CSE123 Discussion. Oct 17th 2017
|
|
|
- Ira Caldwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE123 Discussion Oct 17th 2017
2 Today s Agenda Usage of CRC in project 1 Fragmentation for long messages Buffer/window Timeout handling Homework 2 discussion
3 Getting Started You can use any common CRC polynomials Create crc.h and crc.c. You ll need to implement: char get_bit (char byte, int pos); // return a char with a value of 0 or 1 depending on whether the bit in the pos is 0 or 1 char crc8 (char* array, int byte_len); // or crc16, crc32 etc. void append_crc (char* array, int array_len); // append crc remainder to the char array int is_corrupted (char* array, int array_len); // return 1 if a frame is corrupted, otherwise return 0
4 Steps for using CRC Sender: Construct the frame (header and payload) and set the CRC field to zero. Convert frame to char array by calling convert_frame_to_char() Insert the CRC in the correct position by calling append_crc(). append_crc() will call crc8() to compute the crc remainder. Send the resulting character array by appending to outgoing_frames_head_ptr. Receiver: Check for corruption by calling is_corrupted() function on the character array. If not corrupted, then convert the char array to frame and access the frame fields. Please note that CRC should be included in both data frames and acknowledgment frames. Even ACKs can get corrupted!
5 CRC 8 Computation // Function returns the remainder from a CRC calculation on a char* array of length byte_len char crc8(char* array, int array_len){ // The most significant bit of the polynomial can be discarded in the computation, because: // (1) it is always 1 // (2) it aligns with the next '1' of the dividend; the XOR result for this bit is always 0 char poly =0x07; // char crc = array[0]; int i, j; for(i = 1; i < array_len; i++){ char next_byte = ith byte of array; for(j = 7; j >= 0; j--){ // Start at most significant bit of next byte and work our way down if(crc s most significant bit is 0){ left shift crc by 1; crc = crc OR get_bit(next_byte, j); // get_bit(next_byte, j) returns the a bit in position j from next_byte else{ // crc s most significant bit is 1 left shift crc by 1; crc = crc OR get_bit(next_byte, j); crc = crc XOR poly; return crc;
6 Bitwise operators in C X AND Y -> X&Y X OR Y -> X Y X XOR Y -> X^Y NOT X -> ~X Shift X by Y bits to the left -> X<<Y Shift X by Y bits to the right -> X>>Y Bitwise operators have lower priority than comparison operators E.g. to see whether the most significant bit of a byte is 0 Wrong: if (byte & 0x80==0) Correct: if ((byte & 0x80)==0)
7 Fragmentation One way to implement fragmentation is to use the sender s input command list sender->input_cmd_list_head is a doubly linked list whose nodes are of type struct cmd (in common.h) Before popping off the head node from sender->input_cmd_list_head check if the message > payload_size. If yes, then split the head node into multiple nodes where each node contains a part of the message of length <= payload_size
8 Skeleton code for fragmentation void ll_split_head_if_necessary(llnode ** head_ptr, size_t cut_size){ //TODO: check if head is NULL LLnode* head = *head_ptr; Cmd* head_cmd = (Cmd*) head -> value; char* msg = head_cmd -> message; if(strlen(msg) < cut_size) { return; else{ size_t i; LLnode* curr, * next; Cmd* next_cmd; curr = head; for(i = cut_size; i < strlen(msg); i += cut_size) { // TODO: malloc next, next_cmd char* cmd_msg = (char*) malloc((cut_size + 1) * sizeof(char)); // One extra byte for NULL character memset(cmd_msg, 0, (cut_size + 1) * sizeof(char)); strncpy(cmd_msg, msg + i, cut_size); // TODO: flll the next_mcd // TODO: fill the next_nose and add it to the linked list msg[cut_size] = '\0';
9 Sender Buffer/Window We need to buffer the frames while sending them out. The window : struct sendq_slot { Event timeout; /* event associated with send -timeout */ Frame frame; sendq[sws]; How much timeout? Timeout is of type struct timeval (declared in sys/time.h)
10 struct timeval object in C struct timeval{ time_t tv_sec; //seconds suseconds_t tv_usec; // microseconds To calculate the timeout, get the current time and add 0.1s to it void calculate_timeout(struct timeval * timeout){ gettimeofday(timeout, NULL); timeout->tv_usec+=100000; If(timeout->tv_usec>= ){ timeout->tv_usec-= ; timeout->tv_sec+=1; You can use time_val_usecdiff() given in util.c to compute difference between two timeval objects.
