Faculty of Mechanical Engineering UTM
|
|
|
- Noel Barnett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 1 Introduction to Programming Concept Dr M Kasim A Jalil Faculty of Mechanical Engineering UTM
2 What is PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE? code of reserved words and symbols used in computer programs, which give instructions to the computer on how to accomplish certain computing tasks an artificial language that can be used to control the behaviour of a machine (often a computer) syntax, grammar, and symbols or words used to give instructions to a computer
3 Programming vs Natural Language Elements of language vocabulary, rules/grammar, structure. Natural languages can be ambiguous and make small errors, and still expect their intent to be understood human can guess the intended meaning Programming languages require a greater degree of precision and completeness have syntactic and semantic rules used to define meaning computers do exactly what they are told to do, and cannot understand the code the programmer "intended" to write are used to facilitate communication about the task of organizing and manipulating information, and to express algorithms precisely
4 WHY programming? A prominent purpose of programming languages is to provide instructions to a computer. Basis for developing applications Softwares AutoCAD, Yahoo Messenger, Microsoft Words, MATLAB, etc. Computer games SIMS, Car racing, flight simulators, etc. Developing skills & interests From USER (of softwares) to DEVELOPER (of applications) MSC dream!
5 How many programming languages?? Definitely it more than 50 languages! Many are short-lived and a few are still in-use: Some are application-specific Lack of user and developer To name a few: Ada - Comprehensive, Pascal-based language used by the Department of Defense. ALGOL - International language for expressing algorithms. APL - Used for statistics and mathematical matrices. Requires special keyboard symbols. BASIC - Developed as a timesharing language in the 1960s. It has been widely used in microcomputer programming in the past, and various dialects of BASIC have been incorporated into many different applications. Microsoft's Visual Basic is widely used.
6 Programming languages. C - Developed in the 1980s at AT&T. Widely used to develop commercial applications. Unix is written in C. C++-Object-oriented version of C that is popular because it combines object-oriented capability with traditional C programming syntax. COBOL - Developed in the 1960s. Widely used for mini and mainframe programming. dbase - Used to be widely used in business applications, but FoxPro (Microsoft's dbase) has survived the longest. FORTRAN - Developed in 1954 by IBM, it was the first major scientific programming language and continues to be widely used. Some commercial applications have been developed in FORTRAN. Java - The programming language developed by Sun and repositioned for Web use. It is widely used on the server side, although client applications are increasingly used. JavaScript - A scripting language widely used on the Web. JavaScript is embedded into many HTML pages. LISP - Developed in Used for AI applications. Its syntax is very different than other languages. Logo - Developed in the 1960s, it was noted for its ease of use and "turtle graphics" drawing functions. M - Originally MUMPS (Massachusetts Utility MultiProgramming System), it includes its own database. It is widely used in medical applications. Modula-2 - Enhanced version of Pascal introduced in 1979 Pascal - Originally an academic language developed in the 1970s. Borland commercialized it with its Turbo Pascal. Perl - A scripting language widely used on the Web to write CGI scripts. Prolog - Developed in France in Used throughout Europe and Japan for AI applications. Python - A scripting language used for system utilities and Internet scripts. Developed in Amsterdam by Guido van Rossum. Visual Basic - Version of BASIC for Windows programming from Microsoft that has been widely used. Web Languages - Languages such as JavaScript, Jscript, Perl and CGI are used to automate Web pages as well as link them to other applications running in servers.
7 Talking to Computer Machine Code/Language - The lowest-level programming language understood by a computer s CPU, consisting entirely of numbers, hardly understood by human. Every CPU model has its own machine code. Assembly Language - An assembly language contains the same instructions as a machine language, but the instructions and variables have names instead of being just numbers. Low-level Languages (closer to hardware) High-Level Language - A programming language (such as C, FORTRAN, or Pascal) that enables a programmer to write programs that are more or less independent of a particular type of computer. Such languages are considered high-level because they are closer to human languages and further from machine languages.
8 Assembler & Compiler Assembler - Software that translates assembly language into machine language. Compiler - Software that translates a program written in a high-level programming g language (C/C++, COBOL, etc.) into machine language. A compiler usually generates assembly language first and then translates the assembly language into machine language. A utility known as a "linker" then combines all required machine language modules into an executable program that can run in the computer
9 Program vs Application A collection of instructions ti that t tell the computer what to do. A program is generically known as "software" and the programs users work with, such as word processors and spreadsheets, are called "applications" or "application programs." Thus, the terms software, application, program and instruction are synonymous in the sense that they all tell the computer what to do. A program is written in a programming language, such as C or FORTRAN, and the statements and commands written by the programmer are converted into the computer's machine language by software called "assemblers assemblers, " "compilers" and "interpreters interpreters. " The program contains machine instructions, buffers, constants and counters.
10 Programming Process Just like learning any natural language: Learn the vocabulary Learn how to construct the sentence (grammar & structure) Have the expert check your skill In any computer programming language Knowing the lingo - terms & rules (syntax) Compiling - checking for errors (or called debugging) g)
11 What do we normally program? Repetitive & Duplicative process Sequence/series/multiple of complex operations Repeated applications Computationally expensive for human to do Examples?? Telephone directory searching for a contact number Balance of your prepaid phone Bank transaction withdrawal, balance enquiry, transfer, deposit, etc Advanced Applications matrix inverse, wave simulation.
