CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 8 Dec 2016 Final Exam Answer Key
|
|
|
- Curtis Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 1 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 8 Dec 2016 Final Exam Answer Key 1.) PennKey, Penn Mascot, etc. (2 points total) (a) Check to make certain that your exam has all 10 pages (excluding the cover sheet). (b) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (c) Sign the certification that you comply with the Penn Academic Integrity Code. (d) Which Ivy League university has the Quaker as its mascot? Circle your answer. University of Pennsylvania (Go Quakers!) Dartmouth College Brown University Columbia University Cornell University Harvard University Princeton University Yale University 2.) Brown s Pass/Fail Policy (9 points total) In 1969, Brown University began doing away with letter grades, instead choosing to go with a pass/fail system. On Brown s computer science final, to accommodate their grade policy, students were asked to write down one thing they learned that semester. Those who wrote something true would PASS, those who wrote something false would FAIL. To avoid any appearance of favoritism from the faculty, Brown University outsourced the exam grading to Dr. Brown at Penn. He, in return, is delegating it to you. Help Dr. Brown grade Brown University s exams by determining if the student who wrote each sentence gets a PASS (true) or a FAIL (false). Student s Submission Encapsulation is the idea that more information isn t always better. Pass/Fail MergeSort is called MergeSort because it merges the best parts of a selection sort and an insertion sort. Helper functions in object oriented design should be made public. An instance of an object is a version of the object used only in a local scope, i.e. instantly. A key advantage of a linked list over an array is resizability. A Stack is First In, Last Out. An interface lists and implements a set of functions for a class. Linked lists have a faster access time than arrays, which is why you should usually use Linked Lists. If you do not write a constructor for an object, all primitive data types in your object will be initialized to null.
2 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 2 3.) Hunting Clowns at Yale (8 points total) Little known fact: Dr. McBurney hates clowns almost as much as Joe Biden loves ice cream. That s why he took a year-long trip to Yale the top clown college in the world to hunt the wretched beasts. (Crime-ridden New Haven, CT has been trying to eliminate the clown mafia for decades, with little success.) During his year at Yale, Dr. McBurney put together a clown tracking program, but some of the code was erased when the TSA mishandled his laptop before the flight home. A clown map is a boolean array consisting of only trues and falses. A clown den in the map is defined as a series of 2 or more adjacent trues. In the code below, fill in the blanks to complete the getclowndencount() method that returns the number of Clown dens present in the map field. Examples: boolean[] map = {true, false, false, false, false; ClownSlayer will = new ClownSlayer(map); will.getclowncount() returns 0 boolean[] map = {true, true, true, false, true, true; ClownSlayer will = new ClownSlayer(map); will.getclowncount() returns 2 public class ClownSlayer { boolean[] map; public int getclowndencount() { // error check if (map == null) { return 0; int count = 0; boolean foundden = false; for (int i = 0; i < map.length - 1; i++) { if (map[i] && map[i + 1] &&!foundden) { foundden = true; count++; else if (!map[i]) { foundden = false; return count; //... the rest of ClownSlayer is here
3 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 3 4.) Grade Inflation (22 points total) Harvard is teaching a computer science class this semester, but even very lenient grading isn t yielding enough As. The unversity has therefore decided to give the top student a 100%, and give all other students the score earned by the student scoring immediately higher them. Harvard asked the students in the class to write a function that would compute the revised scores, but the students did a lousy job. So now Harvard wants you to figure out what their students wrote and fix it. For example, if the student grades were int[] studentgrades = {40, 80, 60, 90, 30 Then the function is supposed to modify the grades to be {60, 90, 80, 100, 40. Sometimes multiple students have the same grade, for instance: int[] studentgrades = {60, 40, 40, 90 Then both the 40s should get bumped up to the next higher grade: {90, 60, 60, ) (2 points) To start off, the Harvard students wrote a sorting function. It does work, but the university wants some more information about it: public static void sort(int[] array) { for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) { int a = array[i]; int b = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) { if (array[j] < a) { a = array[j]; b = j; int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[b]; array[b] = temp; printarray(array); (a) What is the name of this sorting algorithm? Selection Sort (b) Does this function sort in ascending (smallest to largest) or descending (largest to smallest) order? Ascending QUESTION CONTINUES ON THE NEXT PAGE
4 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 4 Grade Inflation (Continued) Using the sorting function from the previous page, the Harvard students created the following buggy function to raise all their grades (line numers have been added so you can refer to lines of code easily): 1. public void inflategrades(int[] studentgrades) { 2. int[] copyofgrades = int[studentgrades.length]; // copy the contents of studentgrades 1 at a time 5. copyofgrades = studentgrades; copyofgrades = sort(copyofgrades); // for each grade in student grades for (int i = 0; i <= studentgrades.length; i++) { 11. // if student has maximum grade, give if (studentgrades[i] == copyofgrades[0]) { 13. studentgrades[i] = 100; 14. break; // otherwise find the next grade after tobefound 18. int tobefound = studentgrades[j]; 19. for (int j = 0; j <= studentgrades.length; j++) { 20. if (tobefound == copyofgrades[j]) { 21. while(tobefound == copyofgrades[j]) 22. j--; studentgrades[j] = copyofgrades[j]; On the following page, identify each buggy line in this program, and explain the bug in 20 words or less. If you feel a single bug is rooted in multiple lines of code, list all lines in the same box. You may either explain the bug without fixing it, or provide a snippet of code that would correct it. You do not need to write complete sentences or complete corrected lines of code. There may be fewer bugs than rows in the table! QUESTION CONTINUES ON THE NEXT PAGE
