CSE 130 : Fall Programming Languages. Lecture 11: Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego. programming
|
|
|
- Rafe Ryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 130 : Fall 2009 Programming Languages News Lecture 11: Hello Python Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego What s the point of all this? Final words on functional programming g
2 Advantages of functional progs Functional programming more concise one line of lisp can replace 20 lines of C (quote from Recall reverse function: let reverse = fold (::) [];; How many lines in C, C++? Better reasoning about Programs No side effects Same inputs return same outputs So, can safely reorder computations So, can also parallelize computations An example: Map/Reduce Scalable data processing: MapReduce programming model Hadoop [Yahoo], Hive [Facebook], Dryad [MSR] Programming model based on map, fold apply a function on each data element (map) aggregate the results (fold) Functional easy parallelism scalable So what? Form the authors: Inspired by similar primitives in LISP and other languages g p p p Programmers who only know Java/C/C++ would probably not have come up with this idea For more, take Prof. Vahdat s CSE 124
3 Remember Say hello to Python Free your mind -Morpheus Recap of the course so far 4+ weeks of functional with OCaml Next: 3 weeks of OO with Python OO at the highest level What is OO programming?
4 OO at the highest level What is OO programming? Answer: Objects message sends dynamic dispatch Just to whet your appetite Say we have objects, like cars, ducks, pig, cell_phones Say we have a message name: make_some_noise Just to whet your appetite Each object has its own implementation for make_some_noise: these are traditionally called methods. Oh btw... What s the difference between message What s the difference between message and method... car: vroom vroom, pig : oink oink, duck: quack quack Can send make_some_noise to any object. Depending on the actually run-time object, we ll get a different noise!
5 Oh btw... What s the difference between message and method... Message is just the name of the message, method is the implementation ti Message is the interface / prototype of the method. OO programming Message: the name of an operation Method: the implementation of an operation Dynamic dispatch: dynamic type of object determines which method is run for given message send These are the core ideas of OO This brings us to Python... OCaml/Python comparison We ll use Python as our vehicle for OO programming Fun and useful language Let s compare with OCaml along some of the dimensions we saw last time PL paradigm Basic unit Types DataModel ML Pth Python
6 Python Python has a very relaxed philosophy if something "can be done" then it is allowed. Dynamic types + Everything is an object very flexible very intuitive code No static types No static type system to "prohibit" operations. No more of the compiler giving you tricky error messages! No static types: but what instead? Dynamic typing At runtime, every "operation" is translated to a method call on the appropriate object. If the object supports the method, then the computation proceeds. Duck-typing: if it looks like a duck, quacks like a duck, then it is a duck! Dynamic typing This loose, comfortable, free-style style, philosophy is at the heart of python. But... beware, you can get burned with this flexibility... Q: how many times did OCaml complain to you statically about something that was NOT a bug?
7 Similarities to ML Uniform model everything is an object, including functions Pass functions around functions are objects! Supports functional programming map and fold Other cool things about Python A lot of stuff that you may first think is a "language feature" is actually just translated under the hood to a method call... Very widely used, supported. Has libraries for all sorts of things. Ok, let s start playing with Python! Like Perl, python is a "managed" or "interpreted" language that runs under the python environment, i.e. not compiled to machine code. Makes it convenient to rapidly write, check-in and test t code! Ways to run Python code At an interactive Python prompt like "read-eval-print" loop of ML As shell scripts As stand-alone programs run from the shell.
8 Let s fire it up! Ok, let s give it a try... See lec11.py file for the rest...
Key components of a lang. Deconstructing OCaml. In OCaml. Units of computation. In Java/Python. In OCaml. Units of computation.
 Key components of a lang Deconstructing OCaml What makes up a language Units of computation Types Memory model In OCaml Units of computation In OCaml In Java/Python Expressions that evaluate to values
Key components of a lang Deconstructing OCaml What makes up a language Units of computation Types Memory model In OCaml Units of computation In OCaml In Java/Python Expressions that evaluate to values
Back to OCaml. Summary of polymorphism. Example 1. Type inference. Example 2. Example 2. Subtype. Polymorphic types allow us to reuse code.
 Summary of polymorphism Subtype Parametric Bounded F-bounded Back to OCaml Polymorphic types allow us to reuse code However, not always obvious from staring at code But... Types never entered w/ program!
Summary of polymorphism Subtype Parametric Bounded F-bounded Back to OCaml Polymorphic types allow us to reuse code However, not always obvious from staring at code But... Types never entered w/ program!
Monday Feb 16, 5pm. solve these equalities. Midterm Thursday Feb 12. covers only ocaml part of the course, assignments 1 through 3.
