1. Expressions - 1 point each. -1 for missing or extra " OR.0. differences in capitalization of true and false okay. No limit on points off.
|
|
|
- Derek Blake
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS312 Fall 2017 Final Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise Gacky or Gack - Code very hard to understand even though it works. (Solution is not elegant.) LE - Logic error in code. NAP - No answer provided. No answer given on test NN - Not necessary. Code is unneeded. Generally no points off NPE - Null Pointer Exception may occur OBOE - Off by one error. Calculation is off by one. RTQ - Read the question. Violated restrictions or made incorrect assumption. 1. Expressions - 1 point each. -1 for missing or extra " OR.0. differences in capitalization of true and false okay. No limit on points off. A. "falseh101.5" B C D 25.0 E. true F. false G (-5.0 also accepted due to unexpected weirdness of Math.round() public static long round(double a) Returns the closest long to the argument, with ties rounding to positive infinity. H. false I. 10 J Code Tracing - 1 point each. Answer as shown or for first four occurrences of "'s. Differences in spacing, commas, and grouping symbols okay for array output. 3. Code Tracing - 1 point each. Answer as shown or for first two occurrences of "'s. Differences in spacing, commas, and grouping symbols okay for array output. A. [3, 2, 12, 7, 1] B C. 0 7 D true false E. false true F G. [5] H. [2, 3, 9] I. [1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 33] J. [-3, -3, -1, -9, -9, -35] K. 3 SYSTEMS L. Syntax error (va++ illegal) M. [K, B, A, G] N. 0 O..5 each syntax error (no 0 arg constructor) legal P..5 each syntax error syntax error Q. room: 30 R. room: 30 S. room: 25 T. syntax error (access private field) U. room: 20 V. room: 10 true W. true false X. [-2, 4][-2, 5]
2 3. Critters - 16 Points. JumpinBean public class JumpingBean extends Critter { private int stepssofar; private int maxstepsthisleg; private boolean moving; private Direction dir; // Constructor not necessary. Default value okay // for all fields okay. public Attack fight(string opp) { if (moving) return Attack.FORFEIT; moving = true; maxstepsthisleg += 2; stepssofar = 0; dir = Direction.NORTH; if (Math.random() >= 0.5) dir = Direction.WEST; return Attack.SCRATCH; public Direction getmove() { if(!moving) return Direction.CENTER; stepssofar++; if (stepssofar == maxstepsthisleg) moving = false; // OR moving = stepssofar == maxstepsthisleg; return dir; Points: header correct with extends clause: 2 points instance variables: 1 point (can be different, but must track steps, leg length, current direction, and if moving / celebrating) instance vars private: 1 point Attack method: forfeit if moving: 1 point if not moving, prep for moving correctly: 5 points return SCRATCH if not moving: 1 point getmove if not moving, returns CENTER: 1 point if moving increment steps: 1 point check to see if end of leg and stop moving: 2 points return direction if moving: 1 point -6 if fight calls getmove or getmove calls fight -5 no setting values in fight method so we know if we won -5 picks a random direction every step -7 loop in getmove method / trying to move multiple times in getmove 2
3 4. Data Processing - 18 Points. public static void printmoney(scanner sc) { final double GALLEON_PER_SICKLE = 1 / 17.0; final double GALLEON_PER_KNUT = 1 / 29.0 / 17.0; while(sc.hasnextline()) { Scanner line = new Scanner(sc.nextLine()); while(!line.hasnextint()) { System.out.print(line.next() + " "); double total = 0.0; while (line.hasnext()) { int num = line.nextint(); String symbol = line.next(); if (symbol.equals("k")) { total += GALLEON_PER_KNUT * num; else if (symbol.equals("s")) { total += GALLEON_PER_SICKLE * num; else if (symbol.equals("g")) { total += num; System.out.print(total + " Galleon"); if (total!= 1.0) { System.out.print("s"); System.out.println(); loop through lines correctly: 2 points create Scanner for line: 2 points print out or save name as String correctly: 3 points (-1 if forget space " ") variable for total galleons for current person: 1 point loop while has next in line correctly: 2 points read in int value correctly: 1 point get and check symbol correctly: 4 points (-3 for == instead of.equals) add correct value to running total (okay if 3 separate variables): 2 points print number of Galleon correctly, including no s if 1.0: 1 point 3