12 C Language The C programming language was designed by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Laboratories in the early 1970s Influenced by ALGOL 60 (1960), CPL (Cambridge, 1963), BCPL (Martin Richard, 1967), B (Ken Thompson, 1970)
13 C Language Traditionally used for systems programming, g, though this may be changing g in favor of C++ Traditional C: The C Programming Language, by Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie, 2 nd Edition, Prentice Hall Referred to as K&R
14 Things we need to master. Programming thinking thinking like a programmer. You can t just simply think in Malay and speak in Mandarin. To be a master, you need to think and dream in Mandarin: Program concept Algorithm Development Program Coding Debugging
15 Example Changing your flat tire Open your trunk Get your spare tire (ready) & tools (jack) Check the ground condition Loosen tire nuts Jack your car Remove the nuts and the flat tire Replace the tire Tighten the nuts Lower the car and tighten the nut Place your tools and flat tire back in the trunk End
16 Process Flow Chart Start Open your trunk Get your spare tire (ready) & tools (jack) Check the ground condition Loosen tire nuts Jack your car Remove the nuts and the flat tire Replace the tire Tighten the nuts Lower the car and tighten the nut Place your tools and flat tire back in the trunk End
17 Making chicken curry (from suvir.com) Tools knife, pan, stirrer, etc. Ingredients 4-pound chicken, cut into 8 to 10 pieces and skinned 3/4 teaspoon turmeric 3/4 teaspoon cayenne pepper Salt 1 1/2 medium onions, roughly diced 5 garlic cloves 2 inches fresh ginger, peeled and cut in half crosswise 3 tablespoons canola oil 2 inches cinnamon stick 12 green cardamom pods 9 whole cloves 9 black peppercorns 2 large tomatoes, chopped 2 tablespoons tomato paste 1/4 cup yoghurt, whisked until smooth 1 cup water 1/2 cup chopped fresh cilantro Juice of 1 lemon
18 Step-by by-step instructions 1. Mix the chicken, 1/2 teaspoon of the turmeric, 1/2 6. Heat the remaining 1 tablespoon oil in the same teaspoon of the cayenne and 1/4 teaspoon salt in a pan over medium-high heat. Add the chicken, cook bowl and stir to coat the chicken with the spices. Let stand while you make the sauce. and stir for 2 minutes. 2. Finely mince the onion, garlic and ginger in a food processor and set aside. 3. Mix 2 tablespoons of the oil, the cinnamon, cardamom, cloves and black peppercorns in a large casserole over medium-high heat. Cook & stir, until the cinnamon unfurls, for 1 to 2 minutes. 4. Add the minced onion mixture and 1 teaspoon salt and cook and stir, until the onion turns brownish around the edges, for 10 to 15 minutes. 5. Remove and discard the cinnamon and mix with the remaining 1/4 teaspoon turmeric and 1/4 teaspoon cayenne. Add the tomatoes and tomato paste, cook and stir for 5 minutes. Transfer to a food processor or blender and puree until smooth; set aside. 7. Add the yoghurt, 1 tablespoon at a time and stir well after each addition. Cook and stir for 2 minutes to evaporate some of the moisture. 8. Add the pureed tomato mixture and bring to a boil. Pour in the water. Return to a boil, then reduce the heat and simmer, partially covered, until the chicken is cooked through, about 30 minutes. Stir and scrape the bottom of the pan every 5 to 8 minutes to keep the sauce from sticking. Then uncover and cook for 5 more minutes to reduce and thicken the sauce. Stir in the cilantro and lemon juice. Taste for salt and serve hot.
19 Flow Chart please complete. Mix the chicken, c 1/2 teaspoon of the turmeric, 1/2 teaspoon of the cayenne and 1/4 teaspoon salt in a bowl and stir to coat the chicken with the spices. Let stand while you make the sauce. Heat the remaining i 1 tablespoon oil in the same pan over medium-high heat. Add the chicken, cook and stir for 2 minutes. Finely mince the onion, garlic and ginger in a food processor and set aside. Mix 2 tablespoons of the oil, the cinnamon, cardamom, cloves and black peppercorns in a large casserole over medium-high heat. Cook and, until the cinnamon unfurls, for 1 to 2 minutes. Add the minced onion mixture and 1 teaspoon salt and cook and stir, until the onion turns brownish around the edges, for 10 to 15 minutes. Add the yoghurt, 1 tablespoon at a time and stirring well after each addition. cook and stir for 2 minutes to evaporate some of the moisture. Add the pureed tomato mixture and bring to a boil. Pour in the water. Return to a boil, then reduce the heat and simmer, partially covered, until the chicken is cooked through, about 30 minutes. Stir and scrape the bottom of the pan every 5 to 8 minutes to keep the sauce from sticking. Then uncover and cook for 5 more minutes to reduce and thicken the sauce. Stir in the cilantro and lemon juice. Taste for salt and serve hot. Remove and discard the cinnamon and mix with the remaining 1/4 teaspoon turmeric and 1/4 teaspoon cayenne. Add the tomatoes and tomato paste, cook and stir for 5 minutes. Transfer to a food processor or blender and puree until smooth; set aside.
20 Plotting a Curve Manual Draw the X & Y Axis Plot the Curve Get the governing equations: y=mx+c, y=acosx, y=ax+bx 2 Mark the X & Y axis For each X value, calculate the Y and place the (X,Y) point on the graph paper Connect the points Process Flow Get the input value (X) Get the output value (Y) Repeat until maximum X is reached STOP
21 Flow Chart Start Start Start n=1 Get X first Compute Y first =F(X first ) Stop n=last Increment = 1 Plot (X first,y first ) Get X n Compute Y nt =F(X n ) Repeat until X last is reached Store (X n,y n ) End End
22 Algorithm A formula or set of steps for solving a particular problem. To be an algorithm, a set of rules must be unambiguous and have a clear stopping point. Algorithms can be expressed in any language, from natural languages like English or French to programming glanguages g like C. We use algorithms every day. For example, a recipe for baking a cake is an algorithm. Most programs, with the exception of some artificial intelligence applications, consist of algorithms. Inventing elegant algorithms -- algorithms that are simple and require the fewest steps possible -- is one of the principal challenges in programming.
23 Now Try! Revisit the Chicken Curry problem Think of a better way to represent the process in a y p p systematic flow chart
24 An example of Algorithm
Principles of Programming Languages. Lecture Outline
 Principles of Programming Languages CS 492 Lecture 1 Based on Notes by William Albritton 1 Lecture Outline Reasons for studying concepts of programming languages Programming domains Language evaluation
Principles of Programming Languages CS 492 Lecture 1 Based on Notes by William Albritton 1 Lecture Outline Reasons for studying concepts of programming languages Programming domains Language evaluation
SKILL AREA 304: Review Programming Language Concept. Computer Programming (YPG)
 SKILL AREA 304: Review Programming Language Concept Computer Programming (YPG) 304.1 Demonstrate an Understanding of Basic of Programming Language 304.1.1 Explain the purpose of computer program 304.1.2
SKILL AREA 304: Review Programming Language Concept Computer Programming (YPG) 304.1 Demonstrate an Understanding of Basic of Programming Language 304.1.1 Explain the purpose of computer program 304.1.2
Chapter 1. Preliminaries
 Chapter 1 Preliminaries Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming Languages Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Influences on Language Design Language Categories Language
Chapter 1 Preliminaries Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming Languages Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Influences on Language Design Language Categories Language
COMP 102: Computers and Computing
 COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 5: What is Programming? Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html Motivation The advantage of a computer
COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 5: What is Programming? Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html Motivation The advantage of a computer
Announcements Tues., Aug and 2. to call them ( ) ! For next time, read Learning Computing with Robots, chs.
