Verifying the State Design Pattern using Object Propositions
|
|
|
- Arnold Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Verifying the State Design Pattern using Object Propositions Ligia Nistor Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University
2 Why verify programs? Verification vs. debugging Verification at compile time vs. testing at run time 2
3 Formal verification Use formal rules to reason about correctness of programs Difficult because of aliasing Reference A depends on property A 2 B Reference B can break property 1 1
4 Object Propositions New verification methodology Express specifications about objects object propositions Modularity verify classes independently Single-thread 4
5 Object propositions I want to verify that my program satisfies this property Then I need to provide a specification I ll write the specification using object propositions Object proposition: abstract predicate + fractional permission 5
6 Abstract Predicates Predicate MultipleOf(int a) = the divider field of this object == a && the value field is a multiple of divider obj value = 10 divider = 2 obj satisfies MultipleOf(2) [M. Parkinson] 6
7 Fractional permissions dealing with aliases 0 permission of 1 read/write access 5 permission of 1/2 read/write access, as long as the initial predicate is maintained Contribution: The state referred to by a fraction < 1 is not immutable. That state satisfies an invariant that can be relied on by other objects. [Boyland] 7
8 Putting it together Object proposition = abstract predicate + fractional permission a c value=10 divider=2 a#1/2 MultipleOf(2) c#1 MultipleOf(3) value=15 divider=3 8
9 The Verification of a Method Using proof rules Object propositions in pre-condition Statement (if, let, new..) Proof rule Method Object propositions ( properties about objects) Statement (if, let, new..) Proof rule Object propositions Object propositions in post-condition 9
10 Linear logic Classical logic: from A and (A B) get (A B) A B Linear logic: from A and (A B) get B (transform) Logic of resources Simultaneous occurrence of resources Alternative occurrence of resources Object propositions = resources consumed upon usage 10
11 Formal system x Rules for splitting/adding fractions 1 1/2 1/4 x#1 x#1/2 x#1/2 x#k x#k/2 x#k/2 1/2 1/4 [Boyland] 11
12 Pack, unpack Abstraction: Predicate: from outside MultipleOf(c) from inside get to the fields pack to a predicate unpack a predicate: gain access to fields of object 12
13 Consistency packed predicate consistent unpacked predicate inconsistent In a method, after the first assignment to a field, the unpacked predicate is inconsistent We have aliasing and fractions, how come unpacking is still sound? As long as we have a fraction to an object, we know that the invariant of that object will not be broken. When we pack back the predicate, the invariant is restored. We assume termination, so at end of program all objects are packed 13
14 Invariants Invariants are predicates that always hold at the boundary of methods, for all references pointing to the same object. Aliased objects can only depend on invariants, not on any kind of predicates. 14
15 Oprop Grammar 15
16 Oprop Grammar cont. 16
17 Oprop Online Tool 1 st webpage 17
18 Oprop Online Tool 2 nd webpage 18
19 Oprop Online Tool 3 rd webpage 19
20 Oprop Online Tool 4 th webpage 20
21 Diagram of State Pattern 21
22 My Example of the State Pattern 22
23 Class IntCell 23
24 Interface Statelike 24
25 Class StateLive 25
26 Class StateLive cont. 26
27 Classes StateLimbo and StateSleep 27
28 Class StateContext 28
29 Class StateContext cont. 29
30 Class StateClient 30
31 main() function in StateClient class 31
32 Implementation and code on GitHub aster/statelatest.bpl 32
33 Related work Bierhoff and Aldrich: access permissions Boyland: fractional permissions Parkinson: abstract predicates Barnett & Leino: Boogie verifier Krishnaswami: higher-order separation logic Nanevski: Hoare Type Theory Jacobs, Leino, Smans: multi-threaded OO programs 33
34 Future Work Augment features of Oprop language so that state pattern can be verified using Oprop Extend for multi-threaded programs 34
35 Conclusions Object proposition = abstract predicate + fractional permission Verified instance of State Design Pattern 35
Permissions to Specify the Composite Design Pattern
 Permissions to Specify the Composite Design Pattern Kevin Bierhoff Jonathan Aldrich Institute for Software Research, Carnegie Mellon University 5000 Forbes Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA {kevin.bierhoff,jonathan.aldrich
Permissions to Specify the Composite Design Pattern Kevin Bierhoff Jonathan Aldrich Institute for Software Research, Carnegie Mellon University 5000 Forbes Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA {kevin.bierhoff,jonathan.aldrich
Static program checking and verification
 Chair of Software Engineering Software Engineering Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer March 2007 June 2007 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Static program checking and verification Correctness
Chair of Software Engineering Software Engineering Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer March 2007 June 2007 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Static program checking and verification Correctness
Lecture 4. Towards a Verifying Compiler: Data Abstraction
 Lecture 4 Towards a Verifying Compiler: Data Abstraction W olfram Schulte Microsoft Research Formal Methods 2006 Purity, Model fields, Inconsistency Joint work with Rustan Leino, Mike Barnett, Manuel Fähndrich,
Lecture 4 Towards a Verifying Compiler: Data Abstraction W olfram Schulte Microsoft Research Formal Methods 2006 Purity, Model fields, Inconsistency Joint work with Rustan Leino, Mike Barnett, Manuel Fähndrich,
Verification of Snapshotable Trees using Access Permissions and Typestate
 Verification of Snapshotable Trees using Access Permissions and Typestate Hannes Mehnert 1 and Jonathan Aldrich 2 1 IT University of Copenhagen, 2300 København, Danmark hame@itu.dk 2 School of Computer
Verification of Snapshotable Trees using Access Permissions and Typestate Hannes Mehnert 1 and Jonathan Aldrich 2 1 IT University of Copenhagen, 2300 København, Danmark hame@itu.dk 2 School of Computer
Towards imperative modules: reasoning about invariants and sharing of mutable state
 Towards imperative modules: reasoning about invariants and sharing of mutable state David A. Naumann Joint work with Mike Barnett and Anindya Banerjee Stevens Institute of Technology Supported by NSF CCR-0208984,
Towards imperative modules: reasoning about invariants and sharing of mutable state David A. Naumann Joint work with Mike Barnett and Anindya Banerjee Stevens Institute of Technology Supported by NSF CCR-0208984,
Plural and : Protocols in Practice. Jonathan Aldrich Workshop on Behavioral Types April School of Computer Science
 Plural and : Protocols in Practice Jonathan Aldrich Workshop on Behavioral Types April 2011 School of Computer Science Empirical Study: Protocols in Java Object Protocol [Beckman, Kim, & A to appear in
Plural and : Protocols in Practice Jonathan Aldrich Workshop on Behavioral Types April 2011 School of Computer Science Empirical Study: Protocols in Java Object Protocol [Beckman, Kim, & A to appear in
Trends in Automated Verification
 Trends in Automated Verification K. Rustan M. Leino Senior Principal Engineer Automated Reasoning Group (ARG), Amazon Web Services 2018, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its Affiliates. All rights reserved.