11 Thanks!
CSE 123 Project 1. Discussion Session 3 - the finer details. Notes From Alexander
 CSE 123 Project 1 Discussion Session 3 - the finer details Notes From Alexander Agenda What to add in the structures? What is the Frame Format? Wrap Around How to Handle Big Messages What to do with messages
CSE 123 Project 1 Discussion Session 3 - the finer details Notes From Alexander Agenda What to add in the structures? What is the Frame Format? Wrap Around How to Handle Big Messages What to do with messages
Odds and Ends. Data and File Structures Laboratory. DFS Lab (ISI) Odds and Ends 1 / 8
 Odds and Ends Data and File Structures Laboratory http://www.isical.ac.in/~dfslab/2017/index.html DFS Lab (ISI) Odds and Ends 1 / 8 Topics 1. Generic functions (e.g., swap) 2. Function activation records;
Odds and Ends Data and File Structures Laboratory http://www.isical.ac.in/~dfslab/2017/index.html DFS Lab (ISI) Odds and Ends 1 / 8 Topics 1. Generic functions (e.g., swap) 2. Function activation records;
C Structures in Practice
 CS 2060 Use of C Structures in Unix/Linux To further illustrate C structures, we will review some uses of struct in system calls. Here is a function from BSD to get the current time (found in sys/time.h):
CS 2060 Use of C Structures in Unix/Linux To further illustrate C structures, we will review some uses of struct in system calls. Here is a function from BSD to get the current time (found in sys/time.h):
UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer:
 UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer: Data Link Layer Design Issues: The data link layer has a number of specific functions it can carry out. These functions include 1. Providing
UNIT-II 1. Discuss the issues in the data link layer. Answer: Data Link Layer Design Issues: The data link layer has a number of specific functions it can carry out. These functions include 1. Providing
Linked lists, stacks, queues
 Linked lists, stacks, queues Data and File Structures Laboratory Data and File Structures Laboratory Linked lists, stacks, queues 1 / 9 Preliminaries: measuring time Motivation: to measure the amount of
Linked lists, stacks, queues Data and File Structures Laboratory Data and File Structures Laboratory Linked lists, stacks, queues 1 / 9 Preliminaries: measuring time Motivation: to measure the amount of
CSE 123: Computer Networks
 Student Name: PID: UCSD email: CSE 123: Computer Networks Homework 1 Solution (Due 10/12 in class) Total Points: 30 Instructions: Turn in a physical copy at the beginning of the class on 10/10. Problems:
Student Name: PID: UCSD email: CSE 123: Computer Networks Homework 1 Solution (Due 10/12 in class) Total Points: 30 Instructions: Turn in a physical copy at the beginning of the class on 10/10. Problems:
CS4514 HELP Session 2 Simulation of Datalink Layer Communication
 CS4514 HELP Session 2 Simulation of Datalink Layer Communication Speaker: Jae Chung Description! You are supposed to implement a Positive Acknowledgement with Retransmission (PAR) protocol on top of an
CS4514 HELP Session 2 Simulation of Datalink Layer Communication Speaker: Jae Chung Description! You are supposed to implement a Positive Acknowledgement with Retransmission (PAR) protocol on top of an
CS 640 Introduction to Computer Networks. Role of data link layer. Today s lecture. Lecture16
 Introduction to Computer Networks Lecture16 Role of data link layer Service offered by layer 1: a stream of bits Service to layer 3: sending & receiving frames To achieve this layer 2 does Framing Error
Introduction to Computer Networks Lecture16 Role of data link layer Service offered by layer 1: a stream of bits Service to layer 3: sending & receiving frames To achieve this layer 2 does Framing Error
Point-to-Point Links. Outline Encoding Framing Error Detection Sliding Window Algorithm. Fall 2004 CS 691 1
 Point-to-Point Links Outline Encoding Framing Error Detection Sliding Window Algorithm Fall 2004 CS 691 1 Encoding Signals propagate over a physical medium modulate electromagnetic waves e.g., vary voltage
Point-to-Point Links Outline Encoding Framing Error Detection Sliding Window Algorithm Fall 2004 CS 691 1 Encoding Signals propagate over a physical medium modulate electromagnetic waves e.g., vary voltage
Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08
 Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08 For your solutions you should submit a hard copy; either hand written pages stapled together or a print out of a typeset document
Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08 For your solutions you should submit a hard copy; either hand written pages stapled together or a print out of a typeset document
Any of the descriptors in the set {1, 4} have an exception condition pending
 Page 1 of 6 6.3 select Function This function allows the process to instruct the kernel to wait for any one of multiple events to occur and to wake up the process only when one or more of these events
Page 1 of 6 6.3 select Function This function allows the process to instruct the kernel to wait for any one of multiple events to occur and to wake up the process only when one or more of these events
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Exam 1 Review. 1
 CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Exam 1 Review http://class.ece.iastate.edu/cpre288 1 Overview of Today s Lecture Announcements Exam 1 Review http://class.ece.iastate.edu/cpre288 2 Announcements
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Exam 1 Review http://class.ece.iastate.edu/cpre288 1 Overview of Today s Lecture Announcements Exam 1 Review http://class.ece.iastate.edu/cpre288 2 Announcements
I/O Models. Kartik Gopalan
 I/O Models Kartik Gopalan Types of Concurrency True Concurrency (multiple processes or threads) Multi-processor machines Child processes/threads execute in parallel. Multi-process (forking) servers If
I/O Models Kartik Gopalan Types of Concurrency True Concurrency (multiple processes or threads) Multi-processor machines Child processes/threads execute in parallel. Multi-process (forking) servers If
dmrlib Documentation Release Wijnand Modderman-Lenstra
 dmrlib Documentation Release 0.99.3 Wijnand Modderman-Lenstra September 03, 2016 Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Documentation 3 2.1 bits: bit and byte manipulation...................................... 3 2.2
dmrlib Documentation Release 0.99.3 Wijnand Modderman-Lenstra September 03, 2016 Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Documentation 3 2.1 bits: bit and byte manipulation...................................... 3 2.2
EE 122: Error detection and reliable transmission. Ion Stoica September 16, 2002
 EE 22: Error detection and reliable transmission Ion Stoica September 6, 2002 High Level View Goal: transmit correct information Problem: bits can get corrupted - Electrical interference, thermal noise
EE 22: Error detection and reliable transmission Ion Stoica September 6, 2002 High Level View Goal: transmit correct information Problem: bits can get corrupted - Electrical interference, thermal noise
Recitation #11 Malloc Lab. November 7th, 2017
 18-600 Recitation #11 Malloc Lab November 7th, 2017 1 2 Important Notes about Malloc Lab Malloc lab has been updated from previous years Supports a full 64 bit address space rather than 32 bit Encourages
18-600 Recitation #11 Malloc Lab November 7th, 2017 1 2 Important Notes about Malloc Lab Malloc lab has been updated from previous years Supports a full 64 bit address space rather than 32 bit Encourages
CS4514 Project 2 Help Session (B07) Feng Li Nov 8, 2007
 CS4514 Project 2 Help Session (B07) Feng Li Nov 8, 2007 1 Description The goal is to implement a Positive Acknowledgement with Retransmission (PAR) protocol on top of an emulated physical layer. The receiver
CS4514 Project 2 Help Session (B07) Feng Li Nov 8, 2007 1 Description The goal is to implement a Positive Acknowledgement with Retransmission (PAR) protocol on top of an emulated physical layer. The receiver
SpiNNaker Application Programming Interface (API)
 SpiNNaker Application Programming Interface (API) Version 2.0.0 10 March 2016 Application programming interface (API) Event-driven programming model The SpiNNaker API programming model is a simple, event-driven
SpiNNaker Application Programming Interface (API) Version 2.0.0 10 March 2016 Application programming interface (API) Event-driven programming model The SpiNNaker API programming model is a simple, event-driven
Algorithms, Data Structures, and Problem Solving
 Algorithms, Data Structures, and Problem Solving Masoumeh Taromirad Hamlstad University DT4002, Fall 2016 Container Concepts containers store data container operations: insertion retrieval removal iteration
Algorithms, Data Structures, and Problem Solving Masoumeh Taromirad Hamlstad University DT4002, Fall 2016 Container Concepts containers store data container operations: insertion retrieval removal iteration
file:///c:/users/hpguo/dropbox/website/teaching/fall 2017/CS4470/H...
