PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Computer Science and Engineering
|
|
|
- Imogen Whitehead
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Computer Science and Engineering SOLUTION FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 6/10/2017 Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Data Structures and Applications (15CS33) Class : III CSE A, B & C Name of Faculty : Prof. Sandesh B J & Ms. Sai Prasanna Time : :30 am to 10 am Note: Answer FIVE full questions, selecting any ONE full question from each part. PART 1 1 Write the algorithm to implement a stack using dynamic array whose initial capacity is 1 and array doubling is used to increase the stack s capacity whenever an element is added to a full stack. Implement the operations-push, pop and display. 2 a What are the disadvantages of Linear Queue? Explain how it is overcome in Circular Queue. 2 In linear queue, when rear index equals MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 1, the queuefull condition should move the entire queue to the left so that the first element is again at queue[0] and front is at -1. Shifting anarray is very time consuming and the worst case complexity is O(MAX_QUEUE_SIZE). In Circular queue we permit the queue to wrap around the end of array.
2 b Write the functions for insertion, display and doubling the capacity in circular queue using Dynamic array. 6
3 PART 2 3 Write the function to convert the infix expression to postfix. Trace and illustrate the status of stack for the expression: ((a/(b-c+d))*(e-a)*c) char stack[size]; int top = -1; /* define push operation */ void push(char item) if(top >= SIZE-1) printf("\nstack Overflow."); top = top+1; stack[top] = item; /* define pop operation */ char pop() char item ; if(top <0) printf("stack under flow: invalid infix expression"); /* underflow may occur for invalid expression */ /* where ( and ) are not matched */ exit(1); item = stack[top]; top = top-1; return(item); /* define function that is used to determine whether any symbol is operator or not (that is symbol is operand) * this fucntion returns 1 if symbol is opreator return 0 */ int is_operator(char symbol) if(symbol == '^' symbol == '*' symbol == '/' symbol == '+' symbol =='- ') return 1;
4 return 0; int precedence(char symbol) if(symbol == '^')/* exponent operator, highest precedence*/ return(3); if(symbol == '*' symbol == '/') return(2); if(symbol == '+' symbol == '-') /* lowest precedence */ return(1); return(0); void InfixToPostfix(char infix_exp[], char postfix_exp[]) int i, j; char item; char x; push('('); /* push '(' onto stack */ strcat(infix_exp,")"); /* add ')' to infix expression */ i=0; j=0; item=infix_exp[i]; /* initialize before loop*/ while(item!= '\0') /* run loop till end of infix expression */ if(item == '(') push(item); if( isdigit(item) isalpha(item)) postfix_exp[j] = item; j++; if(is_operator(item))// == 1) /* means symbol is operator */
5 */ stack */ j++; x=pop(); while(precedence(x)>= precedence(item)) postfix_exp[j] = x; x = pop(); /* add them to postfix expresion push(x); /* because just above while loop will terminate we have popped one extra item for which condition fails and loop terminates, so that one*/ push(item); /* push current operator symbol onto if(item == ')') /* if current symbol is ')' then */ x = pop(); /* pop and keep popping until */ while(x!= '(') /* '(' encounterd */ postfix_exp[j] = x; j++; x = pop(); printf("\ninvalid infix Expression.\n"); getchar(); exit(1); i++; if(top>=0) item = infix_exp[i]; printf("\ninvalid infix Expression.\n"); exit(1); getchar(); postfix_exp[j] = '\0'; /* add sentinel puts() fucntion */ /* will print entire postfix[] array upto SIZE */ Enter Infix expression : ((a/(b-c+d))*(e-a)*c) Stack ( Stack ((
6 Stack ((( Stack (( Stack ((( Stack (((/ Stack (((/( Stack (((/ Stack (((/( Stack (((/(- Stack (((/( Stack (((/ Stack (((/( Stack (((/(+ Stack (((/( Stack (((/ Stack ((( Stack (( Stack ( Stack (( Stack ((* Stack ((*( Stack ((* Stack ((*( Stack ((*(- Stack ((*( Stack ((* Stack (( Stack ( Stack (( Stack ((* Stack (( Stack ( Stack Postfix Expression: abc-d+/ea-*c* 4 Write a program to determine if the parentheses in an expression are properly nested using Stacks. Example: (2+(3*6)) : Valid, as equal no of open and close parenthesis. (2+(3*6) : Invalid, as unequal no of open and close parenthesis. //Valid if the student has written the code to check for ( and ) only #include < stdio.h > #include < conio.h > #define max 50
7 void main() char stk[max],exp[100]; int top,i; clrscr(); top = -1; printf("\nenter an infix expression "); gets(exp); for(i=0; exp[i]!= '\0'; i++) if( exp[i]=='(' exp[i] =='[' exp[i] == '' ) top++; stk[top]= exp[i]; if ( exp[i] == ')' ) if( stk[top] == '(' ) top--; printf("unbalanced exp"); exit(0); if ( exp[i] == ']' ) if( stk[top] == '[' ) top--; printf("unbalanced exp"); exit(0); if ( exp[i] == '' ) if( stk[top] == '' ) top--; printf("unbalanced exp"); exit(0); // for if( top == -1 ) printf("exp is balanced"); printf("exp is not balanced"); // main
8 PART 3 5 Write and explain the recursive functions for: (i)towers of Hanoi void hanoi(int n,char from,char other,char to) if(n!=0) hanoi(n-1,from,to,other); printf("\nmove DISK FROM %c TO %c",from,to); hanoi(n-1,other,from,to); (ii) Ackerman s Function. ack(m,n) if (m == 0) return n+1 if (n == 0) return ack( m - 1, 1 ) return ack( m - 1, ack( m, n - 1 ) ) 6 Write a program to implement multiple stacks using arrays. Also, write the functions to add/delete an item in i th stack. #define MEMORY_SIZE 100 /* size of memory */ #define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100 /* max number of stacks plus 1 */ /* global memory declaration */ element memory [MEMORY_SIZE]; int top [MAX_STACKS]; int boundary [MAX_STACKS]; int n; /* number of stacks entered by the user */ //To divide the array into roughly equal segments : top[0] = boundary[0] = -1; for (i = 1; i < n; i++) top [i] =boundary [i] =(MEMORY_SIZE/n)*i; boundary [n] = MEMORY_SIZE-1; Add an item to the stack stack-no void add (int i, element item) /* add an item to the ith stack */ if (top [i] == boundary [i+1]) stack_full (i); may have unused storage memory [++top [i] ] = item; Delete an item from the stack stack-no element delete (int i) /* remove top element from the ith stack */ if (top [i] == boundary [i])
