Administration. Conditional Statements. Agenda. Syntax. Flow of control. Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP
|
|
|
- Harvey Thompson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Administration Conditional Statements CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 Lab 2 due now on floppy Lab 3 due tomorrow via FTP need Instruct account password Lab 4 posted this afternoon Prelim 1 in 1 week review session TBA 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 2 Agenda ifstatements switch statements?:(the conditional operator) if The if (also if-then) statement chooses whether to run code, or not: if (grade > 60) { System.out.println( You are passing! ); 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 3 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 4 Flow of control Syntax condition? true block false if (condition) { Example: if (temperature > 80) { System.out.println( It s hot! ); 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 5 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 6 1
2 Syntax [2] The condition of an if statement can be any Boolean expression There may be any number of statements in the body of the if What isn t allowed in the body? Nested ifs A nested statement is a statement inside another, e.g.: if (month == 12) { if (day == 31) { System.out.println( It s New Year s Eve ); How else could this be written? 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 7 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 8 or else! It s also possible to make an if statement choose between two blocks of code. if (condition) { else { if-else Semantics (meaning): evaluate the condition if the condition is true, execute the first block (the then clause) if the condition is false, execute the second block (the else clause) no matter which block was executed, resume executing with the code after both blocks 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 9 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 10 if-else [2] if-else [3] Example: print the larger of two numbers true then clause condition? false else clause if (num1 > num2) { System.out.println(num1); else { System.out.println(num2); How would this look in a larger program? 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture /5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture
3 class LargerOfTwo { public static void main(string[] args) { int num1 = Console.readInt(); int num2 = Console.readInt(); if (num1 > num2) { System.out.println(num1); else { System.out.println(num2); System.out.println( All done ); 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 13 Robust Programs A robust program is completely protected against all possible crashes from bad data and unexpected values. Example: System.out.print( Enter a positive number: ); p = Console.readInt(); if (p <= 0) { System.out.println( You entered a nonpositive number ); else { // do whatever we expected to do, e.g., Math.sqrt(p) 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 14 Robust Programs [2] A Complicated if This kind of protection can be used many places in a program Requires extra code (and time!) at the tradeoff of fewer possible crashes Essential for professionals For students, can detract from programming principles In this class, you can assume we will always give your program valid input unless we specifically warn you otherwise 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 15 How could we express the following in Java? If a student s grade is: , print A 80-89, print B 70-79, print C 60-69, print D 0-59, print F 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 16 A Complicated if [2] Extended if An extended if expresses a multiway decision a choice of one of several alternatives Allows problems that would require deeply nested ifs to be expressed more concisely if (grade >= 90) { System.out.println( A ); else { if (grade >= 80) { System.out.println( B ); else { if (grade >= 70) { System.out.println( C ); else { if (grade >= 60) { System.out.println( D ); else { System.out.println( F ); 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture /5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture
4 Extended if [2] A Less Complicated if if (condition1) { // block1 else if (condition2) { // block2 else if (conditionn) { // blockn else { // else clause Semantics: Pick the first true condition Execute its block only If no conditions are true, execute the else clause if (grade >= 90) { System.out.println( A ); else if (grade >= 80) { System.out.println( B ); else if (grade >= 70) { System.out.println( C ); else if (grade >= 60) { System.out.println( D ); else { System.out.println( F ); 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture /5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 20 Braces Optional If there s only one statement in the body of an if, the braces are optional: if (temperature < 0) System.out.println( It s c-c-cold! ); Strong recommendation: put them in anyway! fewer bugs don t have to add them later avoid the dangling-else problem Dangling Else Problem // test for a perfect square if (num > 0) if (num == Math.pow(Math.sqrt(num), 2)) System.out.println(num); else System.out.println( Non-positive number ); If num is 20, this prints Non-positive number. Why? 