 News Programming Assignment 4 is up, due Monday Feb 16, 5pm Long assignment, start early Midterm Thursday Feb 12 covers only ocaml part of the course, assignments 1 through 3. Recap: Inferring types Introduce
News Programming Assignment 4 is up, due Monday Feb 16, 5pm Long assignment, start early Midterm Thursday Feb 12 covers only ocaml part of the course, assignments 1 through 3. Recap: Inferring types Introduce
Hi! My name is Sorin. Programming Languages. Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? Course Goals. CSE : Fall 2017
 Hi! My name is Sorin CSE 130-230 : Fall 2017 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
Hi! My name is Sorin CSE 130-230 : Fall 2017 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
Hi! My name is Sorin. Programming Languages. Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? Course Goals. CSE 130 : Fall 2013
 Hi! My name is Sorin CSE 130 : Fall 2013 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
Hi! My name is Sorin CSE 130 : Fall 2013 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2013 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Hi! My name is Sorin Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
CSE 130 : Fall 2013 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Hi! My name is Sorin Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2016 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Hi! My name is Sorin Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
CSE 130 : Fall 2016 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Hi! My name is Sorin Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
Hi! My name is Sorin. Programming Languages. Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? Course Goals. CSE 130 : Fall 2014
 Hi! My name is Sorin CSE 130 : Fall 2014 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
Hi! My name is Sorin CSE 130 : Fall 2014 Programming Languages Sorin Lerner UC San Diego Why study PL? (discussion) Why study PL? A different language is a different vision of life - Fellini - Hypothesis:
A Programming Language. A different language g is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Fall Two variables. L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1 L2:
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1 L2:
News. Programming Languages. Recap. Recap: Environments. Functions. of functions: Closures. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes
 CSE 130 : Fall 2007 Programming Languages News PA deadlines shifted PA #2 now due 10/24 (next Wed) Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables
CSE 130 : Fall 2007 Programming Languages News PA deadlines shifted PA #2 now due 10/24 (next Wed) Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables
A Programming Language. A different language g is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Spring Two variables. L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?
 CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1
CSE 130 : Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, world. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language Two variables x,y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--; (y=0)?l2:l1
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 13: Whats in a name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego f = open( foo.txt, read ) f.readlines() for l in f.readlines(): f.close ou now know enough to do PA5
CSE 130 : Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 13: Whats in a name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego f = open( foo.txt, read ) f.readlines() for l in f.readlines(): f.close ou now know enough to do PA5
Next: What s in a name? Programming Languages. Data model in functional PL. What s in a name? CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 13: What s in a Name?
 Next: What s in a name? CSE 13 : Fall 211 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really mean? Ranjit Jhala UC San
Next: What s in a name? CSE 13 : Fall 211 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really mean? Ranjit Jhala UC San
Recap from last time. Programming Languages. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 3: Data Types. Put it together: a filter function
 CSE 130 : Fall 2011 Recap from last time Programming Languages Lecture 3: Data Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 2 A shorthand for function binding Put it together: a filter function # let neg = fun f
CSE 130 : Fall 2011 Recap from last time Programming Languages Lecture 3: Data Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 2 A shorthand for function binding Put it together: a filter function # let neg = fun f
Programming Languages. So why study PL? A Programming Language. A different language is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Spring 2015
 CSE 130 : Spring 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++;
CSE 130 : Spring 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++;
Programming Languages. So why study PL? A Programming Language. A different language is a different vision of life. CSE 130 : Fall 2015
 CSE 130 : Fall 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World! Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--;
CSE 130 : Fall 2015 Programming Languages Lecture 1: Hello, World! Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A Programming Language So why study PL? Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- (x=0)? L1:L2; L1: x++; y--;
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Datatypes t and Recursion Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 2 Due Fri (and PA3 up) PA3 is a bit difficult, but do it yourself, or repent in the final
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 6: Datatypes t and Recursion Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News PA 2 Due Fri (and PA3 up) PA3 is a bit difficult, but do it yourself, or repent in the final
CSE 130 Programming Languages. Lecture 3: Datatypes. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? PA #2 (coming tonight) Ocaml-top issues? Pleas post questions to Piazza Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax)
CSE 130 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? PA #2 (coming tonight) Ocaml-top issues? Pleas post questions to Piazza Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax)
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity. Story So Far... CSE 130 Programming Languages. Datatypes. A function is a value! Next: functions, but remember.
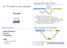 CSE 130 Programming Languages Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Datatypes Compile-time Static Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Datatypes Compile-time Static Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1. Programmer enters expression
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Next: What s in a name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really
CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 13: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Next: What s in a name? More precisely: How should programmer think of data What does a variable x really
CSE 130 Programming Languages. Datatypes. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130 Programming Languages Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression
So what does studying PL buy me?
