SL1.Trig.1718.notebook. April 15, /26 End Q3 Pep talk. Fractal Friday: April 6. I want to I will I can I do
|
|
|
- Sylvia Doyle
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Coming up Explorations! A few ideas that I particularly like: Complex quadratics Fractals (complex numbers) Graphing complex roots of quadratics Geometric interpretation of variance etc. Understanding covariance Multiple regression, Galton, Pearson Dot product as correlation! A two variable box & whisker? Test Newton's law of cooling Matrix transformations in animation...many others on website Topic due here Draft due here Final due here Fractal Friday: April 6 I want to I will I can I do Discuss Probability Exams Quick Quiz 2/26 End Q3 Pep talk 1
2 Spring Break Overview 2
3 Right Angle Trig Review Geogebra Sketch to Explore Lots of ways to use these ideas! 2/26Rt Angle Trig Review 3
4 1. Understand and use radian measure 8A: #1ejo,2de,3hij,4cde,5 (Radians) Handout: Right Angle Trig Review Lots of theories about where 360 degrees came from. The Babylonians has a base 60 number system that may have contributed. One version of a Mayan calendar used 20 cycles of 18 days (360) plus 5 unlucky days! The Persian calendar used 360 days for a year. Note the connection to hours, minutes and seconds time was initially measured based on astronomical cycles that were assumed to be circular. Roger Cotes is generally credited with defining a new unit of measure. The radian. It was natural to measure an angle by the length of the arc that it subtends. But that length would be different for different size circles. Unless, of course, you measure the length in "numbers of radii of the given circle". Thus the name "radians". α = 1 radian So how do we convert between the systems? How many radians (radii) are there in a complete circle? Distance around a circle is 2πr so: 360 degrees = 2π radians or 180 degrees = π radians Try a couple: Pay close attention to #5. Look for a recognizable pattern. 8A: #1ejo,2de,3hij,4cde,5 (Radians) Handout: Right Angle Trig Review RightAngleTrigReview.PDF 2/26 8A Radian Measure 4
5 8A: #1ejo,2de,3hij,4cde,5 (Radians) Present as needed: #5 by memory! Handout: Right Angle Trig Review 1. Understand and find arc length & sector area. 8B: #2 12 even (Arcs & Sectors) QB: #3,10,13,20 (Arcs & Sectors) First, some vocabulary Derive a formula from your understanding of circles. Derive a formula from your understanding of circles. 8B: #2 12 even (Arcs & Sectors) QB: #3,10,13,20 (Arcs & Sectors) 2/27 8B Arc Length and Sector Area 5
6 8B: #2 12 even (Arcs & Sectors) Present 6,8,10,12 QB: #3,10,13,20 (Arcs & Sectors) Present all 1. Understand trig functions as locations on the unit circle. 8C: #1b,2 9 (Trig on the unit circle) QB: #27,33,37,77 (Arcs & Sectors) A circle of radius one is one of the most fundamental geometric shapes. It is a very effective visual reference for many ideas involving trigonometry. What is the equation of a unit circle? (Hint: What is a circle?) The set of points equidistant from a center x 2 + y 2 = 1 for a radius of 1 Let's look at a point on the unit circle, located at an angle θ measured from the +x axis. Unit Circle Trig Tracers From this we see some important principles: For a point on the unit circle: These are more general definitions than SOHCAHTOA since they include negative values and angles greater than 90 deg. This is a more general definition of tangent. Notice that if we add 2π radians to any angle, θ, we have taken one full revolution around the circle and end up at the same position. Thus the trig functions are periodic. This is true for adding any integer multiple of 2π radians to θ we are simply revolving around the circle an integer number of times (in either direction!) Mathematically speaking, For θ in radians and k Z, sin(θ + 2πk) = sin(θ) and cos(θ + 2πk) = cos(θ) Tangent is a little different. Because it is a ratio of sin to cosine, it repeats every half revolution: For θ in radians and k Z, tan(θ + πk) = tan(θ) Pay close attention to the results of #2. You will want to use this opportunity to memorize (re memorize?) these results. 8C: #1b,2 9 (Trig on the unit circle) QB: #27,33,37,77 (Arcs & Sectors) 3/1 8C Unit Circle 6
7 Triangle Trig Quiz Thursday A big week Know your angle identities, inverse trig functions, unit circle and Pythagorean Triples 8C: #1b,2 9 (Trig on the unit circle) Present 3,4,5,8,9 QB: #27,33,37,77 (Arcs & Sectors) Questions as needed 1. Work with trig functions on the unit circle. 8D.1: #1 5cd,6 (More Trig on the Unit Circle) 8D.2: #1adg,2adg (Inverse Trig) Summary of trig relationships so far: The Big Kahuna: sin 2 α + cos 2 α = 1 Supplementary Angles: sin(π α) = sinα cos(π α) = cosα tan(π α) = tanα Complementary Angles: sin(π/2 α) = cosα cos(π/2 α) = sinα tan(π/2 α) = cotα Negative Angles: sin( α) = sinα cos( α) = cosα tan( α) = tanα π plus an Angle: sin(π + α) = sinα cos(π + α) = cosα tan(π + α) = tanα π/2 plus an Angle: sin(π/2 + α) = cosα cos(π/2 + α) = sinα tan(π/2 + α) = cotα 2πk plus an Angle (k Z): sin(2πk + α) = sinα cos(2πk + α) = cosα tan(πk + α) = tanα Do not try to remember these. Just know that they exist. When you see these related angles, construct the relationship in your head by visualizing the unit circle! Try some applications: We can use algebra and the unit circle or "directed triangles" 3 θ 2 1. Draw a triangle with the known ratio 2. Use Pythagorus to quickly find the third side 3. Identify the other ratios from the triangle 4. Remember that there are two answers: ± 2 θ 3 Notice that trig functions are not one to one! For example, the sin or cosine of an angle is a single value, but there are two angles between 0 and 2π that have a particular sin or cosine! Pay attention to domain constraints The domain constraint may lead to a single value for your answer. Consider the previous examples What were we given? (the value of a trig function for some angle a ratio) What were we trying to find? (the value(s) of another trig function for the same angle) We made use of the Pythagorean Identity: sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1 It's a huge idea in trig always look for it! Try another one: Pay attention to domain constraints In this example What are we given? (the value of a trig function for some angle) What are we trying to find? (the angle(s) that have the given trig function value) To do this we use the inverse trig function generally on your calculator (ex: sin 1 ) But remember that trig functions are not one to one. For example there are lots of angles ( actually) with a sin of 0.5. Name some: π/6, 13π/6, etc. 5π/6, 17π/6, etc. The full set is: π/6 + 2πk and 5π/6 + 2πk So why do I call it an inverse trig function? Inverse Trig Functions Inverse trig functions are defined only for a limited domain: To find all the angles that satisfy the conditions of the problem, we must do two things: 1. Identify the domain constraints 2. Use the following identities to find all the angles that meet the constraints For θ in radians sin(π θ) = sin(θ) cos(π θ) = cos(θ) cos(2π θ) = cos(θ) You discovered this in your HW from 8C There are lots of these relationships. Understand where they come from so you can reconstruct them as needed. Do not try to memorize these formulas! Let's try one more: 8D.1: #1 5cd,6 (More Trig on the Unit Circle) 8D.2: #1adg,2adg (Inverse Trig) Triangle Trig Quiz Thursday 3/5 8D Applications of Unit Circle 7