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture /5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 22 Dangling Else [2] switch statements if (num > 0) { if (num == Math.pow(Math.sqrt(num), 2)) { System.out.println(num); else { System.out.println( Non-positive number ); Similar to extended ifs Evaluates a single expression, then chooses one of many paths based on that value Could always be replaced by a nested if, but is sometimes simpler and easier to read No ambiguity when fully braced. 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture /5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture
5 switch Example switch Syntax switch (age) { case 18: System.out.println( Legal voting age ); case 21: System.out.println( Legal drinking age ); case 25: System.out.println( Able to rent a car ); default: System.out.println( Not an interesting age ); 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 25 switch (integer expression) { case constant expression: //statements [] [more cases] [default: // default clause] 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 26 switch Example [2] Conditional Operator switch (num) { case 1: case 2: case 3: case 4: System.out.println( Less than 5 ); case 5: case 6: case 7: case 8: case 9: System.out.println( Less than 10 ); Java s only ternary operator?: boolean-expression? expression : else-expression Semantics: Evaluate the boolean-expression If true, use expression as the value of the operation If false, use else-expression as the value of the operation 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture /5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 4 28 Conditional Operator [2] Acts as an abbreviation for if-else Except that it has a value has operands that are expressions, not full statements is not as easily readable You should avoid this operator unless you have a good reason to use it?: Examples max = (num1 > num2)? num1 : num2; abs = (num1 > 0)? num1 : -num1; 7/5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture /5/00 CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture
Administration. Exceptions. Leftovers. Agenda. When Things Go Wrong. Handling Errors. CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 11
 Administration Exceptions CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 11 Lab 10 due tomorrow No lab tomorrow Work on final projects Remaining office hours Rick: today 2-3 Michael: Thursday 10-noon, Monday
Administration Exceptions CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 11 Lab 10 due tomorrow No lab tomorrow Work on final projects Remaining office hours Rick: today 2-3 Michael: Thursday 10-noon, Monday
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch
 Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2017 January 23, 2017 Lecture 4CGS 3416 Spring 2017 Selection January 23, 2017 1 / 26 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 5 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15
 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
Administration. Classes. Objects Part II. Agenda. Review: Object References. Object Aliases. CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7
 Administration Classes CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7 Lab 7 due tomorrow Question: Lab 6.equals( SquareRoot )? Lab 8 posted today Prelim 2 in six days! Covers two weeks of material: lectures
Administration Classes CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 7 Lab 7 due tomorrow Question: Lab 6.equals( SquareRoot )? Lab 8 posted today Prelim 2 in six days! Covers two weeks of material: lectures
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
1 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1: Introduction Lecture Contents 2 Course info Why programming?? Why Java?? Write once, run anywhere!! Java basics Input/output Variables
Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1
 Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1 Motivation In the programs we have written thus far, statements are executed one after the other, in the order in which they appear. Programs often
Module 3 SELECTION STRUCTURES 2/15/19 CSE 1321 MODULE 3 1 Motivation In the programs we have written thus far, statements are executed one after the other, in the order in which they appear. Programs often
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch
 Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2016 February 2, 2016 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification of the order in which the individual statements, instructions
