CMPT 473 Software Quality Assurance. Security. Nick Sumner - Fall 2014
|
|
|
- Georgiana Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMPT 473 Software Quality Assurance Security Nick Sumner - Fall 2014
2 Basic Security What are attributes of a secure program? CIA 2
3 Basic Security What are attributes of a secure program? CIA (C)onfidentiality No unauthorized information leaks 3
4 Basic Security What are attributes of a secure program? CIA (C)onfidentiality No unauthorized information leaks (I)ntegrity No unauthorized data manipulation/corruption 4
5 Basic Security What are attributes of a secure program? CIA (C)onfidentiality No unauthorized information leaks (I)ntegrity No unauthorized data manipulation/corruption (A)vailability The system must be accessible as needed (no DOS) 5
6 Basic Security What are attributes of a secure program? CIA (C)onfidentiality No unauthorized information leaks (I)ntegrity No unauthorized data manipulation/corruption (A)vailability The system must be accessible as needed (no DOS) (A2 )uthenticity All actions are genuine, taken by the parties they claim/appear to be 6
7 Why Is This Special? Poor security comes from unintended behavior. Quality software shouldn't allow such actions anyway. 7
8 Why Is This Special? Poor security comes from unintended behavior. Quality software shouldn't allow such actions anyway. While our testing techniques so far find some security issues, many slip through! Why? 8
9 Why Is This Special? Poor security comes from unintended behavior. Quality software shouldn't allow such actions anyway. While our testing techniques so far find some security issues, many slip through! Why? We cannot test everything 9
10 Why Is This Special? Poor security comes from unintended behavior. Quality software shouldn't allow such actions anyway. While our testing techniques so far find some security issues, many slip through! Why? We cannot test everything Concessions form part of an attack surface Networks, Software, People 10
11 Why Is This Special? Poor security comes from unintended behavior. Quality software shouldn't allow such actions anyway. While our testing techniques so far find some security issues, many slip through! Why? We cannot test everything Concessions form part of an attack surface Networks, Software, People Need additional policies & testing methods that specifically address security 11
12 What Could Possible Go Wrong? Many ways to attack different programs MITRE groups the most common into: 12
13 What Could Possible Go Wrong? Many ways to attack different programs MITRE groups the most common into: Insecure Interaction Data sent between components in an insecure fashion 13
14 What Could Possible Go Wrong? Many ways to attack different programs MITRE groups the most common into: Insecure Interaction Data sent between components in an insecure fashion Risky Resource Management Bad creation, use, transfer, & destruction of resources 14
15 What Could Possible Go Wrong? Many ways to attack different programs MITRE groups the most common into: Insecure Interaction Data sent between components in an insecure fashion Risky Resource Management Bad creation, use, transfer, & destruction of resources Porous Defenses Standard security practices that are missing or incorrect [ 15
16 Deeper Dive: Memory Safety Memory safety is a fundamental security issue for languages like C, C++, Assembly,. 16
17 Deeper Dive: Memory Safety Memory safety is a fundamental security issue for languages like C, C++, Assembly,. General idea: Accessing memory when you shouldn't be able to might read, write, or execute inappropriately 17
18 Deeper Dive: Memory Safety Memory safety is a fundamental security issue for languages like C, C++, Assembly,. General idea: Accessing memory when you shouldn't be able to might read, write, or execute inappropriately Classic example: stack buffer overflow attacks 18
19 Deeper Dive: Memory Safety Memory safety is a fundamental security issue for languages like C, C++, Assembly,. General idea: Accessing memory when you shouldn't be able to might read, write, or execute inappropriately Classic example: stack buffer overflow attacks Read more input into a buffer than the buffer can hold... 19
20 Deeper Dive: Memory Safety Memory safety is a fundamental security issue for languages like C, C++, Assembly,. General idea: Accessing memory when you shouldn't be able to might read, write, or execute inappropriately Classic example: stack buffer overflow attacks Read more input into a buffer than the buffer can hold... How many of you recall what a stack frame looks like? 20
21 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } 0x000 21
22 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } 0x000 22
23 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } 0x000 23
24 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Return Address Old Frame Ptr securedata buffer[15] buffer[14]... buffer[0] Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } Stack Frame for foo 0x000 24
25 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Return Address Old Frame Ptr securedata buffer[15] buffer[14]... buffer[0] Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } Stack Frame for foo What can go wrong? 0x000 25
26 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Return Address Old Frame Ptr securedata buffer[15] buffer[14]... buffer[0] Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } input = normal input + insecuredata 0x000 26
27 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Return Address Old Frame Ptr securedata buffer[15] buffer[14]... buffer[0] Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } input = normal input + insecuredata 0x000 27
28 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Return Address Old Frame Ptr securedata buffer[15] buffer[14]... buffer[0] Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } input = normal input + insecuredata The integrity of the secure data is corrupted. 0x000 28
29 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Return Address Old Frame Ptr securedata buffer[15] buffer[14]... buffer[0] Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } input = normal input + insecuredata The integrity of the secure data is corrupted. 0x000 What else can go wrong? 29
30 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Return Address Old Frame Ptr securedata buffer[15] buffer[14]... buffer[0] Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } input = input + payload address + payload 0x000 30
31 Stack Buffer Overflows 0xFFF Addresses Stack Previous Frame Return Address Old Frame Ptr securedata buffer[15] buffer[14]... buffer[0] Stack Growth void foo(char *input) { unsigned securedata; char buffer[16]; strcpy(buffer, input); } input = input + payload address + payload What does this mean? 0x000 31
32 Memory Safety Vulnerabilities come from reading/writing/freeing Out of bounds pointers Dangling pointers 32
33 Memory Safety Vulnerabilities come from reading/writing/freeing Out of bounds pointers Dangling pointers Why doesn't Java face this issue? 33
34 Memory Safety Vulnerabilities come from reading/writing/freeing Out of bounds pointers Dangling pointers Why doesn't Java face this issue? Is this intrinsic to languages like C++? Why/Why not? 34
35 Memory Safety Vulnerabilities come from reading/writing/freeing Out of bounds pointers Dangling pointers Why doesn't Java face this issue? Is this intrinsic to languages like C++? Why/Why not? Are these still a real issue? 35
36 Memory Safety Vulnerabilities come from reading/writing/freeing Out of bounds pointers Dangling pointers Why doesn't Java face this issue? Is this intrinsic to languages like C++? Why/Why not? Are these still a real issue? bid=
37 Another Case: SQL Injection SQL a query language for databases Queries like: SELECT grade,id FROM students WHERE name= + username; ID Name Grade 0 Alice 92 1 Bob 87 2 Mallory 75 37