8 8D.1: #1 5cd,6 (More Trig on the Unit Circle) Present #1 5 c or d, 6 8D.2: #1adg,2adg (Inverse Trig) Present #1g,2g Mini Quiz: [2] each Triangle Trig Quiz next Time Know your unit circle and Pythagorean Triples 1. Understand the origins of and memorize exact trig function values for common angles. 8E: #1 4,5cfil,6 10 (Common angles) Unit Circle Handout 8F: #1 2 (Equations of lines) Review Set 8C: #1 12 as needed (Review) Find, showing all your work, the exact values for 1. Sin, cos, and tan of 30 and 60 (Hint: Start with an equilateral triangle) 2. Sin, cos, and tan of 45 (Hint: Start with a square) Use the values you found to fill in the unit circle on the handout with the requested information. Keep it for your records. Memorize it. We will have a quick quiz on this next time and a larger quiz on all trig ideas so far on Tuesday. What about triangles that are Pythagorean Triples? They have rational values for all the trig ratios. The quiz on Thursday will require that you memorize the first four prime Pythagorean Triples. They are: Knowing these four triples will save you a huge amount of time as they are so often used. Do any of them have nice (ie. integer) angles? Check on your calculator. Challenge: Find the smallest Pythagorean Triple that has integer values for the angles in a right triangle...or prove that such a triple does not exist. 3/6 8E Common Angles 8
9 1. Recognize and use the tangent as the slope of a line Find the slope of the line shown. Hence, find its equation. b θ Triangle Trig Next Time Know the unit circle and Pythagorean Triples! 8E: #1 4,5cfil,6 10 (Common angles) Unit Circle Handout 8F: #1 2 (Equations of lines) Review Set 8C: #1 12 as needed (Review) 3/6 8F Straight lines 9
10 Return and discuss Quiz on Ch 8 Arc Length, Sector area, unit circle. 1. Understand how use trig to find the area of a triangle from two sides and the included angle. 9A: #1 11 odd (Areas of triangles) We can use trig to calculate the area of a triangle. First, consider the acute triangle below: We know area to be A = ½ha But notice that sinc = h/b so h = b sinc Thus, A = ½ a b sinc We call C the included angle between a and b. What about obtuse triangles? Again A = ½ha But now C is obtuse and our right triangle has an angle of 180 C. We've already seen that sin(180 C) = sin C = h/b so it's still true that h = b sinc And, again, The idea can also be used in reverse to find an angle, given an area and two sides: Notice two possibilities! 9A: #1 11 odd (Areas of triangles) 4/9 9A Area of a Triangle 10
11 9A: #1 11 odd (Areas of triangles) Present 3 11 Mini Quiz: Find the exact shaded area Find area of sector = ½(64)3π/4 = 24π Find area of triangle = ½(64)sin(3π/4) = 32* 2/2 = 16 2 Subtract triangle from sector = 24π 16 2 M1A1 M1A1 M1A1 8 mm 1. Use the cosine rule to find angles and sides of non-right triangles. 9B: #1b,3,5,6c,8a,9 (Cosine Rule) QB: #1 & pick 2 from 4,5,14,17,19 (Cosine Rule) Consider the triangle at right: Note that h can be computed from ΔADC or from ΔBDC Thus h 2 = b 2 x 2 = a 2 (c x) 2 Let's simplify: b 2 x 2 = a 2 (c 2 2cx + x 2 ) b 2 x 2 + (c 2 2cx + x 2 ) = a 2 b 2 x 2 + c 2 2cx + x 2 = a 2 b 2 + c 2 2cx = a 2 But trig tells us that x = bcosa Substitute to get b 2 + c 2 2bccosA = a 2 (Pythagorus) (Definition of cos) The cosine rule The Law of Cosines (Cosine Rule) For a triangle with sides of length a, b, & c whose opposite angles are given by A, B, & C respectively, the following relationships hold: Notice that the angle is the included angle between the two known sides. If the non included angle is given, the situation is ambiguous as the resulting equation will be quadratic, with two potential solutions. Consider: 6 2 = c 2 2(10)c cos30 36 = c 2 20c( ) 0 = c c + 64 So c = or 5.34 The good news is that using the cosine rule will make it clear that there are multiple solutions because the equation will tell you that! Some rearranging gives some other useful forms: The book work is a warm up for the QB problems. Do 6,8 & 9 minimum. Focus on the QB. 9B: #1b,3,5,6c,8a,9 (Cosine Rule) QB: #1 & pick 2 from 4,5,14,17,19 (Cosine Rule) 4/10 9B Cosine Rule 11
12 Folk Art Market July Quiz on Ch 9 Next Thur 4/19 9B: #1b,3,5,6c,8a,9 (Cosine Rule) Present #3,5,9 QB: #1 & pick 2 from 4,5,14,17,19 (Cosine Rule) Present #4,5,14,17,19 1. Use the sine rule to find angles and sides of non-right triangles. 9C.1: #1b,2b (Sine Rule) 9C.2: #1,2b,3,5,8 (Ambiguous Case) QB: #22,39,49,68(3D) (Sine Rule) We have shown that the area of a triangle can be given as: ½ab sinc = ½ac sinb = ½bc sina By multiplying all three expressions by 2 and dividing them all by the product abc we get the sine rule. The Law of Sines (Sine Rule) For a triangle with sides of length a, b, & c whose opposite angles are given by A, B, & C respectively, the following relationships hold: You can use the sine rule to find sides or angles for non right triangles. Some cases are straightforward. 4/12 9C Sine Rule (sides) 12
13 Now draw a triangle with a = 3, b = 5 and A = 30 and solve the triangle using the sine rule. Did you draw this? 3 Did anyone draw this? The Law of Sines gives you exactly the same result! How can this be? The answer lies in the fact that there are two angles < 180 that have a sin of 5/6. One is which your calculator provides. But the other is = So angle B might also be ! Now notice the given angle, 30. If we add it to we end up less than 180 so there is still 180 ( ) = left for angle C. Thus we have a second solution! The Ambiguous Case of the Law of Sines When given two sides and a non included angle, it is possible two have one, two or no solutions to the triangle! You must explore both solutions to sin 1. Using the cosine rule will help! Do more of 1&2 if you need practice. Quiz on Ch 9 next Thur, 4/19 9C.1: #1b,2b (Sine Rule) 9C.2: #1,2b,3,5,8 (Ambiguous Case) QB: #22,39,49,68(3D) (Sine Rule) 4/12 9C Sine Rule Ambiguous Case 13
14 9C.1: #1b,2b (Sine Rule) 9C.2: #1,2b,3,5,8 (Ambiguous Case) QB: #22,39,49,68(3D) (Sine Rule) Present all Present all Quiz on Ch 9 This Thur, Apr Use the sine and cosine rules in context. 2. Review use of bearings and angles of elevation and depression. 9D: #2 16 even (Using Sin & CosRules) or QB: #43,46,53,60,73 (Cosine Rule) QB: #32,50,57 (Sine Rule) In problems involving solving triangles, you have three options: > Try to find right triangles and use definitions > Use the cosine rule > Use the sine rule Often more than one approach can work. Choose the one that is easiest. Bearings: The clockwise angle measured from North. Use other problem solving skills sketches, naming variables, writing down "raw" equations, break the problem into simpler steps, etc. Quiz on Ch 9 This Thur, Apr 19 9D: #2 16 even (Using Sin & CosRules) or QB: #43,46,53,60,73 (Cosine Rule) QB: #32,50,57 (Sine Rule) 4/16 9D: Applications 14