Control Structures in Java if-else and switch Lecture 4 CGS 3416 Spring 2016 February 2, 2016 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification of the order in which the individual statements, instructions
Following is the general form of a typical decision making structure found in most of the programming languages:
 Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Decision Structures. Lecture 3 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz
 Decision Structures Lecture 3 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Chapter Topics o Relational Operators o The if Statement o The if-else Statement o Nested if statements o The if-else-if
Decision Structures Lecture 3 MIT 12043, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Chapter Topics o Relational Operators o The if Statement o The if-else Statement o Nested if statements o The if-else-if
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Lecture 5 Tao Wang 1
 Lecture 5 Tao Wang 1 Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Selection criteria Relational operators Logical operators The if-else statement Nested if statements C++ for Engineers and Scientists,
Lecture 5 Tao Wang 1 Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Selection criteria Relational operators Logical operators The if-else statement Nested if statements C++ for Engineers and Scientists,
Decision Structures. Lesson 03 MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming
 Decision Structures Lesson 03 MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz M.Sc. in IS (SLIIT), PGD in IS (SLIIT), BBA (Hons.) Spl. In IS (SEUSL), MIEEE, Microsoft Certified Professional
Decision Structures Lesson 03 MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz M.Sc. in IS (SLIIT), PGD in IS (SLIIT), BBA (Hons.) Spl. In IS (SEUSL), MIEEE, Microsoft Certified Professional
AP Computer Science A Summer Assignment 2017
 AP Computer Science A Summer Assignment 2017 The objective of this summer assignment is to ensure that each student has the ability to compile and run code on a computer system at home. We will be doing
AP Computer Science A Summer Assignment 2017 The objective of this summer assignment is to ensure that each student has the ability to compile and run code on a computer system at home. We will be doing
Topics. Chapter 5. Equality Operators
 Topics Chapter 5 Flow of Control Part 1: Selection Forming Conditions if/ Statements Comparing Floating-Point Numbers Comparing Objects The equals Method String Comparison Methods The Conditional Operator
Topics Chapter 5 Flow of Control Part 1: Selection Forming Conditions if/ Statements Comparing Floating-Point Numbers Comparing Objects The equals Method String Comparison Methods The Conditional Operator
Lecture 4. CS118 Term planner. The simple if statement. Control flow: selection. The if... else statement cont... The if... else statement.
 1 Lecture 4 CS118 Term planner You should have done, or be working through, problem sheet 2; next is sheet 3 Coursework - common mistakes do while (robot.look(direction) = IRobot.WALL); if (robot.look(irobot.ahead)
1 Lecture 4 CS118 Term planner You should have done, or be working through, problem sheet 2; next is sheet 3 Coursework - common mistakes do while (robot.look(direction) = IRobot.WALL); if (robot.look(irobot.ahead)
Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups:
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Warmup : Name that tune!
 Warmup : Name that tune! Write, using a loop, Java code to print the lyrics to the song 99 Bottles of Beer on the Wall 99 bottles of beer on the wall. 99 bottles of beer. Take one down, pass it around,
Warmup : Name that tune! Write, using a loop, Java code to print the lyrics to the song 99 Bottles of Beer on the Wall 99 bottles of beer on the wall. 99 bottles of beer. Take one down, pass it around,
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Conditional Statements Boolean Expressions and Methods Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
( &% class MyClass { }
 Recall! $! "" # ' ' )' %&! ( &% class MyClass { $ Individual things that differentiate one object from another Determine the appearance, state or qualities of objects Represents any variables needed for
Recall! $! "" # ' ' )' %&! ( &% class MyClass { $ Individual things that differentiate one object from another Determine the appearance, state or qualities of objects Represents any variables needed for
SELECTION. (Chapter 2)
 SELECTION (Chapter 2) Selection Very often you will want your programs to make choices among different groups of instructions For example, a program processing requests for airline tickets could have the
SELECTION (Chapter 2) Selection Very often you will want your programs to make choices among different groups of instructions For example, a program processing requests for airline tickets could have the
Administration. Objects and Arrays. Objects. Agenda. What is an Object? What is a Class?