 1 of 9 11/26/2017, 11:28 AM Homework 3 solutions 1. A window holds bytes 2001 to 5000. The next byte to be sent is 3001. Draw a figure to show the situation of the window after the following two events:
1 of 9 11/26/2017, 11:28 AM Homework 3 solutions 1. A window holds bytes 2001 to 5000. The next byte to be sent is 3001. Draw a figure to show the situation of the window after the following two events:
Lecture 17 Bit Operations
 Lecture 17 Bit Operations In this lecture Background Left Shifting Negative Numbers, one s complement and two s complement Right Shifting Bit Operators Masking the Bits Getting the Bits Setting the Bits
Lecture 17 Bit Operations In this lecture Background Left Shifting Negative Numbers, one s complement and two s complement Right Shifting Bit Operators Masking the Bits Getting the Bits Setting the Bits
CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren. HW 1 due Thursday!
 CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 1 due Thursday! Error handling through redundancy Adding extra bits to the frame Hamming Distance When we can detect When we can correct Checksum Cyclic Remainder
CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 1 due Thursday! Error handling through redundancy Adding extra bits to the frame Hamming Distance When we can detect When we can correct Checksum Cyclic Remainder
Project 1. 1 Introduction. October 4, Spec version: 0.1 Due Date: Friday, November 1st, General Instructions
 Project 1 October 4, 2013 Spec version: 0.1 Due Date: Friday, November 1st, 2013 1 Introduction The sliding window protocol (SWP) is one of the most well-known algorithms in computer networking. SWP is
Project 1 October 4, 2013 Spec version: 0.1 Due Date: Friday, November 1st, 2013 1 Introduction The sliding window protocol (SWP) is one of the most well-known algorithms in computer networking. SWP is
These problems are provided to you as a guide for practice. The questions cover important concepts covered in class.
 Midterm Written Exam Practice Midterm will cover all concepts covered up to the midterm exam. Concepts of arrays, LL s, pointers (*,**,***), malloc, calloc, realloc, function pointers, Hash tables will
Midterm Written Exam Practice Midterm will cover all concepts covered up to the midterm exam. Concepts of arrays, LL s, pointers (*,**,***), malloc, calloc, realloc, function pointers, Hash tables will
Inst: Chris Davison
 ICS 153 Introduction to Computer Networks Inst: Chris Davison cbdaviso@uci.edu ICS 153 Data Link Layer Contents Simplex and Duplex Communication Frame Creation Flow Control Error Control Performance of
ICS 153 Introduction to Computer Networks Inst: Chris Davison cbdaviso@uci.edu ICS 153 Data Link Layer Contents Simplex and Duplex Communication Frame Creation Flow Control Error Control Performance of
Data Link Protocols. High Level Data. Control Protocol. HDLC Framing ~~~~~~~~ Functions of a Data Link Protocol. Framing PDUs. Addressing Destination
 Data Link Protocols Data Link Services Connection-less services Functions of a Data Link Protocol Framing PDUs ing Destination Error Detection / Error Recovery Link Management Ethernet (covered elsewhere)
Data Link Protocols Data Link Services Connection-less services Functions of a Data Link Protocol Framing PDUs ing Destination Error Detection / Error Recovery Link Management Ethernet (covered elsewhere)
CS61 Section Notes. Section 5 (Fall 2011) Topics to be covered Common Memory Errors Dynamic Memory Allocation Assignment 3: Malloc
 CS61 Section Notes Section 5 (Fall 2011) Topics to be covered Common Memory Errors Dynamic Memory Allocation Assignment 3: Malloc Common Memory Errors In lecture, we learned about several errors programmers
CS61 Section Notes Section 5 (Fall 2011) Topics to be covered Common Memory Errors Dynamic Memory Allocation Assignment 3: Malloc Common Memory Errors In lecture, we learned about several errors programmers
Lab 1 - Reliable Data Transport Protocol
 Lab 1 - Reliable Data Transport Protocol Handout: March 8, 2018 Deadline: March 18 23:00, 2018 (No extension) Assignment overview: In this assignment, you will be implementing the sending and receiving
Lab 1 - Reliable Data Transport Protocol Handout: March 8, 2018 Deadline: March 18 23:00, 2018 (No extension) Assignment overview: In this assignment, you will be implementing the sending and receiving
Systems Programming/ C and UNIX
 Systems Programming/ C and UNIX A. Fischer CSCI 4547/6647 What is Time? November 6, 2017 A. Fischer CSCI 4547/6647[1ex]What is Time? Systems Programming Lecture 8... 1/24 November 6, 2017 1 / 24 Outline
Systems Programming/ C and UNIX A. Fischer CSCI 4547/6647 What is Time? November 6, 2017 A. Fischer CSCI 4547/6647[1ex]What is Time? Systems Programming Lecture 8... 1/24 November 6, 2017 1 / 24 Outline
Fundamental Data Types. CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University