 Announcements Tues., Aug. 24! For next time, read Learning Computing with Robots, chs. 1 and 2.! The Blackboard site is up and operational!! not much content! mostly links back to my course homepage! Printed
Announcements Tues., Aug. 24! For next time, read Learning Computing with Robots, chs. 1 and 2.! The Blackboard site is up and operational!! not much content! mostly links back to my course homepage! Printed
Concepts in Programming Languages
 Concepts in Programming Languages Marcelo Fiore Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge 2012 2013 (Easter Term) 1 Practicalities Course web page: with lecture
Concepts in Programming Languages Marcelo Fiore Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge 2012 2013 (Easter Term) 1 Practicalities Course web page: with lecture
Low-Level Languages. Computer Programs and Programming Languages
 Computer Programs and Programming Languages What is a computer program? Set of instructions that directs computer to perform tasks Programming used to write instructions 1 Computer Programs and Programming
Computer Programs and Programming Languages What is a computer program? Set of instructions that directs computer to perform tasks Programming used to write instructions 1 Computer Programs and Programming
Topic I. Introduction and motivation References: Chapter 1 of Concepts in programming languages by J. C. Mitchell. CUP, 2003.
 Topic I Introduction and motivation References: Chapter 1 of Concepts in programming languages by J. C. Mitchell. CUP, 2003. Chapter 1 of Programming languages: Design and implementation (3RD EDITION)
Topic I Introduction and motivation References: Chapter 1 of Concepts in programming languages by J. C. Mitchell. CUP, 2003. Chapter 1 of Programming languages: Design and implementation (3RD EDITION)
Objective: To learn meaning and concepts of programming. Outcome: By the end of this students should be able to describe the meaning of programming
 30 th September 2018 Objective: To learn meaning and concepts of programming Outcome: By the end of this students should be able to describe the meaning of programming Section 1: What is a programming
30 th September 2018 Objective: To learn meaning and concepts of programming Outcome: By the end of this students should be able to describe the meaning of programming Section 1: What is a programming
Chapter Twelve. Systems Design and Development
 Chapter Twelve Systems Design and Development After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the process of designing, programming, and debugging a computer program Explain why there are many
Chapter Twelve Systems Design and Development After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the process of designing, programming, and debugging a computer program Explain why there are many
Introduction. A. Bellaachia Page: 1
 Introduction 1. Objectives... 2 2. Why are there so many programming languages?... 2 3. What makes a language successful?... 2 4. Programming Domains... 3 5. Language and Computer Architecture... 4 6.
Introduction 1. Objectives... 2 2. Why are there so many programming languages?... 2 3. What makes a language successful?... 2 4. Programming Domains... 3 5. Language and Computer Architecture... 4 6.
Programming Languages, Summary CSC419; Odelia Schwartz
 Programming Languages, Summary CSC419; Odelia Schwartz Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming Languages Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Influences on Language Design
Programming Languages, Summary CSC419; Odelia Schwartz Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming Languages Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Influences on Language Design
What is programming? What are computer languages and how have they evolved? What is the basic process of programming, including the tools involved?
 What is programming? What are computer languages and how have they evolved? What is the basic process of programming, including the tools involved? A step-by-step set of instructions to accomplish a task.
What is programming? What are computer languages and how have they evolved? What is the basic process of programming, including the tools involved? A step-by-step set of instructions to accomplish a task.
Introduction to Programming
 Introduction to Programming session 3 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2010 These slides are created using Deitel s slides Sahrif University of Technology Outlines
Introduction to Programming session 3 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2010 These slides are created using Deitel s slides Sahrif University of Technology Outlines
Lecture 1: Introduction
 Lecture 1: Introduction Doina Precup With many thanks to Prakash Panagaden and Mathieu Blanchette January 6, 2014 1 What is an algorithm? First of all, welcome to this course! Our goal will be to introduce
Lecture 1: Introduction Doina Precup With many thanks to Prakash Panagaden and Mathieu Blanchette January 6, 2014 1 What is an algorithm? First of all, welcome to this course! Our goal will be to introduce
Introduction to Basis and Practice in Programming
 Introduction to Basis and Practice in Programming Fall 2015 Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) 1 Course Overview Course Basics! Class hour GEDB029-45: Mon. 13:00 ~ 14:50 GEDB029-46: Tue. 13:00 ~ 14:50 1~2
Introduction to Basis and Practice in Programming Fall 2015 Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) 1 Course Overview Course Basics! Class hour GEDB029-45: Mon. 13:00 ~ 14:50 GEDB029-46: Tue. 13:00 ~ 14:50 1~2
Organization of Programming Languages (CSE452) Why are there so many programming languages? What makes a language successful?
 Organization of Programming Languages (CSE452) Instructor: Dr. B. Cheng Fall 2004 1 Why are there so many programming languages? Evolution -- we've learned better ways of doing things over time Socio-economic
Organization of Programming Languages (CSE452) Instructor: Dr. B. Cheng Fall 2004 1 Why are there so many programming languages? Evolution -- we've learned better ways of doing things over time Socio-economic
Introduction to programming (LT2111) Lecture 1: Introduction
 Introduction to programming (LT2111) Lecture 1: Introduction Richard Johansson September 2, 2014 Introduction & Administration The main goal of the course is that you will learn how to program using the
Introduction to programming (LT2111) Lecture 1: Introduction Richard Johansson September 2, 2014 Introduction & Administration The main goal of the course is that you will learn how to program using the
EPV TECHNOLOGIES NEWSLETTER April 2018
 EPV TECHNOLOGIES NEWSLETTER April 2018 TECH PAPERS WLM and Container Pricing - Part 2 TECH NEWS IBM ztechnical University 2018 TECH NOTES EPV for MQ V14 entered MA TECH SUPPORT New MIPS tables including
EPV TECHNOLOGIES NEWSLETTER April 2018 TECH PAPERS WLM and Container Pricing - Part 2 TECH NEWS IBM ztechnical University 2018 TECH NOTES EPV for MQ V14 entered MA TECH SUPPORT New MIPS tables including
Copyright 2005 Department of Computer & Information Science
 Introducing Programming Copyright 2005 Goals By the end of this lecture, you should Understand the different types of programming languages. Understand the basic procedures in a program as input, processing
Introducing Programming Copyright 2005 Goals By the end of this lecture, you should Understand the different types of programming languages. Understand the basic procedures in a program as input, processing
Component V Supporting Materials / Learn More Interesting Facts. Interesting Facts
 Component V Supporting Materials / Learn More 1.4.1 Interesting Facts No. Interesting Facts 1. All computers operate by following machine language programs. 2. Machine language programs are long sequence
Component V Supporting Materials / Learn More 1.4.1 Interesting Facts No. Interesting Facts 1. All computers operate by following machine language programs. 2. Machine language programs are long sequence
Why are there so many programming languages? Why do we have programming languages? What is a language for? What makes a language successful?