 Administration Objects and Arrays CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 6 Read clarified grading policies Lab 6 due tomorrow Submit.java files in a folder named Lab6 Lab 7 Posted today Upson Lab closed
Administration Objects and Arrays CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 6 Read clarified grading policies Lab 6 due tomorrow Submit.java files in a folder named Lab6 Lab 7 Posted today Upson Lab closed
CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops
 CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 17, 2009 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements are executed
CMPT 125: Lecture 4 Conditionals and Loops Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 17, 2009 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements are executed
Chapter 3. Selections
 Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Chapter 3 Selections 1 Outline 1. Flow of Control 2. Conditional Statements 3. The if Statement 4. The if-else Statement 5. The Conditional operator 6. The Switch Statement 7. Useful Hints 2 1. Flow of
Building Java Programs. Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops Copyright 2008 2006 by Pearson Education 1 Lecture outline data concepts Primitive types: int, double, char (for now) Expressions: operators,
Intro to Programming. Unit 7. What is Programming? What is Programming? Intro to Programming
 Intro to Programming Unit 7 Intro to Programming 1 What is Programming? 1. Programming Languages 2. Markup vs. Programming 1. Introduction 2. Print Statement 3. Strings 4. Types and Values 5. Math Externals
Intro to Programming Unit 7 Intro to Programming 1 What is Programming? 1. Programming Languages 2. Markup vs. Programming 1. Introduction 2. Print Statement 3. Strings 4. Types and Values 5. Math Externals
CONCORDIA UNIVERSITY Summer 2005 Comp 248 /1 Section AA Introduction to Programming Final Examination/A
 NAME: ID: CONCORDIA UNIVERSITY Summer 2005 Comp 248 /1 Section AA Introduction to Programming Final Examination/A Instructor: N. Acemian Monday June 27, 2005 Duration: 3 hours INSTRUCTIONS: - Answer all
NAME: ID: CONCORDIA UNIVERSITY Summer 2005 Comp 248 /1 Section AA Introduction to Programming Final Examination/A Instructor: N. Acemian Monday June 27, 2005 Duration: 3 hours INSTRUCTIONS: - Answer all
Lab 8: IF statement. Conditionals and Loops. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lab 8: IF statement. Conditionals and Loops The if condition Statement A conditional statement lets us choose which statement will be executed next if is a Java reserved word The condition must be a boolean
Lab 8: IF statement. Conditionals and Loops The if condition Statement A conditional statement lets us choose which statement will be executed next if is a Java reserved word The condition must be a boolean
Repetition, Looping. While Loop
 Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Third Edition
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Third Edition Chapter 4: Control Structures I (Selection) Control Structures A computer can proceed: In sequence Selectively (branch) - making
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Third Edition Chapter 4: Control Structures I (Selection) Control Structures A computer can proceed: In sequence Selectively (branch) - making
BRANCHING if-else statements
 BRANCHING if-else statements Conditional Statements A conditional statement lets us choose which statement t t will be executed next Therefore they are sometimes called selection statements Conditional
BRANCHING if-else statements Conditional Statements A conditional statement lets us choose which statement t t will be executed next Therefore they are sometimes called selection statements Conditional
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
CS 115 Lecture 8. Selection: the if statement. Neil Moore
 CS 115 Lecture 8 Selection: the if statement Neil Moore Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, Kentucky 40506 neil@cs.uky.edu 24 September 2015 Selection Sometime we want to execute
CS 115 Lecture 8 Selection: the if statement Neil Moore Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, Kentucky 40506 neil@cs.uky.edu 24 September 2015 Selection Sometime we want to execute
Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15. Instructor: Craig Duckett
 Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday,
Combo Lecture Lecture 14/15 Instructor: Craig Duckett Assignment Dates (By Due Date) Assignment 1 (LECTURE 5) GRADED! Section 1: Monday, January 22 nd Assignment 2 (LECTURE 8) GRADED! Section 1: Wednesday,
Lecture 5: Methods CS2301
 Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Lecture Programming in C++ PART 1. By Assistant Professor Dr. Ali Kattan
 Lecture 08-1 Programming in C++ PART 1 By Assistant Professor Dr. Ali Kattan 1 The Conditional Operator The conditional operator is similar to the if..else statement but has a shorter format. This is useful
Lecture 08-1 Programming in C++ PART 1 By Assistant Professor Dr. Ali Kattan 1 The Conditional Operator The conditional operator is similar to the if..else statement but has a shorter format. This is useful