4 5. Arrays 12 Points. public static int[] getreversedsublist(int[] vals, int startindex, int stopindex) { int[] result = new int[stopindex - startindex]; int indexvals = stopindex - 1; for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) { result[i] = vals[indexvals]; // or stopindex - i - 1 for vals[] indexvals--; return result; creating resulting array of correct size: 2 points loop of correct bounds (multiple correct alternatives): 4 points copy value into correct spot in resulting array: 4 points return result: 2 points -4 for altering values in the parameter vals 4
5 6. Arrays. 16 Points. public static void insertelementsatfront (int[] one, int[] two) { int nummove = one.length - two.length; // move items in original array down for (int i = nummove - 1; i >= 0; i--) { one[i + two.length] = one[i]; // determine limiting length int limit = two.length; if (one.length < two.length) limit = one.length; for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) { one[i] = two[i]; shift elements down in first array correctly: 7 points (partial credit possible, OBOE -2) determine limit on number of elements to copy in case two is larger: 5 points copy elements from second array into first correctly: 4 points (partial credit possible, OBOE -2) -4 Nested loop, efficiency -4 if creates a new array -2 if try and return a value -3 if forget that these are value parameters. In other words creating a temp array, altering it, and then saying one = temp; 5
6 7. ArrayList - 16 points public static int removevalues(arraylist<string> list, char c, int n){ // start from the back to avoid skipping over values int numremoved = 0; for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { String s = list.get(i); // look for c in first n characters of current String boolean found = false; int index = 0; while (index < n &&!found && index < s.length()) { found = s.charat(index) == c; index++; if (found) { list.remove(i); numremoved++; return numremoved; counter for number removed: 1 point loop from back of ArrayList (or other technique) to avoid skipping elements on remove: 5 points loop through current String: bounds check length of String: 3 points bounds check n: 1 point stop when found: 1 point access char correctly: 1 point if char found in String remove from list: 2 points increment counter: 1 point return number removed: 1 point -4 treating list like an array, [index] instead of get(index) -4 creating new Strings -4 removing excess elements due to logic error 6
7 8. 2D Arrays - 18 points public static int coinscollected(int[][] mat, int initialrow) { int col = 0; int row = initialrow; int total = 0; while (col < mat[0].length - 1) { total += mat[row][col]; mat[row][col] = -1; // so we don't come back int up = -1; if (row > 0) up = mat[row - 1][col]; int down = -1; if (row + 1 < mat.length) down = mat[row + 1][col]; int right = mat[row][col + 1]; if (up >= down && up >= right) { row--; else if (down >= up && down >= right) { row++; else { col++; // get the last cell total += mat[row][col]; return total; Track row and column correctly: 2 points Loop while not in the last column: 4 points Check 3 directions for max coin with bounds checks: 4 points Alter cells visited so robot doesn't go back: 5 points Pick correct direction and break ties correctly: 3 points -4 unnecessary nested for loops -6 infinite loop due to logic error -2 solution does not handle single row matrix correctly -1 return missing 7
1. Code Trace: 2. Program Logic (0.5 each) X <= y y > z x == 1 A S N S N S A A N S S S S A S POINT A POINT B POINT C POINT D POINT E
 CS312 Fall 2017 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS312 Fall 2017 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Exam 2 - Fall Suggested Solution and Criteria 1
 CS314 Fall 2017 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Fall 2017 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Exam 1 - Fall Suggested Solution and Criteria 1
 CS314 Spring 2017 Exam 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Spring 2017 Exam 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
1. Answer as shown or -1 unless question allows partial credit. No points off for minor differences in spacing, capitalization, commas, and braces
 CS314 Spring 2013 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Spring 2013 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
for dequeue will be O(N). (Or words to that effect. Needed to mention both or -1.)