9 return stack_empty (i); return memory [ top [i]--]; PART 4 7 Write a program that creates a Singly Linked List (Use insert at front) consisting of n students data with fields - name, roll no, semester. Search and print the record of student whose name is given by the user. (Print all the occurrences if multiple entries for same name exist) main( ).. // printf("enter the number of nodes to create : "); scanf("%d", &n); create(n); //read the name to be read display(name); void display(char *name) if(head == NULL) printf("linked List is empty.\n"); Node *temp; temp = head; while(temp!= NULL) if(strcmp(name, temp->name)==0) printf("node %d USN : %s Name : %s Branch : %s Semester : %d Phone No. : %ld\n", n + 1, temp -> usn, temp -> name, temp -> branch, temp -> sem, temp -> phno); temp = temp -> link; void create(int n) int i; for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("enter details for node %d :\n", i);
10 insertfront(); void insertfront() char usn1[10], name1[50], branch1[3]; int sem1; long phno1; Node *temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); printf("enter USN : "); scanf("%s", usn1); printf("enter name : "); scanf("%s", name1); printf("enter branch : "); scanf("%s", branch1); printf("enter semester : "); scanf("%d", &sem1); printf("enter phone number : "); scanf("%ld", &phno1); strcpy(temp -> usn, usn1); strcpy(temp -> name, name1); strcpy(temp -> branch, branch1); temp -> sem = sem1; temp -> phno = phno1; if(head == NULL) head = temp; temp -> link = NULL; temp -> link = head; head = temp; count++; a Explain the need for Linked List when Arrays provide similar functionality? 2 In an array, elements are one after the another (successive memory allocation). But in linked list, memory is not contiguous. Advantages : Addition/Deletion of an element from the list at any index which is an O(1) operation in Lists as compared to Arrays.
11 b Write the functions for the following operations on Singly Linked List: (i)inserting a node at the end of SLL void append(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 6 struct Node *last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/ new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = NULL; if (*head_ref == NULL) *head_ref = new_node; while (last->next!= NULL) last = last->next; last->next = new_node; (ii) Deleting n th Node void deletenode(struct Node **head_ref, int position) // If linked list is empty if (*head_ref == NULL) // Store head node struct Node* temp = *head_ref; // If head needs to be removed if (position == 0) *head_ref = temp->next; // Change head free(temp); // free old head // Find previous node of the node to be deleted for (int i=0; temp!=null && i<position-1; i++) temp = temp->next; // If position is more than number of ndoes if (temp == NULL temp->next == NULL) // Node temp->next is the node to be deleted // Store pointer to the next of node to be deleted struct Node *next = temp->next->next; // Unlink the node from linked list free(temp->next); // Free memory temp->next = next; // Unlink the deleted node from list
12 PART 5 9 Write a program to implement the Insertion of an element at Front, Rear and n th position of a Doubly Linked List with a Header Node. (Node in 1 st Position is the one after the Header Node) //modify for header node based on code snippet below /* TO create an empty node */ void create() int data; temp =(struct node *)malloc(1*sizeof(struct node)); temp->prev = NULL; temp->next = NULL; printf("\n Enter value to node : "); scanf("%d", &data); temp->n = data; count++; /* TO insert at beginning */ void insert1() if (h == NULL) create(); h = temp; temp1 = h; create(); temp->next = h; h->prev = temp; h = temp; /* To insert at end */ void insert2() if (h == NULL) create(); h = temp; temp1 = h; create(); temp1->next = temp; temp->prev = temp1; temp1 = temp; /* To insert at any position */ void insert3() int pos, i = 2; printf("\n Enter position to be inserted : ");
13 scanf("%d", &pos); temp2 = h; if ((pos < 1) (pos >= count + 1)) printf("\n Position out of range to insert"); if ((h == NULL) && (pos!= 1)) printf("\n Empty list cannot insert other than 1st position"); if ((h == NULL) && (pos == 1)) create(); h = temp; temp1 = h; while (i < pos) temp2 = temp2->next; i++; create(); temp->prev = temp2; temp->next = temp2->next; temp2->next->prev = temp; temp2->next = temp; 10 Write a program to add two Polynomials using Linked List. typedef struct poly_node *poly_pointer; typedef struct poly_node int coef; int expon; poly_pointer link; ; poly_pointer a, b, c; poly_pointer padd(poly_pointer a, poly_pointer b) poly_pointer front, rear, temp; int sum; rear =(poly_pointer)malloc(sizeof(poly_node)); if (IS_FULL(rear)) fprintf(stderr, The memory is full\n ); exit(1);
14 front = rear; while (a && b) switch (COMPARE(a->expon, b->expon)) case -1: /* a->expon < b->expon */ attach(b->coef, b->expon, &rear); b= b->link; break; case 0: /* a->expon == b->expon */ sum = a->coef + b->coef; if (sum) attach(sum,a->expon,&rear); a = a->link; b = b->link; break; case 1: /* a->expon > b->expon */ attach(a->coef, a->expon, &rear); a = a->link; for (; a; a = a->link) attach(a->coef, a->expon, &rear); for (; b; b=b->link) attach(b->coef, b->expon, &rear); rear->link = NULL; temp = front; front = front->link; free(temp); return front; void attach(float coefficient, int exponent, poly_pointer *ptr) /* create a new node attaching to the node pointed to by ptr. ptr is updated to point to this new node. */ poly_pointer temp; temp = (poly_pointer) malloc(sizeof(poly_node)); if (IS_FULL(temp)) fprintf(stderr, The memory is full\n ); exit(1); temp->coef = coefficient; temp->expon = exponent; (*ptr)->link = temp; *ptr = temp; *******
Fall, 2015 Prof. Jungkeun Park
 Data Structures t and Algorithms Circular lists / Doubly linked lists Fall, 2015 Prof. Jungkeun Park Copyright Notice: This material is modified version of the lecture slides by Prof. Rada Mihalcea in
Data Structures t and Algorithms Circular lists / Doubly linked lists Fall, 2015 Prof. Jungkeun Park Copyright Notice: This material is modified version of the lecture slides by Prof. Rada Mihalcea in
Data Structure. Chapter 4 List (Part II) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan.