15 Quick Quiz: Given the proportion find the exact value of x, giving your answer in the form x = a + b c where a & b and c 9D: #2 16 even (Using sin & cos rules) Present all Review Set 9C: #1 6 (Review) QB: #43,46,53,60,73 (Cosine Rule) Take Home Quiz Ch 9 Today we will 1. Review and begin our exam. Review Set 9C: #1 6 (Review) QB: #43,46,53,60,73 (Cosine Rule) Take Home Quiz Ch 9 4/9 9D: Applications 15
SL1Trig.notebook April 06, 2013
 Unit plan on website has HW assignments for these chapters. 1 Right Angle Trig - Review Geogebra Sketch to Explore 2 Lots of theories about where 360 degrees came from. The Babylonians has a base 60 number
Unit plan on website has HW assignments for these chapters. 1 Right Angle Trig - Review Geogebra Sketch to Explore 2 Lots of theories about where 360 degrees came from. The Babylonians has a base 60 number
Review of Trigonometry
 Worksheet 8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions Section Review of Trigonometry This section reviews some of the material covered in Worksheets 8, and The reader should be familiar with the trig ratios,
Worksheet 8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions Section Review of Trigonometry This section reviews some of the material covered in Worksheets 8, and The reader should be familiar with the trig ratios,
1. Let be a point on the terminal side of θ. Find the 6 trig functions of θ. (Answers need not be rationalized). b. P 1,3. ( ) c. P 10, 6.
 Q. Right Angle Trigonometry Trigonometry is an integral part of AP calculus. Students must know the basic trig function definitions in terms of opposite, adjacent and hypotenuse as well as the definitions
Q. Right Angle Trigonometry Trigonometry is an integral part of AP calculus. Students must know the basic trig function definitions in terms of opposite, adjacent and hypotenuse as well as the definitions
Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes
 First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. Trigonometry Notes.0 PRE-REQUISITES: SOLVING RIGHT TRIANGLES.1 ANGLES IN STANDARD POSITION 6 Ch..1 HW: p. 83 #1,, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 8. - TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF AN ANGLE
First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. Trigonometry Notes.0 PRE-REQUISITES: SOLVING RIGHT TRIANGLES.1 ANGLES IN STANDARD POSITION 6 Ch..1 HW: p. 83 #1,, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 8. - TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF AN ANGLE
3.0 Trigonometry Review
 3.0 Trigonometry Review In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C. Sides are usually labeled with
3.0 Trigonometry Review In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C. Sides are usually labeled with
Trigonometry. 9.1 Radian and Degree Measure
 Trigonometry 9.1 Radian and Degree Measure Angle Measures I am aware of three ways to measure angles: degrees, radians, and gradians. In all cases, an angle in standard position has its vertex at the origin,
Trigonometry 9.1 Radian and Degree Measure Angle Measures I am aware of three ways to measure angles: degrees, radians, and gradians. In all cases, an angle in standard position has its vertex at the origin,
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY TUTORIAL SOME MORE RULES OF TRIGONOMETRY This is the one of a series of basic tutorials in mathematics aimed at beginners or anyone wanting to refresh themselves
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TRIGONOMETRY TUTORIAL SOME MORE RULES OF TRIGONOMETRY This is the one of a series of basic tutorials in mathematics aimed at beginners or anyone wanting to refresh themselves
Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade
 Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight
Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight
Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade
 Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2014-2015 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to
Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2014-2015 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to
Trigonometric Ratios and Functions
 Algebra 2/Trig Unit 8 Notes Packet Name: Date: Period: # Trigonometric Ratios and Functions (1) Worksheet (Pythagorean Theorem and Special Right Triangles) (2) Worksheet (Special Right Triangles) (3) Page
Algebra 2/Trig Unit 8 Notes Packet Name: Date: Period: # Trigonometric Ratios and Functions (1) Worksheet (Pythagorean Theorem and Special Right Triangles) (2) Worksheet (Special Right Triangles) (3) Page
Mathematics for Computer Graphics. Trigonometry
 Mathematics for Computer Graphics Trigonometry Trigonometry...????? The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. trigonon triangle + metron measure
Mathematics for Computer Graphics Trigonometry Trigonometry...????? The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. trigonon triangle + metron measure
Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study
 Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study Timings Topics Autumn Term - 1 st half (7 weeks - 21 lessons) 1. Algebra 1: Expressions, Formulae, Equations and Inequalities
Chislehurst and Sidcup Grammar School Mathematics Department Year 9 Programme of Study Timings Topics Autumn Term - 1 st half (7 weeks - 21 lessons) 1. Algebra 1: Expressions, Formulae, Equations and Inequalities
Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25
 Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25 First, let s review a little right triangle trigonometry: Imagine a right triangle with one side on the x-axis and one vertex at (0,0). We can write the sin(θ) and
Circular Trigonometry Notes April 24/25 First, let s review a little right triangle trigonometry: Imagine a right triangle with one side on the x-axis and one vertex at (0,0). We can write the sin(θ) and
Unit 2: Trigonometry. This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses.
 Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
A lg e b ra II. Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio
 1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc Length & Area of a Sector
1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e tric F u n c tio 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc Length & Area of a Sector
Trigonometry Summer Assignment
 Name: Trigonometry Summer Assignment Due Date: The beginning of class on September 8, 017. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Trigonometry.