 Fundamental Data Types CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University Program Organization in C The C System C consists of several parts: The C language The preprocessor The compiler
Fundamental Data Types CSE 130: Introduction to Programming in C Stony Brook University Program Organization in C The C System C consists of several parts: The C language The preprocessor The compiler
2.4 Error Detection Bit errors in a frame will occur. How do we detect (and then. (or both) frames contains an error. This is inefficient (and not
 CS475 Networks Lecture 5 Chapter 2: Direct Link Networks Assignments Reading for Lecture 6: Sections 2.6 2.8 Homework 2: 2.1, 2.4, 2.6, 2.14, 2.18, 2.31, 2.35. Due Thursday, Sept. 15 2.4 Error Detection
CS475 Networks Lecture 5 Chapter 2: Direct Link Networks Assignments Reading for Lecture 6: Sections 2.6 2.8 Homework 2: 2.1, 2.4, 2.6, 2.14, 2.18, 2.31, 2.35. Due Thursday, Sept. 15 2.4 Error Detection
Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis
 Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis Host Based Attacks Pavel Laskov Wilhelm Schickard Institute for Computer Science Software security threats Modification of program code viruses and self-replicating
Intrusion Detection and Malware Analysis Host Based Attacks Pavel Laskov Wilhelm Schickard Institute for Computer Science Software security threats Modification of program code viruses and self-replicating
Introduction to Computer Systems /18 243, fall th Lecture, Oct. 22 th
 Introduction to Computer Systems 15 213/18 243, fall 2009 16 th Lecture, Oct. 22 th Instructors: Gregory Kesden and Markus Püschel Today Dynamic memory allocation Process Memory Image %esp kernel virtual
Introduction to Computer Systems 15 213/18 243, fall 2009 16 th Lecture, Oct. 22 th Instructors: Gregory Kesden and Markus Püschel Today Dynamic memory allocation Process Memory Image %esp kernel virtual
Lecture 5. Homework 2 posted, due September 15. Reminder: Homework 1 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 8 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 5 1
 Lecture 5 Homework 2 posted, due September 15. Reminder: Homework 1 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 8 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 5 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
Lecture 5 Homework 2 posted, due September 15. Reminder: Homework 1 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 8 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 5 1 Outline Chapter 2 - Getting Connected 2.1 Perspectives on Connecting
CS242: Object-Oriented Design and Programming
 CS242: Object-Oriented Design and Programming Program Assignment 5 Part 1 (Linked List Timer Queue) Due Tuesday, March 18 th ; 1997 Part 2 (Heap Timer Queue) Due Tuesday, April 1 st ; 1997) A Timer Queue
CS242: Object-Oriented Design and Programming Program Assignment 5 Part 1 (Linked List Timer Queue) Due Tuesday, March 18 th ; 1997 Part 2 (Heap Timer Queue) Due Tuesday, April 1 st ; 1997) A Timer Queue
In Java we have the keyword null, which is the value of an uninitialized reference type
 + More on Pointers + Null pointers In Java we have the keyword null, which is the value of an uninitialized reference type In C we sometimes use NULL, but its just a macro for the integer 0 Pointers are
+ More on Pointers + Null pointers In Java we have the keyword null, which is the value of an uninitialized reference type In C we sometimes use NULL, but its just a macro for the integer 0 Pointers are
CSC209H Lecture 10. Dan Zingaro. March 18, 2015
 CSC209H Lecture 10 Dan Zingaro March 18, 2015 Creating a Client To create a client that can connect to a server, call the following, in order: socket: create a communication endpoint This is the same as
CSC209H Lecture 10 Dan Zingaro March 18, 2015 Creating a Client To create a client that can connect to a server, call the following, in order: socket: create a communication endpoint This is the same as
Telematics. 5rd Tutorial - LLC vs. MAC, HDLC, Flow Control, E2E-Arguments
 19540 - Telematics 5rd Tutorial - LLC vs. MAC, HDLC, Flow Control, E2E-Arguments Matthias Wa hlisch Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Institute of Computer Science 19. November, 2009 Institute
19540 - Telematics 5rd Tutorial - LLC vs. MAC, HDLC, Flow Control, E2E-Arguments Matthias Wa hlisch Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Institute of Computer Science 19. November, 2009 Institute
Homework Assignment #2
 Rohit Kabadi Professor Varghese CSE 123 6 May 2010 Homework Assignment #2 1. HDLC Framing a. If we change the stuffing rule to stuff a zero after six consecutive ones, the framing rules will NOT work.
Rohit Kabadi Professor Varghese CSE 123 6 May 2010 Homework Assignment #2 1. HDLC Framing a. If we change the stuffing rule to stuff a zero after six consecutive ones, the framing rules will NOT work.