 CS314 Spring 2017 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Spring 2017 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Final - Fall Suggested Solution and Criteria 1
 CS314 Fall 2016 Final Exam Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Fall 2016 Final Exam Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Exam 1 - Fall Suggested Solution and Criteria 1
 CS314 fall 2016 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 fall 2016 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Exam 2 - Spring Suggested Solution and Criteria 1
 CS314 Spring 2016 Final Exam Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove
CS314 Spring 2016 Final Exam Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove
1. Answer as shown or -2 unless question allows partial credit. No points off for differences in spacing, capitalization, commas, and braces
 CS314 Fall 2012 Midterm 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Fall 2012 Midterm 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Spring 2014 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria.
 CS314 Spring 2014 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Spring 2014 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Exam 1 - Spring Suggested Solution and Criteria 1
 CS314 Spring 2016 Exam 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Spring 2016 Exam 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Exam 2 - Spring Suggested Solution and Criteria 1
 CS314 Spring 2016 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Spring 2016 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
1. Answer as shown or -1 unless question allows partial credit. No points off for minor differences in spacing, capitalization, commas, and braces.
 CS314 Fall 2018 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Fall 2018 Exam 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Fall 2011 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria.
 CS314 Fall 2011 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Fall 2011 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
1. Answer as shown or -2 unless question allows partial credit. No points off for differences in spacing, capitalization, commas, and braces
 CS314 Fall 2012 Final Exam Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Fall 2012 Final Exam Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013
 CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013 SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 arrays 14 3 strings 16 4 program logic 16 5 scanner 23 6 arrays and strings
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013 SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 arrays 14 3 strings 16 4 program logic 16 5 scanner 23 6 arrays and strings
Fall_2010_M1_SuggestedSolutioAndGradingCrit.txt 10/8/2010
 CS307 Spring 2010 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: ABA - Answer by Accident AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code
CS307 Spring 2010 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: ABA - Answer by Accident AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code
1. Answer as shown or -1 unless question allows partial credit. No points off for minor differences in spacing, capitalization, commas, and braces
 CS314 Spring 2013 Midterm 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Spring 2013 Midterm 2 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Final - Spring Suggested Solution and Criteria 1
 CS314 Spring 2017 Final Exam Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove
CS314 Spring 2017 Final Exam Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove
CS314 Fall 2012 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria.
 CS314 Fall 2012 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS314 Fall 2012 Midterm 1 Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms: AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works, but, can't prove otherwise
CS 312 Final Fall Your Name SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION. Your UTEID SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION _
 CS 312 Final Fall 2013 Your Name SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Your UTEID SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION _ Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 short answer 1 12 2 program
CS 312 Final Fall 2013 Your Name SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Your UTEID SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION _ Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 short answer 1 12 2 program