 Data Structure Chapter 4 List (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 2009 Spring Outline Polynomials Sparse matrices Doubly linked
Data Structure Chapter 4 List (Part II) Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 2009 Spring Outline Polynomials Sparse matrices Doubly linked
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 10: Implementation of Linked Lists (Linked stacks and queues, Circular linked lists) 2015-2016 Fall Linked list implementation of stacks The cost of insert and delete at
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 10: Implementation of Linked Lists (Linked stacks and queues, Circular linked lists) 2015-2016 Fall Linked list implementation of stacks The cost of insert and delete at
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 10: Implementation of Linked Lists (Stacks, Queue, Hashtable) 2017-2018 Fall Linked list implementation of stacks The cost of insert and delete at the beginning of a linked
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 10: Implementation of Linked Lists (Stacks, Queue, Hashtable) 2017-2018 Fall Linked list implementation of stacks The cost of insert and delete at the beginning of a linked
Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis. Lecturer: Souad Alonazi
 Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis Lec(3) Stacks Lecturer: Souad Alonazi What is a stack? Stores a set of elements in a particular order Stack principle: LAST IN FIRST OUT = LIFO It means: the last element
Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis Lec(3) Stacks Lecturer: Souad Alonazi What is a stack? Stores a set of elements in a particular order Stack principle: LAST IN FIRST OUT = LIFO It means: the last element
Chapter 4. LISTS. 1. Pointers
 Chap 4: LIST (Page 1) Chapter 4. LISTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. POINTERS 2. SINGLY LINKED LISTS 3. DYNAMICALLY LINKED STACKS AND QUEUES 4. POLYNOMIALS 5. ADDITIONAL LIST OPERATIONS 6. EQUIVALENCE RELATIONS
Chap 4: LIST (Page 1) Chapter 4. LISTS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. POINTERS 2. SINGLY LINKED LISTS 3. DYNAMICALLY LINKED STACKS AND QUEUES 4. POLYNOMIALS 5. ADDITIONAL LIST OPERATIONS 6. EQUIVALENCE RELATIONS
Chapter 4: Lists 2004 년가을학기. 강경란 정보및컴퓨터공학부, 아주대학교
 Chapter 4: Lists 2004 년가을학기 강경란 korykang@ajou.ac.kr 정보및컴퓨터공학부, 아주대학교 1. Pointers 2. Singly Linked Lists Chapter 4 Lists 3. Dynamically Linked Stacks and Queues 4. Polynomials 5. Additional List Operations
Chapter 4: Lists 2004 년가을학기 강경란 korykang@ajou.ac.kr 정보및컴퓨터공학부, 아주대학교 1. Pointers 2. Singly Linked Lists Chapter 4 Lists 3. Dynamically Linked Stacks and Queues 4. Polynomials 5. Additional List Operations
Solution for Data Structure
 Solution for Data Structure May 2016 INDEX Q1 a 2-3 b 4 c. 4-6 d 7 Q2- a 8-12 b 12-14 Q3 a 15-18 b 18-22 Q4- a 22-35 B..N.A Q5 a 36-38 b N.A Q6- a 39-42 b 43 1 www.brainheaters.in Q1) Ans: (a) Define ADT
Solution for Data Structure May 2016 INDEX Q1 a 2-3 b 4 c. 4-6 d 7 Q2- a 8-12 b 12-14 Q3 a 15-18 b 18-22 Q4- a 22-35 B..N.A Q5 a 36-38 b N.A Q6- a 39-42 b 43 1 www.brainheaters.in Q1) Ans: (a) Define ADT
Linked List in Data Structure. By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra
 Linked List in Data Structure By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra Linked List Like arrays, Linked List is a linear data
Linked List in Data Structure By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra Linked List Like arrays, Linked List is a linear data
Pointers. Array. Solution to the data movement in sequential representation
 1 LISTS Pointers Array sequential representation some operation can be very time-consuming (data movement) size of data must be predefined static storage allocation and deallocation Solution to the data
1 LISTS Pointers Array sequential representation some operation can be very time-consuming (data movement) size of data must be predefined static storage allocation and deallocation Solution to the data
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure using C Model wer Subject Code: 22317 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given
WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure using C Model wer Subject Code: 22317 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given
Data Structure. Chapter 3 Stacks and Queues. Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan.