Trends in Automated Verification K. Rustan M. Leino Senior Principal Engineer Automated Reasoning Group (ARG), Amazon Web Services 2018, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its Affiliates. All rights reserved.
Reasoning about Object Structures Using Ownership
 Reasoning about Object Structures Using Ownership Peter Müller ETH Zurich, Switzerland Peter.Mueller@inf.ethz.ch Abstract. Many well-established concepts of object-oriented programming work for individual
Reasoning about Object Structures Using Ownership Peter Müller ETH Zurich, Switzerland Peter.Mueller@inf.ethz.ch Abstract. Many well-established concepts of object-oriented programming work for individual
Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics
 Program Verification March 2014 Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics Lecturer: Noam Rinetzky Scribes by: Nir Hemed 1.1 Axiomatic semantics The development of the theory is contributed to Robert Floyd, C.A.R
Program Verification March 2014 Lecture 5 - Axiomatic semantics Lecturer: Noam Rinetzky Scribes by: Nir Hemed 1.1 Axiomatic semantics The development of the theory is contributed to Robert Floyd, C.A.R
Dafny: An Automatic Program Verifier for Functional Correctness Paper by K. Rustan M. Leino (Microsoft Research)
 Dafny: An Automatic Program Verifier for Functional Correctness Paper by K. Rustan M. Leino (Microsoft Research) Presentation by Patrick Spettel Seminar: Research Topics in Software Engineering, Spring
Dafny: An Automatic Program Verifier for Functional Correctness Paper by K. Rustan M. Leino (Microsoft Research) Presentation by Patrick Spettel Seminar: Research Topics in Software Engineering, Spring
Overview. Verification with Functions and Pointers. IMP with assertions and assumptions. Proof rules for Assert and Assume. IMP+: IMP with functions
 Overview Verification with Functions and Pointers Işıl Dillig The IMP language considered so far does not have many features of realistics PLs Our goal today: Enrich IMP with two features, namely functions
Overview Verification with Functions and Pointers Işıl Dillig The IMP language considered so far does not have many features of realistics PLs Our goal today: Enrich IMP with two features, namely functions
Verifying Correct Usage of Atomic Blocks and Typestate
 Verifying Correct Usage of Atomic Blocks and Typestate Nels E. Beckman Kevin Bierhoff Jonathan Aldrich School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University {nbeckman,kbierhof,aldrich@cs.cmu.edu Abstract
Verifying Correct Usage of Atomic Blocks and Typestate Nels E. Beckman Kevin Bierhoff Jonathan Aldrich School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University {nbeckman,kbierhof,aldrich@cs.cmu.edu Abstract
A Type System for Borrowing Permissions
 A Type System for Borrowing Permissions Karl Naden Jonathan Aldrich May 2012 CMU-CS-11-142 Robert Bocchino Kevin Bierhoff School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 This
A Type System for Borrowing Permissions Karl Naden Jonathan Aldrich May 2012 CMU-CS-11-142 Robert Bocchino Kevin Bierhoff School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 This
Objects and Aspects: Ownership Types
 Objects and Aspects: Ownership Types Neel Krishnaswami Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University neelk@cs.cmu.edu Overview The Problem An Introduction to Ownership Types Evaluating How
Objects and Aspects: Ownership Types Neel Krishnaswami Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University neelk@cs.cmu.edu Overview The Problem An Introduction to Ownership Types Evaluating How
Principles of Program Design. What should be taught in core programming curricula
 Principles of Program Design What should be taught in core programming curricula Basic Principles Design the data first and let the structure of the data guide the structure of the code. Design for unit
Principles of Program Design What should be taught in core programming curricula Basic Principles Design the data first and let the structure of the data guide the structure of the code. Design for unit
Refinement Types for TypeScript
 Refinement Types for TypeScript Panagiotis Vekris Benjamin Cosman Ranjit Jhala University of California, San Diego PLDI 16 Thursday, June 16 Extensible static analyses for modern scripting languages 2
Refinement Types for TypeScript Panagiotis Vekris Benjamin Cosman Ranjit Jhala University of California, San Diego PLDI 16 Thursday, June 16 Extensible static analyses for modern scripting languages 2
Checking Concurrent Typestate with Access Permissions in Plural: A Retrospective
 Checking Concurrent Typestate with Access Permissions in Plural: A Retrospective Kevin Bierhoff, Nels E. Beckman, and Jonathan Aldrich Abstract Objects often define usage protocols that clients must follow
Checking Concurrent Typestate with Access Permissions in Plural: A Retrospective Kevin Bierhoff, Nels E. Beckman, and Jonathan Aldrich Abstract Objects often define usage protocols that clients must follow
API Protocol Compliance in Object-Oriented Software. Kevin Bierhoff
 API Protocol Compliance in Object-Oriented Software Kevin Bierhoff 23 April 2009 CMU-ISR-09-108 Institute for Software Research School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213
API Protocol Compliance in Object-Oriented Software Kevin Bierhoff 23 April 2009 CMU-ISR-09-108 Institute for Software Research School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213
Modular Verification of the Subject-Observer Pattern via Higher-Order Separation Logic
 Modular Verification of the Subject-Observer Pattern via Higher-Order Separation Logic Neelakantan R. Krishnaswami, Jonathan Aldrich 1, and Lars Birkedal 2 1 Carnegie Mellon University, {neelk, aldrich}@cs.cmu.edu
Modular Verification of the Subject-Observer Pattern via Higher-Order Separation Logic Neelakantan R. Krishnaswami, Jonathan Aldrich 1, and Lars Birkedal 2 1 Carnegie Mellon University, {neelk, aldrich}@cs.cmu.edu
Controlling Mutation and Aliases with Fractional Permissions
 Controlling Mutation and Aliases with Fractional Permissions John Boyland University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ECOOP 12 Outline of Session I. Fractional Permissions II. Applications III. Problems I. Fractional
Controlling Mutation and Aliases with Fractional Permissions John Boyland University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ECOOP 12 Outline of Session I. Fractional Permissions II. Applications III. Problems I. Fractional
Hoare Logic. COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering. Rajeev Goré
 Hoare Logic COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering Rajeev Goré Australian National University Semester 2, 2016 (Slides courtesy of Ranald Clouston) COMP 2600 Hoare Logic 1 Australian Capital
Hoare Logic COMP2600 Formal Methods for Software Engineering Rajeev Goré Australian National University Semester 2, 2016 (Slides courtesy of Ranald Clouston) COMP 2600 Hoare Logic 1 Australian Capital
Constraint Semantics for Abstract Read Permissions. Author(s): Boyland, John T.; Müller, Peter; Schwerhoff, Malte; Summers, Alexander J.