 So what does studying PL buy me? Enables you to better choose the right language but isn t that decided by libraries, standards, and my boss? Yes. Chicken-and-egg. My goal: educate tomorrow s tech leaders
So what does studying PL buy me? Enables you to better choose the right language but isn t that decided by libraries, standards, and my boss? Yes. Chicken-and-egg. My goal: educate tomorrow s tech leaders
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
Programming Languages
 What about more complex data? CSE 130 : Fall 2012 Programming Languages Expressions Values Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions
What about more complex data? CSE 130 : Fall 2012 Programming Languages Expressions Values Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
Algorithms and Programming I. Lecture#12 Spring 2015
 Algorithms and Programming I Lecture#12 Spring 2015 Think Python How to Think Like a Computer Scientist By :Allen Downey Installing Python Follow the instructions on installing Python and IDLE on your
Algorithms and Programming I Lecture#12 Spring 2015 Think Python How to Think Like a Computer Scientist By :Allen Downey Installing Python Follow the instructions on installing Python and IDLE on your
Programming Languages
 : Winter 2010 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 1: Welcome, etc. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Computation & Interaction Precisely expressed by PL Dependence means need for analysis Safety Security
: Winter 2010 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 1: Welcome, etc. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Computation & Interaction Precisely expressed by PL Dependence means need for analysis Safety Security
CS252 Advanced Programming Language Principles. Prof. Tom Austin San José State University Fall 2013
 CS252 Advanced Programming Language Principles Prof. Tom Austin San José State University Fall 2013 What are some programming languages? Why are there so many? Different domains Mobile devices (Objective
CS252 Advanced Programming Language Principles Prof. Tom Austin San José State University Fall 2013 What are some programming languages? Why are there so many? Different domains Mobile devices (Objective
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1, sample for Quiz #1 on Thu PA #1 (due next Fri 10/10) No make-up quizzes
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1, sample for Quiz #1 on Thu PA #1 (due next Fri 10/10) No make-up quizzes
Quiz. Programming Languages. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 16: Static Types for Objects. Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Quiz Lecture 16: Static ti Types for Objects Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Last time Tricks with namespaces: decorators Today Inheritance Static Types for Objects
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Quiz Lecture 16: Static ti Types for Objects Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Last time Tricks with namespaces: decorators Today Inheritance Static Types for Objects
MapReduce, Hadoop and Spark. Bompotas Agorakis
 MapReduce, Hadoop and Spark Bompotas Agorakis Big Data Processing Most of the computations are conceptually straightforward on a single machine but the volume of data is HUGE Need to use many (1.000s)
MapReduce, Hadoop and Spark Bompotas Agorakis Big Data Processing Most of the computations are conceptually straightforward on a single machine but the volume of data is HUGE Need to use many (1.000s)
Programming Languages. Example 5. Example 4. CSE 130 : Fall type, can reuse code for all types! let rec cat l = match l with
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 9: s and Signatures Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Previously: Polymorphism enables Reuse Can reuse generic functions: map : a * b b * a filter: ( a bool *
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 9: s and Signatures Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Previously: Polymorphism enables Reuse Can reuse generic functions: map : a * b b * a filter: ( a bool *
Big Data Hadoop Stack
 Big Data Hadoop Stack Lecture #1 Hadoop Beginnings What is Hadoop? Apache Hadoop is an open source software framework for storage and large scale processing of data-sets on clusters of commodity hardware
Big Data Hadoop Stack Lecture #1 Hadoop Beginnings What is Hadoop? Apache Hadoop is an open source software framework for storage and large scale processing of data-sets on clusters of commodity hardware
CSE 544 Principles of Database Management Systems. Alvin Cheung Fall 2015 Lecture 10 Parallel Programming Models: Map Reduce and Spark
 CSE 544 Principles of Database Management Systems Alvin Cheung Fall 2015 Lecture 10 Parallel Programming Models: Map Reduce and Spark Announcements HW2 due this Thursday AWS accounts Any success? Feel
CSE 544 Principles of Database Management Systems Alvin Cheung Fall 2015 Lecture 10 Parallel Programming Models: Map Reduce and Spark Announcements HW2 due this Thursday AWS accounts Any success? Feel
Notes from a Short Introductory Lecture on Scala (Based on Programming in Scala, 2nd Ed.)
 Notes from a Short Introductory Lecture on Scala (Based on Programming in Scala, 2nd Ed.) David Haraburda January 30, 2013 1 Introduction Scala is a multi-paradigm language that runs on the JVM (is totally
Notes from a Short Introductory Lecture on Scala (Based on Programming in Scala, 2nd Ed.) David Haraburda January 30, 2013 1 Introduction Scala is a multi-paradigm language that runs on the JVM (is totally
SCHEME AND CALCULATOR 5b