Supplementary Test 1
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 Supplementary Test 1 Question
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 Supplementary Test 1 Question
Objectives. Chapter 4: Control Structures I (Selection) Objectives (cont d.) Control Structures. Control Structures (cont d.) Relational Operators
 Objectives Chapter 4: Control Structures I (Selection) In this chapter, you will: Learn about control structures Examine relational and logical operators Explore how to form and evaluate logical (Boolean)
Objectives Chapter 4: Control Structures I (Selection) In this chapter, you will: Learn about control structures Examine relational and logical operators Explore how to form and evaluate logical (Boolean)
Constants. Why Use Constants? main Method Arguments. CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD. Lecture 25: Miscellaneous
 CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
CS256 Computer Science I Kevin Sahr, PhD Lecture 25: Miscellaneous 1 main Method Arguments recall the method header of the main method note the argument list public static void main (String [] args) we
Lecture 14. 'for' loops and Arrays
 Lecture 14 'for' loops and Arrays For Loops for (initiating statement; conditional statement; next statement) // usually incremental body statement(s); The for statement provides a compact way to iterate
Lecture 14 'for' loops and Arrays For Loops for (initiating statement; conditional statement; next statement) // usually incremental body statement(s); The for statement provides a compact way to iterate
Introduction to OOP with Java. Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017
 Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 05 / 31 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / Comments? recap and some more details about variables, and if / else statements do lab work
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 05 / 31 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / Comments? recap and some more details about variables, and if / else statements do lab work
Scope of this lecture. Repetition For loops While loops
 REPETITION CITS1001 2 Scope of this lecture Repetition For loops While loops Repetition Computers are good at repetition We have already seen the for each loop The for loop is a more general loop form
REPETITION CITS1001 2 Scope of this lecture Repetition For loops While loops Repetition Computers are good at repetition We have already seen the for each loop The for loop is a more general loop form
COMP 250: Java Programming I. Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette
 COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
Chapter 4: Control Structures I (Selection) Objectives. Objectives (cont d.) Control Structures. Control Structures (cont d.
 Chapter 4: Control Structures I (Selection) In this chapter, you will: Objectives Learn about control structures Examine relational and logical operators Explore how to form and evaluate logical (Boolean)
Chapter 4: Control Structures I (Selection) In this chapter, you will: Objectives Learn about control structures Examine relational and logical operators Explore how to form and evaluate logical (Boolean)
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Control Structures. Lecture 4 COP 3014 Fall September 18, 2017
 Control Structures Lecture 4 COP 3014 Fall 2017 September 18, 2017 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification of the order in which the individual statements, instructions or function calls
Control Structures Lecture 4 COP 3014 Fall 2017 September 18, 2017 Control Flow Control flow refers to the specification of the order in which the individual statements, instructions or function calls
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
Algorithms and Conditionals
 Algorithms and Conditionals CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
Algorithms and Conditionals CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/
CSEN 202 Introduction to Computer Programming
 CSEN 202 Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 3: Decisions Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher and Dr Mohammed Abdel Megeed Salem, slim.abdennadher@guc.edu.eg German University Cairo, Department of Media
CSEN 202 Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 3: Decisions Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher and Dr Mohammed Abdel Megeed Salem, slim.abdennadher@guc.edu.eg German University Cairo, Department of Media
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Jan-Apr 2006 Tamara Munzner
 University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Jan-Apr 2006 Tamara Munzner Conditionals II Lecture 11, Thu Feb 9 2006 based on slides by Kurt Eiselt http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~tmm/courses/cpsc111-06-spr
University of British Columbia CPSC 111, Intro to Computation Jan-Apr 2006 Tamara Munzner Conditionals II Lecture 11, Thu Feb 9 2006 based on slides by Kurt Eiselt http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~tmm/courses/cpsc111-06-spr
