issue 1, Mar 2013, 31-36 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. KINETIC FRICTION TROUGH SURFACE MICRO ANALYSIS NIKOLA
International Journal of Metallurgical & Materials Science and Engineering (IJMMSE) ISSN 2278-2516 Vol. 3, Issue 1, Mar 2013, 31-36 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. KINETIC FRICTION TROUGH SURFACE MICRO ANALYSIS NIKOLA
Simulation of Overhead Crane Wire Ropes Utilizing LS-DYNA
 Simulation of Overhead Crane Wire Ropes Utilizing LS-DYNA Andrew Smyth, P.E. LPI, Inc., New York, NY, USA Abstract Overhead crane wire ropes utilized within manufacturing plants are subject to extensive
Simulation of Overhead Crane Wire Ropes Utilizing LS-DYNA Andrew Smyth, P.E. LPI, Inc., New York, NY, USA Abstract Overhead crane wire ropes utilized within manufacturing plants are subject to extensive
Portable vibration calibrator Model 28959G
 Key features Ideal tool for field validation of vibration sensors Completely self-contained system includes: Built-in vibration exciter Signal generator Computer-controlled amplifier/servo mechanism Reference
Key features Ideal tool for field validation of vibration sensors Completely self-contained system includes: Built-in vibration exciter Signal generator Computer-controlled amplifier/servo mechanism Reference
Active noise control at a moving location in a modally dense three-dimensional sound field using virtual sensing
 Active noise control at a moving location in a modally dense three-dimensional sound field using virtual sensing D. J Moreau, B. S Cazzolato and A. C Zander The University of Adelaide, School of Mechanical
Active noise control at a moving location in a modally dense three-dimensional sound field using virtual sensing D. J Moreau, B. S Cazzolato and A. C Zander The University of Adelaide, School of Mechanical
Challenge Problem 5 - The Solution Dynamic Characteristics of a Truss Structure
 Challenge Problem 5 - The Solution Dynamic Characteristics of a Truss Structure In the final year of his engineering degree course a student was introduced to finite element analysis and conducted an assessment
Challenge Problem 5 - The Solution Dynamic Characteristics of a Truss Structure In the final year of his engineering degree course a student was introduced to finite element analysis and conducted an assessment
K-Beam Accelerometer. Acceleration. Capacitive MEMS, Triaxial Accelerometer. Type 8396A...
 Acceleration K-Beam Accelerometer Type 8396A... Capacitive MEMS, Triaxial Accelerometer Type 8396A is a high-sensitivity, low noise triaxial accelerometer which simultaneously measures acceleration and/or
Acceleration K-Beam Accelerometer Type 8396A... Capacitive MEMS, Triaxial Accelerometer Type 8396A is a high-sensitivity, low noise triaxial accelerometer which simultaneously measures acceleration and/or
FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING OF A TURBINE BLADE TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE CRACKS USING MODAL PARAMETERS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 11, No. 12 (2016) 1758-1770 School of Engineering, Taylor s University FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING OF A TURBINE BLADE TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE CRACKS
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 11, No. 12 (2016) 1758-1770 School of Engineering, Taylor s University FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING OF A TURBINE BLADE TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF MULTIPLE CRACKS
A comparison between large-size shaking table test and numerical simulation results of subway station structure
 October 127, 28, Beijing, China A comparison between large-size shaking table test and numerical simulation results of subway station structure ABSTRACT : CHEN Guo-xing 1, ZUO Xi 1, ZHUANG Hai-yang 1,
October 127, 28, Beijing, China A comparison between large-size shaking table test and numerical simulation results of subway station structure ABSTRACT : CHEN Guo-xing 1, ZUO Xi 1, ZHUANG Hai-yang 1,
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines. ITTC Quality System Manual. Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Offshore Structures with Mooring Lines 7.5 Page 1 of 6 ITTC Quality System Manual Recommended Procedure Offshore Structures with Mooring Lines 7.5 Process Control 7.5- Testing and Extrapolation Methods