 Research Collection Report Constraint Semantics for Abstract Read Permissions Author(s): Boyland, John T.; Müller, Peter; Schwerhoff, Malte; Summers, Alexander J. Publication Date: 2014 Permanent Link:
Research Collection Report Constraint Semantics for Abstract Read Permissions Author(s): Boyland, John T.; Müller, Peter; Schwerhoff, Malte; Summers, Alexander J. Publication Date: 2014 Permanent Link:
A VERIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR DETERMINISTIC PARALLEL PROGRAMS
 A VERIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR DETERMINISTIC PARALLEL PROGRAMS MARIEKE HUISMAN UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE, NETHERLANDS JOINT WORK WITH SAEED DARABI AND STEFAN BLOM THE CHALLENGE OF RELIABLE SOFTWARE ICT problems
A VERIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR DETERMINISTIC PARALLEL PROGRAMS MARIEKE HUISMAN UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE, NETHERLANDS JOINT WORK WITH SAEED DARABI AND STEFAN BLOM THE CHALLENGE OF RELIABLE SOFTWARE ICT problems
Reasoning About Frame Properties in Object-Oriented Programs
 Reasoning About Frame Properties in Object-Oriented Programs Yuyan Bao CS-TR-17-05 Revised April 14, 2018 Keywords: Frame axiom, modifies clause, separation logic, dynamic frames, region logic, finegrained
Reasoning About Frame Properties in Object-Oriented Programs Yuyan Bao CS-TR-17-05 Revised April 14, 2018 Keywords: Frame axiom, modifies clause, separation logic, dynamic frames, region logic, finegrained
Viper A Verification Infrastructure for Permission-Based Reasoning
 Viper A Verification Infrastructure for Permission-Based Reasoning Alex Summers, ETH Zurich Joint work with Uri Juhasz, Ioannis Kassios, Peter Müller, Milos Novacek, Malte Schwerhoff (and many students)
Viper A Verification Infrastructure for Permission-Based Reasoning Alex Summers, ETH Zurich Joint work with Uri Juhasz, Ioannis Kassios, Peter Müller, Milos Novacek, Malte Schwerhoff (and many students)
UML for Embedded Systems IV. Validation
 UML for Embedded Systems IV. Validation Ludovic Apvrille ludovic.apvrille@telecom-paristech.fr Eurecom, Office 470 Memo on Methodology III. Detailed design Behavior of the system IV. Validation of the
UML for Embedded Systems IV. Validation Ludovic Apvrille ludovic.apvrille@telecom-paristech.fr Eurecom, Office 470 Memo on Methodology III. Detailed design Behavior of the system IV. Validation of the
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics
 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
Verification of Object-Oriented Programs with Invariants
 Verification of Object-Oriented Programs with Invariants Dewan Ibtesham 05-03-2012 1 1 Introduction Reliability of computer programs is one of the most important tasks a programmer faces when he writes
Verification of Object-Oriented Programs with Invariants Dewan Ibtesham 05-03-2012 1 1 Introduction Reliability of computer programs is one of the most important tasks a programmer faces when he writes
Safely-Composable Type-Specific Languages
 Safely-Composable Type-Specific Languages Cyrus Omar Darya Kurilova Ligia Nistor Benjamin Chung Alex Potanin (Victoria University of Wellington) Jonathan Aldrich School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon
Safely-Composable Type-Specific Languages Cyrus Omar Darya Kurilova Ligia Nistor Benjamin Chung Alex Potanin (Victoria University of Wellington) Jonathan Aldrich School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon
Modular Reasoning about Aliasing using Permissions
 Modular Reasoning about Aliasing using Permissions John Boyland University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee FOAL 2015 Summary Permissions are non-duplicable tokens that give access to state. Permissions give effective
Modular Reasoning about Aliasing using Permissions John Boyland University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee FOAL 2015 Summary Permissions are non-duplicable tokens that give access to state. Permissions give effective
Semantics of Imperative Objects
 Semantics of Imperative Objects Catalin Hritcu Supervisor: Jan Schwinghammer Responsible: Prof. Gert Smolka Programming Systems Lab Saarland University, Saarbrücken November 2006 1 Overview Imperative
Semantics of Imperative Objects Catalin Hritcu Supervisor: Jan Schwinghammer Responsible: Prof. Gert Smolka Programming Systems Lab Saarland University, Saarbrücken November 2006 1 Overview Imperative
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2)
 #1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember that you can t just define a meaning function in terms of itself you must use some fixed point machinery. #2 #3 Observations
#1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember that you can t just define a meaning function in terms of itself you must use some fixed point machinery. #2 #3 Observations
Controlling Object Allocation Using Creation Guards
 Controlling Object Allocation Using Creation Guards Cees Pierik 1, Dave Clarke 2, and Frank S. de Boer 1,2,3 1 ICS, Utrecht University, The Netherlands 2 CWI, Amsterdam, The Netherlands 3 LIACS, Leiden
Controlling Object Allocation Using Creation Guards Cees Pierik 1, Dave Clarke 2, and Frank S. de Boer 1,2,3 1 ICS, Utrecht University, The Netherlands 2 CWI, Amsterdam, The Netherlands 3 LIACS, Leiden
Introduction to Formal Methods
 2008 Spring Software Special Development 1 Introduction to Formal Methods Part I : Formal Specification i JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@knokuk.ac.kr Reference AS Specifier s Introduction to Formal lmethods Jeannette
2008 Spring Software Special Development 1 Introduction to Formal Methods Part I : Formal Specification i JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@knokuk.ac.kr Reference AS Specifier s Introduction to Formal lmethods Jeannette