High Level View. EE 122: Error detection and reliable transmission. Overview. Error Detection
 High Level View EE 22: Error detection and reliable transmission Ion Stoica September 6, 22 Goal: transmit correct information Problem: bits can get corrupted - Electrical interference, thermal noise Solution
High Level View EE 22: Error detection and reliable transmission Ion Stoica September 6, 22 Goal: transmit correct information Problem: bits can get corrupted - Electrical interference, thermal noise Solution
EL2310 Scientific Programming
 Lecture 11: Memory, Files and Bitoperations (yaseminb@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 11: Memory, Files and Bit operations Main function; reading and writing Bitwise Operations Lecture 11: Memory, Files
Lecture 11: Memory, Files and Bitoperations (yaseminb@kth.se) Overview Overview Lecture 11: Memory, Files and Bit operations Main function; reading and writing Bitwise Operations Lecture 11: Memory, Files
Princeton University. Computer Science 217: Introduction to Programming Systems. Dynamic Memory Management
 Princeton University Computer Science 217: Introduction to Programming Systems Dynamic Memory Management 1 Agenda The need for DMM DMM using the heap section DMMgr 1: Minimal implementation DMMgr 2: Pad
Princeton University Computer Science 217: Introduction to Programming Systems Dynamic Memory Management 1 Agenda The need for DMM DMM using the heap section DMMgr 1: Minimal implementation DMMgr 2: Pad
Data Link Layer. Srinidhi Varadarajan
 Data Link Layer Srinidhi Varadarajan Data Link Layer: Functionality The data link layer must: Detect errors (using redundancy bits) Request retransmission if data is lost (using automatic repeat request
Data Link Layer Srinidhi Varadarajan Data Link Layer: Functionality The data link layer must: Detect errors (using redundancy bits) Request retransmission if data is lost (using automatic repeat request
Advanced Computer Networks. Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS. Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Advanced Computer Networks Department of Computer Science DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Rab Nawaz Jadoon Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan Advanced Computer Networks
Advanced Computer Networks Department of Computer Science DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Rab Nawaz Jadoon Assistant Professor COMSATS University, Lahore Pakistan Advanced Computer Networks
Malloc Lab & Midterm Solutions. Recitation 11: Tuesday: 11/08/2016
 Malloc Lab & Midterm Solutions Recitation 11: Tuesday: 11/08/2016 Malloc 2 Important Notes about Malloc Lab Malloc lab has been updated from previous years Supports a full 64 bit address space rather than
Malloc Lab & Midterm Solutions Recitation 11: Tuesday: 11/08/2016 Malloc 2 Important Notes about Malloc Lab Malloc lab has been updated from previous years Supports a full 64 bit address space rather than
Dynamic Memory Allocation
 Dynamic Memory Allocation CS61, Lecture 11 Prof. Stephen Chong October 6, 2011 Announcements 1/2 Reminder: No section on Monday Monday sections have been rescheduled See website for details Please attend
Dynamic Memory Allocation CS61, Lecture 11 Prof. Stephen Chong October 6, 2011 Announcements 1/2 Reminder: No section on Monday Monday sections have been rescheduled See website for details Please attend
File Descriptors and Piping
 File Descriptors and Piping CSC209: Software Tools and Systems Programming Furkan Alaca & Paul Vrbik University of Toronto Mississauga https://mcs.utm.utoronto.ca/~209/ Week 8 Today s topics File Descriptors
File Descriptors and Piping CSC209: Software Tools and Systems Programming Furkan Alaca & Paul Vrbik University of Toronto Mississauga https://mcs.utm.utoronto.ca/~209/ Week 8 Today s topics File Descriptors
Linux Device Drivers Interrupt Requests
 Overview 1 2 3 Installation of an interrupt handler Interface /proc 4 5 6 7 primitive devices can be managed only with I/O regions, most devices require a more complicated approach, devices cooperate with
Overview 1 2 3 Installation of an interrupt handler Interface /proc 4 5 6 7 primitive devices can be managed only with I/O regions, most devices require a more complicated approach, devices cooperate with
Computer Organization & Systems Exam I Example Questions
 Computer Organization & Systems Exam I Example Questions 1. Pointer Question. Write a function char *circle(char *str) that receives a character pointer (which points to an array that is in standard C
Computer Organization & Systems Exam I Example Questions 1. Pointer Question. Write a function char *circle(char *str) that receives a character pointer (which points to an array that is in standard C
Fall 2018 Discussion 2: September 3, 2018
 CS 61C C Basics Fall 2018 Discussion 2: September 3, 2018 1 C C is syntactically similar to Java, but there are a few key differences: 1. C is function-oriented, not object-oriented; there are no objects.
CS 61C C Basics Fall 2018 Discussion 2: September 3, 2018 1 C C is syntactically similar to Java, but there are a few key differences: 1. C is function-oriented, not object-oriented; there are no objects.
11 'e' 'x' 'e' 'm' 'p' 'l' 'i' 'f' 'i' 'e' 'd' bool equal(const unsigned char pstr[], const char *cstr) {
![11 'e' 'x' 'e' 'm' 'p' 'l' 'i' 'f' 'i' 'e' 'd' bool equal(const unsigned char pstr[], const char *cstr) { 11 'e' 'x' 'e' 'm' 'p' 'l' 'i' 'f' 'i' 'e' 'd' bool equal(const unsigned char pstr[], const char *cstr) {](/thumbs/91/107167676.jpg) This document contains the questions and solutions to the CS107 midterm given in Spring 2016 by instructors Julie Zelenski and Michael Chang. This was an 80-minute exam. Midterm questions Problem 1: C-strings
This document contains the questions and solutions to the CS107 midterm given in Spring 2016 by instructors Julie Zelenski and Michael Chang. This was an 80-minute exam. Midterm questions Problem 1: C-strings
serverbase.txt (1) Server Client1 (3) (2) Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB.
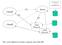 serverbase.txt Client1 (3) (1) (2) Server Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB. Client APP Layer Server APP Layer NW Layer NW Layer DLL DLL PHL
serverbase.txt Client1 (3) (1) (2) Server Client2 Child Process1 Child Process2 Note: each child process keeps a separate copy of the DB. Client APP Layer Server APP Layer NW Layer NW Layer DLL DLL PHL
CPE 448/548 Exam #1 (100 pts) February 14, Name Class: 448
 Name Class: 448 1) (14 pts) A message M = 11001 is transmitted from node A to node B using the CRC code. The CRC generator polynomial is G(x) = x 3 + x 2 + 1 ( bit sequence 1101) a) What is the transmitted
Name Class: 448 1) (14 pts) A message M = 11001 is transmitted from node A to node B using the CRC code. The CRC generator polynomial is G(x) = x 3 + x 2 + 1 ( bit sequence 1101) a) What is the transmitted
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 8: Dynamically Allocated Linked Lists 2017-2018 Fall int x; x = 8; int A[4]; An array is stored as one contiguous block of memory. How can we add a fifth element to the
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 8: Dynamically Allocated Linked Lists 2017-2018 Fall int x; x = 8; int A[4]; An array is stored as one contiguous block of memory. How can we add a fifth element to the
Ashish Gupta, Data JUET, Guna
 Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma studies Unit 4
 Pointer A pointer is a variable that contains address or location of another variable. Pointer is a derived data type in C. Pointers contain memory address as their values, so they can also be used to
Pointer A pointer is a variable that contains address or location of another variable. Pointer is a derived data type in C. Pointers contain memory address as their values, so they can also be used to
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data
 Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Lecture 3: Pointers. Bernhard Boser & Randy Katz
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 3: Pointers Bernhard Boser & Randy Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c Agenda Pointers in C Arrays in C This is not on the test Pointer arithmetic
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 3: Pointers Bernhard Boser & Randy Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c Agenda Pointers in C Arrays in C This is not on the test Pointer arithmetic
Overview of Time Related Data Structures and Functions in Unix/C. It s About Time
 Overview of Time Related Data Structures and Functions in Unix/C It s About Time 1. time_t Same as an unsigned long. Time in seconds since Midnight GMT Jan 1, 1970. a. char * ctime(time_t x) will return
Overview of Time Related Data Structures and Functions in Unix/C It s About Time 1. time_t Same as an unsigned long. Time in seconds since Midnight GMT Jan 1, 1970. a. char * ctime(time_t x) will return
Integers. Today. Next time. ! Numeric Encodings! Programming Implications! Basic operations. ! Floats
 Integers Today! Numeric Encodings! Programming Implications! Basic operations! Programming Implications Next time! Floats Fabián E. Bustamante, 2007 Integers in C! C supports several integral data types
Integers Today! Numeric Encodings! Programming Implications! Basic operations! Programming Implications Next time! Floats Fabián E. Bustamante, 2007 Integers in C! C supports several integral data types
Introduction to C: Pointers
 Introduction to C: Pointers Nils Moschüring PhD Student (LMU) Nils Moschüring PhD Student (LMU), Introduction to C: Pointers 1 1 Introduction 2 Pointers Basics Useful: Function
Introduction to C: Pointers Nils Moschüring PhD Student (LMU) Nils Moschüring PhD Student (LMU), Introduction to C: Pointers 1 1 Introduction 2 Pointers Basics Useful: Function
1d: tests knowing about bitwise fields and union/struct differences.