Offshore Structures with Mooring Lines 7.5 Page 1 of 6 ITTC Quality System Manual Recommended Procedure Offshore Structures with Mooring Lines 7.5 Process Control 7.5- Testing and Extrapolation Methods
COMPARISON OF 3D LASER VIBROMETER AND ACCELEROMETER FREQUENCY MEASUREMENTS
 Proceedings of the IMAC-XXVII February 9-12, 2009 Orlando, Florida USA 2009 Society for Experimental Mechanics Inc. COMPARISON OF 3D LASER VIBROMETER AND ACCELEROMETER FREQUENCY MEASUREMENTS Pawan Pingle,
Proceedings of the IMAC-XXVII February 9-12, 2009 Orlando, Florida USA 2009 Society for Experimental Mechanics Inc. COMPARISON OF 3D LASER VIBROMETER AND ACCELEROMETER FREQUENCY MEASUREMENTS Pawan Pingle,
NV-TECH-Design: Scalable Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) for accurate, repeatable structural dynamics testing
 NV-TECH-Design: Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) for accurate, repeatable structural dynamics testing Figure 1: NV-TECH-Design Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) for structural testing (Patent pending). Modal Testing
NV-TECH-Design: Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) for accurate, repeatable structural dynamics testing Figure 1: NV-TECH-Design Automatic Modal Hammer (SAM) for structural testing (Patent pending). Modal Testing
Blast Load Time History Analysis
 Blast Load Time History Analysis An Example in S-FRAME by Jeremy Knight (Application Engineer) Edited by Kenneth Kutyn (Jr. Application Engineer) S-FRAME Software Inc. S-FRAME Software, LLC #275-13500
Blast Load Time History Analysis An Example in S-FRAME by Jeremy Knight (Application Engineer) Edited by Kenneth Kutyn (Jr. Application Engineer) S-FRAME Software Inc. S-FRAME Software, LLC #275-13500
Design and Dynamic Characteristics Study on structure of MIMU Damping System Tong Zhou, Meiping Wu, Bing Luo, Changfeng Chen
 3rd International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Information Technology Applications (ICMMITA 2015) Design and Dynamic Characteristics Study on structure of MIMU Damping System Tong Zhou, Meiping
3rd International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Information Technology Applications (ICMMITA 2015) Design and Dynamic Characteristics Study on structure of MIMU Damping System Tong Zhou, Meiping
VIBBOX. 32, 48, or 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution Expansion to 256 Channels. Key Feature of Each VIBbox: Table 1. Key Features of VIBbox Models
 VIBBOX 32, 48, or 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution Expansion to 256 Channels VIBbox is a high-accuracy, high channel count, dynamic signal analyzer system for sound and vibration applications. Each
VIBBOX 32, 48, or 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution Expansion to 256 Channels VIBbox is a high-accuracy, high channel count, dynamic signal analyzer system for sound and vibration applications. Each
Example Applications of A Stochastic Ground Motion Simulation Methodology in Structural Engineering
 Example Applications of A Stochastic Ground Motion Simulation Methodology in Structural Engineering S. Rezaeian & N. Luco U.S. Geological Survey, Golden, CO, USA ABSTRACT: Example engineering applications
Example Applications of A Stochastic Ground Motion Simulation Methodology in Structural Engineering S. Rezaeian & N. Luco U.S. Geological Survey, Golden, CO, USA ABSTRACT: Example engineering applications
COMPARISON OF TWO FINITE ELEMENT MODELS OF BRISTLES OF GUTTER BRUSHES FOR STREET SWEEPING
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Fracture Fatigue and Wear, pp. 22-226, 25 COMPARISON OF TWO FINITE ELEMENT MODELS OF BRISTLES OF GUTTER BRUSHES FOR STREET SWEEPING M.M. Abdel-Wahab,
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Fracture Fatigue and Wear, pp. 22-226, 25 COMPARISON OF TWO FINITE ELEMENT MODELS OF BRISTLES OF GUTTER BRUSHES FOR STREET SWEEPING M.M. Abdel-Wahab,
ctbuh.org/papers Structural Member Monitoring of High-Rise Buildings Using a 2D Laser Scanner Title:
 ctbuh.org/papers Title: Authors: Subject: Keyword: Structural Member Monitoring of High-Rise Buildings Using a 2D Laser Scanner Bub-Ryur Kim, Masters Degree Candidate, Yonsei University Dong Chel Lee,
ctbuh.org/papers Title: Authors: Subject: Keyword: Structural Member Monitoring of High-Rise Buildings Using a 2D Laser Scanner Bub-Ryur Kim, Masters Degree Candidate, Yonsei University Dong Chel Lee,
Implementing Machine Learning in Earthquake Engineering
 CS9 MACHINE LEARNING, DECEMBER 6 Implementing Machine Learning in Earthquake Engineering Cristian Acevedo Civil and Environmental Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, CA 9435, USA Abstract The use
CS9 MACHINE LEARNING, DECEMBER 6 Implementing Machine Learning in Earthquake Engineering Cristian Acevedo Civil and Environmental Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, CA 9435, USA Abstract The use
THE KINEMATIC AND INERTIAL SOIL-PILE INTERACTIONS: CENTRIFUGE MODELLING
 THE KINEMATIC AND INERTIAL SOIL-PILE INTERACTIONS: CENTRIFUGE MODELLING Nawel Chenaf, Jean-Louis Chazelas To cite this version: Nawel Chenaf, Jean-Louis Chazelas. THE KINEMATIC AND INERTIAL SOIL-PILE INTER-
THE KINEMATIC AND INERTIAL SOIL-PILE INTERACTIONS: CENTRIFUGE MODELLING Nawel Chenaf, Jean-Louis Chazelas To cite this version: Nawel Chenaf, Jean-Louis Chazelas. THE KINEMATIC AND INERTIAL SOIL-PILE INTER-
Zheng-Dong Ma & Noel C. Perkins Department of MEAM The University of Michigan
 A G e n e r a l T r a c k E l e m e n t F o r T r a c k e d V e h i c l e S i m u l a t i o n Zheng-Dong Ma & Noel C. Perkins Department of MEAM The University of Michigan Major Features of the Track Element
A G e n e r a l T r a c k E l e m e n t F o r T r a c k e d V e h i c l e S i m u l a t i o n Zheng-Dong Ma & Noel C. Perkins Department of MEAM The University of Michigan Major Features of the Track Element
PROBLEMS AND EXERCISES PROBLEMS
 64 Fundamentals of Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines and Mechanisms PROBLEMS AND EXERCISES PROBLEMS 1. In Figure 1.14c an inverted slider-crank mechanism is shown. b. If the input is the displacement
64 Fundamentals of Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines and Mechanisms PROBLEMS AND EXERCISES PROBLEMS 1. In Figure 1.14c an inverted slider-crank mechanism is shown. b. If the input is the displacement
The Art of Fabricating a Rotational Accelerometer. by Mike Insalaco
 The Art of Fabricating a Rotational Accelerometer by Mike Insalaco The Art of Fabricating a Rotational Accelerometer OBJECTIVE Briefly review the need for a device Discuss difficulty using commercial hardware
The Art of Fabricating a Rotational Accelerometer by Mike Insalaco The Art of Fabricating a Rotational Accelerometer OBJECTIVE Briefly review the need for a device Discuss difficulty using commercial hardware
Spring Pendulum * Muhammad Umar Hassan and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar
 Spring Pendulum * Muhammad Umar Hassan and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar Center for Experimental Physics Education, Syed Babar Ali School of Science and Engineering, LUMS V. 2017-1; May 3, 2017 Oscillations are
Spring Pendulum * Muhammad Umar Hassan and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar Center for Experimental Physics Education, Syed Babar Ali School of Science and Engineering, LUMS V. 2017-1; May 3, 2017 Oscillations are
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 10, October-2016 ISSN
 ISSN 2229-5518 1703 Finite element modeling and its validation using experimental modal analysis Hasan Zakir Jafri, Aas Mohammad Abstract The determination of vibration characteristics of a mechanical
ISSN 2229-5518 1703 Finite element modeling and its validation using experimental modal analysis Hasan Zakir Jafri, Aas Mohammad Abstract The determination of vibration characteristics of a mechanical
ScienceDirect. Vibration Response Prediction of the Printed Circuit Boards using Experimentally Validated Finite Element Model
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 144 (2016 ) 576 583 12th International Conference on Vibration Problems, ICOVP 2015 Vibration Response Prediction of the Printed