5 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 5 Grade Inflation (Continued) 4.2) (20 points) Identify each buggy line in the program on the previous page, and explain the bug in 20 words or less. If you feel a single bug is rooted in multiple lines of code, list all lines in the same box. You may either explain the bug without fixing it, or provide a snippet of code that would correct it. You do not need to write complete sentences or complete corrected lines of code. There may be fewer bugs than rows in the table! Line Number Brief description of bug (<= 20 words) 2 Missing new keyword 5 Makes reference, doesn t copy values, so copyofgrades sorts boths arrays 7 sort is void, so cannot assign result to a variable 10 Need to use < studentgrades.length or <= studentgrades.length Maximum value is in copyofgrades[copyofgrades.length - 1] 14 Need continue instead of break 18 Need studentgrades[i], not j 19 Need to use < studentgrades.length or <= studentgrades.length Need j++, not j-- 24 Need studentgrades[i], not j
6 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 6 5.) Animal House (12 points total) Members of Animal House s Delta fraternity (modeled on Dartmouth College) constantly face expulsion over their low GPAs. Recently, some of them have written a (poor) program to manipulate their GPAs, and the dean wants to know exactly what it does. To that end, he has asked you to figure out the values of certain variables at each of four points in the program: public class DartmouthStudent { private double gpa; private String nickname; public DartmouthStudent(double g, String n) { gpa = g; nickname = n; public double getgpa() { return gpa; public void setgpa(double gpa) { gpa = this.gpa; public String getnickname() { return nickname; public void setnickname(string n) { nickname = n; public static void fixgpa(double g, DartmouthStudent delta) { g = 1.0 / 0.0; double gpa = delta.getgpa(); delta.setnickname("qwerty"); // POINT B delta.setgpa(1.6); delta = new DartmouthStudent(0.678, "Bluto"); // POINT C public static void main(string[] args) { double g = 0.05; DartmouthStudent delta = new DartmouthStudent(0.08, "Otter"); // POINT A fixgpa(g, delta); System.out.print(delta.getNickname()); // POINT D Point A Point B Point C Point D g delta.gpa detla.nickname
7 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 7 6.) The Hottest Holiday TOY (15 points total) Because of their proximity to 5th Avenue, Columbia students have an edge over all other Ivy Leaguers in finding out what the hot toy for the holidays will be and in getting hold of it. But this year, they decided it would be ironic to sit around in a dim cafe and play with TOY instead. In one recent afternoon, Columbia students produced the following gem, although they didn t add any comments of their own. As a result, we don t know what output it produces, or even how many values it outputs. 01: 0003 ( , 3) 10: 7301 R[3] < : 5133 R[1] <- R[3] << R[3] 12: 8201 R[2] <- mem[01] 13: 8415 R[4] <- mem[15] 14: D116 if (R[1] > 0) goto 16 15: 0000 halt 16: 93FF write R[3] 17: 94FF write R[4] 18: D415 if (R[4] > 0) goto 15 19: 94FF write R[4] 1A: 2A12 R[A] <- R[1] - R[2] 1B: DA01 if (R[A] > 0) goto 01 1C: 91FF write R[1] 1D: 5332 R[3] <- R[3] << R[2] 1E: 143A R[4] <- R[3] + R[A] 1F: C415 if (R[4] == 0) goto 15 20: 94FF write R[4] 21: D301 if (R[3] > 0) goto 01 22: 93FF write R[3] 23: 0000 halt 6.1) (15 points) What values does this program write to standard output? Write your answer as a list of numbers in ordinary, base 10 notation. 1, 0, 0, 2, 7 [Editor s Note: Apparently the program just print s out Columbia s ZIP code.]
8 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 8 7.) Surfing the Dinky (24 points total) A particulary reprehensible (and thoroughly illegal) Princeton tradition is surfing the Dinky, which involves riding on top of the train connecting Princeton with the main station at Princeton Junction. There are a number of points along this short journey where you are liable to get electrocuted by a low-hanging catenary wire or bludgeoned by a low-hanging tree branch or beam. In a seriously misguided effort to improve the safety of this activity, you propose compiling a list of when to duck to avoid obstacles. More precisely, you suggest recording how many seconds should pass before you have to duck again. Since you would need to refine this list over a few test runs, and update it as overhead lines and obstructions are modified, you decide to implement this with a linked list using the following node class: public class DuckNode { public int interval; // duck after interval seconds public DuckNode next; // next node in the list We ll skip over the part where you construct this list, since surfing the dinky is a really, really bad idea, and instead try and salvage the list that has been so painfully created for legitimate purposes. For example, you could figure out the total travel time from this list, since you would need to duck as the train arrives at the covered station at either end. You can also figure out the average travel time between low-hanging obstacles (total travel time divided by number of obstacles), which might be usefule if NJ Transit ever decides to introduce a double-decker dinky. 7.1) (7 points) Write a public static function iterativetraveltime that is part of the DuckNode class that takes a single DuckNode argument and returns the total travel time as an integer. Return 0 if the argument is null. The function must be iterative, and may not call any functions or methods. Do not write class DuckNode around the function, just write that function itself. You do not have to write any comments, but you are welcome to do so. public static int iterativetraveltime(ducknode head) { if (head == null) return 0; int traveltime = 0; for (Node n = head; n!= null; n = n.next) { traveltime += n.interval; return traveltime; QUESTION CONTINUES ON THE NEXT PAGE
9 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 9 Surfing the Dinky (Cont d) 7.2) (7 points) Write a public non-static method recursivetraveltime that is part of the DuckNode class that takes no arguments and returns the total travel time as an integer. This version must be recursive, may not call any other functions or methods, and many not contain any loops. public int iterativetraveltime() { if (next == null) return traveltime; return traveltime + next.recursivetraveltime(); 7.3) (10 points) Write a public static function avgtimebetweenobstacles that is part of the DuckNode class that takes a single DuckNode argument and returns the average time between obstacles as a double. Return 0 if the argument is null. This function must be self-contained and may not call either of your previous two methods. It can be recursive or iterative or a combination of both. You may write at most one private helper method (you don t have to), which can be static or non-static as you prefer. public static double avgtimebetweenobstacles(ducknode head) { if (head == null) return 0; int count = 0; int traveltime = 0; for (Node n = head; n!= null; n++) { traveltime += n.interval; count++; return traveltime / (double) count; Note: This is extremely difficult or impossible to implement recursively within the constraints of the question because you need to compute both the total travel time and the number of nodes in order to compute the average. That would either require two recursive helper methods, one for each value, or some sort of inelegant gimmick effectively return two values at a time.