Control Structures: if and while A C S L E C T U R E 4
 Control Structures: if and while A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 4 Control structures 3 constructs are essential building blocks for programs Sequences compound statement Decisions if, switch, conditional operator
Control Structures: if and while A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 4 Control structures 3 constructs are essential building blocks for programs Sequences compound statement Decisions if, switch, conditional operator
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
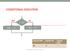 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Programming Constructs Overview. Method Call System.out.print( hello ); Method Parameters
 Programming Constructs Overview Method calls More selection statements More assignment operators Conditional operator Unary increment and decrement operators Iteration statements Defining methods 27 October
Programming Constructs Overview Method calls More selection statements More assignment operators Conditional operator Unary increment and decrement operators Iteration statements Defining methods 27 October
Practice with variables and types
 Practice with variables and types 1. Types. For each literal or expression, state its type (String, int, double, or boolean). Expression Type Expression Type 387 int "pancakes" String true boolean 45.0
Practice with variables and types 1. Types. For each literal or expression, state its type (String, int, double, or boolean). Expression Type Expression Type 387 int "pancakes" String true boolean 45.0
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS
 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
Practice with variables and types
 Practice with variables and types 1. Types. For each literal or expression, state its type (String, int, double, or boolean). Expression Type Expression Type 387 "pancakes" true 45.0 "14" 87.98515 "false"
Practice with variables and types 1. Types. For each literal or expression, state its type (String, int, double, or boolean). Expression Type Expression Type 387 "pancakes" true 45.0 "14" 87.98515 "false"
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Exercise 4: Loops, Arrays and Files
 Exercise 4: Loops, Arrays and Files worth 24% of the final mark November 4, 2004 Instructions Submit your programs in a floppy disk. Deliver the disk to Michele Zito at the 12noon lecture on Tuesday November
Exercise 4: Loops, Arrays and Files worth 24% of the final mark November 4, 2004 Instructions Submit your programs in a floppy disk. Deliver the disk to Michele Zito at the 12noon lecture on Tuesday November
In Java, data type boolean is used to represent Boolean data. Each boolean constant or variable can contain one of two values: true or false.
 CS101, Mock Boolean Conditions, If-Then Boolean Expressions and Conditions The physical order of a program is the order in which the statements are listed. The logical order of a program is the order in
CS101, Mock Boolean Conditions, If-Then Boolean Expressions and Conditions The physical order of a program is the order in which the statements are listed. The logical order of a program is the order in
8. Decision-Making Statements. Java. Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini
 8. Decision-Making Statements Java Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Decision-Making Statements Outline Introduction The if-then Statement The if-then-else Statement The switch Statement References
8. Decision-Making Statements Java Summer 2008 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Decision-Making Statements Outline Introduction The if-then Statement The if-then-else Statement The switch Statement References
Give one example where you might wish to use a three dimensional array
 CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
Exam 2. Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik. Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks:
 كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
كلية الحاسبات وتقنية المعلوما Exam 2 Programming I (CPCS 202) Instructor: M. G. Abbas Malik Date: November 22, 2015 Student Name: Student ID: Total Marks: 40 Obtained Marks: Instructions: Do not open this
The design recipe. Readings: HtDP, sections 1-5. (ordering of topics is different in lectures, different examples will be used)
 The design recipe Readings: HtDP, sections 1-5 (ordering of topics is different in lectures, different examples will be used) Survival and Style Guides CS 135 Winter 2018 02: The design recipe 1 Programs
The design recipe Readings: HtDP, sections 1-5 (ordering of topics is different in lectures, different examples will be used) Survival and Style Guides CS 135 Winter 2018 02: The design recipe 1 Programs
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 3 Branching
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 3 Branching 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements in a program are executed is called the flow of control So far we have only seen