 Question 1 1a: char ptr[] = Hello World ; char a = ptr[1], b = *(ptr+6); Creates an array of 12 elements, 11 visible letters and a character value 0 at the end. i true ii true iii false iv false v true
Question 1 1a: char ptr[] = Hello World ; char a = ptr[1], b = *(ptr+6); Creates an array of 12 elements, 11 visible letters and a character value 0 at the end. i true ii true iii false iv false v true
A Quick Introduction to C Programming
 A Quick Introduction to C Programming 1 C Syntax and Hello World What do the < > mean? #include inserts another file..h files are called header files. They contain stuff needed to interface to libraries
A Quick Introduction to C Programming 1 C Syntax and Hello World What do the < > mean? #include inserts another file..h files are called header files. They contain stuff needed to interface to libraries
CS 33. Storage Allocation. CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XXVII 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved.
 CS 33 Storage Allocation CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XXVII 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. The Unix Address Space stack dynamic bss program break data text CS33 Intro to Computer
CS 33 Storage Allocation CS33 Intro to Computer Systems XXVII 1 Copyright 2017 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. The Unix Address Space stack dynamic bss program break data text CS33 Intro to Computer
MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology. Unit 5.1
 MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology Unit 5.1 Review: automatic vs. static variables Variables declared and passed to functions are automatic variables. As soon as you leave the function,
MPATE-GE 2618: C Programming for Music Technology Unit 5.1 Review: automatic vs. static variables Variables declared and passed to functions are automatic variables. As soon as you leave the function,
CS61C Machine Structures. Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays. 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek. www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/
 CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L04 C Pointers (1) Common C Error There is a difference
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 4 C Pointers and Arrays 1/25/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L04 C Pointers (1) Common C Error There is a difference
A Shotgun Introduction to C
 A Shotgun Introduction to C Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Fall 2011 C History Developed between 1969 and 1973 along with Unix Due mostly to Dennis Ritchie Designed for systems programming Operating
A Shotgun Introduction to C Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Fall 2011 C History Developed between 1969 and 1973 along with Unix Due mostly to Dennis Ritchie Designed for systems programming Operating
No book chapter for this topic! Slides are posted online as usual Homework: Will be posted online Due 12/6
 Announcements No book chapter for this topic! Slides are posted online as usual Homework: Will be posted online Due 12/6 Copyright c 2002 2017 UMaine School of Computing and Information S 1 / 33 COS 140:
Announcements No book chapter for this topic! Slides are posted online as usual Homework: Will be posted online Due 12/6 Copyright c 2002 2017 UMaine School of Computing and Information S 1 / 33 COS 140:
Announcements. No book chapter for this topic! Slides are posted online as usual Homework: Will be posted online Due 12/6
 Announcements No book chapter for this topic! Slides are posted online as usual Homework: Will be posted online Due 12/6 Copyright c 2002 2017 UMaine Computer Science Department 1 / 33 1 COS 140: Foundations
Announcements No book chapter for this topic! Slides are posted online as usual Homework: Will be posted online Due 12/6 Copyright c 2002 2017 UMaine Computer Science Department 1 / 33 1 COS 140: Foundations
Operating System Labs. Yuanbin Wu
 Operating System Labs Yuanbin Wu CS@ECNU Operating System Labs Project 2 Due 21:00, Oct. 24 Project 3 Group of 3 If you can not find a partner, drop us an email You now have 3 late days, but start early!
Operating System Labs Yuanbin Wu CS@ECNU Operating System Labs Project 2 Due 21:00, Oct. 24 Project 3 Group of 3 If you can not find a partner, drop us an email You now have 3 late days, but start early!
