Towards Automatic Generation of Vulnerability- Based Signatures
|
|
|
- Christine Lambert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Towards Automatic Generation of Vulnerability- Based Signatures David Brumley, James Newsome, Dawn Song, Hao Wang, and Somesh Jha (presented by Boniface Hicks) Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1
2 Beware the LION New year ,000 systems affected invades Linux systems through a network exploit infiltrates BIND DNS through TCP or UDP protocol allows infiltration through a legit request, but then can execute arbitrary commands through additional string of characters. incident report March 30 by CERT Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 2
3 3 Vulnerability vulnerability - type of bug that can be used by an attacker to alter the intended operation of software in a malicious way exploit - an actual input that triggers a devastating consequence (these can be polymorphic)
4 4 Overview Goal: automatic signature generation Challenges: polymorphism vulnerability-based (not exploit-based) Approach: vulnerability signature: whether executing an input potentially results in an unsafe program state vulnerability condition: representation (how to express a vulnerability as a signature) coverage (measured by false positive rate)
5 5 Contributions requires single sample exploit to identify vulnerability formal definition of vulnerability signature expose trade-off between matching time and accuracy notion of coverage introduced manual control of introducing imprecision new static analysis techniques and novel application prototype implementation handles COTS binaries
6 6 Vulnerability signature vulnerability signature - representation for set of inputs that define a specified vulnerability condition trade-offs: representation: matching accuracy vs. efficiency signature creation: creation time vs. coverage {P,T,x,c} = binary program (P), instruction trace (T), exploit string (x), vulnerability condition (c).
7 7 Example P given in box x = g/aaaa T= {1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9,8, 10,11,10,11,10,11, 10,11,10,11} c = heap overflow (on 5th iteration of line 11) 1 char geturl (char inp[10]) { 2 char *url = malloc(4); 3 int c = 0; 4 if (inp[c]!= g && inp[c]!= G ) 5 return NULL; 6 inp[c] = G ; 7 c++; 8 while (inp[c] == ) 9 c++; 10 while (inp[c]!= ) { 11 url = inp[c]; c++; url++; 12 } 13 printf( %s, url); 14 return url; 15}
8 8 Vulnerability sig notation (P,c) = (< i 1,...,i k >,c) T(P,x) is the execution trace of running P with input x. T c means T satisfies vulnerability condition c LP,c consists of the set of all inputs x to a program P such that Formally: T (P,x) c L P,c = {x Σ T (P,x) c} An exploit for a vulnerability (P,c) is an input x L P,c
9 9 Vulnerability sig definition A vulnerability signature is a matching function MATCH which for an input x returns either EXPLOIT or BENIGN for a program P without running the program. A perfect vulnerability signature satisfies: MATCH(x) = { EXPLOIT when x L P,c BENIGN when x L P,c completeness: x : x L P,c MATCH(x) = EXPLOIT soundness: x : x L P,c MATCH(x) = BENIGN
10 10 Vulnerability Condition c : Γ D M K I {BENIGN, EXPLOIT} Γ is a memory D is the set of variables defined M is the program s map from memory to values K is the continuation stack I is the next instruction to execute
11 11 Example Formal operational semantics definition of the vulnerability in the example: Γ,D,M,K *exp D,M,K exp Γ[n SafePtr(m,s)],D,M : [n v n ],K n { BENIGN if m n < m + s EXPLOIT 1. In order to dereference a pointer *exp, exp must first be evaluated. 2. Once exp is resolved to address n, get a safe pointer to n, (with base address m, size s) and check whether it s in the specified range.
12 12 Sig representation classes Turing machine signatures precise (no false positive or negatives) may not terminate (in presence of loops, e.g.) symbolic constraint signatures approximates looping, aliasing guaranteed to terminate regular expression signatures approximates elementary constructs (counting) very efficient
13 13 Turing Machine sig Can provide a precise, even exact, characterization of the vulnerability condition in a particular program. A TM that exactly emulates the program has no error rate.
14 14 Example symbolic constraint says that for 10-char input, the first char is g or G, up to four of the next chars may be symbolic constraint sig for example spaces and at least 5 chars are non-spaces regexp: [g G][ ]*[ˆ ]{5,} says g or G followed by 0 or more spaces and at least 5 non-spaces
15 15 Accuracy vs. Efficiency TM - inlining vulnerability condition takes poly time Symb. Constraint - poly-time transformations on TM Regexp - solve constraint (exp time; PSPACEcomplete) or data-flow on TM (poly time)
16 16 MEP and PEP coverage MEP is a straight-line program -- e.g. the path that the exploit took to reach the vulnerability PEP includes different paths to the vulnerability a complete PEP coverage signature accepts all inputs in LP,c complete coverage through a chop of the program includes all paths from the input read (vinit) to the vulnerability point (vfinal).