10 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Final 10 TOY Reference Card INSTRUCTION FORMATS Format 1: opcode d s t (0-6, A-B) Format 2: opcode d addr (7-9, C-F) ARITHMETIC and LOGICAL operations 1: add R[d] <- R[s] + R[t] 2: subtract R[d] <- R[s] - R[t] 3: and R[d] <- R[s] & R[t] 4: xor R[d] <- R[s] ^ R[t] 5: shift left R[d] <- R[s] << R[t] 6: shift right R[d] <- R[s] >> R[t] TRANSFER between registers and memory 7: load address R[d] <- addr 8: load R[d] <- mem[addr] 9: store mem[addr] <- R[d] A: load indirect R[d] <- mem[r[t]] B: store indirect mem[r[t]] <- R[d] CONTROL 0: halt halt C: branch zero if (R[d] == 0) pc <- addr D: branch positive if (R[d] > 0) pc <- addr E: jump register pc <- R[d] F: jump and link R[d] <- pc; pc <- addr Register 0 always reads 0. Loads from mem[ff] come from stdin. Stores to mem[ff] go to stdout.
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming. 17 December 2012 Final Exam
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 17 December 2012 Final Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 17 December 2012 Final Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall Exam 1
 COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2005 Exam 1 This test has 9 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet,
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2005 Exam 1 This test has 9 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet,
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming. 7 May 2012 Final Exam
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 7 May 2012 Final Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 7 May 2012 Final Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Spring 2015
 COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Spring 2015 There are 9 questions on this exam, weighted as indicated below. The exam is closed book, though you are allowed to use a single-page one-sided hand-written cheatsheet.
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Spring 2015 There are 9 questions on this exam, weighted as indicated below. The exam is closed book, though you are allowed to use a single-page one-sided hand-written cheatsheet.
COS 126 Written Exam 2 (Spring 2015)
 COS 126 Written Exam 2 (Spring 2015) There are 8 questions on this exam, weighted as indicated below. This exam is closed book. You may use a single-page two-sided hand-written cheatsheet. There is a blank
COS 126 Written Exam 2 (Spring 2015) There are 8 questions on this exam, weighted as indicated below. This exam is closed book. You may use a single-page two-sided hand-written cheatsheet. There is a blank
COS 126 General Computer Science Spring Written Exam 1
 COS 126 General Computer Science Spring 2014 Written Exam 1 This exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one-page single-sided cheatsheet. No calculators or other electronic devices are
COS 126 General Computer Science Spring 2014 Written Exam 1 This exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one-page single-sided cheatsheet. No calculators or other electronic devices are
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall Exam 1
 COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2008 Exam 1 This test has 11 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet,
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2008 Exam 1 This test has 11 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet,
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall Midterm 1
 COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2001 Midterm 1 This test has 11 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall 2001 Midterm 1 This test has 11 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Final. Recitation # (e.g., 201):
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Final Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Final Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2017 Final. Recitation # (e.g., 201):
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2017 Final Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2017 Final Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. February 29, 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Final. Recitation # (e.g., 201):
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Final Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Final Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
Computer Architecture /
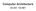 Computer Architecture 02-201 / 02-601 The Conceptual Architecture of a Computer PC CPU register 0 register 1 register 2 registers hold small amounts of data for processing by the CPU Reading / writing
Computer Architecture 02-201 / 02-601 The Conceptual Architecture of a Computer PC CPU register 0 register 1 register 2 registers hold small amounts of data for processing by the CPU Reading / writing
CIS 110 Spring 2014 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 May 2014 Final Exam Answer Key
 CIS 110 Spring 2014 Final Exam 1 CIS 110 Spring 2014 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 May 2014 Final Exam Answer Key 0.) THE EASY ONE (1 point total) Check coversheet for name, recitation #, PennKey,
CIS 110 Spring 2014 Final Exam 1 CIS 110 Spring 2014 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 May 2014 Final Exam Answer Key 0.) THE EASY ONE (1 point total) Check coversheet for name, recitation #, PennKey,
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Fall 2017 Midterm. Recitation ROOM :
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Fall 2017 Midterm Name: Recitation ROOM : Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): DO NOT WRITE YOUR ID# ABOVE, YOU WILL LOSE A POINT My signature below certifies that I have
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Fall 2017 Midterm Name: Recitation ROOM : Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): DO NOT WRITE YOUR ID# ABOVE, YOU WILL LOSE A POINT My signature below certifies that I have
What is TOY? An imaginary machine similar to: ! Ancient computers. ! Today's microprocessors.
 5. The TOY Machine Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 3// 5:3 AM! What is TOY? An imaginary machine similar to:! Ancient computers.!
5. The TOY Machine Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 3// 5:3 AM! What is TOY? An imaginary machine similar to:! Ancient computers.!
CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam
 Name: CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University
Name: CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University
CIS 110 Fall 2014 Introduction to Computer Programming 8 Oct 2014 Midterm Exam Name:
 CIS 110 Fall 2014 Introduction to Computer Programming 8 Oct 2014 Midterm Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University
CIS 110 Fall 2014 Introduction to Computer Programming 8 Oct 2014 Midterm Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University
COS 126 Written Exam 2 Spring 18
 COS 126 Written Exam 2 Spring 18 Instructions. This exam has 7 questions, worth 10 points each. You have 50 minutes. Resources. You may reference your optional two-sided 8.5-by-11 handwritten "cheat sheet"
COS 126 Written Exam 2 Spring 18 Instructions. This exam has 7 questions, worth 10 points each. You have 50 minutes. Resources. You may reference your optional two-sided 8.5-by-11 handwritten "cheat sheet"
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2014 Final. Name:
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2014 Final Name: PennKey (e.g., bhusnur4): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s Code of Academic Integrity
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2014 Final Name: PennKey (e.g., bhusnur4): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s Code of Academic Integrity
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming. February 29, 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 8 October 2013 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 8 October 2013 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 8 October 2013 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
Unit 10: Sorting/Searching/Recursion
 Unit 10: Sorting/Searching/Recursion Notes AP CS A Searching. Here are two typical algorithms for searching a collection of items (which for us means an array or a list). A Linear Search starts at the
Unit 10: Sorting/Searching/Recursion Notes AP CS A Searching. Here are two typical algorithms for searching a collection of items (which for us means an array or a list). A Linear Search starts at the
11. A Computing Machine
 COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E Computer Science Including Programming in Java 11. A Computing Machine Section 5.1 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W
COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W A Y N E Computer Science Including Programming in Java 11. A Computing Machine Section 5.1 http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu COMPUTER SCIENCE S E D G E W I C K / W
CIS 110 Spring 2013 Final Exam, 29 April 2013, Answer Key. Miscellaneous
 CIS 110 1 CIS 110 Spring 2013 Final Exam, 29 April 2013, Answer Key Miscellaneous 0. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification
CIS 110 1 CIS 110 Spring 2013 Final Exam, 29 April 2013, Answer Key Miscellaneous 0. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming. 12 February 2013 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 February 2013 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 February 2013 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam Answer Key
 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Midterm 1 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam Answer Key 1.) The Easy One (1 point total) Check cover sheet for name, recitation #, PennKey,
CIS 110 Fall 2016 Midterm 1 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam Answer Key 1.) The Easy One (1 point total) Check cover sheet for name, recitation #, PennKey,
Lecture A2: X-TOY Programming
 Lecture A2: X-TOY Programming What We ve Learned About X-TOY X-TOY: what s in it, how to use it. Bo with switches and lights. 436 bits = 256 6 + 6 6 + 8. von Neumann architecture. Data representation.
Lecture A2: X-TOY Programming What We ve Learned About X-TOY X-TOY: what s in it, how to use it. Bo with switches and lights. 436 bits = 256 6 + 6 6 + 8. von Neumann architecture. Data representation.
CIS 110 Spring 2012 Final Exam, 7 May 2012, Answer Key. Miscellaneous
 CIS 110 Spring 2012 Final Exam, 7 May 2012, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification that
CIS 110 Spring 2012 Final Exam, 7 May 2012, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification that
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming. 13 February 2013 Make-Up Midterm Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 February 2013 Make-Up Midterm Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 February 2013 Make-Up Midterm Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming. 12 February 2013 Midterm. Answer Key
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 February 2013 Midterm Answer Key 0. (1 point) Miscellaneous (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b)
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 February 2013 Midterm Answer Key 0. (1 point) Miscellaneous (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b)
Computer Science /21/2000
 Computer Science 126 01/21/2000 Final Exam with Answers 1:30-4:30pm 1. Linked Lists and Recursion [11] This is based on final review question #6. Assume the following linked list definition. typedef struct
Computer Science 126 01/21/2000 Final Exam with Answers 1:30-4:30pm 1. Linked Lists and Recursion [11] This is based on final review question #6. Assume the following linked list definition. typedef struct
About this exam review
 Final Exam Review About this exam review I ve prepared an outline of the material covered in class May not be totally complete! Exam may ask about things that were covered in class but not in this review
Final Exam Review About this exam review I ve prepared an outline of the material covered in class May not be totally complete! Exam may ask about things that were covered in class but not in this review
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010
 CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010 Name : Grading TA: Integrity: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor received inappropriate help during the taking of this exam in
CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010 Name : Grading TA: Integrity: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor received inappropriate help during the taking of this exam in
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Midterm. Recitation ROOM :
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Midterm Name: Recitation ROOM : Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2018 Midterm Name: Recitation ROOM : Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s
Chapter 6 SINGLE-DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS
 Chapter 6 SINGLE-DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk What is an Array? A single array variable can reference
Chapter 6 SINGLE-DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS Lecture notes for computer programming 1 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Prepared by: Iyad Albayouk What is an Array? A single array variable can reference
CIS Introduction to Computer Programming Spring Exam 2
 CIS 110 - Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2017 - Exam 2 Name: Recitation (e.g. 201): PennKey (e.g. eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 - Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2017 - Exam 2 Name: Recitation (e.g. 201): PennKey (e.g. eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
************ THIS PROGRAM IS NOT ELIGIBLE FOR LATE SUBMISSION. ALL SUBMISSIONS MUST BE RECEIVED BY THE DUE DATE/TIME INDICATED ABOVE HERE
 Program 10: 40 points: Due Tuesday, May 12, 2015 : 11:59 p.m. ************ THIS PROGRAM IS NOT ELIGIBLE FOR LATE SUBMISSION. ALL SUBMISSIONS MUST BE RECEIVED BY THE DUE DATE/TIME INDICATED ABOVE HERE *************
Program 10: 40 points: Due Tuesday, May 12, 2015 : 11:59 p.m. ************ THIS PROGRAM IS NOT ELIGIBLE FOR LATE SUBMISSION. ALL SUBMISSIONS MUST BE RECEIVED BY THE DUE DATE/TIME INDICATED ABOVE HERE *************
CIS Introduction to Computer Programming. 5 October 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110-001 Introduction to Computer Programming 5 October 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110-001 Introduction to Computer Programming 5 October 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CS 12 Fall 2003 Solutions for mid-term exam #2
 CS 12 Fall 2003 Solutions for mid-term exam #2 1. (10 points) Compilers and interpreters Provide short answers (a few sentences at most) to the following questions. (a) What is the difference between a
CS 12 Fall 2003 Solutions for mid-term exam #2 1. (10 points) Compilers and interpreters Provide short answers (a few sentences at most) to the following questions. (a) What is the difference between a
CIS 110 Spring 2013 Make-Up Midterm, 13 February 2013, Answer Key. Miscellaneous
 CIS 110 Make-Up 1 CIS 110 Spring 2013 Make-Up Midterm, 13 February 2013, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam.