 Chapter 1 :: Introduction Introduction Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Why are there so many programming languages? evolution -- we've learned better ways of doing things over time socio-economic
Chapter 1 :: Introduction Introduction Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Why are there so many programming languages? evolution -- we've learned better ways of doing things over time socio-economic
Unit. Programming Fundamentals. School of Science and Technology INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION Programming Fundamentals Unit 1 In order to communicate with each other, we use natural languages like Bengali, English, Hindi, Urdu, French, Gujarati etc. We have different language around
INTRODUCTION Programming Fundamentals Unit 1 In order to communicate with each other, we use natural languages like Bengali, English, Hindi, Urdu, French, Gujarati etc. We have different language around
Chapter 1. Preview. Reason for Studying OPL. Language Evaluation Criteria. Programming Domains
 Chapter 1. Preview Reason for Studying OPL Reason for Studying OPL? Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Language Categories Language Design Trade-Offs Implementation Methods Programming Environments
Chapter 1. Preview Reason for Studying OPL Reason for Studying OPL? Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Language Categories Language Design Trade-Offs Implementation Methods Programming Environments
Concepts of Programming Languages
 Concepts of Programming Languages Lecture 1 - Introduction Patrick Donnelly Montana State University Spring 2014 Patrick Donnelly (Montana State University) Concepts of Programming Languages Spring 2014
Concepts of Programming Languages Lecture 1 - Introduction Patrick Donnelly Montana State University Spring 2014 Patrick Donnelly (Montana State University) Concepts of Programming Languages Spring 2014
Language Translation, History. CS152. Chris Pollett. Sep. 3, 2008.
 Language Translation, History. CS152. Chris Pollett. Sep. 3, 2008. Outline. Language Definition, Translation. History of Programming Languages. Language Definition. There are several different ways one
Language Translation, History. CS152. Chris Pollett. Sep. 3, 2008. Outline. Language Definition, Translation. History of Programming Languages. Language Definition. There are several different ways one
Discovering Computers Chapter 13 Programming Languages and Program Development
 Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 13 Programming Languages and Program Development Chapter 13 Objectives Differentiate between machine and assembly languages Identify and discuss the purpose of procedural
Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 13 Programming Languages and Program Development Chapter 13 Objectives Differentiate between machine and assembly languages Identify and discuss the purpose of procedural
COMP 201: Principles of Programming
 COMP 201: Principles of Programming 1 Learning Outcomes To understand what computing entails and what the different branches of computing are. To understand the basic design of a computer and how it represents
COMP 201: Principles of Programming 1 Learning Outcomes To understand what computing entails and what the different branches of computing are. To understand the basic design of a computer and how it represents
Discovering Computers 2008
 Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 13 (a) Programming Languages and Program Development 1 Chapter 13 Objectives Differentiate between machine and assembly languages Identify and discuss the purpose of
Discovering Computers 2008 Chapter 13 (a) Programming Languages and Program Development 1 Chapter 13 Objectives Differentiate between machine and assembly languages Identify and discuss the purpose of
EPV TECHNOLOGIES NEWSLETTER July 2018
 EPV TECHNOLOGIES NEWSLETTER July 2018 TECH PAPERS Publishing will restart in August 2018 TECH NEWS EPV User Group 2018 Preliminary Agenda TECH NOTES Db2 for z/os Utilities in Practice IBM Redbooks TECH
EPV TECHNOLOGIES NEWSLETTER July 2018 TECH PAPERS Publishing will restart in August 2018 TECH NEWS EPV User Group 2018 Preliminary Agenda TECH NOTES Db2 for z/os Utilities in Practice IBM Redbooks TECH
What is programming? What are computer languages and how have they evolved? What is the basic process of programming, including the tools involved?
 What is programming? What are computer languages and how have they evolved? What is the basic process of programming, including the tools involved? A step-by-step set of instructions to accomplish a task.
What is programming? What are computer languages and how have they evolved? What is the basic process of programming, including the tools involved? A step-by-step set of instructions to accomplish a task.
CS 50 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 50 Introduction to Computer Science I Michael D. Smith smith@eecs.harvard.edu Fall 2005 CS50 1 Q1: What s in common? Internet commerce and electronic markets Blockbuster movies and their special effects
CS 50 Introduction to Computer Science I Michael D. Smith smith@eecs.harvard.edu Fall 2005 CS50 1 Q1: What s in common? Internet commerce and electronic markets Blockbuster movies and their special effects
General Concepts. Abstraction Computational Paradigms Implementation Application Domains Influence on Success Influences on Design
 General Concepts Abstraction Computational Paradigms Implementation Application Domains Influence on Success Influences on Design 1 Abstractions in Programming Languages Abstractions hide details that
General Concepts Abstraction Computational Paradigms Implementation Application Domains Influence on Success Influences on Design 1 Abstractions in Programming Languages Abstractions hide details that
Chapter 1. Preliminaries
 Chapter 1 Preliminaries Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming Languages Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Influences on Language Design Language Categories Language
Chapter 1 Preliminaries Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming Languages Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Influences on Language Design Language Categories Language
Fundamentals of Programming. Lecture 1: Introduction to C Programming
 1 Fundamentals of Programming Lecture 1: Introduction to C Programming Instructor: Fatemeh Zamani f_zamani@ce.sharif.edu Sharif University of Technology Computer Engineering Department 2 Outline Grading
1 Fundamentals of Programming Lecture 1: Introduction to C Programming Instructor: Fatemeh Zamani f_zamani@ce.sharif.edu Sharif University of Technology Computer Engineering Department 2 Outline Grading
! Learn how to think like a computer scientist. ! Learn problem solving. ! Read and write code. ! Understand object oriented programming
 1 TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE AND PROGRAMMING Topic 1 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia
1 TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE AND PROGRAMMING Topic 1 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia
EL2310 Scientific Programming
 Lecture 6: Introduction to C (pronobis@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 6: Introduction to C Roots of C Getting started with C Closer look at Hello World Programming Environment Schedule Last time (and
Lecture 6: Introduction to C (pronobis@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 6: Introduction to C Roots of C Getting started with C Closer look at Hello World Programming Environment Schedule Last time (and
Search Engines. Exercise 21 Ordered Lists. Instructions:
 Exercise 21 Ordered Lists 1. Create a web page similar to that shown below. Choose an appropriate colour for the page s background and the following title for the web page: Search Engines 1. All4One 2.