17 17 Procedure Get MEP for exploit (e.g. T in example) Compute chop for MEP to get complete coverage Compute initial signature S refine S by adding alternative MEPs from chop Example: initial MEP is T PEP is lines {1-5, 7-12}
18 18 Algorithm 1. Pre-process 1. Disassemble binary 2. Convert to an intermediate representation (IR) 2. Chop P wrt trace T, develop complete PEP 3. Compute the signature 1. Compute TM signature 2. Develop symbolic constraint signature 3. Compute regular expression
19 19 Evaluation 9000 lines C++ code CBMC model checker to build/solve symbolic constraints, generate regexp s disassembler based on Kruegel; IR new ATPhttpd various vulnerabilities; sprintf-style string too long 10 distinct subpaths to regexp in sec BIND stack overflow vulnerability; TSIG vulnerability 10 distinct graphs in symbolic constraint 30 micro-secs for chop 88% of functions were reachable between entry and vulnerability
20 20
Theory and Techniques for Automatic Generation of Vulnerability-Based Signatures
 Theory and Techniques for Automatic Generation of Vulnerability-Based Signatures David Brumley James Newsome Dawn Song 1 Hao Wang Somesh Jha 2 February 2006 CMU-CS-06-108 School of Computer Science Carnegie
Theory and Techniques for Automatic Generation of Vulnerability-Based Signatures David Brumley James Newsome Dawn Song 1 Hao Wang Somesh Jha 2 February 2006 CMU-CS-06-108 School of Computer Science Carnegie
Towards Practical Automatic Generation of Multipath Vulnerability Signatures
 Towards Practical Automatic Generation of Multipath Vulnerability Signatures David Brumley, Zhenkai Liang, James Newsome, and Dawn Song Original manuscript prepared April 19, 2007 1 CMU-CS-07-150 School
Towards Practical Automatic Generation of Multipath Vulnerability Signatures David Brumley, Zhenkai Liang, James Newsome, and Dawn Song Original manuscript prepared April 19, 2007 1 CMU-CS-07-150 School
Polygraph: Automatically Generating Signatures for Polymorphic Worms
 Polygraph: Automatically Generating Signatures for Polymorphic Worms James Newsome Brad Karp Dawn Song Presented by: Jeffrey Kirby Overview Motivation Polygraph Signature Generation Algorithm Evaluation
Polygraph: Automatically Generating Signatures for Polymorphic Worms James Newsome Brad Karp Dawn Song Presented by: Jeffrey Kirby Overview Motivation Polygraph Signature Generation Algorithm Evaluation
Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08
 Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08 For your solutions you should submit a hard copy; either hand written pages stapled together or a print out of a typeset document
Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08 For your solutions you should submit a hard copy; either hand written pages stapled together or a print out of a typeset document
Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs. {livshits,
 Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs {livshits, lam}@cs.stanford.edu 2 Background Software systems are getting bigger Harder to develop Harder to modify Harder
Tracking Pointers with Path and Context Sensitivity for Bug Detection in C Programs {livshits, lam}@cs.stanford.edu 2 Background Software systems are getting bigger Harder to develop Harder to modify Harder
Symbolic Execution for Bug Detection and Automated Exploit Generation
 Symbolic Execution for Bug Detection and Automated Exploit Generation Daniele Cono D Elia Credits: Emilio Coppa SEASON Lab season-lab.github.io May 27, 2016 1 / 29 Daniele Cono D Elia Symbolic Execution
Symbolic Execution for Bug Detection and Automated Exploit Generation Daniele Cono D Elia Credits: Emilio Coppa SEASON Lab season-lab.github.io May 27, 2016 1 / 29 Daniele Cono D Elia Symbolic Execution
Module: Future of Secure Programming
 Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Creating Vulnerability Signatures Using Weakest Preconditions
 Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Institute of Technology 2007 Creating Vulnerability Signatures Using Weakest Preconditions
Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Institute of Technology 2007 Creating Vulnerability Signatures Using Weakest Preconditions
Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input
 Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input Sathish Kuppuswamy & Yufei Fu Department of computer Science University of Texas at Dallas March 21 st, 2012 Outline Bouncer Existing Techniques Bouncer
Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input Sathish Kuppuswamy & Yufei Fu Department of computer Science University of Texas at Dallas March 21 st, 2012 Outline Bouncer Existing Techniques Bouncer
Lecture 4 September Required reading materials for this class
 EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
EURECOM 6/2/2012 SYSTEM SECURITY Σ
 EURECOM 6/2/2012 Name SYSTEM SECURITY 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Σ Course material is not allowed during the exam. Try to keep your answers precise and short. You will not get extra points
EURECOM 6/2/2012 Name SYSTEM SECURITY 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Σ Course material is not allowed during the exam. Try to keep your answers precise and short. You will not get extra points
Buffer overflow is still one of the most common vulnerabilities being discovered and exploited in commodity software.