38 Another Case: SQL Injection SQL a query language for databases Queries like: SELECT grade,id FROM students WHERE name= + username; ID Name Grade 0 Alice 92 1 Bob 87 2 Mallory 75 Values for name, grade often come from user input. 38
39 Another Case: SQL Injection SQL a query language for databases Queries like: SELECT grade,id FROM students WHERE name= + username; ID Name Grade 0 Alice 92 1 Bob 87 2 Mallory 75 Values for name, grade often come from user input. Why is this a problem? 39
40 Another Case: SQL Injection username = 'bob'; DROP TABLE students What happens? 40
41 SQL Injection [ [ The user may include commands in their input! 41
42 SQL Injection [ [ The user may include commands in their input! Need to sanitize the input before use 42
43 SQL Injection [ [ The user may include commands in their input! Need to sanitize the input before use How would you prevent this problem? 43
44 A Subtle Problem in General The problems may be much more subtle: User A can read files X,Y,Z and write to S,T User B can read files X,Y,S and write to Z,T How can we ensure that no information from A is ever written to Z? 44
45 A Subtle Problem in General The problems may be much more subtle: User A can read files X,Y,Z and write to S,T User B can read files X,Y,S and write to Z,T How can we ensure that no information from A is ever written to Z? Can you envision a scenario that creates this problem? 45
46 A Subtle Problem in General The problems may be much more subtle: User A can read files X,Y,Z and write to S,T User B can read files X,Y,S and write to Z,T How can we ensure that no information from A is ever written to Z? Care may be required to enforce access control policies 46
47 A Subtle Problem in General The problems may be much more subtle: User A can read files X,Y,Z and write to S,T User B can read files X,Y,S and write to Z,T How can we ensure that no information from A is ever written to Z? Care may be required to enforce access control policies Discretionary access control owner determines access 47
48 A Subtle Problem in General The problems may be much more subtle: User A can read files X,Y,Z and write to S,T User B can read files X,Y,S and write to Z,T How can we ensure that no information from A is ever written to Z? Care may be required to enforce access control policies Discretionary access control owner determines access Mandatory access control clearance determines access 48
49 Assuring Security Make risky operations someone else's job e.g. Google Checkout, PayPal, Amazon, etc. 49
50 Assuring Security Make risky operations someone else's job e.g. Google Checkout, PayPal, Amazon, etc. Define rigorous security policies What are your CIAA security criteria? 50
51 Assuring Security Make risky operations someone else's job e.g. Google Checkout, PayPal, Amazon, etc. Define rigorous security policies What are your CIAA security criteria? Follow secure design & coding policies And include them in your review criteria 51
52 Assuring Security Make risky operations someone else's job e.g. Google Checkout, PayPal, Amazon, etc. Define rigorous security policies What are your CIAA security criteria? Follow secure design & coding policies And include them in your review criteria Apple secure coding policies CERT Top 10 Practices Mitre Mitigation Strategies 52
53 Assuring Security Make risky operations someone else's job e.g. Google Checkout, PayPal, Amazon, etc. Define rigorous security policies What are your CIAA security criteria? Follow secure design & coding policies And include them in your review criteria Formal certification 53
54 Common Proactive Approaches How are these techniques applied? 54
55 Common Proactive Approaches How are these techniques applied? Security must be part of design Prepared Statements, Safe Arrays, etc. 55
56 Common Proactive Approaches How are these techniques applied? Security must be part of design Prepared Statements, Safe Arrays, etc. Regular security audits Retrospective analysis & suggestions 56
57 Common Proactive Approaches How are these techniques applied? Security must be part of design Prepared Statements, Safe Arrays, etc. Regular security audits Retrospective analysis & suggestions Penetration testing Can someone skilled break it? 57
58 Security Overall Security is now a pressing concern for all software 58
59 Security Overall Security is now a pressing concern for all software Old software was designed in an era of naiveté and is often vulnerable/broken 59
60 Security Overall Security is now a pressing concern for all software Old software was designed in an era of naiveté and is often vulnerable/broken New software is built to perform sensitive operations in a multiuser and networked environment. 60
61 Security Overall Security is now a pressing concern for all software Old software was designed in an era of naiveté and is often vulnerable/broken New software is built to perform sensitive operations in a multiuser and networked environment. Not planning for security concerns from the beginning is a broken approach to development 61
Buffer overflow background
 and heap buffer background Comp Sci 3600 Security Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Address Space and heap buffer
and heap buffer background Comp Sci 3600 Security Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Address Space and heap buffer
CIS 5373 Systems Security
 CIS 5373 Systems Security Topic 1: Introduction to Systems Security Endadul Hoque 1 Why should you care? Security impacts our day-to-day life Become a security-aware user Make safe decisions Become a security-aware
CIS 5373 Systems Security Topic 1: Introduction to Systems Security Endadul Hoque 1 Why should you care? Security impacts our day-to-day life Become a security-aware user Make safe decisions Become a security-aware
Module: Program Vulnerabilities. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
Module: Program Vulnerabilities. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
Module: Program Vulnerabilities. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outline. Language Security
 Language Security Or: bringing a knife to a gun fight #1 One-Slide Summary A language s design principles and features have a strong influence on the security of programs written in that language. C s
Language Security Or: bringing a knife to a gun fight #1 One-Slide Summary A language s design principles and features have a strong influence on the security of programs written in that language. C s
Secure Programming Techniques
 Secure Programming Techniques Meelis ROOS mroos@ut.ee Institute of Computer Science Tartu University spring 2014 Course outline Introduction General principles Code auditing C/C++ Web SQL Injection PHP
Secure Programming Techniques Meelis ROOS mroos@ut.ee Institute of Computer Science Tartu University spring 2014 Course outline Introduction General principles Code auditing C/C++ Web SQL Injection PHP
Beta Mobile app Testing guidelines
 Beta Mobile app Testing guidelines Quality Assurance (QA) plays an important role in the mobile applications development life cycle, but many overlook the critical nature of this piece of the app development
Beta Mobile app Testing guidelines Quality Assurance (QA) plays an important role in the mobile applications development life cycle, but many overlook the critical nature of this piece of the app development
Program Security and Vulnerabilities Class 2
 Program Security and Vulnerabilities Class 2 CEN-5079: 28.August.2017 1 Secure Programs Programs Operating System Device Drivers Network Software (TCP stack, web servers ) Database Management Systems Integrity
Program Security and Vulnerabilities Class 2 CEN-5079: 28.August.2017 1 Secure Programs Programs Operating System Device Drivers Network Software (TCP stack, web servers ) Database Management Systems Integrity
Buffer Overflows. A brief Introduction to the detection and prevention of buffer overflows for intermediate programmers.