 Data Structure Chapter 3 Stacks and Queues Instructor: Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 29 Spring Outline Stack Queue A Mazing Problem
Data Structure Chapter 3 Stacks and Queues Instructor: Angela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 29 Spring Outline Stack Queue A Mazing Problem
MODULE 3: LINKED LIST
 MODULE 3: LINKED LIST DEFINITION A linked list, or one-way list, is a linear collection of data elements, called nodes, where the linear order is given by means of pointers. That is, each node is divided
MODULE 3: LINKED LIST DEFINITION A linked list, or one-way list, is a linear collection of data elements, called nodes, where the linear order is given by means of pointers. That is, each node is divided
17CS33:Data Structures Using C QUESTION BANK
 17CS33:Data Structures Using C QUESTION BANK REVIEW OF STRUCTURES AND POINTERS, INTRODUCTION TO SPECIAL FEATURES OF C Learn : Usage of structures, unions - a conventional tool for handling a group of logically
17CS33:Data Structures Using C QUESTION BANK REVIEW OF STRUCTURES AND POINTERS, INTRODUCTION TO SPECIAL FEATURES OF C Learn : Usage of structures, unions - a conventional tool for handling a group of logically
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communication
 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -0 Department of Electronics and Communication INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 4//2017 Marks: 50 Subject & Code
USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -0 Department of Electronics and Communication INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 4//2017 Marks: 50 Subject & Code
FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours
 TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) (Maximum marks: 100) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours PART
TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) (Maximum marks: 100) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours PART
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 5: Stacks and Queues 2017 Fall Stacks A list on which insertion and deletion can be performed. Based on Last-in-First-out (LIFO) Stacks are used for a number of applications:
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 5: Stacks and Queues 2017 Fall Stacks A list on which insertion and deletion can be performed. Based on Last-in-First-out (LIFO) Stacks are used for a number of applications:
Lecture No.04. Data Structures
 Lecture No.04 Data Structures Josephus Problem #include "CList.cpp" void main(int argc, char *argv[]) { CList list; int i, N=10, M=3; for(i=1; i
Lecture No.04 Data Structures Josephus Problem #include "CList.cpp" void main(int argc, char *argv[]) { CList list; int i, N=10, M=3; for(i=1; i
Write a C program to add two Complex numbers using functions illustrating-
 Scheme of valuvation Date : 29/8/2017 Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Data Structures and Applications (15CS33) Class : III A&B Name of Faculty : Ms. Saritha Time : 8:30 am to 10 am NOTE: ANSWER All FIVE QUESTIONS
Scheme of valuvation Date : 29/8/2017 Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Data Structures and Applications (15CS33) Class : III A&B Name of Faculty : Ms. Saritha Time : 8:30 am to 10 am NOTE: ANSWER All FIVE QUESTIONS
Lecture Data Structure Stack
 Lecture Data Structure Stack 1.A stack :-is an abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
Lecture Data Structure Stack 1.A stack :-is an abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
PES INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY-BSC SESSION: JULY 2018 DECEMBER 2018
 PES INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY-BSC 1Km before Electronic City, Hosur Road, Bangalore-560100. DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DATA STRUCTURES WITH C LABORATORY LAB MANUAL [As per Choice Based
PES INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY-BSC 1Km before Electronic City, Hosur Road, Bangalore-560100. DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DATA STRUCTURES WITH C LABORATORY LAB MANUAL [As per Choice Based
Module III. Linear Data Structures and their Linked Storage Representation
 Module III Linear Data Structures and their Linked Storage Representation 3.1 Linked List Linked list is the collection of inter connected nodes with a head node representing the first node and a tail
Module III Linear Data Structures and their Linked Storage Representation 3.1 Linked List Linked list is the collection of inter connected nodes with a head node representing the first node and a tail
Prepared By: Ms. Nidhi Solanki (Assist. Prof.) Page 1
 QUESTION BANK ON COURSE: 304: PRELIMINARIES: 1. What is array of pointer, explain with appropriate example? 2 2. Differentiate between call by value and call by reference, give example. 3. Explain pointer
QUESTION BANK ON COURSE: 304: PRELIMINARIES: 1. What is array of pointer, explain with appropriate example? 2 2. Differentiate between call by value and call by reference, give example. 3. Explain pointer
Application of Stack (Backtracking)
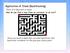 Application of Stack (Backtracking) Think of a labyrinth or maze How do you find a way from an entrance to an exit? Once you reach a dead end, you must backtrack. But backtrack to where? to the previous
Application of Stack (Backtracking) Think of a labyrinth or maze How do you find a way from an entrance to an exit? Once you reach a dead end, you must backtrack. But backtrack to where? to the previous
Data Structure using C++ Lecture 04. Data Structures and algorithm analysis in C++ Chapter , 3.2, 3.2.1
 Data Structure using C++ Lecture 04 Reading Material Data Structures and algorithm analysis in C++ Chapter. 3 3.1, 3.2, 3.2.1 Summary Stack Operations on a stack Representing stacks Converting an expression
Data Structure using C++ Lecture 04 Reading Material Data Structures and algorithm analysis in C++ Chapter. 3 3.1, 3.2, 3.2.1 Summary Stack Operations on a stack Representing stacks Converting an expression
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR Stamp / Signature of the Invigilator
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR Stamp / Signature of the Invigilator EXAMINATION ( End Semester ) SEMESTER ( Spring ) Roll Number Section Name Subject Number C S 1 0 0 0 1 Subject Name Programming
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR Stamp / Signature of the Invigilator EXAMINATION ( End Semester ) SEMESTER ( Spring ) Roll Number Section Name Subject Number C S 1 0 0 0 1 Subject Name Programming
Two abstract data types. performed on them) Stacks Last In First Out (LIFO) Queues First In First Out (FIFO)
 Two abstract data types o Can be implemented using arrays or linked lists o Restricted lists (only a small number of operations are performed on them) Stacks Last In First Out (LIFO) Queues First In First
Two abstract data types o Can be implemented using arrays or linked lists o Restricted lists (only a small number of operations are performed on them) Stacks Last In First Out (LIFO) Queues First In First
The program simply pushes all of the characters of the string into the stack. Then it pops and display until the stack is empty.
 EENG212 Algorithms & Data Structures Fall 0/07 Lecture Notes # Outline Stacks Application of Stacks Reversing a String Palindrome Example Infix, Postfix and Prefix Notations APPLICATION OF STACKS Stacks
EENG212 Algorithms & Data Structures Fall 0/07 Lecture Notes # Outline Stacks Application of Stacks Reversing a String Palindrome Example Infix, Postfix and Prefix Notations APPLICATION OF STACKS Stacks
DATA STRUCUTRES. A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.