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 144 (2016 ) 576 583 12th International Conference on Vibration Problems, ICOVP 2015 Vibration Response Prediction of the Printed
SEISMIC TESTING OF LARGE SCALE STRUCTURES WITH DISSIPATOR DEVICES
 11 th International Conference on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9-12 September 2013 SEISMIC TESTING OF LARGE SCALE STRUCTURES WITH DISSIPATOR DEVICES Beatriz Zapico*
11 th International Conference on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9-12 September 2013 SEISMIC TESTING OF LARGE SCALE STRUCTURES WITH DISSIPATOR DEVICES Beatriz Zapico*
Modal pushover-based scaling of records for nonlinear RHA of one-story unsymmetric-plan buildings
 Modal pushover-based scaling of records for nonlinear RHA of one-story unsymmetric-plan buildings J. C. Reyes & O. A. Quintero Universidad de los Andes, Bogotá, Colombia. A. K. Chopra University of California,
Modal pushover-based scaling of records for nonlinear RHA of one-story unsymmetric-plan buildings J. C. Reyes & O. A. Quintero Universidad de los Andes, Bogotá, Colombia. A. K. Chopra University of California,
REGULARITY INDICES FOR BRIDGE STRUCTURES
 7 REGULARITY INDICES FOR BRIDGE STRUCTURES Tatjana ISAKOVIĆ And Matej FISCHINGER SUMMARY A number of methods can be used for the analysis of bridge structures. Some of these methods are well known, and
7 REGULARITY INDICES FOR BRIDGE STRUCTURES Tatjana ISAKOVIĆ And Matej FISCHINGER SUMMARY A number of methods can be used for the analysis of bridge structures. Some of these methods are well known, and
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Mathematics and Statistics Level 1
 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Mathematics and Statistics Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard (2.2) Apply graphical methods in solving problems An annotated
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Mathematics and Statistics Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard (2.2) Apply graphical methods in solving problems An annotated
Triax Accelerometer for Route-Based Vibration Analysis
 Machinery Health Triax Accelerometer for Route-Based Vibration Analysis A newly-developed triax accelerometer developed specifically for route-based vibration data acquisition for industrial machinery
Machinery Health Triax Accelerometer for Route-Based Vibration Analysis A newly-developed triax accelerometer developed specifically for route-based vibration data acquisition for industrial machinery
Spring Pendulum. Muhammad Umar Hassan and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar
 Spring Pendulum Muhammad Umar Hassan and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar Center for Experimental Physics Education, Syed Babar Ali School of Science and Engineering, LUMS V. 2016-1; April 28, 2016 Oscillations are
Spring Pendulum Muhammad Umar Hassan and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar Center for Experimental Physics Education, Syed Babar Ali School of Science and Engineering, LUMS V. 2016-1; April 28, 2016 Oscillations are
FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING
 FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Purpose of FB-MultiPier Validation testing Performing validation of structural analysis software delineates the capabilities and limitations
FB-MULTIPIER vs ADINA VALIDATION MODELING 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Purpose of FB-MultiPier Validation testing Performing validation of structural analysis software delineates the capabilities and limitations
A NEW SYSTEM FOR COMPARISON CALIBRATION OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS AT LOW FREQUENCIES
 XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology September 6 11, 2009, Lisbon, Portugal A NEW SYSTEM FOR COMPARISON CALIBRATION OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS AT LOW FREQUENCIES Gustavo P. Ripper,
XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology September 6 11, 2009, Lisbon, Portugal A NEW SYSTEM FOR COMPARISON CALIBRATION OF VIBRATION TRANSDUCERS AT LOW FREQUENCIES Gustavo P. Ripper,
LACOSTE & ROMBERG AIR-SEA GRAVITY METER VIBRATION TESTS