Name: Trigonometry Summer Assignment Due Date: The beginning of class on September 8, 017. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Trigonometry.
Trigonometric ratios provide relationships between the sides and angles of a right angle triangle. The three most commonly used ratios are:
 TRIGONOMETRY TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS If one of the angles of a triangle is 90º (a right angle), the triangle is called a right angled triangle. We indicate the 90º (right) angle by placing a box in its corner.)
TRIGONOMETRY TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS If one of the angles of a triangle is 90º (a right angle), the triangle is called a right angled triangle. We indicate the 90º (right) angle by placing a box in its corner.)
Trigonometry Curriculum Guide Scranton School District Scranton, PA
 Trigonometry Scranton School District Scranton, PA Trigonometry Prerequisite: Algebra II, Geometry, Algebra I Intended Audience: This course is designed for the student who has successfully completed Algebra
Trigonometry Scranton School District Scranton, PA Trigonometry Prerequisite: Algebra II, Geometry, Algebra I Intended Audience: This course is designed for the student who has successfully completed Algebra
Trigonometry and the Unit Circle. Chapter 4
 Trigonometry and the Unit Circle Chapter 4 Topics Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. Develop and apply the equation of the unit circle. Solve
Trigonometry and the Unit Circle Chapter 4 Topics Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, expressed in degrees and radians. Develop and apply the equation of the unit circle. Solve
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the.
 2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
1.6 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation
 wwwck1org Chapter 1 Right Triangles and an Introduction to Trigonometry 16 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation Learning Objectives Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angles
wwwck1org Chapter 1 Right Triangles and an Introduction to Trigonometry 16 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation Learning Objectives Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angles
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 162. Slide 2 / 162. Slide 3 / 162. Trigonometric Functions. Trig Functions
 Slide 1 / 162 Algebra II Slide 2 / 162 Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 162 Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Slide 1 / 162 Algebra II Slide 2 / 162 Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 162 Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Math 144 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle
 1 p 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Math 1 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle We use right triangles to study trigonometry. In right triangles, we have found many relationships between the
1 p 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Math 1 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle We use right triangles to study trigonometry. In right triangles, we have found many relationships between the
Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade)
 Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade) PACING Guide SY 2018-2019 Timeline & Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity
Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade) PACING Guide SY 2018-2019 Timeline & Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity
CCSSM Curriculum Analysis Project Tool 1 Interpreting Functions in Grades 9-12
 Tool 1: Standards for Mathematical ent: Interpreting Functions CCSSM Curriculum Analysis Project Tool 1 Interpreting Functions in Grades 9-12 Name of Reviewer School/District Date Name of Curriculum Materials:
Tool 1: Standards for Mathematical ent: Interpreting Functions CCSSM Curriculum Analysis Project Tool 1 Interpreting Functions in Grades 9-12 Name of Reviewer School/District Date Name of Curriculum Materials:
Pre-calculus Chapter 4 Part 1 NAME: P.
 Pre-calculus NAME: P. Date Day Lesson Assigned Due 2/12 Tuesday 4.3 Pg. 284: Vocab: 1-3. Ex: 1, 2, 7-13, 27-32, 43, 44, 47 a-c, 57, 58, 63-66 (degrees only), 69, 72, 74, 75, 78, 79, 81, 82, 86, 90, 94,
Pre-calculus NAME: P. Date Day Lesson Assigned Due 2/12 Tuesday 4.3 Pg. 284: Vocab: 1-3. Ex: 1, 2, 7-13, 27-32, 43, 44, 47 a-c, 57, 58, 63-66 (degrees only), 69, 72, 74, 75, 78, 79, 81, 82, 86, 90, 94,
Mathematics GCSE 9-1 Curriculum Planner (3 Year Course)
 Mathematics GCSE 9-1 Curriculum Planner (3 Year Course) Year 9 Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 HT 9 1 0 Chapter 1 Calculations Chapter 2 Expressions Ch 1, 2 Test Chapter 3 Angles, polygons Chapter 3 11 12 13 14 15
Mathematics GCSE 9-1 Curriculum Planner (3 Year Course) Year 9 Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 HT 9 1 0 Chapter 1 Calculations Chapter 2 Expressions Ch 1, 2 Test Chapter 3 Angles, polygons Chapter 3 11 12 13 14 15
CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and graphs
 Ch 5. Trigonometry 6. Angles 6. Right triangles 6. Trig funs for general angles 5.: Trigonometric functions and graphs 5.5 Inverse functions CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and
Ch 5. Trigonometry 6. Angles 6. Right triangles 6. Trig funs for general angles 5.: Trigonometric functions and graphs 5.5 Inverse functions CCNY Math Review Chapters 5 and 6: Trigonometric functions and
MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry
 Chapter I THE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry INTRODUCTION The word trigonometry literally means triangle measurement. It is concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides,
Chapter I THE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS MATHEMATICS 105 Plane Trigonometry INTRODUCTION The word trigonometry literally means triangle measurement. It is concerned with the measurement of the parts, sides,
Sec 4.1 Trigonometric Identities Basic Identities. Name: Reciprocal Identities:
 Sec 4. Trigonometric Identities Basic Identities Name: Reciprocal Identities: Quotient Identities: sin csc cos sec csc sin sec cos sin tan cos cos cot sin tan cot cot tan Using the Reciprocal and Quotient
Sec 4. Trigonometric Identities Basic Identities Name: Reciprocal Identities: Quotient Identities: sin csc cos sec csc sin sec cos sin tan cos cos cot sin tan cot cot tan Using the Reciprocal and Quotient
SM 2. Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or
 SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
ROCKWOOD CURRICULUM WRITING PROCESS OVERVIEW