 SCHEME AND CALCULATOR 5b COMPUTER SCIENCE 6A July 25, 203 In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
SCHEME AND CALCULATOR 5b COMPUTER SCIENCE 6A July 25, 203 In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
Intro. Scheme Basics. scm> 5 5. scm>
 Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
CS Lecture 6: Map and Fold. Prof. Clarkson Fall Today s music: Selections from the soundtrack to 2001: A Space Odyssey
 CS 3110 Lecture 6: Map and Fold Prof. Clarkson Fall 2014 Today s music: Selections from the soundtrack to 2001: A Space Odyssey Review Features so far: variables, operators, let expressions, if expressions,
CS 3110 Lecture 6: Map and Fold Prof. Clarkson Fall 2014 Today s music: Selections from the soundtrack to 2001: A Space Odyssey Review Features so far: variables, operators, let expressions, if expressions,
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Wed 4/9) Please post questions to WebCT Today: A crash
CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Wed 4/9) Please post questions to WebCT Today: A crash
Programming Languages. Programming with λ-calculus. Lecture 11: Type Systems. Special Hour to discuss HW? if-then-else int
 CSE 230: Winter 2010 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 11: Type Systems News New HW up soon Special Hour to discuss HW? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Programming with λ-calculus Encode: bool if-then-else
CSE 230: Winter 2010 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 11: Type Systems News New HW up soon Special Hour to discuss HW? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Programming with λ-calculus Encode: bool if-then-else
Smalltalk: developed at Xerox Palo Alto Research Center by the Learning Research Group in the 1970 s (Smalltalk-72, Smalltalk-76, Smalltalk-80)
 A Bit of History Some notable examples of early object-oriented languages and systems: Sketchpad (Ivan Sutherland s 1963 PhD dissertation) was the first system to use classes and instances (although Sketchpad
A Bit of History Some notable examples of early object-oriented languages and systems: Sketchpad (Ivan Sutherland s 1963 PhD dissertation) was the first system to use classes and instances (although Sketchpad
CSE : Python Programming
 CSE 399-004: Python Programming Lecture 10: Functional programming, Memoization March 26, 2007 http://www.seas.upenn.edu/~cse39904/ Announcements Should have received email about meeting times Length:
CSE 399-004: Python Programming Lecture 10: Functional programming, Memoization March 26, 2007 http://www.seas.upenn.edu/~cse39904/ Announcements Should have received email about meeting times Length:
Introduction to MapReduce
 Basics of Cloud Computing Lecture 4 Introduction to MapReduce Satish Srirama Some material adapted from slides by Jimmy Lin, Christophe Bisciglia, Aaron Kimball, & Sierra Michels-Slettvet, Google Distributed
Basics of Cloud Computing Lecture 4 Introduction to MapReduce Satish Srirama Some material adapted from slides by Jimmy Lin, Christophe Bisciglia, Aaron Kimball, & Sierra Michels-Slettvet, Google Distributed
CSE 413 Languages & Implementation. Hal Perkins Winter 2019 Structs, Implementing Languages (credits: Dan Grossman, CSE 341)
 CSE 413 Languages & Implementation Hal Perkins Winter 2019 Structs, Implementing Languages (credits: Dan Grossman, CSE 341) 1 Goals Representing programs as data Racket structs as a better way to represent
CSE 413 Languages & Implementation Hal Perkins Winter 2019 Structs, Implementing Languages (credits: Dan Grossman, CSE 341) 1 Goals Representing programs as data Racket structs as a better way to represent
New Programming Paradigms
 New Programming Paradigms Lecturer: Pánovics János (google the name for further details) Requirements: For signature: classroom work and a 15-minute presentation Exam: written exam (mainly concepts and
New Programming Paradigms Lecturer: Pánovics János (google the name for further details) Requirements: For signature: classroom work and a 15-minute presentation Exam: written exam (mainly concepts and
CS6030 Cloud Computing. Acknowledgements. Today s Topics. Intro to Cloud Computing 10/20/15. Ajay Gupta, WMU-CS. WiSe Lab
 CS6030 Cloud Computing Ajay Gupta B239, CEAS Computer Science Department Western Michigan University ajay.gupta@wmich.edu 276-3104 1 Acknowledgements I have liberally borrowed these slides and material
CS6030 Cloud Computing Ajay Gupta B239, CEAS Computer Science Department Western Michigan University ajay.gupta@wmich.edu 276-3104 1 Acknowledgements I have liberally borrowed these slides and material
CSE413: Programming Languages and Implementation Racket structs Implementing languages with interpreters Implementing closures
 CSE413: Programming Languages and Implementation Racket structs Implementing languages with interpreters Implementing closures Dan Grossman Fall 2014 Hi! I m not Hal J I love this stuff and have taught
CSE413: Programming Languages and Implementation Racket structs Implementing languages with interpreters Implementing closures Dan Grossman Fall 2014 Hi! I m not Hal J I love this stuff and have taught
CS457/557 Functional Languages
 CS457/557 Functional Languages Spring 2018 Lecture 1: Course Introduction Andrew Tolmach Portland State University (with thanks to Mark P. Jones) 1 Goals of this course Introduce the beautiful ideas of
CS457/557 Functional Languages Spring 2018 Lecture 1: Course Introduction Andrew Tolmach Portland State University (with thanks to Mark P. Jones) 1 Goals of this course Introduce the beautiful ideas of
Recall that strings and tuples are immutable datatypes, while lists are mutable datatypes. What does this mean?