Formal Verification. Lecture 10
 Formal Verification Lecture 10 Formal Verification Formal verification relies on Descriptions of the properties or requirements of interest Descriptions of systems to be analyzed, and rely on underlying
Formal Verification Lecture 10 Formal Verification Formal verification relies on Descriptions of the properties or requirements of interest Descriptions of systems to be analyzed, and rely on underlying
Specifying Concurrent Programs: a case study in JML and Separation Logic
 Specifying Concurrent Programs: a case study in JML and Separation Logic Martijn Roo University of Twente The Netherlands m.j.roo@student.utwente.nl ABSTRACT This paper presents a case study for the verification
Specifying Concurrent Programs: a case study in JML and Separation Logic Martijn Roo University of Twente The Netherlands m.j.roo@student.utwente.nl ABSTRACT This paper presents a case study for the verification
Rely-Guarantee References for Refinement Types over Aliased Mutable Data
 Rely-Guarantee References for Refinement Types over Aliased Mutable Data Colin S. Gordon, Michael D. Ernst, and Dan Grossman University of Washington PLDI 2013 Static Verification Meets Aliasing 23 x:ref
Rely-Guarantee References for Refinement Types over Aliased Mutable Data Colin S. Gordon, Michael D. Ernst, and Dan Grossman University of Washington PLDI 2013 Static Verification Meets Aliasing 23 x:ref
Programming Languages Third Edition
 Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING. COURSE STRUCTURE AND REQUIREMENTS Saulius Ragaišis saulius.ragaisis@mif.vu.lt WHAT IS SOFTWARE ENGINEERING? First definition Software engineering
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING. COURSE STRUCTURE AND REQUIREMENTS Saulius Ragaišis saulius.ragaisis@mif.vu.lt WHAT IS SOFTWARE ENGINEERING? First definition Software engineering
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING. COURSE STRUCTURE AND REQUIREMENTS Saulius Ragaišis saulius.ragaisis@mif.vu.lt WHAT IS SOFTWARE ENGINEERING? First definition Software engineering
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING. COURSE STRUCTURE AND REQUIREMENTS Saulius Ragaišis saulius.ragaisis@mif.vu.lt WHAT IS SOFTWARE ENGINEERING? First definition Software engineering
Semantics of Imperative Objects
 Semantics of Imperative Objects Catalin Hritcu Supervisor: Jan Schwinghammer Responsible: Prof. Gert Smolka Programming Systems Lab Saarland University, Saarbrücken November 2006 1 Overview Imperative
Semantics of Imperative Objects Catalin Hritcu Supervisor: Jan Schwinghammer Responsible: Prof. Gert Smolka Programming Systems Lab Saarland University, Saarbrücken November 2006 1 Overview Imperative
ÆMINIUM, Freeing Programmers from the Shackles of Sequentiality
 ÆMINIUM Freeing Programmers from the Shackles of Sequentiality Sven Stork Supervisors: Jonathan Aldrich Paulo Marques Carnegie Mellon University University of Coimbra June 15, 2010 1 / 21 Motivation 2
ÆMINIUM Freeing Programmers from the Shackles of Sequentiality Sven Stork Supervisors: Jonathan Aldrich Paulo Marques Carnegie Mellon University University of Coimbra June 15, 2010 1 / 21 Motivation 2
Compilation and Program Analysis (#11) : Hoare triples and shape analysis
 Compilation and Program Analysis (#11) : Hoare triples and shape analysis Laure Gonnord http://laure.gonnord.org/pro/teaching/capm1.html Laure.Gonnord@ens-lyon.fr Master 1, ENS de Lyon dec 2017 Inspiration
Compilation and Program Analysis (#11) : Hoare triples and shape analysis Laure Gonnord http://laure.gonnord.org/pro/teaching/capm1.html Laure.Gonnord@ens-lyon.fr Master 1, ENS de Lyon dec 2017 Inspiration
Substructural Typestates
 Programming Languages meets Program Verification 2014 Substructural Typestates Filipe Militão (CMU & UNL) Jonathan Aldrich (CMU) Luís Caires (UNL) Motivation! File file = new File( out.txt );! file.write(
Programming Languages meets Program Verification 2014 Substructural Typestates Filipe Militão (CMU & UNL) Jonathan Aldrich (CMU) Luís Caires (UNL) Motivation! File file = new File( out.txt );! file.write(
Design by Contract: An Overview
 : An Overview CSCI 5828 Michael M. Vitousek University of Colorado at Boulder michael.vitousek@colorado.edu March 21, 2012 1 / 35 Outline 1 Introduction Motivation and Introduction Simple Example Contract
: An Overview CSCI 5828 Michael M. Vitousek University of Colorado at Boulder michael.vitousek@colorado.edu March 21, 2012 1 / 35 Outline 1 Introduction Motivation and Introduction Simple Example Contract
Proofs-Programs correspondance and Security
 Proofs-Programs correspondance and Security Jean-Baptiste Joinet Université de Lyon & Centre Cavaillès, École Normale Supérieure, Paris Third Cybersecurity Japanese-French meeting Formal methods session
Proofs-Programs correspondance and Security Jean-Baptiste Joinet Université de Lyon & Centre Cavaillès, École Normale Supérieure, Paris Third Cybersecurity Japanese-French meeting Formal methods session
Maintaining Invariants Through Object Coupling Mechanisms
 Maintaining Invariants Through Object Coupling Mechanisms Eric Kerfoot Steve McKeever Oxford University Computing Laboratory {eric.kerfoot, steve.mckeever}@comlab.ox.ac.uk Abstract Object invariants are
Maintaining Invariants Through Object Coupling Mechanisms Eric Kerfoot Steve McKeever Oxford University Computing Laboratory {eric.kerfoot, steve.mckeever}@comlab.ox.ac.uk Abstract Object invariants are
A verification methodology for model fields
 A verification methodology for model fields K. Rustan M. Leino 1 and Peter Müller 2 1 Microsoft Research, leino@microsoft.com 2 ETH Zürich, peter.mueller@inf.ethz.ch Abstract. Model fields are specification-only