 Outline Morris Worm (1998) Infamous attacks Secure Programming Lecture 4: Memory Corruption II (Stack Overflows) David Aspinall, Informatics @ Edinburgh 23rd January 2014 Recap Simple overflow exploit
Outline Morris Worm (1998) Infamous attacks Secure Programming Lecture 4: Memory Corruption II (Stack Overflows) David Aspinall, Informatics @ Edinburgh 23rd January 2014 Recap Simple overflow exploit
System Administration and Network Security
 System Administration and Network Security Master SSCI, M2P subject Duration: up to 3 hours. All answers should be justified. Clear and concise answers will be rewarded. 1 Network Administration To keep
System Administration and Network Security Master SSCI, M2P subject Duration: up to 3 hours. All answers should be justified. Clear and concise answers will be rewarded. 1 Network Administration To keep
CS 330 Lecture 18. Symbol table. C scope rules. Declarations. Chapter 5 Louden Outline
 CS 0 Lecture 8 Chapter 5 Louden Outline The symbol table Static scoping vs dynamic scoping Symbol table Dictionary associates names to attributes In general: hash tables, tree and lists (assignment ) can
CS 0 Lecture 8 Chapter 5 Louden Outline The symbol table Static scoping vs dynamic scoping Symbol table Dictionary associates names to attributes In general: hash tables, tree and lists (assignment ) can
Shuntaint: Emulation-based Security Testing for Formal Verification
 Shuntaint: Emulation-based Security Testing for Formal Verification Bruno Luiz ramosblc@gmail.com Abstract. This paper describes an emulated approach to collect traces of program states, in order to verify
Shuntaint: Emulation-based Security Testing for Formal Verification Bruno Luiz ramosblc@gmail.com Abstract. This paper describes an emulated approach to collect traces of program states, in order to verify
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 14: Software Security Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Software Security Exploiting software vulnerabilities is paramount
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 14: Software Security Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Software Security Exploiting software vulnerabilities is paramount
Outline STRANGER. Background
 Outline Malicious Code Analysis II : An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP 1 Mitchell Adair 2 November 28 th, 2011 Outline 1 2 Credit: [: An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP] Background
Outline Malicious Code Analysis II : An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP 1 Mitchell Adair 2 November 28 th, 2011 Outline 1 2 Credit: [: An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP] Background
Announcements. assign0 due tonight. Labs start this week. No late submissions. Very helpful for assign1
 Announcements assign due tonight No late submissions Labs start this week Very helpful for assign1 Goals for Today Pointer operators Allocating memory in the heap malloc and free Arrays and pointer arithmetic
Announcements assign due tonight No late submissions Labs start this week Very helpful for assign1 Goals for Today Pointer operators Allocating memory in the heap malloc and free Arrays and pointer arithmetic
Program verification. Generalities about software Verification Model Checking. September 20, 2016
 Program verification Generalities about software Verification Model Checking Laure Gonnord David Monniaux September 20, 2016 1 / 43 The teaching staff Laure Gonnord, associate professor, LIP laboratory,
Program verification Generalities about software Verification Model Checking Laure Gonnord David Monniaux September 20, 2016 1 / 43 The teaching staff Laure Gonnord, associate professor, LIP laboratory,
Malicious Code Analysis II
 Malicious Code Analysis II STRANGER: An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP Mitchell Adair November 28 th, 2011 Outline 1 STRANGER 2 Outline 1 STRANGER 2 STRANGER Credit: [STRANGER: An Automata-based
Malicious Code Analysis II STRANGER: An Automata-based String Analysis Tool for PHP Mitchell Adair November 28 th, 2011 Outline 1 STRANGER 2 Outline 1 STRANGER 2 STRANGER Credit: [STRANGER: An Automata-based
Hacking in C. Pointers. Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Spring 2019
 Hacking in C Pointers Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands Spring 2019 Allocation of multiple variables Consider the program main(){ char x; int i; short s; char y;... } What will the layout of
Hacking in C Pointers Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands Spring 2019 Allocation of multiple variables Consider the program main(){ char x; int i; short s; char y;... } What will the layout of
Module: Future of Secure Programming
 Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Module: Future of Secure Programming Professor Trent Jaeger Penn State University Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Laboratory (SIIS) 1 Programmer s Little Survey Problem What does program for
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice
 Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Secure Software Development: Theory and Practice Suman Jana MW 2:40-3:55pm 415 Schapiro [SCEP] *Some slides are borrowed from Dan Boneh and John Mitchell Software Security is a major problem! Why writing
Is stack overflow still a problem?
 Morris Worm (1998) Code Red (2001) Secure Programming Lecture 4: Memory Corruption II (Stack Overflows) David Aspinall, Informatics @ Edinburgh 31st January 2017 Memory corruption Buffer overflow remains
Morris Worm (1998) Code Red (2001) Secure Programming Lecture 4: Memory Corruption II (Stack Overflows) David Aspinall, Informatics @ Edinburgh 31st January 2017 Memory corruption Buffer overflow remains
Static Analysis Basics II
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Static Analysis Basics
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Static Analysis Basics
Memory Corruption 101 From Primitives to Exploit
 Memory Corruption 101 From Primitives to Exploit Created by Nick Walker @ MWR Infosecurity / @tel0seh What is it? A result of Undefined Behaviour Undefined Behaviour A result of executing computer code