Exercise 21 Ordered Lists 1. Create a web page similar to that shown below. Choose an appropriate colour for the page s background and the following title for the web page: Search Engines 1. All4One 2.
CSCI170 Lecture 1: Analysis of Programming Languages. John Magee 1 September 2011 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett
 CSCI170 Lecture 1: Analysis of Programming Languages John Magee 1 September 2011 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett 1 Overview/Questions How can we control the computer s circuits? How does the
CSCI170 Lecture 1: Analysis of Programming Languages John Magee 1 September 2011 Some material copyright Jones and Bartlett 1 Overview/Questions How can we control the computer s circuits? How does the
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
 Computer Fundamentals Pradeep K. Sinha Priti Sinha Chapter 12 Computer Languages Slide 1/64 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer languages or programming languages Three broad
Computer Fundamentals Pradeep K. Sinha Priti Sinha Chapter 12 Computer Languages Slide 1/64 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer languages or programming languages Three broad
COMPUTATIONAL THINKING
 Computational Concepts sequence loops parallelism events conditionals operators variables lists COMPUTATIONAL THINKING PROGRAMMING AS PROBLEM SOLVING Computational Practices incremental/iterative testing/debugging
Computational Concepts sequence loops parallelism events conditionals operators variables lists COMPUTATIONAL THINKING PROGRAMMING AS PROBLEM SOLVING Computational Practices incremental/iterative testing/debugging
Fundamentals of Programming (Python) Basic Concepts. Ali Taheri Sharif University of Technology Spring 2018
 Fundamentals of Programming (Python) Basic Concepts Ali Taheri Sharif University of Technology Outline 1. What is a Computer? 2. Computer System Organization 3. What is a Computer Program? 4. Programming
Fundamentals of Programming (Python) Basic Concepts Ali Taheri Sharif University of Technology Outline 1. What is a Computer? 2. Computer System Organization 3. What is a Computer Program? 4. Programming
CS 113: Introduction to
 CS 113: Introduction to Course information MWF 12:20-1:10pm 1/21-2/15, 306 Hollister Hall Add/drop deadline: 1/28 C Instructor: David Crandall See website for office hours and contact information Prerequisites
CS 113: Introduction to Course information MWF 12:20-1:10pm 1/21-2/15, 306 Hollister Hall Add/drop deadline: 1/28 C Instructor: David Crandall See website for office hours and contact information Prerequisites
The diagram below is only partially complete. Use the terms in the word list to complete the empty boxes. Make dinner
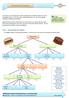 Decomposing Problems As we have seen, decomposition means breaking down a difficult problem into more manageable pieces. A common way to tackle this process is to use a tree diagram showing increasing
Decomposing Problems As we have seen, decomposition means breaking down a difficult problem into more manageable pieces. A common way to tackle this process is to use a tree diagram showing increasing
Spring 2018 NENG 202 Introduction to Computer Programming
 Spring 2018 NENG 202 Introduction to Computer Programming Introductory programming course based on the C language Course Website: http://www.albany.edu/~yx152122/neng202-18.html Instructor: Prof. Y. Alex
Spring 2018 NENG 202 Introduction to Computer Programming Introductory programming course based on the C language Course Website: http://www.albany.edu/~yx152122/neng202-18.html Instructor: Prof. Y. Alex
CS2900 Introductory Programming with Python and C++ Kevin Squire LtCol Joel Young Fall 2007
 CS2900 Introductory Programming with Python and C++ Kevin Squire LtCol Joel Young Fall 2007 Course Web Site http://www.nps.navy.mil/cs/facultypages/squire/cs2900 All course related materials will be posted
CS2900 Introductory Programming with Python and C++ Kevin Squire LtCol Joel Young Fall 2007 Course Web Site http://www.nps.navy.mil/cs/facultypages/squire/cs2900 All course related materials will be posted
Early computers (1940s) cost millions of dollars and were programmed in machine language. less error-prone method needed
 Chapter 1 :: Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Early computers (1940s) cost millions of dollars and were programmed in machine language machine s time more valuable than programmer s machine
Chapter 1 :: Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Early computers (1940s) cost millions of dollars and were programmed in machine language machine s time more valuable than programmer s machine
Outline. Introduction to Programming (in C++) Introduction. First program in C++ Programming examples
 Outline Introduction to Programming (in C++) Introduction Programming examples Algorithms, programming languages and computer programs Jordi Cortadella, Ricard Gavaldà, Fernando Orejas Dept. of Computer
Outline Introduction to Programming (in C++) Introduction Programming examples Algorithms, programming languages and computer programs Jordi Cortadella, Ricard Gavaldà, Fernando Orejas Dept. of Computer
An Introduction to Python (TEJ3M & TEJ4M)
 An Introduction to Python (TEJ3M & TEJ4M) What is a Programming Language? A high-level language is a programming language that enables a programmer to write programs that are more or less independent of
An Introduction to Python (TEJ3M & TEJ4M) What is a Programming Language? A high-level language is a programming language that enables a programmer to write programs that are more or less independent of
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction Outline Introduction What Is a Computer? Computer Hardware Computer Software Computer Programming Languages Machine Code, Assembly Languages and High-Level Languages. The History
Chapter 1: Introduction Outline Introduction What Is a Computer? Computer Hardware Computer Software Computer Programming Languages Machine Code, Assembly Languages and High-Level Languages. The History
Lecture 1: Preliminaries
 Lecture 1: Preliminaries Edgardo Molina Department of Computer Science City College of New York August 30, 2011 Edgardo Molina (CS@CCNY) Lecture 1 August 30, 2011 1 / 44 Info and Schedule Course Info and
Lecture 1: Preliminaries Edgardo Molina Department of Computer Science City College of New York August 30, 2011 Edgardo Molina (CS@CCNY) Lecture 1 August 30, 2011 1 / 44 Info and Schedule Course Info and
LECTURE/ STUDY NOTES ON C
 LECTURE/ STUDY NOTES ON C PART I (Overview of C Programming) Introduction of C language History of C Importance of C Demerits of C Basic Structure of C Working steps of C compiler Source Code Object Code
LECTURE/ STUDY NOTES ON C PART I (Overview of C Programming) Introduction of C language History of C Importance of C Demerits of C Basic Structure of C Working steps of C compiler Source Code Object Code