 Buffer Overflows A brief Introduction to the detection and prevention of buffer overflows for intermediate programmers. By: Brian Roberts What is a buffer overflow? In languages that deal with data structures
Buffer Overflows A brief Introduction to the detection and prevention of buffer overflows for intermediate programmers. By: Brian Roberts What is a buffer overflow? In languages that deal with data structures
Taking White Hats to the Laundry: How to Strengthen Testing in Common Criteria
 Taking White Hats to the Laundry: How to Strengthen Testing in Common Criteria Apostol Vassilev, Principal Consultant September 23,2009. Product Testing in Common Criteria Product Testing in Common Criteria
Taking White Hats to the Laundry: How to Strengthen Testing in Common Criteria Apostol Vassilev, Principal Consultant September 23,2009. Product Testing in Common Criteria Product Testing in Common Criteria
Secure Programming I. Steven M. Bellovin September 28,
 Secure Programming I Steven M. Bellovin September 28, 2014 1 If our software is buggy, what does that say about its security? Robert H. Morris Steven M. Bellovin September 28, 2014 2 The Heart of the Problem
Secure Programming I Steven M. Bellovin September 28, 2014 1 If our software is buggy, what does that say about its security? Robert H. Morris Steven M. Bellovin September 28, 2014 2 The Heart of the Problem
SoK: Eternal War in Memory Laszlo Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, and Dawn Song In: Oakland 14
 SoK: Eternal War in Memory Laszlo Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, and Dawn Song In: Oakland 14 Presenter: Mathias Payer, EPFL http://hexhive.github.io 1 Memory attacks: an ongoing war Vulnerability classes
SoK: Eternal War in Memory Laszlo Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, and Dawn Song In: Oakland 14 Presenter: Mathias Payer, EPFL http://hexhive.github.io 1 Memory attacks: an ongoing war Vulnerability classes
Language Security. Lecture 40
 Language Security Lecture 40 (from notes by G. Necula) Prof. Hilfinger CS 164 Lecture 40 1 Lecture Outline Beyond compilers Looking at other issues in programming language design and tools C Arrays Exploiting
Language Security Lecture 40 (from notes by G. Necula) Prof. Hilfinger CS 164 Lecture 40 1 Lecture Outline Beyond compilers Looking at other issues in programming language design and tools C Arrays Exploiting
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice
 Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring Homework #2
 CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring 2014 Homework #2 Due: 11am CDT (in class), April 17, 2014 YOUR NAME: Collaboration policy No collaboration is permitted on this assignment. Any cheating (e.g.,
CS 361S - Network Security and Privacy Spring 2014 Homework #2 Due: 11am CDT (in class), April 17, 2014 YOUR NAME: Collaboration policy No collaboration is permitted on this assignment. Any cheating (e.g.,
Secure Coding Techniques
 Secure Coding Techniques "... the world outside your function should be treated as hostile and bent upon your destruction" [Writing Secure Code, Howard and LeBlanc] "Distrust and caution are the parents
Secure Coding Techniques "... the world outside your function should be treated as hostile and bent upon your destruction" [Writing Secure Code, Howard and LeBlanc] "Distrust and caution are the parents
Verification & Validation of Open Source
 Verification & Validation of Open Source 2011 WORKSHOP ON SPACECRAFT FLIGHT SOFTWARE Gordon Uchenick Coverity, Inc Open Source is Ubiquitous Most commercial and proprietary software systems have some open
Verification & Validation of Open Source 2011 WORKSHOP ON SPACECRAFT FLIGHT SOFTWARE Gordon Uchenick Coverity, Inc Open Source is Ubiquitous Most commercial and proprietary software systems have some open
Copyright 2015 MathEmbedded Ltd.r. Finding security vulnerabilities by fuzzing and dynamic code analysis
 Finding security vulnerabilities by fuzzing and dynamic code analysis Security Vulnerabilities Top code security vulnerabilities don t change much: Security Vulnerabilities Top code security vulnerabilities
Finding security vulnerabilities by fuzzing and dynamic code analysis Security Vulnerabilities Top code security vulnerabilities don t change much: Security Vulnerabilities Top code security vulnerabilities
Security Principles and Policies CS 136 Computer Security Peter Reiher January 15, 2008
 Security Principles and Policies CS 136 Computer Security Peter Reiher January 15, 2008 Page 1 Outline Security terms and concepts Security policies Basic concepts Security policies for real systems Page
Security Principles and Policies CS 136 Computer Security Peter Reiher January 15, 2008 Page 1 Outline Security terms and concepts Security policies Basic concepts Security policies for real systems Page
Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017*
 600.120 Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017* Misha Kazhdan *Much of the code in these examples is not commented because it would otherwise not fit on the slides. This is bad coding practice in general
600.120 Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017* Misha Kazhdan *Much of the code in these examples is not commented because it would otherwise not fit on the slides. This is bad coding practice in general
Access Control. Tom Chothia Computer Security, Lecture 5
 Access Control Tom Chothia Computer Security, Lecture 5 The Crypto Wars 1993-1996: Clipper chip considered in US congress and rejected. Due partly to Matt Blaze s analysis and strongly attack by John Kerry
Access Control Tom Chothia Computer Security, Lecture 5 The Crypto Wars 1993-1996: Clipper chip considered in US congress and rejected. Due partly to Matt Blaze s analysis and strongly attack by John Kerry
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security. Spring 2007 Lecture 2
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 2 Announcements First project is on the web Due: Feb. 1st at midnight Form groups of 2 or 3 people If you need help finding a group,
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 2 Announcements First project is on the web Due: Feb. 1st at midnight Form groups of 2 or 3 people If you need help finding a group,
Secure Programming Lecture 15: Information Leakage
 Secure Programming Lecture 15: Information Leakage David Aspinall 21st March 2017 Outline Overview Language Based Security Taint tracking Information flow security by type-checking Summary Recap We have
Secure Programming Lecture 15: Information Leakage David Aspinall 21st March 2017 Outline Overview Language Based Security Taint tracking Information flow security by type-checking Summary Recap We have
Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security
 Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security CS 161: Computer Security Prof. Raluca Ada Popa January 17, 2016 Some slides credit to David Wagner and Nick Weaver Announcements Discussion sections and office
Memory Safety (cont d) Software Security CS 161: Computer Security Prof. Raluca Ada Popa January 17, 2016 Some slides credit to David Wagner and Nick Weaver Announcements Discussion sections and office
Software Security II: Memory Errors - Attacks & Defenses