Memory Corruption 101 From Primitives to Exploit Created by Nick Walker @ MWR Infosecurity / @tel0seh What is it? A result of Undefined Behaviour Undefined Behaviour A result of executing computer code
CMPSC 497 Other Memory Vulnerabilities
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA CMPSC 497 Other Memory
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA CMPSC 497 Other Memory
Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study. Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU
 Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU Outline Why static analysis What is it Underlying technology Some tools (Coverity, KlocWork,
Static Analysis methods and tools An industrial study Pär Emanuelsson Ericsson AB and LiU Prof Ulf Nilsson LiU Outline Why static analysis What is it Underlying technology Some tools (Coverity, KlocWork,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture C Pointers. Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic & Nicholas Weaver
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture C Pointers Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic & Nicholas Weaver http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp16 1 Agenda Pointers Arrays in C 2 Address vs. Value Consider
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture C Pointers Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic & Nicholas Weaver http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp16 1 Agenda Pointers Arrays in C 2 Address vs. Value Consider
COS 320. Compiling Techniques
 Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Assignment 4: Semantics
 Assignment 4: Semantics 15-411: Compiler Design Jan Hoffmann Jonathan Burns, DeeDee Han, Anatol Liu, Alice Rao Due Thursday, November 3, 2016 (9:00am) Reminder: Assignments are individual assignments,
Assignment 4: Semantics 15-411: Compiler Design Jan Hoffmann Jonathan Burns, DeeDee Han, Anatol Liu, Alice Rao Due Thursday, November 3, 2016 (9:00am) Reminder: Assignments are individual assignments,
Finding Vulnerabilities in Web Applications
 Finding Vulnerabilities in Web Applications Christopher Kruegel, Technical University Vienna Evolving Networks, Evolving Threats The past few years have witnessed a significant increase in the number of
Finding Vulnerabilities in Web Applications Christopher Kruegel, Technical University Vienna Evolving Networks, Evolving Threats The past few years have witnessed a significant increase in the number of
EURECOM 6/2/2012 SYSTEM SECURITY Σ
 EURECOM 6/2/2012 Name SYSTEM SECURITY 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 10 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Σ Course material is not allowed during the exam. Try to keep your answers precise and short. You will not get extra points
EURECOM 6/2/2012 Name SYSTEM SECURITY 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 10 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Σ Course material is not allowed during the exam. Try to keep your answers precise and short. You will not get extra points
Module: Program Vulnerabilities. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
C and C++ Secure Coding 4-day course. Syllabus
 C and C++ Secure Coding 4-day course Syllabus C and C++ Secure Coding 4-Day Course Course description Secure Programming is the last line of defense against attacks targeted toward our systems. This course
C and C++ Secure Coding 4-day course Syllabus C and C++ Secure Coding 4-Day Course Course description Secure Programming is the last line of defense against attacks targeted toward our systems. This course
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 15: Software Security II Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Software Vulnerabilities Buffer overflow vulnerabilities account
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 15: Software Security II Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Software Vulnerabilities Buffer overflow vulnerabilities account
Module: Program Vulnerabilities. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
Advanced Systems Security: Control-Flow Integrity
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input
 Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input Lidong Zhou Microsoft Research Mountain View, USA lidongz@microsoft.com Manuel Costa Microsoft Research Cambridge, UK manuelc@microsoft.com Lintao Zhang
Bouncer: Securing Software by Blocking Bad Input Lidong Zhou Microsoft Research Mountain View, USA lidongz@microsoft.com Manuel Costa Microsoft Research Cambridge, UK manuelc@microsoft.com Lintao Zhang
Secure Programming. An introduction to Splint. Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E
 Secure Programming An introduction to Splint Christian D. Jensen René Rydhof Hansen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E05-02230 CDJ/RRH (IMM/DTU) Secure Programming
Secure Programming An introduction to Splint Christian D. Jensen René Rydhof Hansen Informatics and Mathematical Modelling Technical University of Denmark E05-02230 CDJ/RRH (IMM/DTU) Secure Programming
Sendmail crackaddr - Static Analysis strikes back
 Sendmail crackaddr - Static Analysis strikes back Bogdan Mihaila Technical University of Munich, Germany December 6, 2014 Name Lastname < name@mail.org > ()()()()()()()()()... ()()() 1 / 25 Abstract Interpretation
Sendmail crackaddr - Static Analysis strikes back Bogdan Mihaila Technical University of Munich, Germany December 6, 2014 Name Lastname < name@mail.org > ()()()()()()()()()... ()()() 1 / 25 Abstract Interpretation
Finding User/Kernel Pointer Bugs with Type Inference p.1
 Finding User/Kernel Pointer Bugs with Type Inference Rob Johnson David Wagner rtjohnso,daw}@cs.berkeley.edu. UC Berkeley Finding User/Kernel Pointer Bugs with Type Inference p.1 User/Kernel Pointer Bugs
Finding User/Kernel Pointer Bugs with Type Inference Rob Johnson David Wagner rtjohnso,daw}@cs.berkeley.edu. UC Berkeley Finding User/Kernel Pointer Bugs with Type Inference p.1 User/Kernel Pointer Bugs