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 3 Branching 1 Flow of Control The order in which statements in a program are executed is called the flow of control So far we have only seen
Object-oriented programming. and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018
 Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
CSE 142, Summer 2015
 CSE 142, Summer 2015 Lecture 2: Static Methods Expressions reading: 1.4 2.1 The Mechanical Turk 2 Escape Characters System.out.println( ab\ \\\\\\/\td ); Output: ab \\\/ d 3 Algorithms algorithm: A list
CSE 142, Summer 2015 Lecture 2: Static Methods Expressions reading: 1.4 2.1 The Mechanical Turk 2 Escape Characters System.out.println( ab\ \\\\\\/\td ); Output: ab \\\/ d 3 Algorithms algorithm: A list
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 2 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 3 The computer s view Internally, computers store everything as 1 s and 0
Building Java Programs Chapter 2 Lecture 2-1: Expressions and Variables reading: 2.1-2.2 1 2 Data and expressions reading: 2.1 3 The computer s view Internally, computers store everything as 1 s and 0
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations
 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations Java Curriculum for AP Computer Science, Student Lesson A12 1 STUDENT LESSON A12 Iterations INTRODUCTION: Solving problems on a computer very often requires a repetition of
CS 101 Spring 2007 Midterm 2 Name: ID:
 You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
You only need to write your name and e-mail ID on the first page. This exam is CLOSED text book, closed-notes, closed-calculator, closed-neighbor, etc. Questions are worth different amounts, so be sure
Lists, loops and decisions
 Caltech/LEAD Summer 2012 Computer Science Lecture 4: July 11, 2012 Lists, loops and decisions Lists Today Looping with the for statement Making decisions with the if statement Lists A list is a sequence
Caltech/LEAD Summer 2012 Computer Science Lecture 4: July 11, 2012 Lists, loops and decisions Lists Today Looping with the for statement Making decisions with the if statement Lists A list is a sequence
CS1004: Intro to CS in Java, Spring 2005
 CS1004: Intro to CS in Java, Spring 2005 Lecture #16: Java conditionals/loops, cont d. Janak J Parekh janak@cs.columbia.edu Administrivia Midterms returned now Weird distribution Mean: 35.4 ± 8.4 What
CS1004: Intro to CS in Java, Spring 2005 Lecture #16: Java conditionals/loops, cont d. Janak J Parekh janak@cs.columbia.edu Administrivia Midterms returned now Weird distribution Mean: 35.4 ± 8.4 What
More Things We Can Do With It! Overview. Circle Calculations. πr 2. π = More operators and expression types More statements
 More Things We Can Do With It! More operators and expression types More s 11 October 2007 Ariel Shamir 1 Overview Variables and declaration More operators and expressions String type and getting input
More Things We Can Do With It! More operators and expression types More s 11 October 2007 Ariel Shamir 1 Overview Variables and declaration More operators and expressions String type and getting input
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. February 29, 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
Boolean Expressions. So, for example, here are the results of several simple Boolean expressions:
 Boolean Expressions Now we have the ability to read in some information, calculate some formulas and display the information to the user in a nice format. However, the real power of computer programs lies
Boolean Expressions Now we have the ability to read in some information, calculate some formulas and display the information to the user in a nice format. However, the real power of computer programs lies
Chapter 3. Iteration
 Chapter 3 Iteration Iteration Iteration is the form of program control that allows us to repeat a section of code. For this reason this form of control is often also referred to as repetition. The programming
Chapter 3 Iteration Iteration Iteration is the form of program control that allows us to repeat a section of code. For this reason this form of control is often also referred to as repetition. The programming
Chapter 3 Selection Statements
 Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
Control Flow. COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science. Christopher Conway 3 June 2003
 Control Flow COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 3 June 2003 Overflow from Last Time: Why Types? Assembly code is typeless. You can take any 32 bits in memory, say this is an
Control Flow COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 3 June 2003 Overflow from Last Time: Why Types? Assembly code is typeless. You can take any 32 bits in memory, say this is an
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION: PART 2
 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION: PART 2 yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Review: The if-else statement The switch statement A look