 6.189 Day 4 Readings How To Think Like A Computer Scientist, chapters 7 and 8 6.01 Fall 2009 Course Notes page 27-29 ( Lists and Iterations over lists ; List Comprehensions is optional); sections 3.2-3.4
6.189 Day 4 Readings How To Think Like A Computer Scientist, chapters 7 and 8 6.01 Fall 2009 Course Notes page 27-29 ( Lists and Iterations over lists ; List Comprehensions is optional); sections 3.2-3.4
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures. Dan Grossman Autumn 2018
 CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures Dan Grossman Autumn 2018 Typical workflow concrete syntax (string) "(fn x => x + x) 4" Parsing Possible errors / warnings
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures Dan Grossman Autumn 2018 Typical workflow concrete syntax (string) "(fn x => x + x) 4" Parsing Possible errors / warnings
Func%onal Programming in Scheme and Lisp
 Func%onal Programming in Scheme and Lisp http://www.lisperati.com/landoflisp/ Overview In a func(onal programming language, func(ons are first class objects You can create them, put them in data structures,
Func%onal Programming in Scheme and Lisp http://www.lisperati.com/landoflisp/ Overview In a func(onal programming language, func(ons are first class objects You can create them, put them in data structures,
CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) First Name: Last Name: NetID:
 CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2016sp/labs/lab01/lab01.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: Goals. Learning a computer language is a lot like learning
CS 1110 SPRING 2016: GETTING STARTED (Jan 27-28) http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1110/2016sp/labs/lab01/lab01.pdf First Name: Last Name: NetID: Goals. Learning a computer language is a lot like learning
Week - 01 Lecture - 04 Downloading and installing Python
 Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms in Python Prof. Madhavan Mukund Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 01 Lecture - 04 Downloading and
Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms in Python Prof. Madhavan Mukund Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 01 Lecture - 04 Downloading and
CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages
![CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages](/thumbs/84/89705892.jpg) CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages Course Introduction! Ravi Chugh! Filling in today for Ranjit Jhala Apr 01 A Programming Language Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- L1: x++; y--; L2:!
CSE 130 [Spring 2014] Programming Languages Course Introduction! Ravi Chugh! Filling in today for Ranjit Jhala Apr 01 A Programming Language Two variables x, y Three operations x++ x-- L1: x++; y--; L2:!
News. Programming Languages. Complex types: Lists. Recap: ML s Holy Trinity. CSE 130: Spring 2012
 News CSE 130: Spring 2012 Programming Languages On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 4/13) Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Please post questions to Piazza Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today: A
News CSE 130: Spring 2012 Programming Languages On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 4/13) Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Please post questions to Piazza Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today: A
Func%onal Programming in Scheme and Lisp
 Func%onal Programming in Scheme and Lisp http://www.lisperati.com/landoflisp/ Overview In a func(onal programming language, func(ons are first class objects You can create them, put them in data structures,
Func%onal Programming in Scheme and Lisp http://www.lisperati.com/landoflisp/ Overview In a func(onal programming language, func(ons are first class objects You can create them, put them in data structures,
CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015)
 CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015) First Name: Last Name: NetID: Completing this lab assignment is very important and you must have a CS 1110 course consultant tell CMS that you did the work. (Correctness
CS1110 Lab 1 (Jan 27-28, 2015) First Name: Last Name: NetID: Completing this lab assignment is very important and you must have a CS 1110 course consultant tell CMS that you did the work. (Correctness
CS 11 Haskell track: lecture 1
 CS 11 Haskell track: lecture 1 This week: Introduction/motivation/pep talk Basics of Haskell Prerequisite Knowledge of basic functional programming e.g. Scheme, Ocaml, Erlang CS 1, CS 4 "permission of
CS 11 Haskell track: lecture 1 This week: Introduction/motivation/pep talk Basics of Haskell Prerequisite Knowledge of basic functional programming e.g. Scheme, Ocaml, Erlang CS 1, CS 4 "permission of
CS61A Discussion Notes: Week 11: The Metacircular Evaluator By Greg Krimer, with slight modifications by Phoebus Chen (using notes from Todd Segal)
 CS61A Discussion Notes: Week 11: The Metacircular Evaluator By Greg Krimer, with slight modifications by Phoebus Chen (using notes from Todd Segal) What is the Metacircular Evaluator? It is the best part
CS61A Discussion Notes: Week 11: The Metacircular Evaluator By Greg Krimer, with slight modifications by Phoebus Chen (using notes from Todd Segal) What is the Metacircular Evaluator? It is the best part
The Haskell HOP: Higher-order Programming