COMP 524 Spring 2018 Midterm Thursday, March 1
 Name PID COMP 524 Spring 2018 Midterm Thursday, March 1 This exam is open note, open book and open computer. It is not open people. You are to submit this exam through gradescope. Resubmissions have been
Name PID COMP 524 Spring 2018 Midterm Thursday, March 1 This exam is open note, open book and open computer. It is not open people. You are to submit this exam through gradescope. Resubmissions have been
Secure Programming I. Steven M. Bellovin September 28,
 Secure Programming I Steven M. Bellovin September 28, 2014 1 If our software is buggy, what does that say about its security? Robert H. Morris Steven M. Bellovin September 28, 2014 2 The Heart of the Problem
Secure Programming I Steven M. Bellovin September 28, 2014 1 If our software is buggy, what does that say about its security? Robert H. Morris Steven M. Bellovin September 28, 2014 2 The Heart of the Problem
Detecting Self-Mutating Malware Using Control-Flow Graph Matching
 Detecting Self-Mutating Malware Using Control-Flow Graph Matching Danilo Bruschi Lorenzo Martignoni Mattia Monga Dipartimento di Informatica e Comunicazione Università degli Studi di Milano {bruschi,martign,monga}@dico.unimi.it
Detecting Self-Mutating Malware Using Control-Flow Graph Matching Danilo Bruschi Lorenzo Martignoni Mattia Monga Dipartimento di Informatica e Comunicazione Università degli Studi di Milano {bruschi,martign,monga}@dico.unimi.it
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE. The University of Tokyo
 Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
The Low-Level Bounded Model Checker LLBMC
 The Low-Level Bounded Model Checker LLBMC A Precise Memory Model for LLBMC Carsten Sinz Stephan Falke Florian Merz October 7, 2010 VERIFICATION MEETS ALGORITHM ENGINEERING KIT University of the State of
The Low-Level Bounded Model Checker LLBMC A Precise Memory Model for LLBMC Carsten Sinz Stephan Falke Florian Merz October 7, 2010 VERIFICATION MEETS ALGORITHM ENGINEERING KIT University of the State of
Buffer overflow prevention, and other attacks
 Buffer prevention, and other attacks Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline 1 2 Two approaches to buffer defense Aim to harden programs to resist attacks in new programs Run time Aim to detect and abort attacks
Buffer prevention, and other attacks Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline 1 2 Two approaches to buffer defense Aim to harden programs to resist attacks in new programs Run time Aim to detect and abort attacks
K-Miner Uncovering Memory Corruption in Linux
 K-Miner Uncovering Memory Corruption in Linux David Gens Simon Schmitt Ahmad-Reza Sadeghi Cyber Security Center (CYSEC) Technische Universität Darmstadt Lucas Davi Universität of Duisburg-Essen Why Static
K-Miner Uncovering Memory Corruption in Linux David Gens Simon Schmitt Ahmad-Reza Sadeghi Cyber Security Center (CYSEC) Technische Universität Darmstadt Lucas Davi Universität of Duisburg-Essen Why Static
Inception: System-Wide Security Testing of Real- World Embedded Systems Software Nassim Corteggiani (Maxim Integrated / EURECOM) Giovanni Camurati
 Inception: System-Wide Security Testing of Real- World Embedded Systems Software Nassim Corteggiani (Maxim Integrated / EURECOM) Giovanni Camurati (EURECOM) Aurélien Francillon (EURECOM) 08/15/18 Embedded
Inception: System-Wide Security Testing of Real- World Embedded Systems Software Nassim Corteggiani (Maxim Integrated / EURECOM) Giovanni Camurati (EURECOM) Aurélien Francillon (EURECOM) 08/15/18 Embedded
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security. Spring 2007 Lecture 2
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 2 Announcements First project is on the web Due: Feb. 1st at midnight Form groups of 2 or 3 people If you need help finding a group,
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 2 Announcements First project is on the web Due: Feb. 1st at midnight Form groups of 2 or 3 people If you need help finding a group,
Confinement (Running Untrusted Programs)
 Confinement (Running Untrusted Programs) Chester Rebeiro Indian Institute of Technology Madras Untrusted Programs Untrusted Application Entire Application untrusted Part of application untrusted Modules
Confinement (Running Untrusted Programs) Chester Rebeiro Indian Institute of Technology Madras Untrusted Programs Untrusted Application Entire Application untrusted Part of application untrusted Modules
Automated Signature Generation: Overview and the NoAH Approach. Bernhard Tellenbach
 Automated Signature Generation: Overview and the NoAH Approach Structure Motivation: The speed of insecurity Overview Building Blocks and Techniques The NoAH approach 2 The speed of insecurity Source:
Automated Signature Generation: Overview and the NoAH Approach Structure Motivation: The speed of insecurity Overview Building Blocks and Techniques The NoAH approach 2 The speed of insecurity Source:
Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures
 Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures Presented by Brian Walker Senior Software Engineer, Video Product Line, Tektronix, Inc. Pacific Northwest Software Quality Conference,
Using Static Code Analysis to Find Bugs Before They Become Failures Presented by Brian Walker Senior Software Engineer, Video Product Line, Tektronix, Inc. Pacific Northwest Software Quality Conference,
Module: Program Vulnerabilities. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
Advanced Systems Security: Ordinary Operating Systems
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Java Security HotJava to Netscape and Beyond
 Java Security HotJava to Netscape and Beyond Drew Dean Ed Felten Dan Wallach Department of Computer Science Princeton University 4/5/96 Introduction Q Remote Code is Everywhere Q Java - A new language
Java Security HotJava to Netscape and Beyond Drew Dean Ed Felten Dan Wallach Department of Computer Science Princeton University 4/5/96 Introduction Q Remote Code is Everywhere Q Java - A new language
Programming Languages and Compilers Qualifying Examination. Answer 4 of 6 questions.