A verification methodology for model fields K. Rustan M. Leino 1 and Peter Müller 2 1 Microsoft Research, leino@microsoft.com 2 ETH Zürich, peter.mueller@inf.ethz.ch Abstract. Model fields are specification-only
6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions
 6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions Program Verification ETH Zurich, Spring Semester 07 Alexander J. Summers 30 Program Correctness There are many notions of correctness properties for a given program
6. Hoare Logic and Weakest Preconditions Program Verification ETH Zurich, Spring Semester 07 Alexander J. Summers 30 Program Correctness There are many notions of correctness properties for a given program
Lecture Notes: Hoare Logic
 Lecture Notes: Hoare Logic 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich (jonathan.aldrich@cs.cmu.edu) Lecture 3 1 Hoare Logic The goal of Hoare logic is to provide a formal system for
Lecture Notes: Hoare Logic 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich (jonathan.aldrich@cs.cmu.edu) Lecture 3 1 Hoare Logic The goal of Hoare logic is to provide a formal system for
Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics
 Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Static Analysis Based on slides by George Necula Pratikakis (CSD) Axiomatic Semantics
Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Static Analysis Based on slides by George Necula Pratikakis (CSD) Axiomatic Semantics
Lecture 21. Lecture 21: Concurrency & Locking
 Lecture 21 Lecture 21: Concurrency & Locking Lecture 21 Today s Lecture 1. Concurrency, scheduling & anomalies 2. Locking: 2PL, conflict serializability, deadlock detection 2 Lecture 21 > Section 1 1.
Lecture 21 Lecture 21: Concurrency & Locking Lecture 21 Today s Lecture 1. Concurrency, scheduling & anomalies 2. Locking: 2PL, conflict serializability, deadlock detection 2 Lecture 21 > Section 1 1.
Pointer Programs, Separation Logic
 Chapter 6 Pointer Programs, Separation Logic The goal of this section is to drop the hypothesis that we have until now, that is, references are not values of the language, and in particular there is nothing
Chapter 6 Pointer Programs, Separation Logic The goal of this section is to drop the hypothesis that we have until now, that is, references are not values of the language, and in particular there is nothing
Chapter 9 State Based Invariants and Object Allocation
 Chapter 9 State Based Invariants and Object Allocation Sharing of objects is often necessary to increase the speed and reduce the resource demands of programs. A system that allocates too many objects
Chapter 9 State Based Invariants and Object Allocation Sharing of objects is often necessary to increase the speed and reduce the resource demands of programs. A system that allocates too many objects
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2)
 #1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember: just do the counterexample guided abstraction refinement part of DPLL(T). If you notice any other errors, those are good
#1 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics (1/2) How s The Homework Going? Remember: just do the counterexample guided abstraction refinement part of DPLL(T). If you notice any other errors, those are good
Why3 Where Programs Meet Provers
 Why3 Where Programs Meet Provers Jean-Christophe Filliâtre, Andrei Paskevich To cite this version: Jean-Christophe Filliâtre, Andrei Paskevich. Why3 Where Programs Meet Provers. ESOP 13 22nd European Symposium
Why3 Where Programs Meet Provers Jean-Christophe Filliâtre, Andrei Paskevich To cite this version: Jean-Christophe Filliâtre, Andrei Paskevich. Why3 Where Programs Meet Provers. ESOP 13 22nd European Symposium
Chapter 1. Introduction
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction An exciting development of the 21st century is that the 20th-century vision of mechanized program verification is finally becoming practical, thanks to 30 years of advances in
1 Chapter 1 Introduction An exciting development of the 21st century is that the 20th-century vision of mechanized program verification is finally becoming practical, thanks to 30 years of advances in
Advances in Programming Languages
 O T Y H Advances in Programming Languages APL8: ESC/Java2 David Aspinall (including slides by Ian Stark and material adapted from ESC/Java2 tutorial by David Cok, Joe Kiniry and Erik Poll) School of Informatics
O T Y H Advances in Programming Languages APL8: ESC/Java2 David Aspinall (including slides by Ian Stark and material adapted from ESC/Java2 tutorial by David Cok, Joe Kiniry and Erik Poll) School of Informatics
Modular Verification with Shared Abstractions
 Modular Verification with Shared Abstractions Uri Juhasz Noam Rinetzky Arnd Poetzsch-Heffter Mooly Sagiv Eran Yahav Tel Aviv University Tel Aviv University Universität Kaiserlautern Tel Aviv University
Modular Verification with Shared Abstractions Uri Juhasz Noam Rinetzky Arnd Poetzsch-Heffter Mooly Sagiv Eran Yahav Tel Aviv University Tel Aviv University Universität Kaiserlautern Tel Aviv University
Side Effects (3A) Young Won Lim 1/13/18
 Side Effects (3A) Copyright (c) 2016-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Side Effects (3A) Copyright (c) 2016-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Sound reasoning about unchecked exceptions
 Sound reasoning about unchecked exceptions Bart Jacobs 1 Peter Müller 2 Frank Piessens 1 1 Katholieke Universiteit Leuven Belgium {bartj,frank@cs.kuleuven.be 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond USA mueller@microsoft.com