 DATA STRUCUTRES A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. An algorithm, which is a finite sequence of instructions, each of which
DATA STRUCUTRES A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. An algorithm, which is a finite sequence of instructions, each of which
MODULE V: POINTERS & PREPROCESSORS
 MODULE V: POINTERS & PREPROCESSORS INTRODUCTION As you know, every variable is a memory-location and every memory-location has its address defined which can be accessed using ampersand(&) operator, which
MODULE V: POINTERS & PREPROCESSORS INTRODUCTION As you know, every variable is a memory-location and every memory-location has its address defined which can be accessed using ampersand(&) operator, which
Stack. 4. In Stack all Operations such as Insertion and Deletion are permitted at only one end. Size of the Stack 6. Maximum Value of Stack Top 5
 What is Stack? Stack 1. Stack is LIFO Structure [ Last in First Out ] 2. Stack is Ordered List of Elements of Same Type. 3. Stack is Linear List 4. In Stack all Operations such as Insertion and Deletion
What is Stack? Stack 1. Stack is LIFO Structure [ Last in First Out ] 2. Stack is Ordered List of Elements of Same Type. 3. Stack is Linear List 4. In Stack all Operations such as Insertion and Deletion
S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures. Primitive Linear Non Linear
![S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures. Primitive Linear Non Linear S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures. Primitive Linear Non Linear](/thumbs/93/111913146.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) Explain different types of data structures with examples. [5] Ans.: Types of Data Structure : Data Structures
S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) Explain different types of data structures with examples. [5] Ans.: Types of Data Structure : Data Structures
DATA STRUCTURES LABORATORY
 DATA STRUCTURES LABORATORY [As per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) scheme] (Effective from the academic year 2017-2018) SEMESTER - III Laboratory Code 15CSL38 IA Marks 20 Number of Lecture Hours/Week
DATA STRUCTURES LABORATORY [As per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) scheme] (Effective from the academic year 2017-2018) SEMESTER - III Laboratory Code 15CSL38 IA Marks 20 Number of Lecture Hours/Week
Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College Sree Sainath Nagar, A. Rangampet
 Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College Sree Sainath Nagar, A. Rangampet 517 102 Department of Computer Science and Engineering I B. Tech C Programming Language Lab Title: Stack SVEC/IT/EXPT-CP-21 PROBLEM
Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College Sree Sainath Nagar, A. Rangampet 517 102 Department of Computer Science and Engineering I B. Tech C Programming Language Lab Title: Stack SVEC/IT/EXPT-CP-21 PROBLEM
UNIT-2 Stack & Queue
 UNIT-2 Stack & Queue 59 13. Stack A stack is an Abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
UNIT-2 Stack & Queue 59 13. Stack A stack is an Abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
Content: Learning Objectives
 1 BLOOM PUBLIC CHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Class: XII ubject: Computer cience Month : July No of s: 21 Chapter:Data structure: Linked List TTT: 8 WT: 12 Content: Learning Objectives At the
1 BLOOM PUBLIC CHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Class: XII ubject: Computer cience Month : July No of s: 21 Chapter:Data structure: Linked List TTT: 8 WT: 12 Content: Learning Objectives At the
DS Lab Manual -17CS33
 Chethan Raj C Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE 6. Design, Develop and Implement a menu driven Program in C for the following operations on Circular QUEUE of Characters (Array Implementation of Queue with
Chethan Raj C Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE 6. Design, Develop and Implement a menu driven Program in C for the following operations on Circular QUEUE of Characters (Array Implementation of Queue with
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 6: Stacks and Queues 2015-2016 Fall Stacks A list on which insertion and deletion can be performed. Based on Last-in-First-out (LIFO) Stacks are used for a number of applications:
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 6: Stacks and Queues 2015-2016 Fall Stacks A list on which insertion and deletion can be performed. Based on Last-in-First-out (LIFO) Stacks are used for a number of applications:
POLYNOMIAL ADDITION. AIM:- To write a C program to represent a polynomial as a linked list and write functions for polynomial addition.
 POLYNOMIAL ADDITION AIM:- To write a C program to represent a polynomial as a linked list and write functions for polynomial addition. ALGORITHM:- 1. Start the program 2. Get the coefficients and powers
POLYNOMIAL ADDITION AIM:- To write a C program to represent a polynomial as a linked list and write functions for polynomial addition. ALGORITHM:- 1. Start the program 2. Get the coefficients and powers
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communication
 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -0 Department of Electronics and Communication INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 1 Date : 30/8/2017 Marks: 0 Subject & Code
USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -0 Department of Electronics and Communication INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 1 Date : 30/8/2017 Marks: 0 Subject & Code
 Class / Sem: I CSE / II Semester Subject Code: CS 6202 Subject: Programming and Data Structures I Prepared by T. Vithya Unit IV - LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES STACKS AND QUEUES Stack ADT Evaluating arithmetic
Class / Sem: I CSE / II Semester Subject Code: CS 6202 Subject: Programming and Data Structures I Prepared by T. Vithya Unit IV - LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES STACKS AND QUEUES Stack ADT Evaluating arithmetic
EC8393FUNDAMENTALS OF DATA STRUCTURES IN C Unit 3
 UNIT 3 LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 1. Define Data Structures Data Structures is defined as the way of organizing all data items that consider not only the elements stored but also stores the relationship between
UNIT 3 LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 1. Define Data Structures Data Structures is defined as the way of organizing all data items that consider not only the elements stored but also stores the relationship between
UNIT 2: STACK & RECURSION Programs demonstrated in class. Tojo Mathew Asst. Professor CSE Dept., NIE Mysuru.
 UNIT 2: STACK & RECURSION Programs demonstrated in class. Tojo Mathew Asst. Professor CSE Dept., NIE Mysuru. Table of Contents 1. C Program to Check for balanced parenthesis by using Stacks...3 2. Program
UNIT 2: STACK & RECURSION Programs demonstrated in class. Tojo Mathew Asst. Professor CSE Dept., NIE Mysuru. Table of Contents 1. C Program to Check for balanced parenthesis by using Stacks...3 2. Program
Bangalore South Campus
 USN: 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before ElectronicCity, Bengaluru -100 Department of Basic Science and Humanities INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Date: 22/11/2017 Time:11:30am- 1.00 pm
USN: 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before ElectronicCity, Bengaluru -100 Department of Basic Science and Humanities INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Date: 22/11/2017 Time:11:30am- 1.00 pm
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Department of MCA Course Information for
 1. GENERAL INFORMATION: PESIT Bangalore South Campus Department of MCA Course Information for Data Structures Using C(13MCA21) Academic Year: 2015 Semester: II Title Code Duration (hrs) Lectures 48 Hrs
1. GENERAL INFORMATION: PESIT Bangalore South Campus Department of MCA Course Information for Data Structures Using C(13MCA21) Academic Year: 2015 Semester: II Title Code Duration (hrs) Lectures 48 Hrs
CT11 (ALCCS) DATA STRUCTURE THROUGH C JUN 2015
 Solutions Q.1 a. What is a pointer? Explain how it is declared and initialized. (4) Different from other normal variables which can store values, pointers are special variables that can hold the address
Solutions Q.1 a. What is a pointer? Explain how it is declared and initialized. (4) Different from other normal variables which can store values, pointers are special variables that can hold the address
DS Assignment II. Full Sized Image
 DS Assignment II 1. A) For the Towers of Hanoi problem, show the call tree during the recursive call Towers(3, A, C, B). In the tree, label the root node as Towers (3, A, C, B) while marking all the intermediate
DS Assignment II 1. A) For the Towers of Hanoi problem, show the call tree during the recursive call Towers(3, A, C, B). In the tree, label the root node as Towers (3, A, C, B) while marking all the intermediate
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code:
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Stacks. CONTENTS 3.1 Introduction 1. Stack as an abstract data type 2. Representation of a Stack as an array 3.2Applications of Stack.