 Programming Languages and Compilers Qualifying Examination Fall 2017 Answer 4 of 6 questions. GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Answer each question in a separate book. 2. Indicate on the cover of each book the
Programming Languages and Compilers Qualifying Examination Fall 2017 Answer 4 of 6 questions. GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Answer each question in a separate book. 2. Indicate on the cover of each book the
Static Code Analysis - CERT C Secure Code Checking
 Static Code Analysis - CERT C Secure Code Checking Frozen Content Modified by on 6-Nov-2013 Related Videos CERT Code Checking The high-level C code written for an embedded software project can sometimes
Static Code Analysis - CERT C Secure Code Checking Frozen Content Modified by on 6-Nov-2013 Related Videos CERT Code Checking The high-level C code written for an embedded software project can sometimes
Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15. Type Systems
 Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 Type Systems Goals Define the simple language of expressions A small subset of Lisp, with minor modifications Define the type system of this language Mathematical definition using
Pierce Ch. 3, 8, 11, 15 Type Systems Goals Define the simple language of expressions A small subset of Lisp, with minor modifications Define the type system of this language Mathematical definition using
Preventing Use-after-free with Dangling Pointers Nullification
 Preventing Use-after-free with Dangling Pointers Nullification Byoungyoung Lee, Chengyu Song, Yeongjin Jang Tielei Wang, Taesoo Kim, Long Lu, Wenke Lee Georgia Institute of Technology Stony Brook University
Preventing Use-after-free with Dangling Pointers Nullification Byoungyoung Lee, Chengyu Song, Yeongjin Jang Tielei Wang, Taesoo Kim, Long Lu, Wenke Lee Georgia Institute of Technology Stony Brook University
Topics in Systems and Program Security
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Topics in Systems and
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Topics in Systems and
Application of Propositional Logic II - How to Test/Verify my C program? Moonzoo Kim
 Application of Propositional Logic II - How to Test/Verify my C program? Moonzoo Kim 2 Solving Various Problems using SAT Solver Sudoku Puzzle Encoding 1 Encoding 2 Verify/Testing C Programs Encoding 3
Application of Propositional Logic II - How to Test/Verify my C program? Moonzoo Kim 2 Solving Various Problems using SAT Solver Sudoku Puzzle Encoding 1 Encoding 2 Verify/Testing C Programs Encoding 3
MWR InfoSecurity Security Advisory. IBM WebSphere MQ - rrilookupget Remote Denial of Service Vulnerability. 4th March 2010
 MWR InfoSecurity Security Advisory IBM WebSphere MQ - rrilookupget Remote Denial of Service Vulnerability 4th March 2010 2010-03-04 Page 1 of 9 Contents Contents 1 Detailed Vulnerability Description...
MWR InfoSecurity Security Advisory IBM WebSphere MQ - rrilookupget Remote Denial of Service Vulnerability 4th March 2010 2010-03-04 Page 1 of 9 Contents Contents 1 Detailed Vulnerability Description...
Outline. Classic races: files in /tmp. Race conditions. TOCTTOU example. TOCTTOU gaps. Vulnerabilities in OS interaction
 Outline CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 3: Low-level vulnerabilities Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Race conditions Classic races: files in /tmp
Outline CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 3: Low-level vulnerabilities Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Race conditions Classic races: files in /tmp
Specification and verification of a simple machine
 March 8, 2006 One slide summary Simple Virtual Machine Modeled a simple virtual machine: an interpreter + a static checker Proved that verified programs never overflow the operand stack Identified a suitable
March 8, 2006 One slide summary Simple Virtual Machine Modeled a simple virtual machine: an interpreter + a static checker Proved that verified programs never overflow the operand stack Identified a suitable
Memory Corruption Vulnerabilities, Part II
 Memory Corruption Vulnerabilities, Part II Gang Tan Penn State University Spring 2019 CMPSC 447, Software Security Integer Overflow Vulnerabilities * slides adapted from those by Seacord 3 Integer Overflows
Memory Corruption Vulnerabilities, Part II Gang Tan Penn State University Spring 2019 CMPSC 447, Software Security Integer Overflow Vulnerabilities * slides adapted from those by Seacord 3 Integer Overflows
Buffer Overflow. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Buffer Overflow Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu x86-64/linux Memory Layout Stack Runtime stack (8MB limit) Heap Dynamically allocated
Buffer Overflow Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu x86-64/linux Memory Layout Stack Runtime stack (8MB limit) Heap Dynamically allocated
CS-527 Software Security
 CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
Protection and Mitigation of Software Bug Exploitation
 Protection and Mitigation of Software Bug Exploitation Vartan Padaryan vartan@ispras.ru 1 How safe is latest Linux release? Command line arguments fuzzer (inspired by Brumley s article) Launch programs
Protection and Mitigation of Software Bug Exploitation Vartan Padaryan vartan@ispras.ru 1 How safe is latest Linux release? Command line arguments fuzzer (inspired by Brumley s article) Launch programs
typedef void (*type_fp)(void); int a(char *s) { type_fp hf = (type_fp)(&happy_function); char buf[16]; strncpy(buf, s, 18); (*hf)(); return 0; }
![typedef void (*type_fp)(void); int a(char *s) { type_fp hf = (type_fp)(&happy_function); char buf[16]; strncpy(buf, s, 18); (*hf)(); return 0; } typedef void (*type_fp)(void); int a(char *s) { type_fp hf = (type_fp)(&happy_function); char buf[16]; strncpy(buf, s, 18); (*hf)(); return 0; }](/thumbs/82/86078968.jpg) Dawn Song Fall 2012 CS 161 Computer Security Practice Questions 1. (6 points) Control Hijacking Indicate whether the statement is always valid. Indicate true or false, and give a one sentence explanation.
Dawn Song Fall 2012 CS 161 Computer Security Practice Questions 1. (6 points) Control Hijacking Indicate whether the statement is always valid. Indicate true or false, and give a one sentence explanation.