 The Haskell HOP: Higher-order Programming COS 441 Slides 6 Slide content credits: Ranjit Jhala, UCSD Agenda Haskell so far: First-order functions This time: Higher-order functions: Functions as data, arguments
The Haskell HOP: Higher-order Programming COS 441 Slides 6 Slide content credits: Ranjit Jhala, UCSD Agenda Haskell so far: First-order functions This time: Higher-order functions: Functions as data, arguments
! Broaden your language horizons! Different programming languages! Different language features and tradeoffs. ! Study how languages are implemented
 Course Goal CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Introduction Learn how programming languages work Broaden your language horizons! Different programming languages! Different language features
Course Goal CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Introduction Learn how programming languages work Broaden your language horizons! Different programming languages! Different language features
CSE 374: Programming Concepts and Tools. Eric Mullen Spring 2017 Lecture 4: More Shell Scripts
 CSE 374: Programming Concepts and Tools Eric Mullen Spring 2017 Lecture 4: More Shell Scripts Homework 1 Already out, due Thursday night at midnight Asks you to run some shell commands Remember to use
CSE 374: Programming Concepts and Tools Eric Mullen Spring 2017 Lecture 4: More Shell Scripts Homework 1 Already out, due Thursday night at midnight Asks you to run some shell commands Remember to use
FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING
 FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING Map, Fold, and MapReduce Prof. Clarkson Summer 2015 Today s music: Selections from the soundtrack to 2001: A Space Odyssey Review Yesterday: Lists: OCaml's awesome built-in datatype
FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING Map, Fold, and MapReduce Prof. Clarkson Summer 2015 Today s music: Selections from the soundtrack to 2001: A Space Odyssey Review Yesterday: Lists: OCaml's awesome built-in datatype
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 12: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A crash course in Python Interpreted, imperative, OO Language g Everything is an object Dynamic Typing
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 12: What s in a Name? Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A crash course in Python Interpreted, imperative, OO Language g Everything is an object Dynamic Typing
SCHEME The Scheme Interpreter. 2 Primitives COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A. October 29th, 2012
 SCHEME COMPUTER SCIENCE 6A October 29th, 202 In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs, we will eventually
SCHEME COMPUTER SCIENCE 6A October 29th, 202 In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs, we will eventually
Chapter 11 :: Functional Languages
 Chapter 11 :: Functional Languages Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Copyright 2016 Elsevier 1 Chapter11_Functional_Languages_4e - Tue November 21, 2017 Historical Origins The imperative
Chapter 11 :: Functional Languages Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Copyright 2016 Elsevier 1 Chapter11_Functional_Languages_4e - Tue November 21, 2017 Historical Origins The imperative
Type Inference. Prof. Clarkson Fall Today s music: Cool, Calm, and Collected by The Rolling Stones
 Type Inference Prof. Clarkson Fall 2016 Today s music: Cool, Calm, and Collected by The Rolling Stones Review Previously in 3110: Interpreters: ASTs, evaluation, parsing Formal syntax Formal semantics
Type Inference Prof. Clarkson Fall 2016 Today s music: Cool, Calm, and Collected by The Rolling Stones Review Previously in 3110: Interpreters: ASTs, evaluation, parsing Formal syntax Formal semantics
Week - 04 Lecture - 01 Merge Sort. (Refer Slide Time: 00:02)
 Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms in Python Prof. Madhavan Mukund Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 04 Lecture - 01 Merge Sort (Refer
Programming, Data Structures and Algorithms in Python Prof. Madhavan Mukund Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Week - 04 Lecture - 01 Merge Sort (Refer
SEER AKADEMI LINUX PROGRAMMING AND SCRIPTINGPERL 7
 SEER AKADEMI LINUX PROGRAMMING AND SCRIPTINGPERL 7 Hi everyone once again welcome to this lecture we are actually the course is Linux programming and scripting we have been talking about the Perl, Perl
SEER AKADEMI LINUX PROGRAMMING AND SCRIPTINGPERL 7 Hi everyone once again welcome to this lecture we are actually the course is Linux programming and scripting we have been talking about the Perl, Perl
Typical workflow. CSE341: Programming Languages. Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures. Reality more complicated
 Typical workflow concrete synta (string) "(fn => + ) 4" Parsing CSE341: Programming Languages abstract synta (tree) Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures Function Constant + 4 Var Var Type
Typical workflow concrete synta (string) "(fn => + ) 4" Parsing CSE341: Programming Languages abstract synta (tree) Lecture 17 Implementing Languages Including Closures Function Constant + 4 Var Var Type
CSE 341: Programming Languages
 CSE 341: Programming Languages Dan Grossman Spring 2008 Lecture 6 Nested pattern-matching; course motivation Dan Grossman CSE341 Spring 2008, Lecture 6 1 Patterns What we know: case-expresssions do pattern-matching
CSE 341: Programming Languages Dan Grossman Spring 2008 Lecture 6 Nested pattern-matching; course motivation Dan Grossman CSE341 Spring 2008, Lecture 6 1 Patterns What we know: case-expresssions do pattern-matching