D. Do inorder traversal on tree, values in ascending order, no repeats.
 CS314 Fall 2011 Final Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms ABA - Answer by Accident AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works,
CS314 Fall 2011 Final Solution and Grading Criteria. Grading acronyms ABA - Answer by Accident AIOBE - Array Index out of Bounds Exception may occur BOD - Benefit of the Doubt. Not certain code works,
CS 312 Final Fall 2016
 CS 312 Final Fall 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 expressions 10 2 program logic 20 3 code tracing 15 4 critters 15 5 arrays 15 6 strings 15 7 2d arrays 15 8 ArrayList
CS 312 Final Fall 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 expressions 10 2 program logic 20 3 code tracing 15 4 critters 15 5 arrays 15 6 strings 15 7 2d arrays 15 8 ArrayList
CS 312 Final Fall 2013
 CS 312 Final Fall 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 short answer 1 12 2 program logic 16 3 short answer 2 14 4 return methods 10 5 arrays 1 20 6 critters 20 7 arrays 2 20
CS 312 Final Fall 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 short answer 1 12 2 program logic 16 3 short answer 2 14 4 return methods 10 5 arrays 1 20 6 critters 20 7 arrays 2 20
CS 312 Final Fall 2015
 CS 312 Final Fall 2015 Your Name: SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 expressions 10 2 program logic 15 3 code tracing 15 4 Strings 15 5 arrays 1 15 6
CS 312 Final Fall 2015 Your Name: SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Your UTEID Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 expressions 10 2 program logic 15 3 code tracing 15 4 Strings 15 5 arrays 1 15 6
CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2008
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2008 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Mario Ruchica Vishvas (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Spring 2008 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Mario Ruchica Vishvas (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
SPRING 13 CS 0007 FINAL EXAM V2 (Roberts) Your Name: A pt each. B pt each. C pt each. D or 2 pts each
 Your Name: Your Pitt (mail NOT peoplesoft) ID: Part Question/s Points available Rubric Your Score A 1-6 6 1 pt each B 7-12 6 1 pt each C 13-16 4 1 pt each D 17-19 5 1 or 2 pts each E 20-23 5 1 or 2 pts
Your Name: Your Pitt (mail NOT peoplesoft) ID: Part Question/s Points available Rubric Your Score A 1-6 6 1 pt each B 7-12 6 1 pt each C 13-16 4 1 pt each D 17-19 5 1 or 2 pts each E 20-23 5 1 or 2 pts
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall Jose Stas Aaron
 CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2014 SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Circle your TA's Name: Dory Tamara Eric Jose Stas Aaron Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 30 2 scanners 15 3 program logic 16 4 strings
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2014 SOLUTION SOLUTION SOLUTION Circle your TA's Name: Dory Tamara Eric Jose Stas Aaron Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 30 2 scanners 15 3 program logic 16 4 strings
CS 314 Exam 2 Spring
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 200 points. 2. You have
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 200 points. 2. You have
CS 314 Exam 1 Fall 2017
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5A 5B Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Gilbert Jacob Jorge Joseph Lucas Rebecca Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on
Points off 1 2 3 4 5A 5B Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Gilbert Jacob Jorge Joseph Lucas Rebecca Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on
CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008
![CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008 CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008](/thumbs/71/65843664.jpg) Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Ruchica Mario Vishvas Instructions: 1. Please turn off or silence your cell
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1[corrected] Spring 2008 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Ruchica Mario Vishvas Instructions: 1. Please turn off or silence your cell
Assignment 11: Critters
 Assignment 11: Critters HW11 Assignment Specification 1 Critters A simulation world with animal objects with behavior: fight animal fighting getcolor color to display getmove movement tostring letter to
Assignment 11: Critters HW11 Assignment Specification 1 Critters A simulation world with animal objects with behavior: fight animal fighting getcolor color to display getmove movement tostring letter to
CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2009
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2009 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Oswaldo Rashid Swati (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2009 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Oswaldo Rashid Swati (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2017
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 175 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 175 points.