 LACOSTE & ROMBERG AIR-SEA GRAVITY METER VIBRATION TESTS Introduction. Our motivation is to compare the vibration sensitivity of our new AirSea II system to the ZLS D-003 (fluid damped) and S-3 (air damped)
LACOSTE & ROMBERG AIR-SEA GRAVITY METER VIBRATION TESTS Introduction. Our motivation is to compare the vibration sensitivity of our new AirSea II system to the ZLS D-003 (fluid damped) and S-3 (air damped)
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2008 COSMOSMotion Tutorial Page 1
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2008 COSMOSMotion Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will learn the basics of performing motion analysis using COSMOSMotion. Although the tutorial can
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2008 COSMOSMotion Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will learn the basics of performing motion analysis using COSMOSMotion. Although the tutorial can
ROSE-HULMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 More Working Model Today we are going to look at even more features of Working Model. Specifically, we are going to 1) Learn how to add ropes and rods. 2) Learn how to connect object using joints and slots.
More Working Model Today we are going to look at even more features of Working Model. Specifically, we are going to 1) Learn how to add ropes and rods. 2) Learn how to connect object using joints and slots.
Structural Vibration Solutions A/S
 Structural Vibration Solutions A/S Structural Vibration Solutions A/S is a supplier and developer of software for Operational Modal Analysis. It is our mission to be the worlds leading provider of Operational
Structural Vibration Solutions A/S Structural Vibration Solutions A/S is a supplier and developer of software for Operational Modal Analysis. It is our mission to be the worlds leading provider of Operational
ksa 400 Growth Rate Analysis Routines
 k-space Associates, Inc., 2182 Bishop Circle East, Dexter, MI 48130 USA ksa 400 Growth Rate Analysis Routines Table of Contents ksa 400 Growth Rate Analysis Routines... 2 1. Introduction... 2 1.1. Scan
k-space Associates, Inc., 2182 Bishop Circle East, Dexter, MI 48130 USA ksa 400 Growth Rate Analysis Routines Table of Contents ksa 400 Growth Rate Analysis Routines... 2 1. Introduction... 2 1.1. Scan
Recent developments in Real-Time Hybrid Simulation (RTHS)
 INFRARISK- PhD Programme 2 nd Summer Workshop Recent developments in Real-Time Hybrid Simulation (RTHS) Gidewon Goitom Tekeste Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil (LNEC) and University of Aveiro (UA)
INFRARISK- PhD Programme 2 nd Summer Workshop Recent developments in Real-Time Hybrid Simulation (RTHS) Gidewon Goitom Tekeste Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil (LNEC) and University of Aveiro (UA)
Finite Element Simulation using SPH Particles as Loading on Typical Light Armoured Vehicles
 10 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Penetration / Blast Finite Element Simulation using SPH Particles as Loading on Typical Light Armoured Vehicles Geneviève Toussaint and Robert Durocher Defence
10 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Penetration / Blast Finite Element Simulation using SPH Particles as Loading on Typical Light Armoured Vehicles Geneviève Toussaint and Robert Durocher Defence
Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model
 Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model 1 Introduction This tutorial is created to outline the steps required to compute radiated noise from a gearbox housing using Coustyx software. Detailed steps are given on
Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model 1 Introduction This tutorial is created to outline the steps required to compute radiated noise from a gearbox housing using Coustyx software. Detailed steps are given on
Plane Wave Imaging Using Phased Array Arno Volker 1
 11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16409 Plane Wave Imaging Using Phased Array
11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16409 Plane Wave Imaging Using Phased Array
9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING
 TUTORIAL MANUAL 9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a long five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading.