 1 Software Security II: Memory Errors - Attacks & Defenses Chengyu Song Slides modified from Dawn Song 2 Administrivia Lab1 Writeup 3 Buffer overflow Out-of-bound memory writes (mostly sequential) Allow
1 Software Security II: Memory Errors - Attacks & Defenses Chengyu Song Slides modified from Dawn Song 2 Administrivia Lab1 Writeup 3 Buffer overflow Out-of-bound memory writes (mostly sequential) Allow
"Secure" Coding Practices Nicholas Weaver
 "Secure" Coding Practices based on David Wagner s slides from Sp 2016 1 Administrivia Computer Science 161 Fall 2016 2 3 This is a Remarkably Typical C Problem Computer Science 161 Fall 2016 if ((options
"Secure" Coding Practices based on David Wagner s slides from Sp 2016 1 Administrivia Computer Science 161 Fall 2016 2 3 This is a Remarkably Typical C Problem Computer Science 161 Fall 2016 if ((options
in memory: an evolution of attacks Mathias Payer Purdue University
 in memory: an evolution of attacks Mathias Payer Purdue University Images (c) MGM, WarGames, 1983 Memory attacks: an ongoing war Vulnerability classes according to CVE Memory
in memory: an evolution of attacks Mathias Payer Purdue University Images (c) MGM, WarGames, 1983 Memory attacks: an ongoing war Vulnerability classes according to CVE Memory
CSCI 420: Mobile Application Security. Lecture 7. Prof. Adwait Nadkarni. Derived from slides by William Enck, Patrick McDaniel and Trent Jaeger
 CSCI 420: Mobile Application Security Lecture 7 Prof. Adwait Nadkarni Derived from slides by William Enck, Patrick McDaniel and Trent Jaeger 1 cryptography < security Cryptography isn't the solution to
CSCI 420: Mobile Application Security Lecture 7 Prof. Adwait Nadkarni Derived from slides by William Enck, Patrick McDaniel and Trent Jaeger 1 cryptography < security Cryptography isn't the solution to
Software Security and Exploitation
 COMS E6998-9: 9: Software Security and Exploitation Lecture 8: Fail Secure; DoS Prevention; Evaluating Components for Security Hugh Thompson, Ph.D. hthompson@cs.columbia.edu Failing Securely and Denial
COMS E6998-9: 9: Software Security and Exploitation Lecture 8: Fail Secure; DoS Prevention; Evaluating Components for Security Hugh Thompson, Ph.D. hthompson@cs.columbia.edu Failing Securely and Denial
Mobile Malfeasance. Exploring Dangerous Mobile Code. Jason Haddix, Director of Penetration Testing
 Mobile Malfeasance Exploring Dangerous Mobile Code Jason Haddix, Director of Penetration Testing Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to
Mobile Malfeasance Exploring Dangerous Mobile Code Jason Haddix, Director of Penetration Testing Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to
CS 161 Computer Security
 Nick Weaver Fall 2018 CS 161 Computer Security Homework 3 Due: Friday, 19 October 2018, at 11:59pm Instructions. This homework is due Friday, 19 October 2018, at 11:59pm. No late homeworks will be accepted
Nick Weaver Fall 2018 CS 161 Computer Security Homework 3 Due: Friday, 19 October 2018, at 11:59pm Instructions. This homework is due Friday, 19 October 2018, at 11:59pm. No late homeworks will be accepted
NET 311 INFORMATION SECURITY
 NET 311 INFORMATION SECURITY Networks and Communication Department Lec12: Software Security / Vulnerabilities lecture contents: o Vulnerabilities in programs Buffer Overflow Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
NET 311 INFORMATION SECURITY Networks and Communication Department Lec12: Software Security / Vulnerabilities lecture contents: o Vulnerabilities in programs Buffer Overflow Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
Lecture 4 September Required reading materials for this class
 EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
Buffer overflow prevention, and other attacks
 Buffer prevention, and other attacks Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline 1 2 Two approaches to buffer defense Aim to harden programs to resist attacks in new programs Run time Aim to detect and abort attacks
Buffer prevention, and other attacks Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline 1 2 Two approaches to buffer defense Aim to harden programs to resist attacks in new programs Run time Aim to detect and abort attacks
Last time. User Authentication. Security Policies and Models. Beyond passwords Biometrics
 Last time User Authentication Beyond passwords Biometrics Security Policies and Models Trusted Operating Systems and Software Military and Commercial Security Policies 9-1 This time Security Policies and
Last time User Authentication Beyond passwords Biometrics Security Policies and Models Trusted Operating Systems and Software Military and Commercial Security Policies 9-1 This time Security Policies and
Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui
 Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui Projects 1 Information flow analysis for mobile applications 2 2 Machine-learning-guide typestate analysis for UAF vulnerabilities 3 3 Preventing
Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui Projects 1 Information flow analysis for mobile applications 2 2 Machine-learning-guide typestate analysis for UAF vulnerabilities 3 3 Preventing
Black Hat Webcast Series. C/C++ AppSec in 2014
 Black Hat Webcast Series C/C++ AppSec in 2014 Who Am I Chris Rohlf Leaf SR (Security Research) - Founder / Consultant BlackHat Speaker { 2009, 2011, 2012 } BlackHat Review Board Member http://leafsr.com
Black Hat Webcast Series C/C++ AppSec in 2014 Who Am I Chris Rohlf Leaf SR (Security Research) - Founder / Consultant BlackHat Speaker { 2009, 2011, 2012 } BlackHat Review Board Member http://leafsr.com
Overflows, Injection, & Memory Safety
 Overflows, Injection, & Memory Safety 1 Announcements... Computer Science 161 Fall 2018 Project 1 is now live! Due Friday September 14th Start it early: The add/drop deadline got reduced to September 12th
Overflows, Injection, & Memory Safety 1 Announcements... Computer Science 161 Fall 2018 Project 1 is now live! Due Friday September 14th Start it early: The add/drop deadline got reduced to September 12th
IS THERE A HOLE IN YOUR RISC-V SECURITY STACK? JOTHY ROSENBERG DOVER MICROSYSTEMS
 IS THERE A HOLE IN YOUR RISC-V SECURITY STACK? JOTHY ROSENBERG DOVER MICROSYSTEMS I understand the difference in destruction is dramatic, but this has a whiff of August 1945. Someone just used a new weapon,
IS THERE A HOLE IN YOUR RISC-V SECURITY STACK? JOTHY ROSENBERG DOVER MICROSYSTEMS I understand the difference in destruction is dramatic, but this has a whiff of August 1945. Someone just used a new weapon,
CNT4406/5412 Network Security Introduction
 CNT4406/5412 Network Security Introduction Zhi Wang Florida State University Fall 2013 Zhi Wang (FSU) CNT4406/5412 Network Security Fall 2013 1 / 35 Introduction What is Security? Protecting information
CNT4406/5412 Network Security Introduction Zhi Wang Florida State University Fall 2013 Zhi Wang (FSU) CNT4406/5412 Network Security Fall 2013 1 / 35 Introduction What is Security? Protecting information
Engineering Your Software For Attack
 Engineering Your Software For Attack Robert A. Martin Senior Principal Engineer Cyber Security Center Center for National Security The MITRE Corporation 2013 The MITRE Corporation. All rights reserved.