 Stacks CONTENTS 3.1 Introduction 1. Stack as an abstract data type 2. Representation of a Stack as an array 3.2Applications of Stack Hours: 12 Marks: 18 3.1 Introduction to Stacks 1. Stack as Abstract
Stacks CONTENTS 3.1 Introduction 1. Stack as an abstract data type 2. Representation of a Stack as an array 3.2Applications of Stack Hours: 12 Marks: 18 3.1 Introduction to Stacks 1. Stack as Abstract
Data Structures. Chapter 06. 3/10/2016 Md. Golam Moazzam, Dept. of CSE, JU
 Data Structures Chapter 06 1 Stacks A stack is a list of elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end, called the top of the stack. This means that elements are removed from
Data Structures Chapter 06 1 Stacks A stack is a list of elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end, called the top of the stack. This means that elements are removed from
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit 3
 Linear and Non-Linear Data Structures Linear data structure: Linear data structures are those data structure in which data items are arranged in a linear sequence by physically or logically or both the
Linear and Non-Linear Data Structures Linear data structure: Linear data structures are those data structure in which data items are arranged in a linear sequence by physically or logically or both the
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in themodel answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in themodel answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Linear Data Structure
 Linear Data Structure Definition A data structure is said to be linear if its elements form a sequence or a linear list. Examples: Array Linked List Stacks Queues Operations on linear Data Structures Traversal
Linear Data Structure Definition A data structure is said to be linear if its elements form a sequence or a linear list. Examples: Array Linked List Stacks Queues Operations on linear Data Structures Traversal
Prepared By:- Dinesh Sharma Asstt. Professor, CSE & IT Deptt. ITM Gurgaon
 Data Structures &Al Algorithms Prepared By:- Dinesh Sharma Asstt. Professor, CSE & IT Deptt. ITM Gurgaon What is Data Structure Data Structure is a logical relationship existing between individual elements
Data Structures &Al Algorithms Prepared By:- Dinesh Sharma Asstt. Professor, CSE & IT Deptt. ITM Gurgaon What is Data Structure Data Structure is a logical relationship existing between individual elements
FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE
 TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours (Maximum marks: 100)
TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours (Maximum marks: 100)
S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis. Primitive Linear Non Linear
![S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis. Primitive Linear Non Linear S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis. Primitive Linear Non Linear](/thumbs/88/115506064.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) Explain different types of data structures with examples. [5] Ans.: Types of Data Structure : Data
S.E. Sem. III [INFT] Data Structures & Analysis Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) Explain different types of data structures with examples. [5] Ans.: Types of Data Structure : Data
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT III LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES PART A 1. What is meant by data
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT III LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES PART A 1. What is meant by data
Data Structure & Algorithms Laboratory Manual (CS 392)
 Institute of Engineering & Management Department of Computer Science & Engineering Data Structure Laboratory for 2 nd year 3 rd semester Code: CS 392 Data Structure & Algorithms Laboratory Manual (CS 392)
Institute of Engineering & Management Department of Computer Science & Engineering Data Structure Laboratory for 2 nd year 3 rd semester Code: CS 392 Data Structure & Algorithms Laboratory Manual (CS 392)
Ashish Gupta, Data JUET, Guna
 Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
Categories of data structures Data structures are categories in two classes 1. Linear data structure: - organized into sequential fashion - elements are attached one after another - easy to implement because
Introduction. Array successive items locate a fixed distance disadvantage. possible solution
 CHAPTER 4 LISTS All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C, CHAPTER 4 1 Introduction Array successive items
CHAPTER 4 LISTS All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C, CHAPTER 4 1 Introduction Array successive items
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING B.E SECOND SEMESTER CS 6202 PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES I TWO MARKS UNIT I- 2 MARKS
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING B.E SECOND SEMESTER CS 6202 PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES I TWO MARKS UNIT I- 2 MARKS 1. Define global declaration? The variables that are used in more
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING B.E SECOND SEMESTER CS 6202 PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES I TWO MARKS UNIT I- 2 MARKS 1. Define global declaration? The variables that are used in more
 CS6202 - PROGRAMMING & DATA STRUCTURES I Unit IV Part - A 1. Define Stack. A stack is an ordered list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top. It is an abstract data type
CS6202 - PROGRAMMING & DATA STRUCTURES I Unit IV Part - A 1. Define Stack. A stack is an ordered list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top. It is an abstract data type
STACKS 3.1 INTRODUCTION 3.2 DEFINITION
 STACKS 3 3.1 INTRODUCTION A stack is a linear data structure. It is very useful in many applications of computer science. It is a list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called
STACKS 3 3.1 INTRODUCTION A stack is a linear data structure. It is very useful in many applications of computer science. It is a list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called
Stacks. Manolis Koubarakis. Data Structures and Programming Techniques
 Stacks Manolis Koubarakis 1 Stacks and Queues Linear data structures are collections of components arranged in a straight line. If we restrict the growth of a linear data structure so that new components
Stacks Manolis Koubarakis 1 Stacks and Queues Linear data structures are collections of components arranged in a straight line. If we restrict the growth of a linear data structure so that new components
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING UNIT-1
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : I / II Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6202 Subject Name : Programming and Data Structures-I Degree & Branch : B.E C.S.E. 2 MARK
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : I / II Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6202 Subject Name : Programming and Data Structures-I Degree & Branch : B.E C.S.E. 2 MARK
Linked List. April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1
 Linked List April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Introduction head A linked list is a data structure which can change during execution. Successive elements are connected by pointers. Last element
Linked List April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Introduction head A linked list is a data structure which can change during execution. Successive elements are connected by pointers. Last element
Now consider the following situation after deleting three elements from the queue...