CS101 Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers
 CS101 Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers In this handout we ll examine different types of programming languages and take a brief look at compilers. We ll only hit the major highlights
CS101 Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers In this handout we ll examine different types of programming languages and take a brief look at compilers. We ll only hit the major highlights
1/14/2014. Introduction to CSE 1325 Object Oriented Programming (Using Java) Introduction (Cont.) Introduction
 Introduction (Cont.) Introduction to CSE 1325 Object Oriented Programming (Using Java) Sharma Chakravarthy Information Technology Laboratory (IT Lab) Computer Science and Engineering Department The University
Introduction (Cont.) Introduction to CSE 1325 Object Oriented Programming (Using Java) Sharma Chakravarthy Information Technology Laboratory (IT Lab) Computer Science and Engineering Department The University
Programming: detailed instructions which tell the computer hardware what to do aka software Computer Science: the study NOT of computers, but of what
 Programming: detailed instructions which tell the computer hardware what to do aka software Computer Science: the study NOT of computers, but of what can be computed what processes a computer can execute
Programming: detailed instructions which tell the computer hardware what to do aka software Computer Science: the study NOT of computers, but of what can be computed what processes a computer can execute
Python - Week 1. Mohammad Shokoohi-Yekta
 Python - Week 1 Mohammad Shokoohi-Yekta 1 An Introduction to Computers and Problem Solving 1.1 An Introduction to Computers 1.2 Program Development Cycle 1.3 Programming Tools 1.4 Starting Python 2 Communicating
Python - Week 1 Mohammad Shokoohi-Yekta 1 An Introduction to Computers and Problem Solving 1.1 An Introduction to Computers 1.2 Program Development Cycle 1.3 Programming Tools 1.4 Starting Python 2 Communicating
CSCI 2132 Software Development. Lecture 2: Introduction to UNIX and Unix-like Operating Systems
 CSCI 2132 Software Development Lecture 2: Introduction to UNIX and Unix-like Operating Systems Instructor: Vlado Keselj Faculty of Computer Science Dalhousie University 7-Sep-2018 (2) CSCI 2132 1 Previous
CSCI 2132 Software Development Lecture 2: Introduction to UNIX and Unix-like Operating Systems Instructor: Vlado Keselj Faculty of Computer Science Dalhousie University 7-Sep-2018 (2) CSCI 2132 1 Previous
ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING. Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University
 ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University Lecture 04: Introduction to C Readings: Chapter 1.5-1.7 What is C? C is a general-purpose, structured
ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University Lecture 04: Introduction to C Readings: Chapter 1.5-1.7 What is C? C is a general-purpose, structured
Administration Computers Software Algorithms Programming Languages
 Administration Computers Software Algorithms Programming Languages http://www.cs.sfu.ca/cc/130/johnwill/ This course does not use Canvas John Edgar 3 Come to class Read ahead Attend the labs You get practice
Administration Computers Software Algorithms Programming Languages http://www.cs.sfu.ca/cc/130/johnwill/ This course does not use Canvas John Edgar 3 Come to class Read ahead Attend the labs You get practice
1. Introduction to Programming
 Computer Science I CS 135 1. Introduction to Programming René Doursat Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Fall 2005 Computer Science I CS 135 0. Course Presentation
Computer Science I CS 135 1. Introduction to Programming René Doursat Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Fall 2005 Computer Science I CS 135 0. Course Presentation
Chapter 1 Preliminaries
 Chapter 1 Preliminaries Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming Languages Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Influences on Language Design Language Categories Language
Chapter 1 Preliminaries Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming Languages Programming Domains Language Evaluation Criteria Influences on Language Design Language Categories Language
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing
 INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 11 Principles of Programming Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of
INFS 214: Introduction to Computing Session 11 Principles of Programming Lecturer: Dr. Ebenezer Ankrah, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eankrah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of
Lecture 09. Ada to Software Engineering. Mr. Mubashir Ali Lecturer (Dept. of Computer Science)
 Lecture 09 Ada to Software Engineering Mr. Mubashir Ali Lecturer (Dept. of dr.mubashirali1@gmail.com 1 Summary of Previous Lecture 1. ALGOL 68 2. COBOL 60 3. PL/1 4. BASIC 5. Early Dynamic Languages 6.
Lecture 09 Ada to Software Engineering Mr. Mubashir Ali Lecturer (Dept. of dr.mubashirali1@gmail.com 1 Summary of Previous Lecture 1. ALGOL 68 2. COBOL 60 3. PL/1 4. BASIC 5. Early Dynamic Languages 6.
Programming Languages 2nd edition Tucker and Noonan"
 Programming Languages 2nd edition Tucker and Noonan" " Chapter 1" Overview" " A good programming language is a conceptual universe for thinking about programming. " " " " " " " " " " " " "A. Perlis" "
Programming Languages 2nd edition Tucker and Noonan" " Chapter 1" Overview" " A good programming language is a conceptual universe for thinking about programming. " " " " " " " " " " " " "A. Perlis" "
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and C++ Programming
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and C++ Programming 1 Outline 1.1 Introduction 1.2 What Is a Computer? 1.3 Computer Organization 1.4 Evolution of Operating Systems 1.5 Personal Computing, Distributed
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and C++ Programming 1 Outline 1.1 Introduction 1.2 What Is a Computer? 1.3 Computer Organization 1.4 Evolution of Operating Systems 1.5 Personal Computing, Distributed
ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING. Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University
 ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University Lecture 02: Algorithms Readings: Not Covered in Textbook Problem Solving Process System Design:
ITC213: STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING Bhaskar Shrestha National College of Computer Studies Tribhuvan University Lecture 02: Algorithms Readings: Not Covered in Textbook Problem Solving Process System Design:
0 Introduction: Computer systems and program development