Engineering Your Software For Attack Robert A. Martin Senior Principal Engineer Cyber Security Center Center for National Security The MITRE Corporation 2013 The MITRE Corporation. All rights reserved.
Computer Security. 04r. Pre-exam 1 Concept Review. Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Spring 2018
 Computer Security 04r. Pre-exam 1 Concept Review Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2018 February 15, 2018 CS 419 2018 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Key ideas from the past four lectures February 15, 2018
Computer Security 04r. Pre-exam 1 Concept Review Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Spring 2018 February 15, 2018 CS 419 2018 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Key ideas from the past four lectures February 15, 2018
typedef void (*type_fp)(void); int a(char *s) { type_fp hf = (type_fp)(&happy_function); char buf[16]; strncpy(buf, s, 18); (*hf)(); return 0; }
![typedef void (*type_fp)(void); int a(char *s) { type_fp hf = (type_fp)(&happy_function); char buf[16]; strncpy(buf, s, 18); (*hf)(); return 0; } typedef void (*type_fp)(void); int a(char *s) { type_fp hf = (type_fp)(&happy_function); char buf[16]; strncpy(buf, s, 18); (*hf)(); return 0; }](/thumbs/82/86078968.jpg) Dawn Song Fall 2012 CS 161 Computer Security Practice Questions 1. (6 points) Control Hijacking Indicate whether the statement is always valid. Indicate true or false, and give a one sentence explanation.
Dawn Song Fall 2012 CS 161 Computer Security Practice Questions 1. (6 points) Control Hijacking Indicate whether the statement is always valid. Indicate true or false, and give a one sentence explanation.
Secure Systems Administration and Engineering
 Secure Systems Administration and Engineering Program Information The job outlook for careers in Cybersecurity and Information Technology continues to be very strong. Many experts predict a continued shortage
Secure Systems Administration and Engineering Program Information The job outlook for careers in Cybersecurity and Information Technology continues to be very strong. Many experts predict a continued shortage
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Fall Quiz I
 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.858 Fall 2010 Quiz I All problems are open-ended questions. In order to receive credit you must answer
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.858 Fall 2010 Quiz I All problems are open-ended questions. In order to receive credit you must answer
Threat Modeling. Bart De Win Secure Application Development Course, Credits to
 Threat Modeling Bart De Win bart.dewin@ascure.com Secure Application Development Course, 2009 Credits to Frank Piessens (KUL) for the slides 2 1 Overview Introduction Key Concepts Threats, Vulnerabilities,
Threat Modeling Bart De Win bart.dewin@ascure.com Secure Application Development Course, 2009 Credits to Frank Piessens (KUL) for the slides 2 1 Overview Introduction Key Concepts Threats, Vulnerabilities,
CS 161 Computer Security
 Paxson Spring 2017 CS 161 Computer Security Midterm 1 Print your name:, (last) (first) I am aware of the Berkeley Campus Code of Student Conduct and acknowledge that any academic misconduct will be reported
Paxson Spring 2017 CS 161 Computer Security Midterm 1 Print your name:, (last) (first) I am aware of the Berkeley Campus Code of Student Conduct and acknowledge that any academic misconduct will be reported
Applications. Cloud. See voting example (DC Internet voting pilot) Select * from userinfo WHERE id = %%% (variable)
 Software Security Requirements General Methodologies Hardware Firmware Software Protocols Procedure s Applications OS Cloud Attack Trees is one of the inside requirement 1. Attacks 2. Evaluation 3. Mitigation
Software Security Requirements General Methodologies Hardware Firmware Software Protocols Procedure s Applications OS Cloud Attack Trees is one of the inside requirement 1. Attacks 2. Evaluation 3. Mitigation
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 12: Database Security Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Review of Access Control Types We previously studied four types
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 12: Database Security Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Review of Access Control Types We previously studied four types
Secure C Coding...yeah right. Andrew Zonenberg Alex Radocea
 Secure C Coding...yeah right Andrew Zonenberg Alex Radocea Agenda Some Quick Review Data Representation Pointer Arithmetic Memory Management Basic C Vulnerabilities Memory Corruption Ignoring Return values
Secure C Coding...yeah right Andrew Zonenberg Alex Radocea Agenda Some Quick Review Data Representation Pointer Arithmetic Memory Management Basic C Vulnerabilities Memory Corruption Ignoring Return values
Unit Testing & Testability
 CMPT 473 Software Quality Assurance Unit Testing & Testability Nick Sumner - Fall 2014 Levels of Testing Recall that we discussed different levels of testing for test planning: Unit Tests Integration Tests
CMPT 473 Software Quality Assurance Unit Testing & Testability Nick Sumner - Fall 2014 Levels of Testing Recall that we discussed different levels of testing for test planning: Unit Tests Integration Tests
CSE509 Spring 2007 Midterm Exam. Electronic devices, including calculators, cell phones, mp3 players, and laptops are all prohibited.