Static Analysis: Overview, Syntactic Analysis and Abstract Interpretation TDDC90: Software Security
 Static Analysis: Overview, Syntactic Analysis and Abstract Interpretation TDDC90: Software Security Ahmed Rezine IDA, Linköpings Universitet Hösttermin 2014 Outline Overview Syntactic Analysis Abstract
Static Analysis: Overview, Syntactic Analysis and Abstract Interpretation TDDC90: Software Security Ahmed Rezine IDA, Linköpings Universitet Hösttermin 2014 Outline Overview Syntactic Analysis Abstract
Analysis of Software Vulnerability
 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conference on Information Security and Privacy, Venice, Italy, November 20-22, 2006 218 Analysis of Software Vulnerability CHUNGUANG KUANG, QING MIAO, HUA CHEN Department
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conference on Information Security and Privacy, Venice, Italy, November 20-22, 2006 218 Analysis of Software Vulnerability CHUNGUANG KUANG, QING MIAO, HUA CHEN Department
Buffer Overflow. Jinkyu Jeong Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Buffer Overflow Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE2030: Introduction to Computer Systems, Spring 2018, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu)
Buffer Overflow Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu SSE2030: Introduction to Computer Systems, Spring 2018, Jinkyu Jeong (jinkyu@skku.edu)
Undefined Behaviour in C
 Undefined Behaviour in C Report Field of work: Scientific Computing Field: Computer Science Faculty for Mathematics, Computer Science and Natural Sciences University of Hamburg Presented by: Dennis Sobczak
Undefined Behaviour in C Report Field of work: Scientific Computing Field: Computer Science Faculty for Mathematics, Computer Science and Natural Sciences University of Hamburg Presented by: Dennis Sobczak
A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur:
 A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur: Buffer overflows, null pointer dereference, use after free, use of uninitialized memory, illegal free Memory safety categories
A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur: Buffer overflows, null pointer dereference, use after free, use of uninitialized memory, illegal free Memory safety categories
Limits of Learning-based Signature Generation with Adversaries
 Limits of Learning-based Signature Generation with Adversaries Shobha Venkataraman Carnegie Mellon University shobha@cs.cmu.edu Avrim Blum Carnegie Mellon University avrim@cs.cmu.edu Dawn Song University
Limits of Learning-based Signature Generation with Adversaries Shobha Venkataraman Carnegie Mellon University shobha@cs.cmu.edu Avrim Blum Carnegie Mellon University avrim@cs.cmu.edu Dawn Song University
Advanced Systems Security: Ordinary Operating Systems
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Advanced Systems Security:
CSE 509: Computer Security
 CSE 509: Computer Security Date: 2.16.2009 BUFFER OVERFLOWS: input data Server running a daemon Attacker Code The attacker sends data to the daemon process running at the server side and could thus trigger
CSE 509: Computer Security Date: 2.16.2009 BUFFER OVERFLOWS: input data Server running a daemon Attacker Code The attacker sends data to the daemon process running at the server side and could thus trigger
1.1 For Fun and Profit. 1.2 Common Techniques. My Preferred Techniques
 1 Bug Hunting Bug hunting is the process of finding bugs in software or hardware. In this book, however, the term bug hunting will be used specifically to describe the process of finding security-critical
1 Bug Hunting Bug hunting is the process of finding bugs in software or hardware. In this book, however, the term bug hunting will be used specifically to describe the process of finding security-critical
Scaling CQUAL to millions of lines of code and millions of users p.1
 Scaling CQUAL to millions of lines of code and millions of users Jeff Foster, Rob Johnson, John Kodumal and David Wagner {jfoster,rtjohnso,jkodumal,daw}@cs.berkeley.edu. UC Berkeley Scaling CQUAL to millions
Scaling CQUAL to millions of lines of code and millions of users Jeff Foster, Rob Johnson, John Kodumal and David Wagner {jfoster,rtjohnso,jkodumal,daw}@cs.berkeley.edu. UC Berkeley Scaling CQUAL to millions
Software and Web Security 1. Root Cause Analysis. Abstractions Assumptions Trust. sws1 1
 Software and Web Security 1 Reflections on using C(++) Root Cause Analysis Abstractions Assumptions Trust sws1 1 There are only two kinds of programming languages: the ones people complain about and the
Software and Web Security 1 Reflections on using C(++) Root Cause Analysis Abstractions Assumptions Trust sws1 1 There are only two kinds of programming languages: the ones people complain about and the
Low level security. Andrew Ruef
 Low level security Andrew Ruef What s going on Stuff is getting hacked all the time We re writing tons of software Often with little regard to reliability let alone security The regulatory environment
Low level security Andrew Ruef What s going on Stuff is getting hacked all the time We re writing tons of software Often with little regard to reliability let alone security The regulatory environment
Structuring an Abstract Interpreter through Value and State Abstractions: EVA, an Evolved Value Analysis for Frama C
 Structuring an Abstract Interpreter through Value and State Abstractions: EVA, an Evolved Value Analysis for Frama C David Bühler CEA LIST, Software Safety Lab Frama-C & SPARK Day 2017 May 30th, 2017 David
Structuring an Abstract Interpreter through Value and State Abstractions: EVA, an Evolved Value Analysis for Frama C David Bühler CEA LIST, Software Safety Lab Frama-C & SPARK Day 2017 May 30th, 2017 David
Baggy bounds with LLVM
 Baggy bounds with LLVM Anton Anastasov Chirantan Ekbote Travis Hance 6.858 Project Final Report 1 Introduction Buffer overflows are a well-known security problem; a simple buffer-overflow bug can often
Baggy bounds with LLVM Anton Anastasov Chirantan Ekbote Travis Hance 6.858 Project Final Report 1 Introduction Buffer overflows are a well-known security problem; a simple buffer-overflow bug can often
Stack Overflow COMP620
 Stack Overflow COMP620 There are two kinds of people in America today: those who have experienced a foreign cyber attack and know it, and those who have experienced a foreign cyber attack and don t know
Stack Overflow COMP620 There are two kinds of people in America today: those who have experienced a foreign cyber attack and know it, and those who have experienced a foreign cyber attack and don t know
Heap, Variables, References, and Garbage. CS152. Chris Pollett. Oct. 13, 2008.