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-4: Static Methods and Data Critter exercise: Snake Method constructor public Snake() eat Never eats fight always forfeits getcolor black Behavior getmove 1 E,
Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-4: Static Methods and Data Critter exercise: Snake Method constructor public Snake() eat Never eats fight always forfeits getcolor black Behavior getmove 1 E,
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Fall 2016
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Fall 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Fall 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013
 CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: EDAENA LEIF MUBASHIR Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 arrays 14 3 strings 16 4 program logic 16 5 scanner 23
CS 312 Midterm 2 Fall 2013 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: EDAENA LEIF MUBASHIR Problem Number Topic Points Possible 1 code trace 28 2 arrays 14 3 strings 16 4 program logic 16 5 scanner 23
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations
 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
Repetition, Looping. While Loop
 Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key
 CS 120 Software Design I Fall 2018 Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key University of Wisconsin - La Crosse Due Date: October 5 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages
CS 120 Software Design I Fall 2018 Practice Midterm 1 Answer Key University of Wisconsin - La Crosse Due Date: October 5 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages
Lecture 7 Tao Wang 1
 Lecture 7 Tao Wang 1 Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Interactive loop break and continue do-while for loop Common programming errors Scientists, Third Edition 2 while Loops while statement
Lecture 7 Tao Wang 1 Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Interactive loop break and continue do-while for loop Common programming errors Scientists, Third Edition 2 while Loops while statement
Table of Contents Date(s) Title/Topic Page #s. Chapter 4: Writing Classes 4.1 Objects Revisited
 Table of Contents Date(s) Title/Topic Page #s 11/6 Chapter 3 Reflection/Corrections 56 Chapter 4: Writing Classes 4.1 Objects Revisited 57 58-59 look over your Ch 3 Tests and write down comments/ reflections/corrections
Table of Contents Date(s) Title/Topic Page #s 11/6 Chapter 3 Reflection/Corrections 56 Chapter 4: Writing Classes 4.1 Objects Revisited 57 58-59 look over your Ch 3 Tests and write down comments/ reflections/corrections
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM
 CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM This assignment focuses on classes and objects. Turn in Ant.java, Bird.java, Hippo.java, Vulture.java,
CSE 142, Autumn 2018 Programming Assignment #9: Critters (20 points) Due Tuesday, December 4th, 9:00 PM This assignment focuses on classes and objects. Turn in Ant.java, Bird.java, Hippo.java, Vulture.java,
AP Computer Science A
 2017 AP Computer Science A Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online
2017 AP Computer Science A Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online
The Basic Parts of Java
 Data Types Primitive Composite The Basic Parts of Java array (will also be covered in the lecture on Collections) Lexical Rules Expressions and operators Methods Parameter list Argument parsing An example
Data Types Primitive Composite The Basic Parts of Java array (will also be covered in the lecture on Collections) Lexical Rules Expressions and operators Methods Parameter list Argument parsing An example
CS 314 Midterm 2 Fall 2012
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 2 Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: John Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 2 hours to
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 2 Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: John Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 2 hours to
CS 314 Final Spring 2013 SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Spring 2013 SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Spring 2013 SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION - SOLUTION Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this
Dept. of CSE, IIT KGP
 Control Flow: Looping CS10001: Programming & Data Structures Pallab Dasgupta Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc. & Engg., Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Types of Repeated Execution Loop: Group of
Control Flow: Looping CS10001: Programming & Data Structures Pallab Dasgupta Professor, Dept. of Computer Sc. & Engg., Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Types of Repeated Execution Loop: Group of
CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: David Joseph Ola Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 4 questions
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Fall 2007 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: David Joseph Ola Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones 2. There are 4 questions
Critters. Critter #2 Attack.ROAR Attack.POUNCE Attack.SCRATCH. Critter #1
 Critters This assignment was co-created by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp. This program focuses on classes, objects, and inheritance. You will write the following files: Ant.java, Bird.java, Crab.java, FireAnt.java,
Critters This assignment was co-created by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp. This program focuses on classes, objects, and inheritance. You will write the following files: Ant.java, Bird.java, Crab.java, FireAnt.java,
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2016 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Sample Midterm Exam #2
 Sample Midterm Exam #2 1. Expressions For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0 rather than 7 for
Sample Midterm Exam #2 1. Expressions For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g., 7.0 rather than 7 for
CSE 142 SPRING 2008 FINAL EXAM
 CSE 142 SPRING 2008 FINAL EXAM 1. Expressions (10 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g.,
CSE 142 SPRING 2008 FINAL EXAM 1. Expressions (10 points) For each expression in the left-hand column, indicate its value in the right-hand column. Be sure to list a constant of appropriate type (e.g.,
CS 314 Final Fall 2012
 Points off 1 2A 2B 2C 3 4A 4B 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this exam. The raw point total on the exam is 110. 2. You have
Points off 1 2A 2B 2C 3 4A 4B 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this exam. The raw point total on the exam is 110. 2. You have
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 9 Inheritance, Polymorphism; reading: 9.2 2 The software crisis software engineering: The practice of developing, designing, documenting, testing large computer programs.