 CSE509 Spring 2007 Midterm Exam Name: You may not use any reference materials during this exam. Electronic devices, including calculators, cell phones, mp3 players, and laptops are all prohibited. You
CSE509 Spring 2007 Midterm Exam Name: You may not use any reference materials during this exam. Electronic devices, including calculators, cell phones, mp3 players, and laptops are all prohibited. You
CS-527 Software Security
 CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++
 Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++ Christian DeLozier, Richard Eisenberg, Peter-Michael Osera, Santosh Nagarakatte*, Milo M. K. Martin, and Steve Zdancewic October 30, 2013 University
Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++ Christian DeLozier, Richard Eisenberg, Peter-Michael Osera, Santosh Nagarakatte*, Milo M. K. Martin, and Steve Zdancewic October 30, 2013 University
Topics in Software Security Vulnerability
 Topics in Software Security Vulnerability Software vulnerability What are software vulnerabilities? Types of vulnerabilities E.g., Buffer Overflows How to find these vulnerabilities and prevent them? Classes
Topics in Software Security Vulnerability Software vulnerability What are software vulnerabilities? Types of vulnerabilities E.g., Buffer Overflows How to find these vulnerabilities and prevent them? Classes
Basic Buffer Overflows
 Operating Systems Security Basic Buffer Overflows (Stack Smashing) Computer Security & OS lab. Cho, Seong-je ( 조성제 ) Fall, 2018 sjcho at dankook.ac.kr Chapter 10 Buffer Overflow 2 Contents Virtual Memory
Operating Systems Security Basic Buffer Overflows (Stack Smashing) Computer Security & OS lab. Cho, Seong-je ( 조성제 ) Fall, 2018 sjcho at dankook.ac.kr Chapter 10 Buffer Overflow 2 Contents Virtual Memory
C1: Define Security Requirements
 OWASP Top 10 Proactive Controls IEEE Top 10 Software Security Design Flaws OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities Mitigated OWASP Mobile Top 10 Vulnerabilities Mitigated C1: Define Security Requirements A security
OWASP Top 10 Proactive Controls IEEE Top 10 Software Security Design Flaws OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities Mitigated OWASP Mobile Top 10 Vulnerabilities Mitigated C1: Define Security Requirements A security
SoK: Eternal War in Memory
 SoK: Eternal War in Memory László Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, Dawn Song Presenter: Wajih 11/7/2017 Some slides are taken from original S&P presentation 1 What is SoK paper? Systematization of Knowledge
SoK: Eternal War in Memory László Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, Dawn Song Presenter: Wajih 11/7/2017 Some slides are taken from original S&P presentation 1 What is SoK paper? Systematization of Knowledge
Introduction. Controlling Information Systems. Threats to Computerised Information System. Why System are Vulnerable?
 Introduction Controlling Information Systems When computer systems fail to work as required, firms that depend heavily on them experience a serious loss of business function. M7011 Peter Lo 2005 1 M7011
Introduction Controlling Information Systems When computer systems fail to work as required, firms that depend heavily on them experience a serious loss of business function. M7011 Peter Lo 2005 1 M7011
DEFENSIVE PROGRAMMING. Lecture for EDA 263 Magnus Almgren Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 DEFENSIVE PROGRAMMING Lecture for EDA 263 Magnus Almgren Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Traditional Programming When writing a program, programmers typically
DEFENSIVE PROGRAMMING Lecture for EDA 263 Magnus Almgren Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Traditional Programming When writing a program, programmers typically
A Crash Course in (Some of) Modern C++
 CMPT 373 Software Development Methods A Crash Course in (Some of) Modern C++ Nick Sumner wsumner@sfu.ca With material from Bjarne Stroustrup & Herb Sutter C++ was complicated/intimidating Pointers Arithmetic
CMPT 373 Software Development Methods A Crash Course in (Some of) Modern C++ Nick Sumner wsumner@sfu.ca With material from Bjarne Stroustrup & Herb Sutter C++ was complicated/intimidating Pointers Arithmetic
Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis
 Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis Host Based Attacks Pavel Laskov Wilhelm Schickard Institute for Computer Science Software security threats Modification of program code viruses and self-replicating
Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis Host Based Attacks Pavel Laskov Wilhelm Schickard Institute for Computer Science Software security threats Modification of program code viruses and self-replicating
HW 8 CS681 & CS392 Computer Security Understanding and Experimenting with Memory Corruption Vulnerabilities DUE 12/18/2005
 HW 8 CS681 & CS392 Computer Security Understanding and Experimenting with Memory Corruption Vulnerabilities 1 Motivation DUE 12/18/2005 Memory corruption vulnerabilities to change program execution flow
HW 8 CS681 & CS392 Computer Security Understanding and Experimenting with Memory Corruption Vulnerabilities 1 Motivation DUE 12/18/2005 Memory corruption vulnerabilities to change program execution flow
1. (6 points) Control Hijacking Indicate whether the statement is always valid. Indicate true or false, and give a one sentence explanation.
 Dawn Song Fall 2012 CS 161 Computer Security Practice Questions 1. (6 points) Control Hijacking Indicate whether the statement is always valid. Indicate true or false, and give a one sentence explanation.
Dawn Song Fall 2012 CS 161 Computer Security Practice Questions 1. (6 points) Control Hijacking Indicate whether the statement is always valid. Indicate true or false, and give a one sentence explanation.