Programming refresher and intro to C programming
 Applied mechatronics Programming refresher and intro to C programming Sven Gestegård Robertz sven.robertz@cs.lth.se Department of Computer Science, Lund University 2018 Outline 1 C programming intro 2
Applied mechatronics Programming refresher and intro to C programming Sven Gestegård Robertz sven.robertz@cs.lth.se Department of Computer Science, Lund University 2018 Outline 1 C programming intro 2
Lists (Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues
 (Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues By: Pramod Parajuli, Department of Computer Science, St. Xavier
(Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues By: Pramod Parajuli, Department of Computer Science, St. Xavier
ECE 2400 Computer Systems Programming Fall 2018 Topic 6: C Dynamic Allocation
 ECE 2400 Computer Systems Programming Fall 2018 Topic 6: C Dynamic Allocation School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2018-10-11-00-22 1 Bookcase Analogy 2 2 Using malloc
ECE 2400 Computer Systems Programming Fall 2018 Topic 6: C Dynamic Allocation School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2018-10-11-00-22 1 Bookcase Analogy 2 2 Using malloc
Solution for Data Structure
 Solution for Data Structure May 2016 INDEX Q1 a 2-3 b 4 c. 4-6 d 7 Q2- a 8-12 b 12-14 Q3 a 15-18 b 18-22 Q4- a 22-35 B..N.A Q5 a 36-38 b N.A Q6- a 39-42 b 43 1 www.brainheaters.in Q1) Ans: (a) Define ADT
Solution for Data Structure May 2016 INDEX Q1 a 2-3 b 4 c. 4-6 d 7 Q2- a 8-12 b 12-14 Q3 a 15-18 b 18-22 Q4- a 22-35 B..N.A Q5 a 36-38 b N.A Q6- a 39-42 b 43 1 www.brainheaters.in Q1) Ans: (a) Define ADT
COMPUTER NETWORK. Homework #2. Due Date: April 12, 2017 in class
 Computer Network Homework#2 COMPUTER NETWORK Homework #2 Due Date: April 12, 2017 in class Question 1 Suppose a process in Host C has a UDP socket with port number 6789. Suppose both Host A and Host B
Computer Network Homework#2 COMPUTER NETWORK Homework #2 Due Date: April 12, 2017 in class Question 1 Suppose a process in Host C has a UDP socket with port number 6789. Suppose both Host A and Host B
Information Science 1
 Information Science 1 Simple Calcula,ons Week 09 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Topics covered l Terms and concepts from Week 8 l Simple calculations Documenting
Information Science 1 Simple Calcula,ons Week 09 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Topics covered l Terms and concepts from Week 8 l Simple calculations Documenting
Algorithm Analysis CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang
 Algorithm Analysis CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Last class Review some algorithms learned in previous classes idea => pseudocode => implementation Correctness? Three sorting algorithms:
Algorithm Analysis CISC4080 CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Last class Review some algorithms learned in previous classes idea => pseudocode => implementation Correctness? Three sorting algorithms:
CSC 1600 Memory Layout for Unix Processes"
 CSC 16 Memory Layout for Unix Processes" 1 Lecture Goals" Behind the scenes of running a program" Code, executable, and process" Memory layout for UNIX processes, and relationship to C" : code and constant
CSC 16 Memory Layout for Unix Processes" 1 Lecture Goals" Behind the scenes of running a program" Code, executable, and process" Memory layout for UNIX processes, and relationship to C" : code and constant
Data Link Control. Surasak Sanguanpong Last updated: 11 July 2000
 1/14 Data Link Control Surasak Sanguanpong nguan@ku.ac.th http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~nguan Last updated: 11 July 2000 Flow Control 2/14 technique for controlling the data transmission so that s have sufficient
1/14 Data Link Control Surasak Sanguanpong nguan@ku.ac.th http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~nguan Last updated: 11 July 2000 Flow Control 2/14 technique for controlling the data transmission so that s have sufficient
UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Final Exam
 Full Name: Student ID #: UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Final Exam March 20, 2013 2:30pm - 4:20pm Instructions: Write your full name and UW student ID number on the front of the exam. When the exam begins, make
Full Name: Student ID #: UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Final Exam March 20, 2013 2:30pm - 4:20pm Instructions: Write your full name and UW student ID number on the front of the exam. When the exam begins, make
CS61, Fall 2012 Section 2 Notes
 CS61, Fall 2012 Section 2 Notes (Week of 9/24-9/28) 0. Get source code for section [optional] 1: Variable Duration 2: Memory Errors Common Errors with memory and pointers Valgrind + GDB Common Memory Errors
CS61, Fall 2012 Section 2 Notes (Week of 9/24-9/28) 0. Get source code for section [optional] 1: Variable Duration 2: Memory Errors Common Errors with memory and pointers Valgrind + GDB Common Memory Errors
Lab # 4. Files & Queues in C
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 4010: Lab # 4 Files & Queues in C Eng. Haneen El-Masry October, 2013 2 FILE * Files in C For C File I/O you need
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 4010: Lab # 4 Files & Queues in C Eng. Haneen El-Masry October, 2013 2 FILE * Files in C For C File I/O you need
Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing
 Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing Στοεργαστήριοθαμελετηθούν: Server High Level View I/O Multiplexing Solutions for Concurrency nonblocking I/O Use alarm and signal handler to interrupt slow system calls. Use
Εργαστήριο 9 I/O Multiplexing Στοεργαστήριοθαμελετηθούν: Server High Level View I/O Multiplexing Solutions for Concurrency nonblocking I/O Use alarm and signal handler to interrupt slow system calls. Use
Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators. JAVA Standard Edition
 Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators JAVA Standard Edition Java - Basic Operators Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables.
Basic operators, Arithmetic, Relational, Bitwise, Logical, Assignment, Conditional operators JAVA Standard Edition Java - Basic Operators Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables.
CS-211 Fall 2017 Test 2 Version A November 29, Name:
 CS-211 Fall 2017 Test 2 Version A November 29, 2017 True/False Questions... Name: 1. (10 points) For the following, Check T if the statement is true, the F if the statement is false. (a) T F : The control
CS-211 Fall 2017 Test 2 Version A November 29, 2017 True/False Questions... Name: 1. (10 points) For the following, Check T if the statement is true, the F if the statement is false. (a) T F : The control
Lecture Notes CPSC 122 (Fall 2014) Today Quiz 7 Doubly Linked Lists (Unsorted) List ADT Assignments Program 8 and Reading 6 out S.