 0 Introduction: Computer systems and program development Outline 1 Introduction 2 What Is a Computer? 3 Computer Organization 4 Evolution of Operating Systems 5 Personal Computing, Distributed Computing
0 Introduction: Computer systems and program development Outline 1 Introduction 2 What Is a Computer? 3 Computer Organization 4 Evolution of Operating Systems 5 Personal Computing, Distributed Computing
8/27/17. CS-3304 Introduction. What will you learn? Semester Outline. Websites INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
 CS-3304 Introduction In Text: Chapter 1 & 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION 2 What will you learn? Survey of programming paradigms, including representative languages Language definition and description methods Overview
CS-3304 Introduction In Text: Chapter 1 & 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION 2 What will you learn? Survey of programming paradigms, including representative languages Language definition and description methods Overview
PROGRAMMAZIONE I A.A. 2017/2018
 PROGRAMMAZIONE I A.A. 2017/2018 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES A programming language is a formal language that specifies a set of instructions that can be used to produce various kinds of output. Programming languages
PROGRAMMAZIONE I A.A. 2017/2018 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES A programming language is a formal language that specifies a set of instructions that can be used to produce various kinds of output. Programming languages
Introduction to Operating Systems. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Introduction to Operating Systems Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Why OS? 2 What is an OS? Software that converts hardware into
Introduction to Operating Systems Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Why OS? 2 What is an OS? Software that converts hardware into
Introduction to Programming: Variables and Objects. HORT Lecture 7 Instructor: Kranthi Varala
 Introduction to Programming: Variables and Objects HORT 59000 Lecture 7 Instructor: Kranthi Varala What is a program? A set of instructions to the computer that perform a specified task in a specified
Introduction to Programming: Variables and Objects HORT 59000 Lecture 7 Instructor: Kranthi Varala What is a program? A set of instructions to the computer that perform a specified task in a specified
Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT
 Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT Outline In this chapter you will learn: About computer hardware, software and programming How to write and execute
Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT Outline In this chapter you will learn: About computer hardware, software and programming How to write and execute
Compilation I. Hwansoo Han
 Compilation I Hwansoo Han Language Groups Imperative von Neumann (Fortran, Pascal, Basic, C) Object-oriented (Smalltalk, Eiffel, C++) Scripting languages (Perl, Python, JavaScript, PHP) Declarative Functional
Compilation I Hwansoo Han Language Groups Imperative von Neumann (Fortran, Pascal, Basic, C) Object-oriented (Smalltalk, Eiffel, C++) Scripting languages (Perl, Python, JavaScript, PHP) Declarative Functional
Com S 541. Programming Languages I
 Programming Languages I Lecturer: TA: Markus Lumpe Department of Computer Science 113 Atanasoff Hall http://www.cs.iastate.edu/~lumpe/coms541.html TR 12:40-2, W 5 Pramod Bhanu Rama Rao Office hours: TR
Programming Languages I Lecturer: TA: Markus Lumpe Department of Computer Science 113 Atanasoff Hall http://www.cs.iastate.edu/~lumpe/coms541.html TR 12:40-2, W 5 Pramod Bhanu Rama Rao Office hours: TR
COSC 2P90 Programming Languages & Object-Orientation
 COSC 2P90 Programming Languages & Object-Orientation Hi! 1 Textbooks Main Text Comparative Programming Languages 3rd ed.; Wilson, LB & Clark, RG; Addison-Wesley (2001); ISBN 0-201-71012-9 Supplemental
COSC 2P90 Programming Languages & Object-Orientation Hi! 1 Textbooks Main Text Comparative Programming Languages 3rd ed.; Wilson, LB & Clark, RG; Addison-Wesley (2001); ISBN 0-201-71012-9 Supplemental
Principles in Programming: Orientation & Lecture 1. SWE2004: Principles in Programming Spring 2014 Euiseong Seo
 Principles in Programming: Orientation & Lecture 1 1 Course Objectives Introduce various subjects in computer science through puzzles and problems Most problems came from ICPC 2 Textbook Programming Challenges
Principles in Programming: Orientation & Lecture 1 1 Course Objectives Introduce various subjects in computer science through puzzles and problems Most problems came from ICPC 2 Textbook Programming Challenges
C++ Programming Language Lecture 1 Introduction
 C++ Programming Language Lecture 1 Introduction By Ghada Al-Mashaqbeh The Hashemite University Computer Engineering Department Introduction In this course you will learn C++ and the legacy C code. It is
C++ Programming Language Lecture 1 Introduction By Ghada Al-Mashaqbeh The Hashemite University Computer Engineering Department Introduction In this course you will learn C++ and the legacy C code. It is
Introduction to Operating Systems. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Introduction to Operating Systems Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics What is OS? History of OS 2 What is OS? (1) Application
Introduction to Operating Systems Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Today s Topics What is OS? History of OS 2 What is OS? (1) Application
CS2303 C14 Systems Programming Concepts. Bob Kinicki
 CS2303 C14 Concepts Bob Kinicki Survey and TA/SA s Pause to Look Backwards and Forwards Course Objectives Course Operation/Expectations Course Plan and Syllabus Systems Concepts Higher Level Language
CS2303 C14 Concepts Bob Kinicki Survey and TA/SA s Pause to Look Backwards and Forwards Course Objectives Course Operation/Expectations Course Plan and Syllabus Systems Concepts Higher Level Language
CP122 CS I. Hello, World!
 CP122 CS I Hello, World! Introductions Webpage and Syllabus cs.coloradocollege.edu/~mwhitehead Tech News! AlphaGo Zero defeats AlphaGo 100 games to 0. Tech News! AlphaGo Zero defeats AlphaGo 100 games
CP122 CS I Hello, World! Introductions Webpage and Syllabus cs.coloradocollege.edu/~mwhitehead Tech News! AlphaGo Zero defeats AlphaGo 100 games to 0. Tech News! AlphaGo Zero defeats AlphaGo 100 games
CP122 CS I. Chapter 1: Introduction
 CP122 CS I Chapter 1: Introduction Introductions Webpage and Syllabus cs.coloradocollege.edu/~mwhitehead Hacker's Tip of the Day Hacker A person interested in how things work. A critical thinker, an endless
CP122 CS I Chapter 1: Introduction Introductions Webpage and Syllabus cs.coloradocollege.edu/~mwhitehead Hacker's Tip of the Day Hacker A person interested in how things work. A critical thinker, an endless
Is it ever useful to be confident that a problem is hard?