Buffer Overflows Defending against arbitrary code insertion and execution
 www.harmonysecurity.com info@harmonysecurity.com Buffer Overflows Defending against arbitrary code insertion and execution By Stephen Fewer Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Where does the problem lie? 2 1.1.1
www.harmonysecurity.com info@harmonysecurity.com Buffer Overflows Defending against arbitrary code insertion and execution By Stephen Fewer Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Where does the problem lie? 2 1.1.1
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Fall Quiz I
 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.858 Fall 2010 Quiz I All problems are open-ended questions. In order to receive credit you must answer
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.858 Fall 2010 Quiz I All problems are open-ended questions. In order to receive credit you must answer
C and C++ Secure Coding 4-day course. Syllabus
 C and C++ Secure Coding 4-day course Syllabus C and C++ Secure Coding 4-Day Course Course description Secure Programming is the last line of defense against attacks targeted toward our systems. This course
C and C++ Secure Coding 4-day course Syllabus C and C++ Secure Coding 4-Day Course Course description Secure Programming is the last line of defense against attacks targeted toward our systems. This course
CSE127 Midterm. Yee Winter 03
 CSE127 Midterm Yee Winter 03 Name and Student ID: Answer Key Wait until everybody has a copy before you start. This exam is closed book, closed notes. There are a total of 14 questions on 8 pages. There
CSE127 Midterm Yee Winter 03 Name and Student ID: Answer Key Wait until everybody has a copy before you start. This exam is closed book, closed notes. There are a total of 14 questions on 8 pages. There
Memory Leak. C++: Memory Problems. Memory Leak. Memory Leak. Pointer Ownership. Memory Leak
 Memory Leak C++ Memory Problems or When Good Memory Goes Bad A bug in a program that prevents it from freeing up memory that it no longer needs. As a result, the program grabs more and more memory until
Memory Leak C++ Memory Problems or When Good Memory Goes Bad A bug in a program that prevents it from freeing up memory that it no longer needs. As a result, the program grabs more and more memory until
Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting. Jonathan Pincus(MSR) and Brandon Baker (MS)
 Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer Overruns Jonathan Pincus(MSR) and Brandon Baker (MS) Buffer Overflows and How they Occur Buffer is a contiguous segment of memory of a fixed
Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer Overruns Jonathan Pincus(MSR) and Brandon Baker (MS) Buffer Overflows and How they Occur Buffer is a contiguous segment of memory of a fixed
Malware, , Database Security
 Malware, E-mail, Database Security Malware A general term for all kinds of software with a malign purpose Viruses, Trojan horses, worms etc. Created on purpose Can Prevent correct use of resources (DoS)
Malware, E-mail, Database Security Malware A general term for all kinds of software with a malign purpose Viruses, Trojan horses, worms etc. Created on purpose Can Prevent correct use of resources (DoS)
Limitations of the stack
 The heap hic 1 Limitations of the stack int *table_of(int num, int len) { int table[len+1]; for (int i=0; i
The heap hic 1 Limitations of the stack int *table_of(int num, int len) { int table[len+1]; for (int i=0; i
CSCE 548 Building Secure Software Integers & Integer-related Attacks & Format String Attacks. Professor Lisa Luo Spring 2018
 CSCE 548 Building Secure Software Integers & Integer-related Attacks & Format String Attacks Professor Lisa Luo Spring 2018 Previous Class Buffer overflows can be devastating It occurs when the access
CSCE 548 Building Secure Software Integers & Integer-related Attacks & Format String Attacks Professor Lisa Luo Spring 2018 Previous Class Buffer overflows can be devastating It occurs when the access
Last week. Data on the stack is allocated automatically when we do a function call, and removed when we return
 Last week Data can be allocated on the stack or on the heap (aka dynamic memory) Data on the stack is allocated automatically when we do a function call, and removed when we return f() {... int table[len];...
Last week Data can be allocated on the stack or on the heap (aka dynamic memory) Data on the stack is allocated automatically when we do a function call, and removed when we return f() {... int table[len];...
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
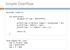 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Defect Based Approach using Defect Taxonomy. Chhavi Raj Dosaj
 Defect Based Approach using Defect Taxonomy Chhavi Raj Dosaj Defect Based Testing Dynamic Testing Techniques White-box Black-box Experience based Defect based Defect Based Testing In defect based testing
Defect Based Approach using Defect Taxonomy Chhavi Raj Dosaj Defect Based Testing Dynamic Testing Techniques White-box Black-box Experience based Defect based Defect Based Testing In defect based testing
Engineering Robust Server Software
 Engineering Robust Server Software Vulnerabilities Common/Famous Vulnerabilities: Do Not Do! Common vulnerabilities Buffer overflow Failure to sanitize SQL Command injection Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
Engineering Robust Server Software Vulnerabilities Common/Famous Vulnerabilities: Do Not Do! Common vulnerabilities Buffer overflow Failure to sanitize SQL Command injection Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE. The University of Tokyo
 Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems. Software Security
 CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Software Security Topics 1. The problem of software security 2. System security standards 3. Secure lifecycle 4. Buffer overflows 5. Integer overflows 6. Format string
CIT 380: Securing Computer Systems Software Security Topics 1. The problem of software security 2. System security standards 3. Secure lifecycle 4. Buffer overflows 5. Integer overflows 6. Format string
Protect Your Application with Secure Coding Practices. Barrie Dempster & Jason Foy JAM306 February 6, 2013
 Protect Your Application with Secure Coding Practices Barrie Dempster & Jason Foy JAM306 February 6, 2013 BlackBerry Security Team Approximately 120 people work within the BlackBerry Security Team Security
Protect Your Application with Secure Coding Practices Barrie Dempster & Jason Foy JAM306 February 6, 2013 BlackBerry Security Team Approximately 120 people work within the BlackBerry Security Team Security
Fundamentals of Computer Security
 Fundamentals of Computer Security Spring 2015 Radu Sion Software Errors Buffer Overflow TOCTTOU 2005-15 Portions copyright by Bogdan Carbunar and Wikipedia. Used with permission Why Security Vulnerabilities?
Fundamentals of Computer Security Spring 2015 Radu Sion Software Errors Buffer Overflow TOCTTOU 2005-15 Portions copyright by Bogdan Carbunar and Wikipedia. Used with permission Why Security Vulnerabilities?