TUTORIAL MANUAL 9 FREE VIBRATION AND EARTHQUAKE ANALYSIS OF A BUILDING This example demonstrates the natural frequency of a long five-storey building when subjected to free vibration and earthquake loading.
Operating vibration analysis in ME scopeves based on ArtemiS SUITE analysis results
 08/17 ME scopeves TM export Operating vibration analysis in ME scopeves based on ArtemiS SUITE analysis results ME scopeves from Vibrant Technology is a software environment for operating vibration analysis
08/17 ME scopeves TM export Operating vibration analysis in ME scopeves based on ArtemiS SUITE analysis results ME scopeves from Vibrant Technology is a software environment for operating vibration analysis
Transducers and Transducer Calibration GENERAL MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
 Transducers and Transducer Calibration Abstracted from: Figliola, R.S. and Beasley, D. S., 1991, Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements GENERAL MEASUREMENT SYSTEM Assigning a specific value to a
Transducers and Transducer Calibration Abstracted from: Figliola, R.S. and Beasley, D. S., 1991, Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements GENERAL MEASUREMENT SYSTEM Assigning a specific value to a
TIME DOMAIN MODELING OF COMPLIANT WORKPIECE MILLING
 TIME DOMAIN MODELING OF COMPLIANT WORKPIECE MILLING Mark A. Rubeo and Tony L. Schmitz Mechanical Engineering and Engineering Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte Charlotte, NC INTRODUCTION
TIME DOMAIN MODELING OF COMPLIANT WORKPIECE MILLING Mark A. Rubeo and Tony L. Schmitz Mechanical Engineering and Engineering Science University of North Carolina at Charlotte Charlotte, NC INTRODUCTION
Vibration Analysis - Ethernet Interface
 LAST UPDATED: 09/19/2018 Vibration Analysis - Ethernet Interface AD0166 Applies to machines built from: January, 1989 Introduction 1. Computer (not included in the kit) 2. Vibration sensor with a magnetic
LAST UPDATED: 09/19/2018 Vibration Analysis - Ethernet Interface AD0166 Applies to machines built from: January, 1989 Introduction 1. Computer (not included in the kit) 2. Vibration sensor with a magnetic
Visual Physics Camera Parallax Lab 1
 In this experiment you will be learning how to locate the camera properly in order to identify and minimize the sources of error that are introduced by parallax and perspective. These sources of error
In this experiment you will be learning how to locate the camera properly in order to identify and minimize the sources of error that are introduced by parallax and perspective. These sources of error
INSTRUCTION MANUAL CALIBRATION EXCITER VE Higashimotomachi, Kokubunji, Tokyo , Japan
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL CALIBRATION EXCITER VE-10 3-20-41 Higashimotomachi, Kokubunji, Tokyo 185-8533, Japan http://www.rion.co.jp/english/ Organization of This Manual This manual describes the features and
INSTRUCTION MANUAL CALIBRATION EXCITER VE-10 3-20-41 Higashimotomachi, Kokubunji, Tokyo 185-8533, Japan http://www.rion.co.jp/english/ Organization of This Manual This manual describes the features and
Comparison Between Scattering Coefficients Determined By Specimen Rotation And By Directivity Correlation
 Comparison Between Scattering Coefficients Determined By Specimen Rotation And By Directivity Correlation Tetsuya Sakuma, Yoshiyuki Kosaka Institute of Environmental Studies, University of Tokyo 7-3-1
Comparison Between Scattering Coefficients Determined By Specimen Rotation And By Directivity Correlation Tetsuya Sakuma, Yoshiyuki Kosaka Institute of Environmental Studies, University of Tokyo 7-3-1
Pulsating flow around a stationary cylinder: An experimental study
 Proceedings of the 3rd IASME/WSEAS Int. Conf. on FLUID DYNAMICS & AERODYNAMICS, Corfu, Greece, August 2-22, 2 (pp24-244) Pulsating flow around a stationary cylinder: An experimental study A. DOUNI & D.