 Scheme of valuvation -1I Subject & Code : Data Structure and Application (15CS33) NOTE: ANSWER All FIVE QUESTIONS 1 Explain the diadvantage of linear queue and how it i olved in circular queue. Explain
Scheme of valuvation -1I Subject & Code : Data Structure and Application (15CS33) NOTE: ANSWER All FIVE QUESTIONS 1 Explain the diadvantage of linear queue and how it i olved in circular queue. Explain
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Using C Model Answer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Using C Model Answer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
Lists (Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues
 (Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues By: Pramod Parajuli, Department of Computer Science, St. Xavier
(Section 5) Lists, linked lists Implementation of lists in C Other list structures List implementation of stacks, queues, priority queues By: Pramod Parajuli, Department of Computer Science, St. Xavier
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MCA
 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MCA INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 (Scheme and Solution) Data Structures Using C (16MCA11) 1) A.
USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MCA INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 (Scheme and Solution) Data Structures Using C (16MCA11) 1) A.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch DATA STRUCTURES ACS002 B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch DATA STRUCTURES ACS002 B. Tech
That means circular linked list is similar to the single linked list except that the last node points to the first node in the list.
 Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Circular Linked Lists and it operations Introduction: Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link
Leaning Objective: In this Module you will be learning the following: Circular Linked Lists and it operations Introduction: Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link
DATA STRUCTURE : A MCQ QUESTION SET Code : RBMCQ0305
 Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
DEEPIKA KAMBOJ UNIT 2. What is Stack?
 What is Stack? UNIT 2 Stack is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner. You must have seen a pile of plates where one plate is placed on top of another. Now, when you
What is Stack? UNIT 2 Stack is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner. You must have seen a pile of plates where one plate is placed on top of another. Now, when you
Stack. Data structure with Last-In First-Out (LIFO) behavior. Out
 Stack and Queue 1 Stack Data structure with Last-In First-Out (LIFO) behavior In Out C B A B C 2 Typical Operations Pop on Stack Push isempty: determines if the stack has no elements isfull: determines
Stack and Queue 1 Stack Data structure with Last-In First-Out (LIFO) behavior In Out C B A B C 2 Typical Operations Pop on Stack Push isempty: determines if the stack has no elements isfull: determines
The time and space are the two measure for efficiency of an algorithm.
 There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
CHAPTER 3 STACKS AND QUEUES
 CHAPTER 3 STACKS AND QUEUES All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C /2nd Edition, Silicon Press, 2008.
CHAPTER 3 STACKS AND QUEUES All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C /2nd Edition, Silicon Press, 2008.
Top of the Stack. Stack ADT
 Module 3: Stack ADT Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Stack ADT Features (Logical View) A List that
Module 3: Stack ADT Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Stack ADT Features (Logical View) A List that
Types of Data Structures
 DATA STRUCTURES material prepared by: MUKESH BOHRA Follow me on FB : http://www.facebook.com/mukesh.sirji4u The logical or mathematical model of data is called a data structure. In other words, a data
DATA STRUCTURES material prepared by: MUKESH BOHRA Follow me on FB : http://www.facebook.com/mukesh.sirji4u The logical or mathematical model of data is called a data structure. In other words, a data
Fundamentals of Programming & Procedural Programming
 Universität Duisburg-Essen PRACTICAL TRAINING TO THE LECTURE Fundamentals of Programming & Procedural Programming Session Eight: Math Functions, Linked Lists, and Binary Trees Name: First Name: Tutor:
Universität Duisburg-Essen PRACTICAL TRAINING TO THE LECTURE Fundamentals of Programming & Procedural Programming Session Eight: Math Functions, Linked Lists, and Binary Trees Name: First Name: Tutor:
Bachelor Level/ First Year/ Second Semester/ Science Full Marks: 60 Computer Science and Information Technology (CSc. 154) Pass Marks: 24
 Prepared By ASCOL CSIT 2070 Batch Institute of Science and Technology 2065 Bachelor Level/ First Year/ Second Semester/ Science Full Marks: 60 Computer Science and Information Technology (CSc. 154) Pass
Prepared By ASCOL CSIT 2070 Batch Institute of Science and Technology 2065 Bachelor Level/ First Year/ Second Semester/ Science Full Marks: 60 Computer Science and Information Technology (CSc. 154) Pass
Sample Question Paper
 Scheme - I Sample Question Paper Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any FIVE of the following. 10 Marks a. Write any four applications of data structure. b. Sketch the diagram of circular queue. c. State
Scheme - I Sample Question Paper Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any FIVE of the following. 10 Marks a. Write any four applications of data structure. b. Sketch the diagram of circular queue. c. State
STACKS AND QUEUES CHAPTER 3
 CHAPTER 3 STACKS AND QUEUES All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C, CHAPTER 3 1 Stack: a Last-In-First-Out
CHAPTER 3 STACKS AND QUEUES All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C, CHAPTER 3 1 Stack: a Last-In-First-Out
This document can be downloaded from with most recent updates. 1 Data Structures using C: Module 4 (16MCA11) LINKED LISTS
 1 Data Structures using C: Module 4 (16MCA11) LINKED LISTS 4.1 MEMORY MANAGEMENT 4.1.1 Basics about Memory When a C program is compiled, the compiler translates the source code into machine code. Now the
1 Data Structures using C: Module 4 (16MCA11) LINKED LISTS 4.1 MEMORY MANAGEMENT 4.1.1 Basics about Memory When a C program is compiled, the compiler translates the source code into machine code. Now the
List, Stack, and Queues
 List, Stack, and Queues R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 02/24/2010 3.1 Abstract Data Type An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is a set of objects with a set of
List, Stack, and Queues R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 02/24/2010 3.1 Abstract Data Type An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is a set of objects with a set of
Introduction. Problem Solving on Computer. Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms
 Introduction Problem Solving on Computer Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms 1 Objective of Data Structures Two Goals: 1) Identify and develop useful high-level data types