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION: PART 2 yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Review: The if-else statement The switch statement A look
MEHMET YAYAN - İSMAİL HAKKI ÖZTÜRK CS101/SEC.-2 CLASS NOTES 1. March 28-30, 2007
 MEHMET YAYAN - İSMAİL HAKKI ÖZTÜRK CS101/SEC.-2 CLASS NOTES 1 March 28-30, 2007 if Single-Selection Statement The conditional statement in Java has the form if (condition) statement The condition must
MEHMET YAYAN - İSMAİL HAKKI ÖZTÜRK CS101/SEC.-2 CLASS NOTES 1 March 28-30, 2007 if Single-Selection Statement The conditional statement in Java has the form if (condition) statement The condition must
COMP 202 Java in one week
 COMP 202 Java in one week... Continued CONTENTS: Return to material from previous lecture At-home programming exercises Please Do Ask Questions It's perfectly normal not to understand everything Most of
COMP 202 Java in one week... Continued CONTENTS: Return to material from previous lecture At-home programming exercises Please Do Ask Questions It's perfectly normal not to understand everything Most of
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science. Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style
 CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style c 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 4 : Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming
CS125 : Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes #4 Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming Style c 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001, 2000 Jason Zych 1 Lecture 4 : Type Checking, Input/Output, and Programming
Lecture 05: Methods. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
 Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
CPSC 219 Extra review and solutions
 CPSC 219 Extra review and solutions Multiple choice questions: Unless otherwise specified assume that all necessary variable declarations have been made. For Questions 1 6 determine the output of the print()
CPSC 219 Extra review and solutions Multiple choice questions: Unless otherwise specified assume that all necessary variable declarations have been made. For Questions 1 6 determine the output of the print()
Handout 4 Conditionals. Boolean Expressions.
 Handout 4 cs180 - Programming Fundamentals Fall 17 Page 1 of 8 Handout 4 Conditionals. Boolean Expressions. Example Problem. Write a program that will calculate and print bills for the city power company.
Handout 4 cs180 - Programming Fundamentals Fall 17 Page 1 of 8 Handout 4 Conditionals. Boolean Expressions. Example Problem. Write a program that will calculate and print bills for the city power company.
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Java basics: Compilation vs Interpretation Program structure Statements Values Variables Types Operators and Expressions
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Java basics: Compilation vs Interpretation Program structure Statements Values Variables Types Operators and Expressions
Logical Operators and switch
 Lecture 5 Relational and Equivalence Operators SYS-1S22 / MTH-1A66 Logical Operators and switch Stuart Gibson sg@sys.uea.ac.uk S01.09A 1 Relational Operator Meaning < Less than > Greater than
Lecture 5 Relational and Equivalence Operators SYS-1S22 / MTH-1A66 Logical Operators and switch Stuart Gibson sg@sys.uea.ac.uk S01.09A 1 Relational Operator Meaning < Less than > Greater than
CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables and constants Top Down Programming For loops Nested Loops
 COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
COMP-202 Unit 4: Programming with Iterations Doing the same thing again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again and again... CONTENTS: While loops Class (static) variables
More Flow Control Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #4
 More Flow Control Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #4 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Administrative CHANGED T.A. OFFICE/OPEN LAB HOURS! Thursday, 10 AM 12 PM
More Flow Control Functions in C++ CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #4 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Administrative CHANGED T.A. OFFICE/OPEN LAB HOURS! Thursday, 10 AM 12 PM
Conditionals, Loops, and Style
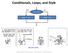 Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
Conditionals, Loops, and Style yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; http://xkcd.com/292/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Control flow thus far public class ArgsExample public
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java
 ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Introduction to Programming for ECE Lecture 1 Course Overview Welcome! What is this class about? Java programming somewhat software somewhat Solving engineering
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving with Java Introduction to Programming for ECE Lecture 1 Course Overview Welcome! What is this class about? Java programming somewhat software somewhat Solving engineering