Building Java Programs Chapter 9 Inheritance, Polymorphism; reading: 9.2 2 The software crisis software engineering: The practice of developing, designing, documenting, testing large computer programs.
Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal
 Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repetition CSC 121 Fall 2014 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #31: Software Reuse through Inheritance Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #31: Software Reuse through Inheritance Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112
Flow Control. Key Notion. Statement Categories. 28-Oct-10
 Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each)
 1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
1 Short Answer (10 Points Each) 1. Write a for loop that will calculate a factorial. Assume that the value n has been input by the user and have the loop create n! and store it in the variable fact. Recall
Exam 2. Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik. Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks:
 كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2012
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: John Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 2 hours to
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off Net Score CS 314 Midterm 1 Fall 2012 Your Name_ Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: John Zihao Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 2. You have 2 hours to
Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue
 Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue General Loops in Java Look at other loop constructions Very common while loop: do a loop a fixed number of times (MAX in the example) int
Lecture 14 CSE11 Fall 2013 For loops, Do While, Break, Continue General Loops in Java Look at other loop constructions Very common while loop: do a loop a fixed number of times (MAX in the example) int
Full file at
 Chapter 1 Primitive Java Weiss 4 th Edition Solutions to Exercises (US Version) 1.1 Key Concepts and How To Teach Them This chapter introduces primitive features of Java found in all languages such as
Chapter 1 Primitive Java Weiss 4 th Edition Solutions to Exercises (US Version) 1.1 Key Concepts and How To Teach Them This chapter introduces primitive features of Java found in all languages such as
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
CS 307 Midterm 1 Spring 2009
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Spring 2009 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Todd Guhan Xiuming(aka David) Instructions: 1. Please turn off or silence your cell phones.
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score CS 307 Midterm 1 Spring 2009 Your Name Your UTEID Circle yours TA s name: Todd Guhan Xiuming(aka David) Instructions: 1. Please turn off or silence your cell phones.
CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2010
 Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2010 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Harsh Yi-Chao (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and other electronic
Points off 1 2 3 4 Total off Net Score Exam Number: CS 307 Midterm 2 Fall 2010 Name UTEID login name TA's Name: Harsh Yi-Chao (Circle One) Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones and other electronic
Flow Control. Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester IDC Herzliya
 Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
Boaz Kantor Introduction to Computer Science, Fall semester 2010-2011 IDC Herzliya Flow Control Raistlin: This alters time. Astinus: This alters nothing...time flows on, undisturbed. Raistlin: And carries
Assignment 2.4: Loops
 Writing Programs that Use the Terminal 0. Writing to the Terminal Assignment 2.4: Loops In this project, we will be sending our answers to the terminal for the user to see. To write numbers and text to
Writing Programs that Use the Terminal 0. Writing to the Terminal Assignment 2.4: Loops In this project, we will be sending our answers to the terminal for the user to see. To write numbers and text to
Programming Constructs Overview. Method Call System.out.print( hello ); Method Parameters
 Programming Constructs Overview Method calls More selection statements More assignment operators Conditional operator Unary increment and decrement operators Iteration statements Defining methods 27 October
Programming Constructs Overview Method calls More selection statements More assignment operators Conditional operator Unary increment and decrement operators Iteration statements Defining methods 27 October
Array. Prepared By - Rifat Shahriyar