Sound reasoning about unchecked exceptions Bart Jacobs 1 Peter Müller 2 Frank Piessens 1 1 Katholieke Universiteit Leuven Belgium {bartj,frank@cs.kuleuven.be 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond USA mueller@microsoft.com
Lecture 5. Towards a Verifying Compiler: Multithreading
 Lecture 5 Towards a Verifying Compiler: Multithreading W olfram Schulte Microsoft Research Formal Methods 2006 Race Conditions, Locks, Deadlocks, Invariants, Locklevels Access Sets Joint work with Rustan
Lecture 5 Towards a Verifying Compiler: Multithreading W olfram Schulte Microsoft Research Formal Methods 2006 Race Conditions, Locks, Deadlocks, Invariants, Locklevels Access Sets Joint work with Rustan
Most of the slides in this lecture are either from or adapted from slides provided by the authors of the textbook Computer Systems: A Programmer s
 Most of the slides in this lecture are either from or adapted from slides provided by the authors of the textbook Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, 2 nd Edition and are provided from the website
Most of the slides in this lecture are either from or adapted from slides provided by the authors of the textbook Computer Systems: A Programmer s Perspective, 2 nd Edition and are provided from the website
The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine
 The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine [PLDI 01] Anders Mφller Michael I. Schwartzbach Presented by K. Vikram Cornell University Introduction Pointer manipulation is hard Find bugs, optimize code General Approach
The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine [PLDI 01] Anders Mφller Michael I. Schwartzbach Presented by K. Vikram Cornell University Introduction Pointer manipulation is hard Find bugs, optimize code General Approach
Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics
 Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings
Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings
PLSV, Mock Test, 2011
 PLSV, Mock Test, 2011 Question 1 The lseg predicate describes a segment of a singly-linked list. It is defined to be the least predicate satisfying the following equation: lseg(e, F ) (E = F emp) (E F
PLSV, Mock Test, 2011 Question 1 The lseg predicate describes a segment of a singly-linked list. It is defined to be the least predicate satisfying the following equation: lseg(e, F ) (E = F emp) (E F
Delegation vs Inheritance for Typestate Analysis
 Delegation vs Inheritance for Typestate Analysis Du Li, Alex Potanin, 1 and Jonathan Aldrich Carnegie Mellon University and Victoria University of Wellington 1 {duli, aldrich}@cs.cmu.edu, alex@ecs.vuw.ac.nz
Delegation vs Inheritance for Typestate Analysis Du Li, Alex Potanin, 1 and Jonathan Aldrich Carnegie Mellon University and Victoria University of Wellington 1 {duli, aldrich}@cs.cmu.edu, alex@ecs.vuw.ac.nz
Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java
 Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 ESC/Java A checker for Java programs Finds null pointers, array dereferences Checks Hoare logic
Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 ESC/Java A checker for Java programs Finds null pointers, array dereferences Checks Hoare logic
Typed Assembly Language for Implementing OS Kernels in SMP/Multi-Core Environments with Interrupts
 Typed Assembly Language for Implementing OS Kernels in SMP/Multi-Core Environments with Interrupts Toshiyuki Maeda and Akinori Yonezawa University of Tokyo Quiz [Environment] CPU: Intel Xeon X5570 (2.93GHz)
Typed Assembly Language for Implementing OS Kernels in SMP/Multi-Core Environments with Interrupts Toshiyuki Maeda and Akinori Yonezawa University of Tokyo Quiz [Environment] CPU: Intel Xeon X5570 (2.93GHz)
BOOGIE. Presentation by Itsik Hefez A MODULAR REUSABLE VERIFIER FOR OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMS MICROSOFT RESEARCH
 BOOGIE A MODULAR REUSABLE VERIFIER FOR OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMS MICROSOFT RESEARCH Presentation by Itsik Hefez Introduction Boogie is an intermediate verification language, intended as a layer on which
BOOGIE A MODULAR REUSABLE VERIFIER FOR OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMS MICROSOFT RESEARCH Presentation by Itsik Hefez Introduction Boogie is an intermediate verification language, intended as a layer on which
Pietro Ferrara and Peter Müller
 Inference of Fractional, Counting and Chalice Access Permissions via Abstract Interpretation Pietro Ferrara and Peter Müller ETH Zurich Switzerland Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain Access permissions
Inference of Fractional, Counting and Chalice Access Permissions via Abstract Interpretation Pietro Ferrara and Peter Müller ETH Zurich Switzerland Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain Access permissions
JML tool-supported specification for Java Erik Poll Radboud University Nijmegen
 JML tool-supported specification for Java Erik Poll Radboud University Nijmegen Erik Poll - JML p.1/41 Overview The specification language JML Tools for JML, in particular runtime assertion checking using
JML tool-supported specification for Java Erik Poll Radboud University Nijmegen Erik Poll - JML p.1/41 Overview The specification language JML Tools for JML, in particular runtime assertion checking using
Manifest Safety and Security. Robert Harper Carnegie Mellon University
 Manifest Safety and Security Robert Harper Carnegie Mellon University Collaborators This work is, in part, joint with Lujo Bauer, Karl Crary, Peter Lee, Mike Reiter, and Frank Pfenning at Carnegie Mellon.
Manifest Safety and Security Robert Harper Carnegie Mellon University Collaborators This work is, in part, joint with Lujo Bauer, Karl Crary, Peter Lee, Mike Reiter, and Frank Pfenning at Carnegie Mellon.