Introduction to computers and Python. Matthieu Choplin
 Introduction to computers and Python Matthieu Choplin matthieu.choplin@city.ac.uk http://moodle.city.ac.uk/ 1 Objectives To get a brief overview of what Python is To understand computer basics and programs
Introduction to computers and Python Matthieu Choplin matthieu.choplin@city.ac.uk http://moodle.city.ac.uk/ 1 Objectives To get a brief overview of what Python is To understand computer basics and programs
CS312: Programming Languages. Lecture 21: JavaScript
 CS312: Programming Languages Lecture 21: JavaScript Thomas Dillig Thomas Dillig, CS312: Programming Languages Lecture 21: JavaScript 1/25 Why Discuss JavaScript? JavaScript is very widely used and growing
CS312: Programming Languages Lecture 21: JavaScript Thomas Dillig Thomas Dillig, CS312: Programming Languages Lecture 21: JavaScript 1/25 Why Discuss JavaScript? JavaScript is very widely used and growing
Introduction to programming with Python
 Introduction to programming with Python Ing. Lelio Campanile 1/61 Main Goal - Introduce you to programming - introduce you to the most essential feature of python programming 2/61 Before to start The name
Introduction to programming with Python Ing. Lelio Campanile 1/61 Main Goal - Introduce you to programming - introduce you to the most essential feature of python programming 2/61 Before to start The name
Project 2: Scheme Interpreter
 Project 2: Scheme Interpreter CSC 4101, Fall 2017 Due: 12 November 2017 For this project, you will implement a simple Scheme interpreter in C++ or Java. Your interpreter should be able to handle the same
Project 2: Scheme Interpreter CSC 4101, Fall 2017 Due: 12 November 2017 For this project, you will implement a simple Scheme interpreter in C++ or Java. Your interpreter should be able to handle the same
Introduction to Computer Vision Laboratories
 Introduction to Computer Vision Laboratories Antonino Furnari furnari@dmi.unict.it www.dmi.unict.it/~furnari/ Computer Vision Laboratories Format: practical session + questions and homeworks. Material
Introduction to Computer Vision Laboratories Antonino Furnari furnari@dmi.unict.it www.dmi.unict.it/~furnari/ Computer Vision Laboratories Format: practical session + questions and homeworks. Material
Lecturer: William W.Y. Hsu. Programming Languages
 Lecturer: William W.Y. Hsu Programming Languages Chapter 9 Data Abstraction and Object Orientation 3 Object-Oriented Programming Control or PROCESS abstraction is a very old idea (subroutines!), though
Lecturer: William W.Y. Hsu Programming Languages Chapter 9 Data Abstraction and Object Orientation 3 Object-Oriented Programming Control or PROCESS abstraction is a very old idea (subroutines!), though
A Big Step. Shell Scripts, I/O Redirection, Ownership and Permission Concepts, and Binary Numbers
 A Big Step Shell Scripts, I/O Redirection, Ownership and Permission Concepts, and Binary Numbers Copyright 2006 2009 Stewart Weiss What a shell really does Here is the scoop on shells. A shell is a program
A Big Step Shell Scripts, I/O Redirection, Ownership and Permission Concepts, and Binary Numbers Copyright 2006 2009 Stewart Weiss What a shell really does Here is the scoop on shells. A shell is a program
Why Discuss JavaScript? CS312: Programming Languages. Lecture 21: JavaScript. JavaScript Target. What s a Scripting Language?
 Why Discuss JavaScript? CS312: Programming Languages Lecture 21: JavaScript Thomas Dillig JavaScript is very widely used and growing Any AJAX application heavily relies on JavaScript JavaScript also has
Why Discuss JavaScript? CS312: Programming Languages Lecture 21: JavaScript Thomas Dillig JavaScript is very widely used and growing Any AJAX application heavily relies on JavaScript JavaScript also has
Functional Languages. CSE 307 Principles of Programming Languages Stony Brook University
 Functional Languages CSE 307 Principles of Programming Languages Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse307 1 Historical Origins 2 The imperative and functional models grew out of work
Functional Languages CSE 307 Principles of Programming Languages Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse307 1 Historical Origins 2 The imperative and functional models grew out of work
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity
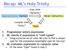 Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
First Programming Language in CS Education The Arguments for Scala
 First Programming Language in CS Education The Arguments for Scala WORLDCOMP 2011 By Dr. Mark C. Lewis Trinity University Disclaimer I am writing a Scala textbook that is under contract with CRC Press.
First Programming Language in CS Education The Arguments for Scala WORLDCOMP 2011 By Dr. Mark C. Lewis Trinity University Disclaimer I am writing a Scala textbook that is under contract with CRC Press.
PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between
 MITOCW Lecture 10A [MUSIC PLAYING] PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between all these high-level languages like Lisp and the query
MITOCW Lecture 10A [MUSIC PLAYING] PROFESSOR: Last time, we took a look at an explicit control evaluator for Lisp, and that bridged the gap between all these high-level languages like Lisp and the query
Lecture 1. Introduction to course, Welcome to Engineering, What is Programming and Why is this the first thing being covered in Engineering?