 ROCKWOOD CURRICULUM WRITING PROCESS OVERVIEW Course Content Area Last Update for this Course Trigonometry Mathematics February 2009 Results of Program Evaluation Program Evaluation Recommendations Continue
ROCKWOOD CURRICULUM WRITING PROCESS OVERVIEW Course Content Area Last Update for this Course Trigonometry Mathematics February 2009 Results of Program Evaluation Program Evaluation Recommendations Continue
Common Core Standards Addressed in this Resource
 Common Core Standards Addressed in this Resource N-CN.4 - Represent complex numbers on the complex plane in rectangular and polar form (including real and imaginary numbers), and explain why the rectangular
Common Core Standards Addressed in this Resource N-CN.4 - Represent complex numbers on the complex plane in rectangular and polar form (including real and imaginary numbers), and explain why the rectangular
Algebra II Trigonometric Functions
 Slide 1 / 162 Slide 2 / 162 Algebra II Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 162 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Slide 1 / 162 Slide 2 / 162 Algebra II Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 162 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
MATH EXAM 1 - SPRING 2018 SOLUTION
 MATH 140 - EXAM 1 - SPRING 018 SOLUTION 8 February 018 Instructor: Tom Cuchta Instructions: Show all work, clearly and in order, if you want to get full credit. If you claim something is true you must
MATH 140 - EXAM 1 - SPRING 018 SOLUTION 8 February 018 Instructor: Tom Cuchta Instructions: Show all work, clearly and in order, if you want to get full credit. If you claim something is true you must
Unit 7: Trigonometry Part 1
 100 Unit 7: Trigonometry Part 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Hypotenuse a) Sine sin( α ) = d) Cosecant csc( α ) = α Adjacent Opposite b) Cosine cos( α ) = e) Secant sec( α ) = c) Tangent f) Cotangent tan(
100 Unit 7: Trigonometry Part 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Hypotenuse a) Sine sin( α ) = d) Cosecant csc( α ) = α Adjacent Opposite b) Cosine cos( α ) = e) Secant sec( α ) = c) Tangent f) Cotangent tan(
Chapter 5. An Introduction to Trigonometric Functions 1-1
 Chapter 5 An Introduction to Trigonometric Functions Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1-1 5.1 A half line or all points extended from a single
Chapter 5 An Introduction to Trigonometric Functions Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1-1 5.1 A half line or all points extended from a single
Monica, Maeve, John, Luke, Lewis & Viraj TRIGONOMETRY AND GEOMETRY
 Monica, Maeve, John, Luke, Lewis & Viraj TRIGONOMETRY AND GEOMETRY Essential Knowledge: Understand and apply the unit circle definitions of the trig. functions and use the unit circle to find function
Monica, Maeve, John, Luke, Lewis & Viraj TRIGONOMETRY AND GEOMETRY Essential Knowledge: Understand and apply the unit circle definitions of the trig. functions and use the unit circle to find function
and how to label right triangles:
 Grade 9 IGCSE A1: Chapter 6 Trigonometry Items you need at some point in the unit of study: Graph Paper Exercise 2&3: Solving Right Triangles using Trigonometry Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics
Grade 9 IGCSE A1: Chapter 6 Trigonometry Items you need at some point in the unit of study: Graph Paper Exercise 2&3: Solving Right Triangles using Trigonometry Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics
Math for Geometric Optics
 Algebra skills Math for Geometric Optics general rules some common types of equations units problems with several variables (substitution) Geometry basics Trigonometry Pythagorean theorem definitions,
Algebra skills Math for Geometric Optics general rules some common types of equations units problems with several variables (substitution) Geometry basics Trigonometry Pythagorean theorem definitions,
Polar Coordinates. 2, π and ( )
 Polar Coordinates Up to this point we ve dealt exclusively with the Cartesian (or Rectangular, or x-y) coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is not always the easiest coordinate system to work
Polar Coordinates Up to this point we ve dealt exclusively with the Cartesian (or Rectangular, or x-y) coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is not always the easiest coordinate system to work
Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1
 Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1 Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before. Strategy
Pre Calculus Worksheet: Fundamental Identities Day 1 Use the indicated strategy from your notes to simplify each expression. Each section may use the indicated strategy AND those strategies before. Strategy
Chapter 2 Trigonometry
 Chapter 2 Trigonometry 1 Chapter 2 Trigonometry Angles in Standard Position Angles in Standard Position Any angle may be viewed as the rotation of a ray about its endpoint. The starting position of the
Chapter 2 Trigonometry 1 Chapter 2 Trigonometry Angles in Standard Position Angles in Standard Position Any angle may be viewed as the rotation of a ray about its endpoint. The starting position of the
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 92. Slide 2 / 92. Slide 3 / 92. Trigonometry of the Triangle. Trig Functions
 Slide 1 / 92 Algebra II Slide 2 / 92 Trigonometry of the Triangle 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 92 Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse
Slide 1 / 92 Algebra II Slide 2 / 92 Trigonometry of the Triangle 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 92 Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse
MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review. Fall 2017
 MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review Fall 2017 Topics Covered Section 4.1: Angles and Their Measure Section 4.2: Trigonometric Functions Defined on the Unit Circle Section 4.3: Right Triangle Geometry Section 4.4:
MATH 1113 Exam 3 Review Fall 2017 Topics Covered Section 4.1: Angles and Their Measure Section 4.2: Trigonometric Functions Defined on the Unit Circle Section 4.3: Right Triangle Geometry Section 4.4:
Cecil Jones Academy Mathematics Fundamentals
 Year 10 Fundamentals Core Knowledge Unit 1 Unit 2 Estimate with powers and roots Calculate with powers and roots Explore the impact of rounding Investigate similar triangles Explore trigonometry in right-angled
Year 10 Fundamentals Core Knowledge Unit 1 Unit 2 Estimate with powers and roots Calculate with powers and roots Explore the impact of rounding Investigate similar triangles Explore trigonometry in right-angled
GCSE-AS Mathematics Bridging Course. Chellaston School. Dr P. Leary (KS5 Coordinator) Monday Objectives. The Equation of a Line.