 Java More Details Array 2 Arrays A group of variables containing values that all have the same type Arrays are fixed length entities In Java, arrays are objects, so they are considered reference types
Java More Details Array 2 Arrays A group of variables containing values that all have the same type Arrays are fixed length entities In Java, arrays are objects, so they are considered reference types
CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2018
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TA's Name: Aish Anthony Chris Dayanny Hailey Ivan Jacob Joseph Lucas Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TA's Name: Aish Anthony Chris Dayanny Hailey Ivan Jacob Joseph Lucas Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions
Arrays. Lecture 11 CGS 3416 Fall October 26, 2015
 Arrays Lecture 11 CGS 3416 Fall 2015 October 26, 2015 Arrays Definition: An array is an indexed collection of data elements of the same type. Indexed means that the array elements are numbered (starting
Arrays Lecture 11 CGS 3416 Fall 2015 October 26, 2015 Arrays Definition: An array is an indexed collection of data elements of the same type. Indexed means that the array elements are numbered (starting
Tutorial 12. Exercise 1: Exercise 2: CSC111 Computer Programming I
 College of Computer and Information Sciences CSC111 Computer Programming I Exercise 1: Tutorial 12 Arrays: A. Write a method add that receives an array of integers arr, the number of the elements in the
College of Computer and Information Sciences CSC111 Computer Programming I Exercise 1: Tutorial 12 Arrays: A. Write a method add that receives an array of integers arr, the number of the elements in the
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Administration. Conditional Statements. Agenda. Syntax. Flow of control. Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP
 Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1
Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1
Give one example where you might wish to use a three dimensional array
 CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8: Classes Lecture 8-3: More Critters, static Testing Critters Focus on one specific Critter of one specific type Only spawn 1 of each Critter type Make sure your fields
Building Java Programs Chapter 8: Classes Lecture 8-3: More Critters, static Testing Critters Focus on one specific Critter of one specific type Only spawn 1 of each Critter type Make sure your fields
Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements
 Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Lecture 13: Two- Dimensional Arrays
 Lecture 13: Two- Dimensional Arrays Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Nested Loops Nested loops nested loop:
Lecture 13: Two- Dimensional Arrays Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Nested Loops Nested loops nested loop:
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-3: Encapsulation; Homework 8 (Critters) reading: 8.3-8.4 Encapsulation reading: 8.4 2 Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding implementation details from clients.
Building Java Programs Chapter 8 Lecture 8-3: Encapsulation; Homework 8 (Critters) reading: 8.3-8.4 Encapsulation reading: 8.4 2 Encapsulation encapsulation: Hiding implementation details from clients.
204111: Computer and Programming
 204111: Computer and Programming Week 4: Control Structures t Monchai Sopitkamon, Ph.D. Overview Types of control structures Using selection structure Using repetition structure Types of control ol structures
204111: Computer and Programming Week 4: Control Structures t Monchai Sopitkamon, Ph.D. Overview Types of control structures Using selection structure Using repetition structure Types of control ol structures
CS 314 Exam 2 Fall 2017
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Gilbert Jacob Jorge Joseph Lucas Rebecca Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 Total off CS 314 Exam 2 Fall 2017 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Gilbert Jacob Jorge Joseph Lucas Rebecca Shelby Instructions: 1. There are 5 questions on this test. 100
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists 1 A programming problem Consider the following task: Double values representing grades are read until the user enters a negative
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 6 ArrayLists 1 A programming problem Consider the following task: Double values representing grades are read until the user enters a negative
Points off Total off Net Score. CS 314 Final Exam Spring Your Name Your UTEID
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Final Exam Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Instructions: 1. There are 6 questions on this test. 100 points available. Scores will be scaled to 300 points.