 Heap, Variables, References, and Garbage. CS152. Chris Pollett. Oct. 13, 2008. Outline. Dynamic Allocation. Variables and Constants. Aliases and Problems. Garbage. Introduction. On Wednesday, we were talking
Heap, Variables, References, and Garbage. CS152. Chris Pollett. Oct. 13, 2008. Outline. Dynamic Allocation. Variables and Constants. Aliases and Problems. Garbage. Introduction. On Wednesday, we were talking
ShieldGen: Automatic Data Patch Generation for Unknown Vulnerabilities with Informed Probing
 ShieldGen: Automatic Data Patch Generation for Unknown Vulnerabilities with Informed Probing Weidong Cui Marcus Peinado Helen J. Wang Microsoft Research One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052 {wdcui, marcuspe,
ShieldGen: Automatic Data Patch Generation for Unknown Vulnerabilities with Informed Probing Weidong Cui Marcus Peinado Helen J. Wang Microsoft Research One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052 {wdcui, marcuspe,
Computer Security Course. Midterm Review
 Computer Security Course. Dawn Song Midterm Review In class: Logistics On time: 4:10-5:30pm Wed 1 8x11 page cheat sheet allowed Special requirements: see TA Part I, II, III Scope Software Security Secure
Computer Security Course. Dawn Song Midterm Review In class: Logistics On time: 4:10-5:30pm Wed 1 8x11 page cheat sheet allowed Special requirements: see TA Part I, II, III Scope Software Security Secure
12 th January MWR InfoSecurity Security Advisory. WebSphere MQ xcsgetmem Heap Overflow Vulnerability. Contents
 Contents MWR InfoSecurity Security Advisory WebSphere MQ xcsgetmem Heap Overflow Vulnerability 12 th January 2009 2009-01-05 Page 1 of 9 Contents Contents 1 Detailed Vulnerability Description...5 1.1 Introduction...5
Contents MWR InfoSecurity Security Advisory WebSphere MQ xcsgetmem Heap Overflow Vulnerability 12 th January 2009 2009-01-05 Page 1 of 9 Contents Contents 1 Detailed Vulnerability Description...5 1.1 Introduction...5
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
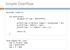 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Language Security. Lecture 40
 Language Security Lecture 40 (from notes by G. Necula) Prof. Hilfinger CS 164 Lecture 40 1 Lecture Outline Beyond compilers Looking at other issues in programming language design and tools C Arrays Exploiting
Language Security Lecture 40 (from notes by G. Necula) Prof. Hilfinger CS 164 Lecture 40 1 Lecture Outline Beyond compilers Looking at other issues in programming language design and tools C Arrays Exploiting
Polymorphic Blending Attacks. Slides by Jelena Mirkovic
 Polymorphic Blending Attacks Slides by Jelena Mirkovic 1 Motivation! Polymorphism is used by malicious code to evade signature-based IDSs Anomaly-based IDSs detect polymorphic attacks because their byte
Polymorphic Blending Attacks Slides by Jelena Mirkovic 1 Motivation! Polymorphism is used by malicious code to evade signature-based IDSs Anomaly-based IDSs detect polymorphic attacks because their byte
Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues
 Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
CS161 Midterm 1 Review
 CS161 Midterm 1 Review Midterm 1: March 4, 18:3020:00 Same room as lecture Security Analysis and Threat Model Basic security properties CIA Threat model A. We want perfect security B. Security is about
CS161 Midterm 1 Review Midterm 1: March 4, 18:3020:00 Same room as lecture Security Analysis and Threat Model Basic security properties CIA Threat model A. We want perfect security B. Security is about
Buffer overflow background
 and heap buffer background Comp Sci 3600 Security Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Address Space and heap buffer
and heap buffer background Comp Sci 3600 Security Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Outline and heap buffer Heap 1 and heap 2 3 buffer 4 5 Heap Address Space and heap buffer
CS527 Software Security
 Security Policies Purdue University, Spring 2018 Security Policies A policy is a deliberate system of principles to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent, and
Security Policies Purdue University, Spring 2018 Security Policies A policy is a deliberate system of principles to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent, and
Computer Security. Robust and secure programming in C. Marius Minea. 12 October 2017
 Computer Security Robust and secure programming in C Marius Minea marius@cs.upt.ro 12 October 2017 In this lecture Write correct code minimizing risks with proper error handling avoiding security pitfalls
Computer Security Robust and secure programming in C Marius Minea marius@cs.upt.ro 12 October 2017 In this lecture Write correct code minimizing risks with proper error handling avoiding security pitfalls
SentinelOne Technical Brief
 SentinelOne Technical Brief SentinelOne unifies prevention, detection and response in a fundamentally new approach to endpoint protection, driven by machine learning and intelligent automation. By rethinking
SentinelOne Technical Brief SentinelOne unifies prevention, detection and response in a fundamentally new approach to endpoint protection, driven by machine learning and intelligent automation. By rethinking
Towards automated detection of buffer overrun vulnerabilities: a first step. NDSS 2000 Feb 3, 2000
 Towards automated detection of buffer overrun vulnerabilities: a first step David Wagner Eric A. Brewer Jeffrey S. Foster Alexander Aiken NDSS 2000 Feb 3, 2000 1 Introduction The state of computer security
Towards automated detection of buffer overrun vulnerabilities: a first step David Wagner Eric A. Brewer Jeffrey S. Foster Alexander Aiken NDSS 2000 Feb 3, 2000 1 Introduction The state of computer security