 GCSE-AS Mathematics Bridging Course Chellaston School Dr (KS5 Coordinator) Monday Objectives The Equation of a Line Surds Linear Simultaneous Equations Tuesday Objectives Factorising Quadratics & Equations
GCSE-AS Mathematics Bridging Course Chellaston School Dr (KS5 Coordinator) Monday Objectives The Equation of a Line Surds Linear Simultaneous Equations Tuesday Objectives Factorising Quadratics & Equations
Unit 3 Higher topic list
 This is a comprehensive list of the topics to be studied for the Edexcel unit 3 modular exam. Beside the topics listed are the relevant tasks on www.mymaths.co.uk that students can use to practice. Logon
This is a comprehensive list of the topics to be studied for the Edexcel unit 3 modular exam. Beside the topics listed are the relevant tasks on www.mymaths.co.uk that students can use to practice. Logon
Important. Compact Trigonometry CSO Prioritized Curriculum. Essential. Page 1 of 6
 Essential Important Compact Trigonometry CSO Prioritized Curriculum M.O.T.3.1 apply the right triangle definition of the six trigonometric functions of an angle to determine the values of the function
Essential Important Compact Trigonometry CSO Prioritized Curriculum M.O.T.3.1 apply the right triangle definition of the six trigonometric functions of an angle to determine the values of the function
by Kevin M. Chevalier
 Precalculus Review Handout.4 Trigonometric Functions: Identities, Graphs, and Equations, Part I by Kevin M. Chevalier Angles, Degree and Radian Measures An angle is composed of: an initial ray (side) -
Precalculus Review Handout.4 Trigonometric Functions: Identities, Graphs, and Equations, Part I by Kevin M. Chevalier Angles, Degree and Radian Measures An angle is composed of: an initial ray (side) -
Chapter 4: Trigonometry
 Chapter 4: Trigonometry Section 4-1: Radian and Degree Measure INTRODUCTION An angle is determined by rotating a ray about its endpoint. The starting position of the ray is the of the angle, and the position
Chapter 4: Trigonometry Section 4-1: Radian and Degree Measure INTRODUCTION An angle is determined by rotating a ray about its endpoint. The starting position of the ray is the of the angle, and the position
Parallel Lines Investigation
 Year 9 - The Maths Knowledge Autumn 1 (x, y) Along the corridor, up the stairs (3,1) x = 3 Gradient (-5,-2) (0,0) y-intercept Vertical lines are always x = y = 6 Horizontal lines are always y = Parallel
Year 9 - The Maths Knowledge Autumn 1 (x, y) Along the corridor, up the stairs (3,1) x = 3 Gradient (-5,-2) (0,0) y-intercept Vertical lines are always x = y = 6 Horizontal lines are always y = Parallel
Solving Trigonometric Equations
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49398 1 Solving Trigonometric Equations OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m49398 1 Solving Trigonometric Equations OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you
ES302 Class Notes Trigonometric Applications in Geologic Problem Solving (updated Spring 2016)
 ES302 Class Notes Trigonometric Applications in Geologic Problem Solving (updated Spring 2016) I. Introduction a) Trigonometry study of angles and triangles i) Intersecting Lines (1) Points of intersection
ES302 Class Notes Trigonometric Applications in Geologic Problem Solving (updated Spring 2016) I. Introduction a) Trigonometry study of angles and triangles i) Intersecting Lines (1) Points of intersection
A lg e b ra II. Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le
 1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse Trig Functions Problem
1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse Trig Functions Problem
1. The Pythagorean Theorem
 . The Pythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean theorem states that in any right triangle, the sum of the squares of the side lengths is the square of the hypotenuse length. c 2 = a 2 b 2 This theorem can be
. The Pythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean theorem states that in any right triangle, the sum of the squares of the side lengths is the square of the hypotenuse length. c 2 = a 2 b 2 This theorem can be
4.1: Angles & Angle Measure
 4.1: Angles & Angle Measure In Trigonometry, we use degrees to measure angles in triangles. However, degree is not user friendly in many situations (just as % is not user friendly unless we change it into
4.1: Angles & Angle Measure In Trigonometry, we use degrees to measure angles in triangles. However, degree is not user friendly in many situations (just as % is not user friendly unless we change it into
Today we will focus on solving for the sides and angles of non-right triangles when given two angles and a side.
 5.5 The Law of Sines Pre-Calculus. Use the Law of Sines to solve non-right triangles. Today we will focus on solving for the sides and angles of non-right triangles when given two angles and a side. Derivation:
5.5 The Law of Sines Pre-Calculus. Use the Law of Sines to solve non-right triangles. Today we will focus on solving for the sides and angles of non-right triangles when given two angles and a side. Derivation:
Warm Up: please factor completely
 Warm Up: please factor completely 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. vocabulary KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED: MA3A2. Students will use the circle to define the trigonometric functions. a. Define and understand angles measured
Warm Up: please factor completely 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. vocabulary KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED: MA3A2. Students will use the circle to define the trigonometric functions. a. Define and understand angles measured
You ll use the six trigonometric functions of an angle to do this. In some cases, you will be able to use properties of the = 46
 Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Math-2 Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -2)
 Math- Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -) Trigonometric Functions sin cos A A SOH-CAH-TOA Some old horse caught another horse taking oats away. opposite ( length ) o sin A hypotenuse ( length ) h SOH adjacent
Math- Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -) Trigonometric Functions sin cos A A SOH-CAH-TOA Some old horse caught another horse taking oats away. opposite ( length ) o sin A hypotenuse ( length ) h SOH adjacent
5.1 Angles & Their Measures. Measurement of angle is amount of rotation from initial side to terminal side. radians = 60 degrees
 .1 Angles & Their Measures An angle is determined by rotating array at its endpoint. Starting side is initial ending side is terminal Endpoint of ray is the vertex of angle. Origin = vertex Standard Position:
.1 Angles & Their Measures An angle is determined by rotating array at its endpoint. Starting side is initial ending side is terminal Endpoint of ray is the vertex of angle. Origin = vertex Standard Position:
Geometry. AIR Study Guide
 Geometry AIR Study Guide Table of Contents Topic Slide Formulas 3 5 Angles 6 Lines and Slope 7 Transformations 8 Constructions 9 10 Triangles 11 Congruency and Similarity 12 Right Triangles Only 13 Other
Geometry AIR Study Guide Table of Contents Topic Slide Formulas 3 5 Angles 6 Lines and Slope 7 Transformations 8 Constructions 9 10 Triangles 11 Congruency and Similarity 12 Right Triangles Only 13 Other
Related Angles WS # 6.1. Co-Related Angles WS # 6.2. Solving Linear Trigonometric Equations Linear
 UNIT 6 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES AND EQUATIONS Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework 13 6.1 (60) 7.1 Related Angles WS # 6.1 15 6. (61) 7.1 Co-Related Angles WS # 6. 16 6.3 (63) 7. Compound Angle Formulas I Sine
UNIT 6 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES AND EQUATIONS Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework 13 6.1 (60) 7.1 Related Angles WS # 6.1 15 6. (61) 7.1 Co-Related Angles WS # 6. 16 6.3 (63) 7. Compound Angle Formulas I Sine
MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY
 MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY SECTION PAGE NUMBERS HOMEWORK Prerequisite p. 0 - # 3 Skills 4. p. 8-9 #4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,, 4. p. 37 39 #bde, acd, 3, 4acde, 5, 6ace, 7, 8, 9, 0,, 4.3 p. 46-47 #aef,, 3, 4, 5defgh,
MCR3U UNIT #6: TRIGONOMETRY SECTION PAGE NUMBERS HOMEWORK Prerequisite p. 0 - # 3 Skills 4. p. 8-9 #4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,, 4. p. 37 39 #bde, acd, 3, 4acde, 5, 6ace, 7, 8, 9, 0,, 4.3 p. 46-47 #aef,, 3, 4, 5defgh,
Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions (Trigonometry)
 Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions (Trigonometry) SSMTH1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions Lecture 8.1: Basic
Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions (Trigonometry) SSMTH1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 8.1: Circular Functions Lecture 8.1: Basic
A-C Valley Junior-Senior High School
 Course of Study A-C Valley Junior-Senior High School Page 1 of 12 Applied Trigonometry (NAME OF COURSE) GRADE LEVEL(S): 11 Educational Curriculum Level Person(s) Revising Curriculum (List Names) 1. Junior-Senior
Course of Study A-C Valley Junior-Senior High School Page 1 of 12 Applied Trigonometry (NAME OF COURSE) GRADE LEVEL(S): 11 Educational Curriculum Level Person(s) Revising Curriculum (List Names) 1. Junior-Senior
A trigonometric ratio is a,
 ALGEBRA II Chapter 13 Notes The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. Section 13.1 Right-Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: 1. Find the trigonometric
ALGEBRA II Chapter 13 Notes The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. Section 13.1 Right-Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: 1. Find the trigonometric
Extended Mathematics for Cambridge IGCSE by David Rayner. Chapter 1. Identify and use rational and irrational numbers, real numbers.