CIS 110 Make-Up 1 CIS 110 Spring 2013 Make-Up Midterm, 13 February 2013, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam.
12/11/ The TOY Machine II. Data Representation. What We've Learned About TOY. What We Do Today. Adding and Subtracting Binary Numbers
 // What We've Learned About TOY. The TOY Machine II TOY machine. Box with switches and lights. 6-bit memory locations, 6-bit registers, 8-bit pc. 4,38 bits = ( 6) + ( 6) + (8) = 4 bytes! von Neumann architecture.
// What We've Learned About TOY. The TOY Machine II TOY machine. Box with switches and lights. 6-bit memory locations, 6-bit registers, 8-bit pc. 4,38 bits = ( 6) + ( 6) + (8) = 4 bytes! von Neumann architecture.
CIS 341 Final Examination 30 April 2013
 CIS 341 Final Examination 30 April 2013 1 /40 2 /30 3 /30 4 /20 Total /120 Do not begin the exam until you are told to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete the exam. There are 12 pages in this exam.
CIS 341 Final Examination 30 April 2013 1 /40 2 /30 3 /30 4 /20 Total /120 Do not begin the exam until you are told to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete the exam. There are 12 pages in this exam.
5. The TOY Machine II
 5. The TOY Machine II Laboratory Instrument Computer (LINC) Introduction to Computer Science: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2011 2/18/2013 9:52:08 AM What
5. The TOY Machine II Laboratory Instrument Computer (LINC) Introduction to Computer Science: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2002 2011 2/18/2013 9:52:08 AM What
Excel Basics Rice Digital Media Commons Guide Written for Microsoft Excel 2010 Windows Edition by Eric Miller
 Excel Basics Rice Digital Media Commons Guide Written for Microsoft Excel 2010 Windows Edition by Eric Miller Table of Contents Introduction!... 1 Part 1: Entering Data!... 2 1.a: Typing!... 2 1.b: Editing
Excel Basics Rice Digital Media Commons Guide Written for Microsoft Excel 2010 Windows Edition by Eric Miller Table of Contents Introduction!... 1 Part 1: Entering Data!... 2 1.a: Typing!... 2 1.b: Editing
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2016 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2016 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2016 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS Introduction to Computer Programming Spring Exam 1
 CIS 110 - Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2017 - Exam 1 Name: Recitation (e.g. 201): PennKey (e.g. eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 - Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2017 - Exam 1 Name: Recitation (e.g. 201): PennKey (e.g. eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CSE373 Fall 2013, Final Examination December 10, 2013 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings.
 CSE373 Fall 2013, Final Examination December 10, 2013 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, closed calculator, closed electronics. Please stop promptly
CSE373 Fall 2013, Final Examination December 10, 2013 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, closed calculator, closed electronics. Please stop promptly
Final Exam CS 152, Computer Programming Fundamentals December 9, 2016
 Final Exam CS 152, Computer Programming Fundamentals December 9, 2016 Name: NetID: Answer all questions in the space provided. Write clearly and legibly, you will not get credit for illegible or incomprehensible
Final Exam CS 152, Computer Programming Fundamentals December 9, 2016 Name: NetID: Answer all questions in the space provided. Write clearly and legibly, you will not get credit for illegible or incomprehensible
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2016 Final. Recitation # (e.g., 201):
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2016 Final Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2016 Final Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
COS 126 MIDTERM 1, FALL
 COS 126 MIDTERM 1, FALL 2000 1 This test has 12 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No calculators
COS 126 MIDTERM 1, FALL 2000 1 This test has 12 questions worth a total of 50 points. You have 120 minutes. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No calculators
! Binary and hex. ! Box with switches and lights. ! 4,328 bits = (255 " 16) + (15 " 16) + (8) = 541 bytes! ! von Neumann architecture.
 What We've Learned About TOY TOY II Data representation. Binary and hex. TOY: what's in it, how to use it. Box with switches and lights. 4,328 bits = (255 " 6) + (5 " 6) + (8) = 54 bytes von Neumann architecture.
What We've Learned About TOY TOY II Data representation. Binary and hex. TOY: what's in it, how to use it. Box with switches and lights. 4,328 bits = (255 " 6) + (5 " 6) + (8) = 54 bytes von Neumann architecture.