 Today Quiz 7 Doubly Linked Lists (Unsorted) List ADT Assignments Program 8 and Reading 6 out S. Bowers 1 of 11 Doubly Linked Lists Each node has both a next and a prev pointer head \ v1 v2 v3 \ tail struct
Today Quiz 7 Doubly Linked Lists (Unsorted) List ADT Assignments Program 8 and Reading 6 out S. Bowers 1 of 11 Doubly Linked Lists Each node has both a next and a prev pointer head \ v1 v2 v3 \ tail struct
CSE 123: Computer Networks
 CSE 123: Computer Networks Homework 1 Solutions Total points = 44 Problems 1. Modified HDLC Framing [6 points] Assume we are following the protocol described in the textbook except our modified HDLC frames
CSE 123: Computer Networks Homework 1 Solutions Total points = 44 Problems 1. Modified HDLC Framing [6 points] Assume we are following the protocol described in the textbook except our modified HDLC frames
Dynamic Memory Allocation
 Dynamic Memory Allocation CS61, Lecture 10 Prof. Stephen Chong October 4, 2011 Announcements 1/2 Assignment 4: Malloc Will be released today May work in groups of one or two Please go to website and enter
Dynamic Memory Allocation CS61, Lecture 10 Prof. Stephen Chong October 4, 2011 Announcements 1/2 Assignment 4: Malloc Will be released today May work in groups of one or two Please go to website and enter
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
Types, Operators and Expressions
 Types, Operators and Expressions EECS 2031 18 September 2017 1 Variable Names (2.1) l Combinations of letters, numbers, and underscore character ( _ ) that do not start with a number; are not a keyword.
Types, Operators and Expressions EECS 2031 18 September 2017 1 Variable Names (2.1) l Combinations of letters, numbers, and underscore character ( _ ) that do not start with a number; are not a keyword.
SYSTEM AND LIBRARY CALLS. UNIX Programming 2015 Fall by Euiseong Seo
 SYSTEM AND LIBRARY CALLS UNIX Programming 2015 Fall by Euiseong Seo Now, It s Programming Time! System Call and Library Call Who does process the following functions? strcmp() gettimeofday() printf() getc()
SYSTEM AND LIBRARY CALLS UNIX Programming 2015 Fall by Euiseong Seo Now, It s Programming Time! System Call and Library Call Who does process the following functions? strcmp() gettimeofday() printf() getc()
Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5)
 Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5) 1. Software development 1. Pre-conditions and Post-conditions 2. Running time analysis Big O Timing loops and nested loops 1) Write the simplest big-o expression to describe
Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5) 1. Software development 1. Pre-conditions and Post-conditions 2. Running time analysis Big O Timing loops and nested loops 1) Write the simplest big-o expression to describe
Project Introduction
 Project 1 Assigned date: 10/01/2018 Due Date: 6pm, 10/29/2018 1. Introduction The sliding window protocol (SWP) is one of the most well-known algorithms in computer networking. SWP is used to ensure the
Project 1 Assigned date: 10/01/2018 Due Date: 6pm, 10/29/2018 1. Introduction The sliding window protocol (SWP) is one of the most well-known algorithms in computer networking. SWP is used to ensure the
Instructions: Submit your answers to these questions to the Curator as OQ02 by the posted due date and time. No late submissions will be accepted.
 Instructions: Submit your answers to these questions to the Curator as OQ02 by the posted due date and time. No late submissions will be accepted. For the next five questions, consider the function to
Instructions: Submit your answers to these questions to the Curator as OQ02 by the posted due date and time. No late submissions will be accepted. For the next five questions, consider the function to
Recap. ANSI C Reserved Words C++ Multimedia Programming Lecture 2. Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam
 Multimedia Programming 2004 Lecture 2 Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam Recap Learning C++ by example No groups: everybody should experience developing and programming in C++! Assignments will determine
Multimedia Programming 2004 Lecture 2 Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam Recap Learning C++ by example No groups: everybody should experience developing and programming in C++! Assignments will determine
Implementing CRCCs. Introduction. in Altera Devices
 Implementing CRCCs in Altera Devices July 1995, ver. 1 Application Note 49 Introduction Redundant encoding is a method of error detection that spreads the information across more bits than the original
Implementing CRCCs in Altera Devices July 1995, ver. 1 Application Note 49 Introduction Redundant encoding is a method of error detection that spreads the information across more bits than the original
GFP Considerations for RPR
 GFP Considerations for RPR Angela T. Faber afaber@telcordia.com IEEE 802.17 RPRWG 1 Agenda GFP Background Why GFP? GFP Core Header GFP Payload Area GFP Options Signal Adaptation (Transparent GFP and Frame-mapped
GFP Considerations for RPR Angela T. Faber afaber@telcordia.com IEEE 802.17 RPRWG 1 Agenda GFP Background Why GFP? GFP Core Header GFP Payload Area GFP Options Signal Adaptation (Transparent GFP and Frame-mapped
Exercise 3 / Ch.7. Given the following array, write code to initialize all the elements to 0: int ed[100]; Hint: It can be done two different ways!
![Exercise 3 / Ch.7. Given the following array, write code to initialize all the elements to 0: int ed[100]; Hint: It can be done two different ways! Exercise 3 / Ch.7. Given the following array, write code to initialize all the elements to 0: int ed[100]; Hint: It can be done two different ways!](/thumbs/78/77661503.jpg) Exercise 3 / Ch.7 Given the following array, write code to initialize all the elements to 0: int ed[100]; Hint: It can be done two different ways! Exercise 3 / Ch.8 Given the following array, write code
Exercise 3 / Ch.7 Given the following array, write code to initialize all the elements to 0: int ed[100]; Hint: It can be done two different ways! Exercise 3 / Ch.8 Given the following array, write code
CS 0449 Sample Midterm
 Name: CS 0449 Sample Midterm Multiple Choice 1.) Given char *a = Hello ; char *b = World;, which of the following would result in an error? A) strlen(a) B) strcpy(a, b) C) strcmp(a, b) D) strstr(a, b)
Name: CS 0449 Sample Midterm Multiple Choice 1.) Given char *a = Hello ; char *b = World;, which of the following would result in an error? A) strlen(a) B) strcpy(a, b) C) strcmp(a, b) D) strstr(a, b)
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Lecture 3: Pointers. Krste Asanović & Randy Katz
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 3: Pointers Krste Asanović & Randy Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c Agenda Pointers in C Arrays in C This is not on the test Pointer arithmetic
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 3: Pointers Krste Asanović & Randy Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c Agenda Pointers in C Arrays in C This is not on the test Pointer arithmetic