 Schemes of Work Overview Structure There are two separate schemes of work laid out in the following units, one for students following the Core Curriculum and one for students following the Extended Curriculum.
Schemes of Work Overview Structure There are two separate schemes of work laid out in the following units, one for students following the Core Curriculum and one for students following the Extended Curriculum.
MADANI BOYS SCHOOL GCSE Maths Scheme of Work for Higher sets. OVERVIEW for Higher sets
 OVERVIEW for Higher sets Chapter Teaching hours Grades UNIT 1: Statistics and Number 1. Data collection 4 D, C, A, Modular topics The data handling cycle, Gathering information, Types of data, Grouped
OVERVIEW for Higher sets Chapter Teaching hours Grades UNIT 1: Statistics and Number 1. Data collection 4 D, C, A, Modular topics The data handling cycle, Gathering information, Types of data, Grouped
Math 26: Fall (part 1) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pythagorean Identity)
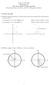 Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
1 Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1 Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.1 Radian and Degree Measure Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Describe angles. Use radian measure. Use degree
1 Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.1 Radian and Degree Measure Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Describe angles. Use radian measure. Use degree
Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work
 Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work Module 1 - Integers and Decimals Understand and order integers (assumed) Use brackets and hierarchy of operations (BODMAS) Add, subtract, multiply and divide
Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work Module 1 - Integers and Decimals Understand and order integers (assumed) Use brackets and hierarchy of operations (BODMAS) Add, subtract, multiply and divide
Mathematics Year 9-11 Skills and Knowledge Checklist. Name: Class: Set : Premier Date Year 9 MEG :
 Personal targets to help me achieve my grade : AFL Sheet Number 1 : Standard Form, Decimals, Fractions and Percentages Standard Form I can write a number as a product of it s prime factors I can use the
Personal targets to help me achieve my grade : AFL Sheet Number 1 : Standard Form, Decimals, Fractions and Percentages Standard Form I can write a number as a product of it s prime factors I can use the
Chapter 4/5 Part 1- Trigonometry in Radians
 Chapter 4/5 Part - Trigonometry in Radians Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to demonstrate an understanding of meaning and application
Chapter 4/5 Part - Trigonometry in Radians Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to demonstrate an understanding of meaning and application
KS4 Curriculum Plan Maths HIGHER TIER Year 9 Autumn Term 1 Unit 1: Number
 KS4 Curriculum Plan Maths HIGHER TIER Year 9 Autumn Term 1 Unit 1: Number 1.1 Number problems and reasoning 1.2 Place value and estimating 1.3 HCF and LCM 1.4 Calculating with powers (indices) 1.5 Zero,
KS4 Curriculum Plan Maths HIGHER TIER Year 9 Autumn Term 1 Unit 1: Number 1.1 Number problems and reasoning 1.2 Place value and estimating 1.3 HCF and LCM 1.4 Calculating with powers (indices) 1.5 Zero,
FURTHER MATHS. WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL
 FURTHER MATHS WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL This two-year Edexcel Pearson syllabus is intended for high ability candidates who have achieved, or are likely to
FURTHER MATHS WELCOME TO A Level FURTHER MATHEMATICS AT CARDINAL NEWMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOL This two-year Edexcel Pearson syllabus is intended for high ability candidates who have achieved, or are likely to
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ АГЕНТСТВО ПО ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования
 ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ АГЕНТСТВО ПО ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования «ТОМСКИЙ ПОЛИТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ» V.V. Konev MATHEMATICS PREPARATORY COURSE: TRIGONOMETRY
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ АГЕНТСТВО ПО ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования «ТОМСКИЙ ПОЛИТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ» V.V. Konev MATHEMATICS PREPARATORY COURSE: TRIGONOMETRY
Triangle Trigonometry
 Honors Finite/Brief: Trigonometry review notes packet Triangle Trigonometry Right Triangles All triangles (including non-right triangles) Law of Sines: a b c sin A sin B sin C Law of Cosines: a b c bccos
Honors Finite/Brief: Trigonometry review notes packet Triangle Trigonometry Right Triangles All triangles (including non-right triangles) Law of Sines: a b c sin A sin B sin C Law of Cosines: a b c bccos
sin30 = sin60 = cos30 = cos60 = tan30 = tan60 =
 Precalculus Notes Trig-Day 1 x Right Triangle 5 How do we find the hypotenuse? 1 sinθ = cosθ = tanθ = Reciprocals: Hint: Every function pair has a co in it. sinθ = cscθ = sinθ = cscθ = cosθ = secθ = cosθ
Precalculus Notes Trig-Day 1 x Right Triangle 5 How do we find the hypotenuse? 1 sinθ = cosθ = tanθ = Reciprocals: Hint: Every function pair has a co in it. sinθ = cscθ = sinθ = cscθ = cosθ = secθ = cosθ
: Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for θ. Special Right Triangles:
 ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER 13 NOTES Section 13-1 Right Triangle Trig Understand and use trigonometric relationships of acute angles in triangles. 12.F.TF.3 CC.9- Determine side lengths of right triangles by using
ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER 13 NOTES Section 13-1 Right Triangle Trig Understand and use trigonometric relationships of acute angles in triangles. 12.F.TF.3 CC.9- Determine side lengths of right triangles by using
HW. Pg. 334 #1-9, 11, 12 WS. A/ Angles in Standard Position: Terminology: Initial Arm. Terminal Arm. Co-Terminal Angles. Quadrants
 MCR 3UI Introduction to Trig Functions Date: Lesson 6.1 A/ Angles in Standard Position: Terminology: Initial Arm HW. Pg. 334 #1-9, 11, 1 WS Terminal Arm Co-Terminal Angles Quadrants Related Acute Angles
MCR 3UI Introduction to Trig Functions Date: Lesson 6.1 A/ Angles in Standard Position: Terminology: Initial Arm HW. Pg. 334 #1-9, 11, 1 WS Terminal Arm Co-Terminal Angles Quadrants Related Acute Angles
GCSE Maths: Formulae you ll need to know not
 GCSE Maths: Formulae you ll need to know As provided by AQA, these are the formulae required for the new GCSE These will not be given in the exam, so you will need to recall as well as use these formulae.
GCSE Maths: Formulae you ll need to know As provided by AQA, these are the formulae required for the new GCSE These will not be given in the exam, so you will need to recall as well as use these formulae.