Lightweight RPC. Robert Grimm New York University
 Lightweight RPC Robert Grimm New York University The Three Questions What is the problem? What is new or different? What are the contributions and limitations? The Structure of Systems Monolithic kernels
Lightweight RPC Robert Grimm New York University The Three Questions What is the problem? What is new or different? What are the contributions and limitations? The Structure of Systems Monolithic kernels
A Programming Model for Concurrent Object-Oriented Programs
 1 A Programming Model for Concurrent Object-Oriented Programs BART JACOBS, FRANK PIESSENS, and JAN SMANS Katholieke Universiteit Leuven and K. RUSTAN M. LEINO and WOLFRAM SCHULTE Microsoft Research Reasoning
1 A Programming Model for Concurrent Object-Oriented Programs BART JACOBS, FRANK PIESSENS, and JAN SMANS Katholieke Universiteit Leuven and K. RUSTAN M. LEINO and WOLFRAM SCHULTE Microsoft Research Reasoning
Hoare Logic: Proving Programs Correct
 Hoare Logic: Proving Programs Correct 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich Reading: C.A.R. Hoare, An Axiomatic Basis for Computer Programming Some presentation ideas from a lecture
Hoare Logic: Proving Programs Correct 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich Reading: C.A.R. Hoare, An Axiomatic Basis for Computer Programming Some presentation ideas from a lecture
Typestate Checking for Actionscript 3
 Typestate Checking for Actionscript 3 Yun-En Liu and Qi Shan December 10, 2010 1 Introduction This project proposes a compile-time check for function calls in a game system written in Actionscript 3, based
Typestate Checking for Actionscript 3 Yun-En Liu and Qi Shan December 10, 2010 1 Introduction This project proposes a compile-time check for function calls in a game system written in Actionscript 3, based
Side Effects (3B) Young Won Lim 11/20/17
 Side Effects (3B) Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Side Effects (3B) Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
VCC: A Practical System for Verifying Concurrent C
 VCC: A Practical System for Verifying Concurrent C Ernie Cohen 1, Markus Dahlweid 2, Mark Hillebrand 3, Dirk Leinenbach 3, Michal Moskal 2, Thomas Santen 2, Wolfram Schulte 4 and Stephan Tobies 2 1 Microsoft
VCC: A Practical System for Verifying Concurrent C Ernie Cohen 1, Markus Dahlweid 2, Mark Hillebrand 3, Dirk Leinenbach 3, Michal Moskal 2, Thomas Santen 2, Wolfram Schulte 4 and Stephan Tobies 2 1 Microsoft
Course Wrap-Up. Software Testing and Verification. Stephen M. Thebaut, Ph.D. Prepared by. University of Florida
 Course Wrap-Up Software Testing and Verification Prepared by Stephen M. Thebaut, Ph.D. University of Florida A few loose ends Final Exam + solution notes will be posted (under Practice Exams ) ASAP probably
Course Wrap-Up Software Testing and Verification Prepared by Stephen M. Thebaut, Ph.D. University of Florida A few loose ends Final Exam + solution notes will be posted (under Practice Exams ) ASAP probably
CoVaC: Compiler Verification by Program Analysis of the Cross-Product. Anna Zaks, Amir Pnueli. May 28, FM 08, Turku, Finland
 CoVaC: Compiler Verification by Program Analysis of the Cross-Product Anna Zaks, Amir Pnueli May 28, 28 FM 8, Turku, Finland Translation Validation source Optimization Pass target Validation Pass proof
CoVaC: Compiler Verification by Program Analysis of the Cross-Product Anna Zaks, Amir Pnueli May 28, 28 FM 8, Turku, Finland Translation Validation source Optimization Pass target Validation Pass proof
ESC/Java2 Use and Features
 ESC/Java2 Use and Features The ESC/Java2 tool David Cok, Joe Kiniry, Erik Poll Eastman Kodak Company, University College Dublin, and Radboud University Nijmegen David Cok, Joe Kiniry & Erik Poll - ESC/Java2
ESC/Java2 Use and Features The ESC/Java2 tool David Cok, Joe Kiniry, Erik Poll Eastman Kodak Company, University College Dublin, and Radboud University Nijmegen David Cok, Joe Kiniry & Erik Poll - ESC/Java2
Uniqueness and Reference Immutability for Safe Parallelism
 Uniqueness and Reference Immutability for Safe Parallelism Colin Gordon (UW), Matt Parkinson (MSR), Jared Parsons (MS), Aleks Bromfield (MS), Joe Duffy (MS) OOPSLA 2012 A Prototype Extension to C# Extend
Uniqueness and Reference Immutability for Safe Parallelism Colin Gordon (UW), Matt Parkinson (MSR), Jared Parsons (MS), Aleks Bromfield (MS), Joe Duffy (MS) OOPSLA 2012 A Prototype Extension to C# Extend
ESC/Java2 Use and Features
 ESC/Java2 Use and Features David Cok, Joe Kiniry, Erik Poll Eastman Kodak Company, University College Dublin, and Radboud University Nijmegen David Cok, Joe Kiniry & Erik Poll - ESC/Java2 & JML Tutorial
ESC/Java2 Use and Features David Cok, Joe Kiniry, Erik Poll Eastman Kodak Company, University College Dublin, and Radboud University Nijmegen David Cok, Joe Kiniry & Erik Poll - ESC/Java2 & JML Tutorial
Capabilities for Uniqueness and Borrowing
 Capabilities for Uniqueness and Borrowing Philipp Haller and Martin Odersky EPFL 24 th European Conference on Object Oriented Programming June 24, 2010 Maribor, Slovenia Motivating Example actor { val
Capabilities for Uniqueness and Borrowing Philipp Haller and Martin Odersky EPFL 24 th European Conference on Object Oriented Programming June 24, 2010 Maribor, Slovenia Motivating Example actor { val
Separation Logic Tutorial
 Separation Logic Tutorial (To appear in Proceedings of ICLP 08) Peter O Hearn Queen Mary, University of London Separation logic is an extension of Hoare s logic for reasoning about programs that manipulate
Separation Logic Tutorial (To appear in Proceedings of ICLP 08) Peter O Hearn Queen Mary, University of London Separation logic is an extension of Hoare s logic for reasoning about programs that manipulate
CITS5501 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Formal methods
 CITS5501 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Formal methods Unit coordinator: Arran Stewart May 1, 2018 1 / 49 Sources Pressman, R., Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, McGraw-Hill, 2005
CITS5501 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Formal methods Unit coordinator: Arran Stewart May 1, 2018 1 / 49 Sources Pressman, R., Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, McGraw-Hill, 2005
Lecture 10 Design by Contract
 CS 5959 Writing Solid Code Fall 2015 Nov-23 Lecture 10 Design by Contract Zvonimir Rakamarić University of Utah Design by Contract Also called assume-guarantee reasoning Developers annotate software components
CS 5959 Writing Solid Code Fall 2015 Nov-23 Lecture 10 Design by Contract Zvonimir Rakamarić University of Utah Design by Contract Also called assume-guarantee reasoning Developers annotate software components
Modular specification of frame properties in JML
 CONCURRENCY PRACTICE AND EXPERIENCE Concurrency: Pract. Exper. 2002; 1:1 [Version: 2001/03/05 v2.01] Modular specification of frame properties in JML Peter Müller 1, Arnd Poetzsch-Heffter 2, and Gary T.