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
Final Exam. COMP Summer I June 26, points
 Final Exam COMP 14-090 Summer I 2000 June 26, 2000 200 points 1. Closed book and closed notes. No outside material allowed. 2. Write all answers on the test itself. Do not write any answers in a blue book
Final Exam COMP 14-090 Summer I 2000 June 26, 2000 200 points 1. Closed book and closed notes. No outside material allowed. 2. Write all answers on the test itself. Do not write any answers in a blue book
New York University Introduction to Computer Science Exam Sample Problems 2013 Andrew I. Case. Instructions:
 Name: New York University Introduction to Computer Science Exam Sample Problems 2013 Andrew I. Case Instructions: KEEP TEST BOOKLET CLOSED UNTIL YOU ARE INSTRUCTED TO BEGIN. This exam is double sided (front
Name: New York University Introduction to Computer Science Exam Sample Problems 2013 Andrew I. Case Instructions: KEEP TEST BOOKLET CLOSED UNTIL YOU ARE INSTRUCTED TO BEGIN. This exam is double sided (front
APCS Semester #1 Final Exam Practice Problems
 Name: Date: Per: AP Computer Science, Mr. Ferraro APCS Semester #1 Final Exam Practice Problems The problems here are to get you thinking about topics we ve visited thus far in preparation for the semester
Name: Date: Per: AP Computer Science, Mr. Ferraro APCS Semester #1 Final Exam Practice Problems The problems here are to get you thinking about topics we ve visited thus far in preparation for the semester
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 20 December 2013 Final Exam. Answer Key
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 20 December 2013 Final Exam Answer Key 0.) THE EASY ONE: (1 point total) Check coversheet for name, recitation #, PennKey, and signature. 1.) MISCELLANEOUS
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming 20 December 2013 Final Exam Answer Key 0.) THE EASY ONE: (1 point total) Check coversheet for name, recitation #, PennKey, and signature. 1.) MISCELLANEOUS
Administration. Exceptions. Leftovers. Agenda. When Things Go Wrong. Handling Errors. CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 11
 Administration Exceptions CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 11 Lab 10 due tomorrow No lab tomorrow Work on final projects Remaining office hours Rick: today 2-3 Michael: Thursday 10-noon, Monday
Administration Exceptions CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 11 Lab 10 due tomorrow No lab tomorrow Work on final projects Remaining office hours Rick: today 2-3 Michael: Thursday 10-noon, Monday
CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your single-side hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during
CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2013 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your single-side hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during
CS 170 Exam 2. Version: A Fall Name (as in OPUS) (print): Instructions:
 CS 170 Exam 2 Version: A Fall 2015 Name (as in OPUS) (print): Section: Seat Assignment: Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do
CS 170 Exam 2 Version: A Fall 2015 Name (as in OPUS) (print): Section: Seat Assignment: Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do
CS 142 Style Guide Grading and Details
 CS 142 Style Guide Grading and Details In the English language, there are many different ways to convey a message or idea: some ways are acceptable, whereas others are not. Similarly, there are acceptable
CS 142 Style Guide Grading and Details In the English language, there are many different ways to convey a message or idea: some ways are acceptable, whereas others are not. Similarly, there are acceptable
CIS 110 Fall 2015 Introduction to Computer Programming 7 Oct 2015 Makeup Midterm Exam
 CIS 110 Fall 2015 Introduction to Computer Programming 7 Oct 2015 Makeup Midterm Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the
CIS 110 Fall 2015 Introduction to Computer Programming 7 Oct 2015 Makeup Midterm Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
Total Score /15 /20 /30 /10 /5 /20 Grader
 NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
CS61B, Fall 2011 Final Examination (corrected) P. N. Hilfinger
 CS61B, Fall 2011 Final Examination (corrected) P. N. Hilfinger READ THIS PAGE FIRST. Your exam should contain 16 problems on 16 pages. Officially, it is worth 50 points. This is an open-book test. You
CS61B, Fall 2011 Final Examination (corrected) P. N. Hilfinger READ THIS PAGE FIRST. Your exam should contain 16 problems on 16 pages. Officially, it is worth 50 points. This is an open-book test. You
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam, Fall 2009
 NAME: login ID: precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam, Fall 2009 This test has 8 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
NAME: login ID: precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam, Fall 2009 This test has 8 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017
 CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017 Main topics for #lecture include #minimum_spanning_trees. Prelude Homework 6 due today. Homework 7 due Wednesday, October 25th. Homework 7 has one normal homework problem.
CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017 Main topics for #lecture include #minimum_spanning_trees. Prelude Homework 6 due today. Homework 7 due Wednesday, October 25th. Homework 7 has one normal homework problem.
Prelim 1. CS 2110, October 1, 2015, 5:30 PM Total Question Name True Short Testing Strings Recursion
 Prelim 1 CS 2110, October 1, 2015, 5:30 PM 0 1 2 3 4 5 Total Question Name True Short Testing Strings Recursion False Answer Max 1 20 36 16 15 12 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and closed notes.
Prelim 1 CS 2110, October 1, 2015, 5:30 PM 0 1 2 3 4 5 Total Question Name True Short Testing Strings Recursion False Answer Max 1 20 36 16 15 12 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and closed notes.
CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016
![CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016 CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016](/thumbs/77/76167327.jpg) Name: USC NetID (e.g., ttrojan): CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016 There are 5 problems on the exam, with 56 points total available. There are 10 pages to the exam (5 pages
Name: USC NetID (e.g., ttrojan): CS 455 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2016 [Bono] Thursday, Sept. 29, 2016 There are 5 problems on the exam, with 56 points total available. There are 10 pages to the exam (5 pages
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2016 Final Exam
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2016 Final Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Spring 2016 Final Exam Name: Recitation # (e.g., 201): Pennkey (e.g., eeaton): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following:
 PART 5 5. Modifier Types The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following: Java Access Modifiers Non Access Modifiers 5.1 Access Control Modifiers Java provides a number of access
PART 5 5. Modifier Types The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following: Java Access Modifiers Non Access Modifiers 5.1 Access Control Modifiers Java provides a number of access
CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010
 CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010 Name : Grading TA: Integrity: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor received inappropriate help during the taking of this exam in
CS 1301 Exam 1 Fall 2010 Name : Grading TA: Integrity: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor received inappropriate help during the taking of this exam in
Faculty of Science FINAL EXAMINATION COMP-250 A Introduction to Computer Science School of Computer Science, McGill University
 NAME: STUDENT NUMBER:. Faculty of Science FINAL EXAMINATION COMP-250 A Introduction to Computer Science School of Computer Science, McGill University Examimer: Prof. Mathieu Blanchette December 8 th 2005,
NAME: STUDENT NUMBER:. Faculty of Science FINAL EXAMINATION COMP-250 A Introduction to Computer Science School of Computer Science, McGill University Examimer: Prof. Mathieu Blanchette December 8 th 2005,
CIS 110: Introduction to computer programming
 CIS 110: Introduction to computer programming Lecture 25 Inheritance and polymorphism ( 9) 12/3/2011 CIS 110 (11fa) - University of Pennsylvania 1 Outline Inheritance Polymorphism Interfaces 12/3/2011
CIS 110: Introduction to computer programming Lecture 25 Inheritance and polymorphism ( 9) 12/3/2011 CIS 110 (11fa) - University of Pennsylvania 1 Outline Inheritance Polymorphism Interfaces 12/3/2011
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Fall 2017 Final Midterm. Recitation Section# :
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Fall 2017 Final Midterm Name: Recitation Section# : Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): DO NOT WRITE YOUR ID# ABOVE, YOU WILL LOSE A POINT My signature below certifies
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Fall 2017 Final Midterm Name: Recitation Section# : Pennkey (e.g., paulmcb): DO NOT WRITE YOUR ID# ABOVE, YOU WILL LOSE A POINT My signature below certifies
Instructions. This exam has 7 questions, worth 10 points each. You have 50 minutes.
 COS 126 Written Exam 1 Spring 18 Instructions. This exam has 7 questions, worth 10 points each. You have 50 minutes. Resources. You may reference your optional one-sided 8.5-by-11 handwritten "cheat sheet"
COS 126 Written Exam 1 Spring 18 Instructions. This exam has 7 questions, worth 10 points each. You have 50 minutes. Resources. You may reference your optional one-sided 8.5-by-11 handwritten "cheat sheet"
CIS Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key. Miscellaneous
 CIS 110-001 1 CIS 110-001 Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification
CIS 110-001 1 CIS 110-001 Fall 2012 Midterm, 7 June 2012, Answer Key Miscellaneous 1. (1 points) (a) Write your name, recitation number, and PennKey (username) on the front of the exam. (b) Sign the certification
CISC-124. Casting. // this would fail because we can t assign a double value to an int // variable
 CISC-124 20180122 Today we looked at casting, conditionals and loops. Casting Casting is a simple method for converting one type of number to another, when the original type cannot be simply assigned to
CISC-124 20180122 Today we looked at casting, conditionals and loops. Casting Casting is a simple method for converting one type of number to another, when the original type cannot be simply assigned to
CSE 143 Au03 Final Exam Page 1 of 15
 CSE 143 Au03 Final Exam Page 1 of 15 Reference information about many standard Java classes appears at the end of the test. You might want to tear off those pages to make them easier to refer to while
CSE 143 Au03 Final Exam Page 1 of 15 Reference information about many standard Java classes appears at the end of the test. You might want to tear off those pages to make them easier to refer to while
XC Total Max Score Grader
 NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2013, Prelim 1 Thursday Oct 10, 2013 (7:30-9:00p) The exam is closed book and closed notes. Do not begin until instructed. You have 90 minutes. Good luck! Write your name and Cornell
NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2013, Prelim 1 Thursday Oct 10, 2013 (7:30-9:00p) The exam is closed book and closed notes. Do not begin until instructed. You have 90 minutes. Good luck! Write your name and Cornell
MARKING KEY The University of British Columbia MARKING KEY Computer Science 260 Midterm #2 Examination 12:30 noon, Thursday, March 15, 2012
 MARKING KEY The University of British Columbia MARKING KEY Computer Science 260 Midterm #2 Examination 12:30 noon, Thursday, March 15, 2012 Instructor: K. S. Booth Time: 70 minutes (one hour ten minutes)
MARKING KEY The University of British Columbia MARKING KEY Computer Science 260 Midterm #2 Examination 12:30 noon, Thursday, March 15, 2012 Instructor: K. S. Booth Time: 70 minutes (one hour ten minutes)
11 Coding Standards CERTIFICATION OBJECTIVES. Use Sun Java Coding Standards
 11 Coding Standards CERTIFICATION OBJECTIVES Use Sun Java Coding Standards 2 Chapter 11: Coding Standards CERTIFICATION OBJECTIVE Use Sun Java Coding Standards Spacing Standards The Developer exam is challenging.
11 Coding Standards CERTIFICATION OBJECTIVES Use Sun Java Coding Standards 2 Chapter 11: Coding Standards CERTIFICATION OBJECTIVE Use Sun Java Coding Standards Spacing Standards The Developer exam is challenging.