Practice Midterm 1. Problem Points Score TOTAL 50
 CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
CS 307 Final Fall 2009
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 307 Final Fall 2009 Name UTEID login name Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones. 2. There are 6 questions on this test. 3. You have 3 hours to
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 307 Final Fall 2009 Name UTEID login name Instructions: 1. Please turn off your cell phones. 2. There are 6 questions on this test. 3. You have 3 hours to
Faculty of Science COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2009) Midterm Examination
 First Name: Last Name: McGill ID: Section: Faculty of Science COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2009) Midterm Examination Monday, March 9, 2009 Examiners: Mathieu Petitpas [Section 1] 18:30
First Name: Last Name: McGill ID: Section: Faculty of Science COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2009) Midterm Examination Monday, March 9, 2009 Examiners: Mathieu Petitpas [Section 1] 18:30
Introduction to Computer Science Midterm 3 Fall, Points
 Introduction to Computer Science Fall, 2001 100 Points Notes 1. Tear off this sheet and use it to keep your answers covered at all times. 2. Turn the exam over and write your name next to the staple. Do
Introduction to Computer Science Fall, 2001 100 Points Notes 1. Tear off this sheet and use it to keep your answers covered at all times. 2. Turn the exam over and write your name next to the staple. Do
Choose 3 of the 1 st 4 questions (#'s 1 through 4) to complete. Each question is worth 12 points.
 Choose 3 of the 1 st 4 questions (#'s 1 through 4) to complete. Each question is worth 12 points. Use the remaining question as extra credit (worth 1/2 of the points earned). Specify which question is
Choose 3 of the 1 st 4 questions (#'s 1 through 4) to complete. Each question is worth 12 points. Use the remaining question as extra credit (worth 1/2 of the points earned). Specify which question is
CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2018
 Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Aish Anthony Chris Dayanny Hailey Ivan Jacob Joseph Lucas Shelby Instructions: 1. There are
Points off 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total off Net Score CS 314 Exam 1 Spring 2018 Your Name Your UTEID Circle your TAs Name: Aish Anthony Chris Dayanny Hailey Ivan Jacob Joseph Lucas Shelby Instructions: 1. There are
CSE 143 Section Handout #13 Practice Midterm #5
 Practice Midterm #5 1. ArrayList Mystery. Consider the following method: public static void mystery5(arraylist list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { int element = list.get(i); list.remove(i);
Practice Midterm #5 1. ArrayList Mystery. Consider the following method: public static void mystery5(arraylist list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { int element = list.get(i); list.remove(i);
CS 302: Introduction to Programming in Java. Lecture 11 Yinggang Huang. CS302 Summer 2012
 CS 302: Introduction to Programming in Java Lecture 11 Yinggang Huang 1 Review How do we call a method? What are method inputs called? How many values can be returned from a method? Write a method header
CS 302: Introduction to Programming in Java Lecture 11 Yinggang Huang 1 Review How do we call a method? What are method inputs called? How many values can be returned from a method? Write a method header
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch
 Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!)
 CS 161 Exam 2: FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!) True (A)/False(B) (2 pts each): 1. Recursive algorithms tend to be less efficient than iterative algorithms. 2. A recursive function
CS 161 Exam 2: FORM 2 (Please put your name and form # on the scantron!!!!) True (A)/False(B) (2 pts each): 1. Recursive algorithms tend to be less efficient than iterative algorithms. 2. A recursive function
Conditionals, Loops, and Style
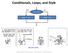 Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Critter #1 Attack.ROAR random winner #2 wins #1 wins Attack.POUNCE #1 wins random winner #2 wins Attack.SCRATCH #2 wins #1 wins random winner
 CSE 142, Winter 2016 Programming Assignment #8: Critters (40 points) Due: Tuesday, March 8, 2016, 11:30 PM (Husky must be submitted on time to be in tournament in class on Friday, March 11) This assignment
CSE 142, Winter 2016 Programming Assignment #8: Critters (40 points) Due: Tuesday, March 8, 2016, 11:30 PM (Husky must be submitted on time to be in tournament in class on Friday, March 11) This assignment