CONCURRENCY PRACTICE AND EXPERIENCE Concurrency: Pract. Exper. 2002; 1:1 [Version: 2001/03/05 v2.01] Modular specification of frame properties in JML Peter Müller 1, Arnd Poetzsch-Heffter 2, and Gary T.
Model-Driven Verifying Compilation of Synchronous Distributed Applications
 Model-Driven Verifying Compilation of Synchronous Distributed Applications Sagar Chaki, James Edmondson October 1, 2014 MODELS 14, Valencia, Spain Copyright 2014 Carnegie Mellon University This material
Model-Driven Verifying Compilation of Synchronous Distributed Applications Sagar Chaki, James Edmondson October 1, 2014 MODELS 14, Valencia, Spain Copyright 2014 Carnegie Mellon University This material
An Operational and Axiomatic Semantics for Non-determinism and Sequence Points in C
 An Operational and Axiomatic Semantics for Non-determinism and Sequence Points in C Robbert Krebbers Radboud University Nijmegen January 22, 2014 @ POPL, San Diego, USA 1 / 16 What is this program supposed
An Operational and Axiomatic Semantics for Non-determinism and Sequence Points in C Robbert Krebbers Radboud University Nijmegen January 22, 2014 @ POPL, San Diego, USA 1 / 16 What is this program supposed
Software and Energy-aware Computing Fundamentals of static analysis of software
 Software and Energy-aware Computing Fundamentals of static analysis of software John Gallagher Roskilde University ICT-Energy: Energy consumption in future ICT devices Summer School, Aalborg, Denmark,
Software and Energy-aware Computing Fundamentals of static analysis of software John Gallagher Roskilde University ICT-Energy: Energy consumption in future ICT devices Summer School, Aalborg, Denmark,
Topic Formal Methods. ICS 121 Lecture Notes. What are Formal Methods? What are Formal Methods? Formal Specification in Software Development
 Lecture Notes What are? 1 Formal Method (FM) = specification language + formal reasoning Body of techniques supported by precise mathematics powerful analysis tools Rigorous effective mechanisms for system
Lecture Notes What are? 1 Formal Method (FM) = specification language + formal reasoning Body of techniques supported by precise mathematics powerful analysis tools Rigorous effective mechanisms for system
Objects as Session-Typed Processes
 Objects as Session-Typed Processes Stephanie Balzer and Frank Pfenning Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University AGERE! 2015 The essence of object-orientation 2 The essence of object-orientation
Objects as Session-Typed Processes Stephanie Balzer and Frank Pfenning Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University AGERE! 2015 The essence of object-orientation 2 The essence of object-orientation
Modular verification of static class invariants
 Modular verification of static class invariants K. Rustan M. Leino 1 and Peter Müller 2 1 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA, leino@microsoft.com 2 ETH Zürich, Switzerland, peter.mueller@inf.ethz.ch
Modular verification of static class invariants K. Rustan M. Leino 1 and Peter Müller 2 1 Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, USA, leino@microsoft.com 2 ETH Zürich, Switzerland, peter.mueller@inf.ethz.ch
Implementing Symmetric Multiprocessing in LispWorks
 Implementing Symmetric Multiprocessing in LispWorks Making a multithreaded application more multithreaded Martin Simmons, LispWorks Ltd Copyright 2009 LispWorks Ltd Outline Introduction Changes in LispWorks
Implementing Symmetric Multiprocessing in LispWorks Making a multithreaded application more multithreaded Martin Simmons, LispWorks Ltd Copyright 2009 LispWorks Ltd Outline Introduction Changes in LispWorks
Hierarchical Composition and Abstraction In Architecture Models
 Hierarchical Composition and Abstraction In Architecture Models Pam Binns and Steve Vestal Honeywell Labs {pam.binns, steve.vestal}@honeywell.com Supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research
Hierarchical Composition and Abstraction In Architecture Models Pam Binns and Steve Vestal Honeywell Labs {pam.binns, steve.vestal}@honeywell.com Supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research
Programming Language Abstractions for Modularly Verified Distributed Systems. James R. Wilcox Zach Tatlock Ilya Sergey
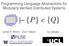 Programming Language Abstractions for Modularly Verified Distributed Systems ` {P } c {Q} James R. Wilcox Zach Tatlock Ilya Sergey Distributed Systems Distributed Infrastructure Distributed Applications
Programming Language Abstractions for Modularly Verified Distributed Systems ` {P } c {Q} James R. Wilcox Zach Tatlock Ilya Sergey Distributed Systems Distributed Infrastructure Distributed Applications
Crafting a Compiler with C (II) Compiler V. S. Interpreter
 Crafting a Compiler with C (II) 資科系 林偉川 Compiler V S Interpreter Compilation - Translate high-level program to machine code Lexical Analyzer, Syntax Analyzer, Intermediate code generator(semantics Analyzer),
Crafting a Compiler with C (II) 資科系 林偉川 Compiler V S Interpreter Compilation - Translate high-level program to machine code Lexical Analyzer, Syntax Analyzer, Intermediate code generator(semantics Analyzer),
A Proposal for Weak-Memory Local Reasoning
 A Proposal for Weak-Memory Local Reasoning Ian Wehrman and Josh Berdine Abstract Program logics are formal systems for specifying and reasoning about software programs. Most program logics make the strong
A Proposal for Weak-Memory Local Reasoning Ian Wehrman and Josh Berdine Abstract Program logics are formal systems for specifying and reasoning about software programs. Most program logics make the strong