JVM (java) compiler. A Java program is either a library of static methods (functions) or a data type definition
 Programming Model Basic Structure of a Java Program The Java workflow editor (Code) P.java compiler (javac) P.class JVM (java) output A Java program is either a library of static methods (functions) or
Programming Model Basic Structure of a Java Program The Java workflow editor (Code) P.java compiler (javac) P.class JVM (java) output A Java program is either a library of static methods (functions) or
Total Score /15 /20 /30 /10 /5 /20 Grader
 NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
Nick Weaver Sp 2019 Great Ideas in Computer Architecture MT 1. Print your name:,
 Nick Weaver CS 61C Sp 2019 Great Ideas in Computer Architecture MT 1 Print your name:, (last) (first) I am aware of the Berkeley Campus Code of Student Conduct and acknowledge that any academic misconduct
Nick Weaver CS 61C Sp 2019 Great Ideas in Computer Architecture MT 1 Print your name:, (last) (first) I am aware of the Berkeley Campus Code of Student Conduct and acknowledge that any academic misconduct
TOY II LINC LINC. !1 Introduction to Computer Science Sedgewick and Wayne Copyright 2007
 TOY II Introduction to Computer Science Sedgewick and Wayne Copyright 27 http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs 2 LINC LINC 5 6 What We've Learned About TOY Quick Review: Multiply Data representation. Binary
TOY II Introduction to Computer Science Sedgewick and Wayne Copyright 27 http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs 2 LINC LINC 5 6 What We've Learned About TOY Quick Review: Multiply Data representation. Binary
Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals. By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014
 Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014 Table of Contents Objectives Definition Pointers vs containers Object vs primitives Constructors Methods Object class
Lesson 10A OOP Fundamentals By John B. Owen All rights reserved 2011, revised 2014 Table of Contents Objectives Definition Pointers vs containers Object vs primitives Constructors Methods Object class
CIS 120 Midterm II November 8, Name (printed): Pennkey (login id):
 CIS 120 Midterm II November 8, 2013 Name (printed): Pennkey (login id): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s Code of Academic Integrity in completing
CIS 120 Midterm II November 8, 2013 Name (printed): Pennkey (login id): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s Code of Academic Integrity in completing
CMPSCI 187 / Spring 2015 Postfix Expression Evaluator
 CMPSCI 187 / Spring 2015 Postfix Expression Evaluator Due on Thursday, 05 March, 8:30 a.m. Marc Liberatore and John Ridgway Morrill I N375 Section 01 @ 10:00 Section 02 @ 08:30 1 CMPSCI 187 / Spring 2015
CMPSCI 187 / Spring 2015 Postfix Expression Evaluator Due on Thursday, 05 March, 8:30 a.m. Marc Liberatore and John Ridgway Morrill I N375 Section 01 @ 10:00 Section 02 @ 08:30 1 CMPSCI 187 / Spring 2015
CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory. Martin Gagne Swarthmore College February 16, 2016
 CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory Martin Gagne Swarthmore College February 16, 2016 So we declared a pointer How do we make it point to something? 1. Assign it the address of an existing variable
CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory Martin Gagne Swarthmore College February 16, 2016 So we declared a pointer How do we make it point to something? 1. Assign it the address of an existing variable
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2014 Midterm. Name:
 CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2014 Midterm Name: PennKey (e.g., bhusnur4): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s Code of Academic
CIS 110 Introduction to Computer Programming Summer 2014 Midterm Name: PennKey (e.g., bhusnur4): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania s Code of Academic
CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your single-sided handwritten 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during
CSCI 136 Written Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your single-sided handwritten 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science. Midterm Sample Solutions CSC324H1 Duration: 50 minutes Instructor(s): David Liu.
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science Midterm Sample s CSC324H1 Duration: 50 minutes Instructor(s): David Liu. No Aids Allowed Name: Student Number: Please read the following guidelines carefully.
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science Midterm Sample s CSC324H1 Duration: 50 minutes Instructor(s): David Liu. No Aids Allowed Name: Student Number: Please read the following guidelines carefully.
CS3L Summer 2011 Exam 2 Time: up to 170 minutes (you may leave when finished; or, you must stop promptly at noon)
 CS3L Summer 2011 Exam 2 Time: up to 170 minutes (you may leave when finished; or, you must stop promptly at noon) Name: Login: cs3- First names of the people to your left and right, if any: Left: Right:
CS3L Summer 2011 Exam 2 Time: up to 170 minutes (you may leave when finished; or, you must stop promptly at noon) Name: Login: cs3- First names of the people to your left and right, if any: Left: Right:
Text Input and Conditionals
 Text Input and Conditionals Text Input Many programs allow the user to enter information, like a username and password. Python makes taking input from the user seamless with a single line of code: input()
Text Input and Conditionals Text Input Many programs allow the user to enter information, like a username and password. Python makes taking input from the user seamless with a single line of code: input()
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Searching and Sorting
 Computer Science 10 Data Structures Siena College Fall 016 Topic Notes: Searching and Sorting Searching We all know what searching is looking for something. In a computer program, the search could be:
Computer Science 10 Data Structures Siena College Fall 016 Topic Notes: Searching and Sorting Searching We all know what searching is looking for something. In a computer program, the search could be:
CS 455 Final Exam Spring 2018 [Bono] May 8, 2018
![CS 455 Final Exam Spring 2018 [Bono] May 8, 2018 CS 455 Final Exam Spring 2018 [Bono] May 8, 2018](/thumbs/88/117208965.jpg) Name: USC NetID (e.g., ttrojan): CS 455 Final Exam Spring 2018 [Bono] May 8, 2018 There are 9 problems on the exam, with 74 points total available. There are 12 pages to the exam (6 pages double-sided),
Name: USC NetID (e.g., ttrojan): CS 455 Final Exam Spring 2018 [Bono] May 8, 2018 There are 9 problems on the exam, with 74 points total available. There are 12 pages to the exam (6 pages double-sided),
CS171 Midterm Exam. October 29, Name:
 CS171 Midterm Exam October 29, 2012 Name: You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed-book and closed-notes exam. You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. Read each problem carefully, and
CS171 Midterm Exam October 29, 2012 Name: You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed-book and closed-notes exam. You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. Read each problem carefully, and
Recitation 3 Class and Objects
 1.00/1.001 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Recitation 3 Class and Objects Spring 2012 1 Scope One method cannot see variables in another; Variables created inside a block: { exist
1.00/1.001 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Recitation 3 Class and Objects Spring 2012 1 Scope One method cannot see variables in another; Variables created inside a block: { exist