Definitions Associated w/ Angles Notation Visualization Angle Two rays with a common endpoint ABC
 Preface to Chapter 5 The following are some definitions that I think will help in the acquisition of the material in the first few chapters that we will be studying. I will not go over these in class and
Preface to Chapter 5 The following are some definitions that I think will help in the acquisition of the material in the first few chapters that we will be studying. I will not go over these in class and
Mathematics GCSE 9 1 Higher Syllabus. Yes. Does the subject set according to ability? Skills Covered. Unit
 Mathematics GCSE 9 1 Higher Syllabus Does the subject set according to ability? Unit Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Yes Skills Covered understand and apply place value correctly. estimate values including
Mathematics GCSE 9 1 Higher Syllabus Does the subject set according to ability? Unit Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Yes Skills Covered understand and apply place value correctly. estimate values including
Integrated Algebra 2 and Trigonometry. Quarter 1
 Quarter 1 I: Functions: Composition I.1 (A.42) Composition of linear functions f(g(x)). f(x) + g(x). I.2 (A.42) Composition of linear and quadratic functions II: Functions: Quadratic II.1 Parabola The
Quarter 1 I: Functions: Composition I.1 (A.42) Composition of linear functions f(g(x)). f(x) + g(x). I.2 (A.42) Composition of linear and quadratic functions II: Functions: Quadratic II.1 Parabola The
To be a grade 1 I need to
 To be a grade 1 I need to Order positive and negative integers Understand addition and subtraction of whole numbers and decimals Apply the four operations in correct order to integers and proper fractions
To be a grade 1 I need to Order positive and negative integers Understand addition and subtraction of whole numbers and decimals Apply the four operations in correct order to integers and proper fractions
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse
 7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
Cambridge IGCSE mapping
 Cambridge IGCSE mapping Specification point Boardworks presentation 1. Number, set notation and language Identify and use natural numbers, integers (positive, negative and zero), prime numbers, square
Cambridge IGCSE mapping Specification point Boardworks presentation 1. Number, set notation and language Identify and use natural numbers, integers (positive, negative and zero), prime numbers, square
CW High School. Advanced Math A. 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph.
 1. Functions and Math Models (10.00%) 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph. 4 Pro cient I can make connections between the algebraic
1. Functions and Math Models (10.00%) 1.1 I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description for a function, its name, and its graph. 4 Pro cient I can make connections between the algebraic
PRECALCULUS MATH Trigonometry 9-12
 1. Find angle measurements in degrees and radians based on the unit circle. 1. Students understand the notion of angle and how to measure it, both in degrees and radians. They can convert between degrees
1. Find angle measurements in degrees and radians based on the unit circle. 1. Students understand the notion of angle and how to measure it, both in degrees and radians. They can convert between degrees
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester Lecture 33 Notes
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 33 Notes These notes correspond to Section 9.3 in the text. Polar Coordinates Throughout this course, we have denoted a point in the plane by an ordered
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 33 Notes These notes correspond to Section 9.3 in the text. Polar Coordinates Throughout this course, we have denoted a point in the plane by an ordered
Assumption High School BELL WORK. Academic institution promoting High expectations resulting in Successful students
 BELL WORK Geometry 2016 2017 Day 52 Topic: Assessment 2.1 Chapter 8.1 8.4 Chapter 8 Big Ideas Measurement Some attributes of geometric figures, such as length, area, volume, and angle measure, are measurable.
BELL WORK Geometry 2016 2017 Day 52 Topic: Assessment 2.1 Chapter 8.1 8.4 Chapter 8 Big Ideas Measurement Some attributes of geometric figures, such as length, area, volume, and angle measure, are measurable.
Year 10 Term 3 Homework
 Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 3 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Year 10 Term 3 Week 3 Homework 1 3.1 Further trigonometry................................... 1 3.1.1 Trigonometric
Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 3 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Year 10 Term 3 Week 3 Homework 1 3.1 Further trigonometry................................... 1 3.1.1 Trigonometric
Basics of Computational Geometry
 Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
MA 154 Lesson 1 Delworth
 DEFINITIONS: An angle is defined as the set of points determined by two rays, or half-lines, l 1 and l having the same end point O. An angle can also be considered as two finite line segments with a common
DEFINITIONS: An angle is defined as the set of points determined by two rays, or half-lines, l 1 and l having the same end point O. An angle can also be considered as two finite line segments with a common
Mathematics Year 9-11 Skills and Knowledge Checklist. Name: Class: Set : 1 Date Year 9 MEG :
 Personal targets to help me achieve my grade : AFL Sheet Number 1 : Standard Form, Decimals, Fractions and Percentages Standard Form I can write a number as a product of it s prime factors I can use the
Personal targets to help me achieve my grade : AFL Sheet Number 1 : Standard Form, Decimals, Fractions and Percentages Standard Form I can write a number as a product of it s prime factors I can use the
Name Trigonometric Functions 4.2H
 TE-31 Name Trigonometric Functions 4.H Ready, Set, Go! Ready Topic: Even and odd functions The graphs of even and odd functions make it easy to identify the type of function. Even functions have a line
TE-31 Name Trigonometric Functions 4.H Ready, Set, Go! Ready Topic: Even and odd functions The graphs of even and odd functions make it easy to identify the type of function. Even functions have a line
CLEP Pre-Calculus. Section 1: Time 30 Minutes 50 Questions. 1. According to the tables for f(x) and g(x) below, what is the value of [f + g]( 1)?
? CLEP Pre-Calculus. Section 1: Time 30 Minutes 50 Questions. 1. According to the tables for f(x) and g(x) below, what is the value of [f + g]( 1)?](/thumbs/72/67898377.jpg) CLEP Pre-Calculus Section : Time 0 Minutes 50 Questions For each question below, choose the best answer from the choices given. An online graphing calculator (non-cas) is allowed to be used for this section..
CLEP Pre-Calculus Section : Time 0 Minutes 50 Questions For each question below, choose the best answer from the choices given. An online graphing calculator (non-cas) is allowed to be used for this section..
Year Term Week Chapter Ref Lesson 18.1 Cubic and reciprocal functions. 18 Graphs 2. (Algebra) 18.4 Gradients and areas under graphs
 Year Term Week Chapter Ref Lesson 18.1 Cubic and reciprocal functions Year 3 Autumn Term 1-2 3-4 18 Graphs 2 (Algebra) 18.2 Exponential and trigonometric functions 18.3 Real-life graphs 18.4 Gradients
Year Term Week Chapter Ref Lesson 18.1 Cubic and reciprocal functions Year 3 Autumn Term 1-2 3-4 18 Graphs 2 (Algebra) 18.2 Exponential and trigonometric functions 18.3 Real-life graphs 18.4 Gradients