Students should have an understanding and a working knowledge in the following topics, or attend these courses as a pre-requisite:
 Secure Java Web Application Development Lifecycle - SDL (TT8325-J) Day(s): 5 Course Code: GK1107 Overview Secure Java Web Application Development Lifecycle (SDL) is a lab-intensive, hands-on Java / JEE
Secure Java Web Application Development Lifecycle - SDL (TT8325-J) Day(s): 5 Course Code: GK1107 Overview Secure Java Web Application Development Lifecycle (SDL) is a lab-intensive, hands-on Java / JEE
CNIT 127: Exploit Development. Ch 18: Source Code Auditing. Updated
 CNIT 127: Exploit Development Ch 18: Source Code Auditing Updated 4-10-17 Why Audit Source Code? Best way to discover vulnerabilities Can be done with just source code and grep Specialized tools make it
CNIT 127: Exploit Development Ch 18: Source Code Auditing Updated 4-10-17 Why Audit Source Code? Best way to discover vulnerabilities Can be done with just source code and grep Specialized tools make it
Buffer Overflows. Buffers. Administrative. COMP 435 Fall 2017 Prof. Cynthia Sturton. Buffers
 dministrative Buffer Overflows COMP 435 Fall 2017 Prof. Cynthia Sturton Exam Mon., Nov. 6 Covers material since last exam, including today s lecture Review in OH Fri., Nov. 3, 10-12 FB 354 Poster group
dministrative Buffer Overflows COMP 435 Fall 2017 Prof. Cynthia Sturton Exam Mon., Nov. 6 Covers material since last exam, including today s lecture Review in OH Fri., Nov. 3, 10-12 FB 354 Poster group
Secure Programming Lecture 3: Memory Corruption I (Stack Overflows)
 Secure Programming Lecture 3: Memory Corruption I (Stack Overflows) David Aspinall, Informatics @ Edinburgh 24th January 2017 Outline Roadmap Memory corruption vulnerabilities Instant Languages and Runtimes
Secure Programming Lecture 3: Memory Corruption I (Stack Overflows) David Aspinall, Informatics @ Edinburgh 24th January 2017 Outline Roadmap Memory corruption vulnerabilities Instant Languages and Runtimes
CSCE 548 Building Secure Software Buffer Overflow. Professor Lisa Luo Spring 2018
 CSCE 548 Building Secure Software Buffer Overflow Professor Lisa Luo Spring 2018 Previous Class Virus vs. Worm vs. Trojan & Drive-by download Botnet & Rootkit Malware detection Scanner Polymorphic malware
CSCE 548 Building Secure Software Buffer Overflow Professor Lisa Luo Spring 2018 Previous Class Virus vs. Worm vs. Trojan & Drive-by download Botnet & Rootkit Malware detection Scanner Polymorphic malware
Who s Afraid of SQL Injection?! Mike Kölbl Sonja Klausburg Siegfried Goeschl
 Who s Afraid of SQL Injection?! Mike Kölbl Sonja Klausburg Siegfried Goeschl 1 http://xkcd.com/327/ 2 What Is SQL Injection? Incorrectly validated or nonvalidated string literals are concatenated into
Who s Afraid of SQL Injection?! Mike Kölbl Sonja Klausburg Siegfried Goeschl 1 http://xkcd.com/327/ 2 What Is SQL Injection? Incorrectly validated or nonvalidated string literals are concatenated into
Buffer Overflow Attacks
 Buffer Overflow Attacks 1. Smashing the Stack 2. Other Buffer Overflow Attacks 3. Work on Preventing Buffer Overflow Attacks Smashing the Stack An Evil Function void func(char* inp){ } char buffer[16];
Buffer Overflow Attacks 1. Smashing the Stack 2. Other Buffer Overflow Attacks 3. Work on Preventing Buffer Overflow Attacks Smashing the Stack An Evil Function void func(char* inp){ } char buffer[16];
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 4 C Pointers 2004-09-08 Lecturer PSOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Cal flies over Air Force We re ranked 13 th in the US and
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 4 C Pointers 2004-09-08 Lecturer PSOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Cal flies over Air Force We re ranked 13 th in the US and
Certified Ethical Hacker
 Certified Ethical Hacker Certified Ethical Hacker Course Objective Describe how perimeter defenses function by ethically scanning and attacking networks Conduct information systems security audits by understanding
Certified Ethical Hacker Certified Ethical Hacker Course Objective Describe how perimeter defenses function by ethically scanning and attacking networks Conduct information systems security audits by understanding
Advanced Systems Security: Ordinary Operating Systems
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Stanford University Computer Science Department CS 295 midterm. May 14, (45 points) (30 points) total
 Stanford University Computer Science Department CS 295 midterm May 14, 2008 This is an open-book exam. You have 75 minutes. Write all of your answers directly on the paper. Make your answers as concise
Stanford University Computer Science Department CS 295 midterm May 14, 2008 This is an open-book exam. You have 75 minutes. Write all of your answers directly on the paper. Make your answers as concise
MIPS Functions and Instruction Formats
 MIPS Functions and Instruction Formats 1 The Contract: The MIPS Calling Convention You write functions, your compiler writes functions, other compilers write functions And all your functions call other
MIPS Functions and Instruction Formats 1 The Contract: The MIPS Calling Convention You write functions, your compiler writes functions, other compilers write functions And all your functions call other
HW1 due Monday by 9:30am Assignment online, submission details to come
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61CL : Machine Structures Lecture #2 - C Pointers and Arrays Administrivia Buggy Start Lab schedule, lab machines, HW0 due tomorrow in lab 2009-06-24 HW1 due Monday by 9:30am
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61CL : Machine Structures Lecture #2 - C Pointers and Arrays Administrivia Buggy Start Lab schedule, lab machines, HW0 due tomorrow in lab 2009-06-24 HW1 due Monday by 9:30am
18-600: Recitation #4 Exploits (Attack Lab)
 18-600: Recitation #4 Exploits (Attack Lab) September 19th, 2017 Announcements Some students have triggered the bomb multiple times Use breakpoints for explode_bomb() Attack lab will be released on Sep.
18-600: Recitation #4 Exploits (Attack Lab) September 19th, 2017 Announcements Some students have triggered the bomb multiple times Use breakpoints for explode_bomb() Attack lab will be released on Sep.
Secure coding practices
 Secure coding practices www.infosys.com/finacle Universal Banking Solution Systems Integration Consulting Business Process Outsourcing Secure coding practices Writing good code is an art but equally important
Secure coding practices www.infosys.com/finacle Universal Banking Solution Systems Integration Consulting Business Process Outsourcing Secure coding practices Writing good code is an art but equally important
CS527 Software Security
 Software Bugs Purdue University, Spring 2018 From Software Bugs to Attack Primitives Attack primitives are exploit building blocks Software bugs map to attack primitives, i.e., enable computation A chain
Software Bugs Purdue University, Spring 2018 From Software Bugs to Attack Primitives Attack primitives are exploit building blocks Software bugs map to attack primitives, i.e., enable computation A chain
Dissecting Data Breaches. What Keeps Going Wrong?
 Dissecting Data Breaches What Keeps Going Wrong? 02 WHO WE ARE Tom Stewart Uriah Robins Senior Manager IT Consulting Protiviti Senior Consultant IT Consulting Protiviti PRESENTATION AGENDA 3 START BREACH
Dissecting Data Breaches What Keeps Going Wrong? 02 WHO WE ARE Tom Stewart Uriah Robins Senior Manager IT Consulting Protiviti Senior Consultant IT Consulting Protiviti PRESENTATION AGENDA 3 START BREACH
Advanced Systems Security: Multics
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