 CS26: Program and Data Representation University of Virginia Computer Science Spring 2006 David Evans Lecture 9: Low-Level Programming Menu Complexity Question Low-Level Programming Exam Out Wednesday,
CS26: Program and Data Representation University of Virginia Computer Science Spring 2006 David Evans Lecture 9: Low-Level Programming Menu Complexity Question Low-Level Programming Exam Out Wednesday,
PLAGIARISM. Administrivia. Course home page: Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers
 Administrivia Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers CS164 11:00-12:00 MWF 306 Soda Notes by G. Necula, with additions by P. Hilfinger Course home page: http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs164
Administrivia Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers CS164 11:00-12:00 MWF 306 Soda Notes by G. Necula, with additions by P. Hilfinger Course home page: http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs164
Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers. CS164 11:00-12:00 MWF 306 Soda
 Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers CS164 11:00-12:00 MWF 306 Soda Notes by G. Necula, with additions by P. Hilfinger Prof. Hilfinger CS 164 Lecture 1 1 Administrivia Course home page:
Introduction to Programming Languages and Compilers CS164 11:00-12:00 MWF 306 Soda Notes by G. Necula, with additions by P. Hilfinger Prof. Hilfinger CS 164 Lecture 1 1 Administrivia Course home page:
Why study Programming Language Concepts? Chapter One. Language Evaluation Criteria. Programming Domains. Readability Writability Reliability Cost
 Chapter One Preliminaries, including Why study PL concepts? Programming domains PL evaluation criteria What influences PL design? Tradeoffs faced by programming languages Implementation methods Programming
Chapter One Preliminaries, including Why study PL concepts? Programming domains PL evaluation criteria What influences PL design? Tradeoffs faced by programming languages Implementation methods Programming
Algorithms and Programming Languages
 Algorithms and Programming Languages Algorithm An algorithm is an set of unambiguous that defines a terminating process. Algorithms are part of many activities, even mundane ones. Note: Researchers believe
Algorithms and Programming Languages Algorithm An algorithm is an set of unambiguous that defines a terminating process. Algorithms are part of many activities, even mundane ones. Note: Researchers believe
Programs are: CMPSCI 105/119/120: Programming, Flowchar<ng, and Running Program Flowcharts
 Programs are: CMPSCI 105/119/120: Programming, Flowchar
Programs are: CMPSCI 105/119/120: Programming, Flowchar
Course and Unix Intro
 Course and Unix Intro Comp-206 : Introduction to Software Systems Lecture 1 Alexandre Denault Computer Science McGill University Fall 2006 Instructor Alexandre Denault Graduate student, working in the
Course and Unix Intro Comp-206 : Introduction to Software Systems Lecture 1 Alexandre Denault Computer Science McGill University Fall 2006 Instructor Alexandre Denault Graduate student, working in the
Food Storage Newsletter #9 - FREE monthly newsletter - September, 1999
 Food Storage Newsletter #9 - FREE monthly Email newsletter - September, 1999 This Month s Food Storage Guidelines: ==================================== This Month s FOOD STORAGE 52 Week Acquisition Plan
Food Storage Newsletter #9 - FREE monthly Email newsletter - September, 1999 This Month s Food Storage Guidelines: ==================================== This Month s FOOD STORAGE 52 Week Acquisition Plan
Vocabulary Platform Computing\ First grade Theoretical number of hours=30 Practical number of hours =60
 Vocabulary Platform Computing\ First grade Theoretical number of hours=30 Practical number of hours =60 Sequence Subject Theoretical number of hours Introduction (Introduction to Computers, the concepts
Vocabulary Platform Computing\ First grade Theoretical number of hours=30 Practical number of hours =60 Sequence Subject Theoretical number of hours Introduction (Introduction to Computers, the concepts
Introduction to Computer Programming Using FORTRAN 77
 Introduction to Computer Programming Using FORTRAN 77 Al-Dhaher, K. Garout, Y. Lafi, A. Al-Muhtaseb, H. Nazzal, A. Saeed, M. Yazdani, J. Zeidan, Y. August 1995 Second Edition Information and Computer Science
Introduction to Computer Programming Using FORTRAN 77 Al-Dhaher, K. Garout, Y. Lafi, A. Al-Muhtaseb, H. Nazzal, A. Saeed, M. Yazdani, J. Zeidan, Y. August 1995 Second Edition Information and Computer Science
Elements of Computers and Programming Dr. William C. Bulko. What is a Computer?
 Elements of Computers and Programming Dr. William C. Bulko What is a Computer? 2017 What is a Computer? A typical computer consists of: a CPU memory a hard disk a monitor and one or more communication
Elements of Computers and Programming Dr. William C. Bulko What is a Computer? 2017 What is a Computer? A typical computer consists of: a CPU memory a hard disk a monitor and one or more communication
Programming Languages
 Chapter 1 :: Introduction Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Programming Languages What programming languages can you name? Which do you know? 1 Introduction Why are there so many programming
Chapter 1 :: Introduction Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Programming Languages What programming languages can you name? Which do you know? 1 Introduction Why are there so many programming
Chapter 1: An Overview of Computers and Programming Languages. Objectives. Objectives (cont d.) Introduction
 Chapter 1: An Overview of Computers and Programming Languages Objectives Objectives (cont d.) In this chapter, you will: Learn about different types of computers Explore hardware and software Learn about
Chapter 1: An Overview of Computers and Programming Languages Objectives Objectives (cont d.) In this chapter, you will: Learn about different types of computers Explore hardware and software Learn about
Software Development. Integrated Software Environment
 Software Development Integrated Software Environment Source Code vs. Machine Code What is source code? Source code and object code refer to the "before" and "after" versions of a computer program that
Software Development Integrated Software Environment Source Code vs. Machine Code What is source code? Source code and object code refer to the "before" and "after" versions of a computer program that
What is a programming language?
 Overview Introduction Motivation Why study programming languages? Some key concepts What is a programming language? What is a programming language?...there is no agreement on what a programming language
Overview Introduction Motivation Why study programming languages? Some key concepts What is a programming language? What is a programming language?...there is no agreement on what a programming language
Why are there so many programming languages?
 Chapter 1 :: Introduction Programming Language Pragmatics, Fourth Edition Michael L. Scott Copyright 2016 Elsevier 1 Chapter01_ Introduction_4e - Tue November 21, 2017 Introduction Why are there so many
Chapter 1 :: Introduction Programming Language Pragmatics, Fourth Edition Michael L. Scott Copyright 2016 Elsevier 1 Chapter01_ Introduction_4e - Tue November 21, 2017 Introduction Why are there so many
C LANGUAGE AND ITS DIFFERENT TYPES OF FUNCTIONS
 C LANGUAGE AND ITS DIFFERENT TYPES OF FUNCTIONS Manish Dronacharya College Of Engineering, Maharishi Dayanand University, Gurgaon, Haryana, India III. Abstract- C Language History: The C programming language
C LANGUAGE AND ITS DIFFERENT TYPES OF FUNCTIONS Manish Dronacharya College Of Engineering, Maharishi Dayanand University, Gurgaon, Haryana, India III. Abstract- C Language History: The C programming language
CSCI.4430/6969 Programming Languages Lecture Notes
 CSCI.4430/6969 Programming Languages Lecture Notes August 28, 2006 1 Brief History of Programming Languages Ada Augusta, the Countess of Lovelace, the daughter of the poet Lord Byron, is attributed as
CSCI.4430/6969 Programming Languages Lecture Notes August 28, 2006 1 Brief History of Programming Languages Ada Augusta, the Countess of Lovelace, the daughter of the poet Lord Byron, is attributed as
Introduction to Java. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Ninth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction to Java 1 Programs Computer programs, known as software, are instructions to the computer. You tell a computer what to do through programs. Programs are written using programming languages.
Introduction to Java 1 Programs Computer programs, known as software, are instructions to the computer. You tell a computer what to do through programs. Programs are written using programming languages.