Introduction Problem Solving on Computer Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms 1 Objective of Data Structures Two Goals: 1) Identify and develop useful high-level data types
Stacks and Queues. CSE Data Structures April 12, 2002
 Stacks and Queues CSE 373 - Data Structures April 12, 2002 Readings and References Reading Section 3.3 and 3.4, Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C, Weiss Other References 12-Apr-02 CSE 373 - Data
Stacks and Queues CSE 373 - Data Structures April 12, 2002 Readings and References Reading Section 3.3 and 3.4, Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C, Weiss Other References 12-Apr-02 CSE 373 - Data
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES
 BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 8: Dynamically Allocated Linked Lists 2017-2018 Fall int x; x = 8; int A[4]; An array is stored as one contiguous block of memory. How can we add a fifth element to the
BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES Lecture 8: Dynamically Allocated Linked Lists 2017-2018 Fall int x; x = 8; int A[4]; An array is stored as one contiguous block of memory. How can we add a fifth element to the
The combination of pointers, structs, and dynamic memory allocation allow for creation of data structures
 Data Structures in C C Programming and Software Tools N.C. State Department of Computer Science Data Structures in C The combination of pointers, structs, and dynamic memory allocation allow for creation
Data Structures in C C Programming and Software Tools N.C. State Department of Computer Science Data Structures in C The combination of pointers, structs, and dynamic memory allocation allow for creation
Introduction. Array successive items locate a fixed distance disadvantage. possible solution
 CHAPTER 4 LISTS All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C, CHAPTER 4 1 Introduction Array successive items
CHAPTER 4 LISTS All the programs in this file are selected from Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni, and Susan Anderson-Freed Fundamentals of Data Structures in C, CHAPTER 4 1 Introduction Array successive items
Solution: The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix to postfix conversion.
 1. What is the full form of LIFO? The full form of LIFO is Last In First Out. 2. Give some examples for stack application. The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix
1. What is the full form of LIFO? The full form of LIFO is Last In First Out. 2. Give some examples for stack application. The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix
DATA STRUCTURES USING C
 DATA STRUCTURES USING C DATA STRUCTURES USING C LECTURE NOTES Prepared by Dr. Subasish Mohapatra Department of Computer Science and Application College of Engineering and Technology, Bhubaneswar Biju Patnaik
DATA STRUCTURES USING C DATA STRUCTURES USING C LECTURE NOTES Prepared by Dr. Subasish Mohapatra Department of Computer Science and Application College of Engineering and Technology, Bhubaneswar Biju Patnaik
NCS 301 DATA STRUCTURE USING C
 NCS Data Structure Using C -8- NCS DATA STRUCTURE USING C Unit- Part- Stack Hammad Mashkoor Lari Assistant Professor Allenhouse Institute of Technology www.ncsds.wordpress.com Introduction Stack is a non
NCS Data Structure Using C -8- NCS DATA STRUCTURE USING C Unit- Part- Stack Hammad Mashkoor Lari Assistant Professor Allenhouse Institute of Technology www.ncsds.wordpress.com Introduction Stack is a non
A. Year / Module Semester Subject Topic 2016 / V 2 PCD Pointers, Preprocessors, DS
 Syllabus: Pointers and Preprocessors: Pointers and address, pointers and functions (call by reference) arguments, pointers and arrays, address arithmetic, character pointer and functions, pointers to pointer,initialization
Syllabus: Pointers and Preprocessors: Pointers and address, pointers and functions (call by reference) arguments, pointers and arrays, address arithmetic, character pointer and functions, pointers to pointer,initialization
Information Science 2
 Information Science 2 - Basic Data Structures- Week 02 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Today s class outline l Basic data structures: Definitions and implementation
Information Science 2 - Basic Data Structures- Week 02 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Today s class outline l Basic data structures: Definitions and implementation
Programming. Lists, Stacks, Queues
 Programming Lists, Stacks, Queues Summary Linked lists Create and insert elements Iterate over all elements of the list Remove elements Doubly Linked Lists Circular Linked Lists Stacks Operations and implementation
Programming Lists, Stacks, Queues Summary Linked lists Create and insert elements Iterate over all elements of the list Remove elements Doubly Linked Lists Circular Linked Lists Stacks Operations and implementation
DC104 DATA STRUCTURE JUNE Q.2 a. If you are using C language to implement the heterogeneous linked list, what pointer type will you use?
 Q.2 a. If you are using C language to implement the heterogeneous linked list, what pointer type will you use? The heterogeneous linked list contains different data types in its nodes and we need a link
Q.2 a. If you are using C language to implement the heterogeneous linked list, what pointer type will you use? The heterogeneous linked list contains different data types in its nodes and we need a link
Some Applications of Stack. Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1
 Some Applications of Stack Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Arithmetic Expressions Polish Notation Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 2 What is Polish Notation? Conventionally,
Some Applications of Stack Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Arithmetic Expressions Polish Notation Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 2 What is Polish Notation? Conventionally,
ESc101: (Linear, Circular, Doubly) Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Trees. Introduction to Linked Lists
 ESc101: (Linear, Circular, Doubly) Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Trees Instructor: Krithika Venkataramani Semester 2, 2011-2012 1 Introduction to Linked Lists Each bead connected to the next through a
ESc101: (Linear, Circular, Doubly) Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Trees Instructor: Krithika Venkataramani Semester 2, 2011-2012 1 Introduction to Linked Lists Each bead connected to the next through a
The Bucharest University of Economic Studies. Data Structures. ADTs-Abstract Data Types Stacks and Queues
 The Bucharest University of Economic Studies Data Structures ADTs-Abstract Data Types Stacks and Queues Agenda Definition Graphical representation Internal interpretation Characteristics Operations Implementations
The Bucharest University of Economic Studies Data Structures ADTs-Abstract Data Types Stacks and Queues Agenda Definition Graphical representation Internal interpretation Characteristics Operations Implementations