 Lecture 1 Introduction to course, Welcome to Engineering, What is Programming and Why is this the first thing being covered in Engineering? Welcome to ENGR 102 Syllabus review Your Time Expectations (in
Lecture 1 Introduction to course, Welcome to Engineering, What is Programming and Why is this the first thing being covered in Engineering? Welcome to ENGR 102 Syllabus review Your Time Expectations (in
Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping
 CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? Formalize first-order type systems Simple types (integers and booleans)
CSE 230: Winter 2008 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 15: Recursive Types & Subtyping Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News? Formalize first-order type systems Simple types (integers and booleans)
CS152 Programming Language Paradigms Prof. Tom Austin, Fall Syntax & Semantics, and Language Design Criteria
 CS152 Programming Language Paradigms Prof. Tom Austin, Fall 2014 Syntax & Semantics, and Language Design Criteria Lab 1 solution (in class) Formally defining a language When we define a language, we need
CS152 Programming Language Paradigms Prof. Tom Austin, Fall 2014 Syntax & Semantics, and Language Design Criteria Lab 1 solution (in class) Formally defining a language When we define a language, we need
CS 360 Programming Languages Interpreters
 CS 360 Programming Languages Interpreters Implementing PLs Most of the course is learning fundamental concepts for using and understanding PLs. Syntax vs. semantics vs. idioms. Powerful constructs like
CS 360 Programming Languages Interpreters Implementing PLs Most of the course is learning fundamental concepts for using and understanding PLs. Syntax vs. semantics vs. idioms. Powerful constructs like
Introduction to MapReduce. Adapted from Jimmy Lin (U. Maryland, USA)
 Introduction to MapReduce Adapted from Jimmy Lin (U. Maryland, USA) Motivation Overview Need for handling big data New programming paradigm Review of functional programming mapreduce uses this abstraction
Introduction to MapReduce Adapted from Jimmy Lin (U. Maryland, USA) Motivation Overview Need for handling big data New programming paradigm Review of functional programming mapreduce uses this abstraction
Dynamically-typed Languages. David Miller
 Dynamically-typed Languages David Miller Dynamically-typed Language Everything is a value No type declarations Examples of dynamically-typed languages APL, Io, JavaScript, Lisp, Lua, Objective-C, Perl,
Dynamically-typed Languages David Miller Dynamically-typed Language Everything is a value No type declarations Examples of dynamically-typed languages APL, Io, JavaScript, Lisp, Lua, Objective-C, Perl,
CS Lecture 6: Map and Fold. Prof. Clarkson Spring Today s music: Selections from the soundtrack to 2001: A Space Odyssey
 CS 3110 Lecture 6: Map and Fold Prof. Clarkson Spring 2015 Today s music: Selections from the soundtrack to 2001: A Space Odyssey Review Course so far: Syntax and semantics of (most of) OCaml Today: No
CS 3110 Lecture 6: Map and Fold Prof. Clarkson Spring 2015 Today s music: Selections from the soundtrack to 2001: A Space Odyssey Review Course so far: Syntax and semantics of (most of) OCaml Today: No
News. CSE 130: Programming Languages. Environments & Closures. Functions are first-class values. Recap: Functions as first-class values
 CSE 130: Programming Languages Environments & Closures News PA 3 due THIS Friday (5/1) Midterm NEXT Friday (5/8) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values,
CSE 130: Programming Languages Environments & Closures News PA 3 due THIS Friday (5/1) Midterm NEXT Friday (5/8) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values,
Environment Diagrams. Administrivia. Agenda Step by Step Environment Diagram Stuff. The Rules. Practice it s on! What are The Rules?
 Administrivia Project 3 Part A due 3/29 (Monday after SB) Part B due 4/5 (a week after) Everyone with a partner that wants a partner? Extra Office Hours on Sunday 3/28 in C50 from 1pm Midterm 3 on 4/14
Administrivia Project 3 Part A due 3/29 (Monday after SB) Part B due 4/5 (a week after) Everyone with a partner that wants a partner? Extra Office Hours on Sunday 3/28 in C50 from 1pm Midterm 3 on 4/14
CS 177 Recitation. Week 1 Intro to Java
 CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
Functional Programming
 The Meta Language (ML) and Functional Programming Daniel S. Fava danielsf@ifi.uio.no Department of informatics University of Oslo, Norway Motivation ML Demo Which programming languages are functional?
The Meta Language (ML) and Functional Programming Daniel S. Fava danielsf@ifi.uio.no Department of informatics University of Oslo, Norway Motivation ML Demo Which programming languages are functional?
Variables, expressions and statements
 Variables, expressions and statements 2.1. Values and data types A value is one of the fundamental things like a letter or a number that a program manipulates. The values we have seen so far are 2 (the
Variables, expressions and statements 2.1. Values and data types A value is one of the fundamental things like a letter or a number that a program manipulates. The values we have seen so far are 2 (the
Using Data From Quandl in EViews
 Department of Economics University of Victoria Using Data From Quandl in EViews David Giles September, 2014 1. What is Quandl? www.quandl.com 1 2 You can use Quandl s data for free, on a limited basis,
Department of Economics University of Victoria Using Data From Quandl in EViews David Giles September, 2014 1. What is Quandl? www.quandl.com 1 2 You can use Quandl s data for free, on a limited basis,
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 4 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 4 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming Hakjoo Oh 2016 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2016 Fall, Lecture 4 September 27, 2016 1 / 21 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 4 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming Hakjoo Oh 2016 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2016 Fall, Lecture 4 September 27, 2016 1 / 21 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming
! Broaden your language horizons. ! Study how languages are implemented. ! Study how languages are described / specified
 Course Goal CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Introduction Instructors: Mike Hicks, Chau-Wen Tseng TAs: Srividya Ramaswamy, Eylul Dogruel, Khoa Doan Learn how programming languages work!
Course Goal CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Introduction Instructors: Mike Hicks, Chau-Wen Tseng TAs: Srividya Ramaswamy, Eylul Dogruel, Khoa Doan Learn how programming languages work!
STATS Data Analysis using Python. Lecture 7: the MapReduce framework Some slides adapted from C. Budak and R. Burns
 STATS 700-002 Data Analysis using Python Lecture 7: the MapReduce framework Some slides adapted from C. Budak and R. Burns Unit 3: parallel processing and big data The next few lectures will focus on big
STATS 700-002 Data Analysis using Python Lecture 7: the MapReduce framework Some slides adapted from C. Budak and R. Burns Unit 3: parallel processing and big data The next few lectures will focus on big