Proceedings of the 3rd IASME/WSEAS Int. Conf. on FLUID DYNAMICS & AERODYNAMICS, Corfu, Greece, August 2-22, 2 (pp24-244) Pulsating flow around a stationary cylinder: An experimental study A. DOUNI & D.
VALIDATION OF SASSI2010 SOLUTION METHODS THROUGH INDEPENDENT VERIFICATION USING SAP2000 FOR DEEPLY EMBEDDED STRUCTURES WITH LARGE FOOTPRINTS
 Transactions, SMiRT-22 VALIDATION OF SASSI2010 SOLUTION METHODS THROUGH INDEPENDENT VERIFICATION USING SAP2000 FOR DEEPLY EMBEDDED STRUCTURES WITH LARGE FOOTPRINTS Lisa M Anderson 1, Tarek Elkhoraibi,
Transactions, SMiRT-22 VALIDATION OF SASSI2010 SOLUTION METHODS THROUGH INDEPENDENT VERIFICATION USING SAP2000 FOR DEEPLY EMBEDDED STRUCTURES WITH LARGE FOOTPRINTS Lisa M Anderson 1, Tarek Elkhoraibi,
Dynamic Characterization of KUKA Light-Weight Robot Manipulators
 Dynamic Characterization of KUKA Light-Weight Robot Manipulators Technical Report GT-RIM-CR-2012-001 Jacob Huckaby and Henrik I. Christensen Center for Robotics & Intelligent Machines Georgia Institute
Dynamic Characterization of KUKA Light-Weight Robot Manipulators Technical Report GT-RIM-CR-2012-001 Jacob Huckaby and Henrik I. Christensen Center for Robotics & Intelligent Machines Georgia Institute
VIBRATION CONTROL REPORT CLEANROOM PHYSICS AND NANOTECHNOLOGY BUILDING UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA MINNEAPOLIS, MINNESOTA
 VIBRATION CONTROL REPORT CLEANROOM PHYSICS AND NANOTECHNOLOGY BUILDING UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA MINNEAPOLIS, MINNESOTA ESI Project 1721 November 15, 2011 (Rev. 2) Prepared for: Ms. Ellen Olson, AIA Architectural
VIBRATION CONTROL REPORT CLEANROOM PHYSICS AND NANOTECHNOLOGY BUILDING UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA MINNEAPOLIS, MINNESOTA ESI Project 1721 November 15, 2011 (Rev. 2) Prepared for: Ms. Ellen Olson, AIA Architectural
Development of a Mover Having One Nanometer Precision and 4mm Moving Range
 Development of a Mover Having One Nanometer Precision and 4mm Moving Range Y. Morita, S. Yamashita International Center for Elementary Particle Physics (ICEPP), University of Tokyo, 7-3-1, Hongo, Bunkyo,
Development of a Mover Having One Nanometer Precision and 4mm Moving Range Y. Morita, S. Yamashita International Center for Elementary Particle Physics (ICEPP), University of Tokyo, 7-3-1, Hongo, Bunkyo,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHAKING TABLE TESTS ON DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF DRY SAND
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHAKING TABLE TESTS ON DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF DRY SAND F. Jafarzadeh 1, D. Faghihi 2 and M. Ehsani 3 1 Assistant Professor, Civil Eng Dept, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SHAKING TABLE TESTS ON DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF DRY SAND F. Jafarzadeh 1, D. Faghihi 2 and M. Ehsani 3 1 Assistant Professor, Civil Eng Dept, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran,
Experimental Dynamic Substructuring of a Catalytic Converter System using the Transmission Simulator Method
 Experimental Dynamic Substructuring of a Catalytic Converter System using the Transmission Simulator Method Matthew S. Allen, Associate Professor Department of Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison
Experimental Dynamic Substructuring of a Catalytic Converter System using the Transmission Simulator Method Matthew S. Allen, Associate Professor Department of Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison
